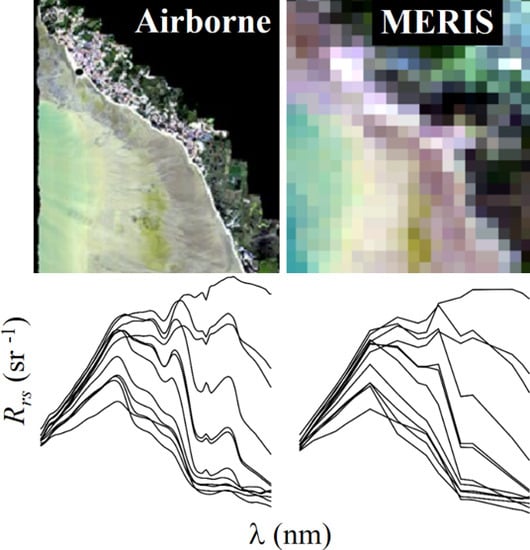
Using High-Resolution Airborne Data to Evaluate MERIS Atmospheric Correction and Intra-Pixel Variability in Nearshore Turbid Waters
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
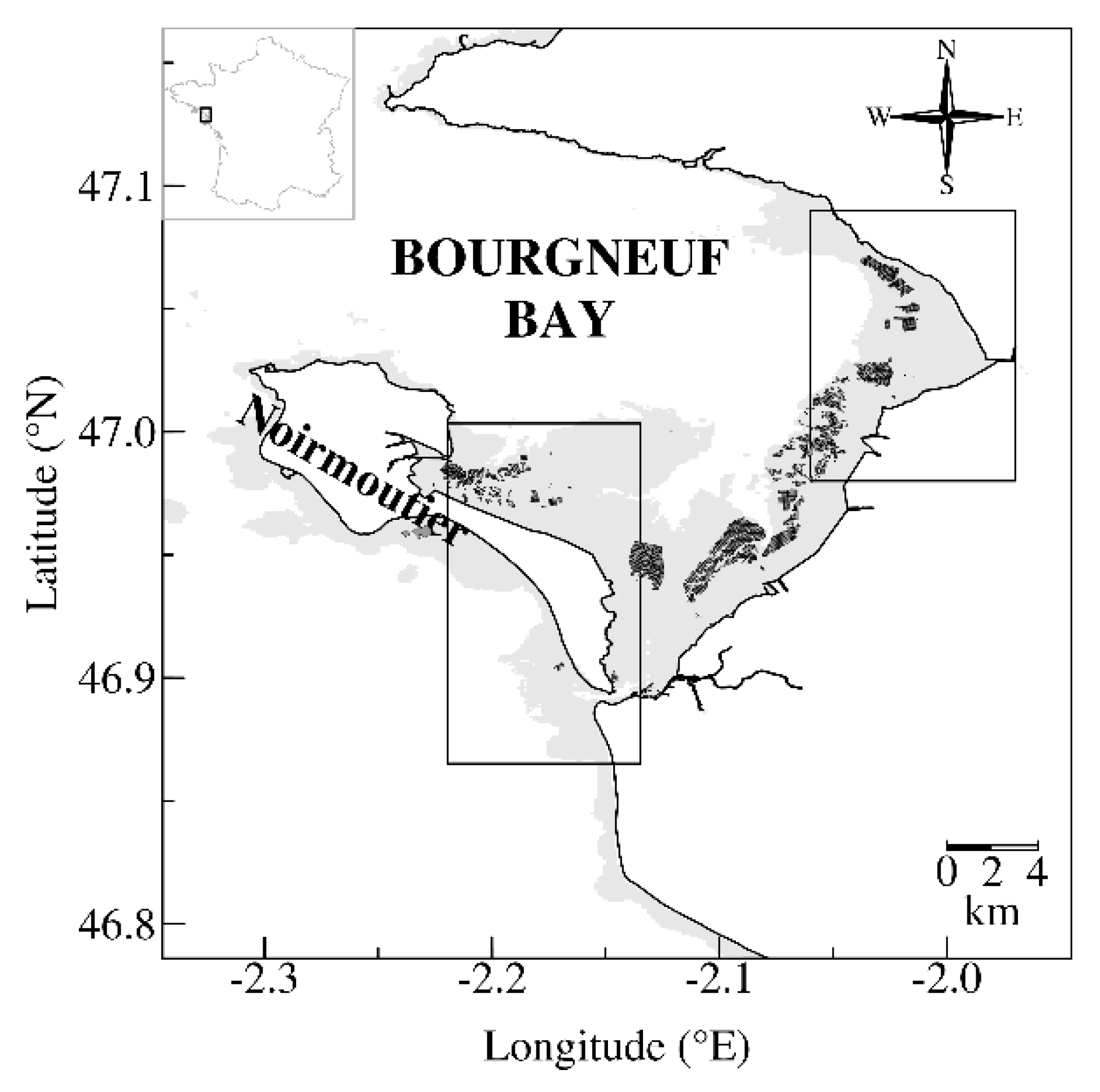
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Remote Sensing Data and Processing
2.2.1. Processing of Airborne Hyperspectral Data
2.2.2. MERIS Data
2.3. Comparison between HySpex Airborne and MERIS Satellite Data
2.3.1. Identification of Land and Water Pixels
2.3.2. Classification of Water Pixels
2.3.3. Evaluation of MERIS Atmospheric Correction Using Airborne Macro-Pixel Data
2.3.4. Evaluation of Intra-Pixel Spatial Variability (300 m)
3. Results
3.1. Performance of MERIS Atmospheric Correction
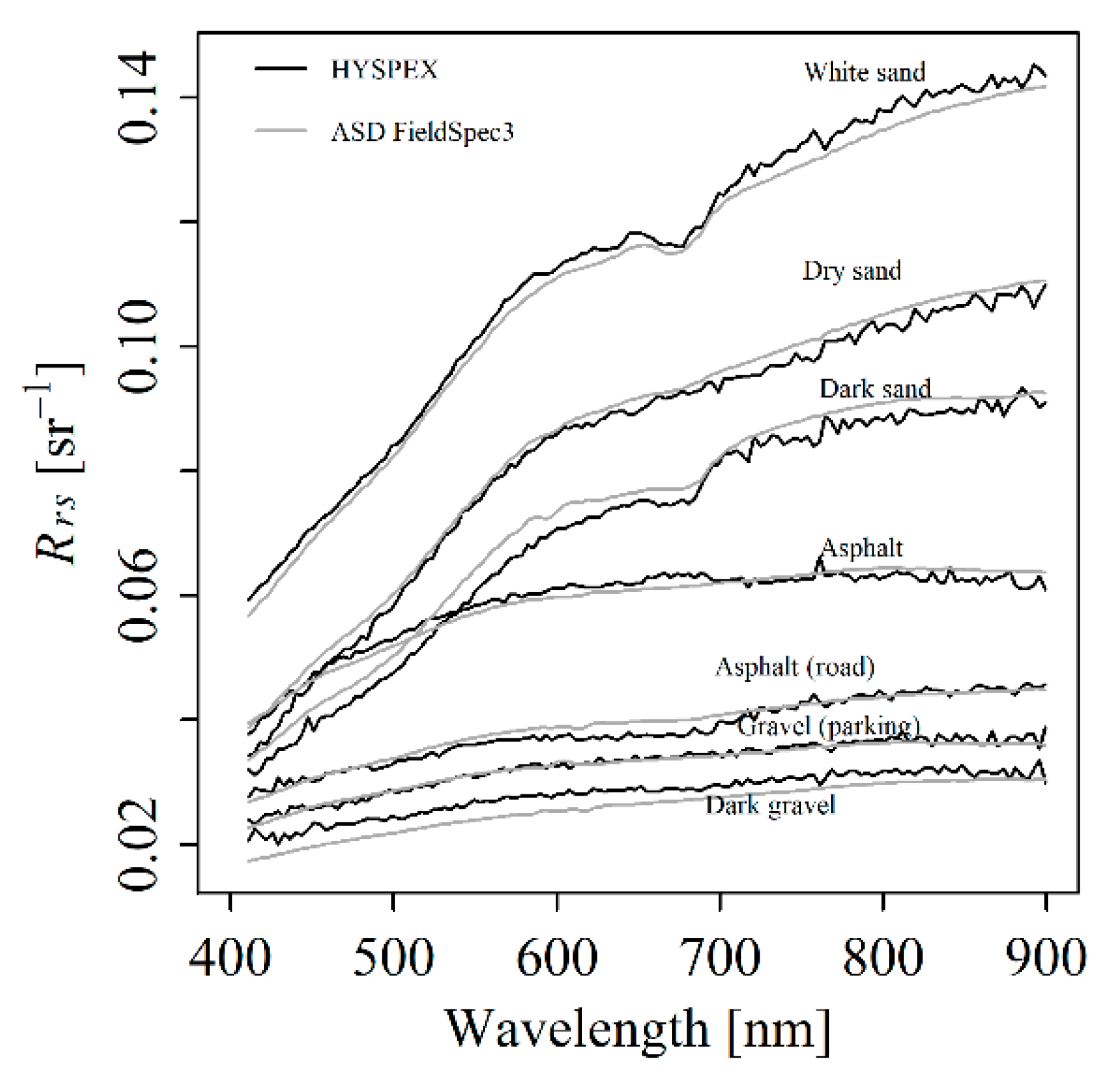
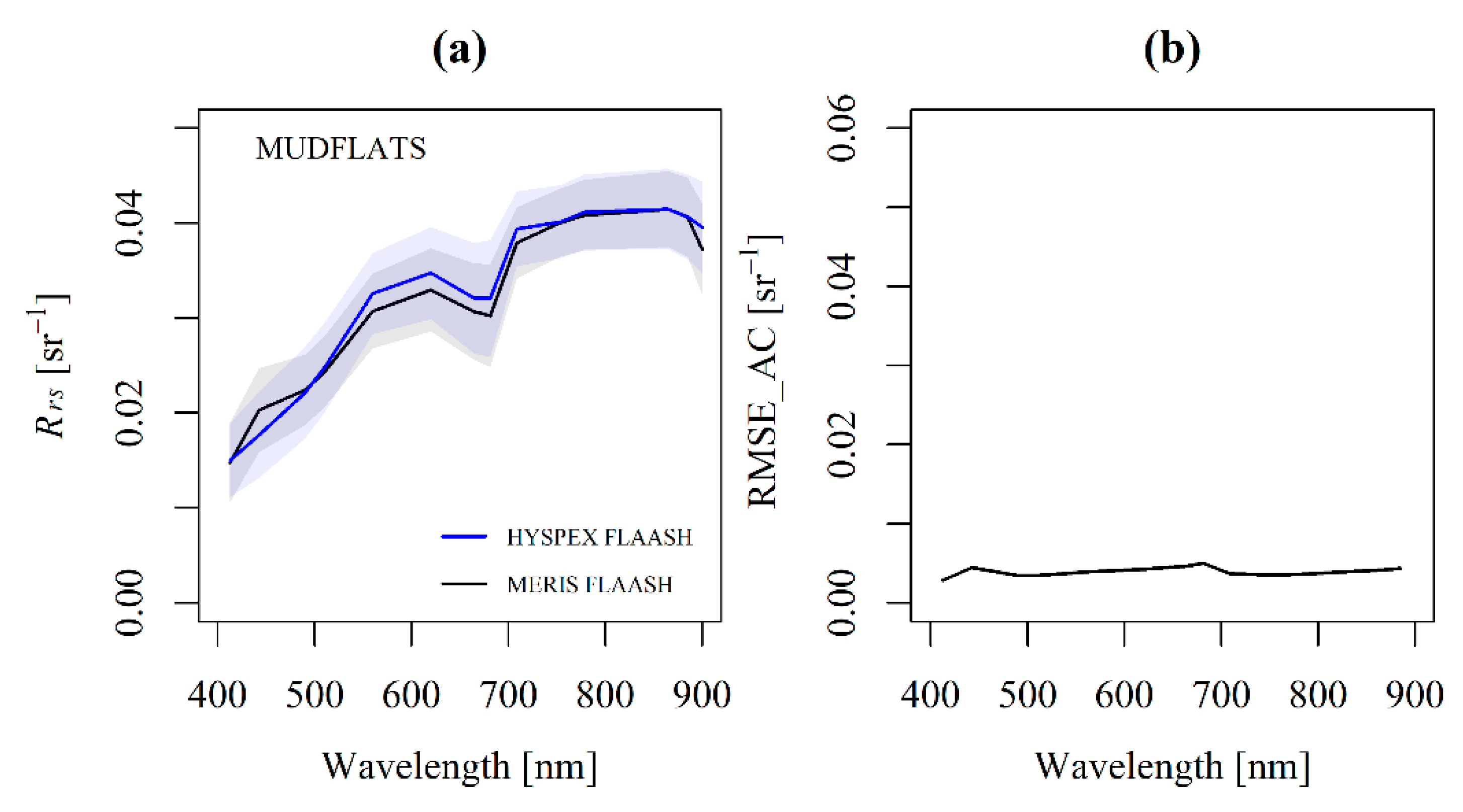
3.1.1. Atmospheric Correction over Land (Mudflat)
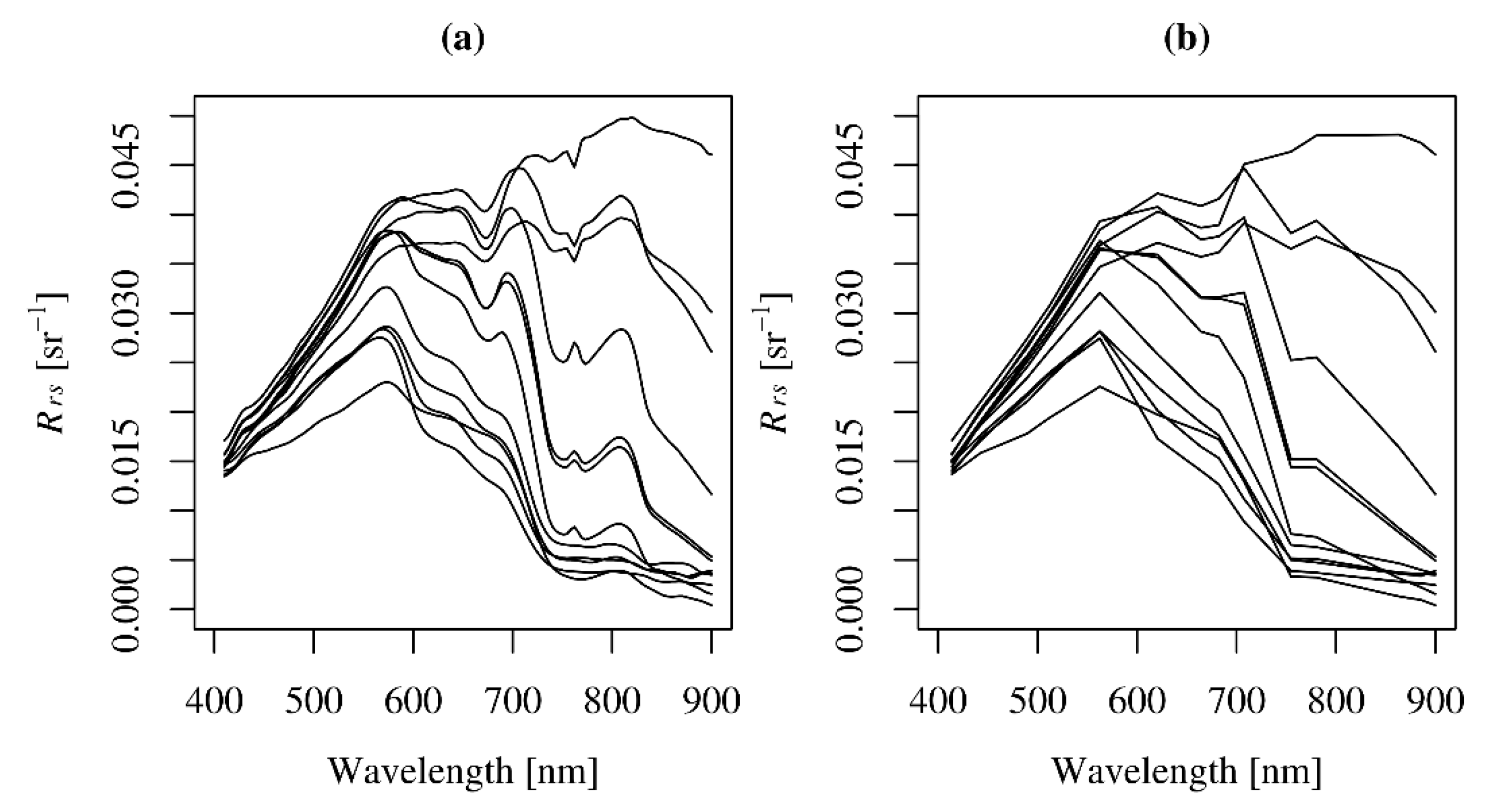
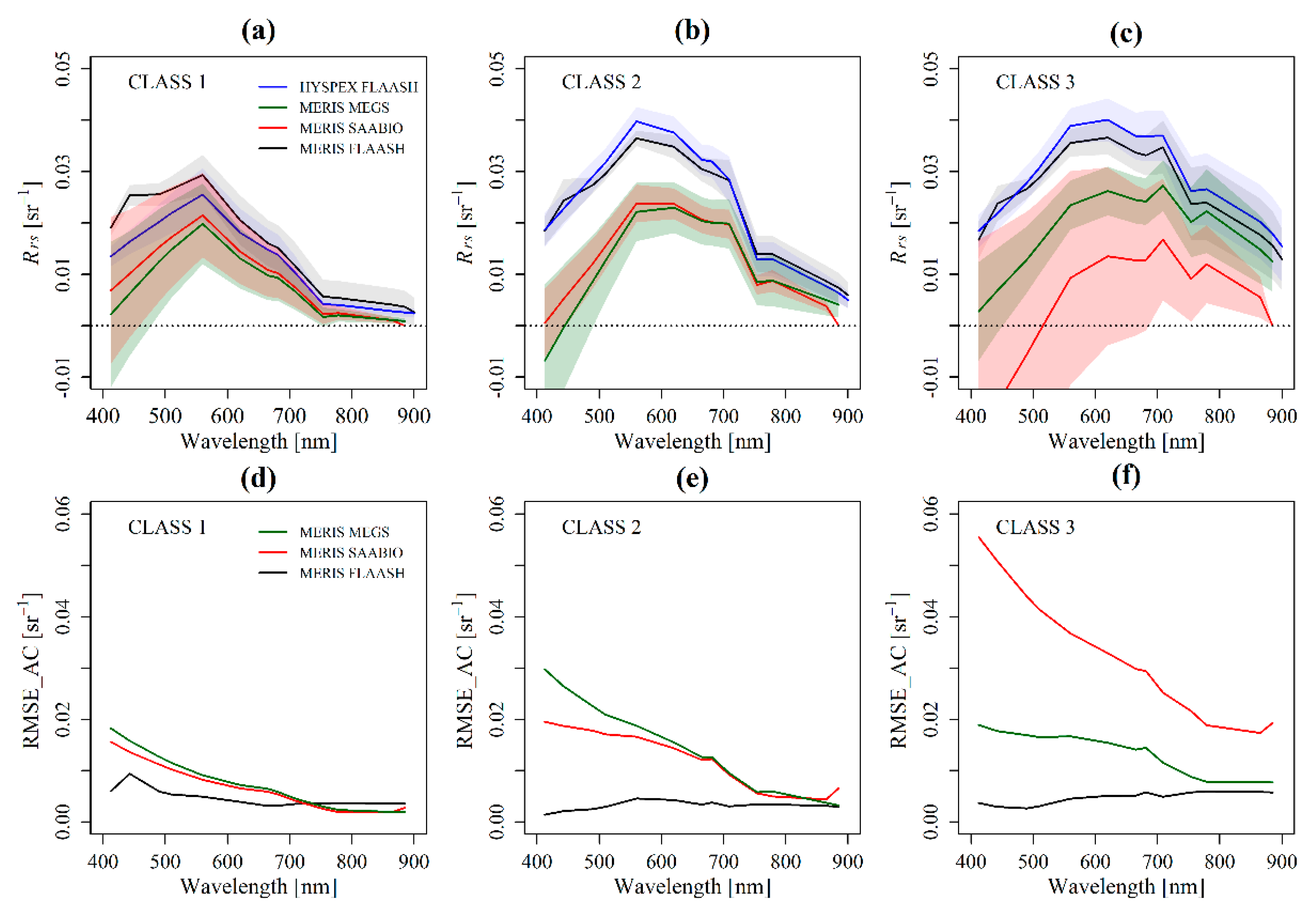
3.1.2. Atmospheric Correction over Water
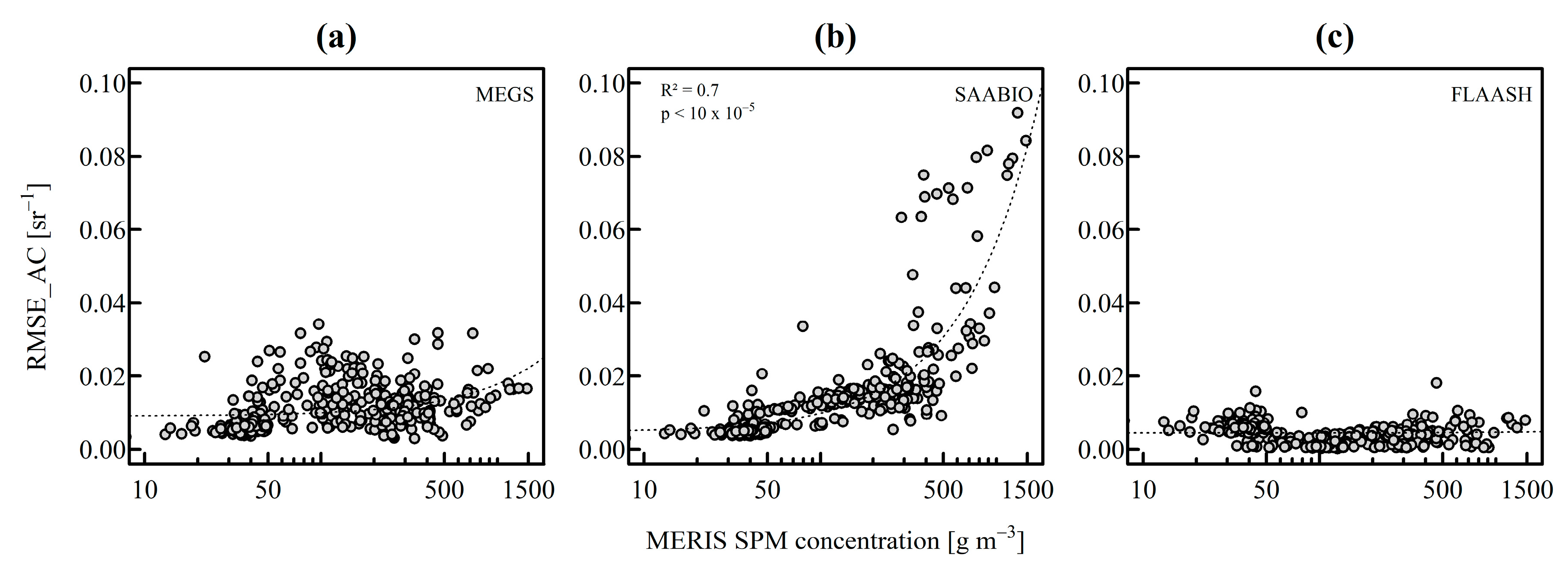
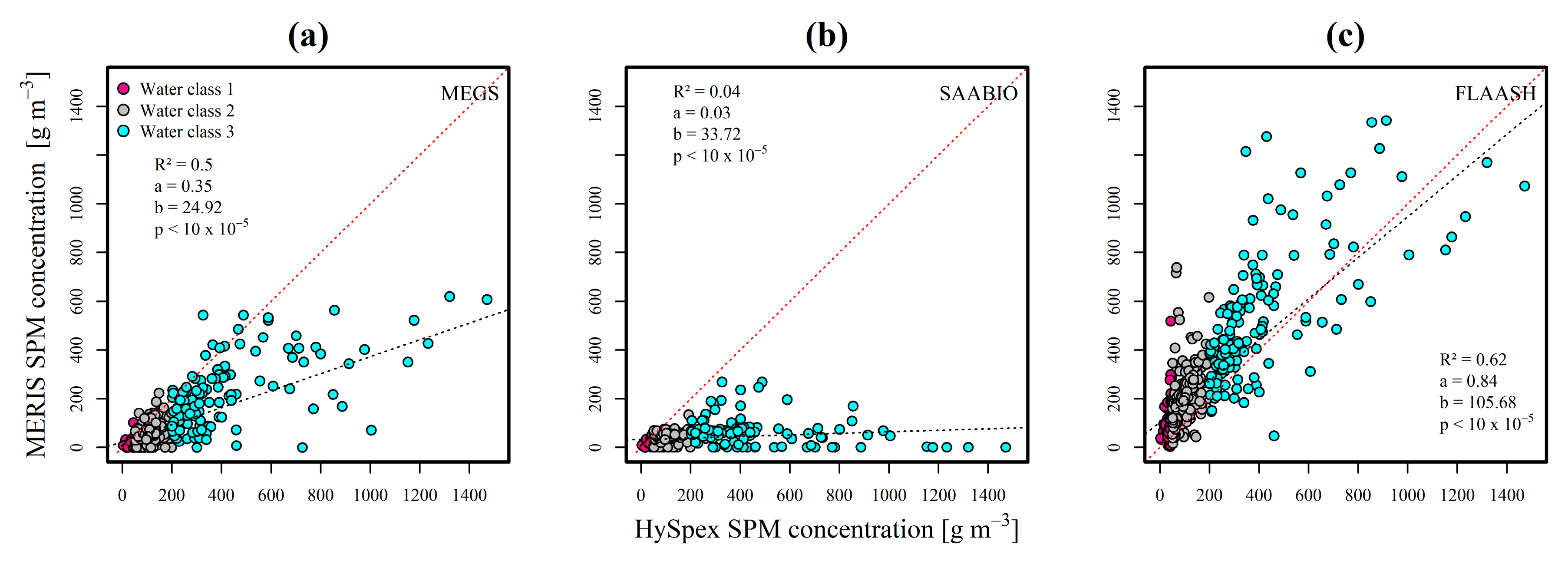
3.1.3. Influence of Turbidity on Atmospheric Correction
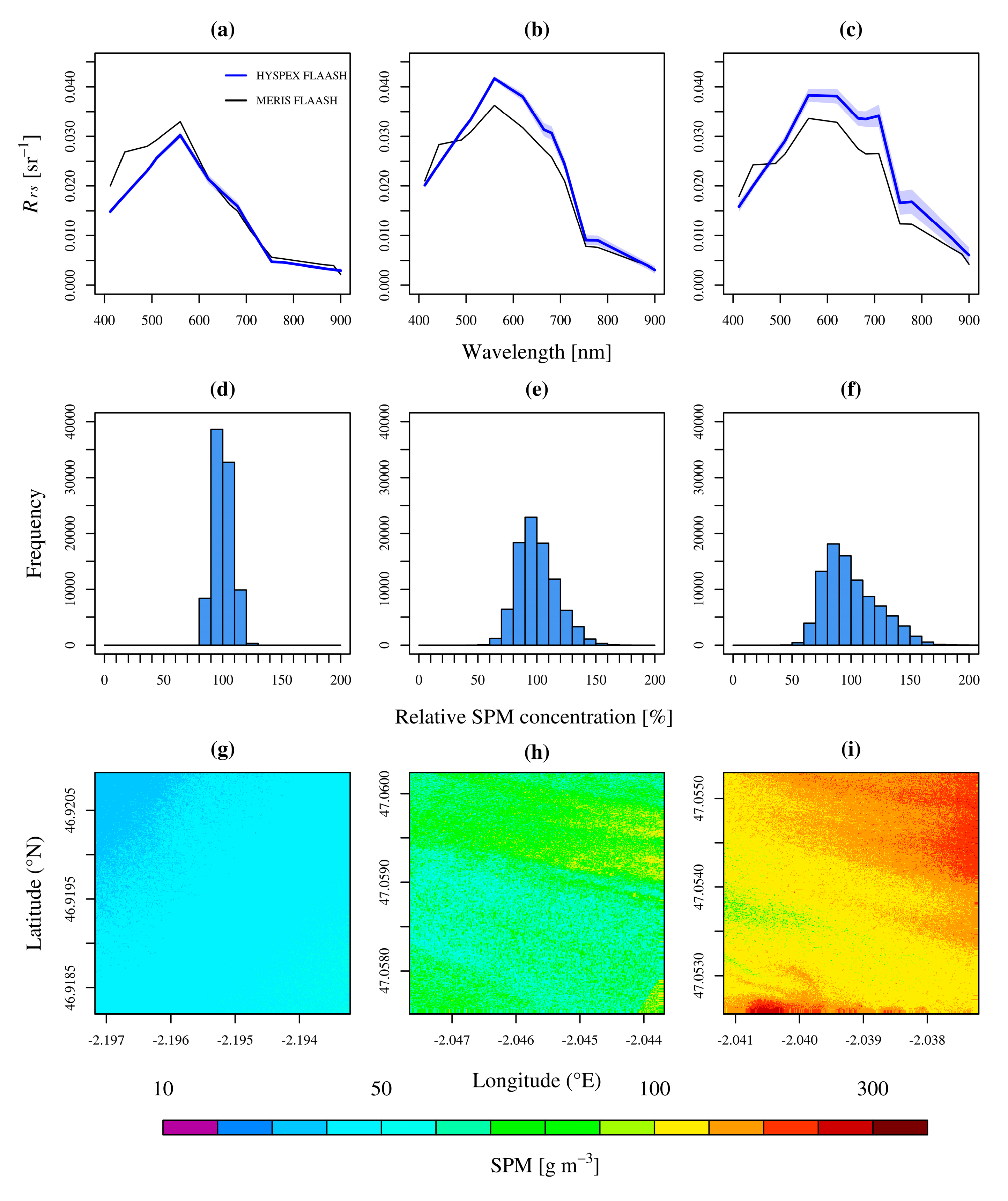
3.2. Evaluation of MERIS Intra-Pixel Variability and Comparison with AC Uncertainty
4. Discussion
4.1. Validity Range of AC Algorithms
4.2. Transmission of AC Errors in SPM Retrieval
4.3. Other Advantages of FLAASH
4.4. Airborne Data, Spatial Scales, and Satellite Validation
5. Conclusions
Data Availability
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cloern, J.E.; Jassby, A.D. Drivers of change in estuarine-coastal ecosystems: Discoveries from four decades of study in San Francisco Bay. Rev. Geophys. 2012, 50, RG4001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morel, A.; Prieur, L. Analysis of variations in ocean color1. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1977, 22, 709–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nechad, B.; Ruddick, K.G.; Park, Y. Calibration and validation of a generic multisensor algorithm for mapping of total suspended matter in turbid waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 854–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyler, A.N.; Hunter, P.D.; Spyrakos, E.; Groom, S.; Constantinescu, A.M.; Kitchen, J. Developments in Earth observation for the assessment and monitoring of inland, transitional, coastal and shelf-sea waters. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 572, 1307–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Gordon, H.R. A simple, moderately accurate, atmospheric correction algorithm for SeaWiFS. Remote Sens. Environ. 1994, 50, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ångström, A. Apparent solar constant variations and their relation to the variability of atmospheric transmission. Tellus 1970, 22, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doron, M.; Bélanger, S.; Doxaran, D.; Babin, M. Spectral variations in the near-infrared ocean reflectance. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 1617–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, D.A.; Wang, M.; Maritorena, S.; Robinson, W. Atmospheric correction of satellite ocean color imagery: The black pixel assumption. Appl. Opt. 2000, 39, 3582–3591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, S.W.; Franz, B.A.; Werdell, P.J. Estimation of near-infrared water-leaving reflectance for satellite ocean color data processing. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 7521–7527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, W.; Wang, M. Satellite views of the Bohai Sea, Yellow Sea, and East China Sea. Prog. Oceanogr. 2012, 104, 30–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Shi, W. The NIR-SWIR combined atmospheric correction approach for MODIS ocean color data processing. Opt. Express 2007, 15, 15722–15733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Son, S.; Shi, W. Evaluation of MODIS SWIR and NIR-SWIR atmospheric correction algorithms using SeaBASS data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 635–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhellemont, Q.; Bailey, S.; Franz, B.; Shea, D. Atmospheric Correction of Landsat-8 Imagery Using SeaDAS. In Proceedings of the ESA Sentinel-2 for Science Workshop, Frascati, Italy, 20–23 May 2014; Volume 726. [Google Scholar]
- Knaeps, E.; Dogliotti, A.I.; Raymaekers, D.; Ruddick, K.; Sterckx, S. In situ evidence of non-zero reflectance in the OLCI 1020nm band for a turbid estuary. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 120, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, G.F.; Aiken, J.; Lavender, S.J. The atmospheric correction of water colour and the quantitative retrieval of suspended particulate matter in Case II waters: Application to MERIS. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1999, 20, 1713–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, G.; Lavender, S. MERIS ATBD 2.6—Case II’s Bright Pixel Atmospheric Correction; ESA: Paris, France, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Antoine, D.; Morel, A. A multiple scattering algorithm for atmospheric correction of remotely sensed ocean colour (MERIS instrument): Principle and implementation for atmospheres carrying various aerosols including absorbing ones. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1999, 20, 1875–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazeran, C.; Babin, M. Développement d’un Algorithme de Corrections Atmosphériques Dédié Aux Eaux Turbides; CNES Report 044-R 661; CNES: Paris, France, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Mazeran, C. Algorithmes Couleur de L’océan en Milieu Côtier—Corrections Atmosphériques; CNES Report 044-R744-RF-v1; CNES: Paris, France, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Schiller, H.; Doerffer, R. Neural network for emulation of an inverse model operational derivation of Case II water properties from MERIS data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1999, 20, 1735–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saulquin, B.; Fablet, R.; Bourg, L.; Mercier, G.; d’Andon, O.F. Use of prior knowledge and a bayesian latent class model for ocean color atmospheric corrections in coastal complex water. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Quebec City, QC, Canada, 27–30 September 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Adler-Golden, S.; Berk, A.; Bernstein, L.S.; Richtsmeier, S.; Acharya, P.K.; Matthew, M.W.; Anderson, G.P.; Allred, C.L.; Jeong, L.S.; Chetwynd, J.H. FLAASH, A MODTRAN4 Atmospheric Correction Package for Hyperspectral Data Retrievals and Simulations. In Proceedings of the 7th Annual JPL Airborne Earth Science Workshop, Pasadena, CA, USA, 12–16 January 1998; Volume 97, pp. 9–14. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, B.-C.; Montes, M.J.; Davis, C.O.; Goetz, A.F.H. Atmospheric correction algorithms for hyperspectral remote sensing data of land and ocean. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, S17–S24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthew, M.W.; Adler-Golden, S.M.; Berk, A.; Felde, G.; Anderson, G.P.; Gorodetzky, D.; Paswaters, S.; Shippert, M. Atmospheric correction of spectral imagery: Evaluation of the FLAASH algorithm with AVIRIS data. In Proceedings of the 31st Applied Imagery Pattern Recognition Workshop, Washington, DC, USA, 16–18 October 2002; pp. 157–163. [Google Scholar]
- Berk, A.; Anderson, G.P.; Bernstein, L.S.; Acharya, P.K.; Dothe, H.; Matthew, M.W.; Adler-Golden, S.M.; Chetwynd, J.H., Jr.; Richtsmeier, S.C.; Pukall, B. MODTRAN 4 radiative transfer modeling for atmospheric correction. In Proceedings of the SPIE- The International Society for Optical Engineering, Denver, CO, USA, 20–23 July 1999; Volume 3756, pp. 348–353. [Google Scholar]
- Berk, A.; Adler-Golden, S.M.; Ratkowski, A.J.; Felde, G.W.; Anderson, G.P.; Hoke, M.L.; Cooley, T.; Chetwynd, J.H.; Gardner, J.A.; Matthew, M.W. Exploiting MODTRAN radiation transport for atmospheric correction: The FLAASH algorithm. In Proceedings of the Fifth International Conference on Information Fusion, Annapolis, MD, USA, 8–11 July 2002; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2002; Volume 2, pp. 798–803. [Google Scholar]
- Kazemipour, F.; Méléder, V.; Launeau, P. Optical properties of microphytobenthic biofilms (MPBOM): Biomass retrieval implication. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2011, 112, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemipour, F.; Launeau, P.; Méléder, V. Microphytobenthos biomass mapping using the optical model of diatom biofilms: Application to hyperspectral images of Bourgneuf Bay. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 127, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.L.; Liu, C.-C.; Buonassissi, C.J.; Wu, A.-M. A Multi-Sensor Approach to Examining the Distribution of Total Suspended Matter (TSM) in the Albemarle-Pamlico Estuarine System, NC, USA. Remote Sens. 2011, 3, 962–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.L.; Haure, J.; Dupuy, B.; Papin, M.; Palvadeau, H.; Nourry, M.; Penisson, C.; Thouard, E. Estimation des Stocks D’huîtres Sauvages sur les Zones non Concédées de la Partie Vendéenne de la Baie de Bourgneuf; Rapport IFREMER, AGS/LGP/Bouin/2005-01; IFREMER: Bouin, France, 2005; p. 17. [Google Scholar]
- Barille-Boyer, A.-L.; Haure, J.; Baud, J.-P. L’ostréiculture en Baie de Bourgneuf. Relation Entre la Croissance des Huîtres Crassostrea Gigas et le Milieu Naturel : Synthèse de 1986 à 1995; IFREMER: Nantes, France, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Dutertre, M.; Beninger, P.G.; Barillé, L.; Papin, M.; Rosa, P.; Barillé, A.-L.; Haure, J. Temperature and seston quantity and quality effects on field reproduction of farmed oysters, Crassostrea gigas, in Bourgneuf Bay, France. Aquat. Living Resour. 2009, 22, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gernez, P.; Barillé, L.; Lerouxel, A.; Mazeran, C.; Lucas, A.; Doxaran, D. Remote sensing of suspended particulate matter in turbid oyster-farming ecosystems. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2014, 119, 7277–7294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gernez, P.; Doxaran, D.; Barillé, L. Shellfish Aquaculture from Space: Potential of Sentinel2 to Monitor Tide-Driven Changes in Turbidity, Chlorophyll Concentration and Oyster Physiological Response at the Scale of an Oyster Farm. Front. Mar. Sci. 2017, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orvain, F.; Lefebvre, S.; Montepini, J.; Sébire, M.; Gangnery, A.; Sylvand, B. Spatial and temporal interaction between sediment and microphytobenthos in a temperate estuarine macro-intertidal bay. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2012, 458, 53–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, R.N.; Swayze, G.A.; Eric Livo, K.; Kokaly, R.F.; King, T.V.V.; Dalton, J.B.; Rockwell, B.W.; Hoefen, T.; McDougal, R.R. Surface Reflectance Calibration of Terrestrial Imaging Spectroscopy Data: A Tutorial Using AVIRIS. In Proceedings of the 10th JPL Airborne Earth Science Workshop; Jet Propulsion laboratory: Pasadena, CA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Delwart, S.; Bourg, L. Radiometric calibration of MERIS. Proc. SPIE 2011, 8176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.-C. NDWI—A normalized difference water index for remote sensing of vegetation liquid water from space. Remote Sens. Environ. 1996, 58, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouse, J., Jr.; Haas, R.H.; Schell, J.A.; Deering, D.W. Monitoring Vegetation Systems in the Great Plains with ERTS; NASA: Washington, DC, USA, 1974.
- Combe, J.-P.; Launeau, P.; Carrère, V.; Despan, D.; Méléder, V.; Laurent, B.; Sotin, C. Mapping microphytobenthos biomass by non-linear inversion of visible-infrared hyperspectral images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 98, 371–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novoa, S.; Doxaran, D.; Ody, A.; Vanhellemont, Q.; Lafon, V.; Lubac, B.; Gernez, P. Atmospheric Corrections and Multi-Conditional Algorithm for Multi-Sensor Remote Sensing of Suspended Particulate Matter in Low-to-High Turbidity Levels Coastal Waters. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barillé, L.; Mouget, J.-L.; Méléder, V.; Rosa, P.; Jesus, B. Spectral response of benthic diatoms with different sediment backgrounds. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 1034–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aznay, O.; Santer, R.; Zagolski, F. Validation of atmospheric scattering functions used in atmospheric correction over the ocean. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 4984–5003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babin, M.; Morel, A.; Fournier-Sicre, V.; Fell, F.; Stramski, D. Light scattering properties of marine particles in coastal and open ocean waters as related to the particle mass concentration. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2003, 48, 843–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babin, M.; Stramski, D.; Ferrari, G.M.; Claustre, H.; Bricaud, A.; Obolensky, G.; Hoepffner, N. Variations in the light absorption coefficients of phytoplankton, nonalgal particles, and dissolved organic matter in coastal waters around Europe. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odermatt, D.; Gitelson, A.; Brando, V.E.; Schaepman, M. Review of constituent retrieval in optically deep and complex waters from satellite imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 118, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spyrakos, E.; O’Donnell, R.; Hunter, P.D.; Miller, C.; Scott, M.; Simis, S.G.H.; Neil, C.; Barbosa, C.C.F.; Binding, C.E.; Bradt, S.; et al. Optical types of inland and coastal waters: Optical types of inland and coastal waters. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Reilly, J.E.; Maritorena, S.; Mitchell, B.G.; Siegel, D.A.; Carder, J.K.; Garver, S.A.; Kahru, M.; McClain, C. Ocean color chlorophyll algorithms for SeaWiFS. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 1998, 103, 24937–24953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gohin, F.; Druon, J.N.; Lampert, L. A five channel chlorophyll concentration algorithm applied to SeaWiFS data processed by SeaDAS in coastal waters. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2002, 23, 1639–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, T.S.; Dowell, M.D.; Bradt, S.; Ruiz Verdu, A. An optical water type framework for selecting and blending retrievals from bio-optical algorithms in lakes and coastal waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 143, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsushita, B.; Yang, W.; Yu, G.; Oyama, Y.; Yoshimura, K.; Fukushima, T. A hybrid algorithm for estimating the chlorophyll-a concentration across different trophic states in Asian inland waters. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 102, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echappé, C.; Gernez, P.; Méléder, V.; Jesus, B.; Cognie, B.; Decottignies, P.; Sabbe, K.; Barillé, L. Satellite remote sensing reveals a positive impact of living oyster reefs on microalgal biofilm development. Biogeosci. 2018, 15, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeye, M.; Fettweis, M.; Voulgaris, G.; Van Lancker, V. Sediment mobility in response to tidal and wind-driven flows along the Belgian inner shelf, southern North Sea. Ocean Dyn. 2011, 61, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorji, P.; Fearns, P. Impact of the spatial resolution of satellite remote sensing sensors in the quantification of total suspended sediment concentration: A case study in turbid waters of Northern Western Australia. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0175042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fettweis, M.; Nechad, B.; Van den Eynde, D. An estimate of the suspended particulate matter (SPM) transport in the southern North Sea using SeaWiFS images, in situ measurements and numerical model results. Cont. Shelf Res. 2007, 27, 1568–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
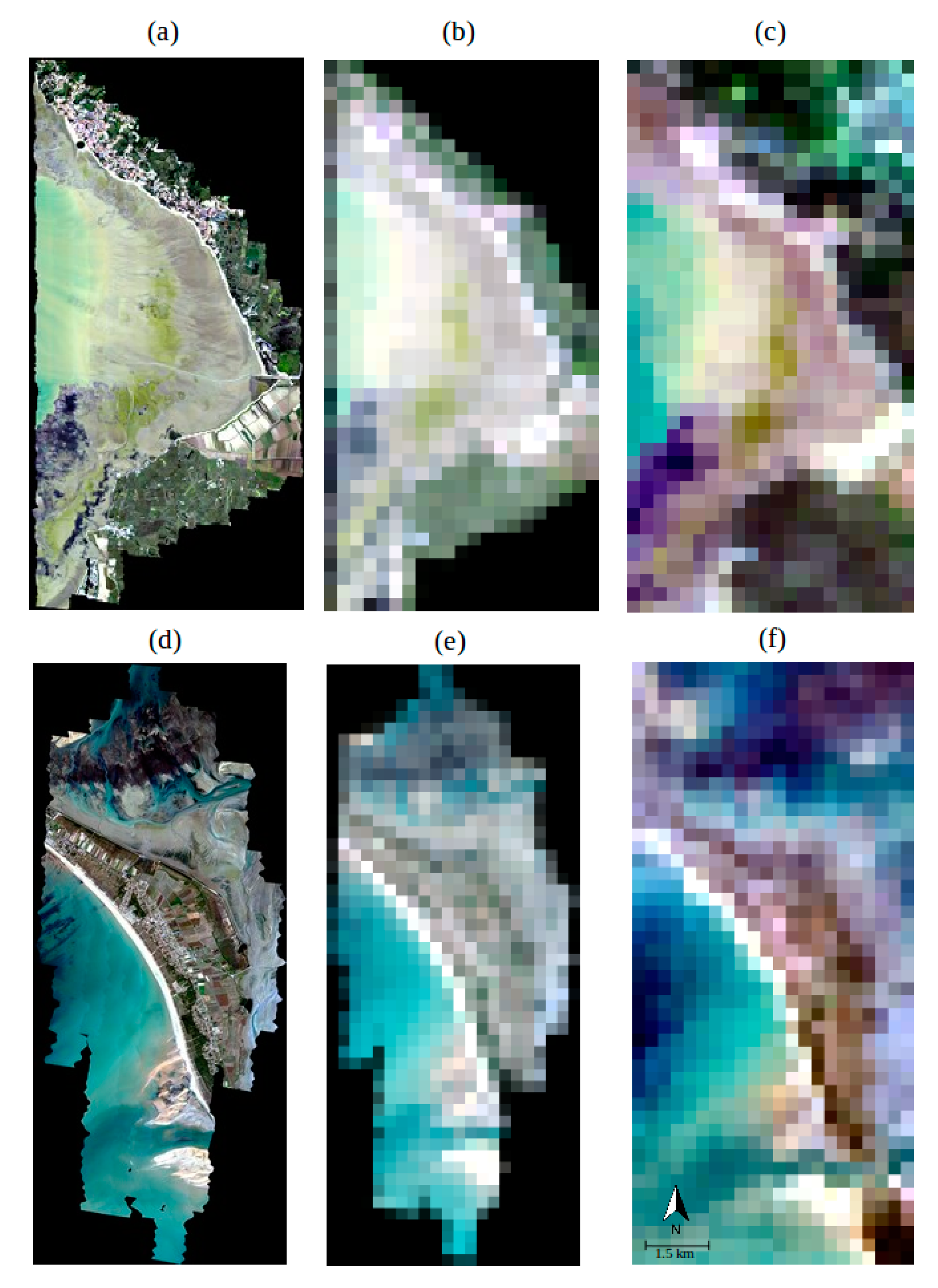

| Date | Observed Site | Airborne Time | MERIS Time | Low Tide Time 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 21 September 2009 | northern mudflat | 11:53–13:12 | 11:11 | 11:22 |
| 22 September 2009 | northern mudflat | 10:00–11:19 | 10:40 | 12:03 |
| 22 September 2009 | off Noirmoutier | 11:33–13:13 | 10:40 | 12:24 |
| 28 September 2011 | northern mudflat | 09:59–11:36 | 10:38 | 10:06 |
| Parameter | HySpex | MERIS |
|---|---|---|
| Atmosphere visibility | 40 km | 40 km |
| Atmosphere model | US standard | US standard |
| Aerosol model | maritime | maritime |
| Water vapor retrieval | 840 nm | none |
| Aerosol retrieval | none | none |
| Pixel Type | HySpex | MERIS-MEGS | MERIS-SAABIO | MERIS-FLAASH |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Land | 426 | NA | NA | 426 |
| Water (all classes) | 398 | 385 | 385 | 398 |
| Water (class 1) | 166 | 163 | 163 | 166 |
| Water (class 2) | 104 | 103 | 103 | 104 |
| Water (class 3) | 128 | 119 | 119 | 128 |
| Pixel Type | Metrics 1 | MEGS | SAABIO | FLAASH |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Land | RMSE | NA | NA | 0.0035 |
| RRMSE | NA | NA | 14 | |
| Water (all) | RMSE | 0.0104 | 0.0137 | 0.0039 |
| RRMSE | 53 | 70 | 45 | |
| Water (class 1) | RMSE | 0.0058 | 0.0041 | 0.0045 |
| RRMSE | 53 | 49 | 81 | |
| Water (class 2) | RMSE | 0.0152 | 0.0128 | 0.0028 |
| RRMSE | 64 | 58 | 22 | |
| Water (class 3) | RMSE | 0.0127 | 0.0274 | 0.0041 |
| RRMSE | 46 | 108 | 16 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Larnicol, M.; Launeau, P.; Gernez, P. Using High-Resolution Airborne Data to Evaluate MERIS Atmospheric Correction and Intra-Pixel Variability in Nearshore Turbid Waters. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10020274
Larnicol M, Launeau P, Gernez P. Using High-Resolution Airborne Data to Evaluate MERIS Atmospheric Correction and Intra-Pixel Variability in Nearshore Turbid Waters. Remote Sensing. 2018; 10(2):274. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10020274
Chicago/Turabian StyleLarnicol, Morgane, Patrick Launeau, and Pierre Gernez. 2018. "Using High-Resolution Airborne Data to Evaluate MERIS Atmospheric Correction and Intra-Pixel Variability in Nearshore Turbid Waters" Remote Sensing 10, no. 2: 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10020274
APA StyleLarnicol, M., Launeau, P., & Gernez, P. (2018). Using High-Resolution Airborne Data to Evaluate MERIS Atmospheric Correction and Intra-Pixel Variability in Nearshore Turbid Waters. Remote Sensing, 10(2), 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10020274