The Inclusion of Forest Hydrological Services in the Sustainable Development Strategy of South Korea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Major Challenges in the Water Sector
3. Key Forest Hydrological Services
4. Combination of Forest and Water Management
5. Inclusion of Key Forest Hydrological Services in the Sustainable Development Strategy
6. Summary
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO). Forests Are Key for High Quality Water Supply. 2011. Available online: http://www.fao.org/news/story/en/item/53391/icode/ (accessed on 1 April 2016).
- Pettenella, D.; Vidale, E.; Gatto, P.; Secco, L. Paying for water-related forest services: A survey on Italian payment mechanisms. iForest-Biogeosci. For. 2012, 5, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP). Overview of the Republic of Korea’s National Strategy for Green Growth; UNEP DTIE: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Min, K.-J.; Shin, T.; Song, W.; Choi, H.; Lee, S.; Rho, H.; Lee, S.; Brewster, M.; Gaillard-Picher, D. Water and Green Growth; K-Water: Daejeon, Korea; World Water Council: Marseille, France, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Presidential Commission on Green Growth—Republic of Korea. Road to Our Future: Green Growth—National Strategy and the Five-Year Plan (2009~2013); Presidential Commission on Green Growth—Republic of Korea: Seoul, Korea, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Andréassian, V. Waters and forests: From historical controversy to scientific debate. J. Hydrol. 2004, 291, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO). Forests and Water-FAO Forestry Paper 155; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Environment. Environmental Statistics Yearbook; Ministry of Environment: Sejong-City, Korea, 2014.
- Hoang, V.-N.; Nguyen, T.T. Analysis of environmental efficiency variations: A nutrient balance approach. Ecol. Econom. 2013, 86, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). OECD Factbook 2008; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). OECD Factbook 2006; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.J.; Lee, K.S.; Lee, S.S.; Shin, H.B.; Yoon, K.S. Classification of water quality management for agricultural reservoirs in Korea. In Agricultural Water Quality and Water Use: Developing Indicators for Policy Analysis; Parris, K., Jung, P.K., Eds.; OECD: Paris, France, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Hoang, V.-N.; Seo, B. Cost and environmental efficiency of rice farms in South Korea. Agric. Econom. 2012, 43, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Water Assessment Programme (WWAP). The United Nations World Water Development Report 3—Case Study Volume: Facing the Challenges; UNESCO: Paris, France; Earthscan: London, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Nguyen, T.T.; Kim, H.N.; Koellner, T.; Shin, H.J. Do Consumers of Environmentally Friendly Farming Products in Downstream Areas Have a WTP for Water Quality Protection in Upstream Areas? Water 2017, 9, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Tenhunen, J. Complex terrain and ecological heterogeneity (TERRECO): Evaluating ecosystem services in production versus water quantity/quality in mountainous landscapes. Korean J. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2010, 12, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raskin, P.; Gleick, P.; Kirshen, P.; Pontius, G.; Strzepek, K. Water Futures: Assessment of Long-Range Patterns and Problems—Comprehensive Assessment of the Freshwater Resources of the World; Stockholm Environment Institute: Stockholm, Sweden, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Nguyen, T.T.; Poppenburg, P.; Shin, H.J.; Koellner, T. Conventional and partially converted and environmentally friendly agriculture in South Korea: Profitability and factors affecting farmers’ choice. Sustainability 2016, 8, 704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, O.K.; Park, S.; Jun, Y.J.; Suh, M.J.; Shin, D.H. The integrated management system (Fims) for the Four Major Rivers Restoration Project in South Korea. In Proceedings of the 5th Civil Engineering Conference in the Asian Region and Australasian Structural Engineering Conference, Sydney, Australia, 8–12 August 2010; Engineers Australia: Sydney, Australia, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, M. Greenstart movement. Korea Environ. Policy Bull. 2013, 11, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.-H.; Duan, L.; Kim, B.; Mitchell, M.J.; Shibata, H. Potential effects of climate change and variability on watershed biogeochemical processes and water quality in Northeast Asia. Environ. Int. 2010, 36, 212–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnhold, S.; Lindner, S.; Lee, B.; Martin, E.; Kettering, J.; Nguyen, T.T.; Koellner, T.; Ok, Y.; Huwe, B. Conventional and organic farming: Soil erosion and conservation potential for row crop cultivation. Geoderma 2014, 219–220, 89–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciccarese, L.; Mattsson, A.; Pettenella, D. Ecosystem services from forest restoration: Thinking ahead. New For. 2012, 43, 543–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masiero, M.; Secco, L.; Pettenella, D.; Brotto, L. Standards and guidelines for forest plantation management: A global comparative study. For. Policy Econom. 2015, 53, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathews, J.A. Green growth strategies—Korean initiatives. Futures 2012, 44, 761–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, I.; Kim, H.; Shin, H.; Tenhunen, J.; Nguyen, T.T. Willingness to pay for a highland agricultural restriction policy to improve water quality in South Korea: Correcting anomalous preference in contingent valuation method. Water 2016, 8, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tockner, K.; Bernhardt, E.S.; Koska, A.; Zarfl, C. A global view on Future Major Water Engineering Projects. In Society-Water-Technology; Hüttl, R.F., Bens, O., Bismuth, C., Hoechstetter, S., Eds.; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 47–64. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, J.-H. Ecosystem geography of Korea. In Ecology of Korea; Lee, D.W., Jin, V., Choe, J.C., Son, Y.H., Lee, H.-Y., Hong, S.K., Ihm, B.-S., Eds.; Bumwoo: Seoul, Korea, 2002; pp. 19–46. [Google Scholar]
- Yihui, D.; Chan, J.C. The East Asian summer monsoon: An overview. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2005, 89, 117–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, Y.J.; Shim, M.-P.; Kim, S.K. The Four Major Rivers Restoration Project (Korea). In Water Planning in the Transition to a Green Economy, Proceedings of Water in the Green Economy in Practice: Toward Rio +20, Zaragoza, Spain, 3–5 October 2011; UN-Water Decade Programme on Advocacy and Communication: Zaragoza, Spain, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, I.; Kim, H.; Shin, H.; Tenhunen, J.; Nguyen, T.T. Economic Valuation of the Aquatic Biodiversity Conservation in South Korea: Correcting for the Endogeneity Bias in Contingent Valuation. Sustainability 2017, 9, 930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishiwatari, M.; Wataya, E.; Shin, T.; Kim, D.; Song, J.; Kim, S. Promoting green growth through water resources management: The case of Republic of Korea. In Green Growth in Action Knowledge Note Series, 3; World Bank Group: Washington, DC, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Ruidish, M.; Koellner, T.; Tenhunen, J. Synergies and tradeoffs between nitrate leaching and net farm income: The case of best nitrogen management practices in South Korea. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 186, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-W.; Byun, H.-R.; Choi, K.-S.; Oh, S.-B. A spatiotemporal analysis of historical droughts in Korea. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2011, 50, 1895–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, K.-J.; Heo, K.-Y.; Lee, S.-S.; Yun, K.-S.; Jhun, J.-G. Variability in the East Asian Monsoon: A review. Meteorol. Appl. 2012, 19, 200–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, Y.-S.; Yoon, M.-B.; Kim, H.-S. On climate variations and changes observed in South Korea. Clim. Chang. 2004, 66, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Institute of Environmental Research (NIER). Korean Climate Change Assessment Report 2010; National Institute of Environmental Research: Seoul, Korea, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Korea Meteorological Administration (KMA). Annual Report. 2014. Available online: http://web.kma.go.kr/download_01/Annual_Report_2014.pdf (accessed on 28 February 2017).
- Choi, G.; Kwon, W.-T.; Boo, K.-O.; Cha, Y.-M. Recent spatial and temporal changes in means and extreme events of temperature and precipitation across the Republic of Korea. J. Korean Geogr. Soc. 2008, 43, 681–700. [Google Scholar]
- Im, E.-S.; Lee, B.-J.; Kwon, J.-H.; In, S.-R.; Han, S.-O. Potential increase of flood hazards in Korea due to global warming from a high-resolution regional climate simulation. Asia-Pac. J. Atmos. Sci. 2012, 48, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, E.-S.; Choi, Y.-W.; Ahn, J.-B. Robust intensification of hydroclimatic intensity over East Asia from multi-model ensemble regional projections. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Environment. Ecorea—Environmental Review 2015, Korea, Volume 1; Ministry of Environment: Sejong-City, Korea, 2015.
- Nam, W.-H.; Hayes, M.J.; Svoboda, M.D.; Tadesse, T.; Wilhite, D.A. Drought hazard assessment in the context of climate change for South Korea. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 160, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Water Assessment Programme (WWAP). The United Nations World Water Development Report 4—Managing Water under Uncertainty and Risk; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, B. Eutrophication of Freshwater Ecosystems in Korea, and the Effect of Monsoon. In Ecology of Korea; Lee, D.W., Jin, V., Choe, J.C., Son, Y.H., Lee, H.-Y., Hong, S.K., Ihm, B.-S., Eds.; Bumwoo: Seoul, Korea, 2002; pp. 385–399. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Environment. Some Success Stories of Korean Environmental Policies—Keeping Water Clean; Ministry of Environment: Sejong-City, Korea, 2011.
- Yang, J.-E.; Ryu, J.-H.; Kim, S.-J.; Chung, D.-Y. Management strategies to conserve soil and water qualities in the sloping uplands in Korea. J. Agric. Sci. 2010, 37, 435–449. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, B.; Park, J.-H.; Hwang, G.; Jun, M.-S.; Choi, K. Eutrophication of reservoirs in South Korea. Limnology 2001, 2, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-Y. A hydrological analysis of current status of turbid water in Soyang River and its mitigation. J. Soil Groundw. Environ. 2008, 13, 85–92. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.-H.; Inam, E.; Abdullah, M.H.; Agustiyani, D.; Duan, L.; Hoang, T.T.; Kim, K.-W.; Kim, S.D.; Nguyen, M.H.; Pekthong, T.; et al. Implications of rainfall variability for seasonality and climate-induced risks concerning surface water quality in East Asia. J. Hydrol. 2011, 400, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, D.-H.; Jung, I.W.; Chang, H. Potential changes in Korean water resources estimated by high-resolution climate simulation. Clim. Res. 2008, 35, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, K.-W.; Lee, H.-J.; Park, J.-H.; Owen, J.S. Effects of monsoon rainfalls on surface water quality in a mountainous watershed under mixed land use. Korean J. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2010, 12, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.-S.; Kim, B.-K.; Kwon, H.-H. Assessment of the impact of climate change on the flow regime of the Han River basin using indicators of hydrologic alteration. Hydrol. Process. 2011, 25, 691–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.J.; Kim, H.N.; Jeon, C.H.; Jo, M.W.; Nguyen, T.T.; Tenhunen, J. Benefit transfer for water management along the Han River in South Korea using Meta-regression analysis. Water 2016, 8, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T. Gains and losses in ecosystem services: Trade-off and efficiency perspectives. Habilitation Thesis, University of Bayreuth, Bayreuth, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, H.M.; Reyers, B.; Watanabe, M.; Bohensky, E.; Foale, S.; Palm, C.; Espaldon, M.V.; Armenteras, D.; Tapia, M.; Rincón, A.; et al. Condition and trends of ecosystem services and biodiversity. In Ecosystems and Human Well-Being: Multi Scale Assessments—Volume 4—Findings of the Sub-global Assessments Working Group of the Millennium Ecosystem Assessment; Capistrano, D., Samper, C., Lee, M.J., Raudsepp-Hearne, C., Eds.; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2005; pp. 171–203. [Google Scholar]
- Van Jaarsveld, A.S.; Biggs, R.; Scholes, R.J.; Bohensky, E.; Reyers, B.; Lynam, T.; Musvoto, C.; Fabricius, C. Measuring conditions and trends in ecosystem services at multiple scales: The Southern African Millennium Ecosystem Assessment (SAfMA) experience. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B 2005, 360, 425–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmqvist, T.; Tuvendal, M.; Krishnaswamy, J.; Hylander, K. Managing Trade-Offs in Ecosystem Services-Ecosystem Services Economics Working Paper Series No. 4; UNEP DEPI: Nairobi, Kenya, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, I.; Shin, H.; Nguyen, T.T.; Tenhunen, J. Water policy reforms in South Korea: A historical review and ongoing challenges for sustainable water governance and management. Water 2017. under review. [Google Scholar]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO). Ecosystem Services & Biodiversity (ESB). 2017. Available online: http://www.fao.org/ecosystem-services-biodiversity/en/ (accessed on 1 November 2016).
- Hewlett, J.D. Principles of Forest Hydrology; University of Georgia Press: Athens, GA, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, M. Forest Hydrology: An Introduction to Water and Forests; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, H.; Franczyk, J.; Kim, C. What is responsible for increasing flood risks? The case of Gangwon Province, Korea. Nat. Hazards 2009, 48, 339–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.S.; Youn, Y.-C. Reforestation policy integration by the multiple sectors toward forest transition in the Republic of Korea. For. Policy Econom. 2017, 76, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.S.; Joo, R.W.; Kim, Y.-S. Forest transition in South Korea: Reality, path and drivers. Land Use Policy 2012, 29, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D. The forest sector’s contribution to a “low carbon, green growth” vision in the Republic of Korea. Unasylva 2012, 63, 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- Statistics Korea. Korea’s Green Growth Based on OECD Green Growth Indicators; Narai Publishing Group: Daejeon, Korea, 2012.
- Korea Forest Service. National Report on Sustainable Forest Management in Korea 2009. 2009. Available online: http://www.rinya.maff.go.jp/j/kaigai/pdf/2009p_4_k.pdf (accessed on 26 January 2016).
- Kim, K.-Y. Implementation of a Watershed Management System: Four Major River Basins. Korea Environ. Policy Bull. 2003, 1, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, B.-K. Water environment management master plan outline (2006~2015)—Clean water, Eco River 2015. Korea Environ. Policy Bull. 2006, 4, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Environment. Ecorea—Environmental Review 2015, Korea, Volume 2; Ministry of Environment: Sejong-City, Korea, 2015.
- Kim, I.-J.; Kim, H. Four Major River Restoration Project of Republic of Korea. Korea Environ. Policy Bull. 2009, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, R.S.; Yoo, B. Achieving the “Low Carbon, Green Growth” Vision in Korea-OECD Economics Department Working Papers No. 964; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H. Water quality forecasting system. Korea Environ. Policy Bull. 2013, 11, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, G.B.; Kim, Y.H.; Ka, P.S.; Lee, S.W.; Byun, D.G. A case study on the system optimization of hydro power generators that are a part of the Four Major Rivers Restoration Project. J. Int. Counc. Electr. Eng. 2013, 3, 348–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, S.-H.; Park, D. The effects of the Four Major Rivers Restoration Project on regional economy. J. Wetl. Res. 2013, 15, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Environment. Ministry of Environment, Republic of Korea; Ministry of Environment: Sejong-City, Korea, 2015.
- Ahn, J.M.; Lee, S.; Kang, T. Evaluation of dams and weirs operating for water resource management of the Geum River. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 478, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.-S.; Kwon, Y.-S.; Hwang, S.-J.; Park, S. Characterizing effects of landscape and morphometric factors on water quality of reservoirs using a self-organizing map. Environ. Model. Softw. 2014, 55, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, K.S.; Kim, J.S. The Four Major Rivers Restoration Project: Impacts on river flows. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2011, 15, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Noh, H.; Jung, J.; Jun, H.; Kim, H.S. Assessment of the impacts of global climate change and regional water projects on streamflow characteristics in the Geum River Basin in Korea. Water 2016, 8, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H. Authoritarian environmentalism under democracy: Korea’s river restoration project. Environ. Polit. 2015, 24, 810–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Han, J.-K.; Park, J. Green Growth and Green Jobs in Korea: Potentials and Perspectives. 2012. Available online: http://www.fes-asia.org/media/publication/2012_GreenGrowthAndGreenJobsInKorea_FES-EoT_Study_Hyun-woo_Jae-kak_Jin-hee.pdf (accessed on 23 May 2016).
- Lah, T.; Park, Y.; Cho, Y.J. The Four Major Rivers Restoration Project of South Korea—An assessment of its process, program, and political dimensions. J. Environ. Dev. 2015, 24, 375–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Chang, H.; Hong, Y. Is a costly river restoration project beneficial to the public? Empirical evidence from the Republic of Korea. Desal. Water Treat. 2015, 54, 3696–3703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Normile, D. Restoration or devastation? Science 2010, 327, 1568–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.S. Inland fisheries resource enhancement and conservation in the republic of Korea. In Inland Fisheries Resource Enhancement and Conservation in Asia; Weimin, M., De Silva, S., Davy, B., Eds.; FAO: Bangkok, Thailand, 2010; p. 80. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.; Koo, M.-H.; Kim, K.; Kim, Y. Spatio-temporal variations in stream—Aquifer interactions following construction of weirs in Korea. Groundwater 2016, 54, 448–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.-S.; Yoon, S.-K.; Choi, M.; Moon, Y.-I. A case study of regional risk assessment of river restoration projects: Nakdong River Basin, South Korea. J. Water Clim. Chang. 2015, 6, 628–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Green Growth Institute. Korea’s Green Growth Experience: Process, Outcomes and Lessons Learned; Global Green Growth Institute: Seoul, Korea, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Jänicke, M. Green growth: From a growing eco-industry to economic sustainability. Energy Policy 2012, 48, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.T. Effect of forest growth and thinning on the long-term water balance in a coniferous forest. Korean J. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2011, 13, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.S.; Yoo, B. Korea’s Green Growth Strategy: Mitigating Climate Change and Developing New Growth Engines-OECD Economics Department Working Papers No. 798; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, S.-D.; Park, Y.-K.; Kim, E.-H. Study on Forest Functions Classification using GIS-Chunyang National Forest Management Planning. J. Korean Assoc. Geogr. Inf. Stud. 2008, 11, 10–21. [Google Scholar]
- Korean Rural Economics Institute. Agriculture in Korea 2014; Korean Rural Economics Institute: Naju, Korea, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). Meeting the Water Reform Challenge; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, I.; Lee, D. Establishment of priority forest areas based on hydrological ecosystem services in northern Vietnam. J. Korea Soc. Environ. Restor. Technol. 2014, 17, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Pham, V.D.; Tenhunen, J. Linking regional land use and payments for forest hydrological services: A case study of Hoa Binh Reservoir in Vietnam. Land Use Policy 2013, 33, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.G.; Park, S.W. An adaptive watershed management assessment based on watershed investigation data. Environ. Manag. 2015, 55, 1006–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, S.-J. Experts’ Social Responsibility in the process of Large-Scale Nature-Transforming National Projects: Focusing on the case of the Four Major Rivers Restoration Project in Korea. Dev. Soc. 2014, 43, 109–141. [Google Scholar]
- Costanza, R.; d’Arge, R.; De Groot, R.; Farber, S.; Grasso, M.; Hannon, B.; Limburg, K.; Naeem, S.; O’Neill, R.V.; Paruelo, J.; et al. The value of the world’s ecosystem services and natural capital. Nature 1997, 387, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Groot, R.S. Environmental functions as a unifying concept for ecology and economics. Environmentalist 1987, 7, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millennium Ecosystem Assessment (MA). Ecosystems and Human Well-Being: Synthesis; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Postel, S.L.; Thompson, B.H. Watershed protection: Capturing the benefits of nature’s water supply services. Nat. Resour. Forum 2005, 29, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Tenhunen, J. Climate change and crop production for bioenergy linkage at local scale: Challenges and implications. Int. J. Clim. Chang. Str. 2013, 5, 324–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Economics of Ecosystems and Biodiversity (TEEB). Économie des Écosystèmes et de la Biodiversité: Intégration de L’économie de la Nature-Une Synthèse de L’approche, des Conclusions et des Recommandations de la TEEB; TEEB: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010. [Google Scholar]
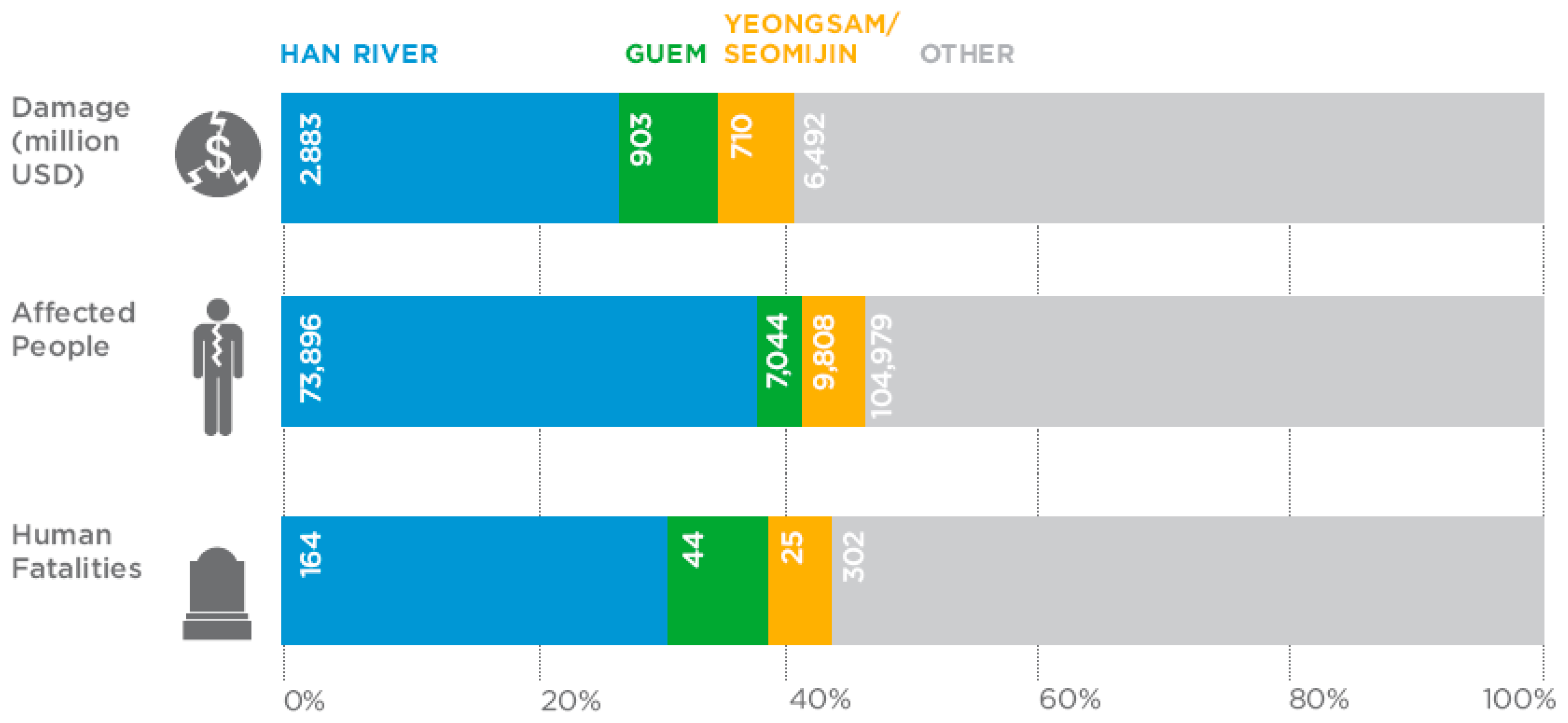
| Year | Damages |
|---|---|
| 1994–1995 | Limited water supply for 222,000 persons in 86 cities and counties |
| 2001 | Limited water supply for 304,815 persons in 86 cities and counties |
| 2002 | Limited water supply for 92,838 persons in 23 cities and counties |
| 2008–2009 | Limited water supply for 228,068 persons |
| Forest Hydrological Services | Specific Benefits | Forest Functions | Forest Management Measures |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water supply |
|
|
|
| Preservation of water quality and purification of water |
|
|
|
| Regulation of water flow |
|
|
|
| Prevention and moderation of natural hazards (e.g., landslides and mudflows) |
|
|
|
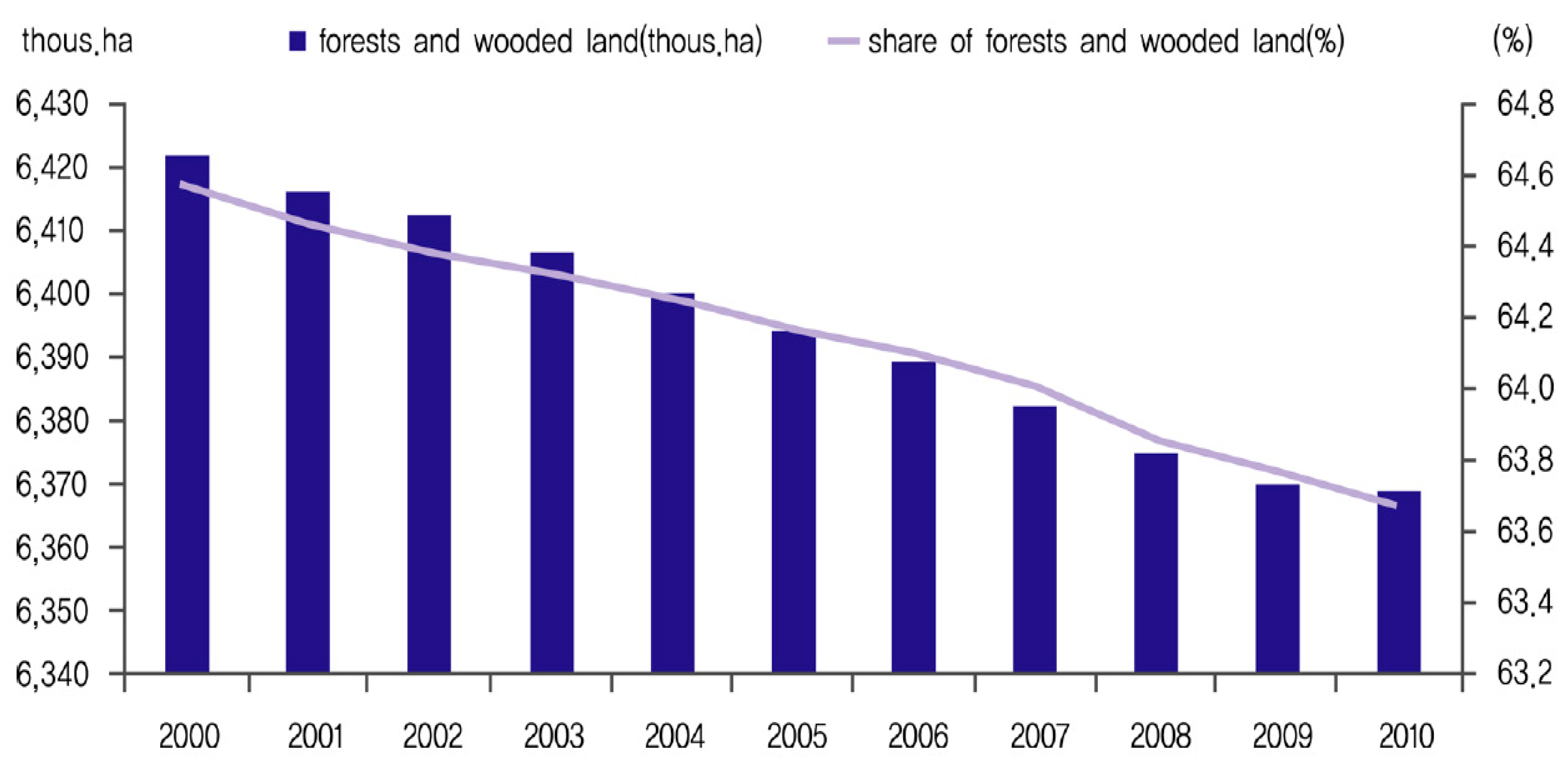
| Year | Area (1000 ha) | Stock (1000 m3) | Growing Stock (m3/ha) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1960 | 6700 | 63,995 | 9.6 |
| 1970 | 6611 | 68,772 | 10.4 |
| 1980 | 6567 | 145,694 | 22.2 |
| 1990 | 6476 | 248,426 | 38.4 |
| 2000 | 6430 | 387,758 | 60.3 |
| 2010 | 6369 | 800,025 | 125.6 |
| Period | Runoff Coefficient Coniferous (%) | Runoff Coefficient Deciduous (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 1982–1986 | 48.6 | 63.7 |
| 1987–1996 | 42.4 | 62.2 |
| 1997–2005 | 61.3 | 61.6 |
| 2006–2009 | 51.0 | 66.9 |
| Normalized Forest Cover (%) | ∆ Overland Flow (million m3 y−1) | ∆ Soil Sedimentation (million t y−1) | ∆ Soil-Retained Water (million m3 y−1) | ∆ Dam Longevity (y) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30.8 | −842 | −17.3 | 2112 | 34.9 |
| 35.0 | −920 | −19.9 | 2309 | 40.5 |
| 40.0 | −1015 | −21.2 | 2546 | 48.3 |
| 45.0 | −1109 | −23.4 | 2783 | 57.2 |
| 50.0 | −1204 | −25.5 | 3021 | 67.5 |
| 55.0 | −1298 | −27.7 | 3258 | 79.7 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Payeur-Poirier, J.-L.; Nguyen, T.T. The Inclusion of Forest Hydrological Services in the Sustainable Development Strategy of South Korea. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1470. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9081470
Payeur-Poirier J-L, Nguyen TT. The Inclusion of Forest Hydrological Services in the Sustainable Development Strategy of South Korea. Sustainability. 2017; 9(8):1470. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9081470
Chicago/Turabian StylePayeur-Poirier, Jean-Lionel, and Trung Thanh Nguyen. 2017. "The Inclusion of Forest Hydrological Services in the Sustainable Development Strategy of South Korea" Sustainability 9, no. 8: 1470. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9081470
APA StylePayeur-Poirier, J.-L., & Nguyen, T. T. (2017). The Inclusion of Forest Hydrological Services in the Sustainable Development Strategy of South Korea. Sustainability, 9(8), 1470. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9081470






