The Evaluation of SMAP Enhanced Soil Moisture Products Using High-Resolution Model Simulations and In-Situ Observations on the Tibetan Plateau
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. SMAP Enhanced Soil Moisture Product
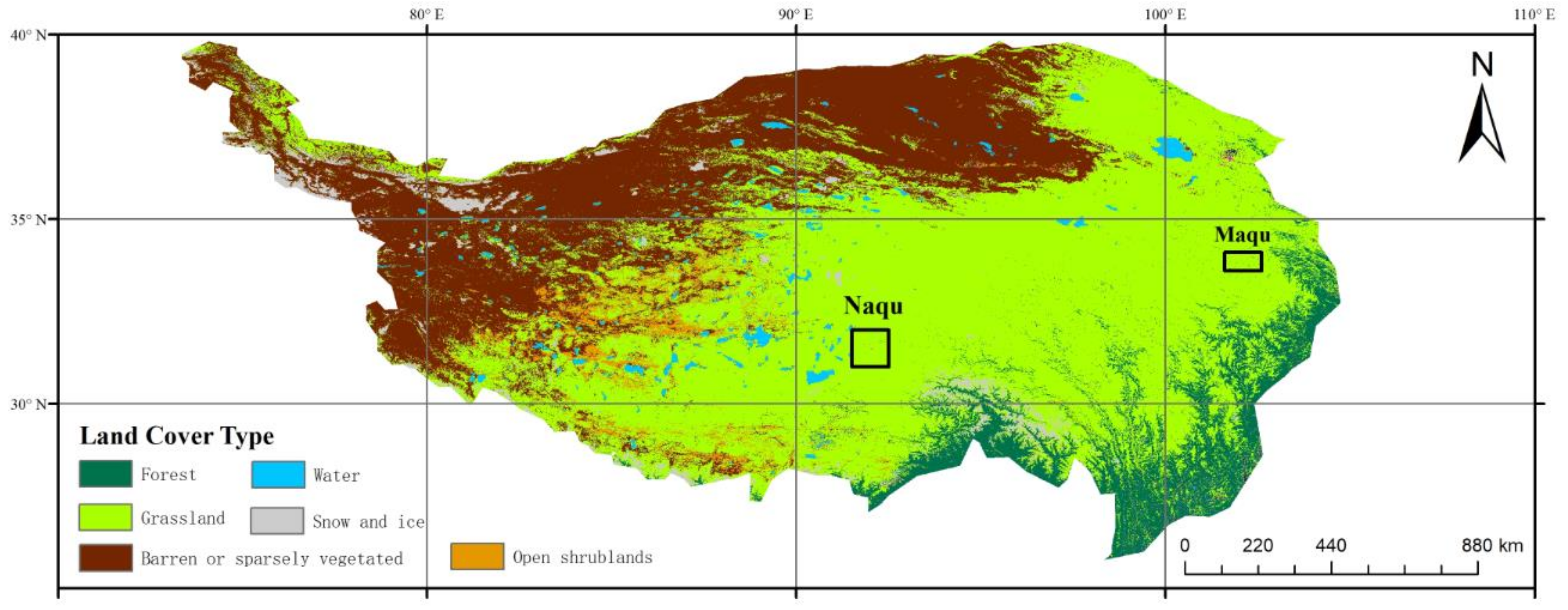
2.2. In-Situ Observations
2.3. High-Resolution Land Surface Modeling
2.4. Methods
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Comparison with In Situ Observations
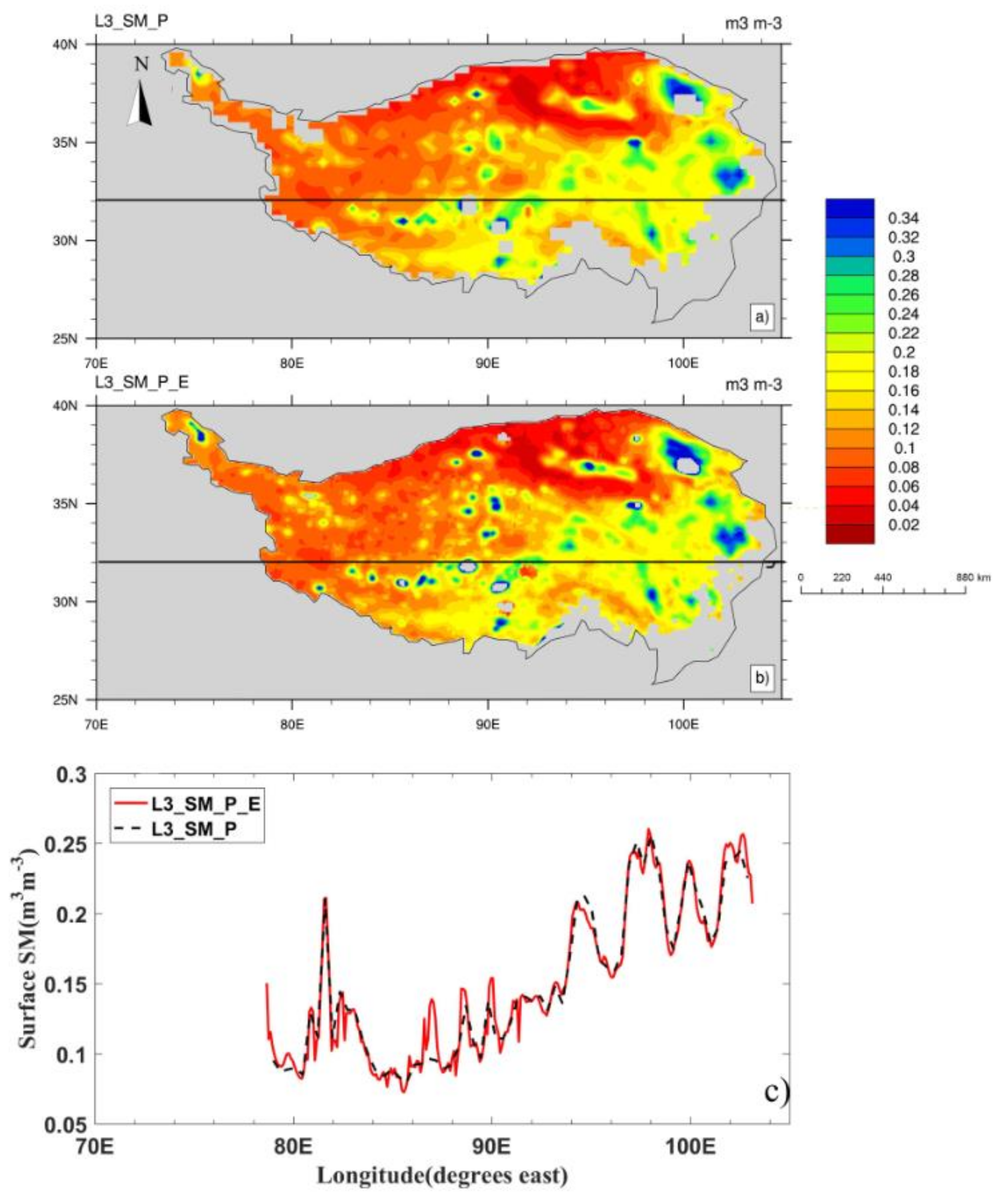
3.2. Comparison between the SMAP L3_SM_P and L3_SM_P_E Products
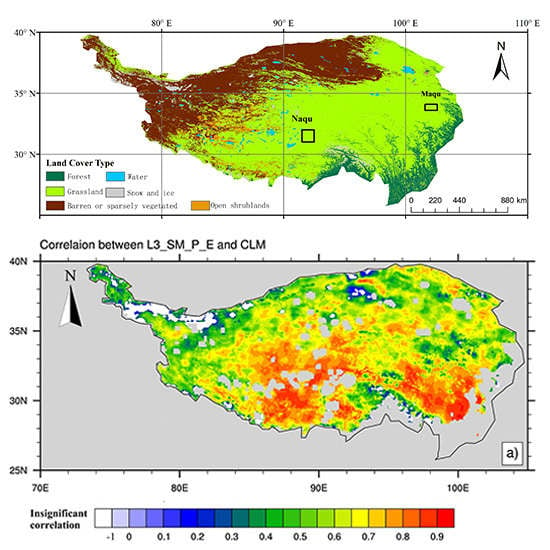
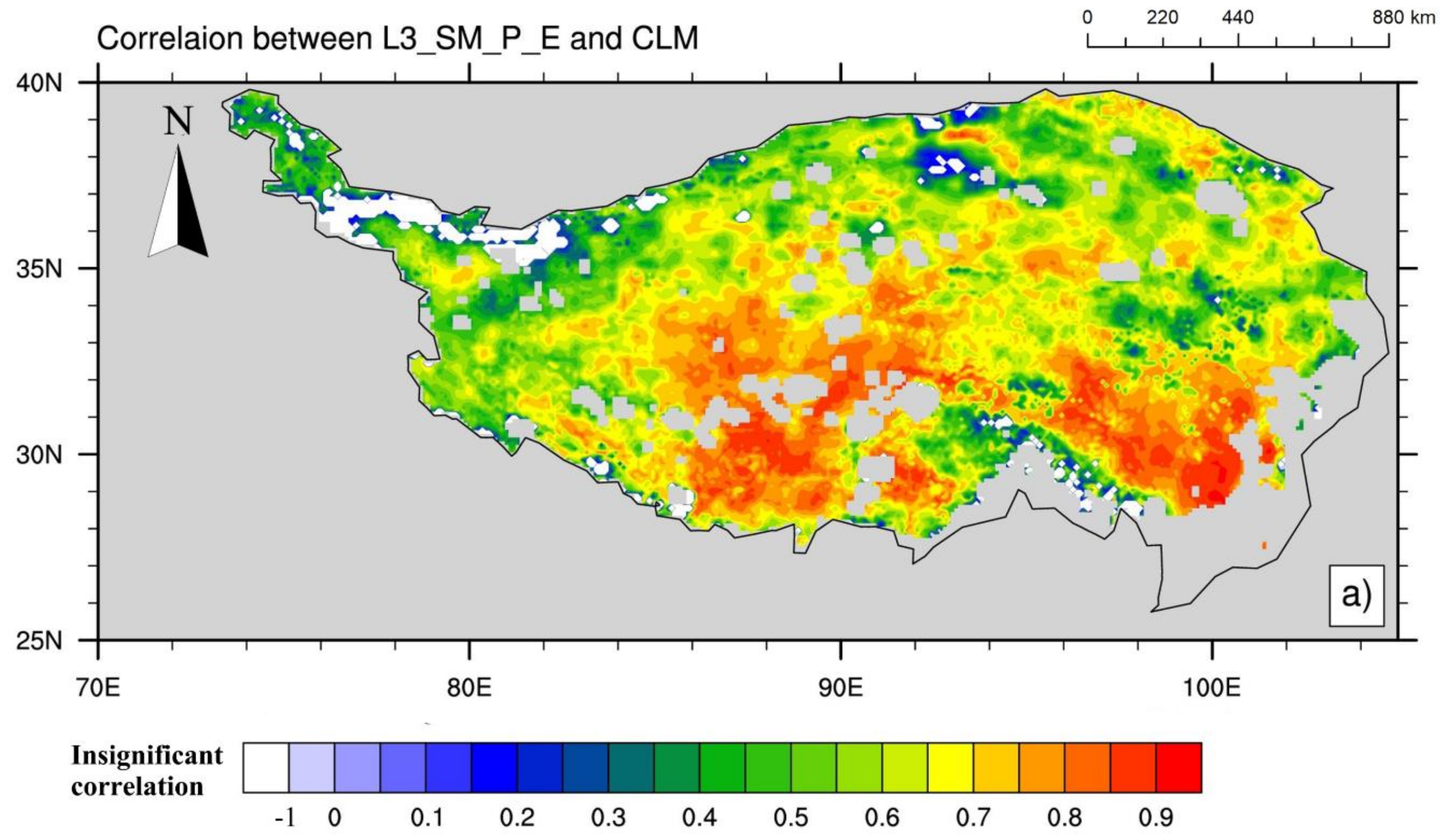
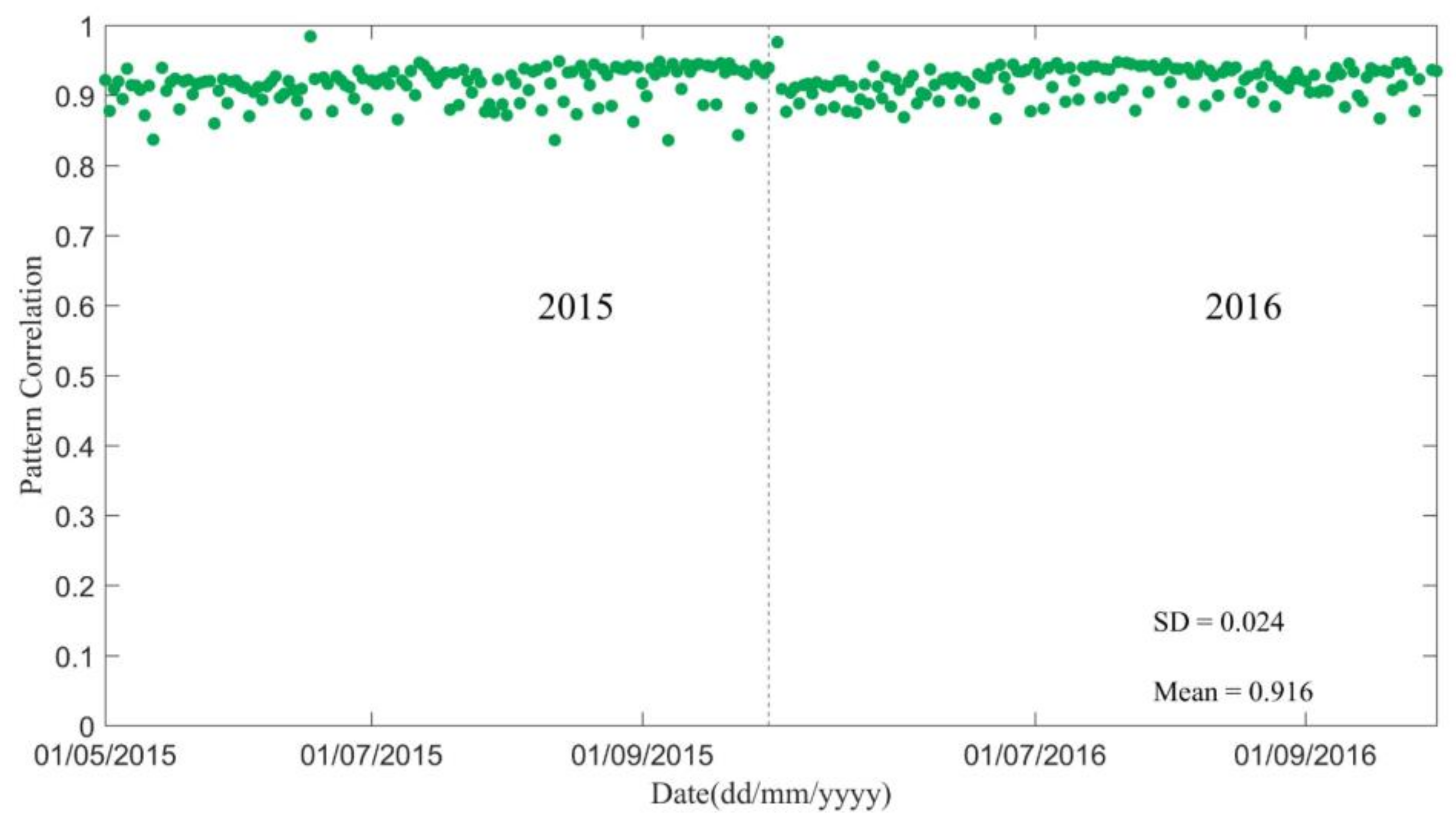
3.3. Correlation between the SMAP L3_SM_P_E Product and CLM Simulations
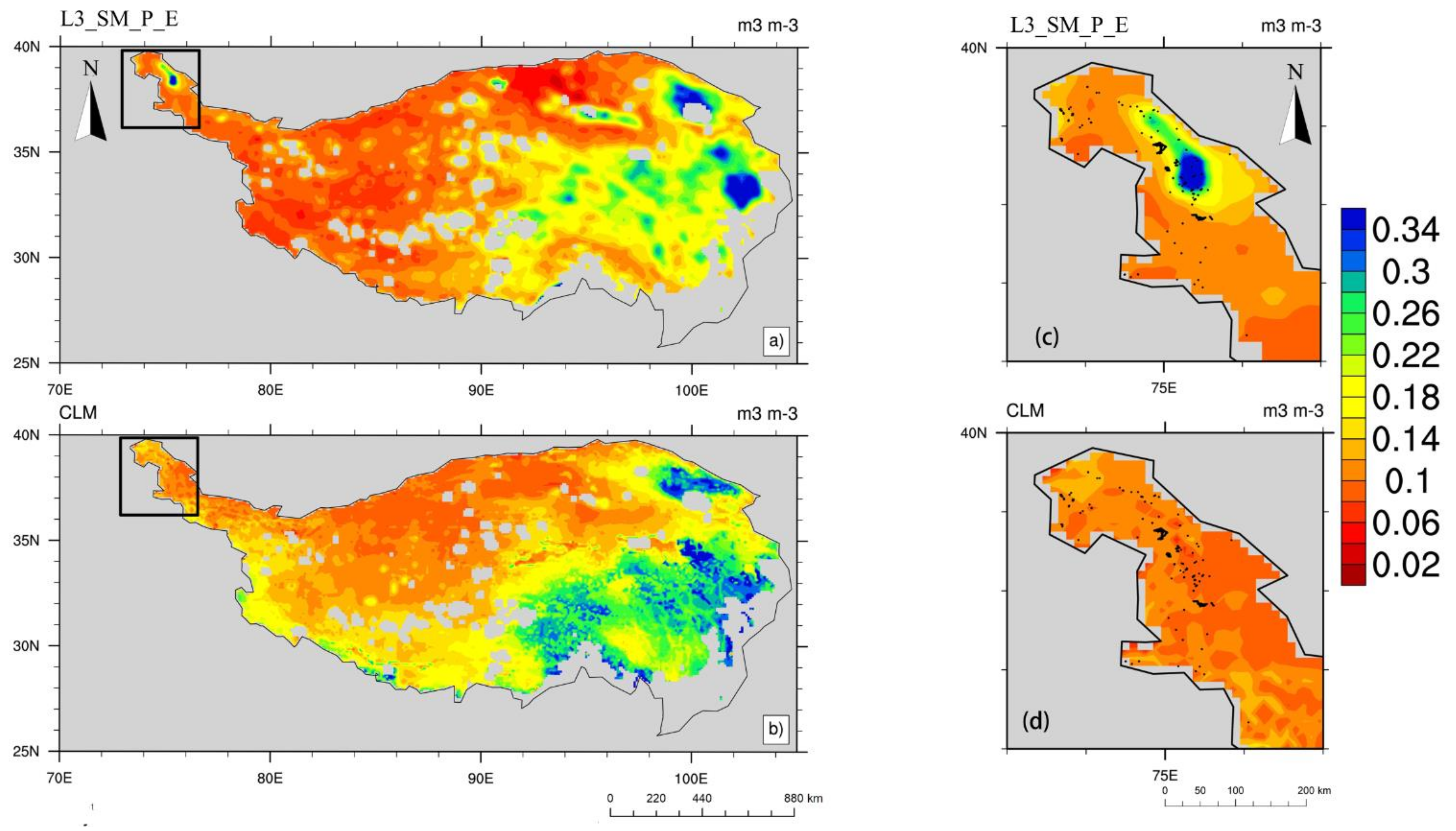
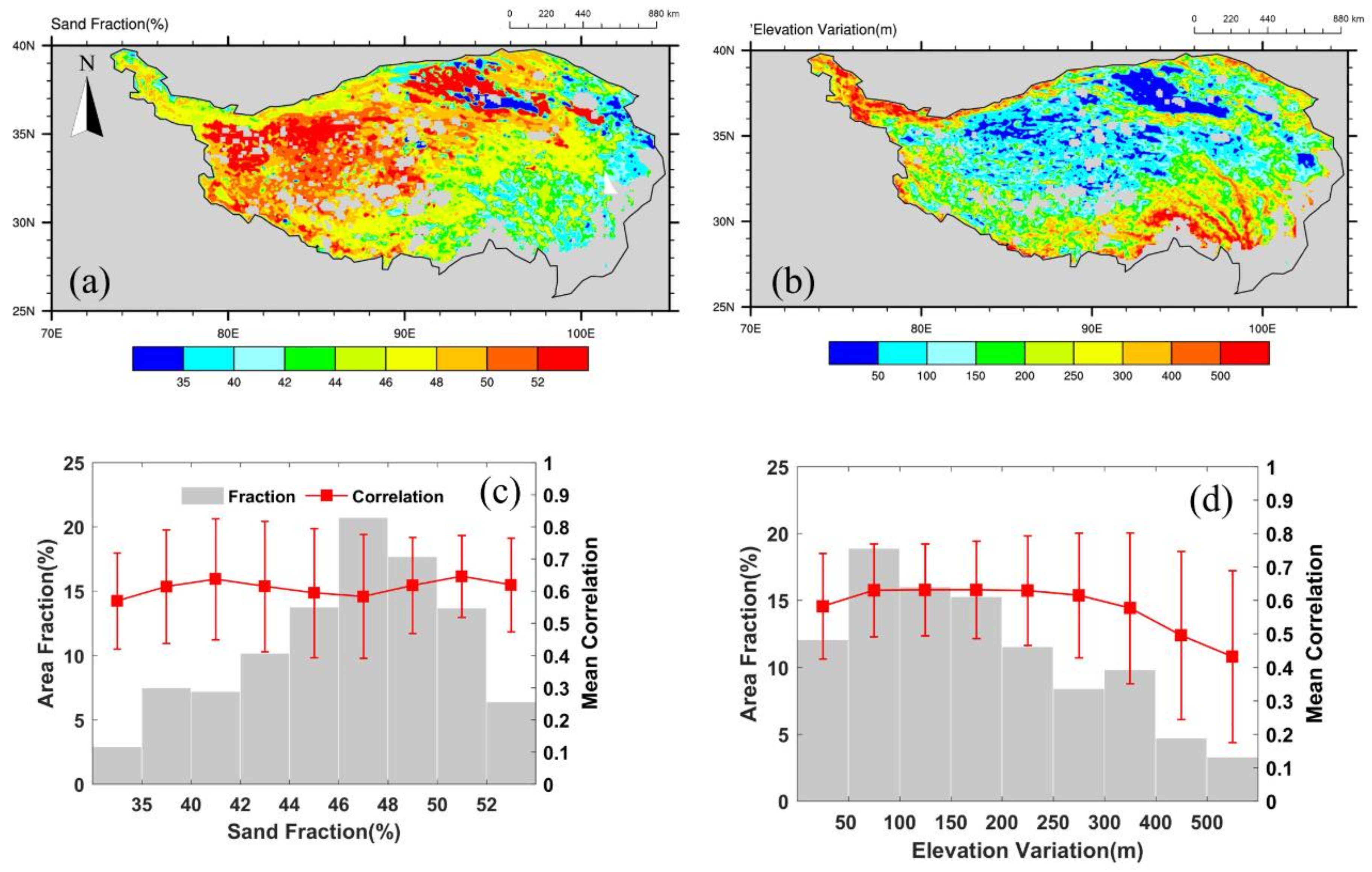
3.4. Spatial Variation of SMAP Product and CLM Simulations
4. Discussions
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, F.; Avissar, R. Impact of land-surface moisture variability on local shallow convective cumulus and precipitation in large-scale models. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2006, 33, 1382–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koster, R.D.; Dirmeyer, P.A.; Guo, Z.; Bonan, G.; Chan, E.; Cox, P.; Gordon, C.T.; Kanae, S.; Kowalczyk, E.; Lawrence, D. Regions of strong coupling between soil moisture and precipitation. Science 2004, 305, 1138–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miralles, D.G.; Berg, M.V.D. El niño-la niña cycle and recent trends in continental evaporation. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2014, 4, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirschi, M.; Seneviratne, S.I.; Alexandrov, V.; Boberg, F.; Boroneant, C.; Christensen, O.B.; Formayer, H.; Orlowsky, B.; Stepanek, P. Observational evidence for soil-moisture impact on hot extremes in southeastern europe. Nat. Geosci. 2011, 4, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massari, C.; Brocca, L.; Moramarco, T.; Tramblay, Y.; Lescot, J.F.D. Potential of soil moisture observations in flood modelling: Estimating initial conditions and correcting rainfall. Adv. Water Resour. 2014, 74, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamilla-Magaña, J.C.; Carrillo-Ávila, E.; Obrador-Olán, J.J.; Landeros-Sánchez, C.; Vera-Lopez, J.; Juárez-López, J.F. Soil moisture tension effect on sugar cane growth and yield. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 177, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ines, A.V.M.; Das, N.N.; Hansen, J.W.; Njoku, E.G. Assimilation of remotely sensed soil moisture and vegetation with a crop simulation model for maize yield prediction. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 138, 149–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Entekhabi, D.; Njoku, E.G.; O’Neill, P.E.; Kellogg, K.H.; Crow, W.T.; Edelstein, W.N.; Entin, J.K.; Goodman, S.D.; Jackson, T.J.; Johnson, J. The soil moisture active passive (SMAP) mission. Proc. IEEE 2010, 98, 704–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, M.; Cai, X.; Chaney, N.W.; Entekhabi, D.; Wood, E.F. An initial assessment of smap soil moisture retrievals using high-resolution model simulations and in situ observations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 9662–9668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, S.K.; Bindlish, R.; O’Neill, P.E.; Njoku, E.; Jackson, T.; Colliander, A.; Chen, F.; Burgin, M.; Dunbar, S.; Piepmeier, J. Assessment of the smap passive soil moisture product. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 4994–5007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, S.K.; Bindlish, R.; O’Neill, P.; Jackson, T.; Njoku, E.; Dunbar, S.; Chaubell, J.; Piepmeier, J.; Yueh, S.; Entekhabi, D. Development and assessment of the smap enhanced passive soil moisture product. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 204, 931–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santi, E.; Paloscia, S.; Pettinato, S.; Brocca, L.; Ciabatta, L.; Entekhabi, D. On the synergy of smap, amsr2 and sentinel-1 for retrieving soil moisture. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinform. 2018, 65, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santi, E.; Paloscia, S.; Pettinato, S.; Entekhabi, D.; Alemohammad, S.H.; Konings, A.G. Integration of passive and active microwave data from SMAP, AMSR2 and Sentinel-1 for soil moisture monitoring. In Proceedings of the Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Beijing, China, 10–15 July 2016; pp. 5252–5255. [Google Scholar]
- Poe, G.A. Optimum interpolation of imaging microwave radiometer data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1990, 28, 800–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stogryn, A. Estimates of brightness temperatures from scanning radiometer data. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1978, 26, 720–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piepmeier, J.R.; Mohammed, P.; Peng, J.; Kim, E.J.; De Amici, G.; Ruf, C. Smap L1b Radiometer Half-Orbit Time-Ordered Brightness Temperatures, 3th ed.; NASA National Snow and Ice Data Center Distributed Active Archive Center: Boulder, CO, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Chaubell, J. Smap Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document: Enhanced L1b Radiometer Brightness Temperature Product; Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology: Pasadena, CA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- O’Neill, P.E.; Chan, S.; Njoku, E.G.; Jackson, T.; Bindlish, R. Smap Enhanced L2 Radiometer Half-Orbit 9 km Ease-Grid Soil Moisture, 1st ed.; NASA National Snow and Ice Data Center Distributed Active Archive Center: Boulder, CO, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Colliander, A.; Jackson, T.J.; Chan, S.K.; O’Neill, P.; Bindlish, R.; Cosh, M.H.; Caldwell, T.; Walker, J.P.; Berg, A.; McNairn, H.; et al. An assessment of the differences between spatial resolution and grid size for the smap enhanced soil moisture product over homogeneous sites. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 207, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lievens, H.; Reichle, R.H.; Liu, Q.; De Lannoy, G.J.M.; Dunbar, R.S.; Kim, S.B.; Das, N.N.; Cosh, M.; Walker, J.P.; Wagner, W. Joint sentinel-1 and smap data assimilation to improve soil moisture estimates. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 6145–6153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mccoll, K.A.; Wang, W.; Peng, B.; Akbar, R.; Short Gianotti, D.J.; Lu, H.; Pan, M.; Entekhabi, D. Global characterization of surface soil moisture drydowns. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 3682–3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadri, S.; Wood, E.F.; Pan, M.; Lettenmaier, D.P. Development of a smap-based drought monitoring product. In Proceedings of the AGU Fall Meeting, San Francisco, CA, USA, 12–16 December 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F.; Crow, W.T.; Colliander, A.; Cosh, M.H.; Jackson, T.J.; Bindlish, R.; Reichle, R.H.; Chan, S.K.; Bosch, D.D.; Starks, P.J. Application of triple collocation in ground-based validation of soil moisture active/passive (smap) level 2 data products. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 489–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colliander, A.; Jackson, T.J.; Bindlish, R.; Chan, S.; Das, N.; Kim, S.B.; Cosh, M.H.; Dunbar, R.S.; Dang, L.; Pashaian, L. Validation of smap surface soil moisture products with core validation sites. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 191, 215–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgin, M.S.; Colliander, A.; Njoku, E.G.; Chan, S.K.; Cabot, F.; Kerr, Y.H.; Bindlish, R.; Jackson, T.J.; Entekhabi, D.; Yueh, S.H. A comparative study of the smap passive soil moisture product with existing satellite-based soil moisture products. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 2959–2971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, K.; Qin, J.; Cui, Q.; Lu, H.; Zhu, L.; Han, M.; Tang, W. Evaluation of SMAP, SMOS, and AMSR2 soil moisture retrievals against observations from two networks on the tibetan plateau. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 5780–5792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albergel, C.; Rosnay, P.D.; Gruhier, C.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Hasenauer, S.; Isaksen, L.; Kerr, Y.; Wagner, W. Evaluation of remotely sensed and modelled soil moisture products using global ground-based in situ observations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 118, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albergel, C.; Rüdiger, C.; Carrer, D.; Calvet, J.C.; Fritz, N.; Naeimi, V.; Bartalis, Z.; Hasenauer, S. An evaluation of ascat surface soil moisture products with in-situ observations in southwestern france. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2009, 5, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Chen, Y.Y.; Qin, J. Some practical notes on the land surface modeling in the tibetan plateau. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 13, 687–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, N.N.; Entekhabi, D.; Njoku, E.G. An algorithm for merging smap radiometer and radar data for high-resolution soil-moisture retrieval. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 1504–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Entekhabi, D.; Yueh, S.; O’Neill, P.E.; Kellogg, K.H.; Allen, A.; Bindlish, R.; Brown, M.; Chan, S.; Colliander, A.; Crow, W.T. Smap Handbook—Soil Moisture Active Passive: Mapping Soil Moisture and Freeze/Thaw from Space; Jet Propulsion Laboratory: Pasadena, CA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Reichle, R.; Crow, W.; Koster, R.; Kimball, J.; De Lannoy, G. Smap Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document: Level 4 Surface and Root-Zone Soil Moisture; Jet Propulsion Laboratory: Pasadena, CA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, S.K. Smap Enhanced Level 2 Passive Soil Moisture Data Product Specification Document; Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology: Pasadena, CA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- O’Neill, P.E.; Njoku, E.G.; Jackson, T.; Chan, S.K.; Bindlish, R. Smap Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document: Level 2 & 3 Soil Moisture (Passive) Data Products; Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology: Pasadena, CA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, K.; Qin, J.; Zhao, L.; Chen, Y.; Han, M. A multi-scale soil moisture and freeze-thaw monitoring network on the third pole. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2013, 94, 1907–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Wen, J.; Dente, L.; Velde, R.v.d.; Wang, L.; Ma, Y.; Yang, K.; Hu, Z. The tibetan plateau observatory of plateau scale soil moisture and soil temperature (Tibet-Obs) for quantifying uncertainties in coarse resolution satellite and model products. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oleson, K.W.; Lawrence, D.M.; Bonan, G.B.; Drewniak, B.; Huang, M.; Koven, C.D.; Levis, S.; Li, F.; Riley, W.J.; Subin, Z.M. Technical Description of Version 4.5 of the Community Land Model (CLM); National Center for Atmospheric Research, Climate and Global Dynamics Division: Boulder, CO, USA, 2013; pp. 256–265. [Google Scholar]
- He, J. Development of Surface Meteorological Dataset of China with High Temporal and Spatial Resolution. Master Dissertation, Institute of Tibetan Plateau Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China, 2010. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Huffman, G.A.; Adler, R.; Bolvin, D.T.; Gu, G.; Nelkin, E.; Bowman, K.; Hong, Y.; Stocker, T.; Wolff, D. The TRMM multi-satellite precipitation analysis (TMPA): Quasi-global, multiyear, combined-sensor precipitation estimates at fine scale. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 38–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatagai, A.; Arakawa, O.; Kamiguchi, K.; Kawamoto, H.; Nodzu, M.I.; Hamada, A. A 44-year daily gridded precipitation dataset for asia based on a dense network of rain gauges. SOLA 2009, 5, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinker, R.T.; Laszlo, I. Modeling surface solar irradiance for satellite applications on a global scale. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1992, 31, 194–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheffield, J.; Goteti, G.; Wood, E.F. Development of a 50-year high-resolution global dataset of meteorological forcings for land surface modeling. J. Clim. 2006, 19, 3088–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, K.; Jie, H.; Qin, J.; Shi, J.; Du, J.; He, Q. Improving land surface temperature modeling for dry land of china. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116, D20104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Lu, H.; Yang, K.; Wang, W.; Li, C.; Han, M.; Li, Y. Evaluation and comparison among multiple forcing data sets for precipitation and shortwave radiation over mainland China. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2017, 21, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.G.; Xie, Z.H. Improving simulation of soil moisture in china using a multiple meteorological forcing ensemble approach. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 3355–3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Wang, H. Simulation of permafrost and seasonally frozen ground conditions on the tibetan plateau, 1981–2010. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 5216–5230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, K.; Qin, J.; Zhao, L.; Tang, W.; Han, M. Evaluation of amsr-e retrievals and gldas simulations against observations of a soil moisture network on the central tibetan plateau. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 4466–4475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, T.J.; Bindlish, R.; Cosh, M.H.; Zhao, T.; Starks, P.J.; Bosch, D.D.; Seyfried, M.; Moran, M.S.; Goodrich, D.C.; Kerr, Y.H. Validation of soil moisture and ocean salinity (smos) soil moisture over watershed networks in the U.S. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 1530–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, T.J.; Cosh, M.H.; Bindlish, R.; Starks, P.J.; Bosch, D.D.; Seyfried, M.; Goodrich, D.C.; Moran, M.S.; Du, J. Validation of advanced microwave scanning radiometer soil moisture products. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 4256–4272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Entekhabi, D.; Reichle, R.H.; Koster, R.D.; Crow, W.T. Performance metrics for soil moisture retrievals and application requirements. J. Hydrometeorol. 2010, 11, 832–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X. Spatial Distribution of Lakes on Tibetan Plateau; Institute of Tibetan Plateau Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Ed.; Institute of Tibetan Plateau Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences: Beijing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, M.; Sahoo, A.K.; Wood, E.F. Improving soil moisture retrievals from a physically-based radiative transfer model. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 140, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvis, A.; Reuter, H.I.; Nelson, A.; Guevara, E. Hole-Filled SRTM for the Globe Version 4.CGIAR-CSI SRTM 90 m Database 2008. Available online: http://srtm.csi.cgiar.org (accessed on 1 February 2018).
- Srivastava, P.K.; Han, D.; Rico-Ramirez, M.A.; O’Neill, P.; Islam, T.; Gupta, M.; Dai, Q. Performance evaluation of wrf-noah land surface model estimated soil moisture for hydrological application: Synergistic evaluation using smos retrieved soil moisture. J. Hydrol. 2015, 529, 200–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanders, N.; Bierkens, M.F.P.; De Jong, S.M.; De Roo, A.; Karssenberg, D. The benefits of using remotely sensed soil moisture in parameter identification of large-scale hydrological models. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 50, 6874–6891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
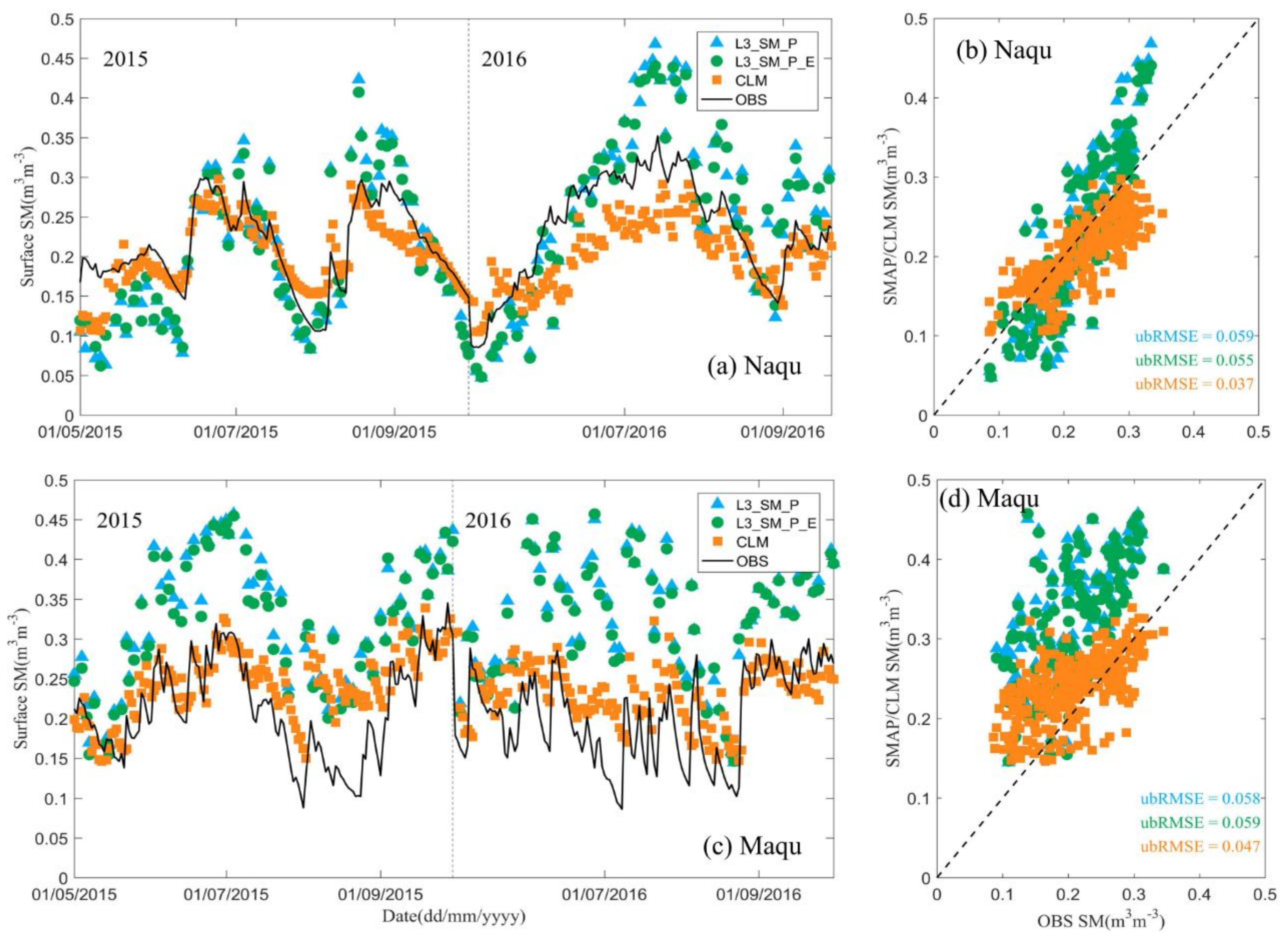
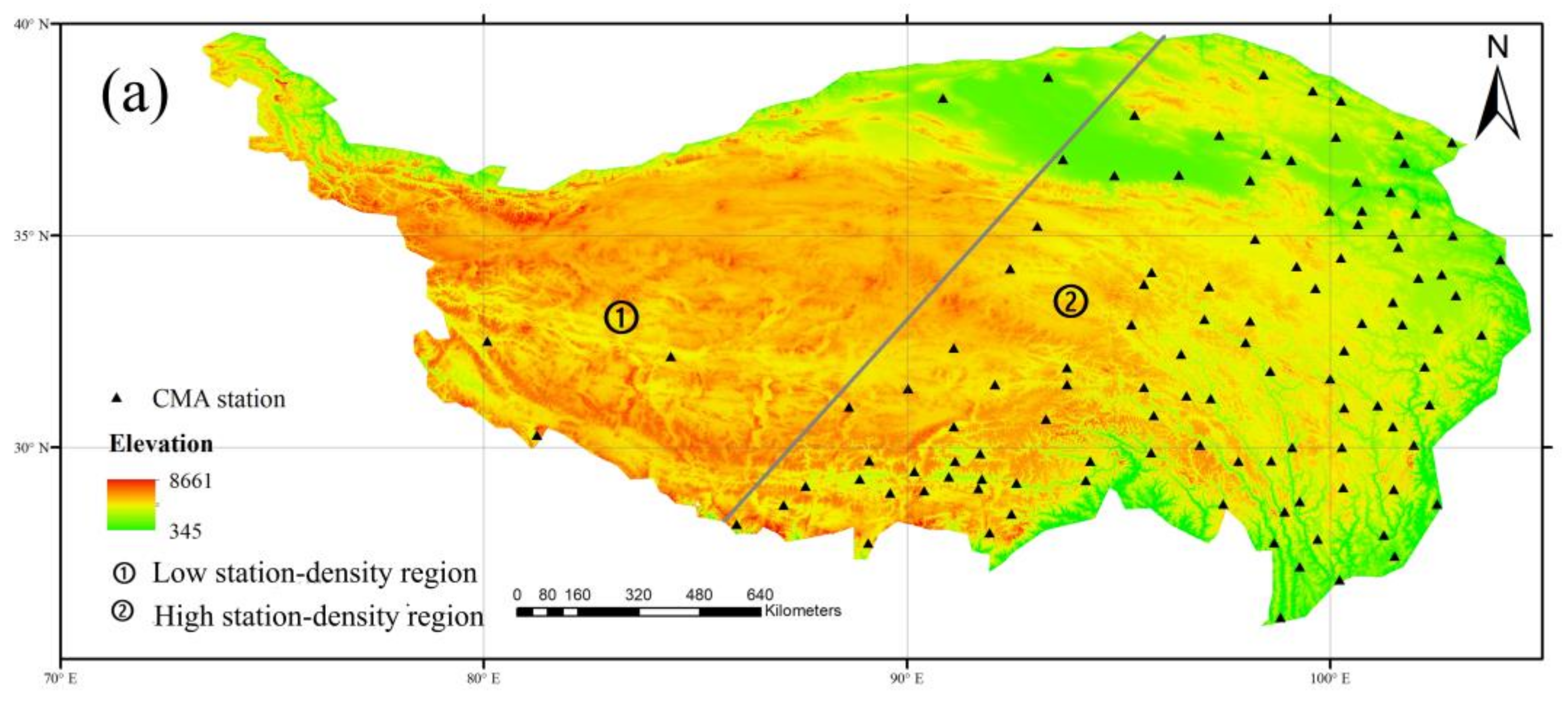
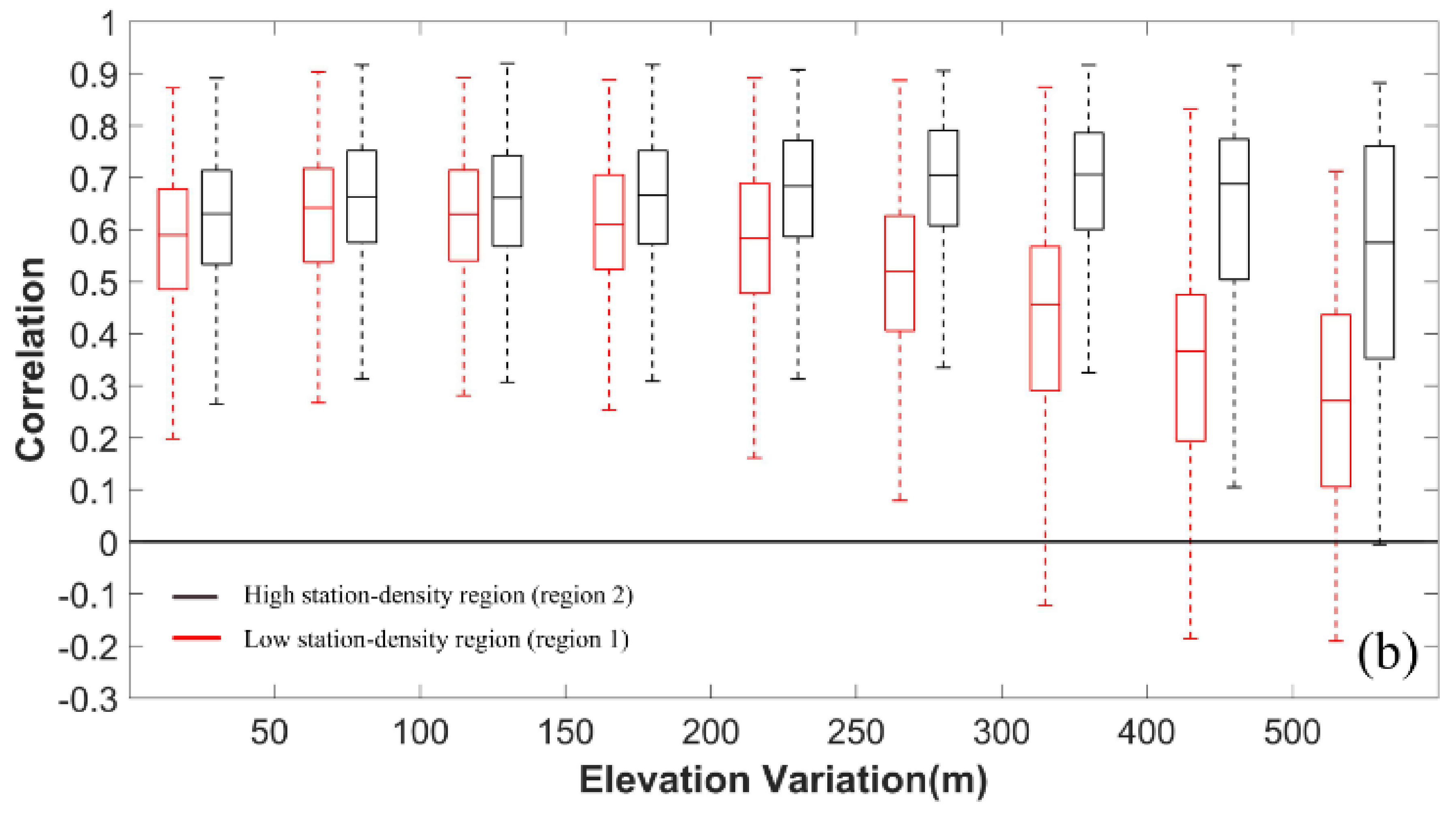
| Networks | Product | ubRMSE | RMSE | BIAS | R |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Naqu | L3_SM_P | 0.059 | 0.060 | 0.007 | 0.88 |
| L3_SM_P_E | 0.055 | 0.055 | 0.005 | 0.88 | |
| CLM | 0.037 | 0.043 | −0.022 | 0.79 | |
| Maqu | L3_SM_P | 0.058 | 0.133 | 0.120 | 0.64 |
| L3_SM_P_E | 0.059 | 0.127 | 0.113 | 0.65 | |
| CLM | 0.047 | 0.057 | 0.030 | 0.58 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, C.; Lu, H.; Yang, K.; Han, M.; Wright, J.S.; Chen, Y.; Yu, L.; Xu, S.; Huang, X.; Gong, W. The Evaluation of SMAP Enhanced Soil Moisture Products Using High-Resolution Model Simulations and In-Situ Observations on the Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 535. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10040535
Li C, Lu H, Yang K, Han M, Wright JS, Chen Y, Yu L, Xu S, Huang X, Gong W. The Evaluation of SMAP Enhanced Soil Moisture Products Using High-Resolution Model Simulations and In-Situ Observations on the Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sensing. 2018; 10(4):535. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10040535
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Chengwei, Hui Lu, Kun Yang, Menglei Han, Jonathon S. Wright, Yingying Chen, Le Yu, Shiming Xu, Xiaomeng Huang, and Wei Gong. 2018. "The Evaluation of SMAP Enhanced Soil Moisture Products Using High-Resolution Model Simulations and In-Situ Observations on the Tibetan Plateau" Remote Sensing 10, no. 4: 535. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10040535
APA StyleLi, C., Lu, H., Yang, K., Han, M., Wright, J. S., Chen, Y., Yu, L., Xu, S., Huang, X., & Gong, W. (2018). The Evaluation of SMAP Enhanced Soil Moisture Products Using High-Resolution Model Simulations and In-Situ Observations on the Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sensing, 10(4), 535. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10040535