Evaluation of the Agronomic Impacts on Yield-Scaled N2O Emission from Wheat and Maize Fields in China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Selection
2.2. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
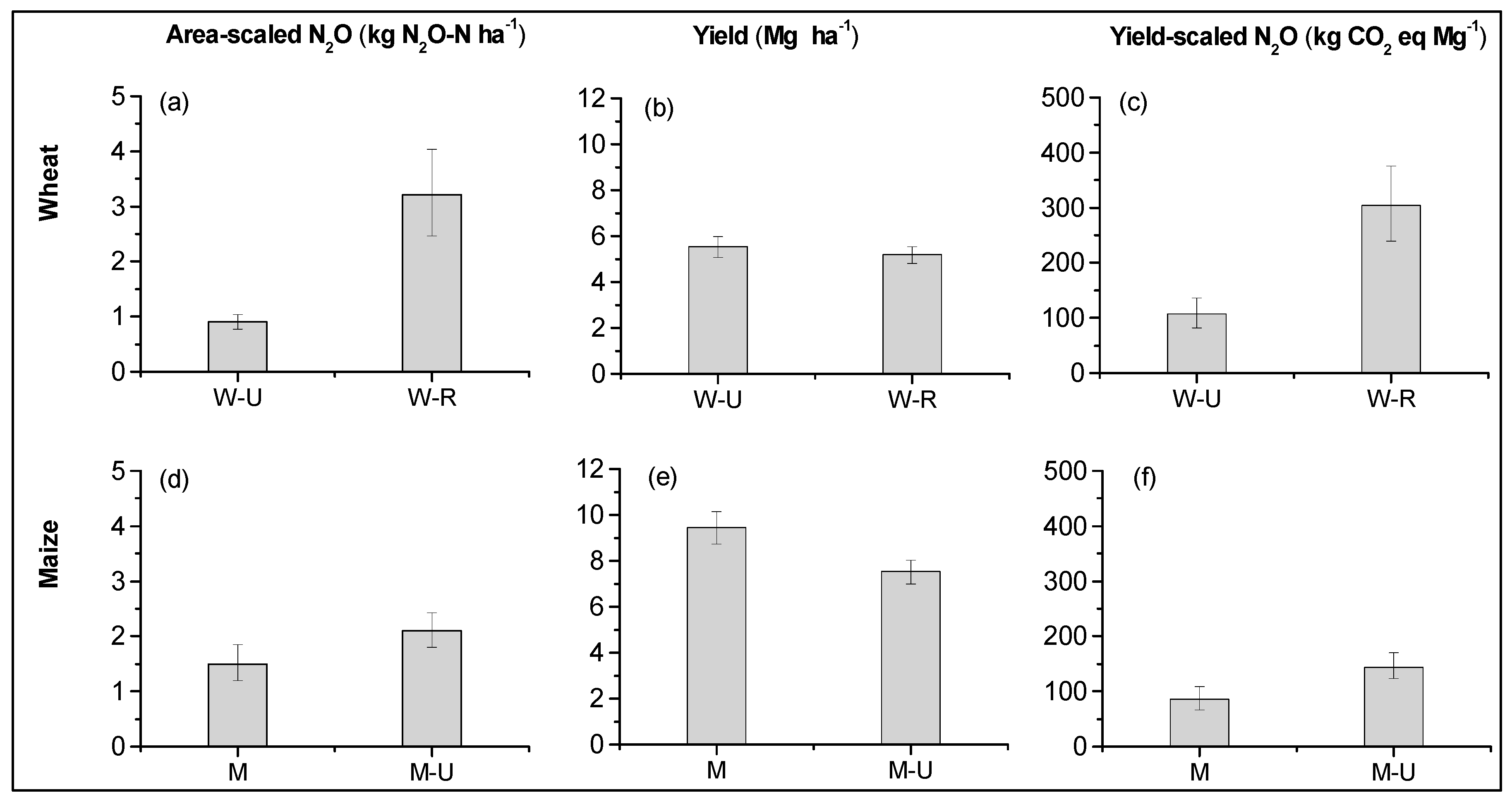
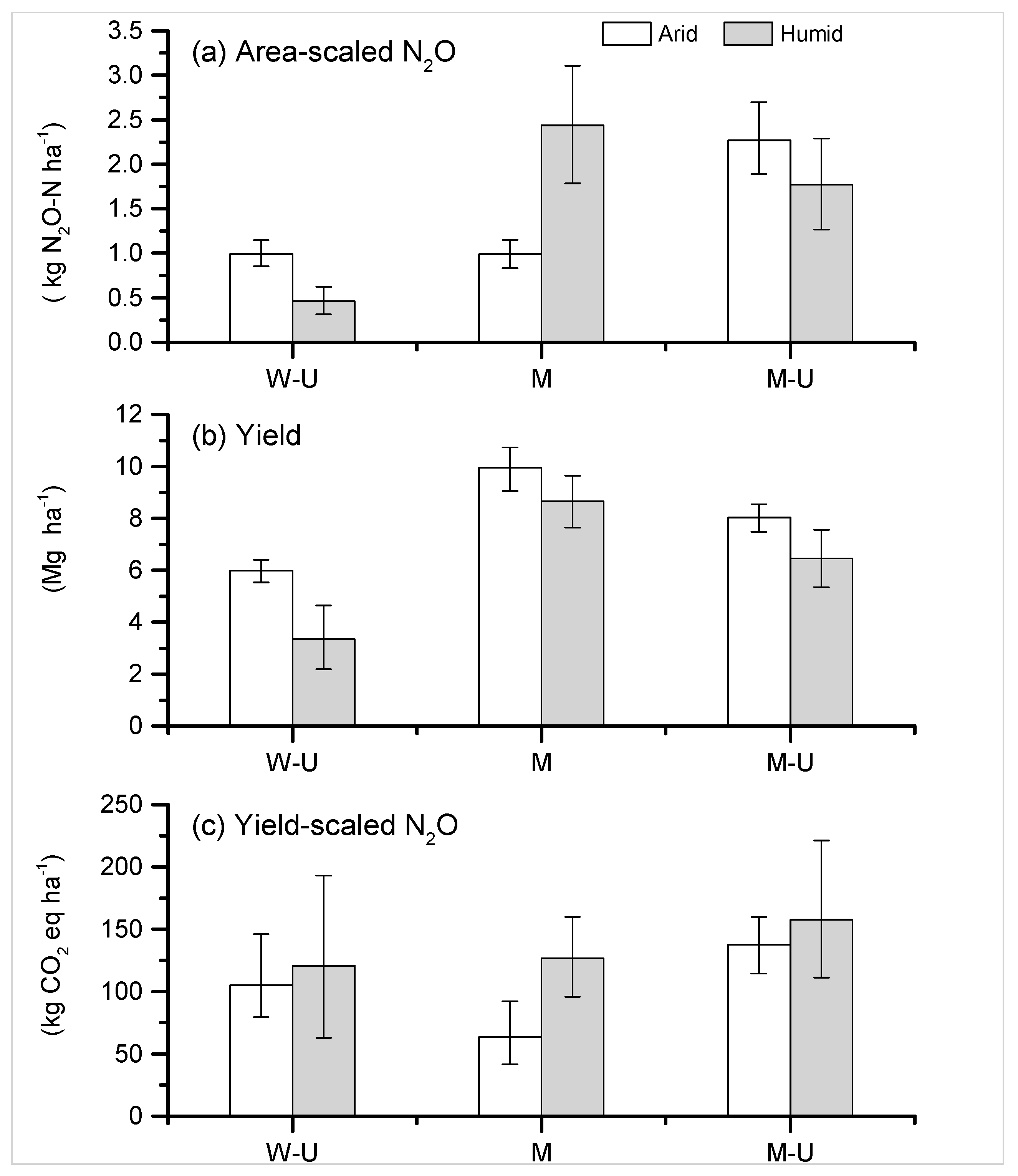
3.1. Mitigation Potential of Cropping Systems
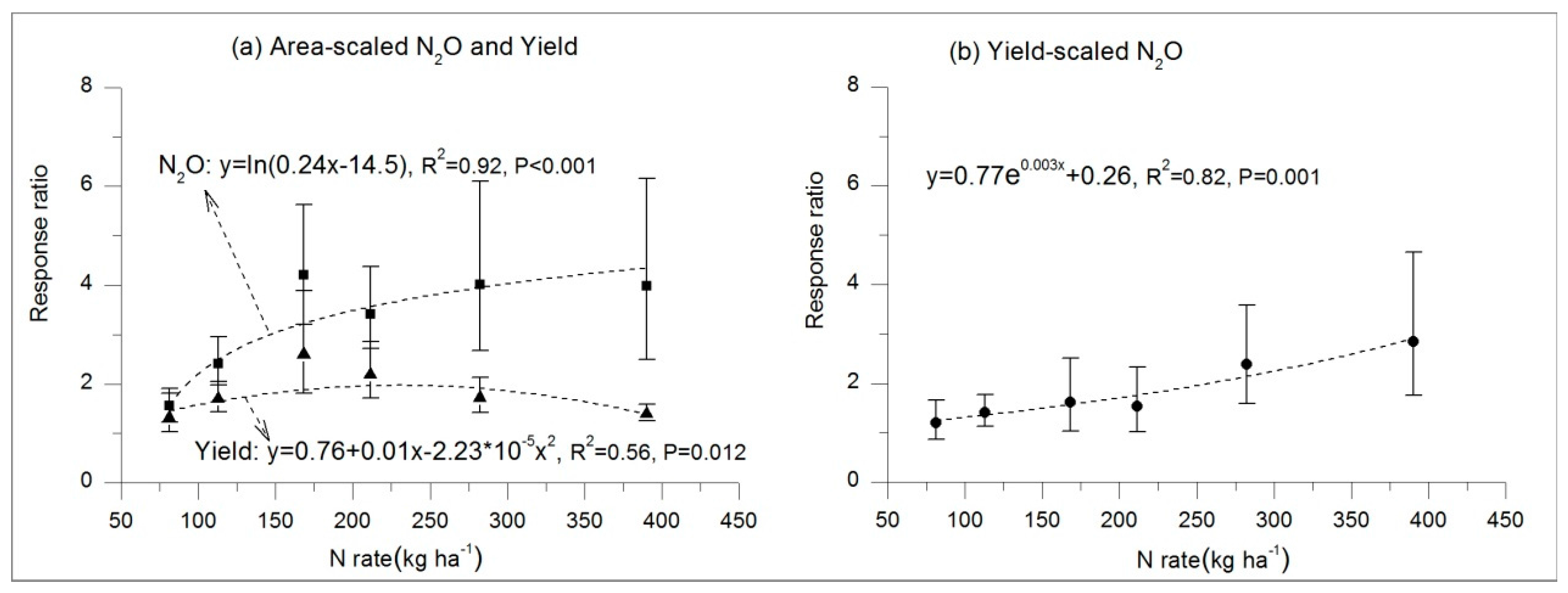
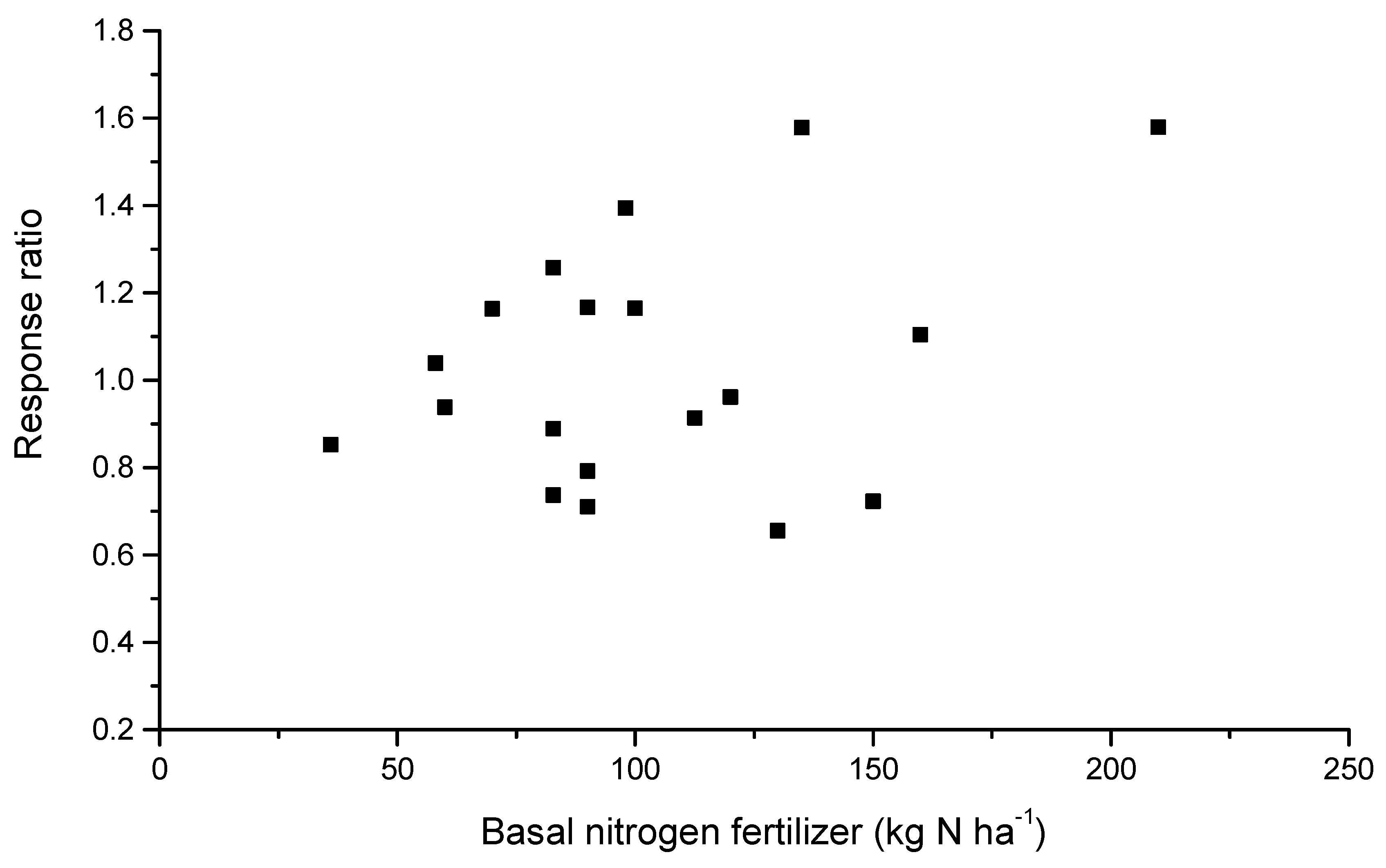
3.2. Mitigation Potential of Inorganic N Fertilizer
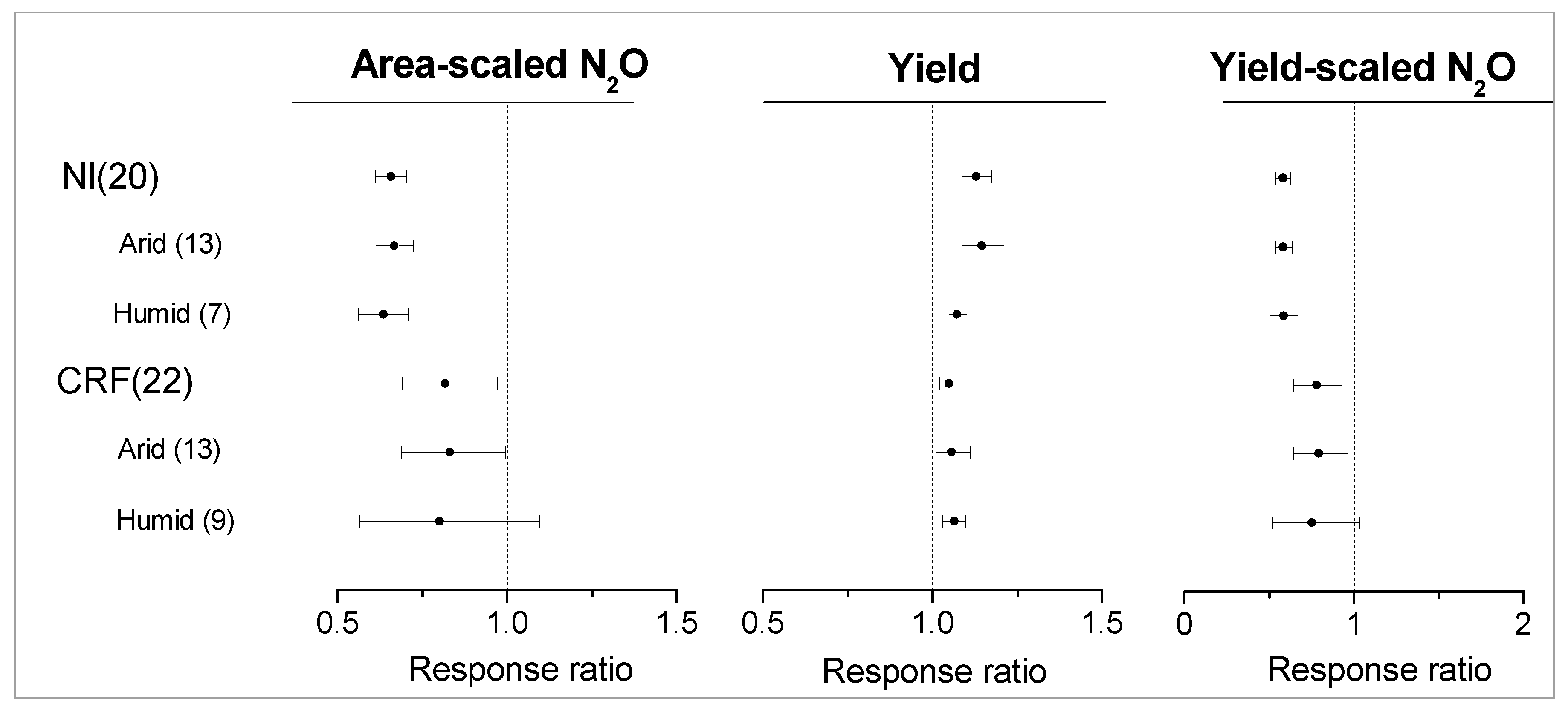
3.3. Mitigation Potential of Enhanced-Efficiency N Fertilizers
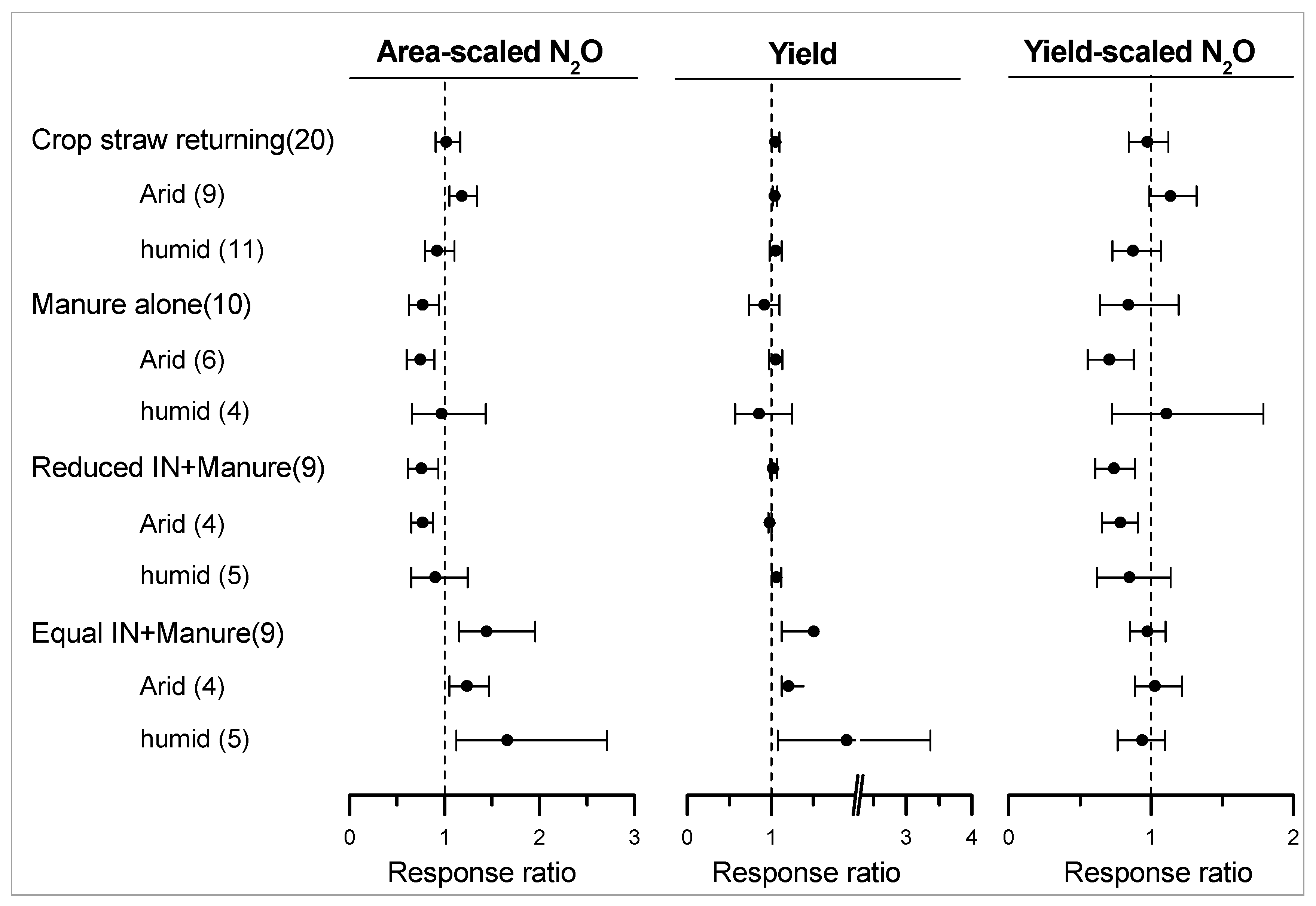
3.4. Mitigation Potential of Organic Amendments
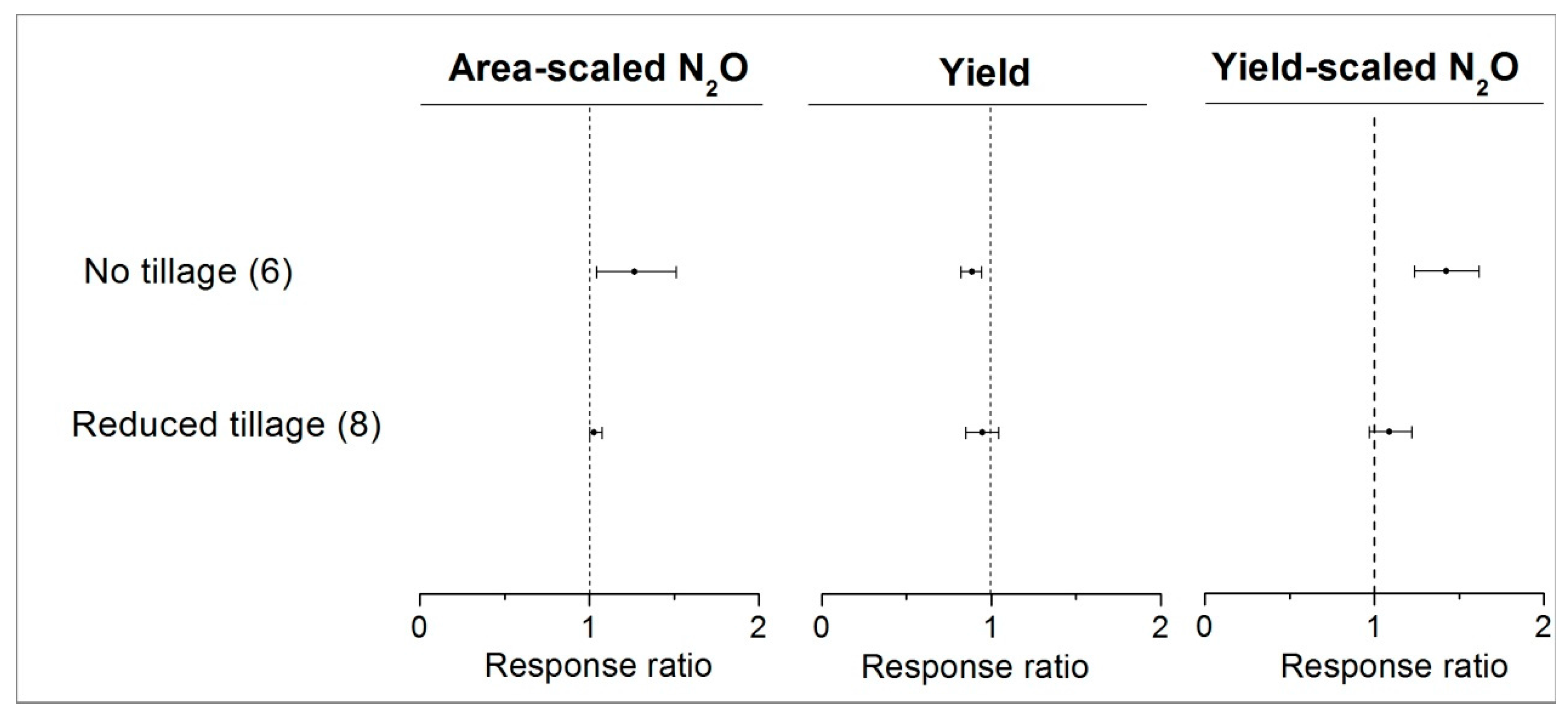
3.5. Mitigation Potential of Soil Tillage
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgements
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wrage, N.; Velthof, G.L.; Van Beusichem, M.L.; Oenema, O. Role of nitrifier denitrification in the production of nitrous oxide. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2001, 33, 1723–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Summary for Policymakers. In Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis; Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Stocker, T.F., Qin, D., Plattner, G.-K., Tignor, M., Allen, S.K., Boschung, J., Nauels, A., Xia, Y., Bex, V., Midgley, P.M., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Alexandratos, N. How to feed the world in 2050. In Proceedings of the Technical Meeting of Experts, Rome, Italy, 24–26 June 2009; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Tilman, D.; Balzer, C.; Hill, J.; Befort, B.L. Global food demand and the sustainable intensification of agriculture. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 20260–20264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, D. Land availability for biofuel production. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 45, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popp, A.; Lotze-Campen, H.; Bodirsky, B. Food consumption, diet shifts and associated non-CO2 greenhouse gases from agricultural production. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2010, 20, 451–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Beek, C.L.; Meerburg, B.G.; Schils, R.L.M.; Verhagen, J.; Kuikman, P.J. Feeding the world’s increasing population while limiting climate change impacts: Linking N2O and CH4 emissions from agriculture to population growth. Environ. Sci. Policy 2010, 13, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heffer, P. Assessment of Fertilizer Use by Crop at the Global Level; International Fertilizer Industry Association (IFA): Paris, France, 2013; Available online: www.fertilizer.org//En/Statistics/Agriculture_Committee_Databases.aspx (accessed on 21 May 2014).
- Smith, P.; Martino, D.; Cai, Z.; Gwary, D.; Janzen, H.; Kumar, P.; McCarl, B.; Ogle, S.; O’Mara, F.; Rice, C.; et al. Agriculture. In Climate Change 2007: Mitigation; Contribution of Working Group III to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Metz, B., Davidson, O.R., Bosch, P.R., Dave, R., Meyer, L.A., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Y.; Ding, W.; Luo, J. Nitrous oxide emissions from Chinese maize-wheat rotation systems: A 3-year field measurement. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 65, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkin, T.; Hatfield, J. Influence of nitrapyrin on N2O losses from soil receiving fall-applied anhydrous ammonia. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2010, 136, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Sun, L.; Zhang, X.; Yang, B.; Wang, J.; Yin, B.; Yan, X.; Xiong, Z. Mitigation of nitrous oxide emissions from paddy soil under conventional and no-till practices using nitrification inhibitors during the winter wheat-growing season. Biol. Fert. Soils 2013, 49, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venterea, R.T.; Bijesh, M.; Dolan, M.S. Fertilizer source and tillage effects on yield-scaled nitrous oxide emissions in a corn cropping system. J. Environ. Qual. 2011, 40, 1521–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Su, F.; Ju, X.; Gao, B.; Oenema, O.; Christie, P.; Huang, B.; Jiang, R.; Zhang, F. Greenhouse gas emissions from a wheat-maize double cropping system with different nitrogen fertilization regimes. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 176, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, C.V.; Duxbury, J.; Freney, J.; Heinemeyer, O.; Minami, K.; Mosier, A.; Paustian, K.; Rosenberg, N.; Sampson, N.; Sauerbeck, D.; et al. Global estimates of potential mitigation of greenhouse gas emissions by agriculture. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 1997, 49, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Six, J.; Ogle, S.M.; Conant, R.T.; Mosier, A.R.; Paustian, K. The potential to mitigate global warming with no-tillage management is only realized when practised in the long term. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2004, 10, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochette, P.; Worth, D.E.; Lemke, R.L.; McConkey, B.G.; Pennock, D.J.; Wagner-Riddle, C.; Desjardins, R. Estimation of N2O emissions from agricultural soils in Canada. I. Development of a country-specific methodology. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2008, 88, 641–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, H.; Yan, X.; Yagi, K. Evaluation of effectiveness of enhanced-efficiency fertilizers as mitigation options for N2O and NO emissions from agricultural soils: Meta-analysis. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2010, 16, 1837–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.G.; Hernandez-Ramirez, G.; Giltrap, D. Linear and nonlinear dependency of direct nitrous oxide emissions on fertilizer nitrogen input: A meta-analysis. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2013, 168, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Li, X.; Hu, F.; Shi, W. Soil nitrous oxide emissions following crop residue addition: A meta-analysis. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2013, 19, 2956–2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Liu, S.; Pu, C.; Zhang, X.; Xue, J.; Zhang, R.; Wang, Y.; Lal, R.; Zhang, H.; Chen, F. Methane and nitrous oxide emissions under no-till farming in China: A meta-analysis. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2016, 22, 1372–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, L.; Lam, S.K.; Chen, D.; Wang, J.; Tang, Q.; Yan, X. Can knowledge-based N management produce more staple grain with lower greenhouse gas emission and reactive nitrogen pollution? A meta-analysis. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2017, 23, 1917–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Groenigen, J.W.; Velthof, G.L.; Oenema, O.; Van Groenigen, K.J.; Van Kessel, C. Towards an agronomic assessment of N2O emissions: A case study for arable crops. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2010, 61, 903–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linquist, B.; Groenigen, K.J.; Adviento-Borbe, M.A.; Pittelkow, C.; Kessel, C. An agronomic assessment of greenhouse gas emissions from major cereal crops. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2012, 18, 194–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Kessel, C.; Venterea, R.; Six, J.; Adviento-Borbe, M.A.; Linquist, B.; Van Groenigen, K.J. Climate, duration, and N placement determine N2O emissions in reduced tillage systems: A meta-analysis. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2013, 19, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Agriculture, Forestry and Other Land Use (AFOLU). In Climate Change 2014, Mitigation of Climate Change; Contribution of Working Group III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Edenhofer, O., Pichs-Madruga, R., Sokona, Y., Farahani, E., Kadner, S., Seyboth, K., Adler, A., Baum, I., Brunner, S., Eickemeier, P., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2014; Chapter 11. [Google Scholar]
- FAOSTAT. Available online: http://faostat.fao.org (accessed on 12 October 2014).
- Xing, G. N2O emission from cropland in China. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 1998, 52, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis; Solomon, S., Qin, D., Manning, M., Chen, Z., Marquis, M., Averyt, K.B., Tignor, M., Miller, H.L., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, J.; Chen, C.; Zhang, Y.; Song, Z.; Deng, A.; Zheng, C.; Zhang, W. Impacts of cropping practices on yield-scaled greenhouse gas emissions from rice fields in China: A meta-analysis. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2013, 164, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedges, L.V.; Gurevitch, J.; Curtis, P.S. The Meta-analysis of response ratios in experimental ecology. Ecology 1999, 80, 1150–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, M.S.; Adams, D.C.; Gurevitch, J. MetaWin-Statistical Software for Meta-Analysis; Sinauer Associates Inc.: Sunderland, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, S.; Hou, H.; Xu, J.; Yang, S.; Mao, Z. Lasting effects of controlled irrigation during rice-growing season on nitrous oxide emissions from winter wheat croplands in Southeast China. Paddy Water Environ. 2013, 11, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G. Study on Chinese wheat planting regionalization (I). J. Triticeae Crop. 2010, 30, 886–895, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Smith, K.A.; Thomson, P.E.; Clayton, H.; McTaggart, I.P.; Conen, F. Effects of temperature, water content and nitrogen fertilisation on emissions of nitrous oxide by soils. Atmos. Environ. 1998, 32, 3301–3309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, P.; Gao, Q.; Xie, R.; Li, S.; Meng, Q.; Kirkby, E.A.; Römheld, V.; Müller, T.; Zhang, F.; Cui, Z.; et al. Grain yields in relation to N requirement: Optimizing nitrogen management for spring maize grown in China. Field Crop. Res. 2012, 129, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J. Regional pattern change and its influencing factors of cereals crops production in China. Macroeconomics 2014, 3, 94–100, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Banger, K.; Tian, H.; Lu, C. Do nitrogen fertilizers stimulate or inhibit methane emissions from rice fields? Glob. Chang. Biol. 2012, 18, 3259–3267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoben, J.; Gehl, R.; Millar, N.; Grace, P.; Robertson, G. Nonlinear nitrous oxide (N2O) response to nitrogen fertilizer in on-farm corn crops of the US Midwest. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2011, 17, 1140–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China. Fertilizer Recommendation for Rice, Wheat and Maize Production in Major Growing Regions. Available online: http://www.moa.gov.cn/govpublic/ZZYGLS/201307/t20130729_3541508.htm (accessed on 29 July 2013). (In Chinese)
- Decock, C. Mitigating nitrous oxide emissions from corn cropping systems in the Midwestern U.S.: Potential and data gaps. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 4247–4256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venterea, R.T.; Halvorson, A.D.; Kitchen, N.; Liebig, M.A.; Cavigelli, M.A.; Grosso, S.J.D.; Motavalli, P.P.; Nelson, K.A.; Spokas, K.A.; Singh, B.P.; et al. Challenges and opportunities for mitigating nitrous oxide emissions from fertilized cropping systems. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2012, 10, 562–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, K.; Zheng, X. Effects of nitrification inhibitors (DCD and DMPP) on nitrous oxide emission, crop yield and nitrogen uptake in a wheat-maize cropping system. Biogeosciences 2013, 10, 2427–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Liu, G.; Ma, J.; Xu, H.; Yagi, K. Effect of controlled-release fertilizer on nitrous oxide emission from a winter wheat field. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2012, 94, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Li, F.; Deng, A.; Feng, X.; Fang, F.; Zhang, W. Integrated assessment of the impact of enhanced-efficiency nitrogen fertilizer on N2O emission and crop yield. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 231, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Hu, Z.; Sun, W.; Huang, Y. Nitrous oxide emissions from Chinese cropland fertilized with a range of slow-release nitrogen compounds. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2010, 135, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abalos, D.; Jeffery, S.; Sanz-Cobena, A.; Guardia, G.; Vallejo, A. Meta-analysis of the effect of urease and nitrification inhibitors on crop productivity and nitrogen use efficiency. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 189, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, E.; Zhang, G.; Ma, J.; Xu, H.; Cai, Z.; Yagi, K. Effects of rice straw returning methods on N2O emission during wheat-growing season. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2010, 88, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, K.; Meng, S.; Zheng, X.; Zhou, Z.; Han, S.; Chen, D.; Yang, Z. Effects of irrigation, fertilization and crop straw management on nitrous oxide and nitric oxide emissions from a wheat-maize rotation field in northern China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2011, 140, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenney, D.; Wang, S.; Drury, C.; Findlay, W. Dentrification and mineralization in soil amended with legume, grass, and corn residues. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1993, 57, 1013–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Liu, S.; Cao, Q. Effect of allelochemicals on N2O emission from soil. Acta Sci. Circumst. 1999, 19, 478–482, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Hao, X.; Chang, C.; Carefoot, J.M.; Janzen, H.H.; Ellert, B.H. Nitrous oxide emissions from an irrigated soil as affected by fertilizer and straw management. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2001, 60, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baggs, E.M.; Stevenson, M.; Pihlatie, M.; Regar, A.; Cook, H.; Cadisch, G. Nitrous oxide emissions following application of residues and fertiliser under zero and conventional tillage. Plant Soil 2003, 254, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adviento-Borbe, M.; Kaye, J.; Bruns, M.; McDaniel, M.; McCoy, M.; Harkcom, S. Soil greenhouse gas and ammonia emissions in long-term maize-based cropping systems. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2010, 74, 1623–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Martín, L.; Vallejo, A.; Dick, J.; Skiba, U. The influence of soluble carbon and fertilizer nitrogen on nitric oxide and nitrous oxide emissions from two contrasting agricultural soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2008, 40, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Jia, Z.; Liang, L.; Yang, B.; Ding, R.; Nie, J.; Wang, J. Impacts of manure application on soil environment, rainfall use efficiency and crop biomass under dryland farming. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Groenigen, J.W.; Kasper, G.J.; Velthof, G.L.; Van den Pol-van Dasselaar, A.; Kuikman, P.J. Nitrous oxide emissions from silage maize fields under different mineral nitrogen fertilizer and slurry applications. Plant Soil 2004, 263, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Putte, A.; Govers, G.; Diels, J.; Gillijns, K.; Demuzere, M. Assessing the effect of soil tillage on crop growth: A meta-regression analysis on European crop yields under conservation agriculture. Eur. J. Agron. 2010, 33, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venterea, R.T.; Stanenas, A.J. Profile analysis and modeling of reduced tillage effects on soil nitrous oxide flux. J. Environ. Qual. 2008, 37, 1360–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, S.; Wang, Y.; Ning, T.; Zhao, H.; Wang, B.; Li, N.; Li, Z.; Chi, S. Greenhouse gas flux and crop productivity after 10 years of reduced and no tillage in a wheat-maize cropping system. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, W.; Bian, X. Evaluation of the Agronomic Impacts on Yield-Scaled N2O Emission from Wheat and Maize Fields in China. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1201. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9071201
Gao W, Bian X. Evaluation of the Agronomic Impacts on Yield-Scaled N2O Emission from Wheat and Maize Fields in China. Sustainability. 2017; 9(7):1201. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9071201
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Wenling, and Xinmin Bian. 2017. "Evaluation of the Agronomic Impacts on Yield-Scaled N2O Emission from Wheat and Maize Fields in China" Sustainability 9, no. 7: 1201. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9071201
APA StyleGao, W., & Bian, X. (2017). Evaluation of the Agronomic Impacts on Yield-Scaled N2O Emission from Wheat and Maize Fields in China. Sustainability, 9(7), 1201. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9071201



