Entropy Analysis of the Coupled Human–Earth System: Implications for Sustainable Development
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Dissipative Structure Theory
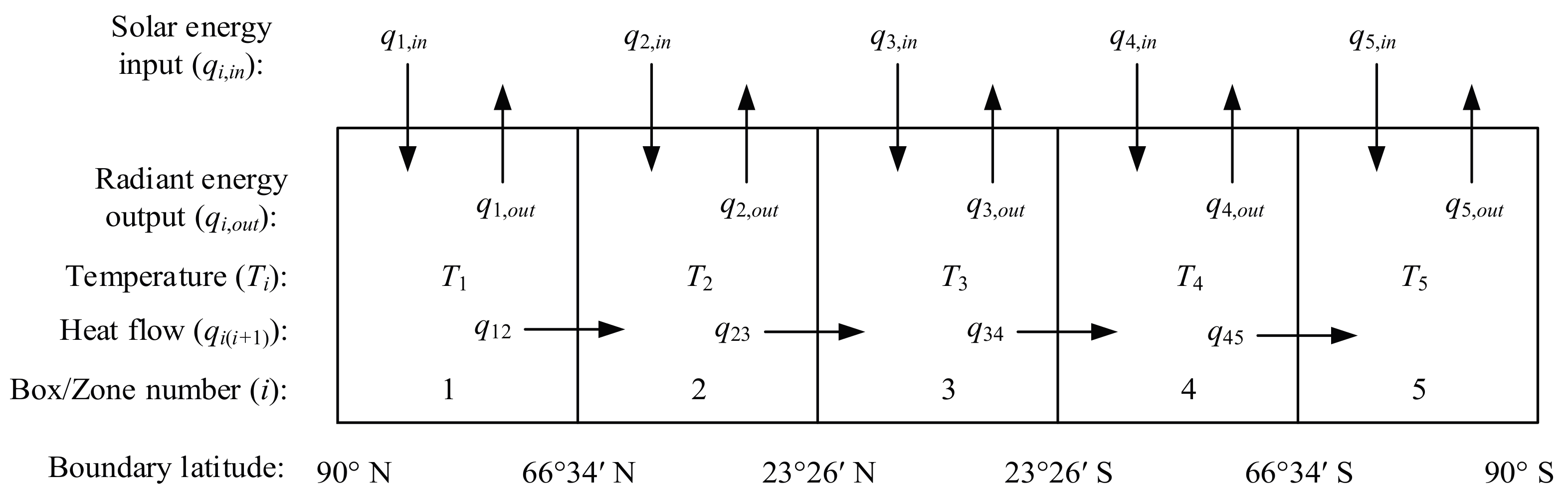
2.2. Entropy Budget of the Coupled System from Exchange with Space
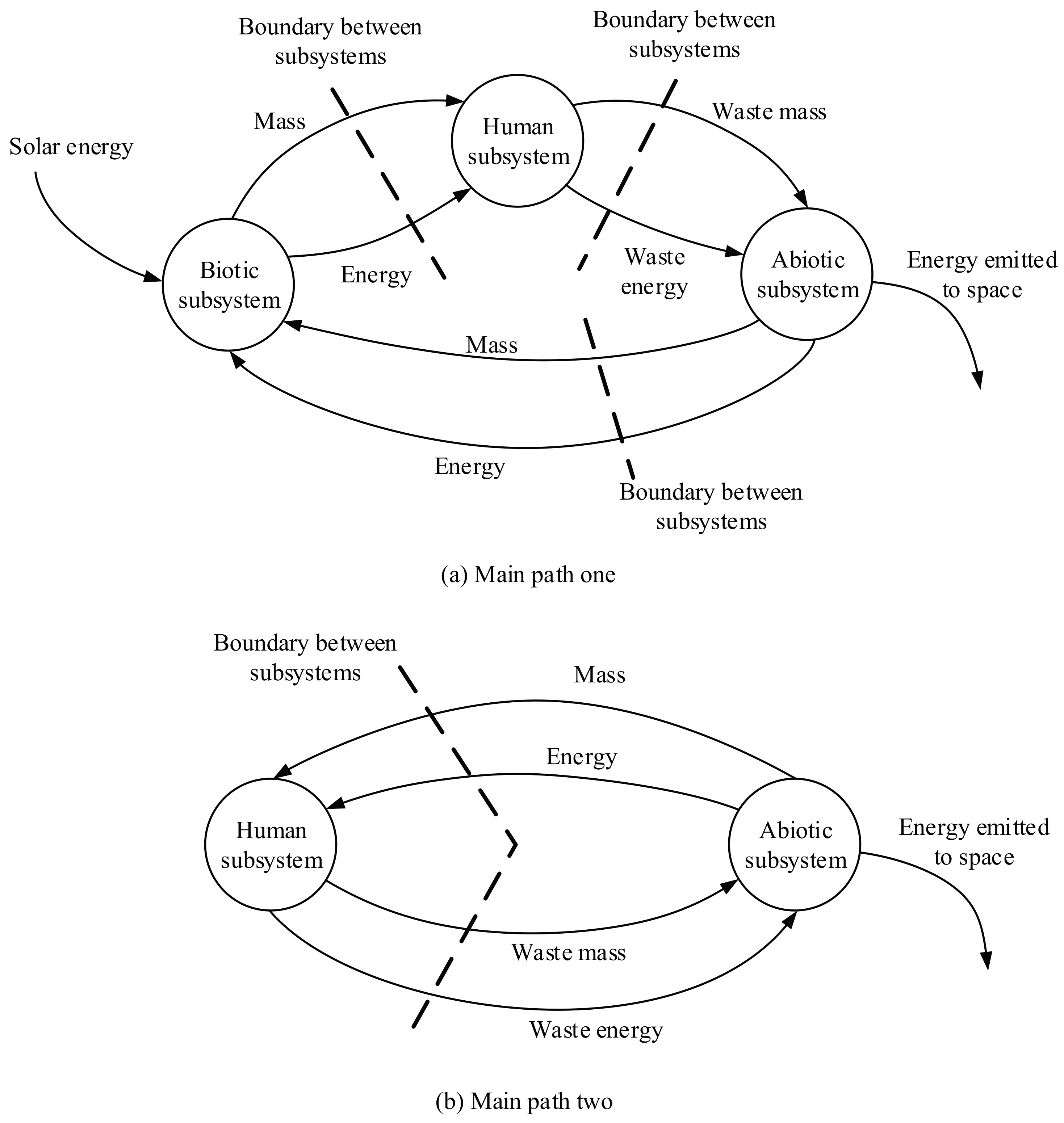
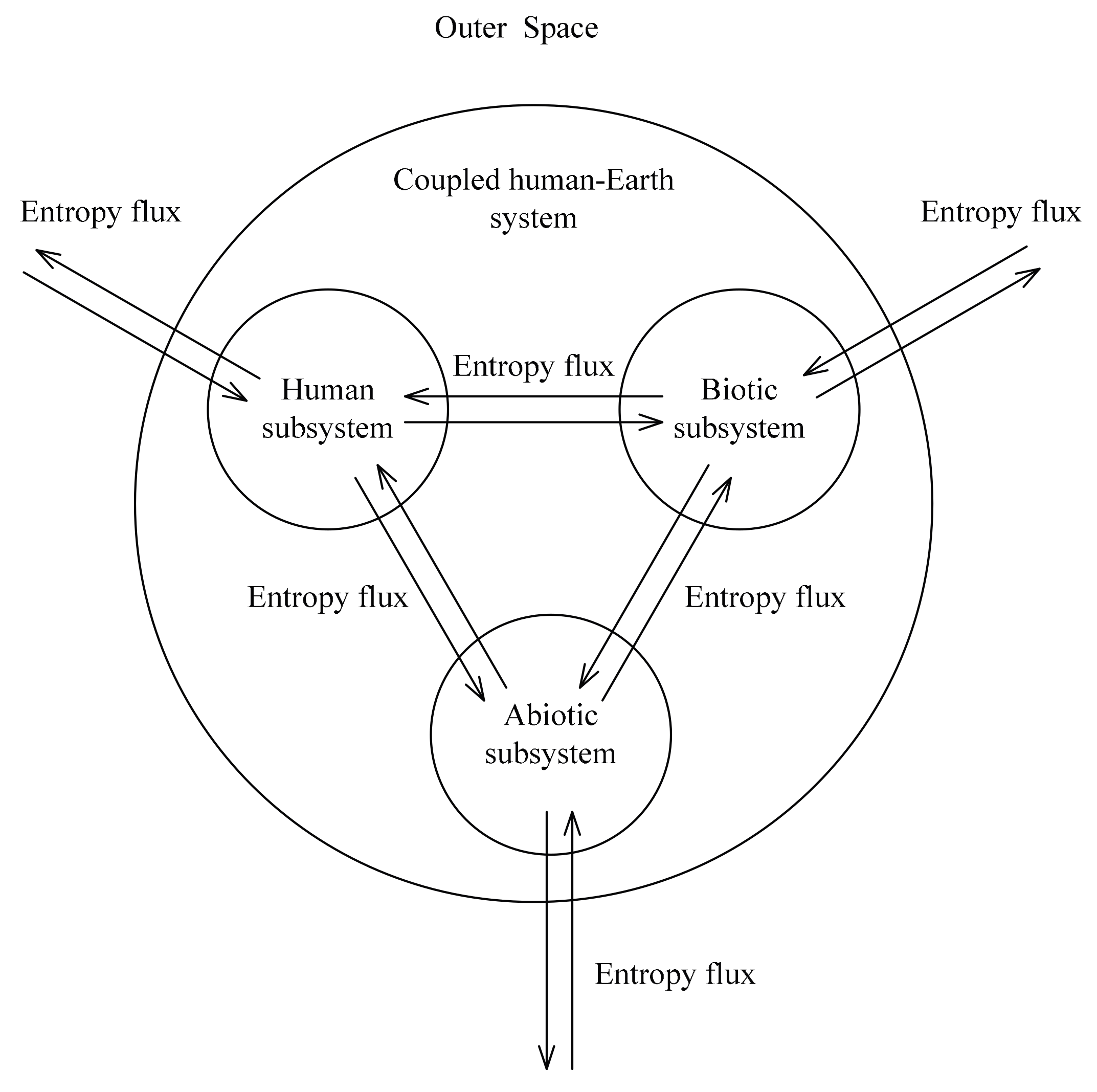
2.3. Entropy Exchange Framework on the Processes of the Subsystems
2.4. Entropy Budget of the Biotic Subsystem from Sunlight
2.5. Entropy Budget Associated with Life Activities of the Human Subsystem
2.6. Entropy Budget Associated with Fuels Use of the Human Subsystem
3. Entropy Budget Calculation Results
3.1. Negative Entropy of the Whole Coupled System from Exchange with Space
3.2. Negative Entropy for Sustaining Life Activities of the Whole Coupled System
3.3. Negative Entropy Associated with Life Activities of the Human Subsystem
3.4. Negative Entropy Associated with Fossil Fuels Used by Human Subsystem
4. Implications for Sustainable Development
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sneddon, C.; Howarth, R.B.; Norgaard, R.B. Sustainable development in a post-Brundtland world. Ecol. Econ. 2006, 57, 253–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, P.; Everard, M.; Santillo, D.; Robert, K.H. Reclaiming the definition of sustainability. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2007, 14, 60–66. [Google Scholar]
- Wills-Johnson, N. Lessons for sustainability from the world’s most sustainable culture. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2010, 12, 909–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolis, I.; Morioka, S.N.; Sznelwar, L.I. When sustainable development risks losing its meaning. Delimiting the concept with a comprehensive literature review and a conceptual model. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 83, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, T.R. Sustainable development: Agents, systems and the environment. Curr. Sociol. 2016, 64, 875–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midilli, A.; Dincer, I.; Ay, M. Green energy strategies for sustainable development. Energy Policy 2006, 34, 3623–3633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, H. Renewable energy strategies for sustainable development. Energy 2007, 32, 912–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrom, E. A general framework for analyzing sustainability of social-ecological systems. Science 2009, 325, 419–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazim, A. Strategy for a sustainable development in the UAE through hydrogen energy. Renew. Energy 2010, 35, 2257–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakosta, C.; Pappas, C.; Marinakis, V.; Psarras, J. Renewable energy and nuclear power towards sustainable development: Characteristics and prospects. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 22, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekhilef, S.; Faramarzi, S.Z.; Saidur, R.; Salam, Z. The application of solar technologies for sustainable development of agricultural sector. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 18, 583–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruelle, D.P. Extending the definition of entropy to nonequilibrium steady states. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 3054–3058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martyushev, L.M.; Seleznev, V.D. Maximum entropy production principle in physics, chemistry and biology. Phys. Rep.-Rev. Sec. Phys. Lett. 2006, 426, 1–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleidon, A.; Zehe, E.; Ehret, U.; Scherer, U. Thermodynamics, maximum power, and the dynamics of preferential river flow structures at the continental scale. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 225–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, C.J.; Li, Z.H. Implication of negative entropy flow for local rainfall. Entropy 2013, 15, 3449–3457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quijano, J.; Lin, H. Entropy in the Critical Zone: A Comprehensive Review. Entropy 2014, 16, 3482–3536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bristow, D.; Kennedy, C. Why do cities grow? Insights from nonequilibrium thermodynamics at the urban and global scales. J. Ind. Ecol. 2015, 19, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann-Pillath, C. Energy, growth, and evolution: Towards a naturalistic ontology of economics. Ecol. Econ. 2015, 119, 432–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, E.D.; Kay, J.J. Life as a manifestation of the second law of thermodynamics. Math. Comput. Model. 1994, 19, 25–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, I. Entropy and exergy in the development of living systems: A case study of lake-ecosystems. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 1998, 67, 2132–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, I. Entropy law in aquatic communities and the general entropy principle for the development of living systems. Ecol. Model. 2008, 215, 89–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holdaway, R.J.; Sparrow, A.D.; Coomes, D.A. Trends in entropy production during ecosystem development in the Amazon Basin. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B-Biol. Sci. 2010, 365, 1437–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H. Thermodynamic entropy fluxes reflect ecosystem characteristics and succession. Ecol. Model. 2015, 298, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleidon, A. Nonequilibrium thermodynamics and maximum entropy production in the Earth system. Naturwissenschaften 2009, 96, 653–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyke, J.; Kleidon, A. The maximum entropy production principle: Its theoretical foundations and applications to the Earth system. Entropy 2010, 12, 613–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleidon, A. Non-equilibrium thermodynamics, maximum entropy production and Earth-system evolution. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A-Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2010, 368, 181–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feistel, R. Radiative entropy balance and vertical stability of a gray atmosphere. Eur. Phys. J. B 2011, 82, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucarini, V.; Pascale, S.; Boschi, R.; Kirk, E.; Iro, N. Habitability and multistability in Earth-like planets. Astron. Nachr. 2013, 334, 576–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dincer, I.; Rosen, M.A. Thermodynamic aspects of renewables and sustainable development. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2005, 9, 169–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krysiak, F.C. Entropy, limits to growth, and the prospects for weak sustainability. Ecol. Econ. 2006, 58, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, W. Sustainable product development based on second law of thermodynamics. Appl. Energy 2011, 88, 3248–3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samiei, K.; Froling, M. Sustainability assessment of biomass resource utilization based on production of entropy—Case study of a bioethanol concept. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 45, 590–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peixoto, J.P.; Oort, A.H.; De Almeida, M.; Tomé, A. Entropy budget of the atmosphere. J. Geophys. Res. 1991, 96, 10981–10988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutowski, T.G. Environmentally benign manufacturing and ecomaterials; Product induced material flows. Mater. Trans. 2002, 43, 359–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabezas, H.; Fath, B.D. Towards a theory of sustainable systems. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2002, 194, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabezas, H.; Karunanithi, A.T. Fisher information, entropy, and the second and third laws of thermodynamics. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2008, 47, 5243–5249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabezas, H.; Pawlowski, C.W.; Mayer, A.L.; Hoagland, N.T. Sustainable systems theory: Ecological and other aspects. J. Clean. Prod. 2005, 13, 455–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prigogine, I.; Nicolis, G.; Babloyantz, A. Thermodynamics of evolution. Phys. Today 1972, 25, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prigogine, I. Time, structure, and fluctuations. Science 1978, 201, 777–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleidon, A. How does the Earth system generate and maintain thermodynamic disequilibrium and what does it imply for the future of the planet? Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A-Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2012, 370, 1012–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baierlein, R. Thermal Physics, 1st ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1999; pp. 118–128. [Google Scholar]
- Stephens, G.L.; O’Brien, D.M. Entropy and climate. I: ERBE observations of the entropy production of the earth. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1993, 119, 121–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paltridge, G.W. Global dynamics and climate—A system of minimum entropy exchange. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1975, 101, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisio, G.; Bisio, A. Some thermodynamic remarks on photosynthetic energy conversion. Energy Convers. Manag. 1998, 39, 741–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Zone Number | Surface Area(km2) | Projected Area (km2) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spring | Summer | Autumn | Winter | ||
| 1 | 21,033,596.8 | 1,790,192.4 | 8,019,634.6 | 1,790,192.4 | 0.0 |
| 2 | 132,578,334.3 | 30,557,112.4 | 48,108,964.0 | 30,557,112.4 | 13,438,080.8 |
| 3 | 202,840,609.8 | 62,821,508.5 | 57,949,438.5 | 62,821,508.5 | 57,949,438.5 |
| 4 | 132,578,334.3 | 30,557,112.4 | 13,438,080.8 | 30,557,112.4 | 48,108,964.0 |
| 5 | 21,033,596.8 | 1,790,192.4 | 0.0 | 1,790,192.4 | 8,019,634.6 |
| Zone Number | Absorbed Solar Energy (W) | Effective Temperature (K) | Emitted Radiant Energy (W) | Net Entropy Import from Space (W/K) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2.7783 × 1015 | 240.1 | 3.9637 × 1015 | −2.1370 × 1013 |
| 2 | 2.9378 × 1016 | 252.0 | 3.0320 × 1016 | −1.5364 × 1014 |
| 3 | 5.7850 × 1016 | 261.3 | 5.3595 × 1016 | −2.6016 × 1014 |
| 4 | 2.9378 × 1016 | 252.0 | 3.0320 × 1016 | −1.5364 × 1014 |
| 5 | 2.7783 × 1015 | 240.1 | 3.9637 × 1015 | −2.1370 × 1013 |
| Zone Number | Surface Area (%) | Absorbed Solar Energy (%) | Emitted Radiant Energy (%) | Net Entropy Import from Space (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4.1 | 2.3 | 3.2 | 3.5 |
| 2 | 26.0 | 24.0 | 24.8 | 25.2 |
| 3 | 39.8 | 47.4 | 43.9 | 42.6 |
| 4 | 26.0 | 24.0 | 24.8 | 25.2 |
| 5 | 4.1 | 2.3 | 3.2 | 3.5 |
© 2017 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, W. Entropy Analysis of the Coupled Human–Earth System: Implications for Sustainable Development. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1264. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9071264
Shi W. Entropy Analysis of the Coupled Human–Earth System: Implications for Sustainable Development. Sustainability. 2017; 9(7):1264. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9071264
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Weifang. 2017. "Entropy Analysis of the Coupled Human–Earth System: Implications for Sustainable Development" Sustainability 9, no. 7: 1264. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9071264
APA StyleShi, W. (2017). Entropy Analysis of the Coupled Human–Earth System: Implications for Sustainable Development. Sustainability, 9(7), 1264. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9071264




