Signaling Product Quality Information in Supply Chains via Corporate Social Responsibility Choices
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. The Model
4. Benchmark Model: Symmetric Information Case
- (i)
- The supplier’s CSR levels are and the wholesale price are and ;
- (ii)
- The retail prices are and , the order quantity are and ;
- (iii)
- The supplier’s profits are and , while the retailer’s profits are and .
5. Model Analysis: Asymmetric Information Case
5.1. Separating Equilibriums
- (i)
- and ;
- (ii)
- and for all .
- (i)
- The supplier’s CSR levels are and . The corresponding wholesale prices are given by (i) in Proposition 1;
- (ii)
- The retail prices and order qualities are given by (ii) in Proposition 1;
- (iii)
- The retailer and uninformed consumers form a belief of
- (iv)
- The supplier’s profits are and with , and the retailer’s profits are and .
5.2. Equilibrium Selection with the Intuitive Criterion
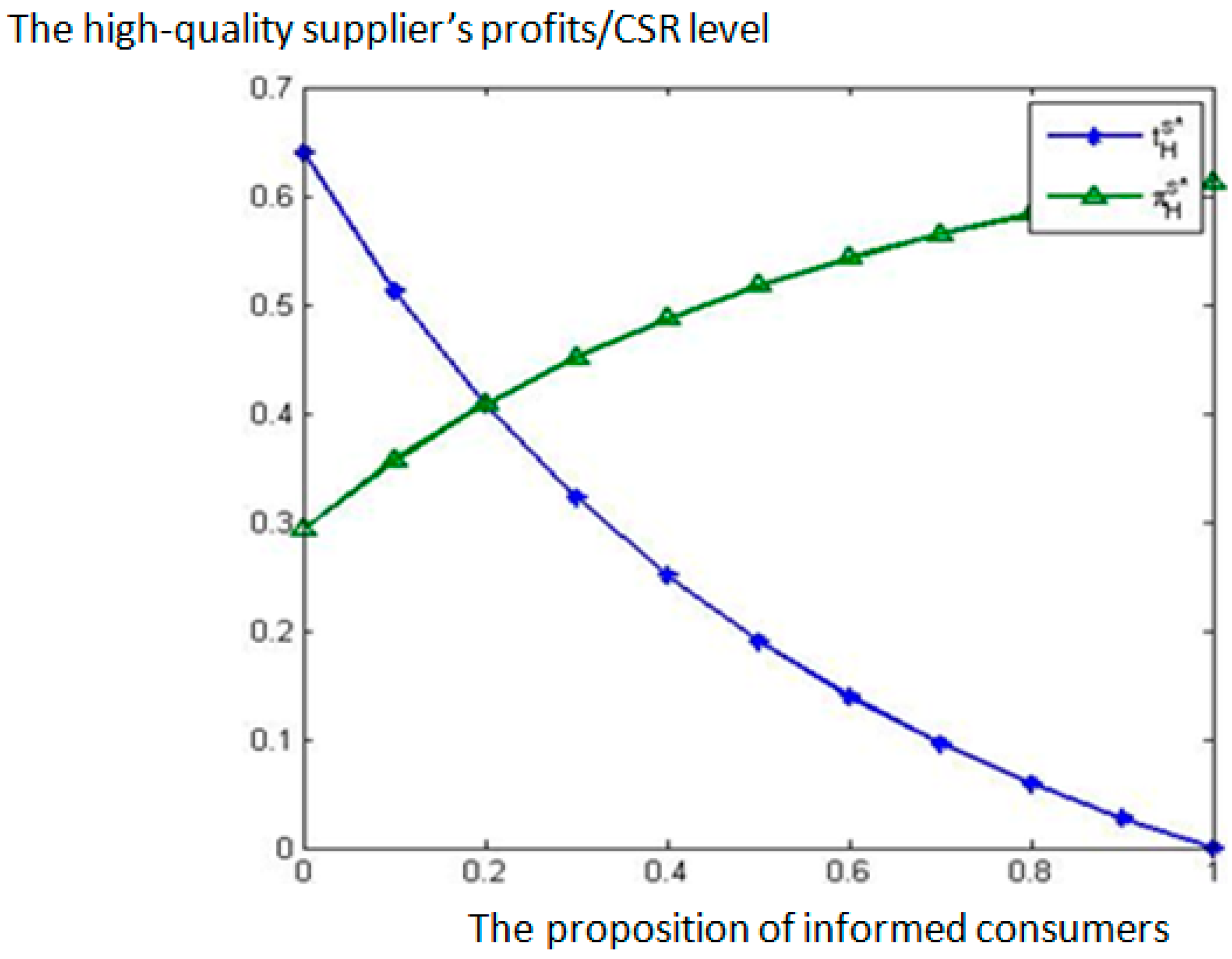
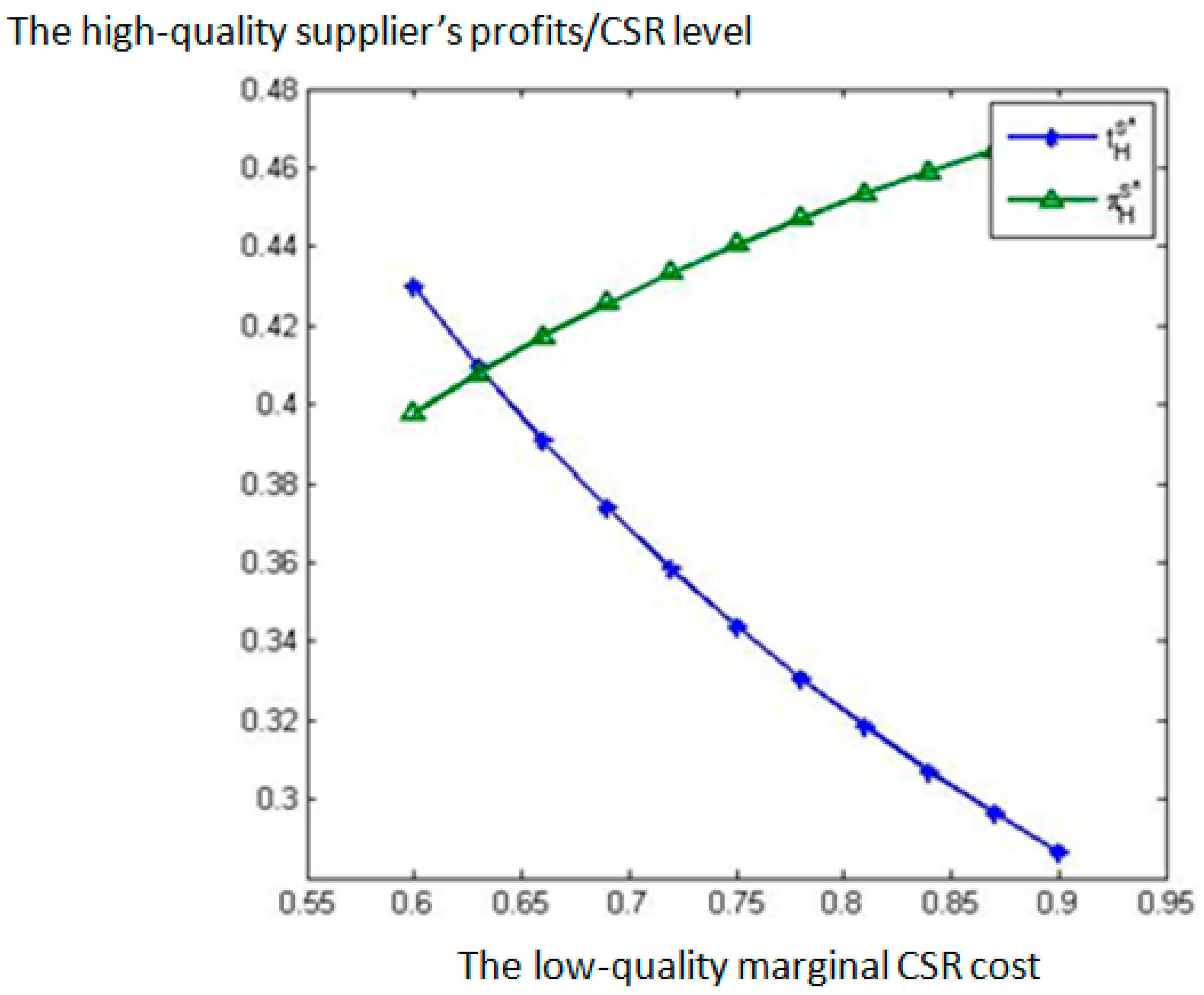
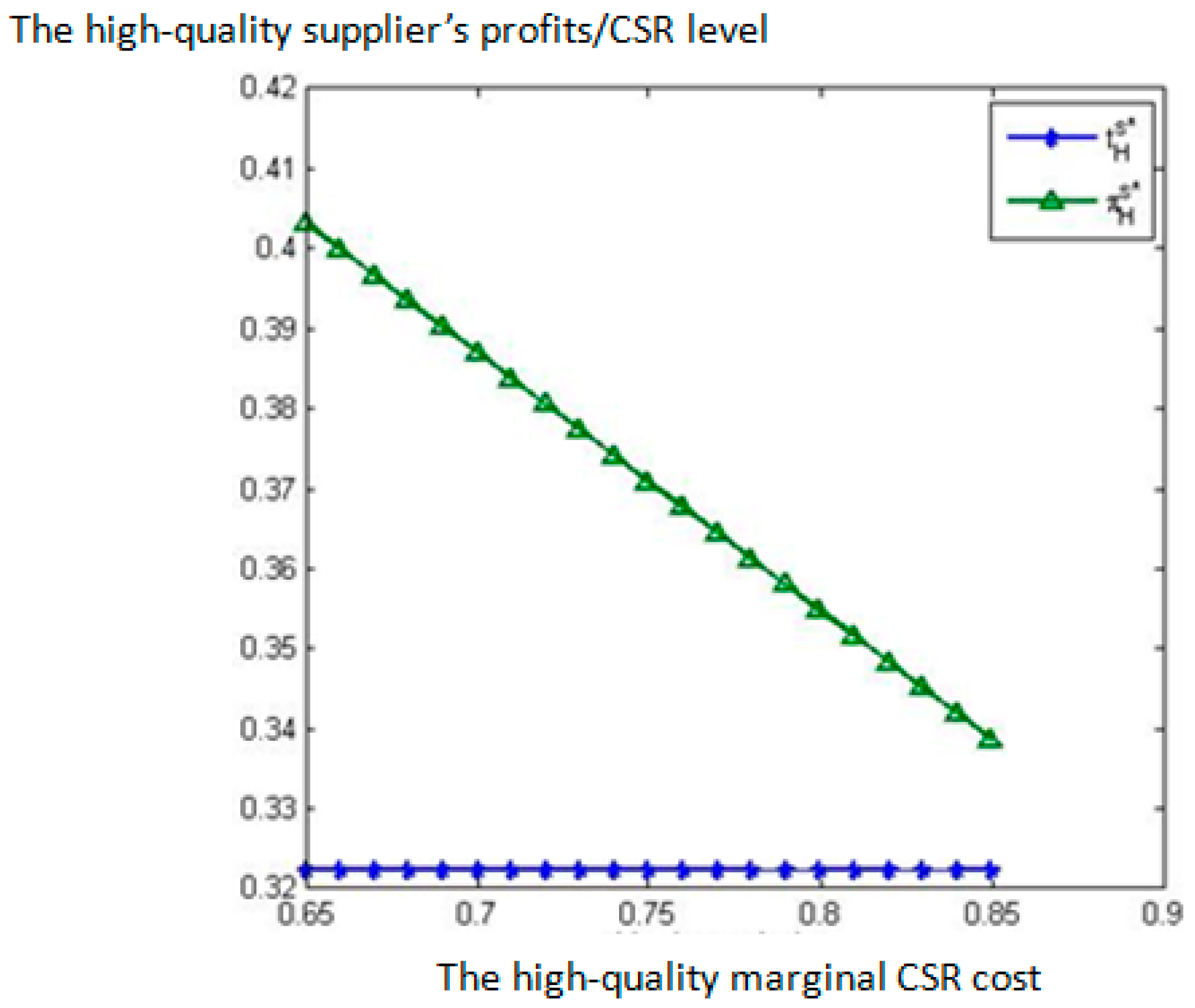
6. Comparative Static Analysis
- (i)
- decreases in the proportion of informed consumers and the low-quality supplier’s CSR marginal cost respectively, but it is independent of the high-quality supplier’s CSR marginal cost .
- (ii)
- the high-quality supplier’s equilibrium profits increase in the proportion of informed consumers and the low-quality supplier’s CSR marginal cost respectively, but decrease in the high-quality supplier’s CSR marginal cost . The low-quality supplier’s equilibrium profits are independent of , , and .
7. Discussion
8. Concluding Remarks
- (1)
- There are a set of moderate levels of CSR conduct that allow an upstream supplier can choose to truthfully report its product quality in the sense of a separating equilibrium. This implies a role of costly CSR in signaling the product quality information to a downstream retailer and uninformed consumers in the final market.
- (2)
- By ruling out the unreasonable posterior beliefs on off-equilibrium paths according to the classic intuitive criterion, we select a unique one with the lowest CSR from the set of PBEs as the most likely observation, because it is with reasonable beliefs and the lowest information cost that a high-quality supplier has to incur.
- (3)
- Based on the unique PBE satisfying the intuitive criterion, the high-quality supplier benefits from, in terms of profitability, a lower level of final-market information asymmetry, and/or a higher marginal CSR cost of the low-quality supplier, but becomes worse off as her marginal CSR cost increases. On the other hand, the low-quality supplier’s profitability is independent of the final-market information asymmetry, and the marginal CSR costs of the high-quality and low-quality suppliers alike.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schwartz, M.S.; Carroll, A.B. Corporate social responsibility: A three-domain approach. Bus. Ethics Q. 2003, 13, 503–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlsrud, A. How corporate social responsibility is defined: An analysis of 37 definitions. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2008, 15, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, I.; Hasnaoui, A. The meaning of corporate social responsibility: The vision of four nations. J. Bus. Ethics 2011, 100, 419–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, S.; Modak, N.M.; Basu, M.; Goyal, S.K. Channel coordination and profit distribution in a social responsible three-layer supply chain. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2015, 168, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaeshi, K.M.; Osuji, O.K.; Nnodim, P. Corporate social responsibility in supply chains of global brands: A boundaryless responsibility? Clarifications, exceptions and implications. J. Bus. Ethics 2008, 81, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrian, K.; Wim, B. The Kpmg Survey of Corporate Responsibility Reporting. Available online: https://home.kpmg.com/xx/en/home/insights/2015/11/kpmg-international-survey-of-corporate-responsibility-reporting-2015.html (accessed on 10 November 2017).
- Baron, D.P. Private politics, corporate social responsibility, and integrated strategy. J. Econ. Manag. Strategy 2001, 10, 7–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, T.J.; Dacin, P.A. The Company and the product: Corporate associations and consumer product responses. J. Mark. 1997, 61, 68–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaen, V.; Chumpitaz, R. Impact of corporate social responsibility on consumer trust. Rech. Appl. Mark. (Engl. Ed.) 2008, 23, 7–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, M.S.; Linda, F.; LeClair, D.T. Consumers’ trust of salesperson and manufacturer: An empirical study. J. Bus. Res. 2001, 51, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pivato, S.; Misani, N.; Tencati, A. The impact of corporate social responsibility on consumer trust: The case of organic food. Bus. Ethics A Eur. Rev. 2008, 17, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabrizio, Z. CSR Initiatives as Market Signals: A review and research agenda. J. Bus. Ethics 2015, 146, 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Siegel, D.S.; Vitaliano, D.F. An empirical analysis of the strategic use of corporate social responsibility. J. Econ. Manag. Strategy 2007, 16, 773–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomer, B.; Yoram, M.; Adi, S. The Signaling Role of Corporate Social Responsibility; Working Paper; Uppsala University: Uppsala, Sweden, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Connelly, B.; Ireland, R.; Reutzel, C. Signaling theory: A review and assessment. J. Manag. 2011, 37, 39–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, D.E.; Speckman, R.E.; Werhane, P. Corporate Social Responsibility and Global Supply Chain Management: A Normative Perspective; Working paper (No. 04-05); University of Virginia: Charlottesville, WV, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Ageron, B.; Gunasekaran, A.; Spalanzani, A. Sustainable supply management: An empirical study. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2011, 140, 168–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Formentini, M.; Taticchi, P. Corporate sustainability approaches and governance mechanisms in sustainable supply chain management. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 1920–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stindt, D. A generic planning approach for sustainable supply chain management-How to integrate concepts and methods to address the issues of sustainability? J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 153, 146–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahimnia, B.; Sarkis, J.; Gunasekaran, A.; Farahani, R. Decision models for sustainable supply chain design and management. Ann. Oper. Res. 2017, 250, 277–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, J.M. Dynamics of supply chain networks with corporate social responsibility through integrated environmental decision-making. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2008, 184, 1005–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, R.; Gunasekaran, A.; Papadopoulos, T.; Childe, S.J.; Shibin, K.T.; Wamba, S.F. Sustainable supply chain management: Framework and further research directions. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 142, 1119–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, J.A.; Thomsen, C.G.; Arenas, D.; Pagell, M. NGOs’ initiatives to enhance social sustainability in the supply chain: Poverty alleviation through supplier development programs. J. Supply Chain Manag. 2016, 52, 83–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, R.E. Strategic Management: A Stakeholder Approach; Pitman/Ballinger: Boston, MA, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, D.B.; Kevin, L.W.; Tang, X.W. Social responsibility allocation in two-echelon supply chains: Insights from wholesale price contracts. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2010, 207, 1269–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsueh, C.F. A bilevel programming model for corporate social responsibility collaboration in sustainable supply chain management. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2015, 73, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, S. Coordination of a socially responsible supply chain using revenue sharing contract. Transp. Res. E 2014, 67, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modak, N.M.; Panda, S.; Sana, S.S.; Basu, M. Corporate social responsibility, coordination and profit distribution in a dual-channel supply chain. Pac. Sci. Rev. 2014, 16, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, C.R.; Jennings, M.M. Social responsibility and supply chain relationships. Transp. Res. E 2002, 38, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golicic, S.L.; Smith, C.D. A meta-analysis of environmentally sustainable supply chain management practices and firm performance. J. Supply Chain Manag. 2013, 49, 78–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crifo, P.; Forget, V.D. The economics of corporate social responsibility: A firm-level perspective survey. J. Econ. Surv. 2015, 29, 112–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Liu, J.; Lai, K. Corporate social responsibility practices and performance improvement among Chinese national state-owned enterprises. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2016, 171, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullmann, A. Data in search of a theory: A critical examination of the relationship among social performance, social disclosure, and economic performance. Acad. Manag. Rev. 1985, 10, 540–577. [Google Scholar]
- Fleury, A.M.; Davies, B. Sustainable supply chains-minerals and sustainable development, going beyond the mine. Resour. Policy 2012, 37, 175–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestre, B.S. Sustainable supply chain management in emerging economies: Environmental turbulence, institutional voids and sustainability trajectories. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2015, 167, 156–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chkanikova, O. Sustainable purchasing in food retailing: Interorganizational relationship management to green product supply. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2016, 25, 478–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cachon, G.P.; Fisher, M. Supply chain inventory management and the value of shared information. Manag. Sci. 2000, 46, 1032–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Zhang, H. Information sharing in a supply chain with a make-to-stock manufacturer. Omega 2015, 50, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittendorf, B.; Shin, J.; Yoon, D.H. Manufacturer marketing initiatives and retailer information sharing. Quant. Mark. Econ. 2013, 11, 263–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, A.Y.; Tong, S. Contracting and information sharing under supply chain competition. Manag. Sci. 2008, 54, 701–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, A.Y.; Tong, S.; Zhang, H. Sharing demand information in competing supply chains with production diseconomies. Manag. Sci. 2011, 57, 566–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annand, K.S.; Goyal, M. Strategic information management under leakage in a supply chain. Manag. Sci. 2009, 55, 438–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, G.; Rajagopalan, S.; Zhang, H. Revenue sharing and information leakage in a supply chain. Manag. Sci. 2013, 59, 556–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, I.K.; Kreps, D. Signaling games and stable equilibrium. Q. J. Econ. 1987, 102, 179–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ağan, Y.; Kuzey, C.; Acar, M.F.; Açıkgöz, A. The relationships between corporate social responsibility, environmental supplier development, and firm performance. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 1872–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fombrun, C.; Shanley, M. What’s in a name? Reputation building and corporate strategy. Acad. Manag. J. 1990, 33, 233–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starbucks. What Is the Role and Responsibility of a for-Profit, Public Company? Available online: http://www.starbucks.com/responsbility (accessed on 3 November 2017).
- Mary, J.; Meixell, P.L. Stakeholder pressure in sustainable supply chain management. Int. J. Phys. Distrib. Logist. Manag. 2015, 45, 69–89. [Google Scholar]
- Wolf, J. The relationship between sustainable supply chain management, stakeholder pressure and corporate sustainability performance. J. Bus. Ethics 2014, 119, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Xu, Y. Consumers’ responses to corporate social responsibility initiatives: The mediating role of consumer–company identification. J. Bus. Ethics 2017, 142, 515–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.; Shang, J.; Wang, H. Enhancing corporate social responsibility: Contract design under information asymmetry. Omega 2017, 67, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, X. Free or bundled: Channel selection decisions under different power structures. Omega 2015, 53, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Liu, N. Effects of e-commerce channel entry in a two-echelon supply chain: A comparative analysis of single-and dual-channel distribution systems. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2015, 165, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Ni, D.; Xiao, Z.; Tang, X. Signaling Product Quality Information in Supply Chains via Corporate Social Responsibility Choices. Sustainability 2017, 9, 2113. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9112113
Li Y, Ni D, Xiao Z, Tang X. Signaling Product Quality Information in Supply Chains via Corporate Social Responsibility Choices. Sustainability. 2017; 9(11):2113. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9112113
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yuhui, Debing Ni, Zhuang Xiao, and Xiaowo Tang. 2017. "Signaling Product Quality Information in Supply Chains via Corporate Social Responsibility Choices" Sustainability 9, no. 11: 2113. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9112113
APA StyleLi, Y., Ni, D., Xiao, Z., & Tang, X. (2017). Signaling Product Quality Information in Supply Chains via Corporate Social Responsibility Choices. Sustainability, 9(11), 2113. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9112113



