Abstract
Satellite thermal remote sensing provides land surface temperatures (LST) over extensive areas that are vital in various applications, but this technique suffers from its sampling style and the impenetrability of clouds, which frequently generates data gaps. Annual temperature cycle (ATC) models can fill these gaps and estimate continuous daily LST dynamics from a number of thermal observations. However, the standard ATC model (termed ATCS) remains incapable of quantifying the short-term LST variations caused by synoptic conditions. By incorporating in-situ surface air temperatures (SATs) and satellite-derived normalized difference vegetation indexes (NDVIs), here we proposed an enhanced ATC model (ATCE) to describe the daily LST fluctuations. With Aqua/MODIS LST products as validation data, we implemented and tested the ATCE over the Yangtze River Delta region of China. The results demonstrate that, when compared with the ATCS, the overall root mean square errors of the ATCE decrease by 1.0 and 0.8 K for the day and night, respectively. The accuracy improvements vary with land cover types with greater improvements over the forest, grassland, and built-up areas than over cropland and wetland. The assessments at different time scales further confirm that LST fluctuations can be better described by the ATCE. Though with limitations, we consider this new model and its associated parameters hold great potentials in various applications.
1. Introduction
Satellite thermal infrared remote sensing allows generating land surface temperature (LST) products over extensive areas, which are indispensable for various applications [1], such as the quantification of land-atmosphere interactions [2], investigation of urban thermal environments [3], identification of forest fires [4], and monitoring of volcanoes [5] and earthquakes [6]. However, spaceborne thermal sensors, especially for those onboard polar-orbiting satellites, typically sample the surface in a temporally discontinuous and even sporadic manner, which results in regular data gaps. These data gaps may become even more frequent in consideration of the prevalent occurrence of clouds especially for low-latitude areas.
To estimate temporally continuous LST dynamics, various models have been designed at different time scales [7,8,9]. These models can be generally divided into three categories with respect to the time scale: inter-annual temperature dynamics (ATD) models [8,10,11], inner-annual temperature cycle (ATC) models [7,12], and diurnal temperature cycle (DTC) models [13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20]. At the yearly timescale, ATD models primarily aim at analyzing the inter-annual LST variations. The linear function, Mann-Kendall framework, and Breaks For Additive Seasonal and Trend (BFAST) algorithm, which are flexible for handling time series of visible and near infrared remote sensing data, have been illustrated applicable for modeling long time-series LSTs [8,10,11]. At the sub-daily timescale, DTC models have been the research foci because of their ability to generate temporally continuous LSTs with very limited thermal observations in a diurnal cycle. A variety of DTC models have therefore been conceived. According to the amount of using physical laws and auxiliary data, they can be divided into four categories [19]: the physical methods [13], quasi-physical methods [14,15,19], semi-physical methods [16,18], and statistical methods [17]. Between the yearly and sub-daily timescales, ATC models have recently received particular attention due to their potentials in various applications [7,12]. These applications include the generation of spatio-temporally seamless LST products [21,22], improvement of the spatio-temporal downscaling of LSTs [23,24,25], and examination of surface urban heat islands (SUHIs) [9,26,27,28].
Similar to those DTC models, the ATC dynamics can as well be modelled either by statistical time-series analysis methods or semi-physical methods, or by synthetic methods that combine the statistical and physical methods with/without additional data. From the statistical time-series analysis perspective, the classic Harmonic ANalysis of Time Series (HANTS) algorithm can be well adapted to simulate the LST dynamics and then to reconstruct the LST data gaps induced by clouds, though the reconstructed LSTs are expected to be higher than the true LST under overcast conditions especially for the daytime [29]. While from the semi-physical perspective, Bechtel [30] presented the modeling of annual LST variations by a standard sinusoidal function (termed the ATCS hereafter) and later suggested the use of a second sinusoidal term outside the mid-latitudes [31]. This sinusoidal model generally performs well on the reconstruction of LST dynamics; and the derived model parameters are worthwhile for the quantification of surface properties [12,27]. Nevertheless, such a sinusoidal model is temporally smooth and therefore insensitive to short-term LST variations due to the alteration of synoptic conditions. To improve the prediction of these short-term LST fluctuations, more advanced ATC models were consequently proposed by incorporating either statistical methods such as the Gaussian process regression [9] or auxiliary data such as in-situ measurements [7].
The previous years have witnessed great achievements on ATC modeling, but issues remain. The time series statistical methods can usually achieve a high accuracy, but their accuracies greatly depend on the number of LST observations, wherein dense LSTs are typically required to achieve a robust modeling. By comparison, semi-physical methods such as the ATCS can predict LST variations within an annual cycle with a relatively limited number of LST observations, because their number of free parameters is relatively small when compared with those of the statistical methods. The prediction accuracies of semi-physical methods are, nevertheless, relatively lower, especially for periods with unstable synoptic conditions. Although the incorporation of statistical processes/functions into physical methods can handle the LST fluctuations due to synoptic conditions and vegetation phenology, they become less effective once the number of temporal thermal observations is limited.
To resolve these issues, this study continues to employ the synthetic approach by combining the ATCS originally proposed by Bechtel [30] with auxiliary remote sensing and in-situ data. In particular, in-situ surface air temperatures (SATs) were assimilated to explain the short-term LST variations owing to synoptic conditions. The rest of this paper is organized as follows: Section 2 includes the study area, data, and new method proposed, which is then followed by the results and discussion in Section 3; and the conclusions are finally drawn in Section 4.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Data
The Yangtze River Delta (YRD) was chosen as the study area (refer to Figure 1) as this region is characterized by diverse terrains and land cover types and therefore suitable for the test of ATC modeling. The YRD is located in the middle of the coastline in Eastern China (26.9°–34.6°N, 116.8°–124.2°E). It mainly consists of Shanghai, the southern Jiangsu Province, and the northern Zhejiang Province (Figure 1a). Its terrain is comparably flat in the northern regions whereas relatively rugged in the southern ones (Figure 1b). The YRD is typified by a characteristic subtropical monsoon climate, usually with hot and humid summers while cold and dry winters. According to the International Geosphere-Biosphere Programme (IGBP) classification scheme, the main land cover types in the YRD include forest, grassland, cropland, built-up land, wetland, and water area (Figure 1c).
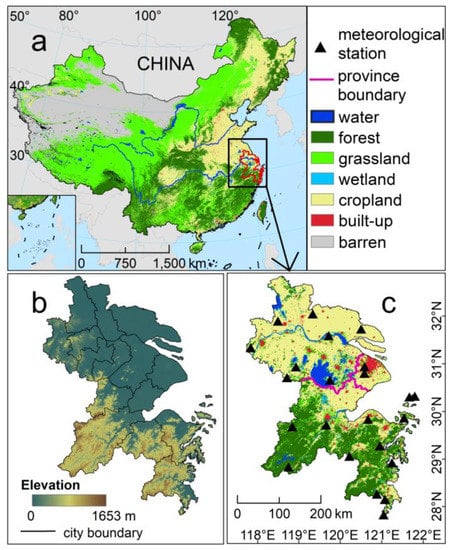
Figure 1.
Information on the study area (i.e., the Yangtze River Delta, YRD). (a–c) denote the general location, digital elevation model, and land cover type map, respectively.
The satellite data used in this study are from the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) collection-5 products generated in four years ranging from 2010 to 2013. Note that the following results are therefore provided as averages for these four years. They include the daily LST product MYD11A1 (with the spatial resolution of 1 km), the sixteen-day composite NDVI product MYD13A2 (1 km), and yearly land cover product MCD12Q1 (500 m), wherein the IGBP classification scheme was employed. Note that the water bodies were masked because they do not belong to land surfaces. The resolution of MCD12Q1 was further resampled to 1 km to match that of the LST products. The transit times of MYD11A1 LSTs are around 13:30 (day) and 1:30 (night) local time per daily cycle, which closely approximate the moments when daily minimum and maximum LST values occur. The MODIS LSTs have been used in various applications and demonstrated with an acceptable accuracy within 1.0 K [32].
For the MODIS LSTs, more than 60% of the data are invalid due to clouds. The seasonal mean percentages of clear-sky pixels in the chosen four years are presented in Table 1. The percentages of clear-sky data in the spring (March, April and May) and autumn (September, October and November) are generally higher than those in summer (June, July, and August) and winter (January, February and December). The high cloud coverage in the summer results from the heavy rainfall during this season over the YRD; while the high percentage in the winter is closely related to increased haze that reduces valid LST data [27].

Table 1.
Seasonal mean percentages (%) of valid LST data over the YRD from 2010 to 2013.
In addition to the satellite data, in-situ SATs from 23 meteorological stations from 2010 to 2013 were used (Figure 1b). They include the daily maximum and minimum measurements on SATs. These in-situ SATs were further resampled into raster images with the resolution of 1 km by the inverse distance weighted method, wherein the impacts from surface elevations on SATs were considered [33].
2.2. Method
2.2.1. Standard ATC Model
The ATC model originally proposed by Bechtel [30] uses a single sinusoidal function to describe the inner-annual LST dynamics (Figure 2a). Its general formula can be written as follows [7,8,12,27,30]:
where d is the day of the temperature cycle relative to the spring equinox; T0, A, and θ are the annual mean LST, the ATC amplitude, and the corresponding phase shift relative to the spring equinox, respectively; and N is the number of days in a year, which is equal to 366 for 2012, while 365 for 2010, 2011 and 2013. This classic ATC model is hereafter termed the standard ATC model (ATCS).
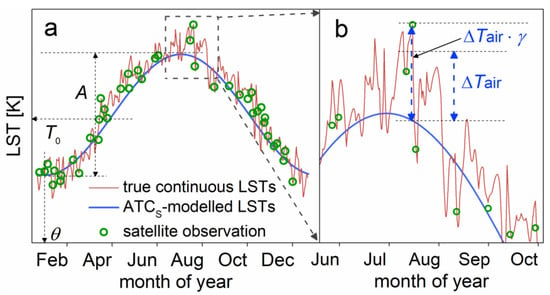
Figure 2.
A demonstration of the standard ATC model (represented by the ATCS) and the observed continuous daily LST dynamics. LST dynamics and the model predictions are presented for (a) an entire year and (b) a shorter period ranging from Jun. to Oct. T0, A, and θ are the annual mean LST, ATC amplitude, and the corresponding phase shift relative to the spring equinox, respectively; ΔTair denotes the SAT fluctuation; and γ is the ratio between the LST and SAT fluctuations.
2.2.2. Enhanced ATC Model
Given the simplicity of the ATCS, two predetermined assumptions are required. The first is that the annual LST dynamics is dominantly controlled by the top-of-atmosphere solar radiation flux; and the second is that the land surface properties remain unchanged across an annual cycle. The first assumption can be undermined because LSTs are truly controlled by climatic background and local synoptic conditions in addition to solar radiation, resulting in short-term LST fluctuations. The ATCS is therefore not suitable to describe the short-term LST fluctuations induced by the alteration of synoptic conditions. The second assumption can as well be undermined for areas where alterations of land surface properties do occur, e.g., as a result of soil moisture variation or vegetation phenology. For example, the LSTs over dry croplands are anticipated to rise considerably once crops have been harvested (bare soils are exposed).
To quantify the LST fluctuations due to synoptic conditions, we incorporated in-situ SATs to represent those variations of the LSTs because of their responses to day-by-day synoptic alterations are related, though with different magnitudes [34]. In other words, since LST and SAT are linked via the surface energy balance they simultaneously increase with changing synoptic conditions. To measure the LST variations caused by vegetation phenology, we moreover assimilated the information on surface vegetation status (quantified by vegetation index). By these two procedures, we obtained an enhanced annual temperature cycle model (termed the ATCE hereafter). Its formula is given as follows:
where the symbol d, T0, A, θ and N equal Equation (1); and ΔTair(d) and γ(d) are two intermediate functions that can be calculated by Equations (3) and (4), respectively. More precisely, ΔTair represents the SAT fluctuations induced by synoptic conditions when referenced to their standard inter-annual variations (Figure 2b). ΔTair is calculated by the following expression:
where Tair(d) is the in-situ daily mean SATs; f(∙) is the sinusoidal function given by Equation (1), with its parameters T0_air, Aair, and θair denoting the annual mean, annual amplitude, and phase shift for the SATs. Note that the day-to-day variations of the LSTs and SATs are correlated but also depend on the vegetation cover. We thus added a multiplier function after ΔTair(d), i.e., γ(d), to transform the SAT fluctuations into LST ones (Figure 2b). The multiplier function is provided by the following formula:
where λ is the time-independent coefficient on this multiplier; Vmax and Vmin are the annual maximum and minimum vegetation index values, respectively; and V(d) is the vegetation index at a certain specific day. Here the normalization of the vegetation index at the specific day (i.e., V(d)) by incorporating Vmax and Vmin aims at the quantification the temporal differences between the SATs and LSTs induced by vegetation phenology. From Equation (4), one may infer that the multiplier γ(d) would decease once the vegetation index at a specific day V(d) increases, which is reasonable because enhanced evapotranspiration over more vegetated areas usually reduce the difference between the LST and SAT, i.e., full vegetation cover can indicate little difference between these two temperatures. Note that the addition of 1.0 just aims at keeping the denominator not equal to zero to avoid unstable solutions.
2.2.3. Solution of the Forward ATCE and Validation Schemes
The formulas of the ATCE as demonstrated by Equations (2) to (4) indicate that this model possesses four free parameters, including T0, A, θ, and the regulator λ. In other words, at least four thermal observations are required to obtain the solution of the ATCE, which can be satisfied using MODIS LSTs (Note that in practice more observations are usually needed to achieve a robust modeling). This study directly used the NDVI data to reflect the vegetation status. To achieve a better model stability and avoid unpredictable factors that may influence the SAT, we calculated the average of the daily maximum and minimum SATs for each pixel of the spatially interpolated SAT images to represent the daily mean SAT. For the model validation, the training and test data were split by days for each pixel: 70% of the valid LSTs across the year were randomly selected as the training samples to drive the solution of T0, A, θ, and λ; while the remaining 30% of the data were used as for verifications. The least square method was applied to solve the four free parameters for each pixel; and the model performances were evaluated by the mean square error (RMSE) between the predicted and observed LSTs.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Overall and Spatial Patterns of Model Performances
The overall performances (represented by the RMSE) as well as the spatial distributions of the predicted RMSEs for the ATCS and ATCE are provided in Figure 3 and Figure 4 as well as Table 2. In general, these results demonstrate that the ATCE has a better performance than the ATCS. The mean RMSEs of the ATCS are 3.8 and 2.8 K in the day and night, respectively (Figure 3a), while those for the ATCE are 2.8 and 2.0 K, indicating an improved accuracy of 1.0 and 0.8 K for the day and night, respectively.
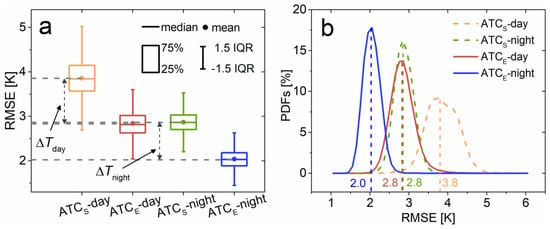
Figure 3.
Performances of the ATCS and ATCE for the day and night. (a) is the boxplot on the predicted RMSEs; while (b) denotes the probability distribution functions (PDFs) of the associated RMSEs. ΔTday and ΔTnight are the accuracy improvements for the ATCE when referenced to the ATCS for the day and night, respectively. The end of each whisker of the boxplot indicates the highest or lowest value within 1.5 times of the inter-quartile range (IQR).
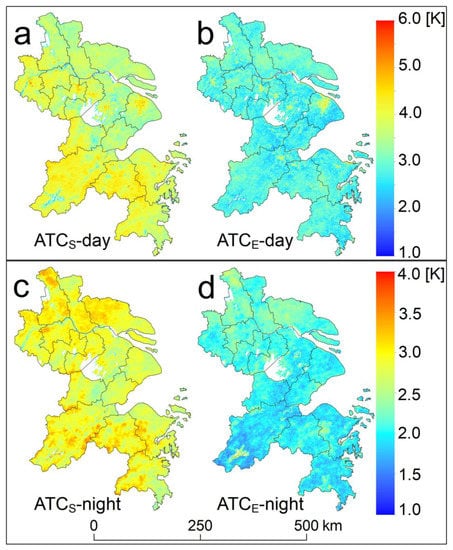
Figure 4.
Spatial distributions on the predicted RMSEs for the ATCS (left) and ATCE (right) during the day (a,b) and the night (c,d).

Table 2.
Predicted RMSEs (unit: K) of the ATCS and ATCE for different land cover types. Diff-day and -night denote the accuracy improvements of the ATCS when referenced to the ATCE.
For the ATCS, the probability distribution functions (PDFs) on the RMSE given in Figure 3b illustrate that 61% and 70% of the RMSEs are within 3.0–4.0 K and 2.0–3.0 K for the day and night, respectively. By comparison, a majority of the RMSEs predicted by the ATCE are well within 2.0–3.0 K and 1.0–2.0 K for the day and night, respectively. We further observe that the RMSEs for both the ATCS and ATCE are higher for the day than for the night. This is simply because the LST variations during the day when the solar insolation is strong are higher [16].
Further we analysed if the improvement differed by land cover (see Table 2). During the night, the assessments in terms of different land cover types indicate that the RMSEs by the ATCE, when compared with the ATCS, decrease by around 0.7 to 0.9 K. Such an improvement indicates that the performance improvement is rarely related to the land cover type. We however observed an opposite phenomenon during the day—the model performances greatly depend on the land cover types:
Notably, the differences in RMSE between the daytime models are greatest for the regions with higher terrains (i.e., the southern part of the YRD mainly covered by grasslands and forests, refer to Figure 1), with RMSEs of ATCS exceeding 4.0 K. By comparison, the mean RMSEs for these two land cover types when using the ATCE possess the largest decline, with an accuracy improvement of around 1.1 to 1.3 K. This phenomenon suggests that the incorporation of the NDVI data is particularly beneficial for improving the ATC modeling in strongly vegetated areas, because vegetation phenology plays an important role on the local LST fluctuations here.
For the built-up (urban) regions, the RMSEs by the ATCS are as high as those for the forests, especially for the cities near the Yangtze River and Taihu Lake, with the average RMSE reaching 4.0 K (Table 2). The evaluations interestingly show that the performance of the ATCE is better, but the accuracy improvement becomes lower (i.e., only 0.9 K), especially when compared with those values for the forests and grasslands. The comparably high modeling errors for both the ATCS and ATCE in urban areas are most likely related to additional anomalies of urban LSTs such as the more significant urban thermal anisotropy effect, as well as the more frequent prevalence of haze over urban areas [32], which destabilize the normal ATC dynamics. While the relatively smaller improvement of accuracy is probably due to the use of less accurate urban SATs, as urban SATs can be underestimated based on the measurements from meteorological stations that are mostly not within urban areas owing to the urban heat island effect [3]. An improved SAT estimation accounting for the UHI effect, therefore, might improve further the ATCE model for these areas.
For the cropland and wetland, the assessments also illustrate the ATCE possesses a higher accuracy when referenced to the ATCS, with the accuracy of improvement of 0.9 and 0.7 K, respectively. These improvements are as well lower compared with forests, which might be related to their relatively high soil moisture content, since soil moisture is an additional and crucial factor that regulates the differences between the LSTs and SATs. Note that more discussions the prospects and limitations of the ATCE are provided in Section 3.3.
3.2. Temporal Patterns of Model Performances
The aforementioned results primarily assessed the model performances from the spatial perspective, insights in the temporal performances are provided in Figure 5. To illustrate the daily comparisons between the model-predicted and observed LSTs, we display the temporally continuous LST dynamics at a random pixel (Figure 5a). The associated curves suggest that the ATCE reflects the day-to-day LST fluctuations induced by specific synoptic conditions, mostly by the use of the SATs. For example, two heat waves occurred between DOY (day of year) 170 to 220 as seen from the SAT fluctuations; and the predicted LSTs follow similar variations, although with different magnitudes. We also observe that the predicted LSTs occasionally mismatch the observed values, probably because of the inaccuracy of the interpolated LSTs and the uncertainties from the original MODIS LSTs. More analysis on the remaining errors is provided in Section 3.3.
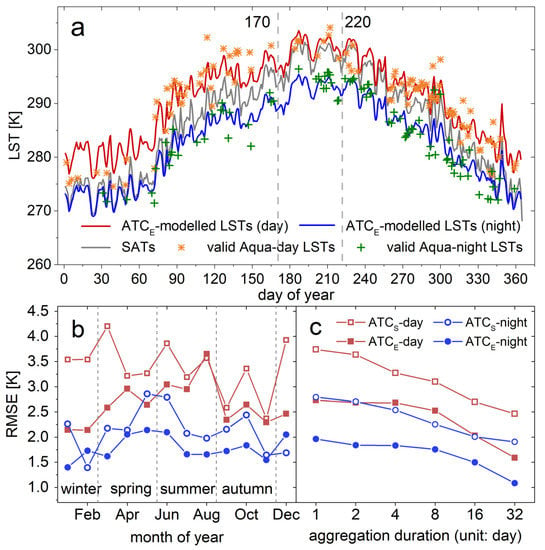
Figure 5.
Model performances at different time scales. (a) denotes the daily comparisons between the ATCE-predicted and observed LSTs at a selected pixel; (b,c) show the model performances at the monthly scale and a series of time scales ranging from 1 to 32 days, respectively.
In order to discern the model performances at the monthly scale, we further provide the monthly/seasonal variations of the RMSEs within an annual cycle (Figure 5b). These assessments suggest that the RMSEs by the ATCS fluctuate greatly during the year, with the higher values occurring in spring and winter than in the other two seasons. By comparison, the RMSEs by the ATCE are higher in the summer than in the other seasons. The accuracy improvements are larger in the spring and winter than those in the summer and autumn. For instance, the mean accuracy improvement for the period from July to September is only 0.2 K, while the mean improvement is 1.5 K for December, January, February, and March. Detailed examinations by checking the temporal distributions of the available valid LSTs and the temporal RMSE variations (refer to Table 1 and Figure 5b) reveal that the accuracy of the ATCE is only slightly better than that of the ATCS during the period when there are abundant valid LSTs (from July to September), while it is significantly better than its counterpart when data gaps frequently occur (around winter). During the nighttime, the performances of both the ATCS and ATCE are relatively stable. The ATCE performs better than the ATCS in all months except for November and February (Figure 5b). The decreased accuracies for the ATCE in the two months around the winter are speculated attributable to the over-addition of LST fluctuations, because nighttime LSTs are relatively less correlated to the vegetation status.
To further evaluate the model performances at different time scales, this study presents the comparison of the associated RMSE variations for these two models based on temporally aggregated LSTs (e.g., 8-day composite LSTs) in addition to the original daily LSTs. The aggregation period ranges from 1 to 32 days (Figure 5c). The results illustrate that the model performances increase with the aggregation duration. This phenomenon is reasonable because the impacts from the factors that distort the normal dynamics, such as the synoptic condition and surface thermal anisotropy effect, diminish as the aggregation duration enlarges. In detail, the RMSEs by the ATCS and ATCE in the day are 3.7 and 2.7 K respectively at the daily scale, while they decrease to 2.4 and 1.6 K once the aggregation duration is 32 days. By comparison, the accuracy improvements (represented by the RMSE) by these two models are between 0.5 and 1.0 K when the aggregation duration increases from 1 to 32 days.
3.3. Prospects and Limitations
By considering the LST fluctuations due to the synoptic conditions and local vegetation phenology, the preceding results show that this study improved the ATC modeling. The ATCE inherits the design philosophy of the ATCS attempting to model the annual LST dynamics with very limited controlling parameters. Though the accuracy for the LST reconstruction may not be necessarily better than the statistical methods that are based on direct or implicit spatio-temporal interpolations, the feature of using very limited free parameters is potentially beneficial. For example, by the ATCE, the reconstruction of daily LSTs only with Landsat-derived LSTs becomes possible [9], because there likely are at least four valid (clear-sky) Landsat thermal observations across a year. In addition, when compared with the pure statistical/interpolation methods, the physical meanings of the resolved controlling parameters (e.g., T0, A, θ, and λ) are explicit and clear. This gives rise to their potentials in various applications such as the monitoring of SUHI, as those that have been done for the parameters of the ATCS [26,27], and the estimation of SATs from remotely sensed LST observations [35,36].
Besides, the ATCE, to some extent, inherits the thought of the spatio-temporal interpolation method, by the incorporation of the easily accessible auxiliary data obtained simultaneously with the thermal data (e.g., in-situ SATs), which are valuable for the ATC modeling. This explains the improved prediction accuracy when compared with the ATCS. We however acknowledge that limitations remain for the current ATCE on the following aspects. First, the time difference of LSTs among transits on different days and surface thermal anisotropy effect [37,38,39] remain unconsidered, which may be the culprits of the low prediction accuracy especially for the urban areas. Second, the spatial interpolation of SATs with only limited in-situ SATs (i.e., 23 for this study) is far from accurate because SATs are impacted by the other local effect in addition to the elevation, though with a lower heterogeneity than the LSTs. Third, the vegetation status (represented by the NDVI in this study) is not the only surface factor that determines the LST-SAT differences. Surface characteristics such as the soil moisture are also expected to contribute to these differences. The consideration of these three aspects is anticipated to further improve the ATC modeling. We finally have to note that the improved ATC model is only valid for more or less cloud free conditions.
4. Conclusions
In terms of the LST fluctuations induced by the synoptic conditions and vegetation phenology, this study enhanced the standard sinusoidal ATC model (ATCS) by incorporating in-situ surface air temperatures (SATs) measured at meteorological stations as well as the NDVI data. The proposed enhanced ATC model (ATCE) has four free parameters and the assessments over the Yangtze River Delta (YRD) demonstrate that it improves the ATC modeling effectively. When compared with the ATCS, the overall RMSE of the enhanced model decreases about 0.9 K, with the accuracy improvement during the day greater than that for the night. The accuracy improvement nevertheless is related to the land cover types, with the highest improvement occurring over the built-up areas, grasslands, and forests. Further evaluations reveal that the improvement is valid at different time scales ranging from the daily to monthly aggregations. We finally discussed the remaining limitations of ATCE that could become the research foci of future investigations. We consider this approach useful for the generation of better aggregated LST products as well as the quantification of land surface properties that are potentially valuable in related applications.
Acknowledgments
This work is jointly supported by the Key Research and Development Programs for Global Change and Adaptation under Grant number 2016YFA0600201, the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 41671420, and the Key Research and Development Programs for Global Change and Adaptation under Grants number 2017YFA0603604. This study was also supported by the Cluster of Excellence ‘CliSAP’ (EXC177), University of Hamburg, funded through the German Science Foundation (DFG), as well as by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities. We are also grateful for the financial support provided by the Deng-Feng Program-B of Nanjing University.
Author Contributions
Z.Z. and W.Z. conceived and designed the experiments; Z.Z. performed the experiments; Z.Z., W.Z, and Z.L. analyzed the data; B.B., L.G., F.H., F.H., and J.L. contributed to the analysis and interpretation of results; all the authors participate in the writing of the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Li, Z.; Tang, B.; Wu, H.; Ren, H.; Yan, G.; Wan, Z.; Trigo, I.F.; Sobrino, J.A. Satellite-derived land surface temperature: Current status and perspectives. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 131, 14–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cammalleri, C.; Anderson, M.C.; Gao, F.; Hain, C.R.; Kustas, W.P. Mapping daily evapotranspiration at field scales over rainfed and irrigated agricultural areas using remote sensing data fusion. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2014, 186, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voogt, J.A.; Oke, T.R. Thermal remote sensing of urban climates. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 86, 370–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giglio, L.; Descloitres, J.; Justice, C.O.; Kaufman, Y.J. An enhanced contextual fire detection algorithm for MODIS. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 87, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsey, M.S.; Harris, A.J.L. Volcanology 2020: How will thermal remote sensing of volcanic surface activity evolve over the next decade. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2013, 249, 217–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, K.; Wu, L.; De, S.A.; Gianfranco, C. Preliminary analysis of surface temperature anomalies that preceded the two major Emilia 2012 earthquakes (Italy). Ann. Geophys. 2012, 55, 823–828. [Google Scholar]
- Zhan, W.; Zhou, J.; Ju, W.; Li, M.; Sandholt, I.; Voogt, J.; Yu, C. Remotely sensed soil temperatures beneath snow-free skin-surface using thermal observations from tandem polar-orbiting satellites: An analytical three-time-scale model. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 143, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, J.; Zhan, W.; Chen, Y.; Wang, M.; Wang, J. Time series decomposition of remotely sensed land surface temperature and investigation of trends and seasonal variations in surface urban heat islands. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 2638–2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, P.; Weng, Q. Consistent land surface temperature data generation from irregularly spaced Landsat imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 184, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobrino, J.A.; Julien, Y. Time series corrections and analyses in thermal remote sensing. In Thermal Infrared Remote Sensing: Sensors, Methods, Applications; Kuenzer, C., Dech, S., Eds.; Springer Science & Business Media: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 267–285. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, P.; Weng, Q. Temporal dynamics of land surface temperature from Landsat TIR time series images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 2175–2179. [Google Scholar]
- Bechtel, B. Robustness of annual cycle parameters to characterize the urban thermal landscapes. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2012, 9, 876–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, R.; Henderson-Sellers, A.; Kennedy, P. Biosphere-Atmosphere Transfer Scheme (BATS) Version 1e as Coupled to the NCAR Community Climate Model; Technical Note; NCAR: Boulder, CO, USA, 1993; p. 72. [Google Scholar]
- Sobrino, J.A.; El Kharraz, M.H. Combining afternoon and morning NOAA satellites for thermal inertia estimation: 1. Algorithm and its testing with Hydrologic Atmospheric Pilot Experiment-Sahel data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1999, 104, 9445–9453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, K. A diurnal animation of thermal images from a day-night pair. Remote Sens. Environ. 2000, 72, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göttsche, F.M.; Olesen, F.S. Modelling of diurnal cycles of brightness temperature extracted from METEOSAT data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2001, 76, 337–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aires, F.; Prigent, C.; Rossow, W.B. Temporal interpolation of global surface skin temperature diurnal cycle over land under clear and cloudy conditions. J. Geophys. Res. 2004, 109, 385–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, S.; Li, Z.; Wu, H.; Tang, B.; Jiang, X.; Zhou, G. Modeling of day-to-day temporal progression of clear-sky land surface temperature. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 10, 1050–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Zhan, W.; Duan, S.; Ju, W.; Quan, J. A generic framework for modeling diurnal land surface temperatures with remotely sensed thermal observations under clear sky. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 150, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zhong, L.; Ma, Y.; Zou, M.; Xu, K.; Huang, Z.; Feng, L. Estimation of the land surface temperature over the Tibetan Plateau by using Chinese FY-2C geostationary satellite data. Sensors 2018, 18, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bechtel, B. A new global climatology of annual land surface temperature. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 2850–2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sismanidis, P.; Bechtel, B.; Keramitsoglou, I.; Kiranoudis, C.T. Mapping the spatiotemporal dynamics of Europe’s land surface temperatures. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 15, 202–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Q.; Gao, F.; Fu, P. Generating daily land surface temperature at Landsat resolution by fusing Landsat and MODIS data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 145, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sismanidis, P.; Keramitsoglou, I.; Bechtel, B.; Kiranoudis, C.T. Improving the downscaling of diurnal land surface temperatures using the annual cycle parameters as disaggregation kernels. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, X.; Pan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, C. Downscaling land surface temperature in complex regions by using multiple scale factors with adaptive thresholds. Sensors 2017, 17, 744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bechtel, B.; Zakšek, K.; Hoshyaripour, G. Downscaling land surface temperature in an urban area: A case study for Hamburg, Germany. Remote Sens. 2012, 4, 3184–3200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Zhan, W.; Voogt, J.; Hu, L.; Wang, Z.; Quan, J.; Ju, W.; Guo, Z. Temporal upscaling of surface urban heat island by incorporating an annual temperature cycle model: A tale of two cities. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 186, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baiocchi, V.; Zottele, F.; Dominici, D. Remote sensing of urban microclimate change in L’Aquila city (Italy) after post-earthquake depopulation in an open source GIS environment. Sensors 2017, 17, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Shen, Y. Reconstruction of the land surface temperature time series using harmonic analysis. Comput. Geosci. 2013, 61, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechtel, B. Multitemporal Landsat data for urban heat island assessment and classification of local climate zones. In Proceedings of the IEEE Joint Urban Remote Sensing Event (JURSE), Munich, Germany, 11–13 April 2011; pp. 129–132. [Google Scholar]
- Bechtel, B.; Sismanidis, P. Time series analysis of moderate resolution land surface temperatures. In Remote Sensing: Time Series Image Processing; Weng, Q., Ed.; Taylor & Francis: Oxfordshire UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, Z. New refinements and validation of the collection-6 MODIS land-surface temperature/emissivity product. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 140, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xiao, J.; Ju, W.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, S.; Wu, X. Water use efficiency of China’s terrestrial ecosystems and responses to drought. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benali, A.; Carvalho, A.C.; Nunes, J.P.; Carvalhais, N.; Santos, A. Estimating air surface temperature in Portugal using MODIS LST data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 124, 108–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vancutsem, C.; Ceccato, P.; Dinku, T.; Connor, S.J. Evaluation of MODIS land surface temperature data to estimate air temperature in different ecosystems over Africa. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 449–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Wardlow, B.; Tadesse, T.; Shan, J.; Hayes, M.; Li, D.; Xiang, D. Estimation of daily air temperature based on MODIS land surface temperature products over the corn belt in the US. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 951–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Yan, G.; Chen, L.; Li, Z. Angular effect of MODIS emissivity products and its application to the split-window algorithm. ISPSR J. Photogramm. 2011, 66, 498–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Liang, S. Effects of thermal-infrared emissivity directionality on surface broadband emissivity and longwave net radiation estimation. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 11, 499–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Santos, V.; Coll, C.; Valor, E.; Niclòs, R.; Caselles, V. Analyzing the anisotropy of thermal infrared emissivity over arid regions using a new MODIS land surface temperature and emissivity product (MOD21). Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 169, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).