Abstract
Increased industrialization has introduced a lot of hazardous materials into ecosystems. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) are among the most toxic and persistent organic pollutants emanating from petrochemical industrial areas. Remediation of PAHs-contaminated soil has been a particularly big challenge. Photochemical oxidation–reduction processes have gained attention because of their high efficiency and robustness for PAH removal from contaminated soils. In this study, the efficacy of Fe-based and Zn-based Fenton reagents for remediating soil contaminated with pyrene (Pyr) and fluoranthene (Flr) is evaluated. UV treatment (2-h exposure) at 254 nm resulted in 21.6 and 28.5% degradations of Pyr and Flr, respectively. The Zn-based Fenton reagent performed better than the Fe-based reagent by degrading 99.9% of Pyr. The Fe-based Fenton reagent (under UV light) resulted in 97.1–99.7% and 95.1–98.9% Pyr and Flr degradations, respectively, in 0.5–2 h. Notably, the temperature increase during UV irradiation facilitated the enhanced degradation of Pyr and Flr, as observed from negative correlations (r = (−)0.902–0.961 and p = 0.039–0.098) between the temperature and PAH concentrations. The newly tested Zn-based Fenton reagent was equally effective as the Fe-based Fenton reagent in degrading Pyr and Flr in soil. Hence, it can be used as a new alternative reagent to remediate PAH-polluted soils.
1. Introduction
Emissions of hazardous organic contaminants from industrial activities (such as in oil-producing areas) and warfare are of foremost concern in Arabian Gulf countries, including Saudi Arabia [1]. Among hazardous organic pollutants, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) are recognized as persistent, bio-accumulative, toxic, and ubiquitous substances in the soil in Saudi Arabia and other Gulf countries [2,3,4]. The sources of PAHs in soil are principally petrogenic, followed by pyrogenic ones [4,5,6]. PAHs have highly hydrophobic properties and are primarily diffusive in nature; additionally, they can be transported over long distances after being sorbed onto atmospheric particles [7,8,9].
Different types of physical, biological, and chemical treatment processes, either exclusively or in combination, have been examined to reduce PAH levels in soil [10]. Physical processes, such as liquid–liquid extraction and adsorption, are less effective because of material recovery and pollutant disposal. Biodegradation is a slow process and, in some cases, there is tough competition between PAHs and other pollutants present in the environment for microbial degradation, which can inhibit the biodegradation process. Recently, advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) have been employed as robust and efficient remediation processes for PAH degradation in water and soil [11,12,13]. Products of these processes are generally carbon dioxide and water, or at least a biodegradable product (like phenols, quinones, etc.) [14]. Compared to other remediation processes, AOPs may become expensive when treating relatively high concentrations of organic contaminants (>50 ppm), due to high energy and oxidant consumption [15]. In AOPs, a special emphasis has been levied on the use of a Fenton reagent, which liberates hydroxyl radicals (•OH) with a high oxidation potential (E° = 2.73 V). The Fe-based Fenton reagents have been well established for this purpose. In the last two decades, intensive use of integrated Fenton or Fenton-like reagents has contributed greatly to the scientific arena. However, there are certain limitations for using the Fe-based Fenton reagent in soil [16]. For instance, the optimum pH should be 3.0 for PAH degradation in soil when using a Fenton reagent. At pH > 3.0, colloidal Fe+3 species are dominant, which hinders the oxidation reaction. At pH < 3.0, H2O2 can solvate protons to form oxonium ions (H3O2+), which would augment the stability of H2O2 and lessen its reactivity with Fe+2 ions [17,18]. The lifetime of H2O2 is an important factor in Fenton and Fenton-like reactions and it depends on the pH [19]. As pH increases the decomposition of H2O2 increases and it is more stable in acidic conditions however Fenton like reactions favors the stability of H2O2 on wide range of pH and also helps to prevent the metal precipitation [20]. Zn could be more toxic than Fe depending on the permissible limit in soil (200 mg/kg for Zn and 21,000 mg/kg for Fe [21]. However, the applied concentrations of Zn and Fe in this experiment were 0.005 mg/g and 0.011 mg/g of soil, which were quite low enough to be ignored. Therefore, alternative metal-based Fenton reagents should be tested for their suitability toward PAH degradation in soil.
Photolysis constitute a promising technique for the PAHs degradation from many years. However, the long exposure time, light intensity, wavelength dependence, soil particle size, and sample thickness limit the feasibility of photolysis. Likewise, practical catalysis applications are hindered in the absence of visible light [16]. The combination of photolysis with catalytic oxidation—i.e., photocatalytic oxidation—has recently evolved as an attractive technique for PAH degradation, in which oxidative degradation is triggered by the generation of •OH by photocatalysts [22].
The use of transition metal salts and UV-light to form strong oxidation agents (such as •OH) is very helpful in bottom-up approaches for synthesizing photocatalysts, which can effectively be used for the degradation of PAHs [23]. However, the use of metal oxides by a top-down approach is relatively expensive and requires critically controlled conditions. Moreover, the high energy requirement, difficulty in grinding the hard metals, presence of impurities, and non-uniform product size make the top-down approach more inconvenient than the bottom-up approach [24].
Flr and Pyr are considered to be the main representatives of PAHs due to their presence in soil, water and air [25]. Among PAHs, Flr and Pyr are the most ubiquitous and abundant compounds from pyrogenic and pyrolytic sources respectively and their ratios are usually used to pinpoint the origin of PAHs [26,27]. Flr and Pyr both have four ring structure with a solubility of (0.26 mg L−1) and (0.14 mg L–1) respectively and are mostly selected as model compounds for high molecular weight PAHs [28,29]. In this study, we examine the use of common ZnCl2 as a precursor of Zn in the Fenton reagent (instead of Fe) as a catalyst and explore its effectiveness for the degradation of pyrene and fluoranthene (as example PAHs) in soil. The Zn-based Fenton reagent may possess an equivalent degradation efficiency for organic pollutants as the Fe-based Fenton reagent. Specifically, in an arid environment with highly alkaline soils, such as that in Saudi Arabia, there is a dire need to investigate new oxidative catalysts with or without photolysis. Therefore, the new Zn-based Fenton reagent is compared with the conventional Fe-based Fenton reagent for the oxidative catalytic degradation pyrene and fluoranthene in sandy soil. The integrated effect of photolysis (by UV treatment) and the Fenton reagent (Fe- and Zn-based) is also evaluated. The photocatalytic oxidation reaction rates and half-lives are calculated from pseudo-first-order kinetic models.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Soil Preparation
A sample of natural sandy soil, which represents the texture of typical Saudi Arabian soil and a pH value of 7.4, was collected from a greenhouse at King Saud University. Pyrene (Pyr) and fluoranthene (Flr) (AccuStandard, Inc., New Haven, CT, USA) stock solutions (100 mg L−1 each) were prepared in methanol. The soil was simultaneously spiked with Pyr and Flr solutions, mixed thoroughly for homogenization, and air-dried in the dark to evaporate the solvent. These spiked soils were used in the photolysis experiment. Pyr and Flr were selected because of their high molecular weights (HMW-PAHs) and toxicity. The spiked soil shows a representative concentration. We surveyed the soils of an industrial area located at southern of Riyadh city (Saudi Arabia) for 23 PAHs, and found maximum concentrations of fluoranthene and pyrene to be 242.4 and 124.4 ng/g, respectively [4].
2.2. Photolysis Experiment
The PAH-contaminated soil was subjected to photodegradation under UV light in the presence or absence of the oxidative Fe and Zn catalysts. The catalysts were 0.2 M FeCl3 or ZnCl2 with 33% H2O2 (as an oxidizing agent) and deionized water at a 1:1:1 (v/v) ratio. Specifically, 5 g of soil was placed in a sterile Petri plate (KIMAX® Petri Dish Set: New York, NY, USA; 5-cm diameter) at a thickness of about 2.5 mm. The oxidative catalyst was then mixed with the soil and exposed to UV radiation for 0.25, 0.5, 1, and 2 h. A UV device (Boekel UV Crosslinker Boekel Scientific, Feasterville, PA, USA) with a wavelength of 254 nm was employed. The distance between the UV lamps and soil samples was 15 cm, and the UV irradiation intensity was 1071 μW cm−2. For comparison purposes, soil without any catalyst was also exposed to UV radiation for the same time intervals. Additionally, individual treatments with the oxidative catalysts, i.e., FeCl3 + H2O2, ZnCl2 + H2O2, and H2O2 alone, were also performed. Therefore, seven treatments were used to evaluate PAH degradation: (1) soil only (control), (2) soil + UV, (3) soil + FeCl3 + H2O2 + UV, (4) soil + ZnCl2 + H2O2 + UV, (5) soil + FeCl3 + H2O2, (6) soil + ZnCl2 + H2O2, and (7) soil + H2O2 + UV. All treatments were performed at least twice. The temperature of the UV chamber was monitored at 0.25, 0.5, 1, and 2 h to assess the impact of the temperature increase on Pyr and Flr degradation.
2.3. Sample Preparation and Analysis
A spiked soil sample (5 g) was weighed on an analytical balance (0.01 g readability) in a 100-mL beaker and thoroughly mixed with diatomaceous earth. The sample blend was transferred to a 35-mL stainless steel accelerated solvent extractor (ASE) cell (Dionex, Sunnyvale, CA, USA). The cells were capped, loaded into the ASE, and extracted with HPLC-grade ultrapure acetone/dichloromethane. The conditions for ASE were 1500 psi, 100 °C, one 5-min cycle, and a 60% flush volume. The sample extract was collected in a 60-mL ASE vial, transferred to a round bottom flask, and concentrated to 1.0 mL in a rotary evaporator (BÜCHI, Essen, Germany). The concentrated sample extract was then filtered in the solid-phase extraction (SPE) barrels and packed in silica with methanol, dichloromethane, and n-hexane. Finally, 1 mL of the extract was transferred to a gas chromatography (GC) vial and analyzed for PAHs on a GC-MS-MS (MS = mass spectrometer; Thermo Scientific™ TSQ™ 8000, Evo Triple Quadrupole: Waltham, MA, USA). The PAHs were analyzed in splitless mode with 1-µL injection volumes and an inlet temperature of 270 °C. The GC oven temperature was ramped from 50 to 310 °C (3 min) at a rate of 10 °C min−1, and then to 325 °C (10 min) at a rate of 4 °C min−1. Quantitative data analysis was performed for each method [4].
To ensure quality control/assurance, the sequence of each sample batch (18 samples) was supplemented by six quality control samples with known concentrations of Pyr and Flr. These samples were prepared and analyzed in triplicate by the GC-MS-MS. Certified reference materials (M-8100-QC, AccuStandard: New Haven, CT, USA. nd spiked samples were used to calculate the percentage recovery of each compound for each batch of samples (Table 1) [4].

Table 1.
Retention time (RT), ion polarity, mass, product mass, and collision energy (CE) for Pyr and Flr analysis using GC-MS-MS.
2.4. Kinetic Modeling
The degradation kinetics of Pyr and Flr were modeled by the most commonly used pseudo-first-order rate equation
where C0 and Ct are the PAH concentrations at times 0 and t, respectively, and k is the rate constant. A plot of ln C0/Ct versus t provides a straight line. The slope of the straight line was calculated to determine k. The half-life (t1/2) of each reaction was calculated using the equation
The pseudo-first-order approximation covers the flaws of first-order kinetics by keeping the concentration constant for one of the reactants as it is supplied in great excess. In other words, the rate depends on the concentration of only one reactant.
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. PAH Degradation
The effects of various treatments on the Flr and Pyr concentrations in sandy soil and their degradation percentages with respect to time are presented in Figure 1 and Figure 2, respectively. UV treatment at 254 nm resulted in 1.1, 8.1, 20.3, and 21.6% degradation of Pyr at 0.25, 0.5, 1, and 2 h of light exposure, respectively (Figure 2a). Flr degradations were 10.5, 24.5, 20.8, and 28.5% over the same respective time intervals under UV treatment. However, the decrease in the Pyr concentration under UV treatment with time was not significant compared to that for the control (Figure 1a). Likewise, UV treatment did not show any significant reductions in the Flr concentration at any of the time intervals, except after 2 h, compared to that for the control (Figure 1b). Comparatively, the lesser PAH degradation under UV treatment could be attributed to the relatively short exposure time of 2 h. Generally, an exposure time of several days is required for effective Pyr photodegradation [30], which is the main limitation of photolysis. However, we obtained a higher percentage of PAH photodegradation than that in other studies [30,31], which may be due to the large soil particle size (1.5 mm) [31] and reduced soil thickness (1 mm) [32]. Vela et al. [28] reported a maximum Pyr photodegradation in 1-mm thick soils with 1-mm particles. Nevertheless, other parameters, such as the UV wavelength distribution, soil physicochemical individualities, and photolysis machine structure and mechanism could influence the PAH photodegradation. The variations in photodegradation of Pyr and Flr could be due to the different physicochemical and structural properties of the PAHs [33].
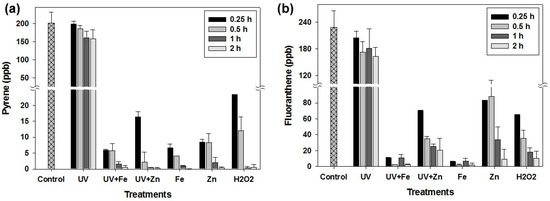
Figure 1.
Pyrene (a) and fluoranthene (b) concentrations in untreated (control) and treated sandy soils.
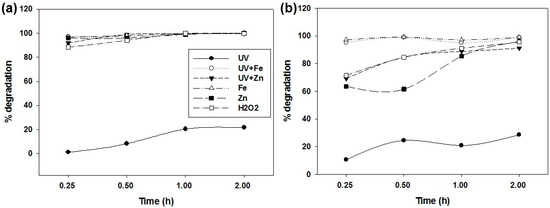
Figure 2.
Pyrene (a) and fluoranthene (b) degradation in untreated (control) and treated sandy soils with time.
UV treatment in the presence of the Fe-based Fenton reagent provided exceptional results, resulting in 97.1–99.7% Pyr degradation and 95.1–98.9% Flr degradation in 0.5–2 h. A sharp decrease in Pyr and Flr concentrations was observed within 15 min of UV exposure in the presence of the Fe-based Fenton reagent, which then further decreased to a minimum after 2 h of UV exposure (Figure 1). The oxidative effect of the Fenton reagent on Pyr and Flr degradation in the absence of UV light was also investigated. The Fe-based Fenton reagent performed equally well in the absence of UV light for Pyr degradation, resulting in 96.7, 97.9, 99.5, and 100% degradation at 0.25, 0.5, 1, and 2 h, respectively. The Flr degradations with the Fe-based Fenton reagent were 97.2, 97.1, 98.9, and 99.0% at 0.25, 0.5, 1, and 2 h, respectively, which is slightly better than that with the UV treatment. Direct oxidation of PAHs from sorbed media using strong oxidizing agents is a well-established process [34]. The Fe-based Fenton reagent has the ability to break down the organic compounds via oxidation; the reaction is summarized as
The highly reactive •OH attacks the aromatic rings of the PAHs, further generating organic radicals and eventually causing oxidative degradation of the original PAH. The efficiency of the Fenton reagent can be accelerated using UV light by photochemical reduction of Fe3+ to Fe2+ [35]
In this study, the Zn-based Fenton reagent was also employed to degrade the PAHs with UV treatment. Similar to the Fe-based Fenton reagent, the Zn-based Fenton reagent resulted in 91.8–99.9% Pyr degradation with 0.5–2 h exposures of UV light. The Zn-based Fenton reagent performed better than the Fe-based Fenton reagent by degrading Pyr to 99.7 and 99.9% at 1 and 2 h of UV exposure, respectively. However, in the case of Flr degradation under UV treatment, the Zn-based Fenton reagent did not perform better than the Fe-based Fenton reagent at all of the time intervals. The UV treatment in the presence of the Zn-based Fenton reagent resulted in 69.2, 84.7, 88.8, and 91.1% Flr degradation at 0.25, 0.5, 1, and 2 h, respectively. Flr degradation by the Fe-based Fenton reagent accounted for 25.96, 14.26, 6.25, and 7.76% more degradation than that for the Zn-based Fenton reagent at 0.25, 0.5, 1, and 2 h of UV exposure, respectively. The mode of action of the Zn-based Fenton reagent could be different from that for the Fe-based Fenton reagent, summarized as [36,37]
The generation of an electron (e−)-hole (h+) pair governs the formation of •OH and O2•− and causes degradation of the PAHs.
In the case of Flr, the degradation percentages were 63.6, 61.5, 85.3, and 95.96% at 0.25, 0.5, 1, and 2.0 h, respectively, with the Zn-based Fenton reagent in the absence of UV light, which were 1.1, 1.0, 1.4, and 0.95 times lower, at the respective time intervals, than in the presence of UV light. The Fe-based Fenton reagent performed better than the Zn-based reagent in the absence of the UV light source for the degradation of both Pyr and Flr. Particularly, in the case of Flr degradation, the Fe-based Fenton reagent resulted in 33.6, 37.5, 11.78, and 3.1% more degradation than the Zn-based Fenton reagent after 0.25, 0.5, 1, and 2 h, respectively.
The effect of H2O2 alone on Pyr and Flr degradation was also evaluated in the presence of UV light. With H2O2 treatment, Pyr degradations of 88.4, 94.0, 99.8, and 99.7% and Flr degradations of 71.4, 84.5, 92.0, and 95.5% were observed at 0.25, 0.5, 1, and 2 h, respectively. The oxidizing efficiency of H2O2 is enhanced using UV irradiation according to the equation [38]
Generally, it is the •OH that controls the degradation of Pyr and Flr. However, the reaction rate can be increased by the use of transition metals as catalysts and/or by exposure to UV irradiation.
Overall, all treatments (except UV treatment) significantly decreased the Pyr and Flr concentrations in the soil compared to the control, and the degradation was generally gradual with respect to time. The Fe-based Fenton reagent treatment proved to be the most efficient treatment, resulting in >95% degradation of Pyr and Flr within 15 min. Use of the Fe-based Fenton reagent with and without UV provided very similar PAH degradations. However, the Zn-based Fenton reagent performed well in the presence of UV light for Flr degradation in sandy soil. Except for the UV treatments, all treatments showed >90% degradation of Pyr and Flr after 2 h.
3.2. Effect of UV Chamber Temperature on Degradation
The effect of temperature during UV irradiation was also considered. The temperature of the UV chamber was recorded at different time intervals (0.25, 0.5, 1, and 2 h), and it was correlated with the Pyr and Flr concentrations. The results are shown in Figure 3. It is evident that temperature had a direct impact on the degradation of Pyr and Flr. The temperature of the UV chamber increased with respect to the exposure time and increased the Pyr and Flr degradations. Specifically, Pyr and Flr concentrations showed strong negative correlations (r = −0.902–0.961 and p = 0.039–0.098) with temperature under UV and UV + Fe treatments [24]. In addition, higher PAH degradations were observed inside the UV chamber with increasing temperature. The increased temperature may have decreased PAH sorption onto the soil particles, thereby facilitating photodegradation.
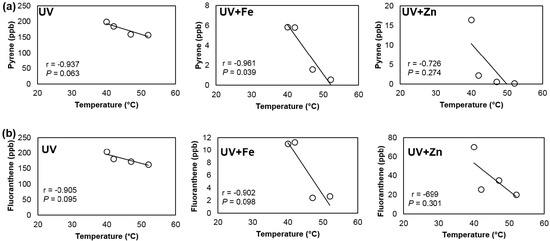
Figure 3.
Temperature effect on pyrene (a) and fluoranthene (b) concentrations in soil exposed to UV irradiation in the presence of Fe-based and Zn-based Fenton reagents.
3.3 Dynamics of PAH Degradation
A conventionally used pseudo-first-order kinetics model was applied to the Pyr and Flr degradations by each treatment. The rate constant (k), half-life (t1/2), and determination coefficient (R2) values calculated using Equations (1) and (2) are presented in Table 2. The R2 values for the pseudo-first-order reactions ranged from 0.928–0.988 for Pyr degradation and 0.909–0.986 for Flr degradation. The rate constant determines the time required to complete a chemical reaction. A high k value indicates that a short time is required to complete the reaction [39]. The highest k value obtained from the pseudo-first-order model for Pyr degradation was 0.060 min−1 for the Fe-based Fenton reagent in the absence of UV light; thus, this treatment was the most effective and it almost completely degraded Pyr within a very short time interval (also shown in Figure 1). In the case of Flr degradation, the highest k value of 0.018 min−1 was obtained for the Zn-based Fenton reagent in the absence of UV light, followed by 0.015 min−1 for the treatment using UV + Fe. These k values revealed that oxidative reagents, either in the presence or absence of UV light, were more efficient for PAH degradation than the UV treatment. Correspondingly, the t1/2 values for the Fe-based Fenton reagent in the absence of UV light were 11.552 min and 63.013 min for Pyr and Flr degradation, respectively. In contrast, the t1/2 value calculated from the pseudo-first-order UV treatment was 346.574 min, which is nine times higher than that for Flr degradation with the Fe-based Fenton reagent. This indicates that UV treatment requires a long time for photodegradation of Pyr and Flr in sandy soil. In our previous study [4], we reported t1/2 values of five and four days for Pyr and Flr, respectively.

Table 2.
Determination coefficient (R2), rate constant (k), and half-life (t1/2) values calculated from the pseudo-first-order kinetic model.
The UV treatment was equally effective for photodegradation of both Pyr and Flr (Table 2). However, all of the other treatments were more effective toward Pyr degradation than Flr degradation, indicating that the structural chemistry of the PAH compound may also affect the degradation reaction process.
4. Conclusions
In the current study, the remediation of Pyr and Flr contaminated soil using a Zn-based Fenton reagent was compared with the conventional Fe-based Fenton reagent and H2O2 in the presence and absence of UV light. The results reveal that the Zn-based Fenton reagent could be an alternative reagent for Pyr and Flr degradation in sandy soil, in either the presence or absence of UV light. Nevertheless, the efficiency of the Fe-based Fenton reagent was slightly higher than that for the Zn-based Fenton reagent toward photodegradation of Pyr and Flr. Formation of •OH and O2•− governed the rate of PAH degradation. The Zn-based Fenton reagent could be a better choice for soil remediation because it can perform better in neutral and alkaline soils.
Acknowledgments
Funding: This research was supported by the Research Center, College of Food and Agricultural Sciences, Deanship of Scientific Research, King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
We thank, Andreas Paul Loibner, Department of Environmental Biotechnology, Institute for Agrobio-technology, Konrad Lorenz Strasse 20, 3430 Tulln, Austria, for his help to improve this manuscript.
Author Contributions
Abid Hussain conceived and designed the experiment; Abid Hussain and Muhammad Waqar performed the experiments; Mahtab Ahmad analyzed the data; Fahad N. Albarakah and Hamza Elsaied contributed reagents/materials/analysis tools; and Sewailum help to write the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Freije, A.M. Heavy metal, trace element and petroleum hydrocarbon pollution in the Arabian Gulf: Review. J. Assoc. Arab Univ. Basic Appl. Sci. 2015, 17, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Primbs, T.; Piekarz, A.; Wilson, G.; Schmedding, D.; Higginbotham, C.; Field, J.; Simonich, S.M. Influence of Asian and Western United States Urban Areas and Fires on the Atmospheric Transport of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons, Polychlorinated Biphenyls, and Fluorotelomer Alcohols in the Western United States. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 6385–6391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genualdi, S.A.; Killin, R.K.; Woods, J.; Wilson, G.; Schmedding, D.; Simonich, S.L.M. Trans-Pacific and regional atmospheric transport of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and pesticides in biomass burning emissions to western North America. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 1061–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EL-Saeid, M.H.; Al-Turki, A.M.; Nadeem, M.E.A.; Hassanin, A.S.; Al-Wabel, M.I. Photolysis degradation of polyaromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) on surface sandy soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 9603–9616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Mubarak, A.H.; Rushdi, A.I.; Al-Mutlaq, K.F.; Bazeyad, A.Y.; Simonich, S.L.M.; Simoneit, B.R.T. Identification and source apportionment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in ambient air particulate matter of Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 21, 558–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrestha, G.; Traina, S.J.; Swanston, C.W. Black Carbon’s Properties and Role in the Environment: A Comprehensive Review. Sustainability 2010, 2, 294–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcke, W. Global patterns of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in soil. Geoderma 2007, 141, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindra, K.; Sokhi, R.; Van Grieken, R. Atmospheric polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: Source attribution, emission factors and regulation. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 2895–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, B.; Alves, C.A.; Gonçalves, C.; Pio, C.; Gonçalves, F.; Pereira, R. Mutagenicity assessment of aerosols in emissions from wood combustion in Portugal. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 166, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, S.; Lau, E.V.; Ng, H.K. Remediation of soils contaminated with polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 172, 532–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, K.; Rodriguez, W.; Kukor, J.J. Enhanced degradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by biodegradation combined with a modified Fenton reaction. Chemosphere 2001, 45, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, C.L.; Gan, S.; Ng, H.K. Fenton based remediation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons-contaminated soils. Chemosphere 2011, 83, 1414–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canzano, S.; Capasso, S.; Natale, M.D.; Erto, A.; Iovino, P.; Musmarra, D. Remediation of Groundwater Polluted by Aromatic Compounds by Means of Adsorption. Sustainability 2014, 6, 4807–4822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreozzi, R.; Caprio, V.; Insola, A.; Marotta, R. Advanced oxidation processes (AOP) for water purification and recovery. Catal. Today 1999, 53, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munter, R. Advanced oxidation processes—Current status and prospects. Proc. Estonian Acad. Sci. Chem. 2001, 50, 59–80. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, M.; Zeng, G.; Huang, D.; Lai, C.; Xu, P.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Y. Hydroxyl radicals based advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) for remediation of soils contaminated with organic compounds: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 284, 582–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, R.J.; Stanton, P.C.; Howsawkeng, J.; Teel, A.L. Mineralization of a sorbed polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon in two soils using catalyzed hydrogen peroxide. Water Res. 2002, 36, 4283–4292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaee, E.; Gitipour, S.; Mousavi, M.; Amini, S. Optimization of total petroleum hydrocarbons removal from Mahshahr contaminated soil using magnetite nanoparticle catalyzed Fenton-like oxidation. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collivignarelli, M.C.; Pedrazzani, R.; Sorlini, S.; Abbà, A.; Bertanza, G. H2O2 Based Oxidation Processes for the Treatment of Real High Strength Aqueous Wastes. Sustainability 2017, 9, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.S.; Lim, W.T.; Park, J.-Y.; Kim, Y.-H. Effect of pH on Fenton and Fenton-like oxidation. Environ. Technol. 2009, 30, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, Z.I.; Ahmad, K.; Ashraf, M.; Parveen, R.; Mustafa, I.; Khan, A.; Bibi, Z.; Akram, N.A. Bioaccumulation of heavy metals and metalloids in luffa (Luffa cylinderica L.) irrigated with domestic wastewater in Jhang, Pakistan: A prospect for human nutrition. Pak. J. Bot. 2015, 47, 217–224. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, O.T.; Chung, W.K.; Wong, K.H.; Chow, A.T.; Wong, P.K. Photocatalytic oxidation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: Intermediates identification and toxicity testing. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 168, 1192–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karaca, G.; Baskaya, H.S.; Tasdemir, Y. Removal of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) from inorganic clay mineral: Bentonite. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2016, 23, 242–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuzuki, T. Commercial scale production of inorganic nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanotechnol. 2009, 6, 567–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Tang, X.Y.; Zhu, Y.G.; Zheng, M.H.; Miao, Q.L. Contamination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in urban soils in Beijing, China. Environ. Int. 2005, 31, 822–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.-F.; Cullen, W.R.; Reimer, K.J.; Le, X.C. Microbial degradation of pyrene and characterization of a metabolite. Sci. Total Environ. 1996, 177, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rababah, A.; Matsuzawa, S. Treatment system for solid matrix contaminated with fluoranthene. I—Modified extraction technique. Chemosphere 2002, 46, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šepič, E.; Bricelj, M.; Leskovšek, H. Toxicity of fluoranthene and its biodegradation metabolites to aquatic organisms. Chemosphere 2003, 52, 1125–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, A.P.; Hu, Z.L.; Wong, Y.S.; Tam, N.F.-Y. Removal of fluoranthene and pyrene by different microalgal species. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vela, N.; Martínez-Menchón, M.; Navarro, G.; Pérez-Lucas, G.; Navarro, S. Removal of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) from groundwater by heterogeneous photocatalysis under natural sunlight. J. Photochem. Photobiol. Chem. 2012, 232, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Xu, C.; Chen, Z.; Li, X.; Li, P. Photodegradation of pyrene on soil surfaces under UV light irradiation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 173, 168–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, Y.D.; Hua, R.M.; Tang, F.; Chen, X. Effects of soil particle size on distribution and photodegradation of selected pesticides in soil. J. Anhui Agric. Univ. China 1993, 4, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Cavoski, I.; Caboni, P.; Sarais, G.; Cabras, P.; Miano, T. Photodegradation of Rotenone in Soils under Environmental Conditions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 7069–7074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonsson, S.; Persson, Y.; Frankki, S.; van Bavel, B.; Lundstedt, S.; Haglund, P.; Tysklind, M. Degradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in contaminated soils by Fenton’s reagent: A multivariate evaluation of the importance of soil characteristics and PAH properties. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 149, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitti, A.; Harju, M.; Tysklind, M.; van Bavel, B. Multivariate characterization of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons using semi-empirical molecule orbital calculations and physical data. Chemosphere 2003, 50, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauporté, T.; Lincot, D. Hydrogen peroxide oxygen precursor for zinc oxide electrodeposition II—Mechanistic aspects. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2001, 517, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machulek, A.; Oliveira, S.C.; Osugi, M.E.; Ferreira, V.S.; Quina, F.H.; Dantas, R.F.; Oliveira, S.L.; Casagrande, G.A.; Anaissi, F.J.; Silva, V.O.; et al. Application of Different Advanced Oxidation Processes for the Degradation of Organic Pollutants. In Organic Pollutants—Monitoring, Risk and Treatment; Rashed, M.N., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Mondal, K.; Sharma, A. Photocatalytic oxidation of pollutant dyes in wastewater by TiO2 and ZnO nano-materials—A mini-review. In Nanoscience & Technology for Mankind; The Academy of Sciences India (NASI): Allahabad, India, 2014; pp. 36–72. [Google Scholar]
- Plazinski, W.; Rudzinski, W.; Plazinska, A. Theoretical models of sorption kinetics including a surface reaction mechanism: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 152, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).