Impacts of Global Warming and Sea Level Rise on Service Life of Chloride-Exposed Concrete Structures
Abstract
:1. Introduction
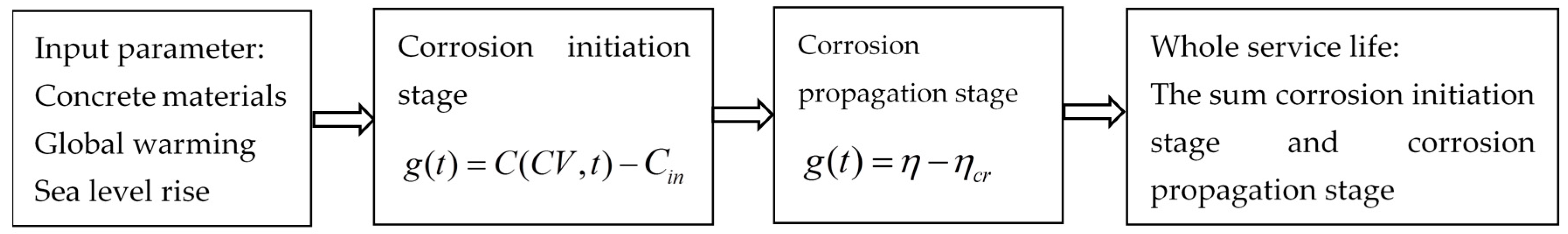
2. Methods and Model
2.1. Corrosion Initiation Due to Chloride Ingress
2.2. Corrosion Propagation Stage
2.3. Summary of Service Life Prediction Model
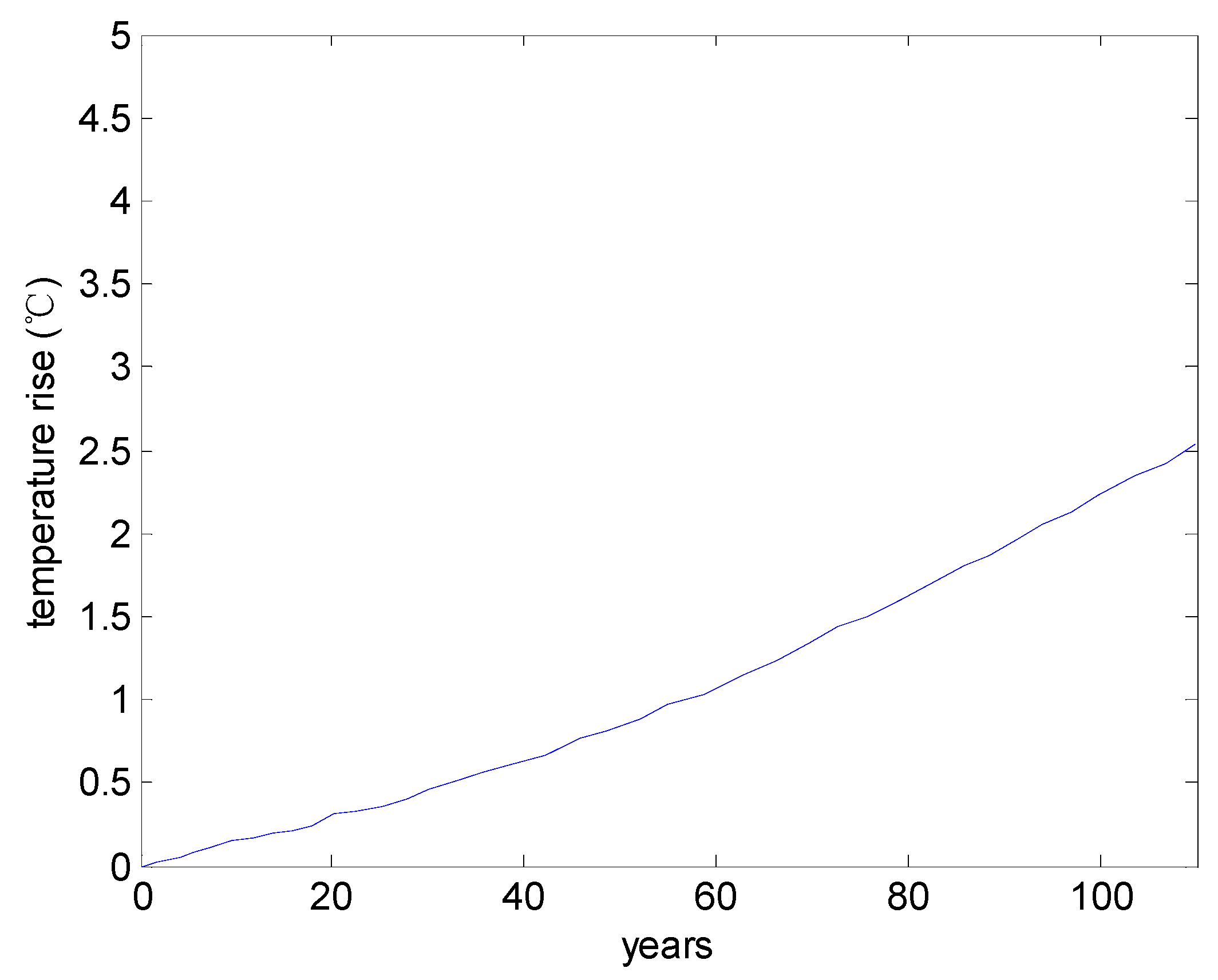
3. Illustrative Examples
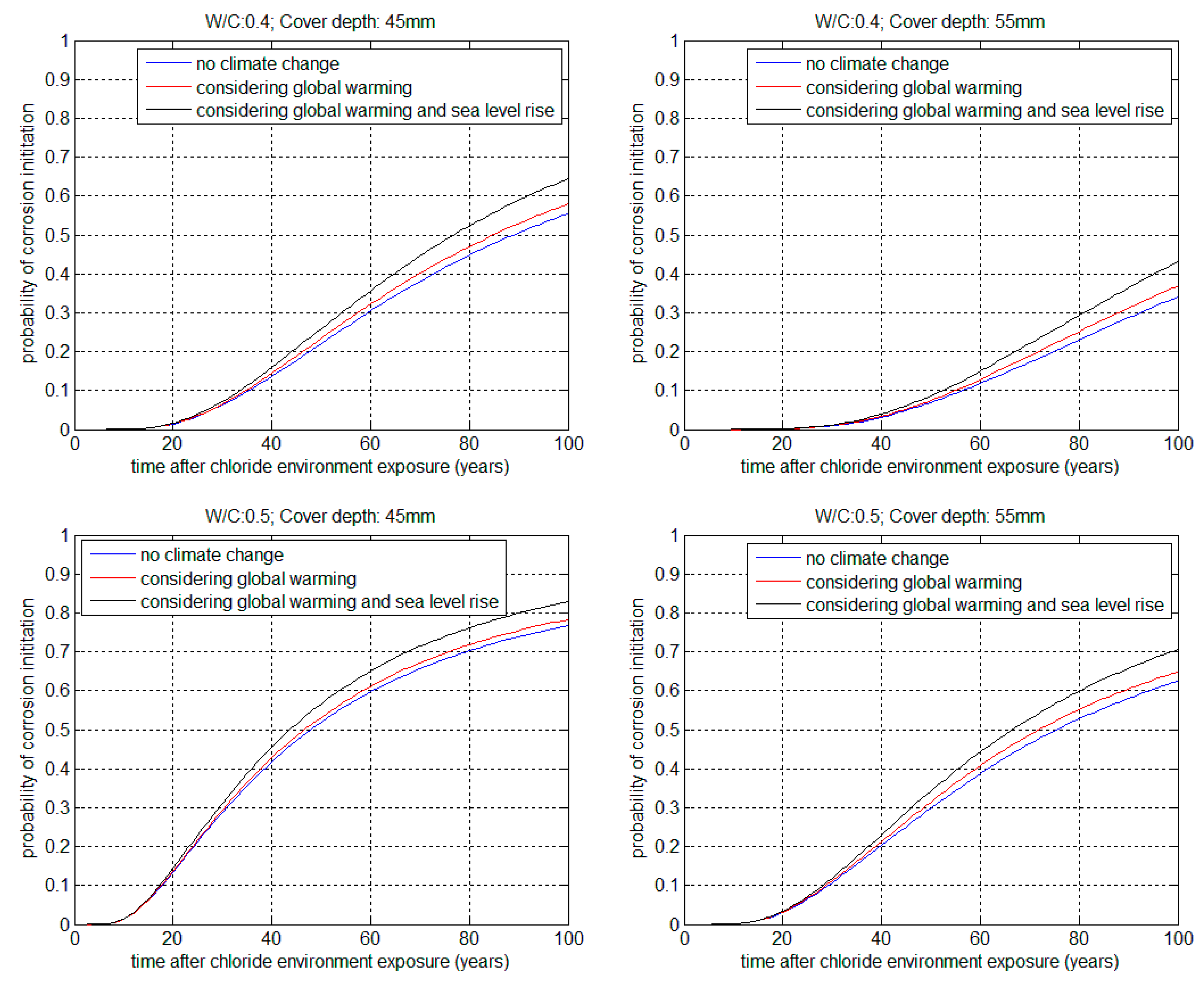
3.1. Service Life in Corrosion Initiation Stage
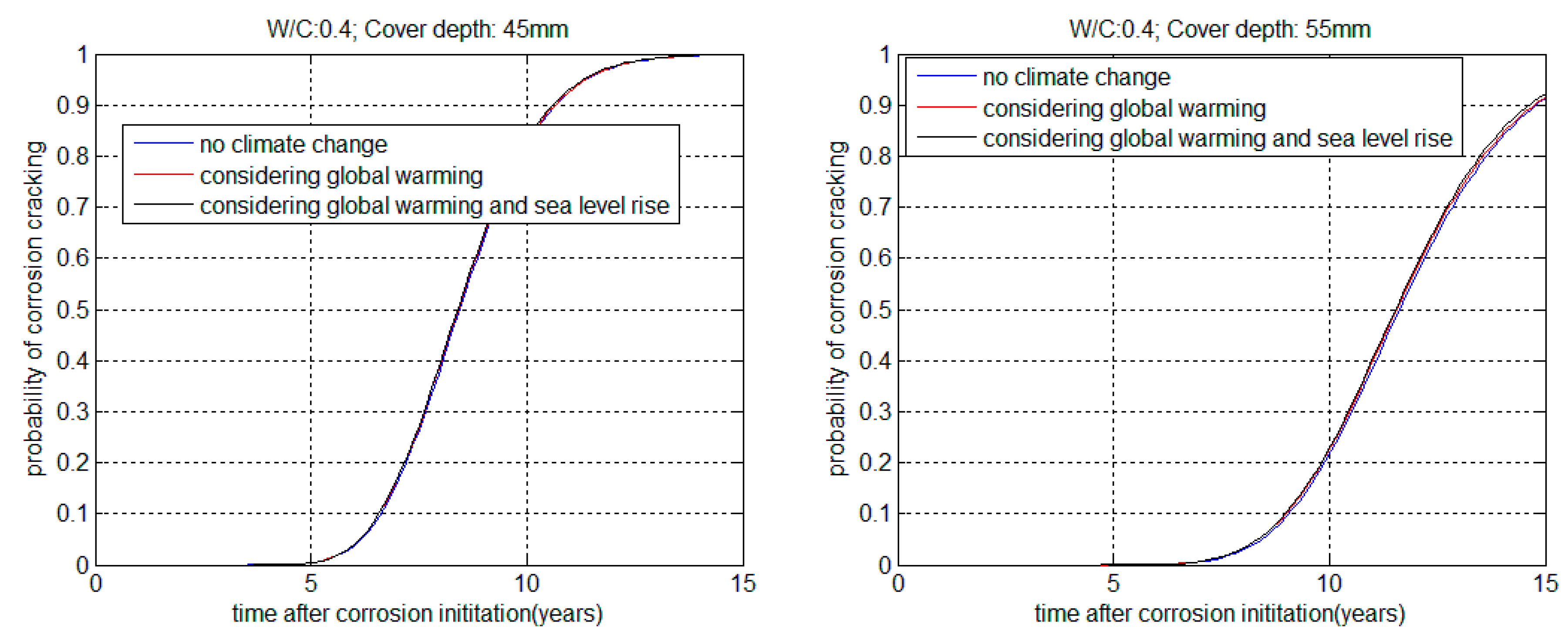
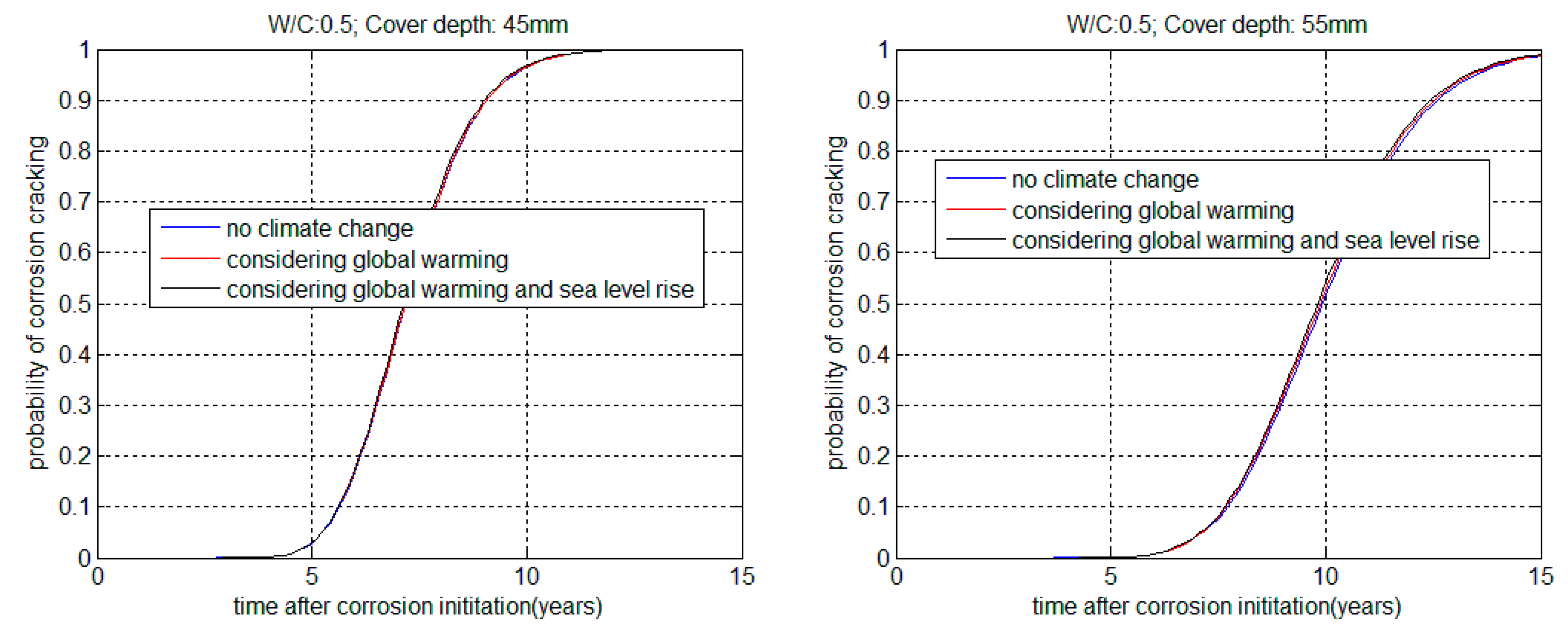
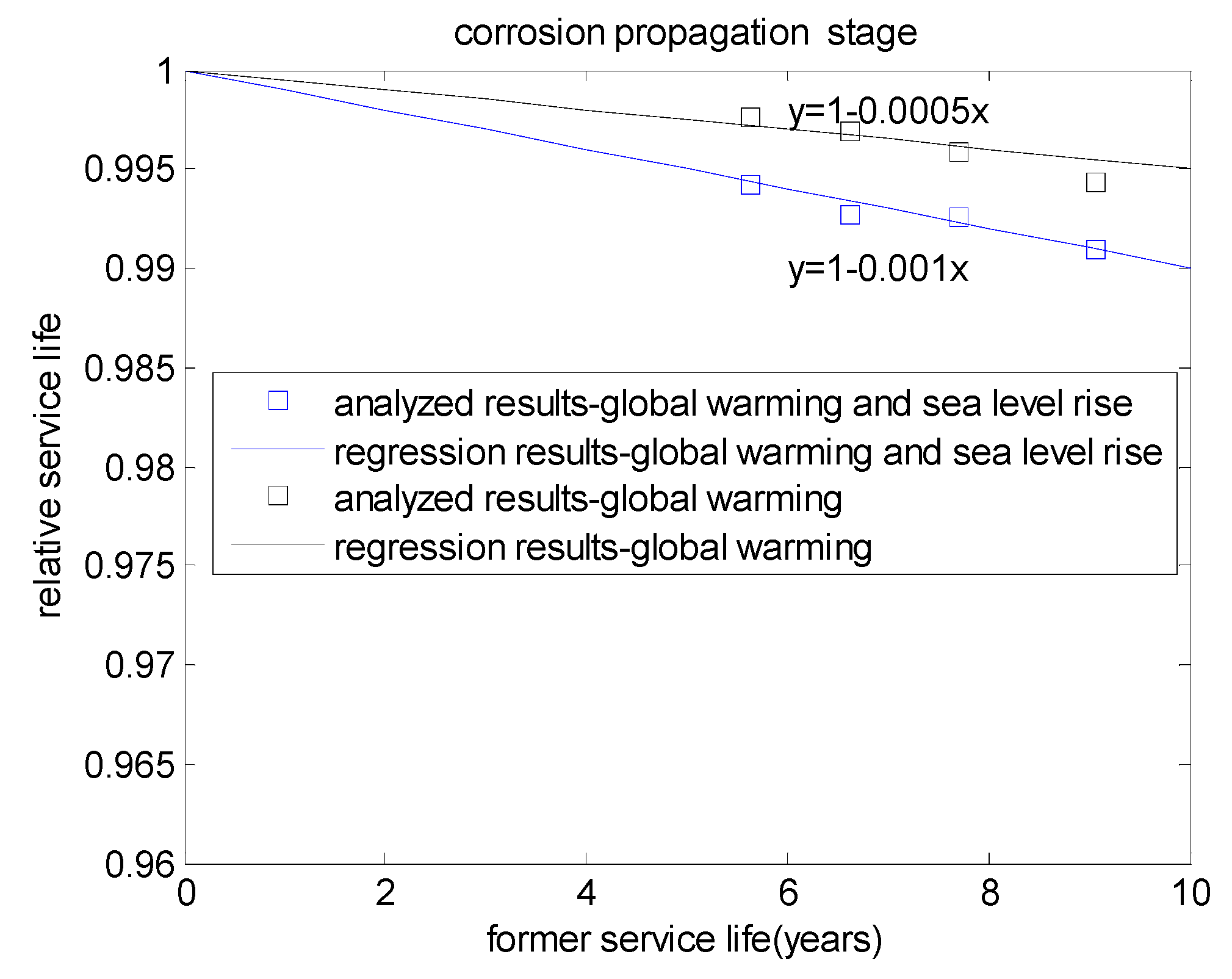
3.2. Service Life in Corrosion Propagation Stage
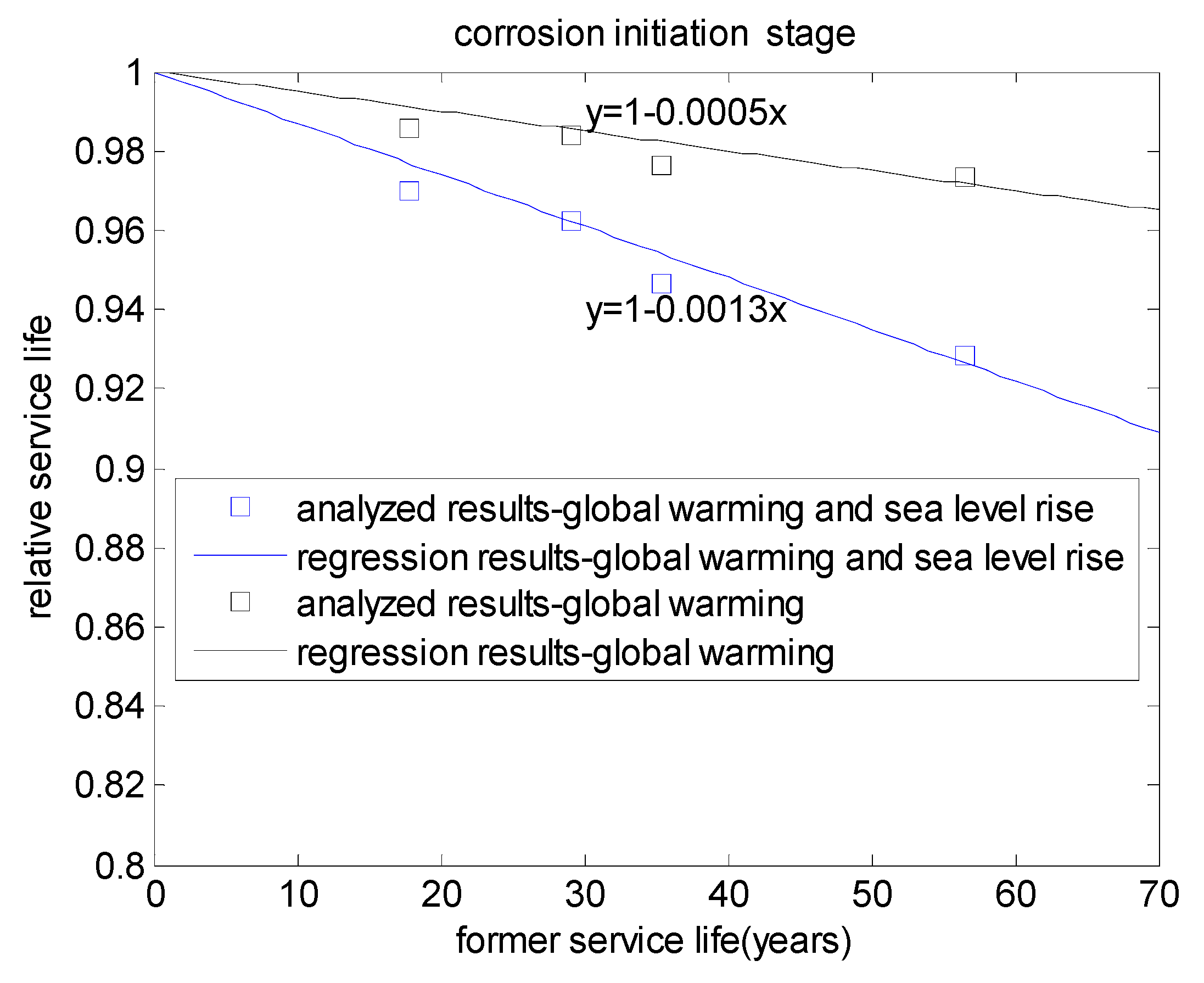
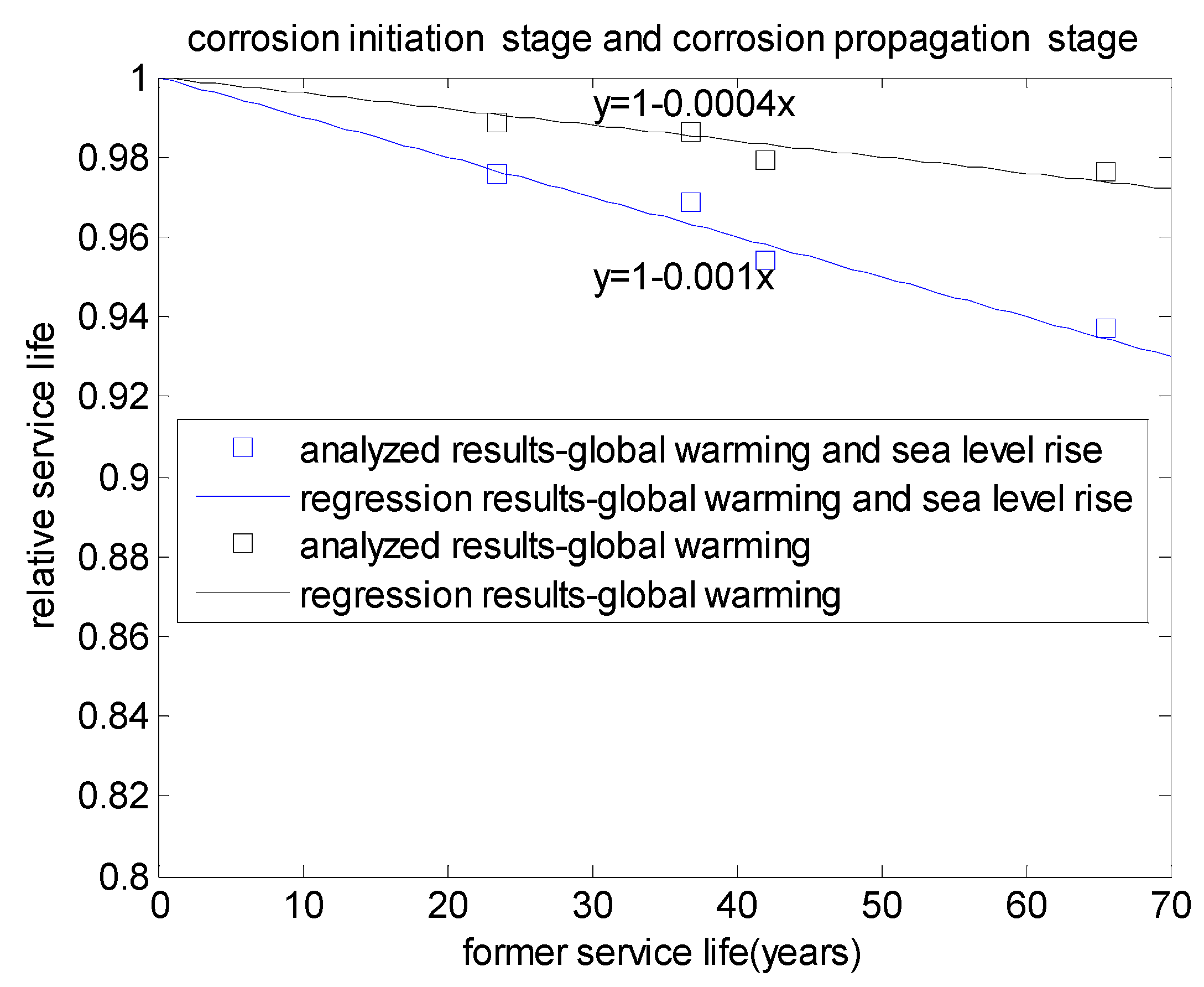
3.3. Whole Effects of Global Warming and Sea Level Rise on Service Life
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Al-Khaja, W.A. Influence of temperature, cement type and level of concrete consolidation on chloride ingress in conventional and high-strength concretes. Constr. Build. Mater. 1997, 11, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Perez, B.; Zibara, H.; Hooton, R.D.; Thomas, M.D.A. A study of the effect of chloride binding on service life predictions. Cem. Concr. Res. 2000, 30, 1215–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.P. Engineering expression of the ClinConc model for prediction of free and total chloride ingress in submerged marine concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2008, 38, 1092–1097. [Google Scholar]
- Conciatori, D.; Laferriere, F.; Bruhwiler, E. Comprehensive modeling of chloride ion and water ingress into concrete considering thermal and carbonation state for real climate. Cem. Concr. Res. 2010, 40, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conciatori, D.; Sadouki, H.; Bruhwiler, E. Capillary suction and diffusion model for chloride ingress into concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2008, 38, 1401–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Mahadevan, S. Chloride-induced reinforcement corrosion and concrete cracking simulation. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2008, 30, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, K.A.T.; Stewart, M.G. Structural reliability of concrete bridges including improved chloride-induced corrosion models. Struct. Saf. 2000, 22, 313–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, R.H.; Tae, S.H.; Yang, K.H.; Kim, T.H.; Roh, S.J. Analysis of Lifecycle CO2 Reduction Performance for Long-Life Apartment House. Environ. Prog. Sustain. 2015, 34, 555–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demis, S.; Efstathiou, M.P.; Papadakis, V.G. Computer-aided modeling of concrete service life. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2014, 47, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cusson, D.; Lounis, Z.; Daigle, L. Benefits of internal curing on service life and life-cycle cost of high-performance concrete bridge decks—A case study. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2010, 32, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.H.; Chae, C.U.; Kim, G.H.; Jang, H.J. Analysis of CO2 Emission Characteristics of Concrete Used at Construction Sites. Sustainability 2016, 8, 348–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Den Heede, P.V.; Maes, M.; De Belie, N. Influence of active crack width control on the chloride penetration resistance and global warming potential of slabs made with fly ash + silica fume concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 67, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Medeiros-Junior, R.A.; de Lima, M.G.; de Medeiros, M.H.F. Service life of concrete structures considering the effects of temperature and relative humidity on chloride transport. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2015, 17, 1103–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastidas-Arteaga, E.; Chateauneuf, A.; Sanchez-Silva, M.; Bressolette, P.; Schoefs, F. Influence of weather and global warming in chloride ingress into concrete: A stochastic approach. Struct. Saf. 2010, 32, 238–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastidas-Arteaga, E.; Stewart, M.G. Damage risks and economic assessment of climate adaptation strategies for design of new concrete structures subject to chloride-induced corrosion. Struct. Saf. 2015, 52, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.M.; Stewart, M.G.; Nguyen, M. Impact of climate change on corrosion and damage to concrete infrastructure in Australia. Clim. Chang. 2012, 110, 941–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, M.G.; Wang, X.M.; Nguyen, M. Climate change adaptation for corrosion control of concrete infrastructure. Struct. Saf. 2012, 35, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, S.J.; Na, U.J.; Park, S.S.; Jung, S.H. Service life prediction of concrete wharves with early-aged crack: Probabilistic approach for chloride diffusion. Struct. Saf. 2009, 31, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Life-365 Service Life Prediction Model. 2014. Available online: http://www.life-365.org/ (accessed on 10 March 2017).
- Houghton, J.T.; Ding, Y.; Griggs, D.J.; Noguer, M.; van der Linden, P.J.; Dai, X.; Maskell, K.; Johnson, C.A. Climate Change 2001: The Scientific Basis; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Bruun, P. Review of conditions for uses of the Bruun rule of erosion. Coast. Eng. 1983, 7, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranasinghe, R.; Callaghan, D.; Stive, M.J.F. Estimating coastal recession due to sea level rise: Beyond the Bruun rule. Clim. Chang. 2012, 110, 561–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, W.Y.; Yoon, Y.S.; Sohn, Y.M. Predicting the remaining service life of land concrete by steel corrosion. Cem. Concr. Res. 2003, 33, 663–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, M.T.; Jin, W.L.; Yang, R.J.; Huang, N.M. Predeterminate model of corrosion rate of steel in concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2005, 35, 1827–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Meng, H.; Xue, S.G. FEM analysis on the crack process of concrete cover induced by non-uniform corrosion of re-bar. J. Xi’an Univ. Archit. Technol. 2011, 43, 747–775. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.X.; Jin, W.L. Steel Corrosion-Induced Concrete Cracking; China Science Publishing: Beijing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Park, K.B.; Wang, X.Y. Effect of Climate Change on Service Life of High Volume Fly Ash Concrete Subjected to Carbonation—A Korean Case Study. Sustainability 2017, 9, 157–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.W.; Lee, C.H.; Ann, K.Y. Factors influencing chloride transport in concrete structures exposed to marine environments. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2008, 30, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, P.F.; Chastre, C.; Nunes, A. Carbonation service life modelling of RC structures for concrete with Portland and blended cements. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2013, 37, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, P.F.; Costa, A. Service life of RC structures: Carbonation induced corrosion. Prescriptive vs. performance-based methodologies. Constr. Build. Mater. 2010, 24, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weyers, R.E. Service life model for concrete structures in chloride laden environments. ACI Mater. J. 1998, 95, 445–453. [Google Scholar]
- García-Segura, T.; Yepes, V.; Alcalá, J. Life cycle greenhouse gas emissions of blended cement concrete including carbonation and durability. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2014, 19, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Exposure Class | Mean (μA/cm2) | Standard Deviation (μA/cm2) | Distribution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cl1 wet-rarely dry | 0.345 | 0.258 | lognormal |
| Cl2 cyclic wet dry | 2.586 | 1.724 | lognormal |
| Cl3 airborne sea water | 2.586 | 1.724 | lognormal |
| Cl4 submerged | - | - | - |
| Cl5 tidal zone | 6.035 | 3.448 | lognormal |
| Material Properties | Environmental Conditions | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water to Cement Ratios | Concrete Cover Depth | Diameter of Steel Rebar (mm) | Exposure Class | Distance from Coast | Slope of Beach | Initial Temperature (°C) |
| 0.4, 0.5 | 45 mm, 55 mm | 16 | Cl3 airborne sea water | 500 m | 1/100 | 20 |
| Parameter | Mean | Coefficient of Variance | Distribution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Concrete cover depth () | 45 mm | 0.2 [7] | Normal |
| 55 mm | |||
| Chloride diffusion coefficient | 0.2 [7] | Normal | |
| Surface chloride content | 0.1 [18] | Normal | |
| Time exponent | 0.2 | 0.2 [18] | Normal |
| Threshold chloride content | 1.2 | 0.2 [18] | Normal |
| 28 days’ compressive strength (MPa) | [22] | 0.15 [26] | Normal |
| 28 days’ tensile strength (MPa) | 0.15 [26] | Normal | |
| Rate of corrosion (μA/cm2) | 2.586 | 0.667 [16] | Lognormal |
| Sea level rise | COVmax(t) = 0.06 [16] | Normal | |
| Temperature rise | COVmax(t) = 0.06 [16] | Normal |
| W/B | Cover Depth (mm) | Service Life in the Corrosion Initiation Stage (Years) | Service Life Reduction | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No Global Warming or Sea Level Rise | With Global Warming | With Global Warming and Sea Level Rise | Effect of Global Warming | Effects of Global Warming and Sea Level Rise | ||
| 0.4 | 45 | 35.443 | 34.596 | 33.552 | 0.976 | 0.946 |
| 0.4 | 55 | 56.468 | 54.969 | 52.431 | 0.973 | 0.928 |
| 0.5 | 45 | 17.802 | 17.548 | 17.268 | 0.985 | 0.969 |
| 0.5 | 55 | 29.163 | 28.687 | 28.071 | 0.983 | 0.962 |
| W/B | Cover Depth (mm) | Service Life in the Corrosion Initiation Stage (Years) | Service Life Reduction | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No Global Warming or Sea Level Rise | With Global Warming | With Global Warming and Sea Level Rise | Effect of Global Warming | Effects of Global Warming and Sea Level Rise | ||
| 0.4 | 45 | 6.616 | 6.596 | 6.568 | 0.9969 | 0.9926 |
| 0.4 | 55 | 9.058 | 9.006 | 8.976 | 0.9942 | 0.9909 |
| 0.5 | 45 | 5.633 | 5.619 | 5.600 | 0.9976 | 0.9942 |
| 0.5 | 55 | 7.709 | 7.678 | 7.652 | 0.9958 | 0.9925 |
| W/B | Cover Depth (mm) | Service Life (Years) | Service Life Reduction | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No Global Warming or Sea Level Rise | With Global Warming | With Global Warming and Sea Level Rise | Effect of Global Warming | Effects of Global Warming and Sea Level Rise | ||
| 0.4 | 45 | 42.059 | 41.192 | 40.121 | 0.979 | 0.954 |
| 0.4 | 55 | 65.526 | 63.976 | 61.407 | 0.976 | 0.937 |
| 0.5 | 45 | 23.435 | 23.168 | 22.868 | 0.989 | 0.976 |
| 0.5 | 55 | 36.873 | 36.365 | 35.724 | 0.986 | 0.968 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, X.-J.; Wang, X.-Y. Impacts of Global Warming and Sea Level Rise on Service Life of Chloride-Exposed Concrete Structures. Sustainability 2017, 9, 460. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9030460
Gao X-J, Wang X-Y. Impacts of Global Warming and Sea Level Rise on Service Life of Chloride-Exposed Concrete Structures. Sustainability. 2017; 9(3):460. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9030460
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Xiao-Jian, and Xiao-Yong Wang. 2017. "Impacts of Global Warming and Sea Level Rise on Service Life of Chloride-Exposed Concrete Structures" Sustainability 9, no. 3: 460. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9030460
APA StyleGao, X.-J., & Wang, X.-Y. (2017). Impacts of Global Warming and Sea Level Rise on Service Life of Chloride-Exposed Concrete Structures. Sustainability, 9(3), 460. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9030460







