Mandatory Targets and Environmental Performance: An Analysis Based on Regression Discontinuity Design
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Data and Research Design
3.1. Variables and Measures
3.1.1. Dependent Variable: Environmental Performance
3.1.2. Mandatory Targets System
3.1.3. Performance Accomplishment
3.1.4. Control Variables
3.1.5. Descriptive Summary
3.2. Research Design
4. Empirical Results
4.1. Mandatory Targets and Environmental Performance
4.2. Sanction-and-Incentive Measures and Environmental Performance
5. Discussion
6. Policy Implications
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kostka, G. Environmental protection bureau leadership at the provincial level in China: Examining diverging career backgrounds and appointment patterns. J. Environ. Policy Plan. 2013, 15, 41–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Ma, L.; Zhang, H. Translating a Global Issue into Local Priority China’s Local Government Response to Climate Change. J. Environ. Dev. 2008, 17, 379–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, B.; Bi, J. Reforming China’s multi-level environmental governance: Lessons from the 11th Five-Year Plan. Environ. Sci. Policy 2012, 21, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, A.; Yan, Y.; Liu, S. The “Planning Hand” under the Market Economy—Evidence from Energy Intensity. China Ind. Econ. 2010, 268, 26–35. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, J. Who Maximizes (or Satisfices) in Performance management? An Empirical Study of the Effects of Motivation-Related Institutional Contexts on Energy Efficiency Policy in China. Public Perform. Manag. Rev. 2014, 38, 284–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, C.; Liu, Z. Administrative Accountability and Bandwagoning in Policy Implementation: Regional Variations in Energy Saving Policy Implementation. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2012, 22, 127–134. [Google Scholar]
- Ran, R. Political Incentives and Local Environmental Governance under a “Pressurized System”. Comp. Econ. Soc. Syst. 2013, 167, 111–118. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J. Governing by goals and numbers: A case study in the use of performance measurement to build state capacity in China. Public Adm. Dev. 2009, 29, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Liu, X.Y. Tournament system, promotion game and local political theatre. J. Public Manag. 2011, 18, 21–33. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J. Pernicious Manipulation of Performance Measures in China’s Cadre Evaluation System. China Q. 2015, 223, 618–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Lian, H.; Ortolano, L.; Ye, Y. A behavioral model of “muddling through” in the Chinese bureaucracy: The case of environmental protection. China J. 2013, 70, 120–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabatier, P.; Mazmanian, D. The implementation of public policy: A framework of analysis. Policy Stud. J. 1980, 8, 538–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholz, J.T. Cooperation, deterrence, and the ecology of regulatory enforcement. Law Soc. Rev. 1984, 18, 179–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, W.B.; Scholz, J.T. Does regulatory enforcement work? A panel analysis of OSHA enforcement. Law Soc. Rev. 1993, 27, 177–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholz, J.T.; Wei, F.H. Regulatory enforcement in a federalist system. Am. Political Sci. Rev. 1986, 80, 1249–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabatier, P.A. Top-down and bottom-up approaches to implementation research: A critical analysis and suggested synthesis. J. Public Policy 1986, 6, 21–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, E.; Franklin, A.L. The paradox of implementing the government performance and results act: Top-down direction for bottom-up implementation. Public Adm. Rev. 2004, 64, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, K.E.; Klinger, T. Obstacles to Bottom-up Implementation of Marine Ecosystem Management. Conserv. Biol. 2008, 22, 1135–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ioppolo, G.; Cucurachi, S.; Salomone, R.; Saija, G.; Shi, L. Sustainable Local Development and Environmental Governance: A Strategic Planning Experience. Sustainability 2016, 8, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sovacool, B.K.; Cooper, C. Big is beautiful: The case for federal leadership on a national renewable portfolio standard. Electr. J. 2007, 20, 48–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, T.; Jaccard, M. The renewable portfolio standard: Design considerations and an implementation survey. Energy Policy 2001, 29, 263–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menz, F.C.; Vachon, S. The effectiveness of different policy regimes for promoting wind power: Experiences from the states. Energy Policy 2006, 34, 1786–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiser, R.; Namovicz, C.; Gielecki, M.; Smith, R. The experience with renewable portfolio standards in the United States. Electr. J. 2007, 20, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delmas, M.A.; Montes-Sancho, M.J. US state policies for renewable energy: Context and effectiveness. Energy Policy 2011, 39, 2273–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carley, S. State renewable energy electricity policies: An empirical evaluation of effectiveness. Energy Policy 2009, 37, 3071–3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, W.M.; Park, S.; Elvery, J.A. Empirical estimates of the influence of renewable energy portfolio standards on the green economies of states. Econ. Dev. Q. 2013, 27, 338–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H. Green businesses in a clean energy economy: Analyzing drivers of green business growth in US states. Energy 2014, 68, 922–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H. Clean energy policies and green jobs: An evaluation of green jobs in US metropolitan areas. Energy Policy 2013, 56, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.; Feiock, R.C. Renewable energy politics: Policy typologies, policy tools, and state deployment of renewables. Policy Stud. J. 2014, 42, 391–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselin, L. Spatial effects in econometric practice in environmental and resource economics. Am. J. Agric. Econ. 2001, 83, 705–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.-A. The Incentive and Cooperation of Government Officials in the Political Tournaments: An Interpretation of the Prolonged Local Protectionism and Duplicative Investments in China. Econ. Res. J. 2004, 6, 33–40. [Google Scholar]
- Skjærseth, J.B.; Stokke, O.S.; Wettestad, J. Soft law, hard law, and effective implementation of international environmental norms. Glob. Environ. Politics 2006, 6, 104–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaels, R.J. National renewable portfolio standard: Smart policy or misguided gesture. Energy Law J. 2008, 29, 79. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, A. The Search for Sustainable Legitimacy: Environmental Law and Bureaucracy in China. Harv. Environ. Law Rev. 2013, 37, 365–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X. Formal and Informal Incentives: A Research on Policy Implementation Institution of Mandatory Indexes on Environment; Tsinghua University: Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, R.D.F.; Tzavalis, E. Inference for unit roots in dynamic panels where the time dimension is fixed. J. Econom. 1999, 91, 201–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, A.; Lin, C.-F.; Chu, C.-S.J. Unit root tests in panel data: Asymptotic and finite-sample properties. J. Econom. 2002, 108, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hausman, J.A. Specification tests in econometrics. Econom. J. Econom. Soc. 1978, 46, 1251–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Lian, H. Bureaucratic Bargaining in the Chinese Government: The Case of Environmental Policy Implementation. Soc. Sci. China 2011, 5, 80–96. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, X.; Hu, A.; Hang, C. Binary Incentive Mechanism in China’s Environmental Policy Implementation—A Research Based on Grounded Theory. J. Tsinghua Univ. Philos. Soc. Sci. 2016, 31, 38–49. [Google Scholar]
- Lo, K. How authoritarian is the environmental governance of China? Environ. Sci. Policy 2015, 54, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guttman, D.; Song, Y. Making central-local relations work: Comparing America and China environmental governance systems. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. China 2007, 1, 418–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, K. What motivates municipal governments? Uncovering the institutional incentives for municipal governance of forest resources in Bolivia. J. Environ. Dev. 2003, 12, 5–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.; Liu, Y. Green economy in China: Regional variations and policy drivers. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2015, 31, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, D.; Liu, Y.; Yi, H. Wind Power Development in China: An Assessment of Provincial Policies. Sustainability 2016, 8, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
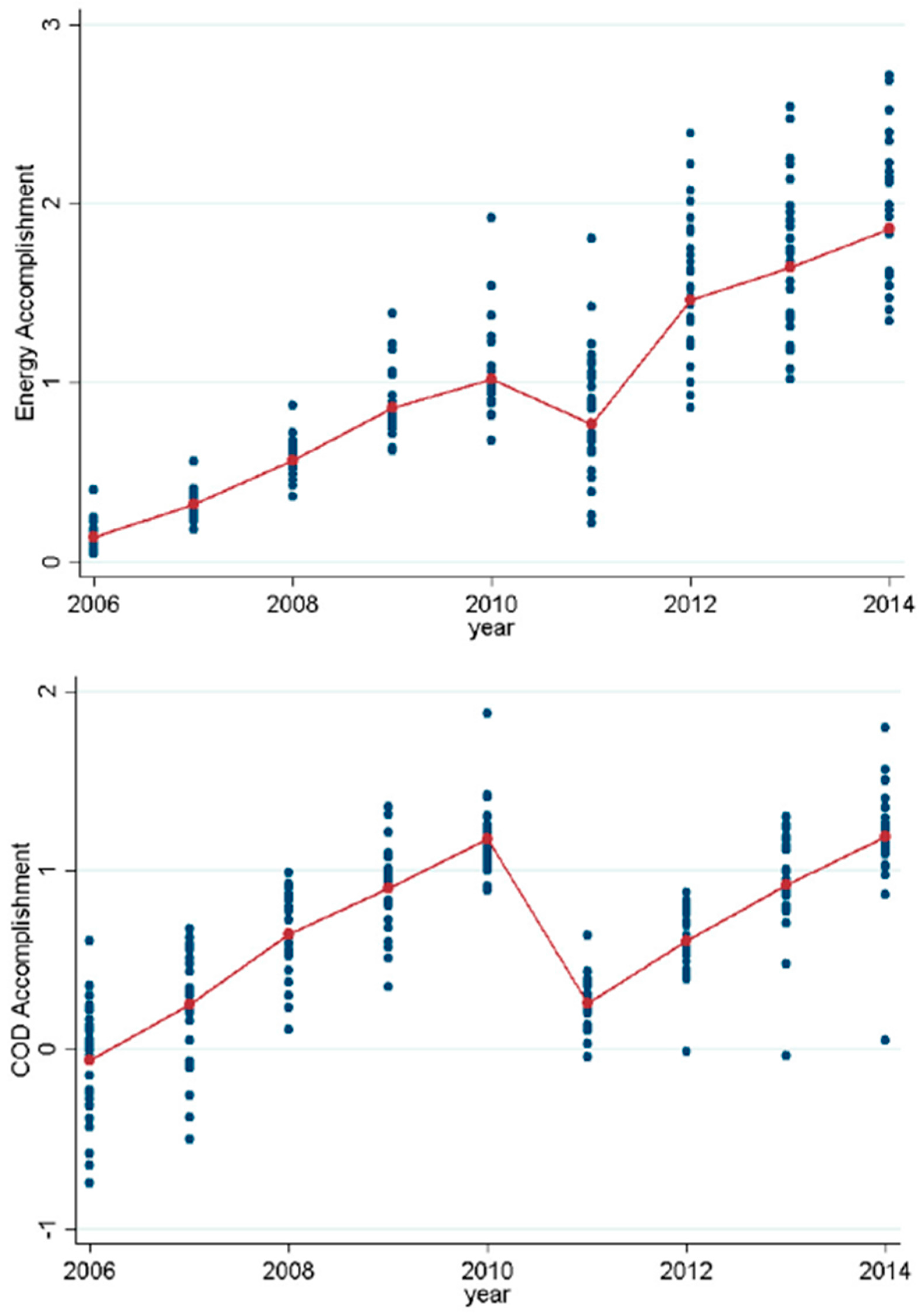
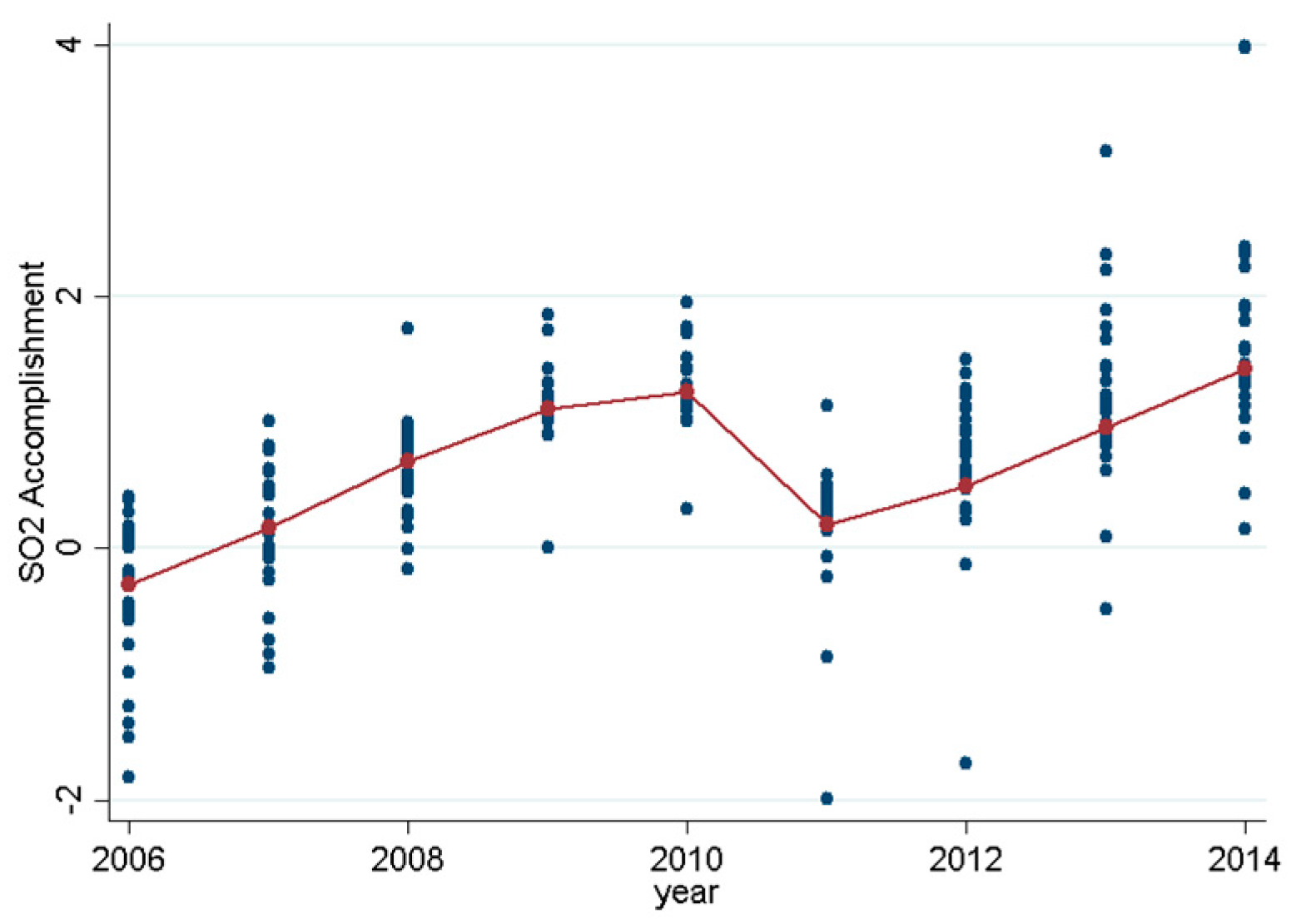
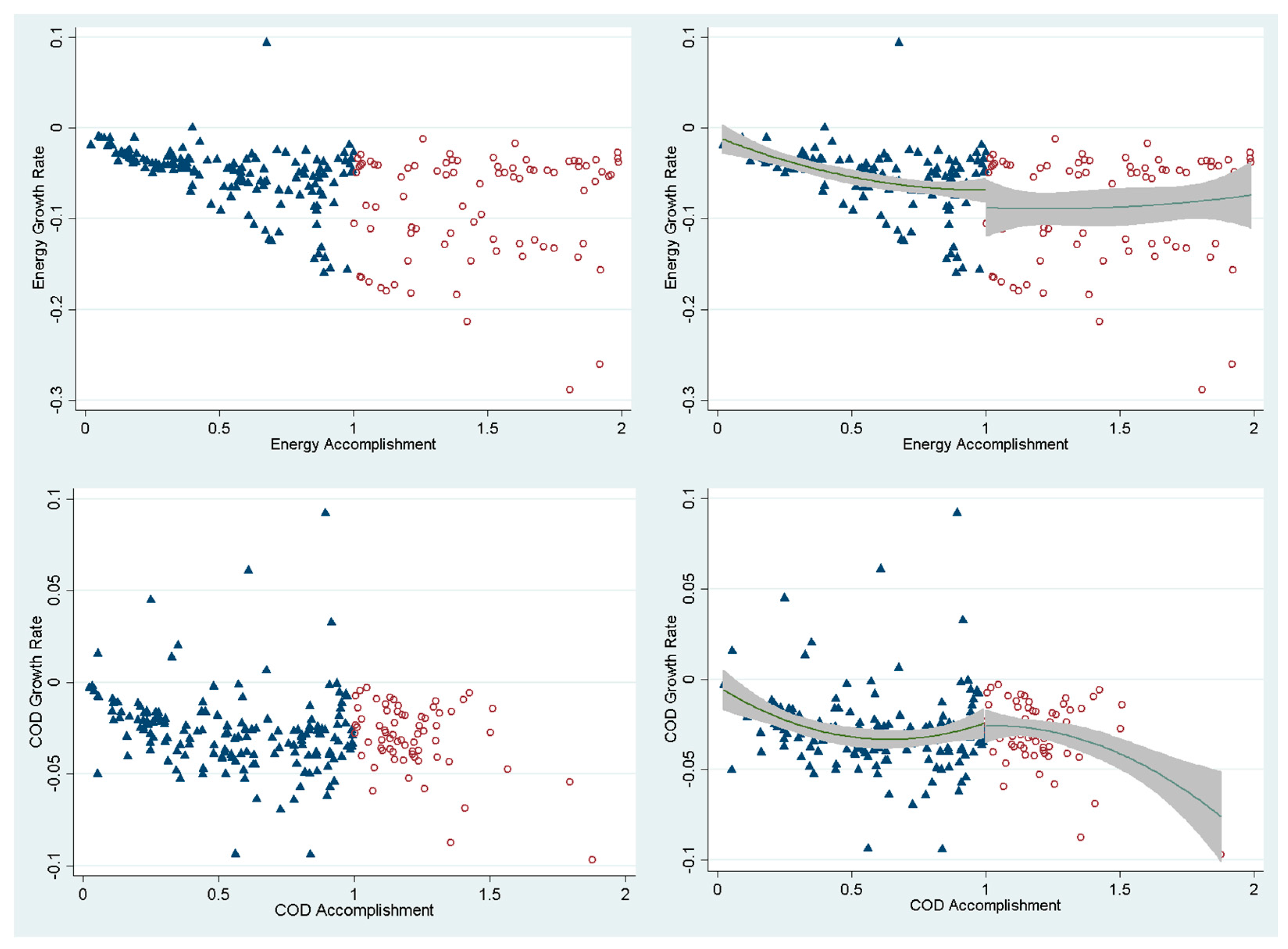
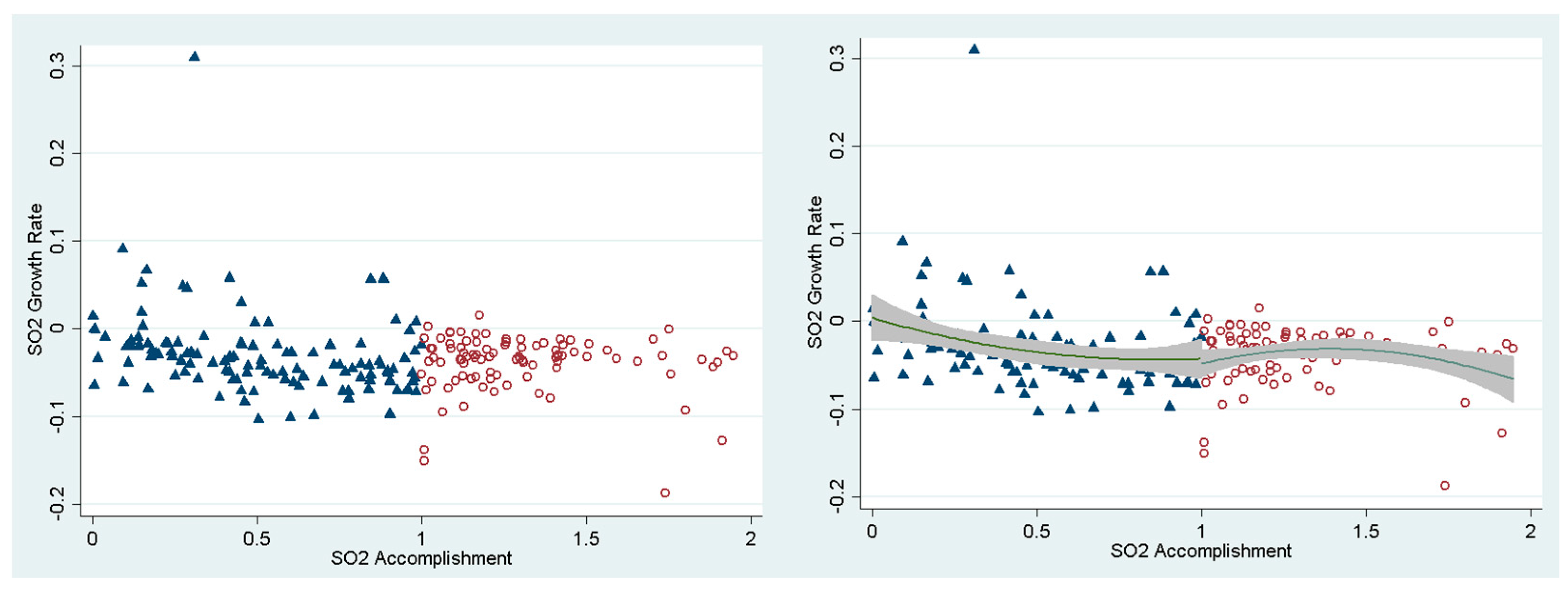
| Variable | Obs. | Mean | Std. Dev. | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indicator Growth Rate (2001–2014) (unit: percentage) | |||||
| Energy/GDP Growth Rate | 420 | −0.049 | 0.081 | −0.471 | 0.715 |
| COD Growth Rate | 360 | −0.004 | 0.096 | −0.348 | 1.156 |
| SO2 Growth Rate | 360 | 0.015 | 0.119 | −0.188 | 0.884 |
| Mandatory Target System (2000–2014) (0–1 dummy) | |||||
| D | 450 | 0.600 | 0.490 | 0 | 1 |
| Degree of Target Completion (2006–2014) (unit: percentage) | |||||
| Ener Accomp1 | 270 | 0.960 | 0.908 | −2.844 | 4.894 |
| COD Accomp1 | 257 a | 0.652 | 0.478 | −0.743 | 1.878 |
| SO2 Accomp1 | 261 b | 0.664 | 0.959 | −4.823 | 3.977 |
| Control Variables (2000–2014) | |||||
| Second Share (unit: percentage) | 450 | 0.466 | 0.079 | 0.198 | 0.664 |
| GDP Growth Rate (unit: percentage) | 450 | 0.107 | 0.027 | 0.038 | 0.236 |
| log Pop/Square (unit: log 1/km2) | 450 | 8.144 | 0.762 | 6.247 | 9.280 |
| Average Education (unit: Year) | 450 | 8.188 | 1.027 | 5.300 | 11.836 |
| Leader Age Initial (unit: log Age) | 450 | 4.048 | 0.067 | 3.850 | 4.190 |
| Leader: above Master (unit: 0, 1) | 450 | 0.471 | 0.500 | 0 | 1 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indicator Growth Rate (EG)= | Energy | Energy | COD | COD | SO2 | SO2 |
| Mandatory Target (D) | −0.0484 *** | −0.0822 *** | −0.0510 ** | −0.0672 ** | −0.103 *** | −0.124 *** |
| (−2.65) | (−3.26) | (−2.31) | (−2.13) | (−5.46) | (−4.95) | |
| L.EG | −0.318 *** | −0.343 *** | −0.171 *** | −0.190 *** | −0.0337 | −0.0777 * |
| (−6.57) | (−7.04) | (−3.12) | (−3.47) | (−0.79) | (−1.80) | |
| Second Share | −0.0806 | −0.246 | −0.113 | |||
| (−0.73) | (−1.52) | (−0.95) | ||||
| GDPG | −0.129 | −0.0800 | 0.269 | |||
| (−0.54) | (−0.26) | (1.18) | ||||
| log Pop | 0.246 ** | −0.0250 | 0.148 | |||
| (2.57) | (−0.18) | (1.46) | ||||
| Edu | 0.00473 | 0.00627 | 0.00737 | |||
| (0.31) | (0.27) | (0.44) | ||||
| Age | −3.443 | −14.10 * | −15.10 *** | |||
| (−0.60) | (−1.89) | (−2.74) | ||||
| Age2 | 0.437 | 1.740 * | 1.866 *** | |||
| (0.61) | (1.87) | (2.71) | ||||
| above Master | 0.00506 | 0.0180 | 0.0149 | |||
| (0.45) | (1.23) | (1.39) | ||||
| cons | −0.00950 | 4.786 | 0.0238 | 28.85 * | 0.0685 *** | 29.36 *** |
| (−0.71) | (0.41) | (1.53) | (1.91) | (4.86) | (2.62) | |
| N | 390 | 390 | 330 | 330 | 330 | 330 |
| R2 | 0.298 | 0.324 | 0.224 | 0.252 | 0.516 | 0.546 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EG= | Energy | Energy | COD | COD | SO2 | SO2 |
| T | −0.0140 | −0.0145 | −0.00187 | −0.00234 | −0.00684 | −0.00513 |
| (−1.50) | (−1.58) | (−0.42) | (−0.51) | (−0.85) | (−0.62) | |
| E Accomp | −0.112 *** | −0.116 *** | −0.0263 *** | −0.0263 *** | −0.0104 ** | −0.00896 ** |
| (−20.24) | (−21.15) | (−4.12) | (−3.75) | (−2.59) | (−2.14) | |
| E Accomp2 | 0.0189 *** | 0.0201 *** | 0.00626 | 0.00766 | 0.000107 | 0.000344 |
| (11.55) | (12.29) | (1.37) | (1.55) | (0.09) | (0.27) | |
| L.EG | −0.330 *** | −0.325 *** | −0.00760 | −0.00673 | 0.00107 | −0.00458 |
| (−10.14) | (−10.20) | (−0.66) | (−0.57) | (0.03) | (−0.12) | |
| Second Share | −0.00427 | 0.00506 | −0.0289 | |||
| (−0.04) | (0.13) | (−0.34) | ||||
| GDPG | −0.414 ** | 0.0802 | 0.0980 | |||
| (−2.39) | (1.13) | (0.62) | ||||
| log Pop | −0.00728 | 0.00885 | 0.0856 | |||
| (−0.08) | (0.25) | (1.05) | ||||
| Edu | −0.0296 ** | −0.00145 | −0.00730 | |||
| (−2.58) | (−0.32) | (−0.71) | ||||
| Age | −7.385 * | 2.002 | 1.193 | |||
| (−1.90) | (1.29) | (0.35) | ||||
| Age2 | 0.920 * | −0.252 | −0.151 | |||
| (1.89) | (−1.30) | (−0.35) | ||||
| above Master | 0.0145 * | −0.0000933 | −0.00201 | |||
| (1.93) | (−0.03) | (−0.31) | ||||
| cons | −0.0234 *** | 15.15 * | 0.00495 | −4.049 | 0.0178 ** | −2.974 |
| (−3.25) | (1.90) | (1.58) | (−1.27) | (2.13) | (−0.42) | |
| N | 270 | 270 | 257 | 257 | 261 | 261 |
| R2 | 0.801 | 0.817 | 0.488 | 0.498 | 0.401 | 0.409 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EG= | Energy | Energy | COD | COD | SO2 | SO2 |
| T | 0.00556 | 0.00299 | −0.00475 | −0.00593 * | −0.0157 ** | −0.0150 * |
| (0.57) | (0.30) | (−1.43) | (−1.71) | (−2.12) | (−1.95) | |
| E Accomp | −0.117 *** | −0.120 *** | −0.0221 *** | −0.0214 *** | −0.00866 ** | −0.00711 * |
| (−20.49) | (−21.16) | (−3.16) | (−2.83) | (−2.18) | (−1.71) | |
| E Accomp2 | 0.0191 *** | 0.0203 *** | 0.00544 | 0.00685 | 0.000151 | 0.000431 |
| (11.54) | (12.20) | (1.27) | (1.49) | (0.12) | (0.34) | |
| L.EG | −0.324 *** | −0.320 *** | −0.0104 | −0.00940 | −0.0126 | −0.0160 |
| (−9.89) | (−9.96) | (−0.90) | (−0.80) | (−0.35) | (−0.43) | |
| Second Share | −0.00147 | 0.00428 | −0.0102 | |||
| (−0.01) | (0.11) | (−0.12) | ||||
| GDPG | −0.415 ** | 0.0815 | 0.122 | |||
| (−2.37) | (1.16) | (0.77) | ||||
| log Pop | 0.000539 | −0.000511 | 0.0829 | |||
| (0.01) | (−0.01) | (1.03) | ||||
| Edu | −0.0305 *** | −0.00248 | −0.00755 | |||
| (−2.64) | (−0.55) | (−0.74) | ||||
| Age | −6.876 * | 2.408 | 1.317 | |||
| (−1.76) | (1.54) | (0.39) | ||||
| Age2 | 0.857 * | −0.302 | −0.166 | |||
| (1.76) | (−1.55) | (−0.39) | ||||
| above Master | 0.0133 * | −0.000642 | −0.00162 | |||
| (1.77) | (−0.21) | (−0.25) | ||||
| cons | −0.0230 *** | 14.06 * | 0.00626 * | −4.781 | 0.0235 *** | −3.213 |
| (−3.19) | (1.76) | (1.93) | (−1.49) | (2.70) | (−0.46) | |
| N | 270 | 270 | 257 | 257 | 261 | 261 |
| R2 | 0.799 | 0.815 | 0.492 | 0.505 | 0.411 | 0.418 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type 1 | Type 2 | Type 1 | Type 2 | Type 1 | Type 2 | |
| EG= | Energy | Energy | COD | COD | SO2 | SO2 |
| T | 0.0209 | −0.00122 | −0.00812 ** | −0.00445 | −0.0131 * | 0.00262 |
| (1.68) | (−0.22) | (−2.14) | (−0.18) | (−2.04) | (0.10) | |
| E Accomp | −0.308 *** | −0.590 *** | −0.0178 ** | 0.0194 | −0.0461 | 0.00329 |
| (−14.71) | (−4.27) | (−2.73) | (0.23) | (−1.43) | (0.02) | |
| E Accomp2 | −0.135 *** | −0.332 *** | −0.0267 ** | 0.00211 | −0.00630 | −0.109 |
| (−13.27) | (−6.31) | (−2.17) | (0.05) | (−1.38) | (−0.76) | |
| L.EG | 0.0234 *** | 0.0418 ** | 0.00506 | 0.0183 | 0.0000154 | −0.00465 |
| (11.62) | (2.45) | (0.60) | (1.15) | (0.01) | (−0.08) | |
| Second Share | 0.150 ** | 0.333 | 0.0592 | −0.291 | −0.0441 | 0.283 |
| (2.31) | (1.29) | (1.65) | (−0.91) | (−0.58) | (0.10) | |
| GDPG | −0.324 * | −0.0673 | 0.115 | 0.281 | −0.131 | −0.370 |
| (−1.77) | (−0.44) | (1.36) | (1.21) | (−1.20) | (−0.20) | |
| log Pop | −0.110 | 0.409 *** | −0.000798 | 0.0827 | −0.0205 | 0.681 |
| (−0.67) | (4.46) | (−0.02) | (0.13) | (−0.31) | (0.78) | |
| Edu | −0.0440 | −0.0119 | −0.000788 | 0.0511 | −0.00944 | −0.0784 |
| (−1.36) | (−0.81) | (−0.17) | (1.71) | (−1.65) | (−0.87) | |
| Age | −1.844 | −14.73 | 2.740 | 23.51 | 0.478 | 1.288 |
| (−0.57) | (−1.63) | (1.63) | (1.32) | (0.16) | (0.02) | |
| Age2 | 0.235 | 1.811 | −0.342 | −2.938 | −0.0594 | −0.154 |
| (0.58) | (1.58) | (−1.61) | (−1.34) | (−0.16) | (−0.02) | |
| above Master | 0.00630 | −0.0284 | −0.0000857 | −0.0401 | −0.00135 | 0.0496 |
| (0.63) | (−1.45) | (−0.03) | (−1.46) | (−0.24) | (0.56) | |
| cons | 4.828 | 26.80 | −5.520 | −48.01 | −0.647 | −7.980 |
| (0.70) | (1.53) | (−1.57) | (−1.21) | (−0.10) | (−0.06) | |
| N | 216 | 54 | 187 | 43 | 196 | 28 |
| R2 | 0.874 | 0.978 | 0.560 | 0.765 | 0.517 | 0.845 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, X.; Liu, Z.; Yi, H. Mandatory Targets and Environmental Performance: An Analysis Based on Regression Discontinuity Design. Sustainability 2016, 8, 931. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8090931
Tang X, Liu Z, Yi H. Mandatory Targets and Environmental Performance: An Analysis Based on Regression Discontinuity Design. Sustainability. 2016; 8(9):931. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8090931
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Xiao, Zhengwen Liu, and Hongtao Yi. 2016. "Mandatory Targets and Environmental Performance: An Analysis Based on Regression Discontinuity Design" Sustainability 8, no. 9: 931. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8090931
APA StyleTang, X., Liu, Z., & Yi, H. (2016). Mandatory Targets and Environmental Performance: An Analysis Based on Regression Discontinuity Design. Sustainability, 8(9), 931. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8090931







