A Road to Sustainable Development of Chinese Cities: A Perception of Improving Urban Management Efficiency Based on Two-Level Production Factors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Description of the Study Area and Data Foundation
2.2. Methods
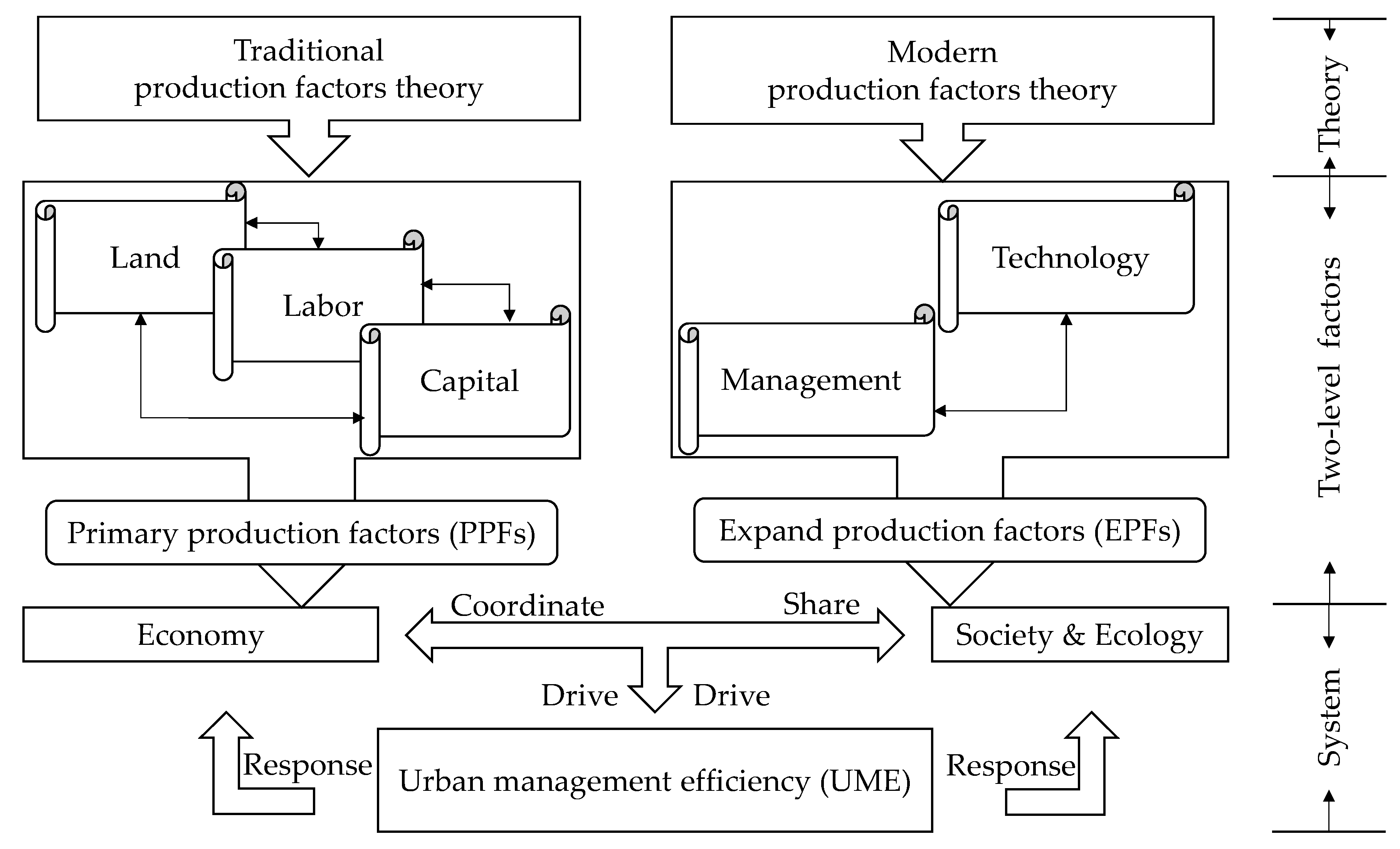
2.2.1. Considerations of Two-Level Production Factors Involved in Measuring UME
2.2.2. Multi-Scale Analyses Involved in Measuring the Response of UME to PPFs and EPFs
3. Results
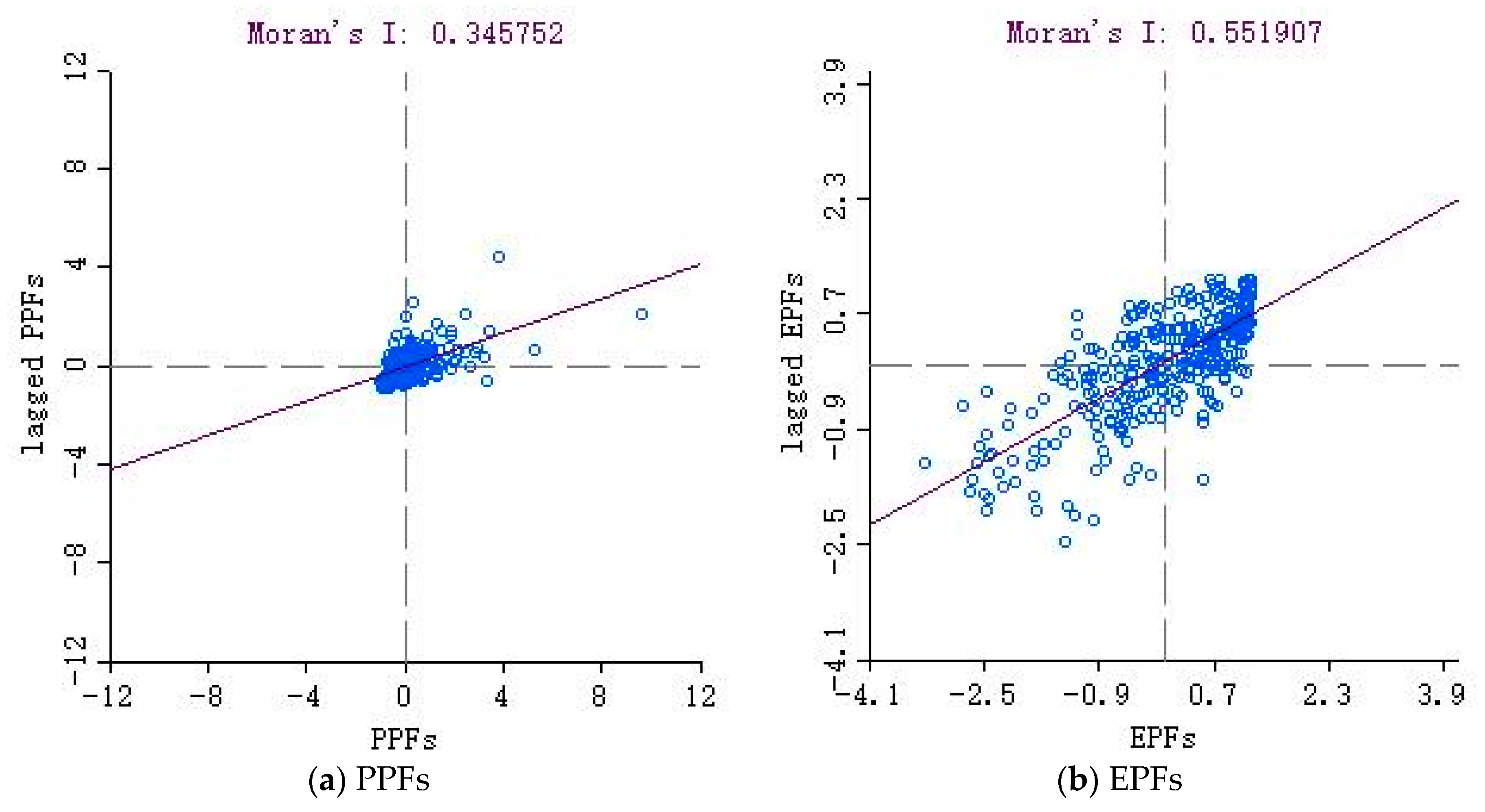
3.1. Agglomeration Effects by Global Analysis
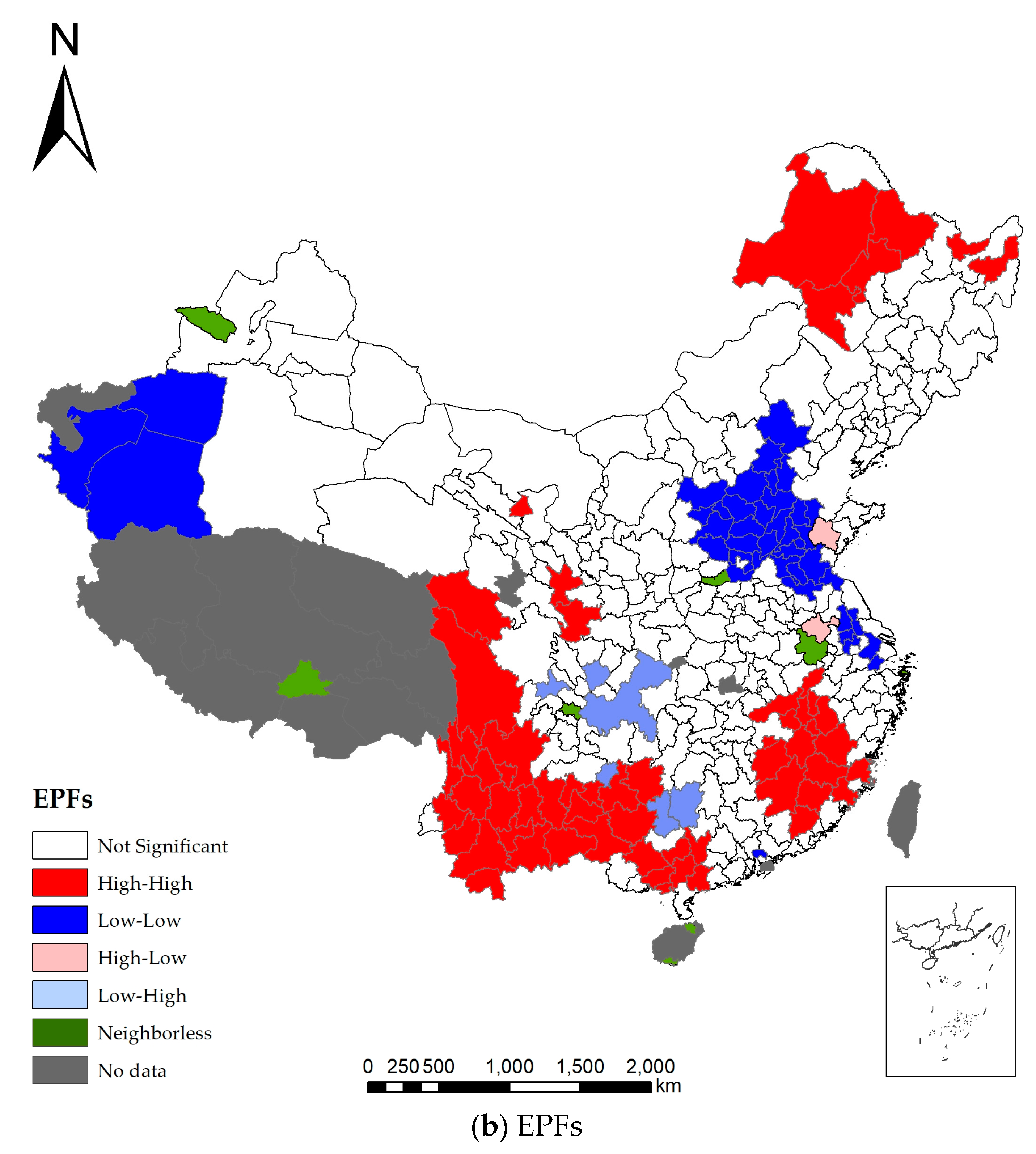
3.2. Variant Effects by Local Analysis
4. Conclusions and Discussion
4.1. Main Achievements
4.2. Limitations and Uncertainties
4.3. Implications and Applications
4.3.1. Advantageous Applications
4.3.2. Implications for Policy-Making
Supplementary Files
Supplementary File 1Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Krugman, P.; Elizondo, R.L. Trade policy and the third world metropolis. J. Dev. Econ. 1996, 49, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauchard, A.; Aguayo, M.; Peña, E.; Urrutia, R. Multiple effects of urbanization on the biodiversity of developing countries: The case of a fast-growing metropolitan area (Concepción, Chile). Biol. Conserv. 2006, 127, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameen, R.F.M.; Mourshed, M. Urban environmental challenges in developing countries—A stakeholder perspective. Habitat Int. 2017, 64, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, W. The economics of urban size. Pap. Reg. Sci. 1971, 26, 66–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephan, H. The Optimal Size of German Cities an Efficiency Analysis Perspective. In Darmstadt Discussion Papers in Economics; Darmstadt University of Technology: Darmstadt, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Camagni, R.; Capello, R.; Caragliu, A. One or infinite optimal city sizes? In search of an equilibrium size for cities. Ann. Reg. Sci. 2013, 51, 309–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xu, X.; Chen, H. Temporal and spatial changes of urban efficiency in the 1990s. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2005, 60, 615. [Google Scholar]
- Mera, K. Income Distribution and Regional Development; University of Tokyo Press: Tokyo, Japan, 1975; Volume 87, p. 159. [Google Scholar]
- David, Q.; Peeters, D.; Van Hamme, G.; Vandermotten, C. Is bigger better? Economic performances of european cities, 1960–2009. Cities 2013, 35, 237–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deilmann, C.; Lehmann, I.; Reißmann, D.; Hennersdorf, J. Data envelopment analysis of cities—Investigation of the ecological and economic efficiency of cities using a benchmarking concept from production management. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 67, 798–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostaei, S.; Bagheri, M. A study of the function of small towns in local development (Case study: Razan town). PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1001239. [Google Scholar]
- Stephen, N. Income inequality and city size: An examination of alternative hypotheses for large and small cities. Rev. Econ. Stat. 1980, 62, 502. [Google Scholar]
- Glaeser, E.L. Are Cities Dying? J. Econ. Perspect. 1998, 12, 139–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capello, R.; Camagni, R. Beyond optimal city size: An evaluation of alternative urban growth patterns. Urban Stud. 2000, 37, 1479–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Campbell, D.E. Ecological and economic dynamics of the shunde agricultural system under China’s small city development strategy. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 2589–2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Bank. Entering the 21st Century: World Development Report 1999/2000: Summary; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations. World Urbanization Prospects: The 1999 Revision; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, T.; He, S.; Dong, G. Metropolitan resources efficiencies, change trends and causes in china under the goal to build an international metropolis. J. Geogr. Sci. 2011, 21, 746–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, W.; Ding, C.; Guo, H.; Guo, W.; Yao, L.; Xiong, H.; Tan, H. Metropolis parking problems and management planning solutions for traffic operation effectiveness. Math. Probl. Eng. 2012, 2012, 233–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiroaki, T.; Kazuhiko, T. Japanese 3R policies based on material flow analysis. J. Ind. Ecol. 2010, 12, 792–798. [Google Scholar]
- Leal Filho, W. The new sustainability advantage: Seven business case benefits of a triple bottom line. Int. J. Sustain. High. Educ. 2002, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Yang, X.; Cheng, G.; Wang, S. A comprehensive eco-efficiency model and dynamics of regional eco-efficiency in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 67, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seppäläa, J.; Melanen, M.; Mäenpää, I.; Koskela, S.; Tenhunen, J.; Hiltunen, M.R. How can the eco-efficiency of a region be measured and monitored? J. Ind. Ecol. 2005, 9, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prud’homme, R.; Lee, C.W. Size, sprawl, speed and the efficiency of cities. Urban Stud. 1999, 36, 1849–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuebs, M.; Sun, L. Business reputation and labor efficiency, productivity, and cost. J. Bus. Ethics 2010, 96, 265–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athanassopoulos, A.D.; Karkazis, J. The efficiency of social and economic image projection in spatial configurations. J. Reg. Sci. 1997, 37, 75–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, H. The economic efficiency of energy-consuming equipment: A DEA approach. Energy Effic. 2015, 8, 281–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariano, E.B. Transformation of wealth produced into quality of life: Analysis of the social efficiency of nation-states with the DEA’s triple index approach. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 2014, 65, 1664–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, D.J. Productivity and efficiency in urban railways: Parametric and non-parametric estimates. Transp. Res. Part E 2008, 44, 84–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boame, A.K. The technical efficiency of Canadian urban transit systems. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2004, 40, 401–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergendahl, G.; Lindblom, T. Evaluating the performance of swedish savings banks according to service efficiency. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2008, 185, 1663–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannister, G.J.; Stolp, C. Regional concentration and efficiency in mexican manufacturing. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1995, 80, 672–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Bergh, J.C. The GDP paradox. J. Econ. Psychol. 2009, 30, 117–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhou, T.; Hu, D.; Li, F.; Liu, J. Cultivating eco-sustainability: Social–economic–natural complex ecosystem case studies in China. Ecol. Complex. 2011, 8, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Yang, Z. Towards green growth and management: Relative efficiency and gaps of chinese cities. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 80, 481–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rydin, Y. Environmental Governance for Sustainable Urban Development: A European Model? Local Environ. 1999, 4, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neirotti, P.; De Marco, A.; Cagliano, A.C.; Mangano, G.; Scorrano, F. Current trends in smart city initiatives: Some stylised facts. Cities 2014, 38, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, E.S., Jr. A statistical and analytical technique for regional analysis. Pap. Reg. Sci. 1960, 6, 97–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macmillan, W.D. The estimation and application of multi-regional economic planning models using data envelopment analysis. Pap. Reg. Sci. 1986, 60, 41–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Wen, Z. Evaluating China’s urban environmental sustainability with data envelopment analysis. Ecol. Econ. 2010, 69, 1748–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Guan, X.; Lu, S.; Zhou, M.; Deng, Y. Input–output efficiency of urban agglomerations in China: An application of data envelopment analysis (DEA). Urban Stud. 2013, 50, 2766–2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.P.; Cheng, X.M.; Yuan, J.H.; Gao, X.J. Total-factor energy efficiency in developing countries. Energy Policy 2011, 39, 644–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, M.J. The measurement of productive efficiency. J. R. Stat. Soc. 1957, 120, 253–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charnes, A.; Cooper, W.W.; Rhodes, E. Measuring the efficiency of decision making unit. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1978, 2, 429–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullinane, K.; Wang, T.F.; Song, D.W.; Ji, P. The technical efficiency of container ports: Comparing data envelopment analysis and stochastic frontier analysis. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2006, 40, 354–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meeusen, W.; van Den Broeck, J. Efficiency estimation from cobb-douglas production functions with composed error. Int. Econ. Rev. 1977, 18, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aigner, D.; Lovell, C.K.; Schmidt, P. Formulation and estimation of stochastic frontier production function models. J. Econ. 1977, 6, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, C.C.; Henderson, J.V. Are Chinese cities too small? Rev. Econ. Stud. 2006, 73, 549–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.M.; Wen, Z.G. Review and challenges of policies of environmental protection and sustainable development in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2008, 88, 1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziegler, E.H. China’s cities, globalization, and sustainable development: Comparative thoughts on urban planning, energy, and environmental policy. Metab. Brain Dis. 2006, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Say, J.B. A treatise on political economy; or the production, distribution, and consumption of wealth. Soc. Sci. Electron. Publ. 2009, 136, 199. [Google Scholar]
- Mankiw, N.G.; Phelps, E.S.; Romer, P.M. The growth of nations. Brook. Pap. Econ. Act. 1995, 1995, 275–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Chaudhry, S.S.; Li, Y. Factors of production: Historical theories and new developments. Syst. Res. Behav. Sci. 2009, 26, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, H.E. Toward some operational principles of sustainable development. Ecol. Econ. 1990, 2, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Yu, X. Measurement and evaluation of interactions in complex urban ecosystem. Ecol. Model. 2006, 196, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Button, K. City management and urban environmental indicators. Ecol. Econ. 2002, 40, 217–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sveikauskas, L. The productivity of cities. Quart. J. Econ. 1975, 89, 393–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abel, R.J.; Dey, I.; Gabe, T.M. Productivity and the density of human capital. J. Reg. Sci. 2012, 52, 562–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Yang, Z.; Tang, Y.; Ulgiati, S. Spatial correlation model of economy-energy-pollution interactions: The role of river water as a link between production sites and urban areas. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 69, 1018–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, D.; Tiwari, G. Sustainable Mobility Indicators for Indian Cities: Selection Methodology and Application. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 79, 310–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Hao, J. Air quality management in china: Issues, challenges, and options. J. Environ. Sci. 2012, 24, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, P.A.P. Notes on continuous stochastic phenomena. Biometrika 1950, 37, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voss, P.R.; Long, D.D.; Hammer, R.B.; Friedman, S. County child poverty rates in the US: A spatial regression approach. Popul. Res. Policy Rev. 2006, 25, 369–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, J.H.; Chan, T.C.; Lai, F.; Lin, B.C.; Sun, W.Z.; Chang, K.W.; Leu, F.Y.; Lin, J.W. Spatial analysis and data mining techniques for identifying risk factors of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. Int. J. Inform. Manag. 2017, 37, 1528–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wong, K.K. Spatial distribution of tourist flows to China’s cities. Tour. Geogr. 2013, 15, 338–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messner, S.F.; Anselin, L. Spatial analyses of homicide with areal data. Spat. Integr. Soc. Sci. 2004, 12, 127–144. [Google Scholar]
- Anselin, L. Local indicators of spatial association—LISA. Geogr. Anal. 1995, 27, 93–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselin, L.; McCann, M. OpenGeoDa, open source software for the exploration and visualization of geospatial data. In Proceedings of the ACM International Symposium on Advances in Geographic Information Systems, Seattle, DC, USA, 4–6 November 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Ye, X.; Wei, Y.H. Analyzing the space-time dynamics of innovation in China: Esda and spatial panel approaches. Growth Chang. 2016, 47, 111–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getis, A.; Ord, J.K. The analysis of spatial association by use of distance statistics. Geogr. Anal. 1992, 24, 189–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S. Research on the urban influence domains in China. Int. J. Geogr. Inform. Sci. 2009, 23, 1527–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Deng, Y.; Sun, D.; Song, T. Evolution and spatial patterns of spheres of urban influence in China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2014, 24, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, J. The Economy of Cities; Random House: New York, NY, USA, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Brülhart, M.; Sbergami, F. Agglomeration and growth: Cross-country evidence. J. Urban Econ. 2009, 65, 48–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dijk, M.P.; Mingshun, Z. Sustainability indices as a tool for urban managers, evidence from four medium-sized chinese cities. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2005, 25, 667–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, R.C.; Zhao, X.B. The relationship between administrative hierarchy position and city size development in China. GeoJournal 2002, 56, 97–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Partridge, M.D. When are cities engines of growth in China? Spread and backwash effects across the urban hierarchy. Reg. Stud. J. Reg. Stud. Assoc. 2013, 47, 1313–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Dai, J.; Bu, J. City size distributions in China 1949 to 2010 and the impacts of government policies. Cities 2013, 32, S51–S57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M. Uneven growth of urban clusters in megaregions and its policy implications for new urbanization in China. Land Use Policy 2017, 66, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhu, Q.; Chu, J.; Liu, H.; Liang, L. Measuring energy and environmental efficiency of transportation systems in China based on a parallel DEA approach. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2016, 48, 460–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Bai, B.; Qiao, Q.; Kang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, J. Study on eco-efficiency of industrial parks in China based on data envelopment analysis. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 192, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Qin, C.X.; Zhang, Y.J. Energy-environment efficiency of road and railway sectors in China: Evidence from the provincial level. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 69, 559–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Level | Data | Description |
|---|---|---|
| PPF | Population density | The amount of population in per land area, reflecting the number of population resources |
| Per area GDP | The gross national product in per land area, reflecting the land productivity | |
| Per capita GDP | The gross national production in per person, reflecting the number of capital accumulation | |
| EPF | Per area energy consumption | The degree of energy utilization in regional economic activities, reflecting the energy efficiency |
| Air quality level two or above | The air quality , reflecting the environmental condition |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Li, C.; Li, Z.; Rao, Y.; Lu, T. A Road to Sustainable Development of Chinese Cities: A Perception of Improving Urban Management Efficiency Based on Two-Level Production Factors. Sustainability 2017, 9, 2212. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9122212
Xu Z, Zhang J, Li C, Li Z, Rao Y, Lu T. A Road to Sustainable Development of Chinese Cities: A Perception of Improving Urban Management Efficiency Based on Two-Level Production Factors. Sustainability. 2017; 9(12):2212. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9122212
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Ze, Jianjun Zhang, Chu Li, Zhenyu Li, Yongheng Rao, and Tianyu Lu. 2017. "A Road to Sustainable Development of Chinese Cities: A Perception of Improving Urban Management Efficiency Based on Two-Level Production Factors" Sustainability 9, no. 12: 2212. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9122212
APA StyleXu, Z., Zhang, J., Li, C., Li, Z., Rao, Y., & Lu, T. (2017). A Road to Sustainable Development of Chinese Cities: A Perception of Improving Urban Management Efficiency Based on Two-Level Production Factors. Sustainability, 9(12), 2212. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9122212





