Longitudinal Control for Mengshi Autonomous Vehicle via Gauss Cloud Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Model and Problem Formulation
2.1. Gauss Cloud Model
2.2. Cloud Reasoning
2.2.1. Preconditioned Gauss Cloud Generators
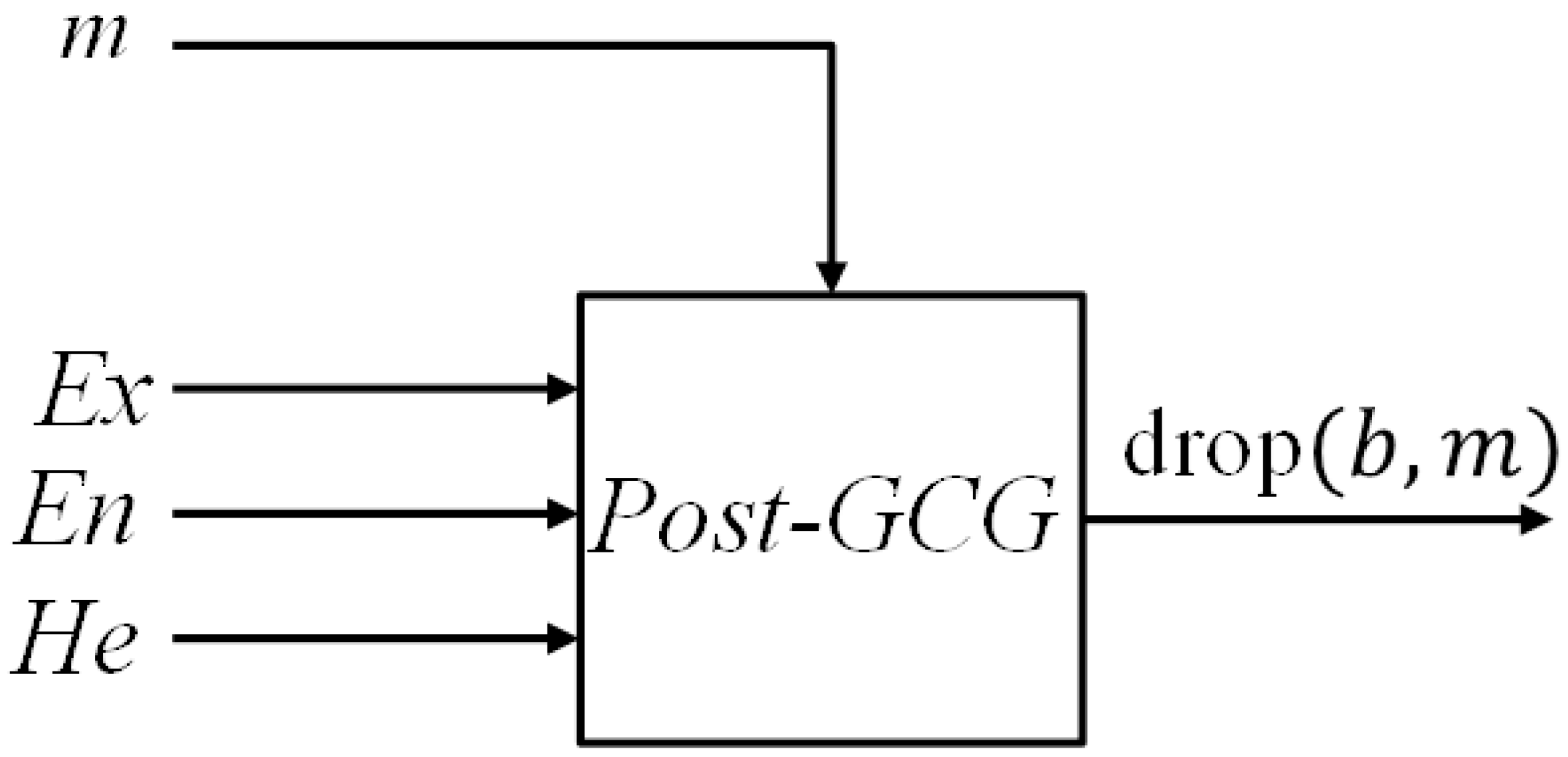
2.2.2. Post-Conditioned Gauss Cloud Generators
3. Longitudinal Control Based on Gauss Cloud Model
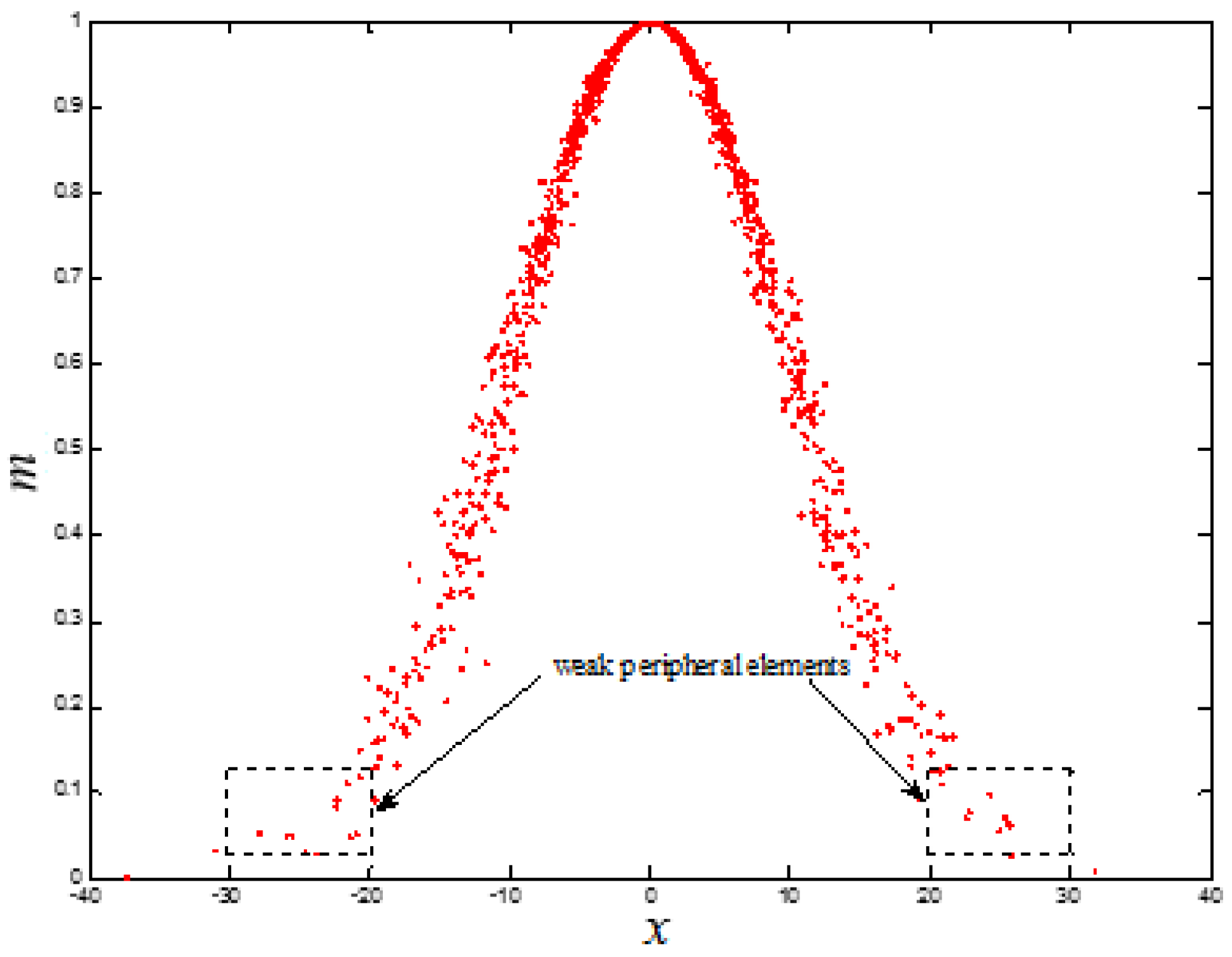
3.1. Data Analysis
3.2. Longitudinal Control Rules and Algorithm
4. Experiment Result and Analysis
4.1. Experiment Setup
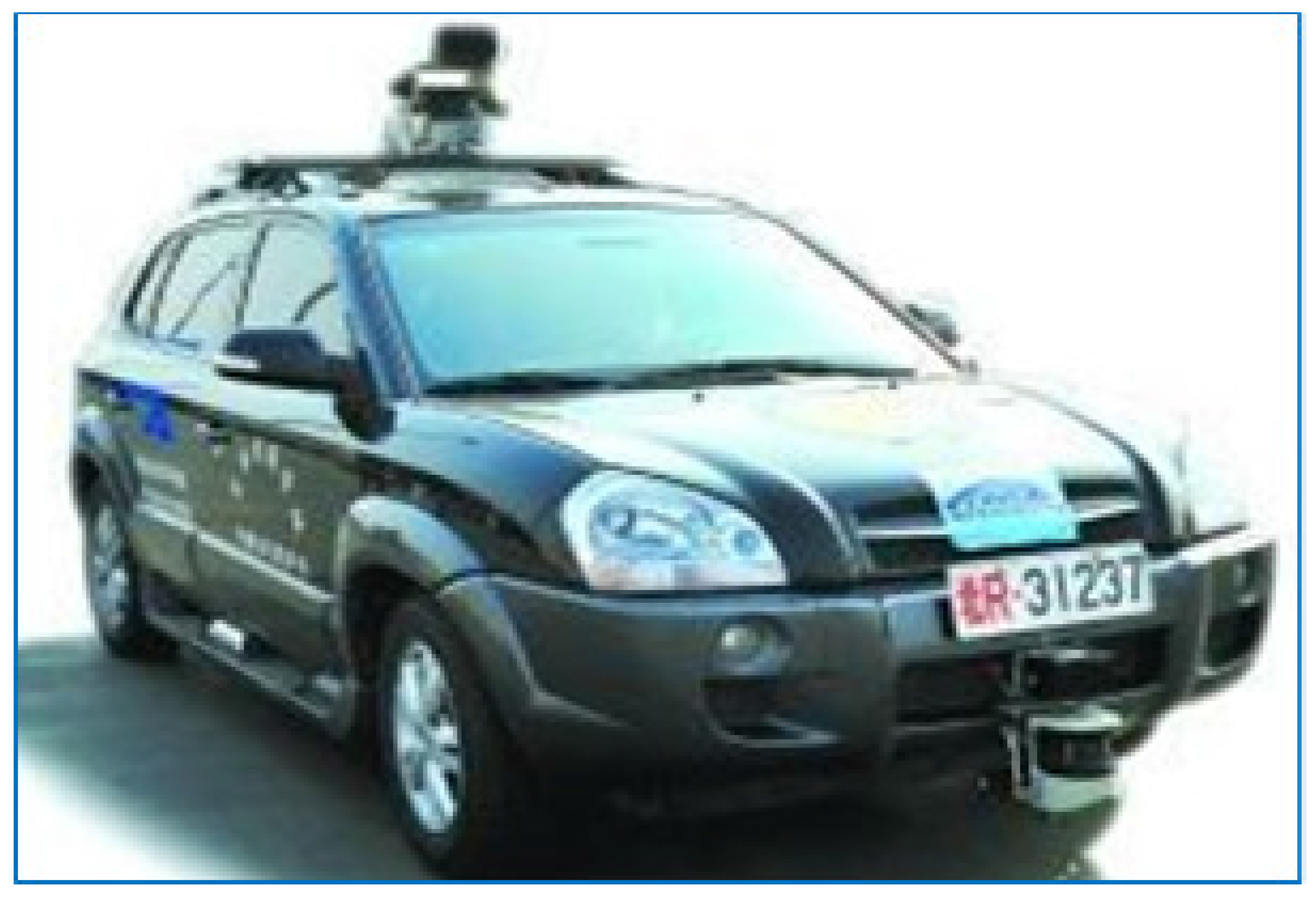
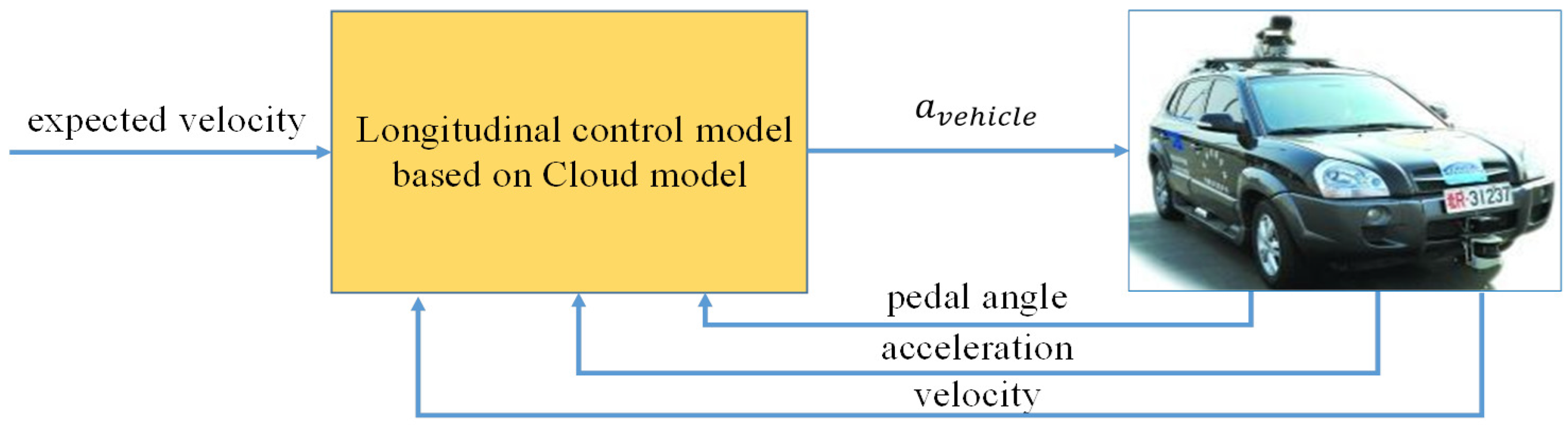
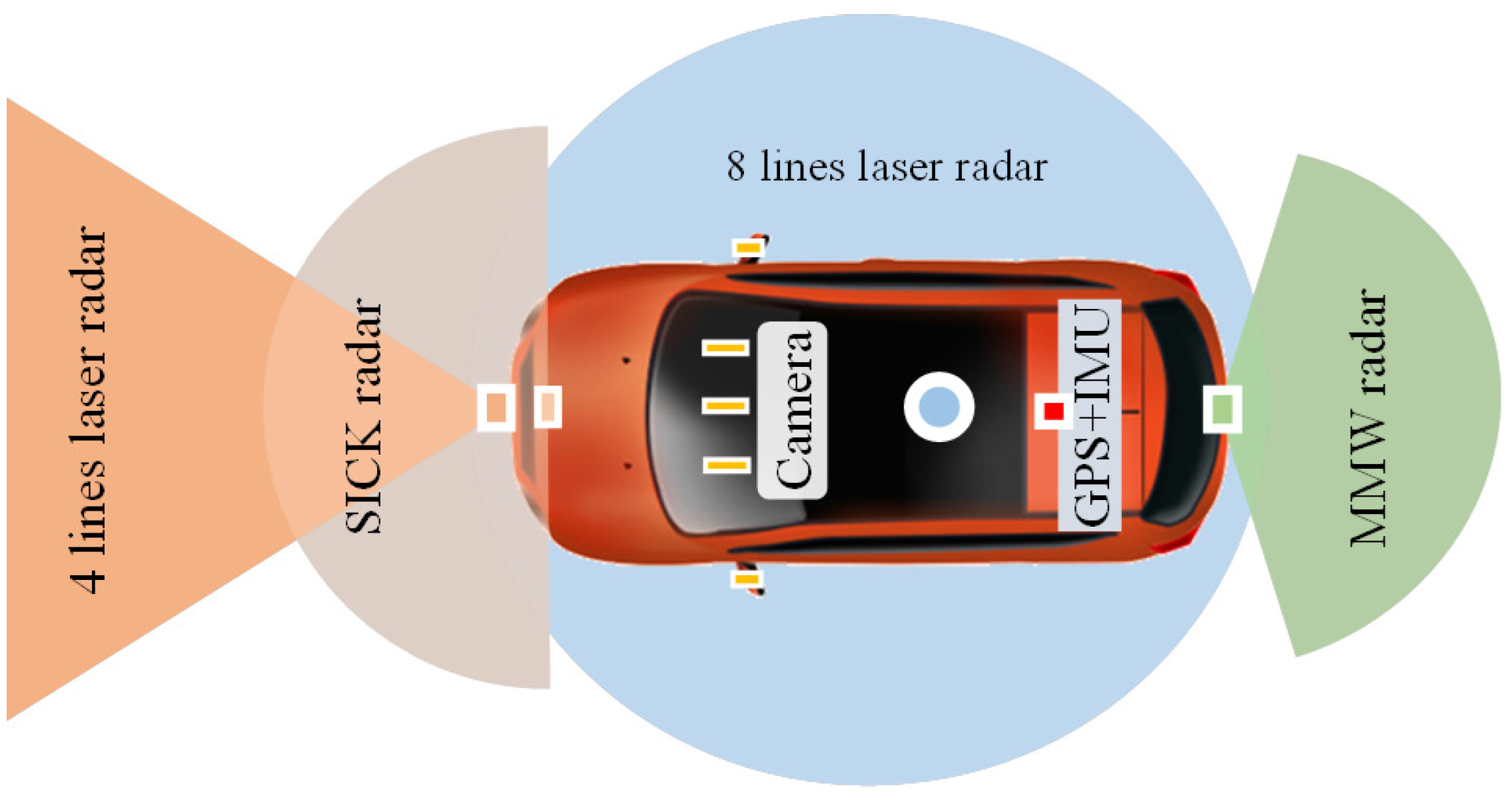
4.1.1. Hardware Architecture of an Autonomous Vehicle System
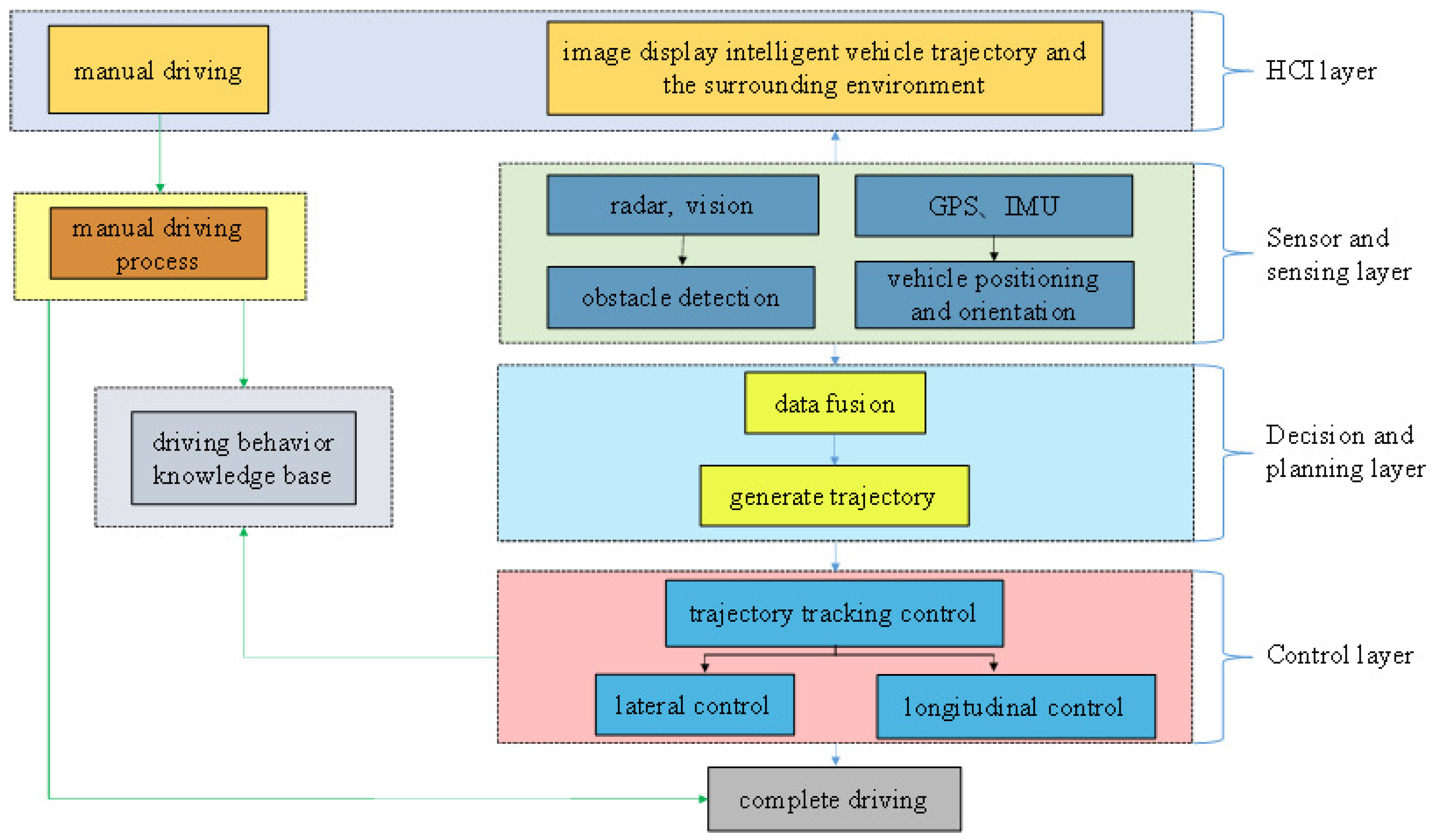
4.1.2. Software Architecture of an Autonomous Vehicle System
4.1.3. Experimental Environment
4.2. Experiment Result and Analysis
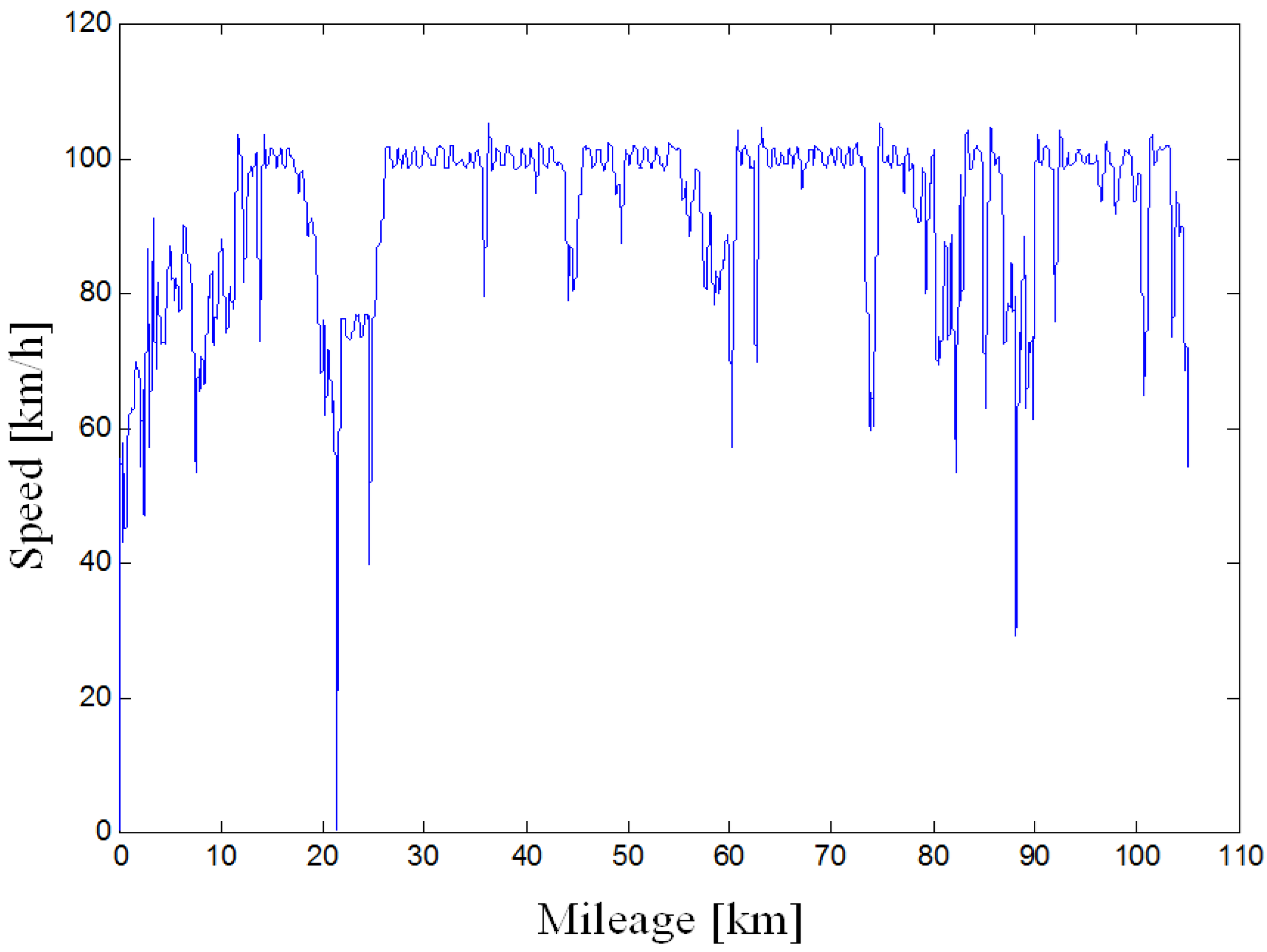
4.2.1. Speed and Acceleration Analysis Based on Mileage
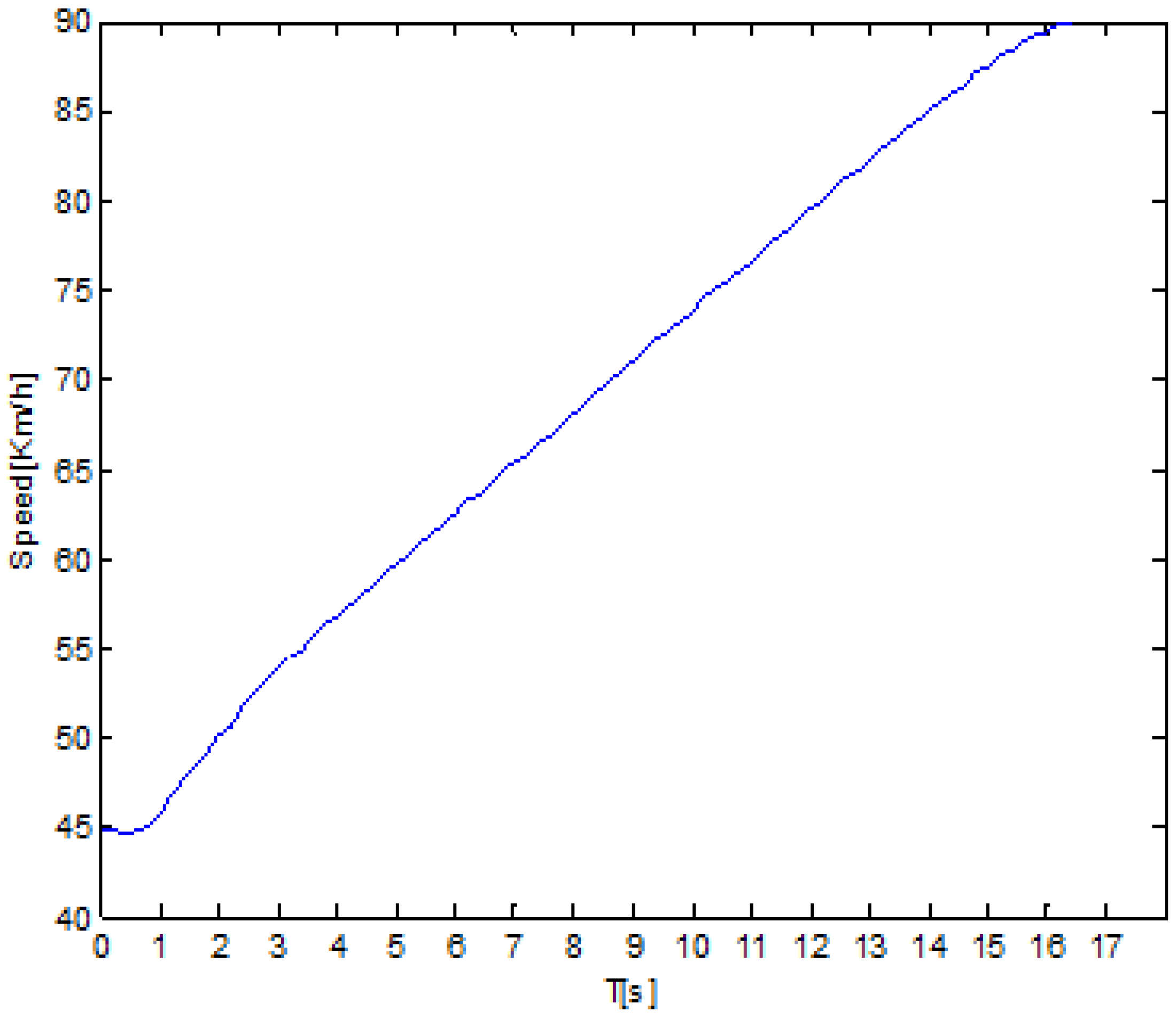
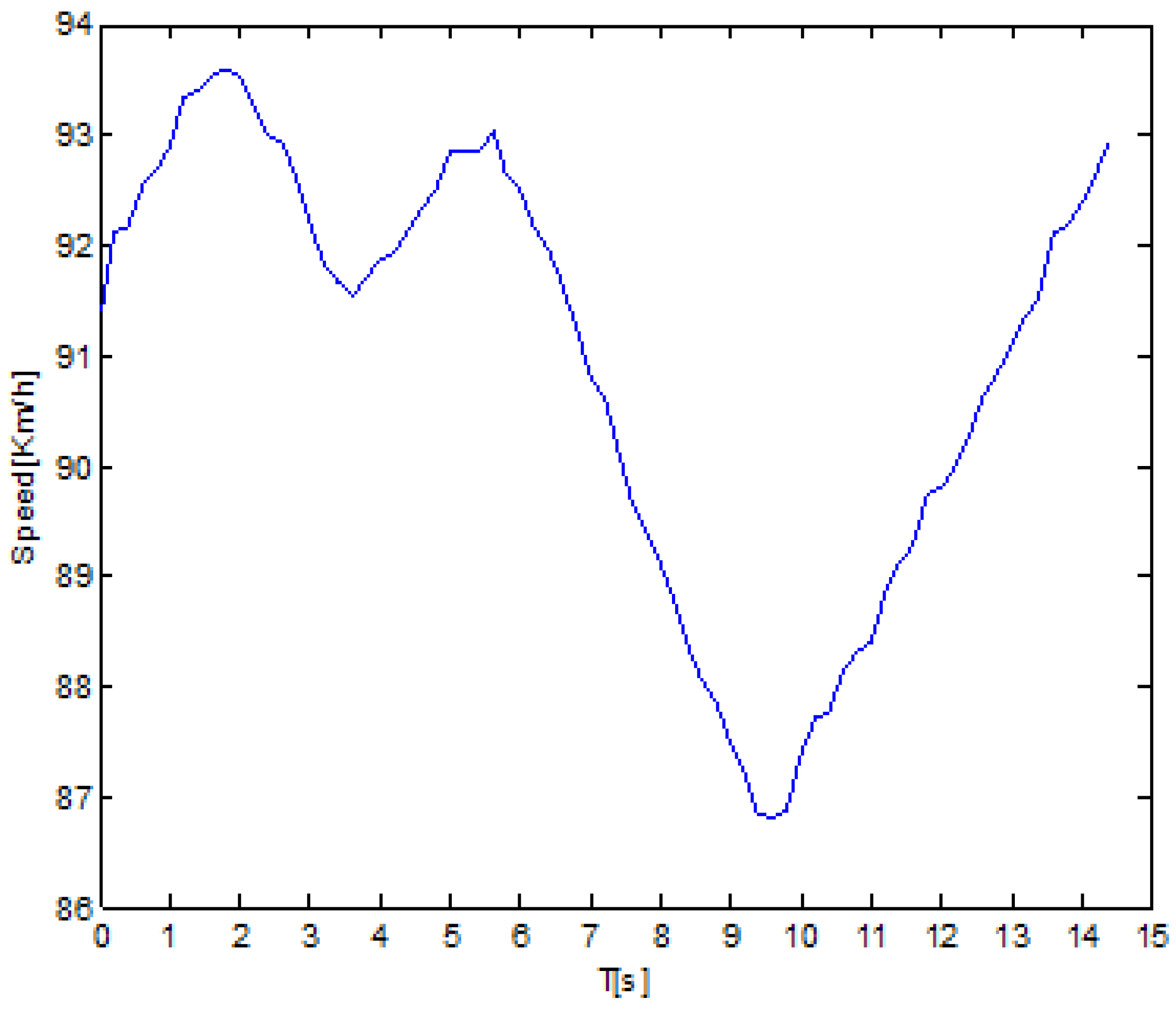
4.2.2. Speed Analysis Based on Time
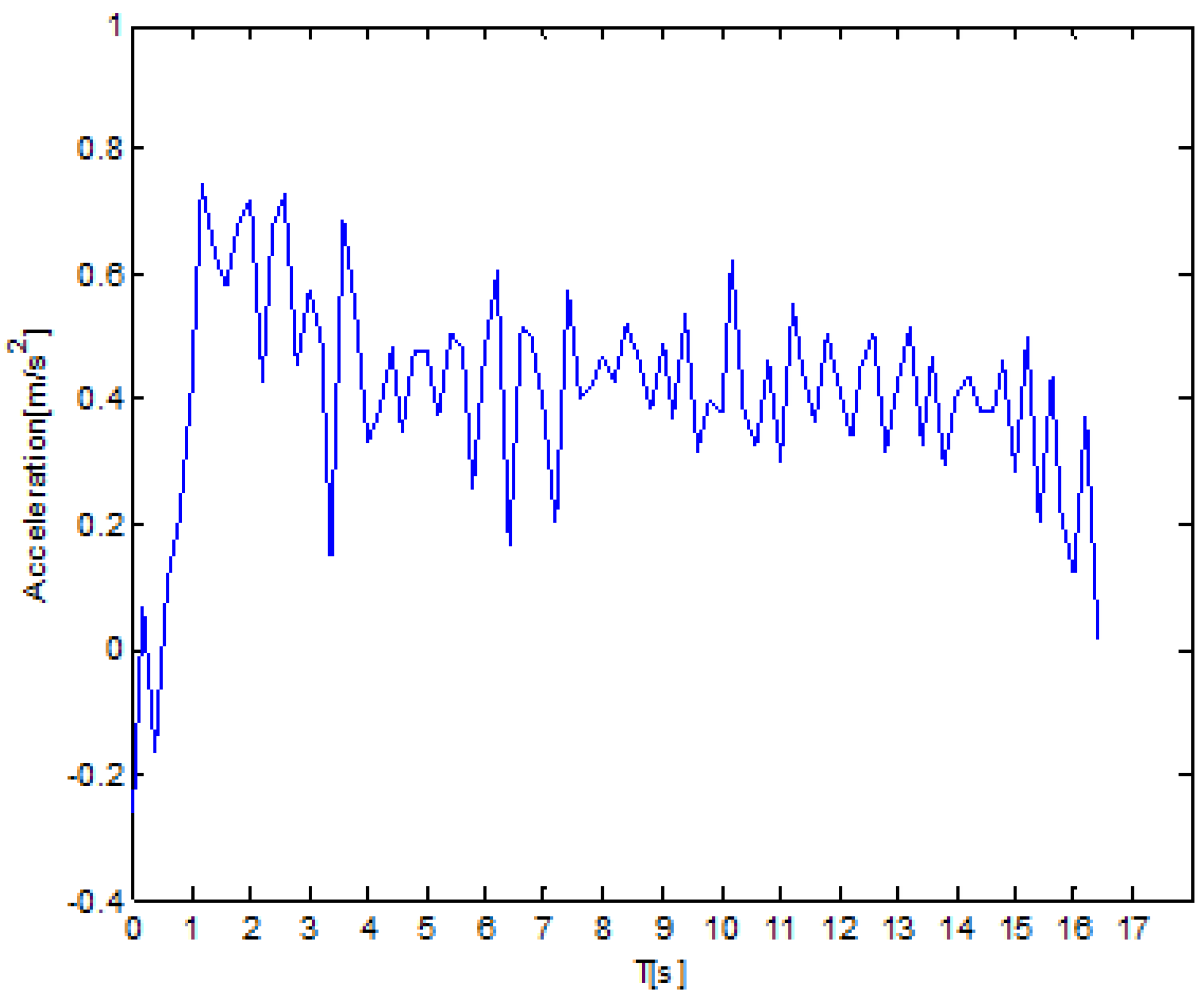
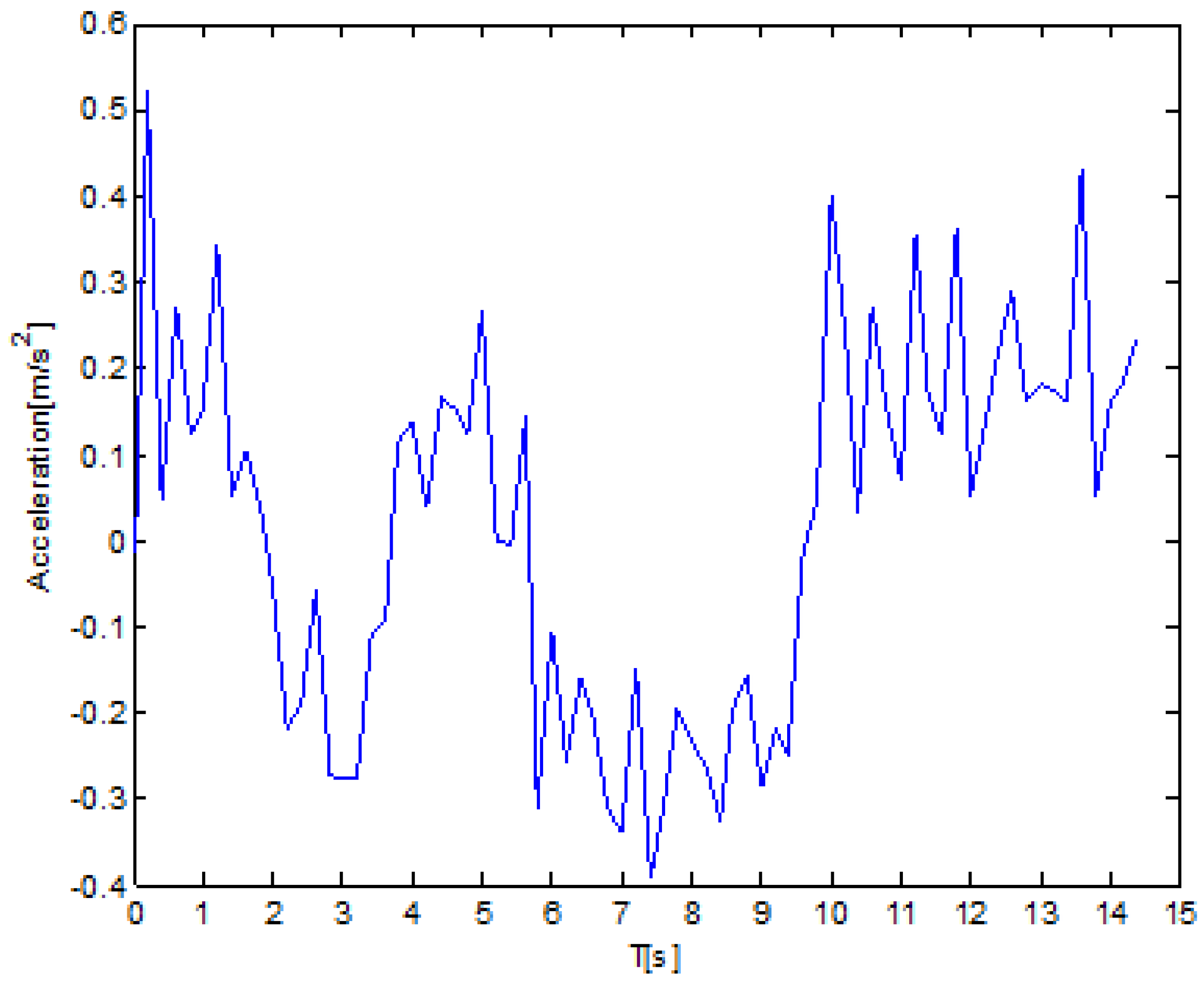
4.2.3. Acceleration Analysis Based on Time
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, L.; Chen, X.; Ling, Y. The Application of Fuzzy Control Algorithm in the Longitudinal Control System for a Platoon of Vehicles. In Proceedings of the 6th World Congress on Intelligent Control and Automation, Dalian, China, 21–23 June 2006; pp. 1242–1245. [Google Scholar]
- Sheikholeslam, S.; Charles, A. Longitudinal Control of a Platoon of Vehicles with no Communication of Lead Vehicle Information: A System Level Study. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 1993, 42, 546–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, P.; McDonald, M. Application of Fuzzy Systems in the Car-Following Behavior Analysis. In Fuzzy Systems and Knowledge Discovery; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; Volume 3613, pp. 782–791. [Google Scholar]
- Qiang, G.; Liang, H.; Chao, D. The Modeling and Simulation of the Car-following Behavior Based on Fuzzy Inference. In Proceedings of the 2008 International Workshop on Modelling, Simulation and Optimization, Hong Kong, China, 27–28 December 2008; pp. 322–325. [Google Scholar]
- Kumarawadu, S.; Lee, T. A Model Based Neuro Control Approach for Car Following Collision Prevention. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Networking, Sensing and Control, Taipei, Taiwan, 21–23 March 2004; pp. 152–157. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, C.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Yuan, Y. Mechanism analysis and evaluation methodology of regenerative braking contribution to energy efficiency improvement of electrified vehicles. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 92, 469–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Dickerson, J.; Kosko, B. Fuzzy throttle and brake control for platoons of smart cars. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 1996, 84, 209–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Rad, A.; Chan, W. An Intelligent Longitudinal Controller for Application in Semiautonomous Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2010, 57, 1487–1497. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.; Tomizuka, M. Adaptive Vehicle Traction Force Control for Intelligent Vehicle Highway Systems (IVHSs). IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2003, 50, 37–47. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, C.; Wang, H.; Cao, D. High-Precision Hydraulic Pressure Control Based on Linear Pressure-Drop Modulation in Valve Critical Equilibrium State. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 7984–7993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Hsu, C.; Lin, C.; Lee, T. Robust Intelligent Backstepping Longitudinal Control of Vehicle Platoons with H Tracking Performance. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Taipei, Taiwan, 8–11 October 2006; pp. 4648–4653. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrara, A.; Pisu, P. Minimum Sensor Second-Order Sliding Mode Longitudinal Control of Passenger Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2004, 5, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouveliere, L.; Mammar, S. Experimental Vehicle Longitudinal Control. Using Second Order Sliding Modes. In Proceedings of the American Control Conference, Denver, CO, USA, 4–6 June 2003; pp. 4705–4710. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.; Hedrick, J. Longitudinal Control Algorithm for Automated Vehicle Merging. In Proceedings of the 39th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, Sydney, Australia, 12–15 December 2000; pp. 450–455. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.; Sun, Z.; Zhao, H.; Li, Z. Longitudinal Controller Design For Autonomous Ground Vehicle in Off-road Environment. In Proceedings of the 27th Chinese Control Conference, Kunming, China, 16–18 July 2008; pp. 687–690. [Google Scholar]
- Tai, M.; Tomizuka, M. Robust Longitudinal Velocity Tracking of Vehicles Using Traction and Brake Control. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Advanced Motion Control, Nagoya, Japan, 30 March–1 April 2000; pp. 305–310. [Google Scholar]
- Raffin, A.; Taragna, M.; Giorelli, M. Adaptive longitudinal control of an autonomous vehicle with an approximate knowledge of its parameters. In Proceedings of the 11th International Workshop on Robot Motion and Control, Wasowo, Poland, 3–5 July 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Naeem, H.M.Y.; Mahmood, A. Robust and optimal control of longitudinal dynamics of automotive vehicle. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Electrical Engineering, Lahore, Pakistan, 2–4 March 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Boulkroune, B.; Aalst, S.V.; Lehaen, K.; Smet, J.D. Observer-based Controller with Integral Action for Longitudinal Vehicle Speed Control. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Intellient Vehicles Symposium (IV), Los Angeles, CA, USA, 11–14 June 2017; pp. 322–327. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, C.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y. Extended-Kalman-filter-based regenerative and friction blended braking control for electric vehicle equipped with axle motor considering damping and elastic properties of electric powertrain. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 2014, 52, 1372–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.E.; Gao, F.; Gao, D. Multiple-Model Switching Control of Vehicle Longitudinal Dynamics for Platoon-Level Automation. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2016, 65, 4480–4492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Xu, X.; He, H.; Tan, J.; Sun, Z. Parameterized Batch Reinforcement Learning for Longitudinal Control of Autonomous Land Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2017, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Gong, J.; Kurt, A.; Chen, H.; Ozguner, U. A Model Predictive-based Approach for Longitudinal Control in Autonomous Driving with Lateral Interruptions. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), Los Angeles, CA, USA, 11–14 June 2017; pp. 359–364. [Google Scholar]
- Menhour, L.; D’Andréa-Novel, B.; Fliess, M.; Gruyer, D.; Mounier, H. An Efficient Model-Free Setting for Longitudinal and Lateral Vehicle Control: Validation through the Interconnected Pro-SiVIC/RTMaps Prototyping Platform. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2017, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Gao, F.; Li, K.; Wang, L.-Y.; You, K.; Cao, D. Robust Longitudinal Control of Multi-Vehicle Systems—A Distributed H-Infinity Method. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2017, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, A.; Vijayaraghavan, V.; Zhang, J.; Liang, X. Design of robust battery capacity model for electric vehicle by incorporation of uncertainties. Int. J. Energy Res. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajan, A.; Vijayaraghavan, V.; Ooi, M.P.; Kuang, Y.C. A Simulation-based Probabilistic Framework for Lithium-ion Battery Modelling. Measurement 2018, 115, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayaraghavan, V.; Garg, A.; Liang, G. Fracture Mechanics Modelling of Lithium-ion Batteries under pinch torsion test. Measurement 2017, 114, 382–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Wang, H.; Tang, X. Cyber-Physical Control for Energy-Saving Vehicle Following with Connectivity. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 8578–8587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wang, S.; Li, D. Spatial Data Mining: Theory and Application; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; ISBN 978-3-662-58536-1. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Liu, Y.; Du, Y. Artificial Intelligence with Uncertainty. J. Softw. 2004, 15, 1538–1594. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, B.; Li, D.; Qin, K.; Chen, G.; Liu, Y.; Han, P. An Uncertain Control Framework of Cloud Model. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Rough Set and Knowledge Technology (RSK), Beijing, China, 15–17 October 2010; pp. 618–625. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Liu, Y.; Gan, W. A new cognitive model-Cloud model. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 2009, 24, 357–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H. Statistical Calculation; Peking University Press: Beijing, China, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Du, Y. Artificial Intelligence with Uncertainay; National Defence Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2005; pp. 137–185. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, H.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, D. Cloud Model-Detect Unsupervised Communities in Social tagging Network. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Information Science and Cloud Computing, Guangzhou, China, 7–8 December 2013; pp. 317–323. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X. Research and Application of Association Rules in Data Mining. Comput. Study 2010, 3, 049. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Du, Y.; Yin, G. Commonsense Knowledge Modeling. In Proceedings of the 16th World Computer Congress, Beijing, China, 1 August 2000; pp. 34–45. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, T.; Liu, Y.; Li, D. Research of intelligent vehicle variable granularity evaluation based on cloud model. Acta Electron. Sin. 2016, 44, 365–373. [Google Scholar]
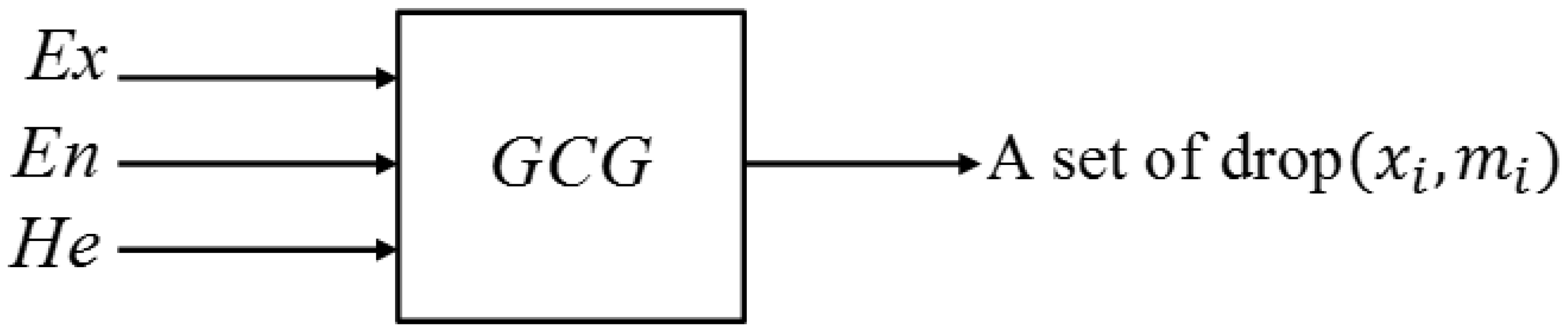





| Input: and . (Three numerical features of qualitative concept represent |
|---|
| the quantification of a concept, the value of represents the number of cloud drops) |
| Output: . (The drop of and the certainty degree of .) |
| (1) to generate a Gauss random number: |
| (2) to generate a Gauss random number: |
| (3) to calculate the certainty degree of : = |
| (4) to add the drop of to a set of drop |
| (5) Repeat (1)–(4) until the number of cloud drops equals to N. |
| v | |
|---|---|
| Positive greater | (9.8, 1.1, 0.18) |
| Positive less | (4.9, 1, 0.19) |
| Zero | (0, 1, 0.01) |
| Negative less | (−4.7, 1, 0.03) |
| Negative greater | (−9.8, 1.2, 0.03) |
| a | |
|---|---|
| Positive greater | (19, 2.5, 0.045) |
| Positive less | (9, 2.1, 0.02) |
| Zero | (0, 2, 0.007) |
| Negative less | (−9, 2, 0.02)) |
| Negative greater | (19, 2.8, 0.05) |
| Input: Three figures , three figures , and a specific value . |
|---|
| Output: The drop distribution . |
| (1) To generate a Gauss random |
| (2) To calculate the certainty: = |
| (3) To generate a Gauss random |
| (4) If , then to calculate the certainty: |
| (5) If , then to calculate the certainty: |
| (6) To generate the distribution of drops |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, H.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, D. Longitudinal Control for Mengshi Autonomous Vehicle via Gauss Cloud Model. Sustainability 2017, 9, 2259. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9122259
Gao H, Zhang X, Liu Y, Li D. Longitudinal Control for Mengshi Autonomous Vehicle via Gauss Cloud Model. Sustainability. 2017; 9(12):2259. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9122259
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Hongbo, Xinyu Zhang, Yuchao Liu, and Deyi Li. 2017. "Longitudinal Control for Mengshi Autonomous Vehicle via Gauss Cloud Model" Sustainability 9, no. 12: 2259. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9122259
APA StyleGao, H., Zhang, X., Liu, Y., & Li, D. (2017). Longitudinal Control for Mengshi Autonomous Vehicle via Gauss Cloud Model. Sustainability, 9(12), 2259. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9122259






