Urbanization Impacts on Vegetation Phenology in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
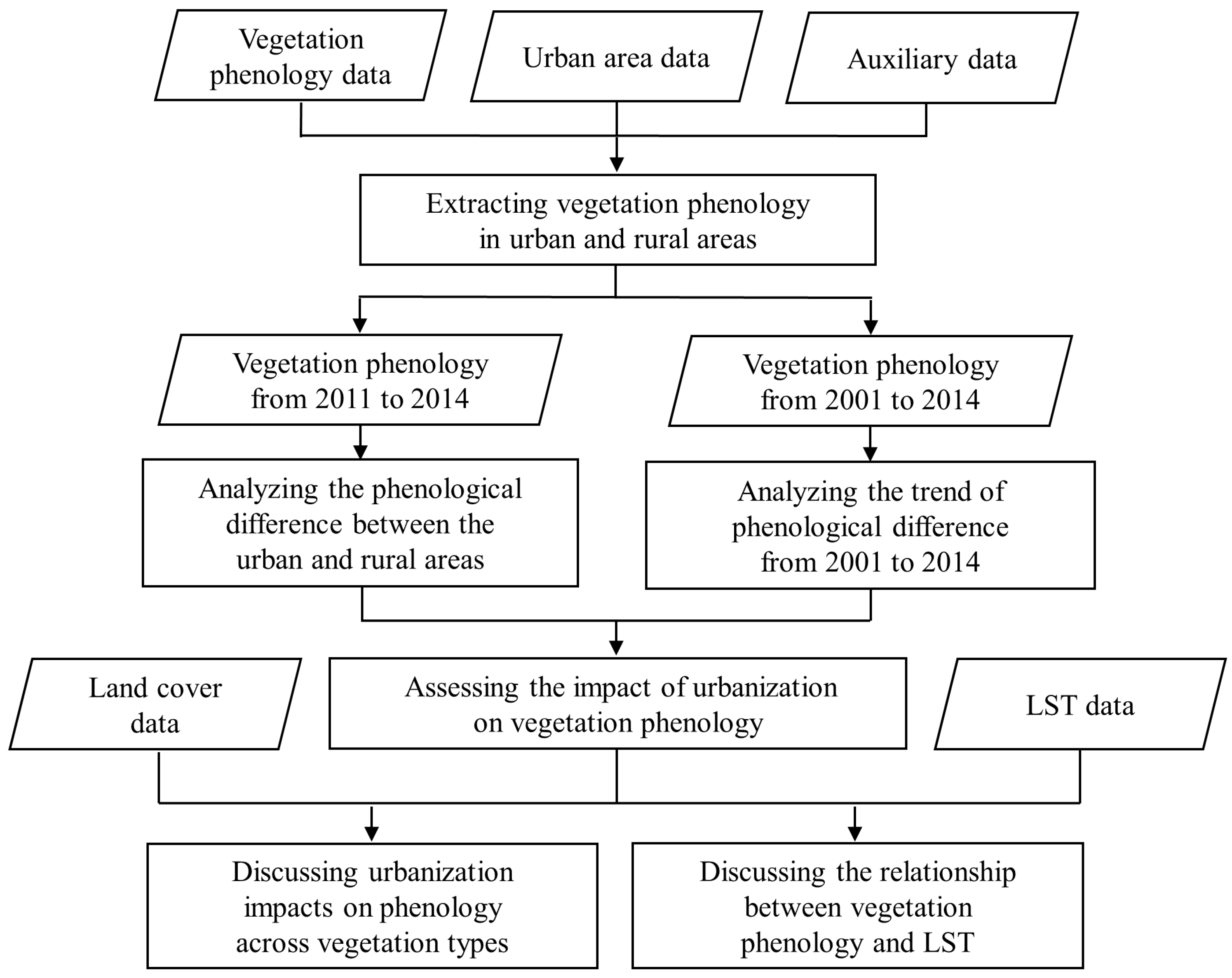
2. Materials and Methods
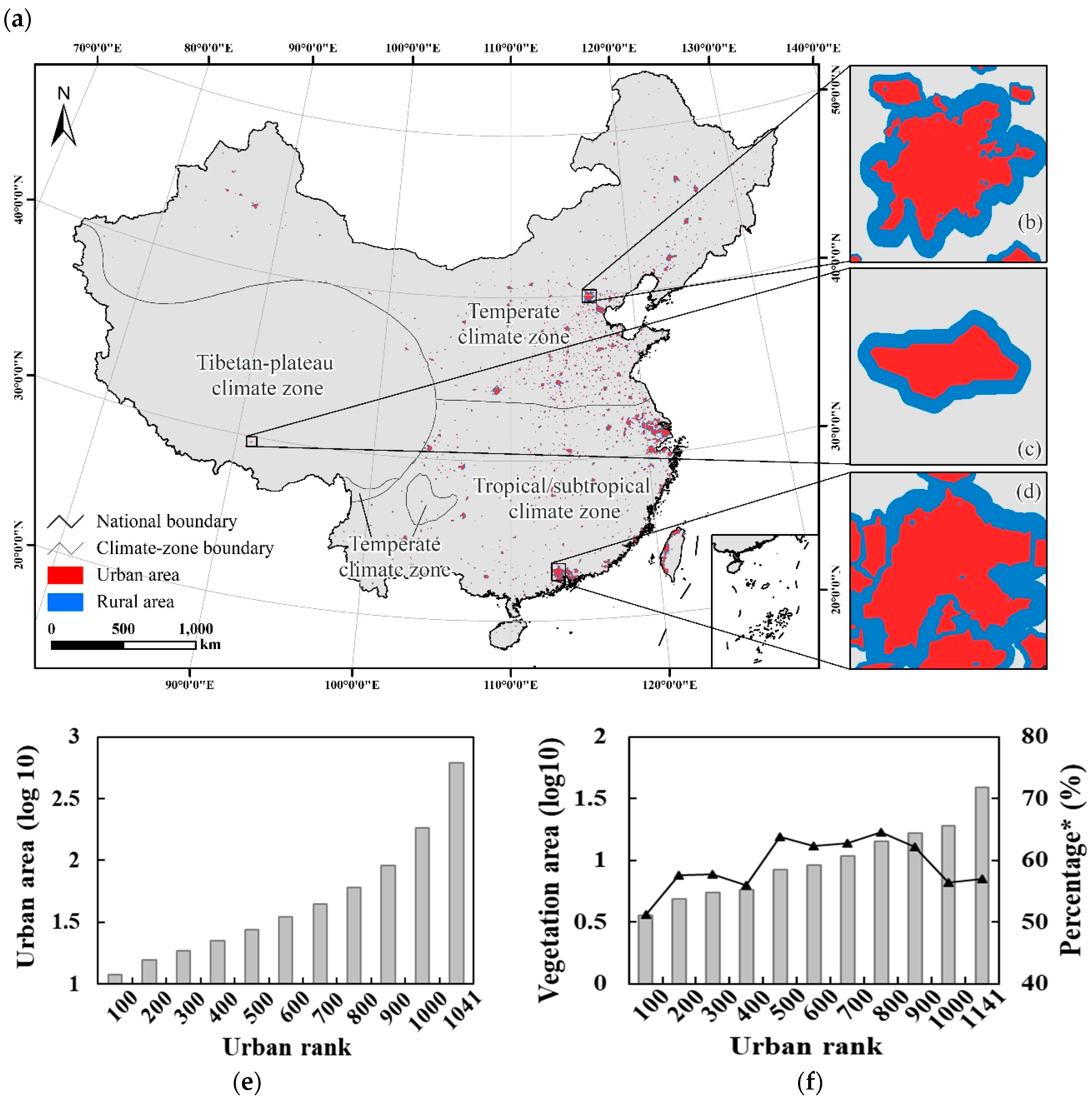
2.1. Study Area
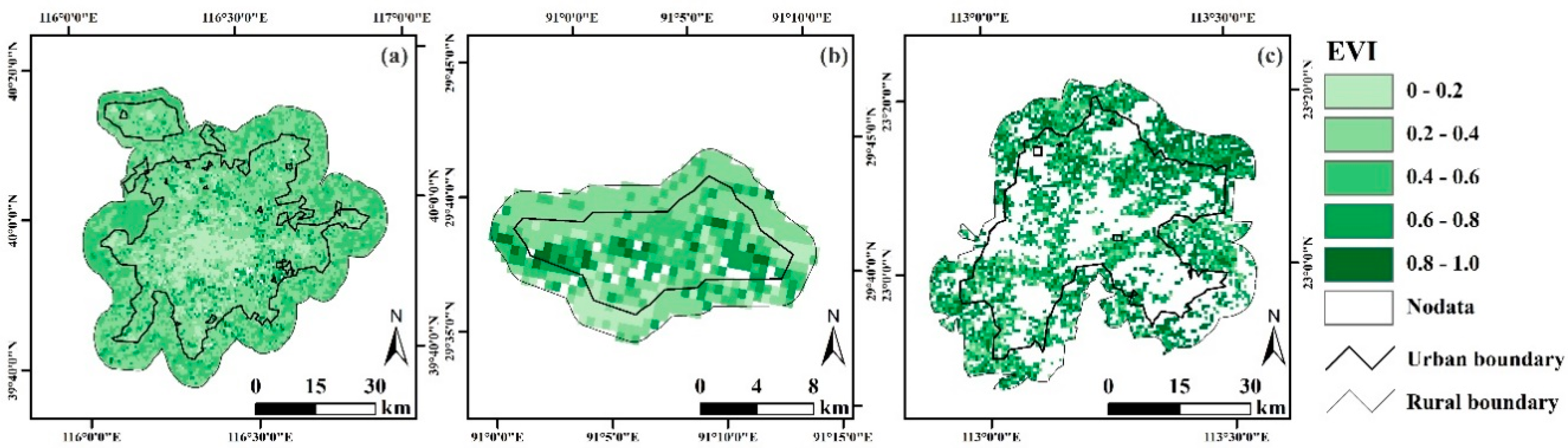
2.2. Data
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Phenology Indicators
2.3.2. Differences in Phenology between the Urban and Rural Areas
2.3.3. Trend of the Phenological Differences between the Urban and Rural Areas
2.3.4. Relationship between Vegetation Phenology and LST
3. Results
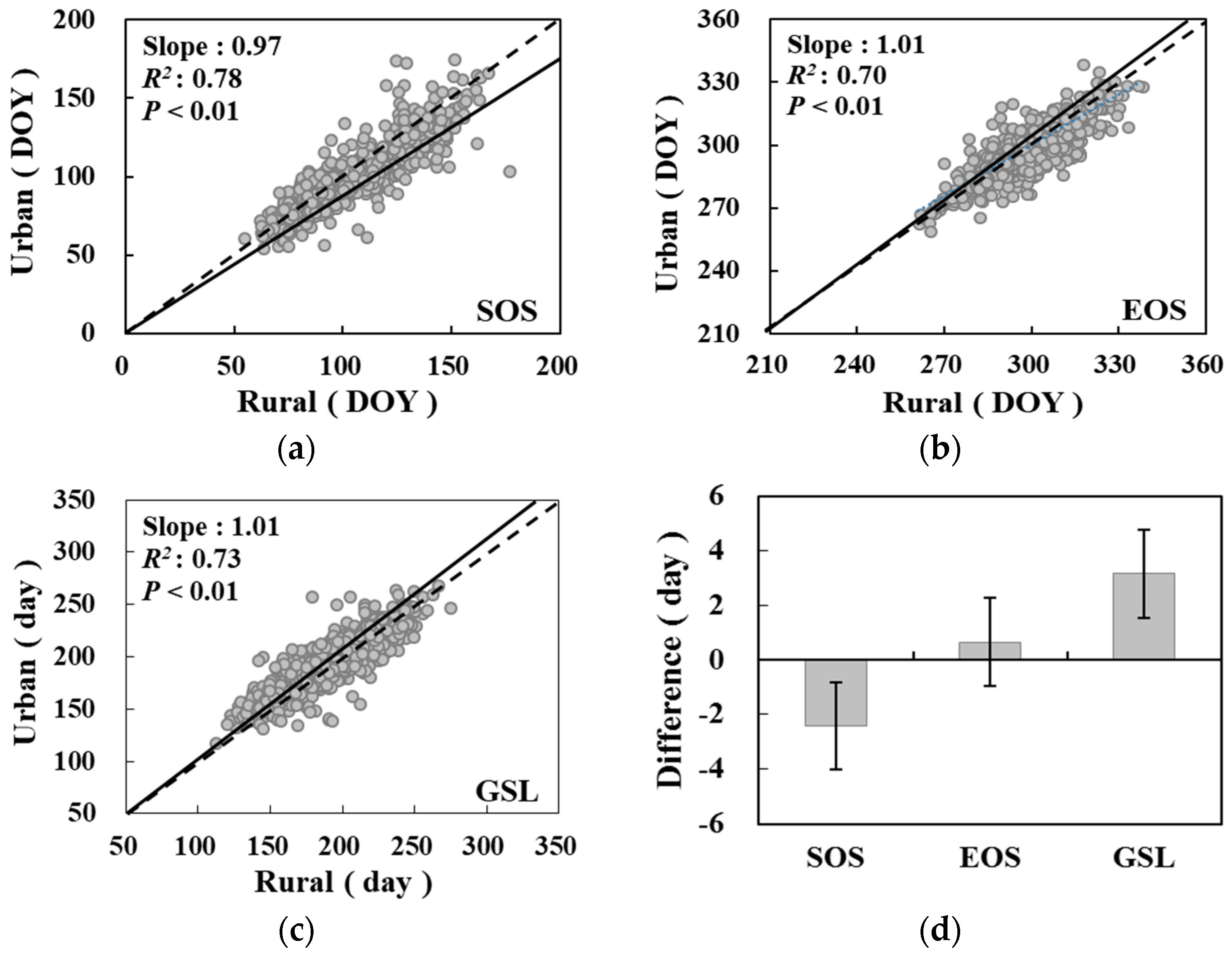
3.1. Differences in Phenology between the Urban and Rural Areas
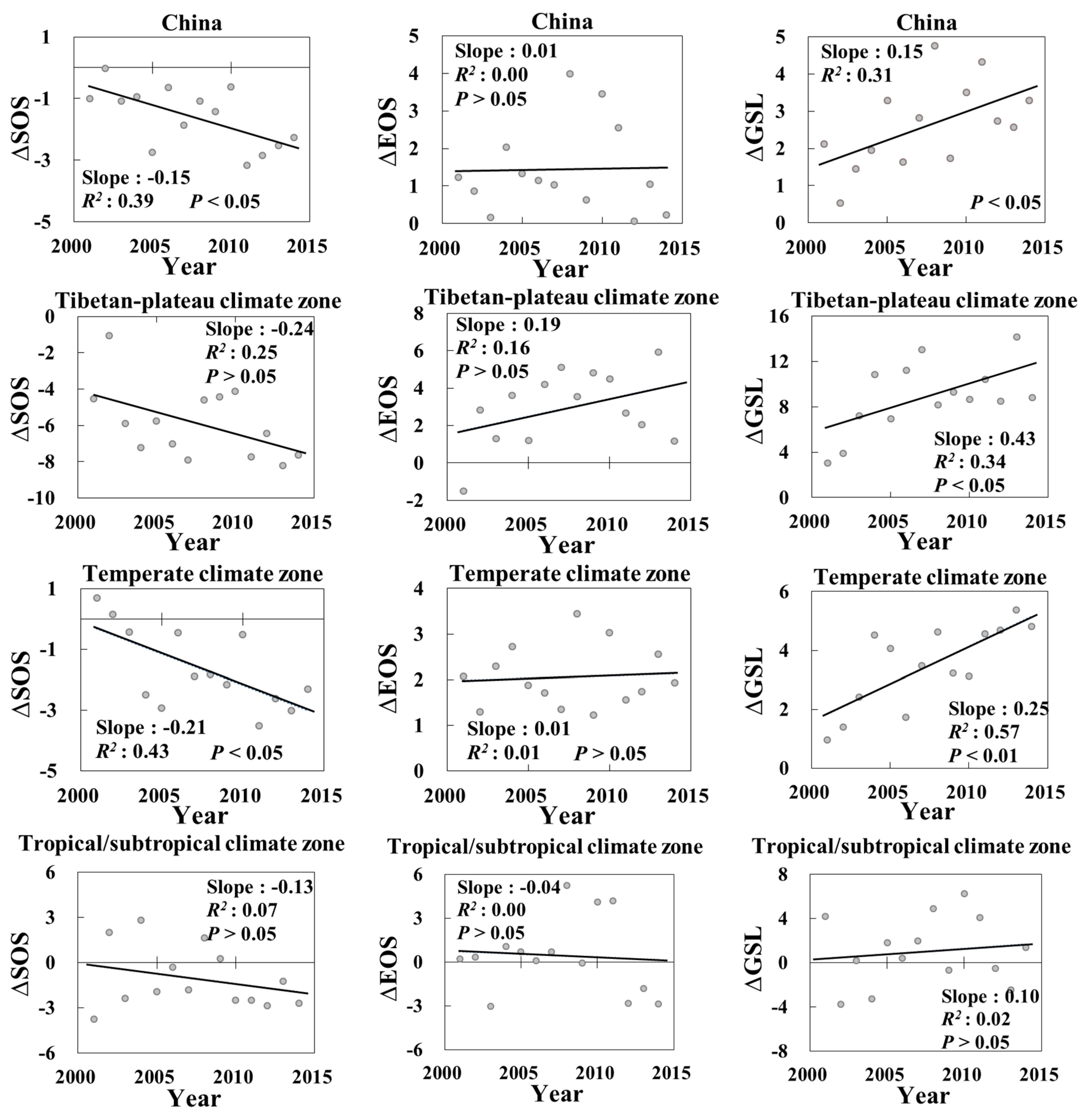
3.2. Trend of the Phenological Differences between the Urban and Rural Areas
4. Discussion
4.1. Impacts of Urbanization on Phenology across Vegetation Types
4.2. Relationship between Phenology and LST
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, X.; Wang, D.; Chen, J.; Wang, C.; Shen, M. The mixed pixel effect in land surface phenology: A simulation study. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 211, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, M.A.; de Beurs, K.M.; Didan, K.; Inouye, D.W.; Richardson, A.D.; Jensen, O.P.; O’Keefe, J.; Zhang, G.; Nemani, R.R.; van Leeuwen, W.J.D.; et al. Intercomparison, interpretation, and assessment of spring phenology in North America estimated from remote sensing for 1982–2006. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2009, 15, 2335–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linderholm, H.W. Growing season changes in the last century. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2006, 137, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badeck, F.W.; Bondeau, A.; Bottcher, K.; Doktor, D.; Lucht, W.; Schaber, J.; Sitch, S. Responses of spring phenology to climate change. New Phytol. 2004, 162, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, A.; Valcu, M.; Kempenaers, B. Light pollution alters the phenology of dawn and dusk singing in common European songbirds. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 2015, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahlin, K.M.; Fisher, R.A.; Lawrence, P.J. Environmental drivers of drought deciduous phenology in the Community Land Model. Biogeosciences 2015, 12, 5061–5074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Yu, Q.; Liu, J.; Lee, X. Advance of tree-flowering dates in response to urban climate change. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2006, 138, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seto, K.C.; Guneralp, B.; Hutyra, L.R. Global forecasts of urban expansion to 2030 and direct impacts on biodiversity and carbon pools. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 16083–16088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, H.; Li, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Chen, B.; Zhang, B.; Xin, X. Variability and climate change trend in vegetation phenology of recent decades in the Greater Khingan Mountain area, Northeastern China. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 11914–11932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keenan, T.F.; Gray, J.; Friedl, M.A.; Toomey, M.; Bohrer, G.; Hollinger, D.Y.; Munger, J.W.; O’Keefe, J.; Schmid, H.P.; Wing, I.S.; et al. Net carbon uptake has increased through warming-induced changes in temperate forest phenology. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2014, 4, 598–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, A.D.; Keenan, T.F.; Migliavacca, M.; Ryu, Y.; Sonnentag, O.; Toomey, M. Climate change, phenology, and phenological control of vegetation feedbacks to the climate system. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2013, 169, 156–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, S.; Ciais, P.; Friedlingstein, P.; Peylin, P.; Reichstein, M.; Luyssaert, S.; Margolis, H.; Fang, J.; Barr, A.; Chen, A.; et al. Net carbon dioxide losses of northern ecosystems in response to autumn warming. Nature 2008, 451, 49–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, D.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, L.; Liu, S. Remotely sensed assessment of urbanization effects on vegetation phenology in China’s 32 major cities. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 176, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Körner, C.; Muraoka, H.; Piao, S.; Shen, M.; Thackeray, S.J.; Yang, X. Emerging opportunities and challenges in phenology: A review. Ecosphere 2016, 7, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Shi, P.; Li, H. Urban spring phenology in the middle temperate zone of China: Dynamics and influence factors. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2016, 60, 531–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J. Urban ecology and sustainability: The state-of-the-science and future directions. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2014, 125, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimm, N.B.; Faeth, S.H.; Golubiewski, N.E.; Redman, C.L.; Wu, J.; Bai, X.; Briggs, J.M. Global change and the ecology of cities. Science 2008, 319, 756–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, T.; Song, C.; Li, J. Impacts of urbanization on vegetation phenology over the past three decades in Shanghai, China. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bounoua, L.; Zhang, P.; Mostovoy, G.; Thome, K.; Masek, J.; Imhoff, M.; Shepherd, M.; Quattrochi, D.; Santanello, J.; Silva, J.; et al. Impact of urbanization on US surface climate. Environ. Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 084010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buyantuyev, A.; Wu, J. Urbanization diversifies land surface phenology in arid environments: Interactions among vegetation, climatic variation, and land use pattern in the Phoenix metropolitan region, USA. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2012, 105, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, N.; Piao, S.; Chen, A.; Wang, X.; Lin, X.; Chen, S.; Han, S.; Zhou, G.; Zhang, X. Spring vegetation green-up date in China inferred from SPOT NDVI data: A multiple model analysis. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2012, 165, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecchi, L.; D’Amato, G.; Ayres, J.G.; Galan, C.; Forastiere, F.; Forsberg, B.; Gerritsen, J.; Nunes, C.; Behrendt, H.; Akdis, C.; et al. Projections of the effects of climate change on allergic asthma: The contribution of aerobiology. Allergy 2010, 65, 1073–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Vliet, A.J.H.; Overeem, A.; De Groot, R.S.; Jacobs, A.F.G.; Spieksma, F.T.M. The influence of temperature and climate change on the timing of pollen release in the Netherlands. Int. J. Climatol. 2002, 22, 1757–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Shi, P.; Liu, Y. Society: Realizing China’s urban dream. Nature 2014, 509, 158–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, C.; Gao, B.; Huang, Q.; Ma, Q.; Dou, Y. Environmental degradation in the urban areas of China: Evidence from multi-source remote sensing data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 193, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Bureau of Statistics of China. China Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2013; ISBN 978-7-5037-6963-4.
- Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development PRC. China Urban Construction Statistical Yearbook 2011; China Planning Press: Beijing, China, 2012; ISBN 978-7-80242-909-3.
- Jochner, S.; Menzel, A. Urban phenological studies—Past, present, future. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 203, 250–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neil, K.; Wu, J. Effects of urbanization on plant flowering phenology: A review. Urban Ecosyst. 2006, 9, 243–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hepper, F.N. Phenological records of English garden plants in Leeds (Yorkshire) and Richmond (Surrey) from 1946 to 2002. An analysis relating to global warming. Biodivers. Conserv. 2003, 12, 2503–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traidl-Hoffmann, C.; Kasche, A.; Menzel, A.; Jakob, T.; Thiel, M.; Ring, J.; Behrendt, H. Impact of pollen on human health: More than allergen carriers? Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2003, 131, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitter, A.H.; Fitter, R.S. Rapid changes in flowering time in British plants. Science 2002, 296, 1689–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mimet, A.; Pellissier, V.; Quenol, H.; Aguejdad, R.; Dubreuil, V.; Roze, F. Urbanisation induces early flowering: Evidence from Platanus acerifolia and Prunus cerasus. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2009, 53, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Friedl, M.A.; Schaaf, C.B.; Strahler, A.H. Climate controls on vegetation phenological patterns in northern mid- and high latitudes inferred from MODIS data. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2004, 10, 1133–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Primack, D.; Imbres, C.; Primack, R.B.; Millerrushing, A.J.; Tredici, P.D. Herbarium specimens demonstrate earlier flowering times in response to warming in Boston. Am. J. Bot. 2004, 91, 1260–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franklin, K.A.; Whitelam, G.C. Light signals, phytochromes and cross-talk with other environmental cues. J. Exp. Bot. 2004, 55, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, M.; Tang, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhu, X.; Zheng, Y. Influences of temperature and precipitation before the growing season on spring phenology in grasslands of the central and eastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2011, 151, 1711–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, G.; Nishikawa, Y.; Kasagi, T.; Kosuge, S. Does seed production of spring ephemerals decrease when spring comes early? Ecol. Res. 2010, 19, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziello, C.; Böck, A.; Estrella, N.; Ankerst, D.; Menzel, A. First flowering of wind-pollinated species with the greatest phenological advances in Europe. Ecography 2012, 35, 1017–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jochner, S.C.; Sparks, T.H.; Estrella, N.; Menzel, A. The influence of altitude and urbanisation on trends and mean dates in phenology (1980–2009). Int. J. Biometeorol. 2012, 56, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, Q.; Broich, M.; Suyker, A.E.; Yu, L.; Gong, P. Multi-scale evaluation of light use efficiency in MODIS gross primary productivity for croplands in the Midwestern United States. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2015, 201, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Sun, O.J.; Ge, Q.; Xu, W.; Zheng, J. Phenological responses of plants to climate change in an urban environment. Ecol. Res. 2006, 22, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jochner, S.; Caffarra, A.; Menzel, A. Can spatial data substitute temporal data in phenological modelling? A survey using birch flowering. Tree Physiol. 2013, 33, 1256–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkinson, P.M.; Jeganathan, C.; Dash, J.; Atzberger, C. Inter-comparison of four models for smoothing satellite sensor time-series data to estimate vegetation phenology. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 123, 400–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhou, Y.; Asrar, G.R.; Mao, J.; Li, X.; Li, W. Response of vegetation phenology to urbanization in the conterminous United States. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2017, 23, 2818–2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gazal, R.; White, M.A.; Gillies, R.; Rodemaker, E.L.I.; Sparrow, E.; Gordon, L. GLOBE students, teachers, and scientists demonstrate variable differences between urban and rural leaf phenology. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2008, 14, 1568–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atzberger, C.; Klisch, A.; Mattiuzzi, M.; Vuolo, F. Phenological Metrics Derived over the European Continent from NDVI3g Data and MODIS Time Series. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 257–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Leeuwen, W.J.D.; Orr, B.J.; Marsh, S.E.; Herrmann, S.M. Multi-sensor NDVI data continuity: Uncertainties and implications for vegetation monitoring applications. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 100, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, P.S.A.; Atzberger, C.; Høgda, K.A.; Johansen, B.; Skidmore, A.K. Improved monitoring of vegetation dynamics at very high latitudes: A new method using MODIS NDVI. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 100, 321–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meroni, M.; Atzberger, C.; Vancutsem, C.; Gobron, N.; Baret, F.; Lacaze, R.; Eerens, H.; Leo, O. Evaluation of Agreement Between Space Remote Sensing SPOT-VEGETATION fAPAR Time Series. IEEE Transa. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 1951–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Xu, J. Land surface phenology and land surface temperature changes along an urban-rural gradient in Yangtze River Delta, China. Environ. Manag. 2013, 52, 234–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zuo, W. Geographic Atlas of China; SinoMaps Press: Beijing, China, 2009; ISBN 9787503152337. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Tao, F. Modeling the response of rice phenology to climate change and variability in different climatic zones: Comparisons of five models. Eur. J. Agron. 2013, 45, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rishmawi, K.; Prince, S.; Xue, Y. Vegetation Responses to Climate Variability in the Northern Arid to Sub-Humid Zones of Sub-Saharan Africa. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machar, I.; Vlckova, V.; Bucek, A.; Vozenilek, V.; Salek, L.; Jerabkova, L. Modelling of Climate Conditions in Forest Vegetation Zones as a Support Tool for Forest Management Strategy in European Beech Dominated Forests. Forests 2017, 8, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Yu, S. Spatiotemporal Variability of Land Surface Phenology in China from 2001–2014. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.X.; Wang, B.; Cheng, H.; Fasullo, J.; Guo, Z.; Kiefer, T.; Liu, Z. The global monsoon across time scales: Mechanisms and outstanding issues. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2017, 174, 84–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, S.; Ciais, P.; Huang, Y.; Shen, Z.; Peng, S.; Li, J.; Zhou, L.; Liu, H.; Ma, Y.; Ding, Y.; et al. The impacts of climate change on water resources and agriculture in China. Nature 2010, 467, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Smith, S.J.; Elvidge, C.D.; Zhao, K.; Thomson, A.; Imhoff, M. A cluster-based method to map urban area from DMSP/OLS nightlights. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 147, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Smith, S.J.; Zhao, K.; Imhoff, M.; Thomson, A.; Bond-Lamberty, B.; Asrar, G.R.; Zhang, X.; He, C.; Elvidge, C.D. A global map of urban extent from nightlights. Environ. Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 054011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, X.; Asrar, G.R.; Smith, S.J.; Imhoff, M. A global record of annual urban dynamics (1992–2013) from nighttime lights. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 219, 206–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.Y.; Liu, Z.F.; Tian, J.; Ma, Q. Urban expansion dynamics and natural habitat loss in China: A multiscale landscape perspective. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2014, 20, 2886–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.F.; He, C.Y.; Zhou, Y.Y.; Wu, J.G. How much of the world’s land has been urbanized, really? A hierarchical framework for avoiding confusion. Landsc. Ecol. 2014, 29, 763–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, S.; Friedl, M.A.; Tan, B.; Zhang, X.; Verma, M. Land surface phenology from MODIS: Characterization of the Collection 5 global land cover dynamics product. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 1805–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Friedl, M.A.; Schaaf, C.B. Global vegetation phenology from Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS): Evaluation of global patterns and comparison with in situ measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2006, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Friedl, M.A.; Schaaf, C.B.; Strahler, A.H.; Schneider, A. The footprint of urban climates on vegetation phenology. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belward, A.S.; Estes, J.E.; Kline, K.D. The IGBP-DIS global 1-km land-cover data set DISCover: A project overview. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1999, 65, 1013–1020. [Google Scholar]
- Svirejeva-Hopkins, A.; Schellnhuber, H.J. Modelling carbon dynamics from urban land conversion: Fundamental model of city in relation to a local carbon cycle. Carbon Balanc. Manag. 2006, 1, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, Z. New refinements and validation of the MODIS Land-Surface Temperature/Emissivity products. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 265–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Z.; Dozier, J. A generalized split-window algorithm for retrieving land-surface temperature from space. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1996, 34, 892–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhou, Y.; Asrar, G.R.; Imhoff, M.; Li, X. The surface urban heat island response to urban expansion: A panel analysis for the conterminous United States. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 605–606, 426–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clinton, N.; Gong, P. MODIS detected surface urban heat islands and sinks: Global locations and controls. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 134, 294–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krehbiel, C.; Zhang, X.; Henebry, G. Impacts of Thermal Time on Land Surface Phenology in Urban Areas. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Friedl, M.A.; Schaaf, C.B.; Strahler, A.H.; Hodges, J.C.F.; Gao, F.; Reed, B.C.; Huete, A. Monitoring vegetation phenology using MODIS. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 84, 471–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atzberger, C.; Eilers, P.H.C. Evaluating the effectiveness of smoothing algorithms in the absence of ground reference measurements. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 32, 3689–3709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhou, Y.; Asrar, G.R.; Meng, L. Characterizing spatiotemporal dynamics in phenology of urban ecosystems based on Landsat data. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 605–606, 721–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melaas, E.K.; Friedl, M.A.; Zhu, Z. Detecting interannual variation in deciduous broadleaf forest phenology using Landsat TM/ETM+ data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 132, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, J.; Mustard, J.; Vadeboncoeur, M. Green leaf phenology at Landsat resolution: Scaling from the field to the satellite. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 100, 265–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
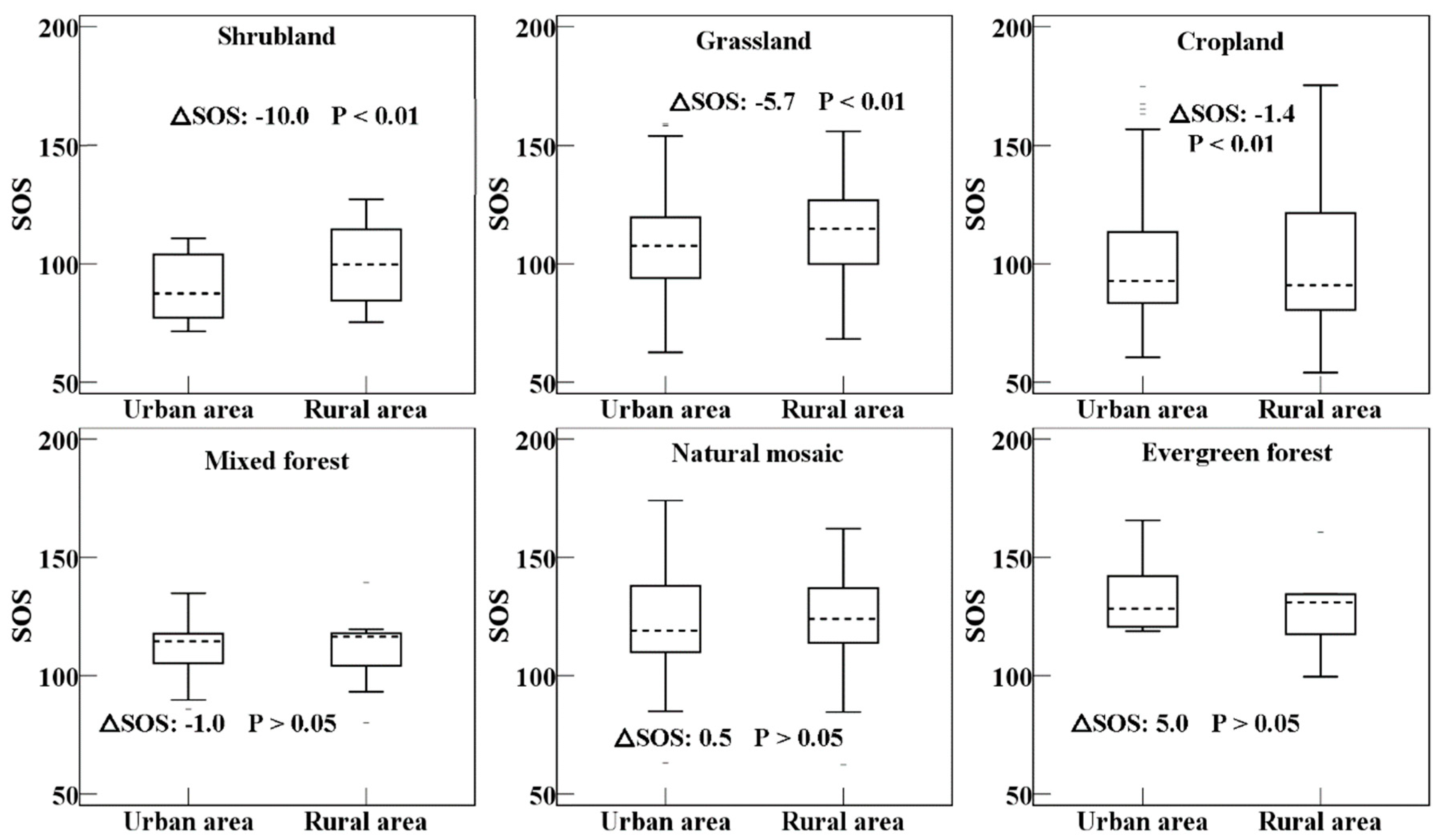
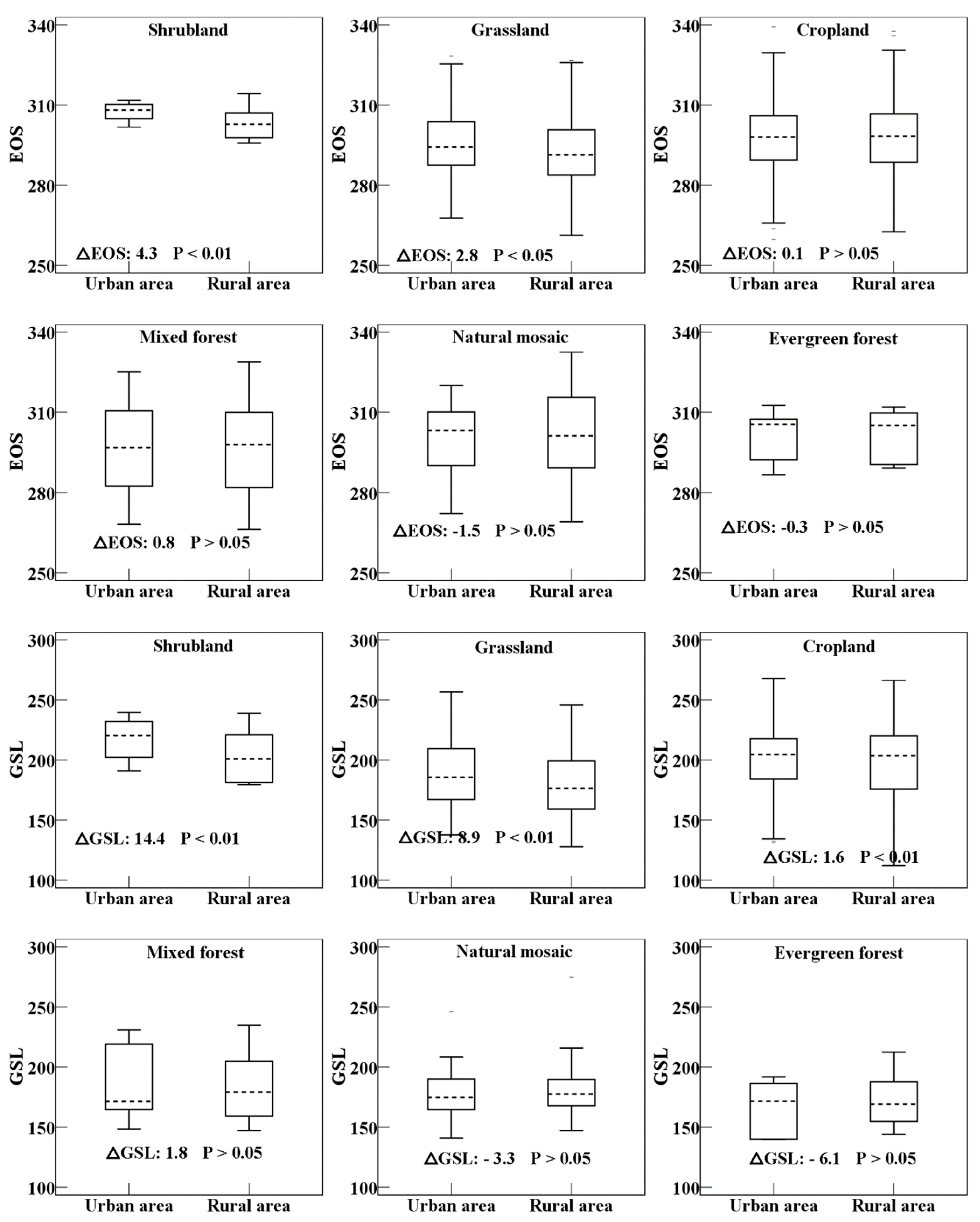
| Area | SOS (DOY) | EOS (DOY) | GSL (Day) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Urban | Rural | △SOS | Urban | Rural | △EOS | Urban | Rural | △GSL | ||
| China | Mean | 101.8 | 104.2 | −2.4 ** | 297.9 | 297.2 | 0.7 ** | 196.1 | 193.0 | 3.1 ** |
| SD | 20.9 | 23.4 | 10.1 | 11.9 | 12.8 | 6.4 | 26.9 | 30.4 | 13.7 | |
| Tibetan-plateau climate zone | Mean | 99.1 | 106.6 | −7.5 ** | 306.7 | 303.7 | 3.0 ** | 207.6 | 197.1 | 10.5 ** |
| SD | 14.2 | 13.4 | 5.7 | 8.2 | 10.0 | 2.8 | 21.5 | 21.8 | 5.9 | |
| Temperate climate zone | Mean | 101.5 | 105.1 | −3.6 ** | 295.0 | 293.2 | 1.8 ** | 193.5 | 188.1 | 5.4 ** |
| SD | 17.9 | 22.4 | 8.1 | 10.9 | 11.4 | 5.5 | 25.9 | 30.7 | 11.3 | |
| Tropical/subtropical climate zone | Mean | 102.4 | 102.4 | 0 | 303.3 | 305.2 | −1.9 ** | 200.9 | 202.8 | −1.9 |
| SD | 26.0 | 25.4 | 12.9 | 11.9 | 11.8 | 7.5 | 28.1 | 27.7 | 16.8 | |
| Area | Tibetan-Plateau Climate Zone | Temperate Climate Zone | Tropical/Subtropical Climate Zone | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| △SOS | △EOS | △GSL | △SOS | △EOS | △GSL | △SOS | △EOS | △GSL | ||
| Evergreen forest | Mean | - | - | - | - | - | - | 5.0 | −0.3 | −6.1 |
| SD | - | - | - | - | - | - | 8.2 | 4.7 | 12.0 | |
| Mixed forest | Mean | - | - | - | −0.6 | 1.0 | 1.7 | −1.7 | 0.4 | 2.1 |
| SD | 3.4 | 1.3 | 4.3 | 6.8 | 3.1 | 8.0 | ||||
| Shrubland | Mean | −4.6 ** | 6.0 ** | 10.5 ** | −10.8 ** | 4.1 * | 14.9 ** | - | - | - |
| SD | - | - | - | 6.9 | 4.2 | 9.3 | - | - | - | |
| Grassland | Mean | −7.8 ** | 2.6 * | 10.5 ** | −6.3 ** | 3.1 ** | 9.4 ** | −1.3 | 1.1 | 5.0 |
| SD | 5.9 | 2.7 | 6.2 | 6.2 | 3.6 | 8.6 | 16.7 | 10.1 | 25.0 | |
| Cropland | Mean | - | - | - | −2.2 ** | 1.3 ** | 3.6 ** | 0.1 | −2.4 ** | −2.2 * |
| SD | - | - | - | 8.6 | 6.1 | 11.8 | 12.6 | 7.2 | 14.8 | |
| Natural mosaic | Mean | - | - | - | −2.2 | 2.0 ** | 4.1 * | 1.6 | −2.9 | −6.3 |
| SD | - | - | - | 3.2 | 1.3 | 3.9 | 16.4 | 8.6 | 23.7 | |
| Phenological Indicator | China | Tibetan-Plateau Climate Zone | Temperate Climate Zone | Tropical/Subtropical Climate Zone | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SOS | Correlation coefficient | −0.24 ** | −0.44 * | −0.80 ** | 0.68 ** |
| RMSE | 21.3 | 12.9 | 11.9 | 18.8 | |
| EOS | Correlation coefficient | 0.56 ** | 0.64 ** | 0.58 ** | 0.16 ** |
| RMSE | 10.1 | 7.1 | 8.9 | 11.7 | |
| GSL | Correlation coefficient | 0.44 ** | 0.55 * | 0.81 ** | −0.52 ** |
| RMSE | 25.3 | 18.7 | 16.5 | 23.7 | |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ren, Q.; He, C.; Huang, Q.; Zhou, Y. Urbanization Impacts on Vegetation Phenology in China. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1905. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10121905
Ren Q, He C, Huang Q, Zhou Y. Urbanization Impacts on Vegetation Phenology in China. Remote Sensing. 2018; 10(12):1905. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10121905
Chicago/Turabian StyleRen, Qiang, Chunyang He, Qingxu Huang, and Yuyu Zhou. 2018. "Urbanization Impacts on Vegetation Phenology in China" Remote Sensing 10, no. 12: 1905. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10121905
APA StyleRen, Q., He, C., Huang, Q., & Zhou, Y. (2018). Urbanization Impacts on Vegetation Phenology in China. Remote Sensing, 10(12), 1905. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10121905







