An Evaluation Study of Urban Development Strategy Based on of Extreme Climate Conditions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Research Method
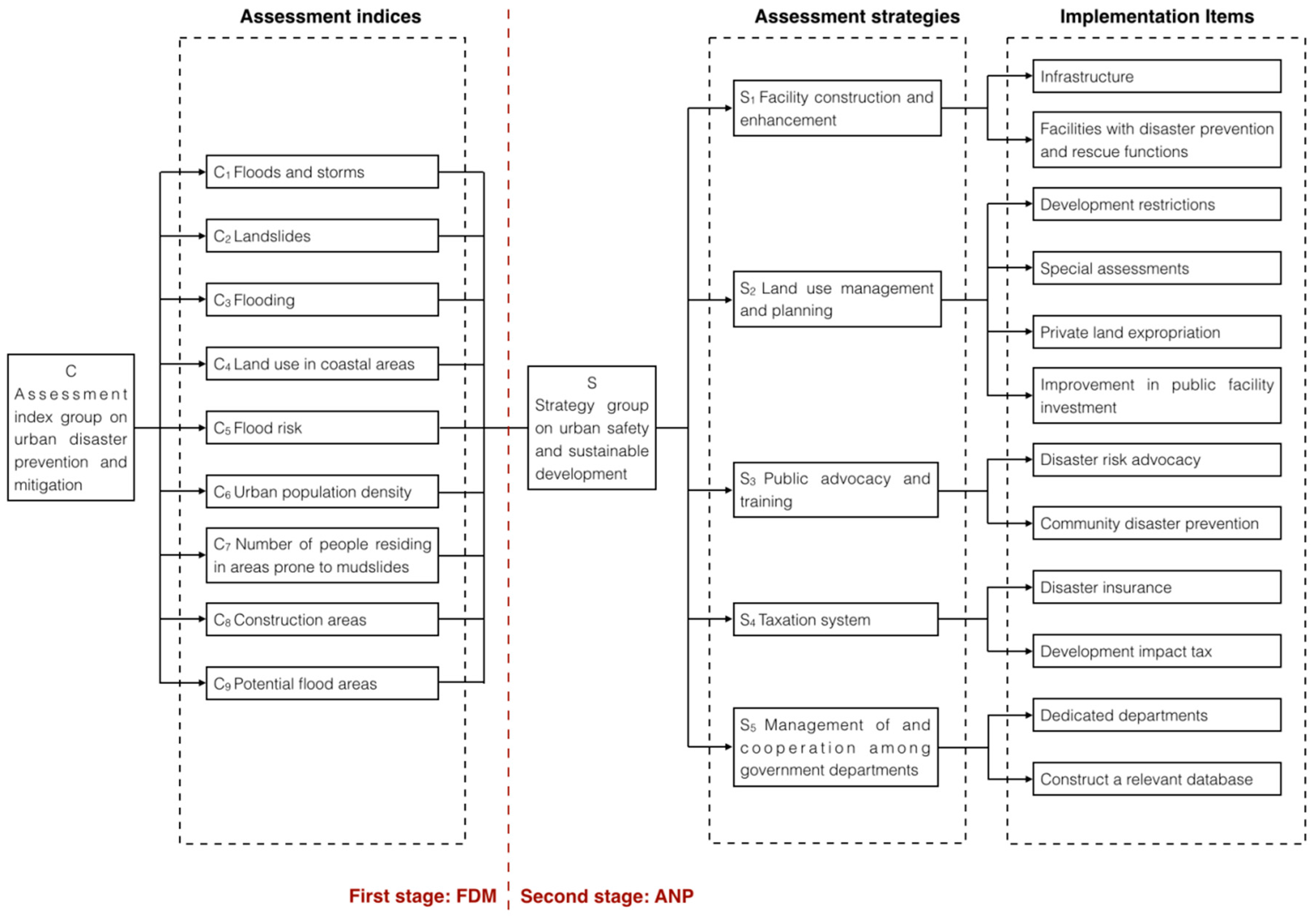
3.1. Assessment Indices of Urban Disaster Prevention and Mitigation
3.2. Proposal and Selection of Strategies for Urban Safety and Sustainable Planning
3.3. Establishment and Application of the Procedure for the Climate Responsive Strategy for Urban Planning
4. Establishing the Assessment Index System for the Strategies of Urban Disaster Prevention and Mitigation
5. Establishment of Climate Responsive Strategy for Urban Planning
6. Discussion
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Unite Nation International Strategy for Disaster Reduction (UNISDR). Words into Action: A Guide for Implementing the Hyogo Framework; UN International Strategy for Disaster Reduction: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Unite Nation World Conference on Disaster Risk Reduction. Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction 2015–2030; UN World Conference on Disaster Risk Reduction: Sendai, Japan, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Bouwer, L.M.; Bubeck, P.; Aerts, J.C.J.H. Changes in future flood risk due to climate and development in a Dutch polder area. Glob. Environ. Chang. Hum. Policy Dimens. 2010, 20, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis; Working Group I Contribution to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Satterthwaite, D. Climate change and urbanization: Effects and implications for urban governance. In Proceedings of the United Nations Expert Group Meeting on Population Distribution, Urbanization, Internal Migration and Development, New York, NY, USA, 21–23 January 2008; pp. 21–23.
- Karl, T.R.; Knight, R.W. Secular trends of precipitation amount, frequency, and intensity in the United States. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1998, 79, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, B.N.; Venugopal, V.; Sengupta, D.; Madhusoodanan, M.S.; Xavier, P.K. Increasing trend of extreme rain events over India in a warming environment. Science 2006, 314, 1442–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, K.M.; Wu, H.T. Detecting trends in tropical rainfall characteristics, 1979–2003. Int. J. Climatol. 2007, 27, 979–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.-M.; Chan, S.-L.; Chen, Y.-J.; Pai, J.-T.; Kang, C.-C. The National Land Planning on Globalization and Climate Change; Ministry of Science and Technology, R.O.C.: Taipei, Taiwan, 2007.
- Ho, M.-C.; Chan, S.-L.; Lin, C.-Y.; Huang, G.C. Early-Stage Research Project on the Disaster Patterns and Impact Assessment of Urban Cities in Taiwan under the Effects of Climate Change; Architecture and Building Research Institute, Ministry of the Interior: Taipei, Taiwan, 2008.
- Mileti, D.S. Disasters by Design; Joseph Henry Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Maa, S.-Y. A Study for Establishing a Structure of Integrated Emergency/Disaster Management System. Ph.D. Thesis, Graduate Institute of Building and Planning, National Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.-C.; Chen, H.-L. Exploring Flooding Vulnerability during Urban Developing Process: Learning from the Formation of Taipei Basin Floods. J. City Plan. 2007, 34, 293–315. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, S.-L.; Huang, S.-L.; Wang, S.-H. On the risk zoning of flood hazard in Taipei areas. J. City Plan. 2003, 30, 263–280. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, C.-H.; Tsao, T.-C.; Chi, C.-C.; Tseng, C.-C. The Study of Zoning in Debris-Flow Geologically-Sensitive Area. Sinotech Eng. 2014, 124, 61–70. [Google Scholar]
- Kundzewicz, Z.W. Non-structural flood protection and sustainability. Water Int. 2002, 27, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.-Y.; Lee, Y.-S. Applying Non-Structural Mitigation Measures to Space Planning and Management. J. Archit. 2010, 72, 169–186. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, B.-S.; Pai, J.-T. Flood Adaptation Strategic Planning in Response to Climate Chang. J. Disaster Manag. 2012, 1, 81–100. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.-P.; Ho, Y.-F.; Yang, H.-M. Prediction and Analysis of Percentage of Impervious Area in Taichung City. J. City Plan. 2005, 32, 333–353. [Google Scholar]
- Arnold, C.L.; Gibbons, C.J. Impervious surface coverage—The emergence of a key environmental indicator. J. Am. Plan. Assoc. 1996, 62, 243–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, Q.; Shao, M.-A. Influence of different drainage conditions on soil erosion and nutrient loss of slope land. Sci. Soil Water Conserv. 2006, 3, 21–25. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, K.-M.; Lin, H.-T.; Sun, C.-Y.; Liu, C.-C.; Cheng, R.-L. Analysis, Prediction, and Control of the Artificial Cover Ratio in Cities in Taiwan. J. City Plan. 2011, 8, 171–193. [Google Scholar]
- Bowler, D.E.; Buyung-Ali, L.; Knight, T.M. Urban greening to cool towns and cities: A systematic review of the empirical evidence. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2010, 97, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.-J.; Chiu, Y.-H. An Investigation into the Effects of Plants on Outdoor Thermal Comfort. J. Archit. 2015, 92, 43–60. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, P.-Y. The Planning of Disasters-Rescuing and Refusing Space While in the Disasters of Earthquake from the Viewpoint of Neighborhood Unit. Master’s Thesis, Graduate Institute of Urban Planning, National Cheng Kung University, Tainan, Taiwan, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, W.-I.; Ho, M.-C. Operating Manual for Urban Planning and Disaster Prevention; Architecture and Building Research Institute, Ministry of the Interior: Taipei, Taiwan, 2000.
- Ho, M.-C.; Lee, Y.-L.; Tai, C.-A. Public Participation in Urban Disaster Prevention Spatial System Planning—Application of Google Earth. J. Archit. 2009, 68, 89–102. [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa, A. The Max-Min Delphi Method and Fuzzy Delphi Method via Fuzzy Integration. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 1993, 55, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeng, T.-B. Fuzzy Assessment Model for Maturity of Software Organization in Improving Its Staff’s Capability. Master’s Thesis, Graduate Institute of Information Management, National Taiwan University of Science and Technology, Taipei, Taiwan, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Saaty, T.L. The Analytic Network Process; RWS Publications: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Saaty, T.L. Theory and Applications of the Analytic Network Process; RWS Publications: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.-Y.; Huang, Y.-S. The Establishment of Vulnerability Evaluation Indexes: The Case of Shueili Township, Nantou, Taiwan. J. City Plan. 2011, 38, 195–218. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, M.-C.; Hong, H.-C.; Chan, S.-L.; Wang, H.-Y. Compilation and Revision of the Handbook of Urban Prevention Spatial System; Architecture and Building Research Institute, Ministry of the Interior: Taipei, Taiwan, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Schwab, J.; Topping, K.C.; Eadie, C.C.; Deyle, R.E.; Smith, R.A. Planning for Post-Disaster Recovery and Reconstruction; American Planning Association: Chicago, IL, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Pauleit, S.; Ennos, R.; Golding, Y. Modeling the environmental impacts of urban land use and land cover change—A study in Merseyside, UK. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2005, 71, 295–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.; Levermore, G. Designing urban spaces and buildings to improve sustainability and quality of life in a warmer world. Energy Policy 2008, 36, 4558–4562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-J.; Tsai, N.-Y.; Yang, Y.-Y.; Chung, P.-J.; Shen, C.-W.; Cheng, C.-T. Convergence between Geological Act and Space Related Regulations toward Hazard Mitigation: A Preliminary Study. J. Disaster Manag. 2013, 2, 19–40. [Google Scholar]
- Cutter, S.L.; Barnes, L.; Berry, M.; Burton, C.; Evans, E.; Tate, E.; Webb, J. A place-based model for understanding community resilience to natural disasters. Glob. Environ. Chang. Hum. Policy Dimens. 2008, 18, 598–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wamsler, C.; Brink, E. Planning for Climatic Extremes and Variability: A Review of Swedish Municipalities’ Adaptation Responses. Sustainability 2014, 6, 1359–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Geneletti, D. How are climate change concerns addressed by spatial plans? An evaluation framework, and an application to Indian cities. Land Use Policy 2015, 42, 210–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
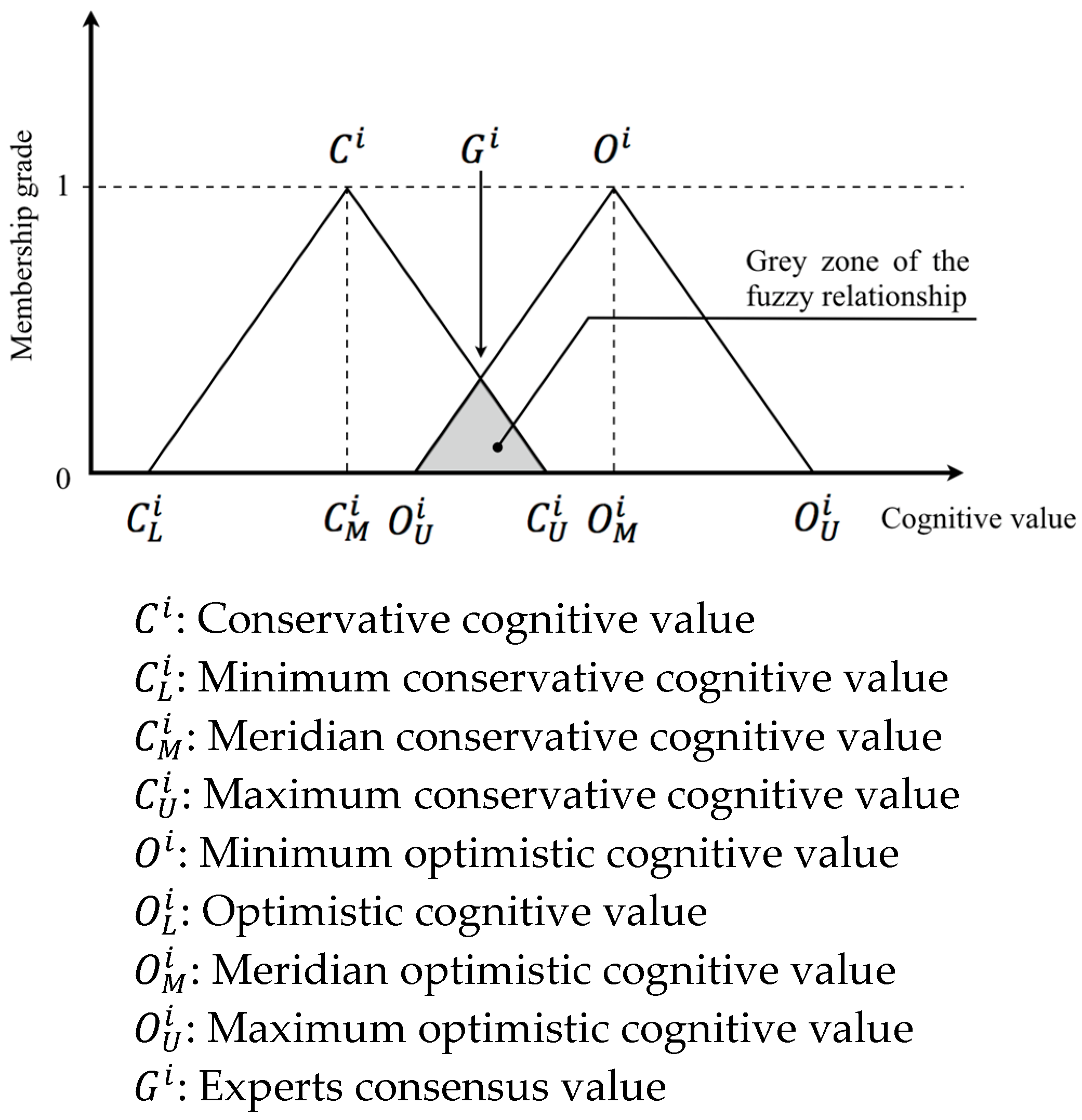
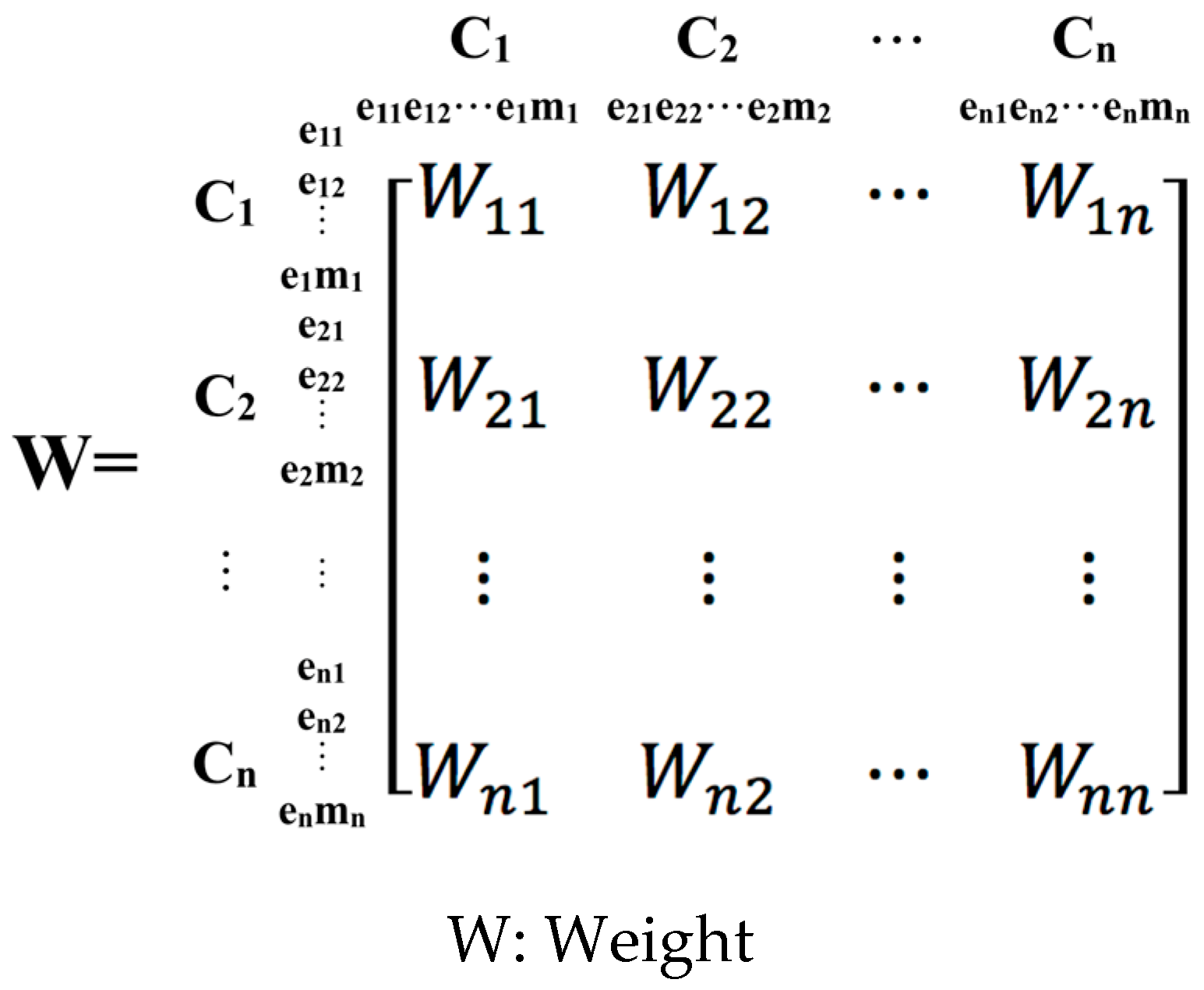
| Conference | Country/Location | Year | Outline of the Main Content |
|---|---|---|---|
| First WCNDR | Japan/Yokohama | 1994 |
|
| Second WCNDR | Japan/Kobe | 2005 |
|
| Third WCNDR | Japan/Sendai | 2015 |
|
| Climate Change Phenomenon | Current Influence/Vulnerability | Social Factors and Related Facilities | Areas/Group under Influence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tropical cyclone/storm | Casualties and damages caused by floods and storms; Increased vulnerability of coastal areas; economic loss; transportation; tourism industry; infrastructures (e.g., energy and transport facilities); and disaster insurance | Land use and population density in flood risk areas; flood prevention; and government response | Residents living in coastal areas; areas with limited capability and resources; infrastructure; and disaster insurance |
| Extreme rainfall/torrential floods | Soil erosion and landslides; floods; inhabited areas; transportation system; and infrastructure | Basic drainage systems; land development regulation (flood plain, potential flooding area, development regulation of geologically sensitive slope area) | Residential areas in geologically sensitive slopes and potential flood area |
| Heat wave/cold front | Influences on health, social stability, energy, water resource, people’s other basic needs (e.g., water, food, and infrastructure) (e.g., energy facility) | Architectural design and internal temperature control; social environment; and government responsiveness | Mid-latitude areas; older adults; children, and people living in poverty |
| Drought | Water supply; people’s livelihoods; electricity infrastructure; population migration; and water transportation | Water supply system; distribution of limited water resources; energy demand; and limited water supply | The first, second and third level industries in Taiwan |
| Temperature | Energy demand and cost; air quality in urban cities; permafrost thawing; tourism and entertainment; retail consumption; people’s livelihoods; and ice melting and loss | Population and economic changes; land use changes; technological innovation; air pollution; and government responsiveness | The influences are widespread, with high-population-density areas in particular being required to adapt to the changes in resources and the environment |
| Saltwater intrusion | Impacts on water infrastructure | Flow of groundwater | Coastal and lowland areas, particularly areas with limited resources and capability |
| Rising sea levels | Coastal land use; flood risk; flooding; and water infrastructure | Coastal areas, and development of and land use in inhabited areas | Coastal and lowland areas, specially areas with limited resources and capability |
| Abrupt climate change | Disaster potential analysis | Population, economic, and technological changes; and system development | Numerous areas and groups |
| Initiative | Definition and Description | Example | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mitigation | Structural mitigation | Prevent disasters by reducing the risks of human and architectural disasters and by strengthening the architecture | Dyke and flood control channel |
| Basic structural mitigation | Strengthen urban infrastructures | Hydropower system and sewer system | |
| Non-structural mitigation | Disperse crowds and minimize loss in built environments | Land planning and management and disaster insurance | |
| Risk reduction | Risk reduction is a goal in disaster mitigation | Disaster insurance | |
| Prevention | Prevent disasters such as fires from occurring | Relevant regulations on architecture, fire control, and labour safety and health. | |
| Preparedness | Develop emergency response and management capacity in advance to offer timely and effective emergency responses in the event of a disaster | Analysis of potential hazards, risk analysis and detection, early warning and evacuation systems, maintenance of emergency supplies and communication systems, and community education and training | |
| Response | Immediately rescue people, mitigate loss, and strengthen effective actions before, during, and after disasters | Disaster forecasting, casualty evacuations, settlement and emergency treatment of victims, search and rescue initiatives, and property safety and protection | |
| Recovery | Restore or reconstruct urban facilities and systems in stages | Architectural reconstruction, restoration of life support system (short term), and restoration of industrial and living functions (long term) | |
| Strategy for Spatial Planning and Management | Adaptation Strategy |
|---|---|
| Land use planning and management |
|
| Infrastructure |
|
| Disaster prevention facilities |
|
| Staging and partitioning |
|
| Risk communication |
|
| Taxation system |
|
| Public education and community disaster prevention |
|
| Cooperation mechanisms of government |
|
| Assessed Subject | Assessment Item | Assessment Index | Index Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Index Group A (natural environmental conditions) | A1 Typhoon/storm | A1-1 Flood and storm | A flood refers to an overflow of water from water bodies, such as rivers, lakes, or the ocean, in which the water body exceeds the regular water level. A storm refers to winds measuring 10 or 11 on the Beaufort scale, which is an equivalent wind speed of 88–117 km/h (48–63 NM/h or 24–33 m/s). |
| A1-2 Disease infection | Infectious diseases such as dysentery and cholera frequently breakout following disasters. | ||
| A1-3 Vulnerability of coastal areas | Vulnerability can be viewed as a function of impact, sensitivity, and adaptability. | ||
| A2 Extreme rainfall (flood) | A2-1 Landslide | Landslides are geological phenomena involving downward slope movements of the ground, often resulting from extremely heavy rainfall. | |
| A2-2 Flooding | Flooding, which can also be known as inundation, is a natural disaster caused by a flood. | ||
| A2-3 Soil erosion loss | The problems caused by soil erosion loss involved land losses and reduced productivity of agricultural lands and forest lands, in which the influences are long-term and irreversible. Soil erosion may simultaneously cause sedimentation in reservoirs, rivers, irrigation canals, and other water channels. | ||
| A3 Drought | A3-1 Water supply | Water supply refers to the supply of necessary domestic and industrial water. | |
| A3-2 Energy supply | Energy supply refers to the supply of necessary domestic and industrial energy. | ||
| A3-3 Transfer of water resources | In conditions of imbalance between water supply and demand, water resources are transferred to balance the water supply with demand. | ||
| A4 Rising sea levels | A4-1 Land use in coastal areas | Land use methods in coastal areas are influenced by rising sea levels. | |
| A4-2 Flood risk | Flood risk refers to the increased flooding risk in low-lying areas resulting from rising sea levels. | ||
| A4-3 Coastal retreat | Coastal retreat causes farmlands, villages, and land to be eroded and flooded by seawater. | ||
| Index Group B (socioeconomic environmental conditions) | B1 Characteristics of the population easily affected by disasters | B1-1 Urban population density | Urban population density is the average population of a specific unit area of land at a specific time. |
| B1-2 Death toll from disasters over the years | Number of people killed by natural disasters over the years. | ||
| B1-3 Number of people residing in areas prone to mudslides | Number of people who are residing in areas prone to mudslides. | ||
| B2 Industrial economy | B2-1 Household income | Total income per household | |
| B2-2 National workforce | The employed population refers to the population aged 15 or above and meeting the following conditions within the standard survey period (i.e., 1 year): engaged in paid employment for 6 months or longer with an annual income of ≥NT$115,000. | ||
| B3 Built environment | B3-1 Construction area | Construction area refers to the maximum horizontal projection area calculated from the centreline of the building’s outer wall or substituted construction post. | |
| B3-2 Potential flood areas | Demographic surveys are conducted to design the rainfall condition, collect topographic and geomorphologic data, and construct a hydrodynamic model for simulating potential flooding conditions while flood control facilities are operating normally. |
| Critical Assessment Indices that Passed the Threshold Value of 6.51 | Critical Assessment Indices that Did Not Pass the Threshold Value of 6.51 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | Assessment Factors | Expert Consensus Value Gi | Rank | Assessment Factors | Expert Consensus Value Gi | ||
| 1 | B3-2 | Potential flood areas | 8.50 | 10 | A2-3 | Soil erosion loss | 6.43 |
| 2 | A2-2 | Flooding | 7.52 | 11 | A3-1 | Water supply | 6.42 |
| 3 | A4-1 | Land use in coastal areas | 7.46 | 12 | B2-2 | Employed population | 6.11 |
| 4 | A1-1 | Floods and storms | 7.43 | 13 | A3-3 | Transfer of water resources | 5.94 |
| 5 | B3-1 | Construction area | 7.37 | 14 | A1-3 | Vulnerability of coastal areas | 5.88 |
| 6 | B1-1 | Urban population density | 7.34 | 15 | A3-2 | Energy supply | 5.62 |
| 7 | B1-3 | Vulnerability of coastal areas | 6.96 | 16 | A1-2 | Disease infection | 5.61 |
| 8 | A2-1 | Landslides | 6.91 | 17 | B2-1 | Household income | 5.60 |
| 9 | A4-2 | Flood risk | 6.64 | 18 | A4-3 | Coastal retreat | 5.58 |
| - | - | - | 19 | B1-2 | Death toll in disasters over the years | 5.47 | |
| Strategy Selection | Item Implementation | Item Explanation | Author/Source, Year |
|---|---|---|---|
| Facility construction and enhancement | Infrastructure |
| Bowler et al. (2010) [23]; Maa (2001) [12]; Wu and Huang (2011) [32]; Lin et al. (2005) [19] |
| Facilities with disaster prevention and rescue functions |
| Maa (2001) [12]; Ho et al. (2007) [33]; Wu and Huang (2011) [32] | |
| Land use management and planning | Development restrictions |
| Schwab et al. (1998) [34]; Bouwer et al., 2010 [3]; Pauleit et al. (2005) [35]; Wu and Lee (2010) [17]; Wu and Huang (2011) [32] |
| Special assessments |
| Schwab et al. (1998) [34]; Smith et al. (2008) [36]; Wu and Lee (2010) [17]; Wang et al. (2013) [37] | |
| Expropriation of private land |
| Schwab et al. (1998) [34]; Wu and Lee (2010) [17] | |
| Improve public facility investment |
| Schwab et al. (1998) [34]; Wu and Lee (2010) [17] | |
| Public advocacy and training | Disaster risk advocacy |
| Schwab et al. (1998) [34]; Wu and Lee (2010) [17]; Wu and Huang (2011) [32] |
| Community disaster prevention |
| Schwab et al. (1998) [34]; Cutter et al. (2008) [38]; Ho et al. (2007) [33]; Wu and Lee (2010) [17] | |
| Taxation system | Disaster insurance |
| Schwab et al. (1998) [34]; Wu and Lee (2010) [17]; Wu and Huang (2011) [32] |
| Development impact tax |
| Wu and Lee (2010) [17]; Wu and Huang (2011) [32] | |
| Management of and cooperation among government departments | Dedicated government departments |
| Schwab et al. (1998) [34]; Wu and Lee (2010) [17]; Wu and Huang (2011) [32] |
| Construct a relevant database |
| Schwab et al. (1998) [34]; Wu and Lee (2010) [17] |
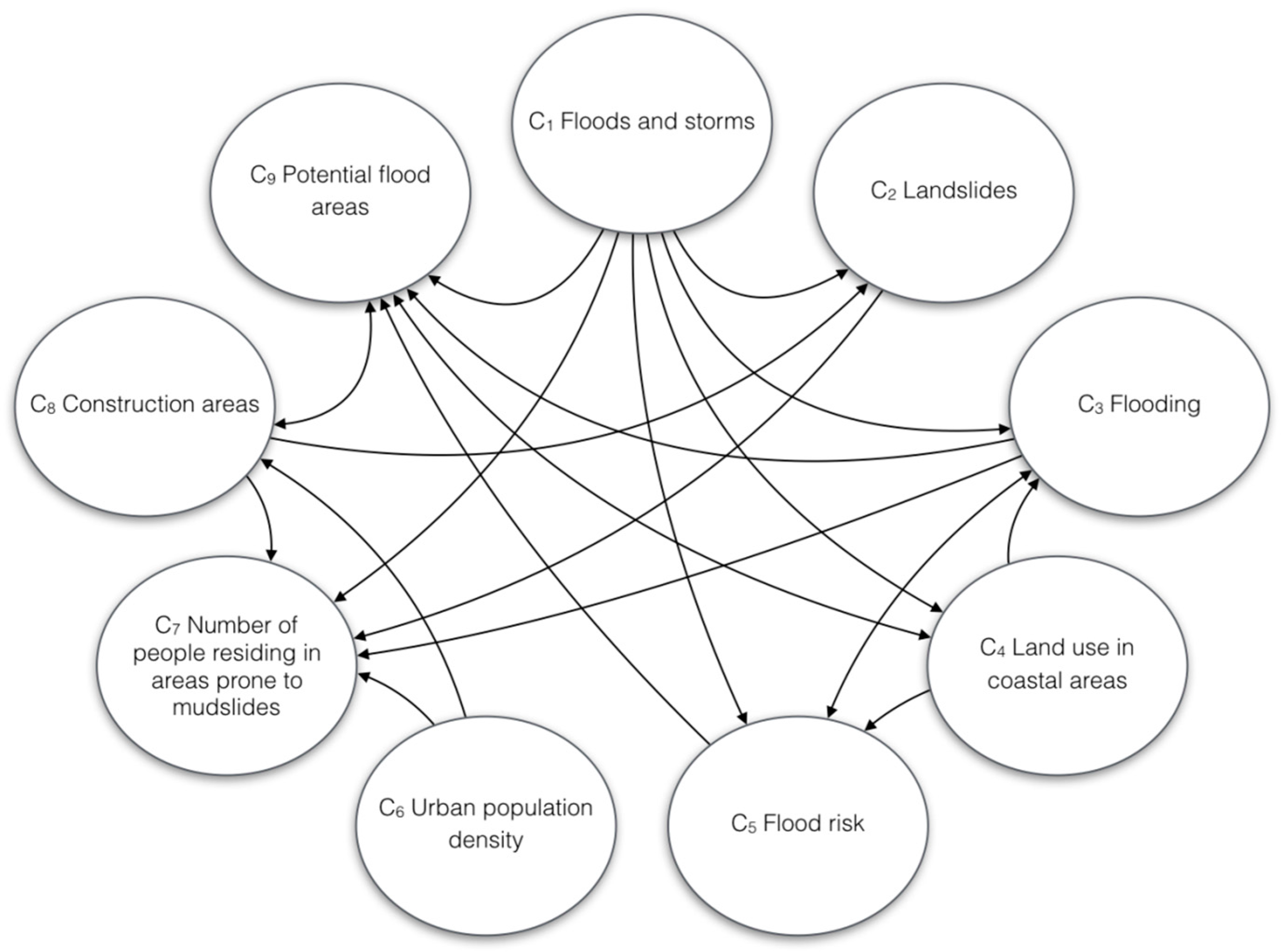
| Ranking (Importance) | Weighted Indices of Urban Disaster Prevention and Mitigation (WC) | Weighted Strategies for Urban Safety and Sustainable Planning (WANP) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Item | Weight | % | Item | Weight | % | |
| 1 | C1 Floods and storms | 0.41593 | 41.6 | S2 Land use management and planning | 0.29787 | 29.8 |
| 2 | C6 Urban population density | 0.15982 | 16.0 | S3 Public advocacy and training | 0.21140 | 21.1 |
| 3 | C4 Land use in coastal areas | 0.11414 | 11.4 | S1 Facility construction and enhancement | 0.17640 | 17.6 |
| 4 | C3 Flooding | 0.08685 | 8.7 | S5 Management of and cooperation among government departments | 0.16991 | 17.0 |
| 5 | C8 Construction areas | 0.06371 | 6.4 | S4 Taxation system | 0.14442 | 14.4 |
| 6 | C5 Flood risk | 0.05623 | 5.6 | - | - | - |
| 7 | C9 Potential flood areas | 0.04928 | 4.9 | - | - | - |
| 8 | C2 Landslides | 0.04162 | 4.2 | - | - | - |
| 9 | C7 Number of people residing in areas prone to mudslides | 0.01242 | 1.2 | - | - | - |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kao, L.-S.; Chiu, Y.-H.; Tsai, C.-Y. An Evaluation Study of Urban Development Strategy Based on of Extreme Climate Conditions. Sustainability 2017, 9, 284. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9020284
Kao L-S, Chiu Y-H, Tsai C-Y. An Evaluation Study of Urban Development Strategy Based on of Extreme Climate Conditions. Sustainability. 2017; 9(2):284. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9020284
Chicago/Turabian StyleKao, Li-Shin, Yin-Hao Chiu, and Chi-Yao Tsai. 2017. "An Evaluation Study of Urban Development Strategy Based on of Extreme Climate Conditions" Sustainability 9, no. 2: 284. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9020284
APA StyleKao, L.-S., Chiu, Y.-H., & Tsai, C.-Y. (2017). An Evaluation Study of Urban Development Strategy Based on of Extreme Climate Conditions. Sustainability, 9(2), 284. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9020284





