The Effect of Surface Waves on Airborne Lidar Bathymetry (ALB) Measurement Uncertainties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
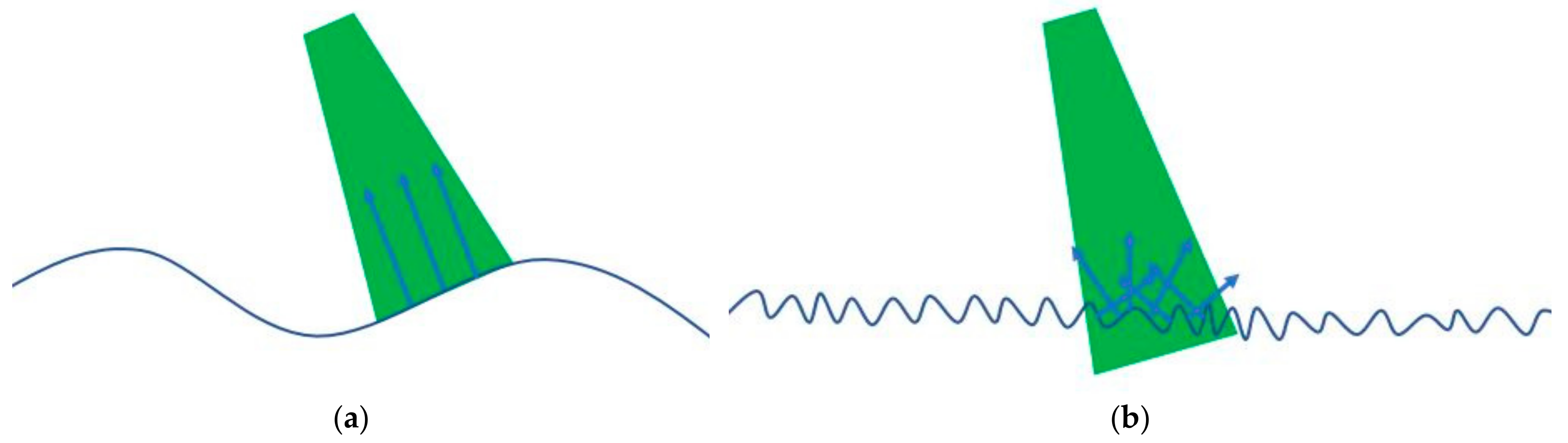
2.1. Water Surface and Ray Tracing Models
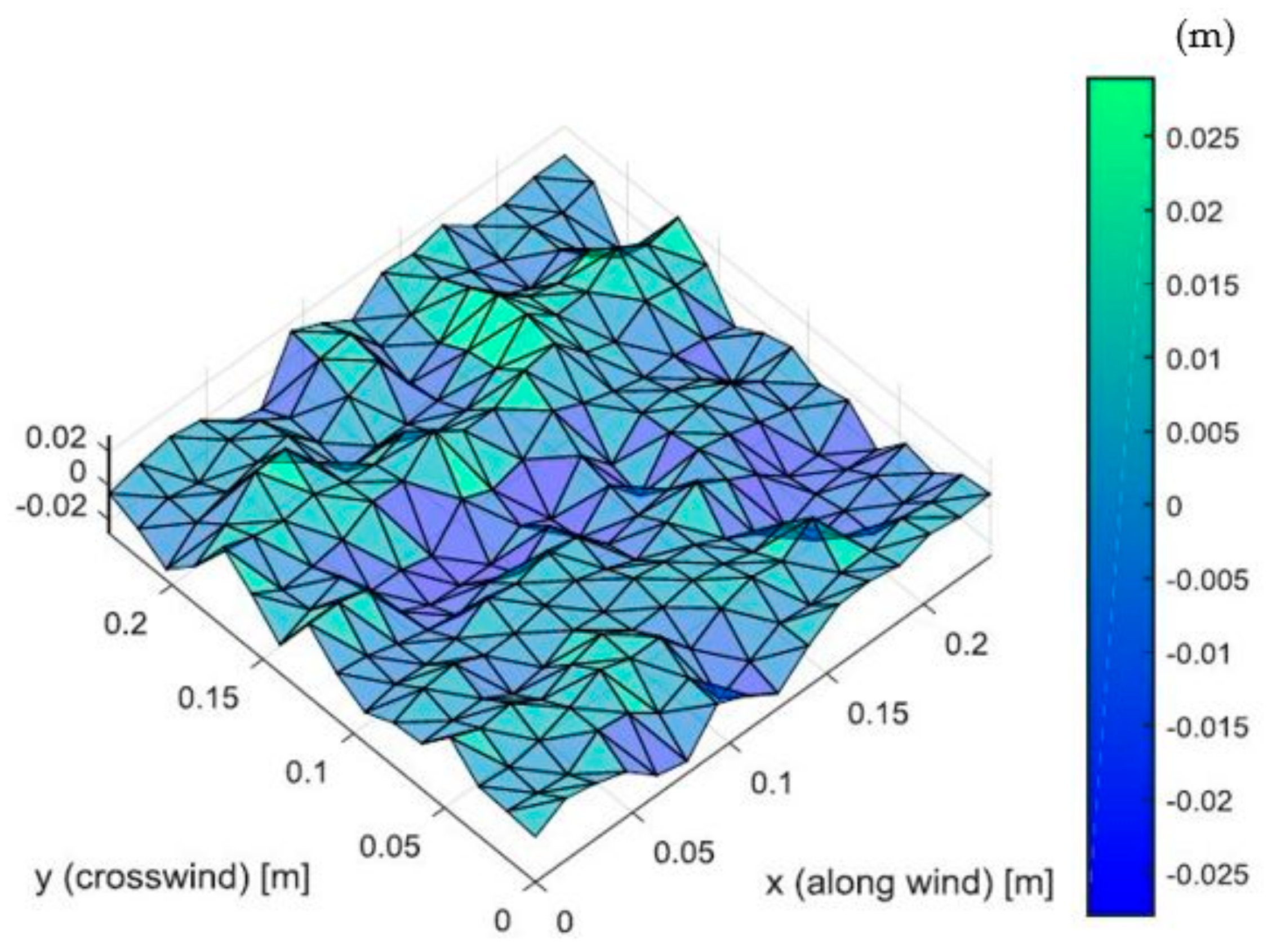
2.1.1. Water Surface Model
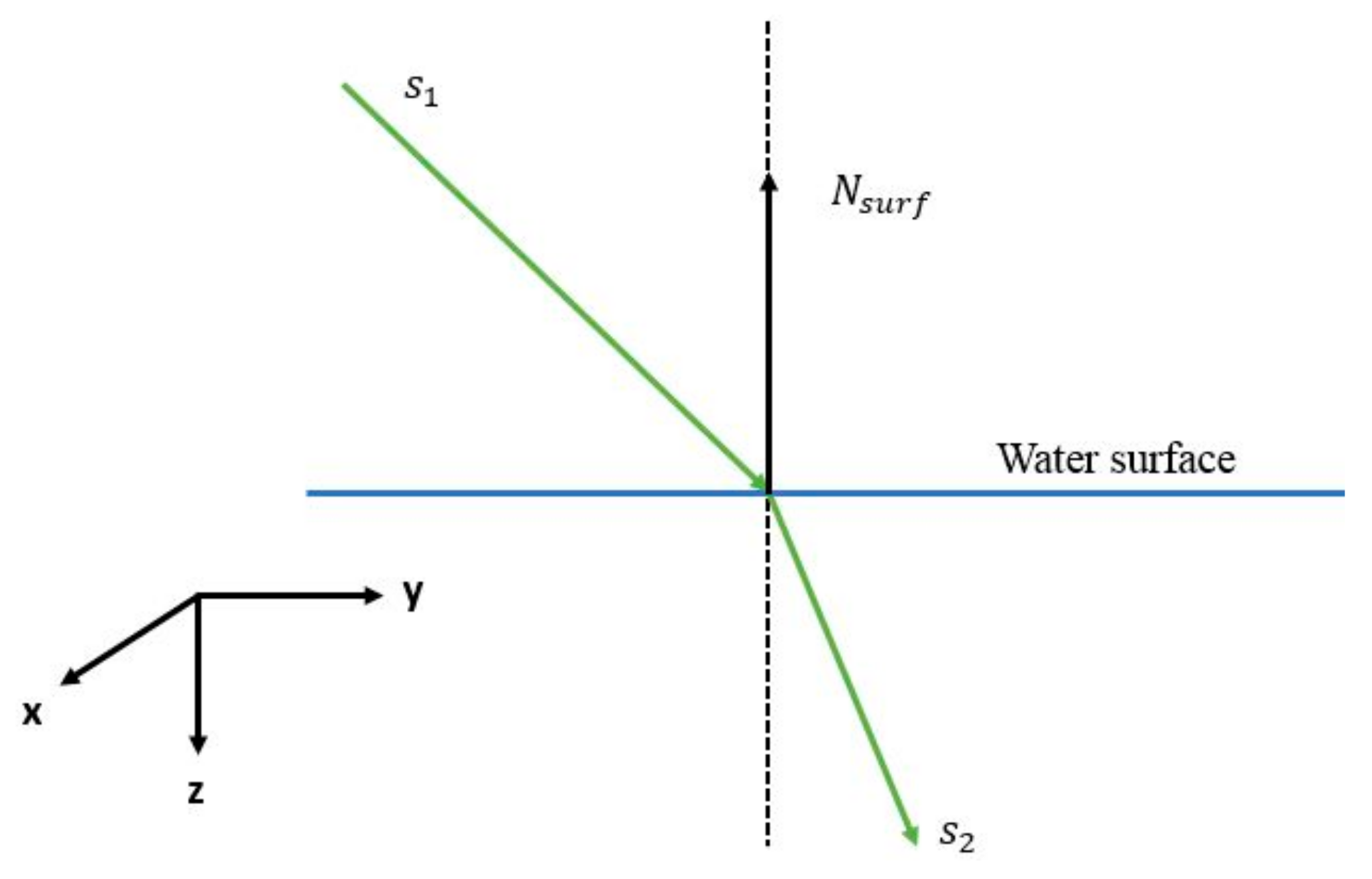
2.1.2. Ray-Tracing Model
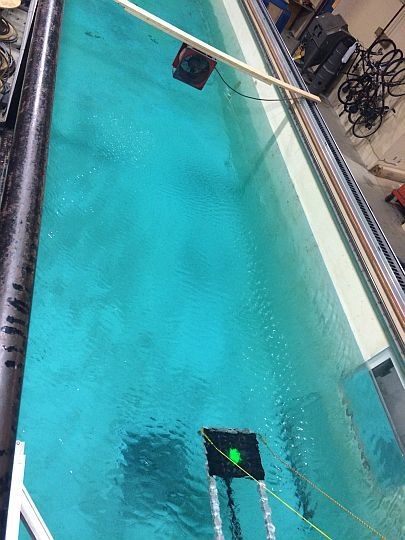
2.2. Data Acquisition and Experimental Setup
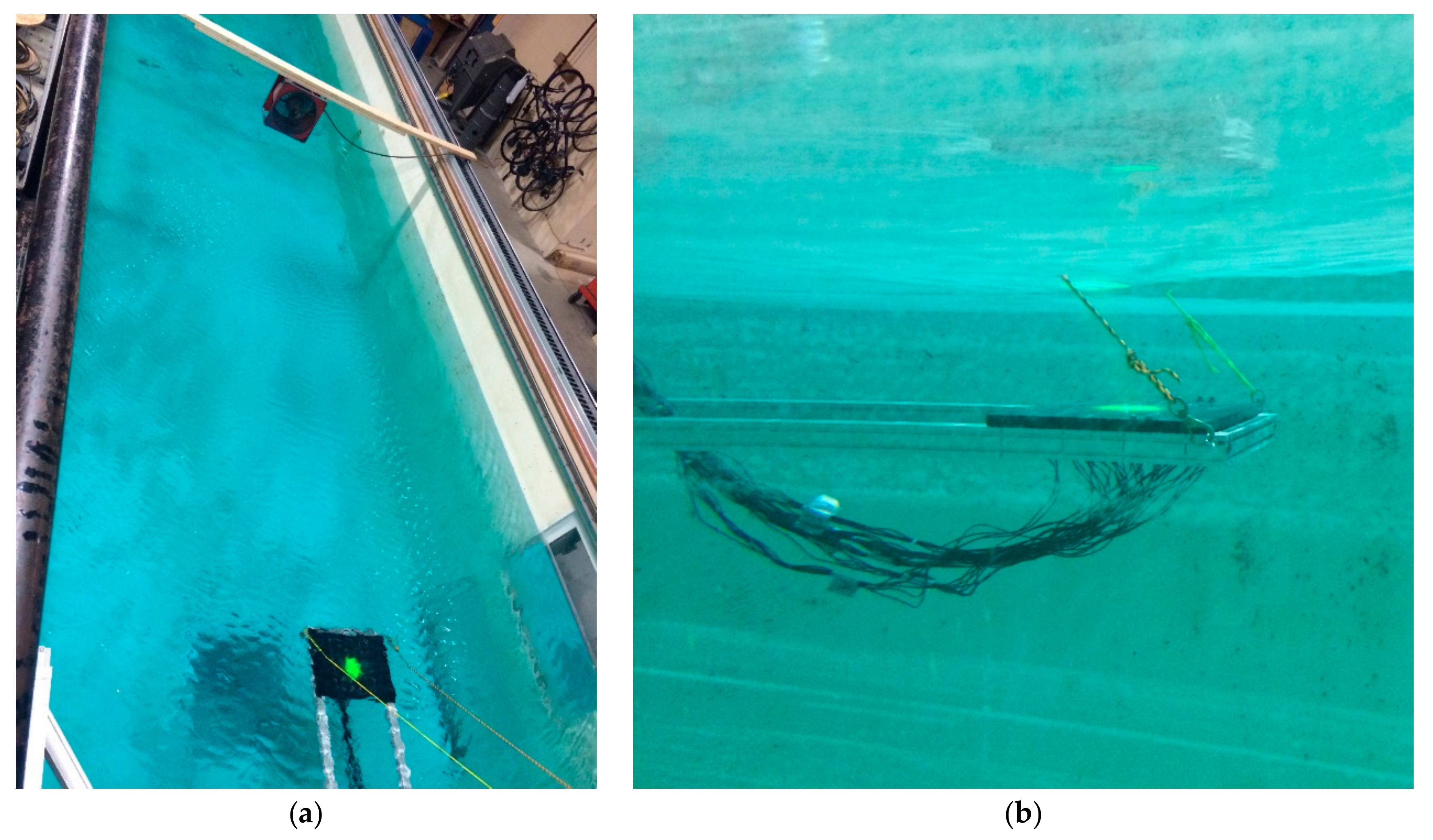
2.2.1. Data Acquisition and Image Processing
2.2.2. Experimental Setup
3. Results
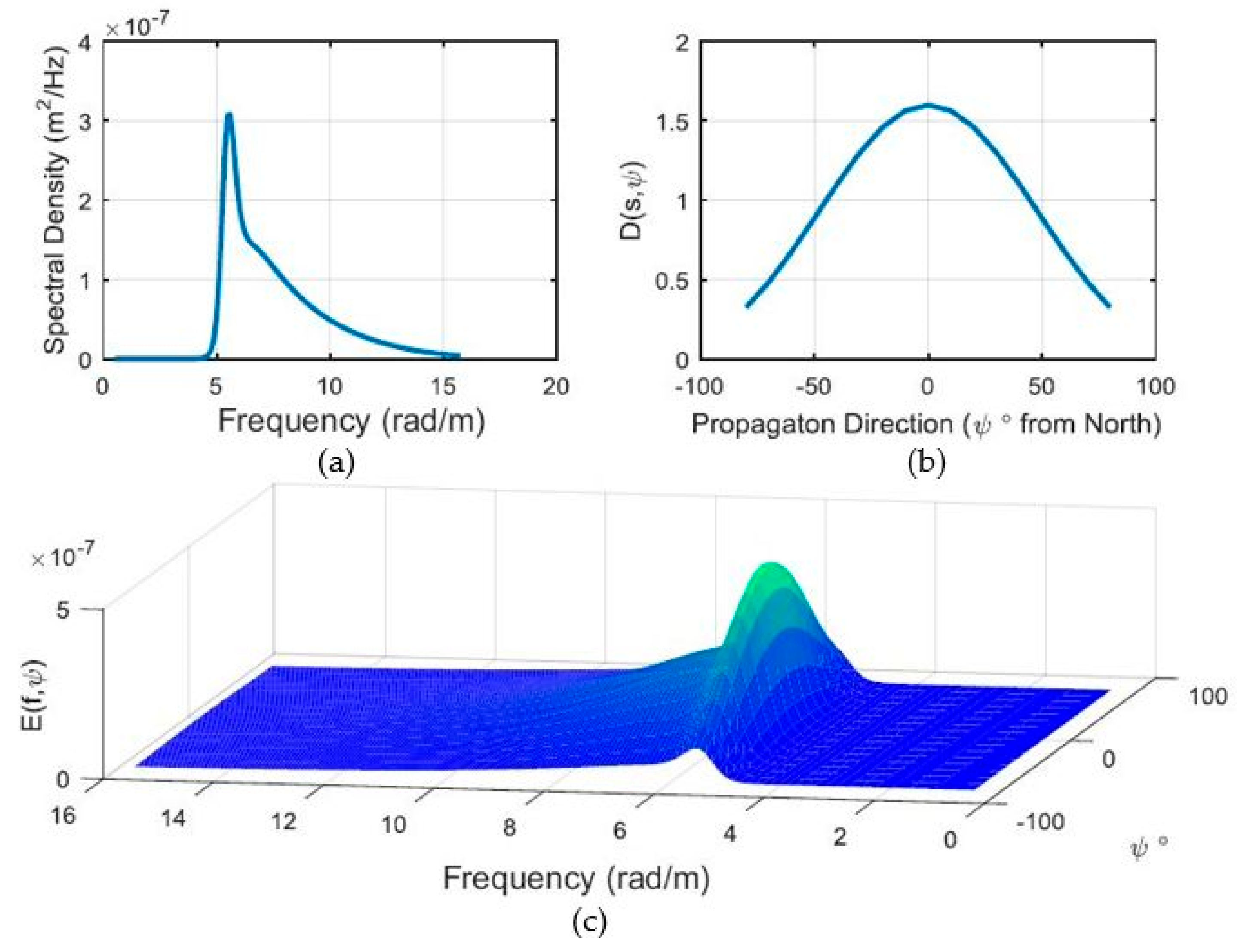
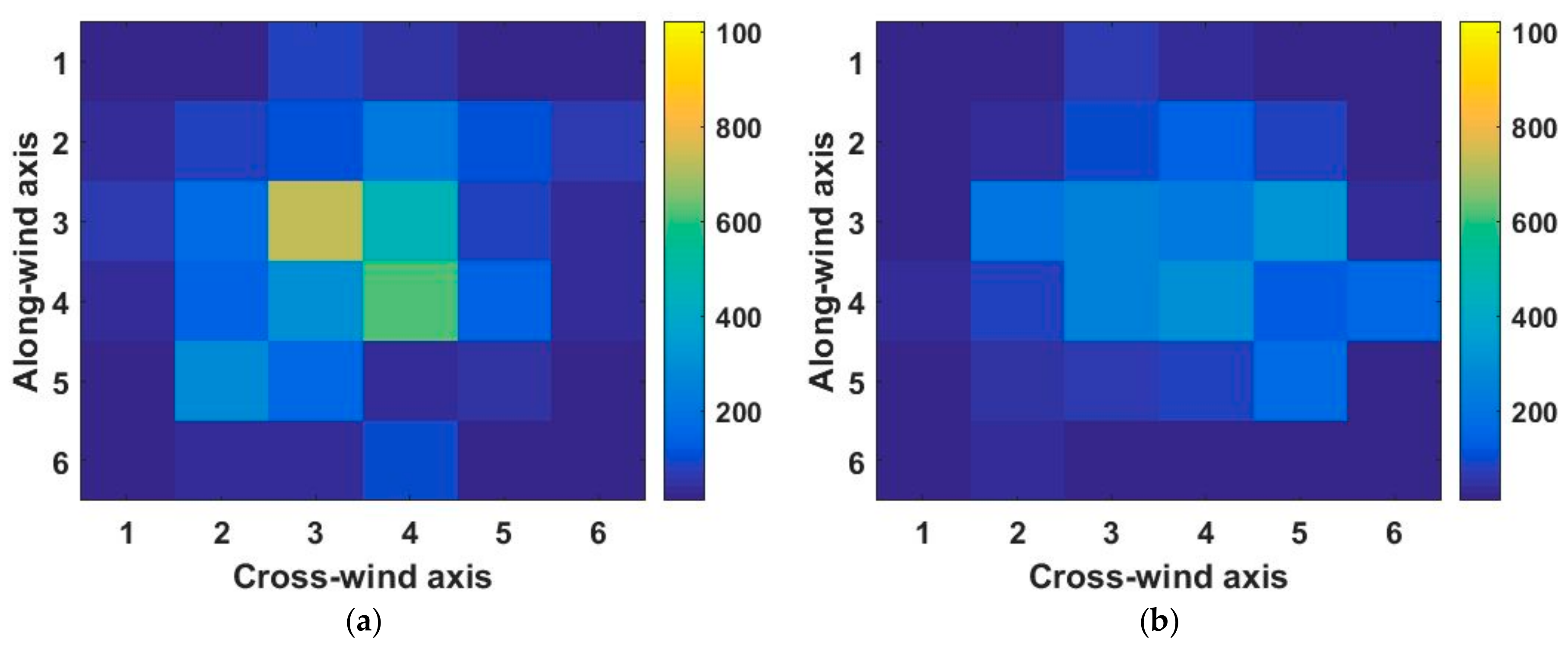
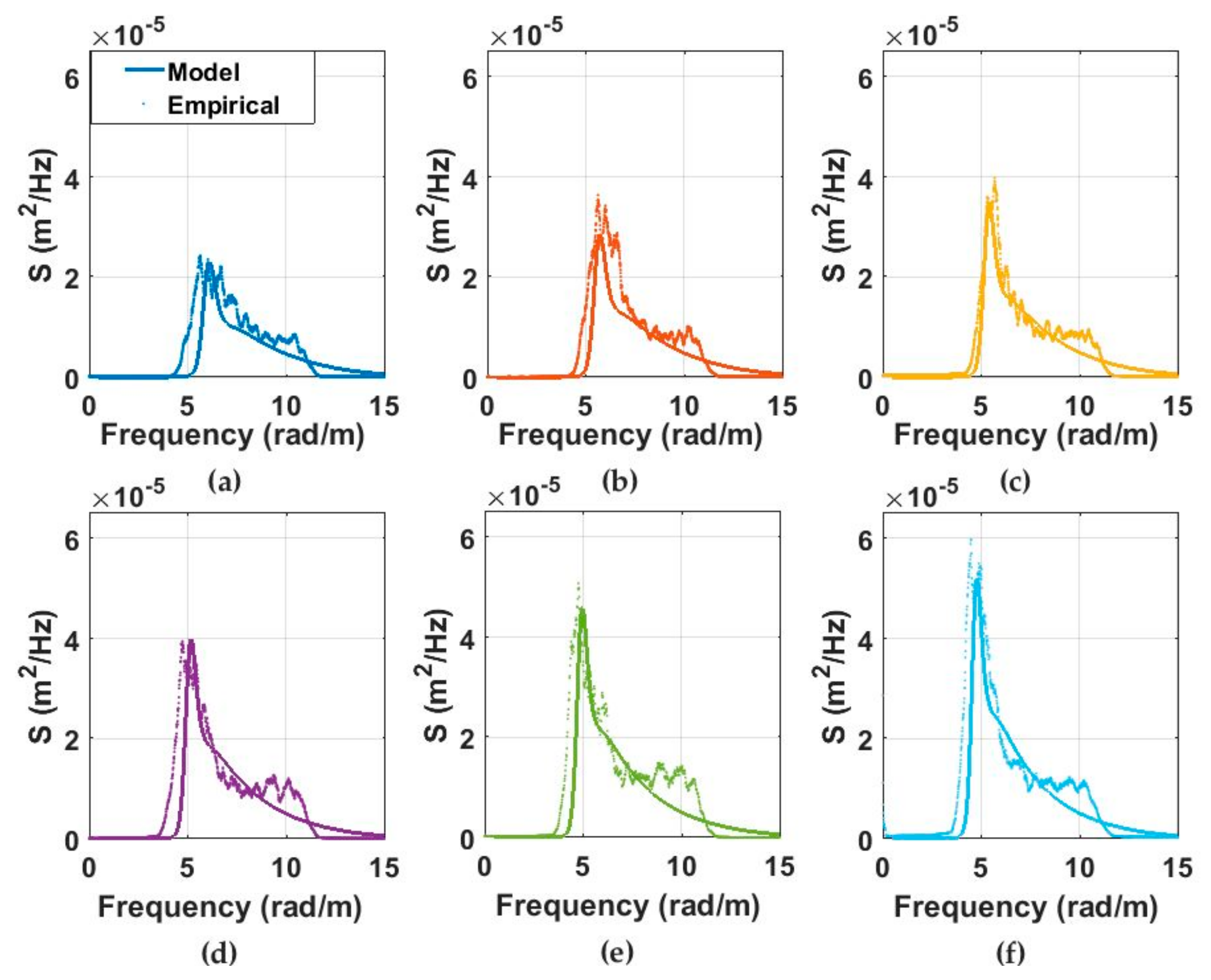
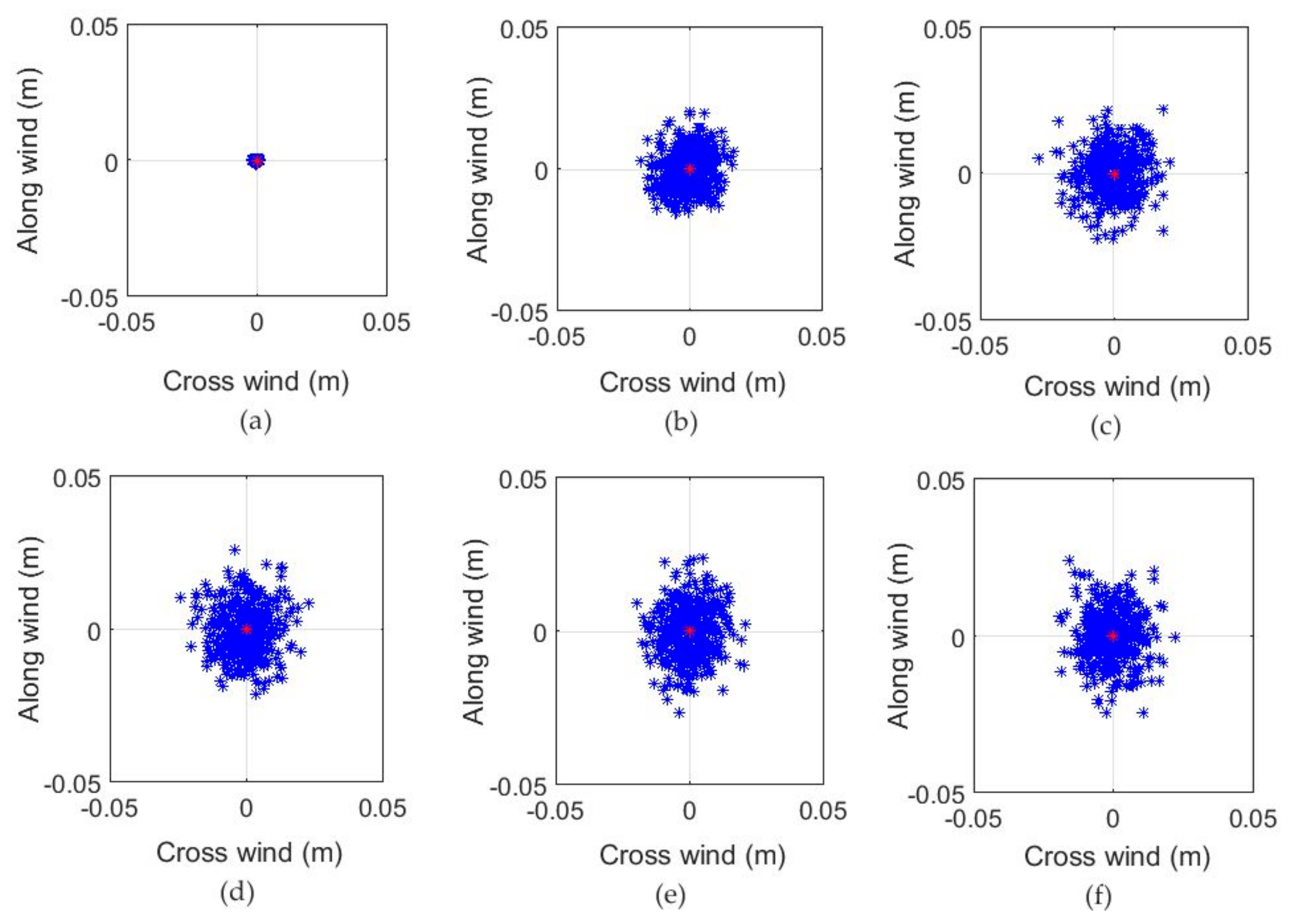
3.1. Wave Spectrum Results
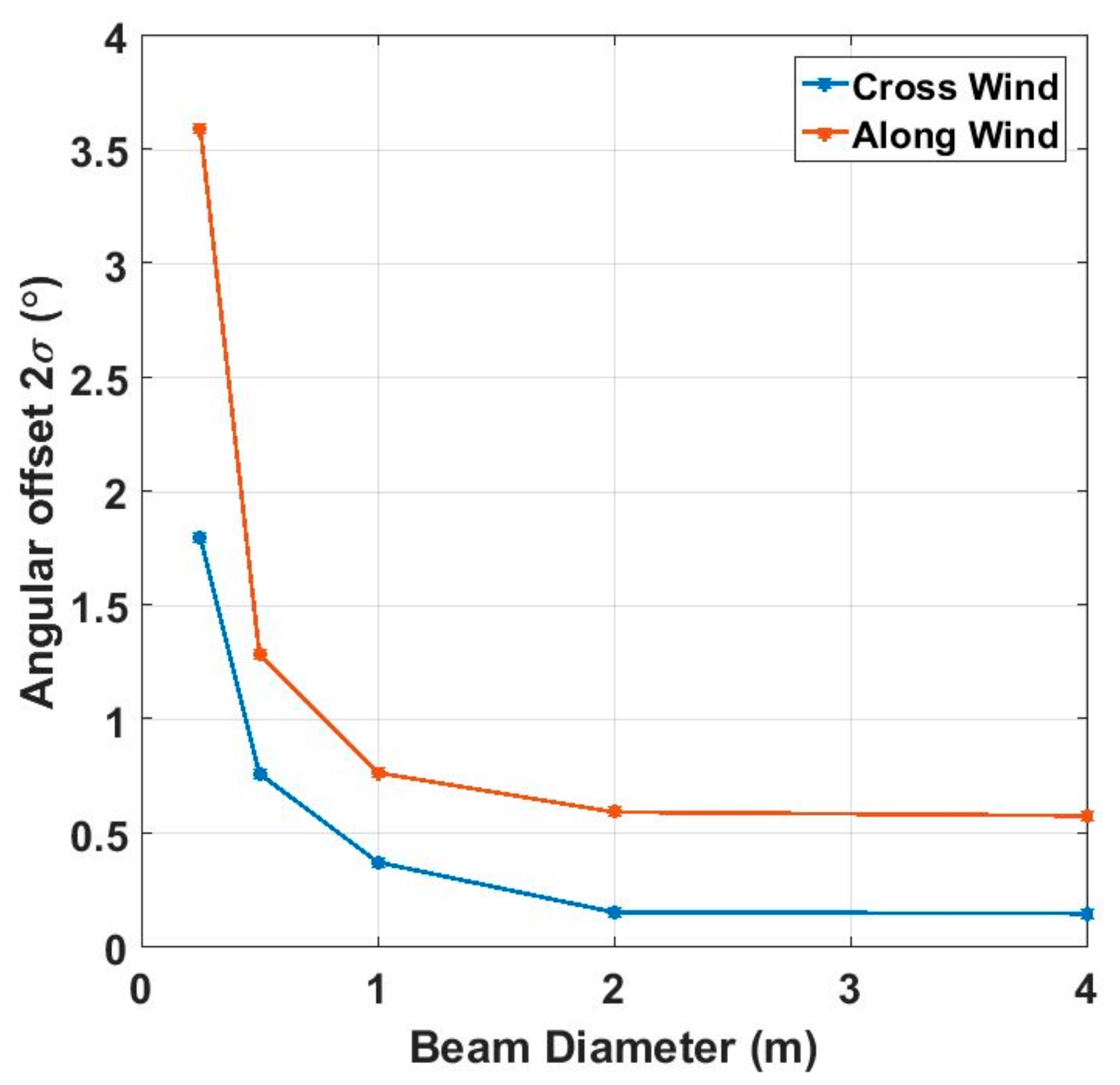
3.2. Monte Carlo Simulation Results
3.3. Empirical Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guenther, G. Airborne Laser Hydrography: System Design and Performance Factors; NOAA Professional Paper Series; NOAA: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.K.; Philpot, W.D. Using airborne bathymetric lidar to detect bottom type variation in shallow waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 106, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eren, F.; Pe’eri, S.; Rzhanov, Y.; Ward, L. Bottom characterization by using airborne lidar bathymetry (ALB) waveform features obtained from bottom return residual analysis. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 206, 260–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeri, S.; Gardner, J.V.; Ward, L.G.; Morrison, J.R. The seafloor: A key factor in lidar bottom detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 1150–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riegl VQ-880-G Laser Scanner System for Topo-Bathymetric Surveying with New Optional IR Laser Scanner Channel. Available online: http://www.3dlasermapping.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/02/3DLM-RIEGL-User-Conference_VQ-880-GOverview_Rg_PDF_low.pdf (accessed on 20 December 2017).
- Pan, Z.; Glennie, C.; Hartzell, P.; Fernandez-Diaz, J.C.; Legleiter, C.; Overstreet, B. Performance assessment of high resolution airborne full waveform LiDAR for shallow river bathymetry. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 5133–5159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guenther, G.C.; Cunningham, A.G.; Larocque, P.E.; Reid, D.J.; Service, N.O.; Highway, E.; Spring, S. Meeting the Accuracy Challenge in Airborne Lidar Bathymetry. In Proceedings of the 20th EARSeL Symposium: Workshop on Lidar Remote Sensing of Land and Sea, Dresden, Germany, 16–17 June 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Mobley, C.D. Light and Water: Radiative Transfer in Natural Waters; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Lockhart, C.; Lockhart, D.; Martinez, J. Total Propagated Uncertainty (TPU) for hydrographic lidar to aid objective comparison to acoustic datasets. Int. Hydrogr. Rev. 2008, 9, 19–27. [Google Scholar]
- International Hydrographic Organization (IHO). IHO Standards for Hydrographic Surveys: Special Publication No. 44, 5th ed.; IHO: Monaco, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Imahori, G.; Ferguson, J.; Wozumi, T.; Scharff, D.; Pe’eri, S.; Parrish, C.E.; White, S.A.; Jeong, I.; Sellars, J.; Aslaksen, M. A Procedure for Developing an Acceptance Test for Airborne Bathymetric Lidar Data Application to NOAA Charts in Shallow Waters; National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) National Ocean Survey (NOS) Technical Memorenadom CS 32; NOAA: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Krekov, G.M.; Krekova, M.M.; Shamanaev, V.S. Laser sensing of a subsurface oceanic layer I Effect of the atmoshpere and wind-driven sea waves. Appl. Opt. 1998, 37, 1589–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLean, J.W.; Freeman, J.D. Effects of ocean waves on airborne lidar imaging. Appl. Opt. 1996, 35, 3261–3269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tulldahl, H.M.; Steinvall, O.K. Simulation of sea surface wave influence on small target detection with airborne laser depth sounding. Appl. Opt. 2004, 43, 2462–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mclean, J.W. Modeling of Ocean Wave Effects for Lidar Remote Sensing. SPIE 1302, Ocean Optics X, 1 September 1990. In Proceedings of the Technical Symposium on Optics, Electro-Optics, and Sensors, Orlando, FL, USA, 16–20 April 1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinvall, O.V.E.; Koppari, K. Depth Sounding Lidarperformance and Models. SPIE 2748, Laser Radar Technology and Applications, 26 June 1996. In Proceedings of the Aerospace/Defense Sensing and Controls, Orlando, FL, USA, 8–12 April 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Westfeld, P.; Maas, H.G.; Richter, K.; Weiss, R. Analysis and correction of ocean wave pattern induced systematic coordinate errors in airborne LiDAR bathymetry. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 128, 314–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, T. Uncertainties Introduced by the Ocean Surface when Conducting Airborne Lidar Bathymetry Surveys. Master Thesis, Lund Institute of Technology, Lund, Sweden, 9 December 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Dean, R.; Dalrymple, R. Water Wave Mechanics for Engineers and Scientists; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Mobley, C.D. Modeling Sea Surfaces: A Tutorial on Fourier Transform Techniques. Available online: http://www.oceanopticsbook.info/view/references/publications#mobley_2016 (accessed on 12 December 2017).
- Apel, J.R. An improved model of the ocean surface wave vector spectrum and its effects on radar backscatter. J. Geophys. Res. 1994, 99, 16269–16291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasselmann, K.; Olbers, D.J. Measurements of Wind-Wave Growth and Swell Decay during the Joint North Sea Wave Project (JONSWAP). Dtsch. Hydrogr. Z. 1973, A, 95. [Google Scholar]
- Elfouhaily, T.; Chapron, B.; Katsaros, K.; Vandemark, D. A unified directional spectrum for long and short wind-driven waves. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1997, 102, 15781–15796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinke, J.; Jahne, B. 2D Wave Number Spectra of Short Wind Waves—Results from Wind Wave Facilities and Extrapolation to the Ocean. In Proceedings of the SPIE, Optics of the Air-Sea Interface: Theory and Measurement, San Diego, CA, USA, 22–22 July 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Preisendorfer, R.W.; Mobley, C. Albedos and glitter patterns of a wind-roughened sea surface. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1986, 16, 1293–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirbilek, Z.; Linwood, C. Coastal Engineerin Manual; Manual Number: EM 1110-2-1100; U.S. Army Corps of Engineers (USACE): Washington, DC, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Mitsuyasu, H.; Tasai, F.; Suhara, T.; Mizuno, S.; Ohkusu, M.; Honda, T.; Rikiishi, K. Observations of the directional spectrum of ocean waves using a coverleaf buoy. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1975, 5, 750–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greve, B. Reflections and Refractions in Ray Tracing. Available online: https://graphics.stanford.edu/courses/cs148-10-summer/docs/2006--degreve--reflection_refraction.pdf (accessed on 5 November 2017).
- Eren, F.; Pe’eri, S.; Rzhanov, Y.; Thein, M.; Celikkol, B. Optical detector array design for navigational feedback between unmanned underwater vehicles (UUVs). IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2016, 41, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eren, F.; Pe’eri, S.; Thein, M.W.; Rzhanov, Y.; Celikkol, B.; Swift, M.R. Position, orientation and velocity detection of Unmanned Underwater Vehicles (UUVs) using an optical detector array. Sensors 2017, 17, 1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rzhanov, Y.; Eren, F.; Thein, M.-W.; Pe’eri, S. An Image Processing Approach for Determining the Relative Pose of Unmanned Underwater Vehicles. In Proceedings of the OCEANS 2014—TAIPEI, Taipei, Taiwan, 7–10 April 2014; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X. Capillary–gravity and capillary waves generated in a wind wave tank: Observations and theories. J. Fluid Mech. 1995, 289, 51–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Wind Speed (m/s) | 2 | 2.5 | 3 | 3.5 | 4 | 5.25 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Incidence Angle (degrees) | 0 | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | |
| Laser Beam Diameter (m) | 0.25 | 0.5 | 1 | 2 | 4 | |
| Fetch (m) | 3.5 | 4.5 | 5.5 | 6.5 | 7.5 | 8.5 |
| Distance Downwind (m) | 3.5 | 4.5 | 5.5 | 6.5 | 7.5 | 8.5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peak Frequency (Hz) | 5.6 | 5.5 | 5.3 | 4.6 | 4.4 | 4.3 |
| Peak Wavelength (m) | 0.050 | 0.051 | 0.055 | 0.074 | 0.080 | 0.085 |
| Significant Wave Height (m) | 0.008 | 0.010 | 0.011 | 0.009 | 0.009 | 0.009 |
| Laser Beam Incidence Angle (°) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wind Speed (m/s) | Along-wind Direction | Cross-Wind Direction | ||||||||
| 0° | 5° | 10° | 15° | 20° | 0° | 5° | 10° | 15° | 20° | |
| 2 | 2.67° | 2.49° | 2.66° | 2.99° | 3.27° | 2.02° | 2.08° | 2.00° | 1.76° | 1.68° |
| 2.5 | 2.84° | 2.74° | 2.94° | 3.23° | 3.39° | 2.03° | 2.25° | 2.04° | 1.83° | 1.72° |
| 3 | 3.12° | 2.93° | 3.11° | 3.47° | 3.68° | 2.29° | 2.14° | 2.09° | 1.87° | 1.80° |
| 3.5 | 3.05° | 3.12° | 3.23° | 3.53° | 4.12° | 2.27° | 2.19° | 2.03° | 1.80° | 1.75° |
| 4 | 3.40° | 3.52° | 3.55° | 3.84° | 4.12° | 2.25° | 2.24° | 1.99° | 1.75° | 1.75° |
| 5.25 | 4.11° | 3.79° | 4.21° | 4.52° | 4.80° | 2.44° | 2.10° | 2.05° | 1.79° | 1.64° |
| Wind Speed (m/s) | Laser Beam Incidence Angle (°) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The Along-Wind Direction | Cross-Wind Direction | |||||||
| 0° | 10° | 15° | 20° | 0° | 10° | 15° | 20° | |
| 2 | 3.33° | 3.42° | 3.24° | 3.61° | 3.11° | 3.13° | 3.00° | 3.00° |
| 2.5 | 3.78° | 3.43° | 3.61° | 3.54° | 3.73° | 3.20° | 3.55° | 3.09° |
| 3 | 3.58° | 3.55° | 3.73° | 3.92° | 3.50° | 3.38° | 3.48° | 3.49° |
| 3.5 | 3.64° | 3.56° | 3.98° | 3.94° | 3.55° | 3.48° | 3.32° | 3.23° |
| 4 | 3.68° | 3.80° | 3.73° | 4.21° | 3.67° | 3.36° | 3.25° | 3.69° |
| 5.25 | 4.04° | 3.88° | 4.33° | 4.58° | 4.68° | 3.15° | 3.55° | 3.30° |
| Depth (m) | THU (m) | IHO-1b THU(m) | TVU (m) | IHO-1b TVU (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.10 | 5.02 | 0.03 | 0.50 |
| 2 | 0.21 | 5.04 | 0.05 | 0.50 |
| 3 | 0.32 | 5.06 | 0.08 | 0.50 |
| 4 | 0.42 | 5.08 | 0.11 | 0.50 |
| 5 | 0.52 | 5.10 | 0.13 | 0.50 |
| 6 | 0.63 | 5.12 | 0.16 | 0.51 |
| 7 | 0.74 | 5.14 | 0.19 | 0.51 |
| 8 | 0.84 | 5.16 | 0.21 | 0.51 |
| 9 | 0.95 | 5.18 | 0.24 | 0.51 |
| 10 | 1.05 | 5.20 | 0.27 | 0.52 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Birkebak, M.; Eren, F.; Pe’eri, S.; Weston, N. The Effect of Surface Waves on Airborne Lidar Bathymetry (ALB) Measurement Uncertainties. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 453. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10030453
Birkebak M, Eren F, Pe’eri S, Weston N. The Effect of Surface Waves on Airborne Lidar Bathymetry (ALB) Measurement Uncertainties. Remote Sensing. 2018; 10(3):453. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10030453
Chicago/Turabian StyleBirkebak, Matthew, Firat Eren, Shachak Pe’eri, and Neil Weston. 2018. "The Effect of Surface Waves on Airborne Lidar Bathymetry (ALB) Measurement Uncertainties" Remote Sensing 10, no. 3: 453. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10030453
APA StyleBirkebak, M., Eren, F., Pe’eri, S., & Weston, N. (2018). The Effect of Surface Waves on Airborne Lidar Bathymetry (ALB) Measurement Uncertainties. Remote Sensing, 10(3), 453. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10030453






