Decomposition Analysis of Aggregate Energy Consumption in China: An Exploration Using a New Generalized PDA Method
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Production Technology
2.2. Decomposition Approach
2.3. Joint Decomposition Approach
3. Date Description
4. Results and Discussions
4.1. China’s Energy Situation
4.2. Empirical Analysis
4.2.1. Temporal Decomposition Analysis
4.2.2. Sectoral Decomposition Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contribution
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ang, B.W.; Zhang, F.Q. A survey of index decomposition analysis in energy and environmental analysis. Energy 2000, 25, 1149–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, A.; Casler, S. Input-output structure structural decomposition analysis: A critical appraisal. Econ. Syst. Res. 1996, 8, 33–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Chen, J.; Zou, J. Decomposition of energy-related CO2 emission in China: 1957–2000. Energy 2005, 32, 1326–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Qi, Y. A structure decomposition analysis of China’s production-source CO2 emissions: 1992–2002. Environ. Resour. Econ. 2011, 49, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, B.W.; Liu, N. Handling zero values in the logarithmic mean Divisia index decomposition approach. Energy Policy 2007, 35, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Ang, B.W. Index decomposition analysis applied to CO2 emission studies. Ecol. Econ. 2013, 93, 313–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, B.; Ang, B.W. Structural decomposition analysis applied to energy and emissions: Some methodological developments. Energy Econ. 2012, 34, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, B.; Ang, B.W. Attribution of changes in the generalized Fisher index with application to embodied emission studies. Energy 2014, 69, 778–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Ang, B.W.; Su, B. Multiplicative structural decomposition analysis of energy and emission intensities: Some methodological issues. Energy 2017, 123, 47–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, B.W. Decomposition analysis for policy making in energy: Which is the preferred method? Energy Policy 2004, 32, 1131–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirst, E.; Marlay, R.; Greene, D. Recent changes in US energy consumption: What happened and why. Annu. Rev. Energy 1983, 8, 193–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.W. Changes in energy consumption and energy intensity: A complete decomposition model. Energy Econ. 1998, 20, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreoni, V.; Galmarini, S. European CO2 emission trends: A decomposition analysis for water and aviation transport sectors. Energy 2012, 45, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Mu, H.L.; Ning, Y.D. Accounting for energy-related CO2 emission in China, 1991–2006. Energy Policy 2009, 37, 767–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y. LMDI decomposition analysis of energy consumption in the Korean manufacturing sector. Sustainability 2017, 2, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, D.L.; Zhou, D.Q.; Zhou, P. Driving forces of residential CO2 emissions in urban and rural China: An index decomposition analysis. Energy Policy 2010, 38, 3377–3383. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.W.; Liu, X.; Zhang, M.; Song, X.F. Using a new generalized LMDI (logarithmic mean Divisia index) method to analyze China’s energy consumption. Energy 2014, 67, 617–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Song, Y.; Li, P.; Li, H.N. Study on affecting factors of residential energy consumption in urban and rural Jiangsu. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 53, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasurka, J.A. Decomposing electric power plant emissions within a joint production framework. Energy Econ. 2006, 28, 26–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C. Decomposing energy productivity change: A distance function approach. Energy 2007, 32, 1326–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Ang, B.W. Decomposition of aggregate CO2 emissions: A production-theoretical approach. Energy Econ. 2008, 30, 1054–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M. Decomposing the change of CO2 emissions in China: A distance function approach. Ecol. Econ. 2010, 70, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.P.; Tan, Y.K.; Tan, L.Q.; Yuan, J.H. Decomposition of aggregate CO2 emissions within a joint production framework. Energy Econ. 2012, 34, 1088–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Kim, Y. International comparison of industrial CO2 emission trends and energy efficiency paradox utilizing production-based decomposition. Energy Econ. 2012, 34, 1724–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.W.; Chiu, Y.H.; Chiu, C.R. Driving factors behind carbon dioxide emissions in china: A modified production-theoretical decomposition analysis. Energy Econ. 2015, 51, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Färe, R.; Primont, D. Multi-Output Production and Duality: Theory and Applications; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Boston, MA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Färe, R.; Grosskopf, S.; Norris, M. Productivity growth, technical progress and efficiency change in industrialized countries. Am. Econ. Rev. 1994, 84, 66–83. [Google Scholar]
- National Bureau of Statistics of China. China Energy Statistical Yearbook; National Bureau of Statistics of China: Beijing, China, 2013.
- National Bureau of Statistics of China. China Statistical Yearbook; National Bureau of Statistics of China: Beijing, China, 2013.
- Lin, B.Q.; Du, K.R. Decomposing energy intensity change: A combination of index decomposition analysis and production-theoretical decomposition analysis. Appl. Energy 2014, 129, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.L.; Zhang, Y.J.; Wang, B. The impact of urbanization on residential energy consumption in China: An aggregated and disaggregated analysis. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 75, 220–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
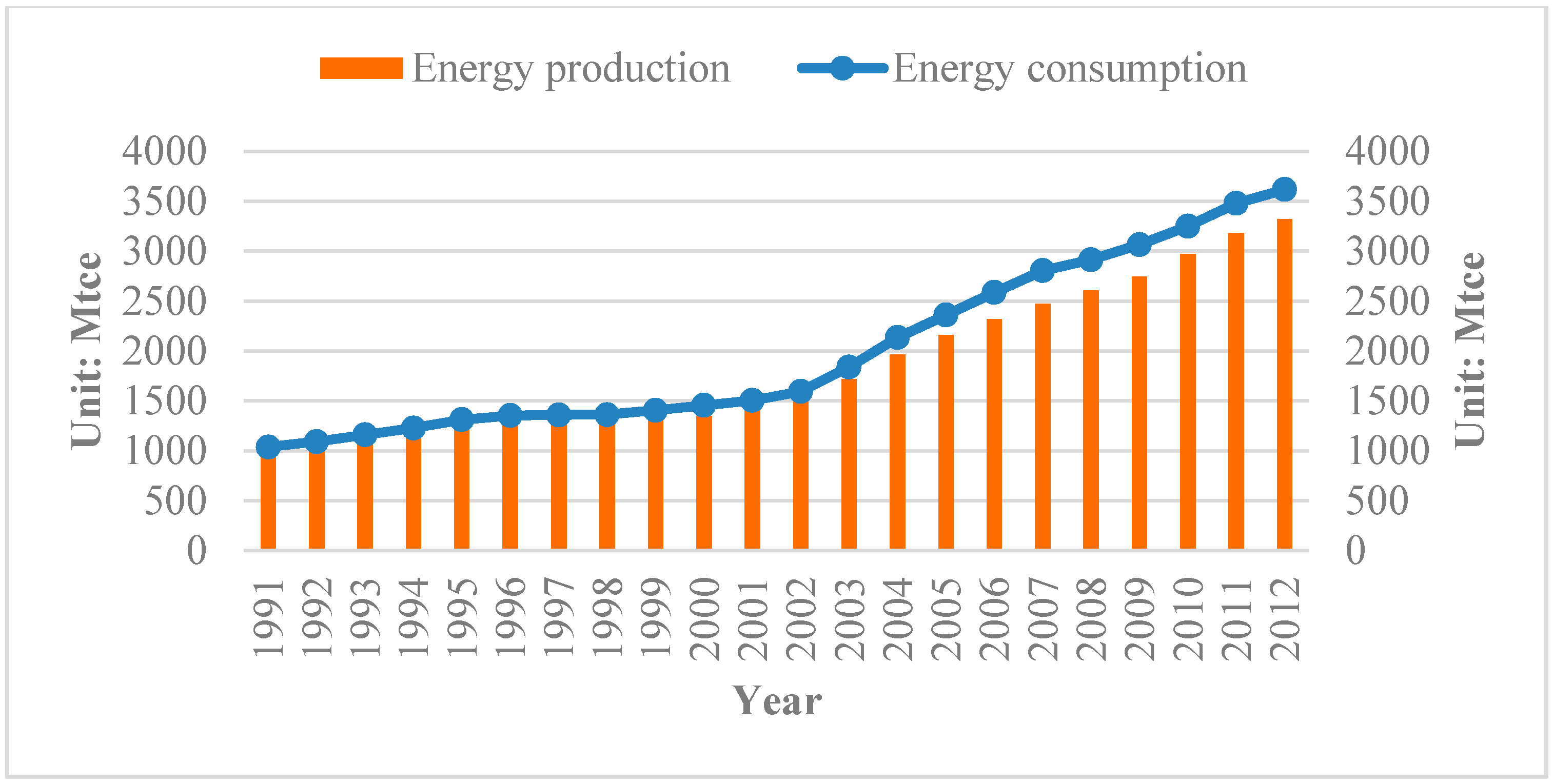
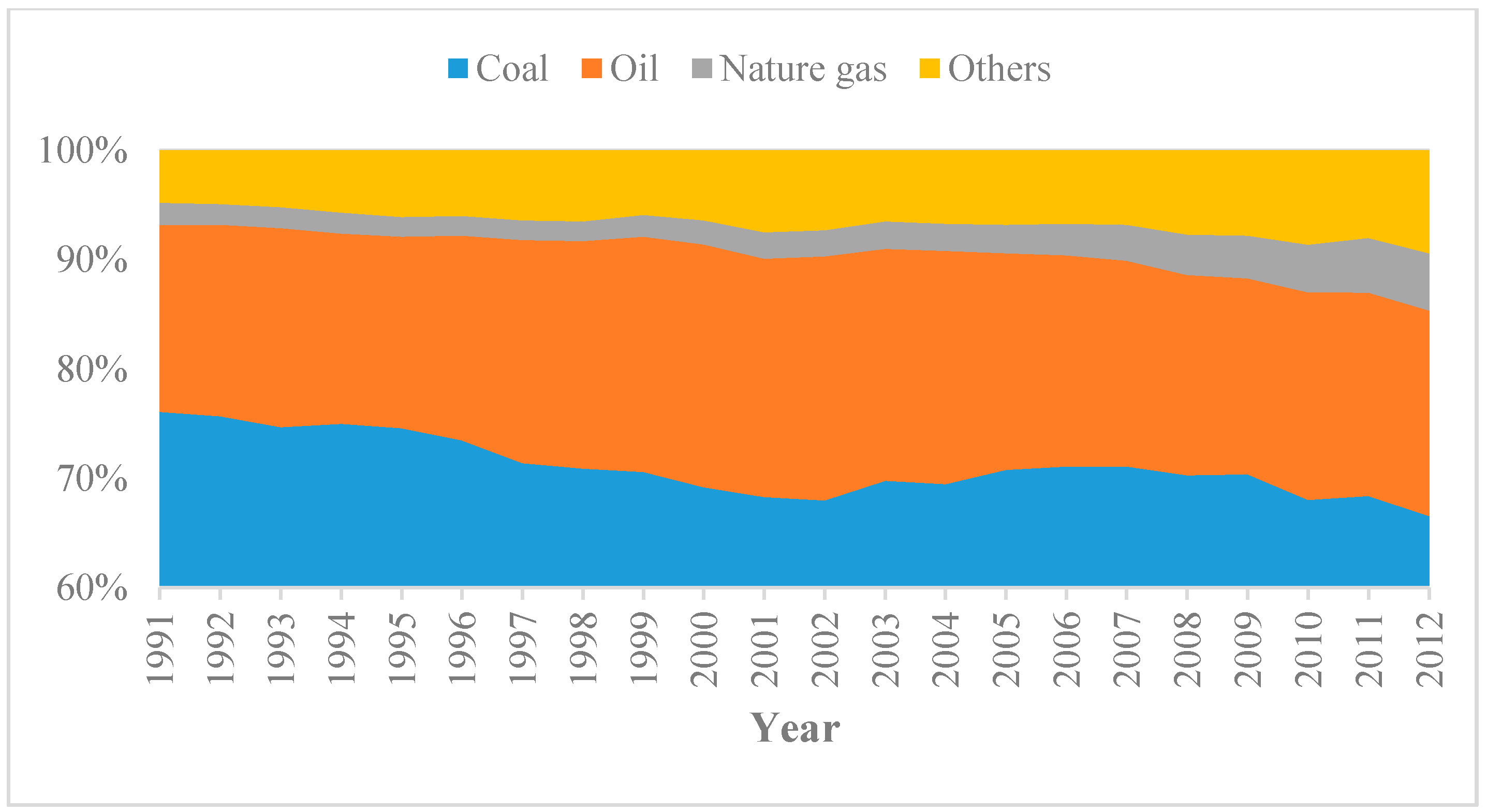


| Factor | Value (Mtce) | Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| 74.32 | 4.27% | |
| 3.30 | 0.19% | |
| −989.01 | −56.87% | |
| 3436.40 | 197.61% | |
| −311.93 | −17.94% | |
| 124.51 | 7.16% | |
| −37.99 | −2.19% | |
| −560.58 | −32.24% |
| Sector | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.01 | −0.40 | −25.17 | 72.40 | 0.97 | −0.01 | 18.08 | −22.35 |
| 2 | 2.97 | 19.72 | −598.06 | 1720.63 | 23.04 | −0.13 | 429.61 | −531.06 |
| 3 | 0.22 | 1.37 | −17.13 | 49.27 | 0.66 | −0.01 | 12.30 | −15.21 |
| 4 | 4.81 | 35.74 | −92.08 | 264.92 | 3.54 | −0.02 | 66.14 | −81.76 |
| 5 | 0.97 | −0.63 | −18.26 | 52.52 | 0.70 | −0.01 | 13.11 | −16.21 |
| 6 | 3.85 | −11.30 | −97.86 | 281.55 | 3.77 | −0.02 | 70.30 | −86.89 |
| 7 | 1.71 | −2.20 | −37.06 | 106.63 | 1.43 | −0.01 | 26.62 | −32.91 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, D.; Liu, X.; Zhou, P.; Wang, Q. Decomposition Analysis of Aggregate Energy Consumption in China: An Exploration Using a New Generalized PDA Method. Sustainability 2017, 9, 685. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9050685
Zhou D, Liu X, Zhou P, Wang Q. Decomposition Analysis of Aggregate Energy Consumption in China: An Exploration Using a New Generalized PDA Method. Sustainability. 2017; 9(5):685. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9050685
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Dequn, Xiao Liu, Peng Zhou, and Qunwei Wang. 2017. "Decomposition Analysis of Aggregate Energy Consumption in China: An Exploration Using a New Generalized PDA Method" Sustainability 9, no. 5: 685. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9050685
APA StyleZhou, D., Liu, X., Zhou, P., & Wang, Q. (2017). Decomposition Analysis of Aggregate Energy Consumption in China: An Exploration Using a New Generalized PDA Method. Sustainability, 9(5), 685. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9050685





