Modeling Microseism Generation by Inhomogeneous Ocean Surface Waves in Hurricane Bonnie Using the Non-Linear Wave Equation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ocean Surface Gravity Waves
2.2. Non-Linear Wave Equation
2.3. Power Spectral Density Due to Ocean Surface Gravity Waves
2.4. Microseismic Source Levels in Hurricane Bonnie
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Spectral Properties Surface Waves
Appendix A.1. Homogeneous Surface Wave Fields
Appendix A.2. Inhomogeneous Surface Wave Fields
Appendix B. Adiabatic Propagation of Generalized Rayleigh Waves in a Range-Dependent Ocean Environment
Appendix C. Range-Independent Half-Space
References
- Chi, W.-C.; Chen, W.-J.; Kuo, B.-Y.; Dolenc, D. Seismic Monitoring of Western Pacific Typhoons. Mar. Geophys. Res. 2010, 31, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davy, C.; Barruol, G.; Fontaine, F.R.; Sigloch, K.; Stutzmann, E. Tracking Major Storms from Microseismic and Hydroacoustic Observations on the Seafloor. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 10, 8825–8831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerstoft, P.; Shearer, P.M.; Harmon, N.; Zhang, J. Global P, PP and PKP Wave Microseisms Observed from Distant Storms. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L23306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilmore, M.H. Microseisms and ocean storms. Seismol. Soc. Bull. 1946, 36, 89–119. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Fang, S.; Chen, C.; Zheng, H. Seismic Remote Sensing of Super Typhoon Lupit (2009) with Seismological Array Observations in NE China. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Lin, J.; Xu, M. Microseisms Generated by Super Typhoon Megi in the Western Pacific Ocean. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2017, 10, 9518–9529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, J.E. An experimental investigation of the nature and origin of microseisms at St. Louis, Missouri. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 1940, 30, 35–84. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Gerstoft, P.; Bromirski, P.D. Pelagic and Coastal Sources of P-Wave Microseisms. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37, L15301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.W. The effect of geologic structure upon microseismic disturbance. R. Astron. Soc. Mon. Not. Geophys. Suppl. 1932, 3, 83–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Press, F.; Ewing, M. A Theory of Microseisms with Geologic Applications. Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1948, 29, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, S.C. Broadband seismology and noise under the ocean. Rev. Geophys. 1998, 36, 105–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, I.-J.; Ginis, I.; Hara, T.; Tolman, H.L.; Wright, C.W.; Walsh, E.J. Numerical simulation of sea surface directional wave spectra under hurricane wind forcing. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2003, 33, 1680–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, C.W.; Walsh, E.J.; Vandemark, D.; Krabill, W.B.; Garcia, A.W.; Houston, S.H.; Powell, M.D.; Black, P.G.; Marks, F.D., Jr. Hurricane directional wave spectrum spatial variation in the open ocean. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2001, 31, 2472–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longuet-Higgins, M.S. A theory of the origin of microseisms. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A 1950, 243, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brekhovskikh, L.M. Underwater sound waves generated by surface waves in the ocean. Izv. Atmos. Ocean. Phys. 1966, 2, 582–587. [Google Scholar]
- Guralnik, Z.; Bourdelais, J.; Zabalgogeazcoa, X.; Farrell, W.E. Wave-Wave Interactions and Deep Ocean Acoustics. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2013, 134, 3161–3173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasselmann, K. A statistical analysis of the generation of microseisms. Rev. Geophys. 1963, 1, 177–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, B. Estimates of underwater sound (and infrasound) produced by nonlinearly interacting ocean waves. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1976, 60, 1032–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibblewhite, A.C.; Wu, C.Y. The generation of infrasonic ambient noise in the ocean by nonlinear interactions of ocean surface waves. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1989, 85, 1935–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, S.P. Underwater sound from surface waves according to the Lighthill-Ribner theory. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1981, 69, 425–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibblewhite, A.C.; Wu, C.Y. The theoretical description of wave-wave interactions as a noise source in the ocean. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1991, 89, 2241–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibblewhite, A.C.; Wu, C.Y. Acoustic source levels associated with the nonlinear interactions of ocean waves. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1993, 94, 3358–3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cato, D.H. Sound generation in the vicinity of the sea surface: Source mechanisms and the coupling to the received sound field. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1991, 89, 1076–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cato, D.H. Theoretical and measured underwater noise from surface wave orbital motion. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1991, 89, 1096–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westervelt, P.J. Parametric Acoustic Array. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1963, 35, 535–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerji, S.K. Microseisms associated with disturbed weather in the Indian seas. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A 1930, 229, 287–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, S.P.; Richard, J.C.; Mancini, J.D.; Fessatidis, V.; Crooker, B. Microseism and infrasound generation by cyclones. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2003, 113, 2562–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerji, S.K. Theory of microseisms. Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. 1935, 1, 727–753. [Google Scholar]
- Darbyshire, J. Microseisms, in the Sea, Ideas and Observations on Progress in the Study of the Seas; Hill, M.N., Ed.; Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 1966; p. 701. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, J.D. Classifying Hurricanes with Undersea Sound. Ph.D. Thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Miche, M. Mouvements ondulatoires de la mer en profonder constante ou decroissante. Ann. Ponts Chaussées 1944, 114, 131–164. [Google Scholar]
- Walsh, E.J.; Wright, C.W.; Vandemark, D.; Krabill, W.B.; Garcia, A.W.; Houston, S.H.; Murillo, S.T.; Powell, M.D.; Black, P.G.; Marks, F.D., Jr. Hurricane directional wave spectrum spatial variation at landfall. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2002, 32, 1667–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, P. Short Review and Recent Results on Microseisms. Geophys. Surv. 1983, 5, 395–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradner, H.; De Jerphanion, L.G.; Langlois, R. Ocean Microseism Measurements with a Neutral Buoyancy Free-Floating Midwater Seismometer. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 1970, 60, 1134–1150. [Google Scholar]
- Goodman, D.; Yamamoto, T.; Trevorrow, M.; Abbott, C.; Turgut, A.; Badiey, M.; Ando, K. Directional Spectra Observations of Seafloor Microseisms from an Ocean-Bottom Seismometer Array. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1989, 86, 2309–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutenberg, B. Microseisms in North America. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 1931, 21, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, A.W. On the direction of Approach of Microseismic Waves. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A 1935, 886, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haubrich, R.A. Earth noise, 5 to 500 millicycles per second 1. Spectral stationarity, normality, and nonlinearity. J. Geophys. Res. 1965, 70, 1415–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haubrich, R.A.; MacKenzie, G.S. Earth noise, 5 to 500 millicycles per second 2. Reaction of the earth to oceans and atmosphere. J. Geophys. Res. 1965, 70, 1429–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haubrich, R.A.; McCamy, K. Microseisms: coastal and pelagic sources. Rev. Geophys. 1969, 7, 539–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibblewhite, A.C.; Ewans, K.C. Wave-wave interactions, microseisms, and infrasonic ambient noise in the ocean. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1985, 78, 981–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichols, R.H. Infrasonic ambient ocean noise measurements: Eleuthera. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1981, 69, 974–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schimmel, M.; Stutzmann, E.; Ardhuin, F.; Gallart, J. Polarized Earth’s ambient microseismic noise. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2005, 12, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, S.C. The equilibrium oceanic microseism spectrum. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1992, 92, 2141–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, G.J. (Ed.) Global Guide to Tropical Cyclone Forecasting; World Meteorological Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Komen, G.J.; Cavaleri, L.; Donelan, M.; Hasselmann, K.; Hasselmann, S.; Janssen, P.A.E.M. Dynamics and Modeling of Ocean Waves; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1994; pp. 16–27. [Google Scholar]
- Kinsman, B. Wind Waves, Their Generation and Propagation on the Sea Surface; Prentice-Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1965; pp. 336–352. [Google Scholar]
- Mandel, L.; Wolf, E. Optical Coherence and Quantum Optics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1995; pp. 58–59. [Google Scholar]
- Forristall, G.Z.; Ward, E.G.; Cardone, V.J.; Borgmann, L.E. The directional spectra and kinematics of surface gravity waves in tropical storm Delia. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1978, 8, 888–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toleman, H.L. User Manual and System Documentation of WAVEWATCH-III; Version 1.18; Techreport Note. 166; Ocean Modeling Branch, NCEP National Weather Service, NOAA, US Department of Commerce: College Park, MD, USA, 1999; p. 110.
- Dean, L.W., III. Interactions between sound waves. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1962, 34, 1039–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westervelt, P.J. Scattering of sound by sound. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1957, 29, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morse, P.M.; Ingard, K.U. Theoretical Acoustics; Mc-Graw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1968; pp. 245–866. [Google Scholar]
- Beyer, R.T. Nonlinear Acoustics; Acoustical Society of America, Woodbury: New York, NY, USA, 1997; p. 101. [Google Scholar]
- Van Trees, H.L. Optimum Array Processing. Part IV of Detection, Estimation and Modulation Theory; Wiley-Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 95–118. [Google Scholar]
- Papoulis, A.; Pillai, S.U. Probability, Random Variables and Stochastic Processes; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1965; p. 515. [Google Scholar]
- Tucker, M.J.; Pitt, E.G. Waves in Ocean Engineering; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 2001; pp. 33–34. [Google Scholar]
- Avila, L.A. Preliminary Report, Hurricane Bonnie 19–30 August 1998; National Hurricane Center: Miami, FL, USA, 1998.
- Makris, N.C.; Avelino, L.Z.; Menis, R. Deterministic Reverberation from Ocean Ridges. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1995, 97, 3547–3574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lay, T.; Wallace, T.C. Modern Global Seismology; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1995; pp. 252–254. [Google Scholar]
- Stoneley, R. The Effect of the Ocean on Rayleigh Waves. Geophys. Suppl. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1926, 1, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Press, F.; Ewing, M. Propagation of Explosive Sound in a Liquid Layer Overlying a Semi-Infinite Elastic Solid. Geophysics 1950, 15, 426–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, D.D.; Chapman, D.M.F. A Simple Shallow Water Propagation Model Including Shear Wave Effects. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1985, 78, 2087–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewing, W.M.; Jardetzky, W.S.; Press, F. Elastic Waves in Layered Media; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1957; pp. 157–189. [Google Scholar]
- Arvello, J.I.; Überall, H. Adiabatic Normal-Mode Theory of Sound Propagating Including Shear Waves in a Range-Dependent Ocean Floor. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1990, 88, 2316–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, F.H.; Vernon, F.L.; Orcutt, J.A.; Collins, J.A.; Stephen, R.A. Results from OSNPE; improved teleseismic earthquake detection at the seafloor. Bull. Seism. Soc. Am. 2001, 94, 1868–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, B.J. Monitoring the Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty; Preface. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2001, 158, 1339–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritzwoller, M.H.; Levshin, A.L. Monitoring the Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty; Introduction. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2001, 158, 1341–1348. [Google Scholar]
- Barmin, M.P.; Ritzwoller, M.H.; Levshin, A.L. A fast and reliable method for surface wave tomography. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2001, 158, 1351–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilidou, S.; Priestley, K.; Debayle, E.; Gudmundsson, Ó. Rayleigh wave tomography in the North Atlantic: High resolution images of the Iceland, Azores and Eifel mantle plumes. Lithos 2005, 79, 453–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.D. Rayleigh wave group-velocity studies beneath the Indian Ocean. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2005, 95, 502–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, A.D. Extension of the Method of Normal Modes to Sound Propagation in an Almost-Stratified Medium. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1965, 37, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



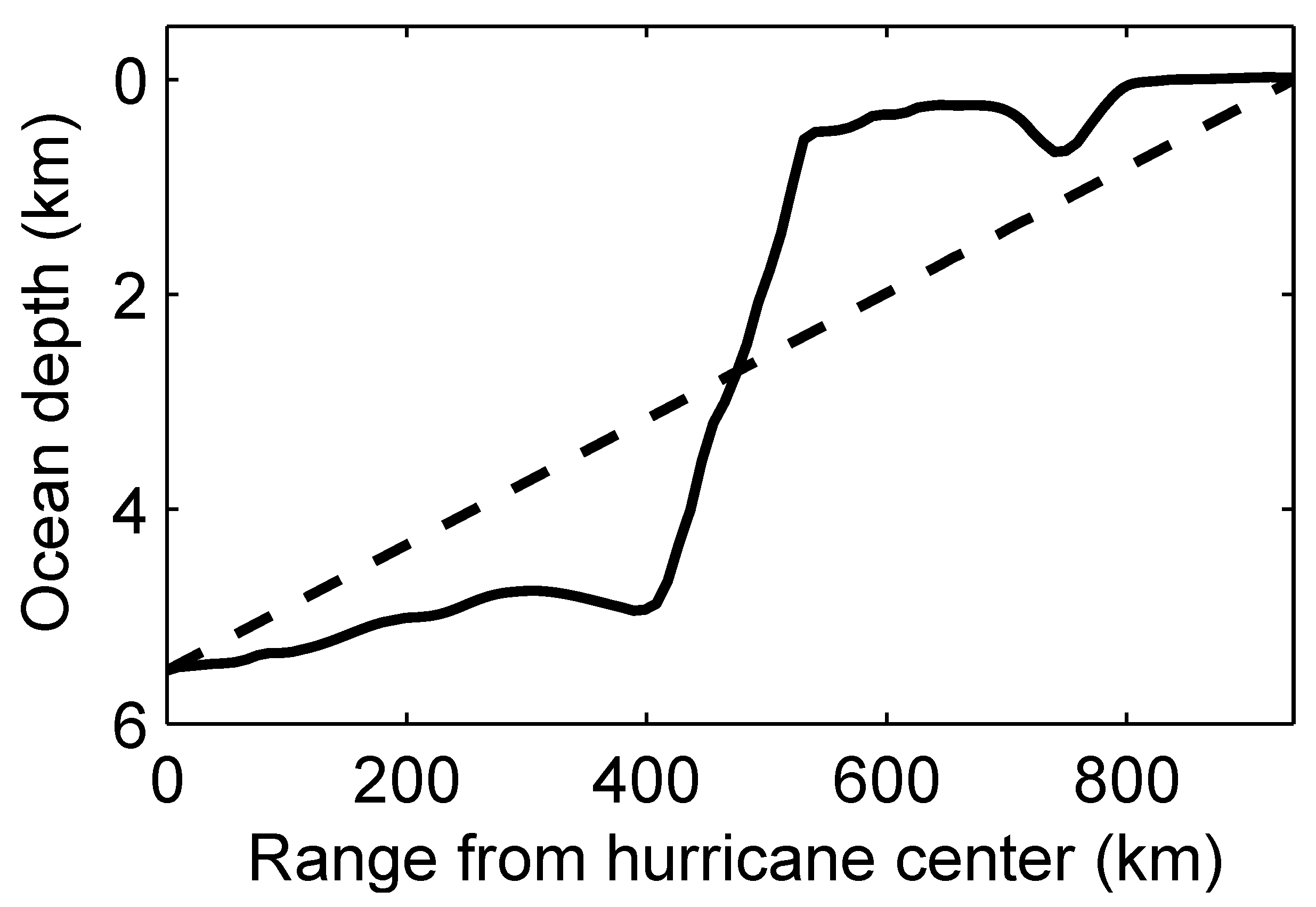

| Time | Hurricane Center Position | Range from | Ocean Depth at | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lat (N) | Lon (W) | Sensor (km) | Hurricane Center (km) | |
| 0000 | 24.8 | 71.8 | 1028 | 5.1 |
| 0600 | 25.2 | 72.1 | 983 | 5.5 |
| 1200 | 25.6 | 72.4 | 939 | 5.5 |
| 1800 | 26.1 | 72.8 | 881 | 5.2 |
© 2018 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wilson, J.D. Modeling Microseism Generation by Inhomogeneous Ocean Surface Waves in Hurricane Bonnie Using the Non-Linear Wave Equation. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1624. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10101624
Wilson JD. Modeling Microseism Generation by Inhomogeneous Ocean Surface Waves in Hurricane Bonnie Using the Non-Linear Wave Equation. Remote Sensing. 2018; 10(10):1624. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10101624
Chicago/Turabian StyleWilson, Joshua D. 2018. "Modeling Microseism Generation by Inhomogeneous Ocean Surface Waves in Hurricane Bonnie Using the Non-Linear Wave Equation" Remote Sensing 10, no. 10: 1624. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10101624
APA StyleWilson, J. D. (2018). Modeling Microseism Generation by Inhomogeneous Ocean Surface Waves in Hurricane Bonnie Using the Non-Linear Wave Equation. Remote Sensing, 10(10), 1624. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10101624




