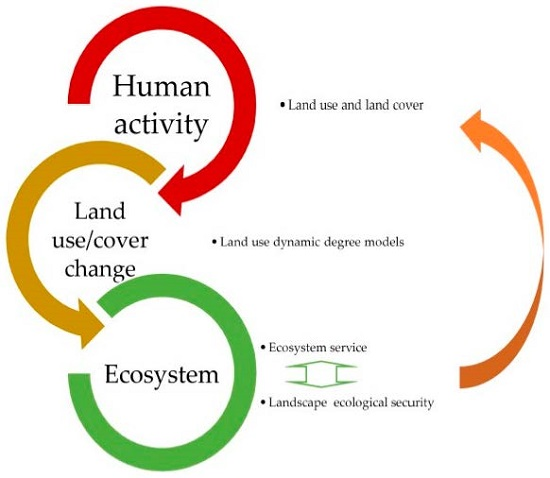
Ecological Security and Ecosystem Services in Response to Land Use Change in the Coastal Area of Jiangsu, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methodology
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Land-Use and Land-Cover Classification
2.4. Methodology
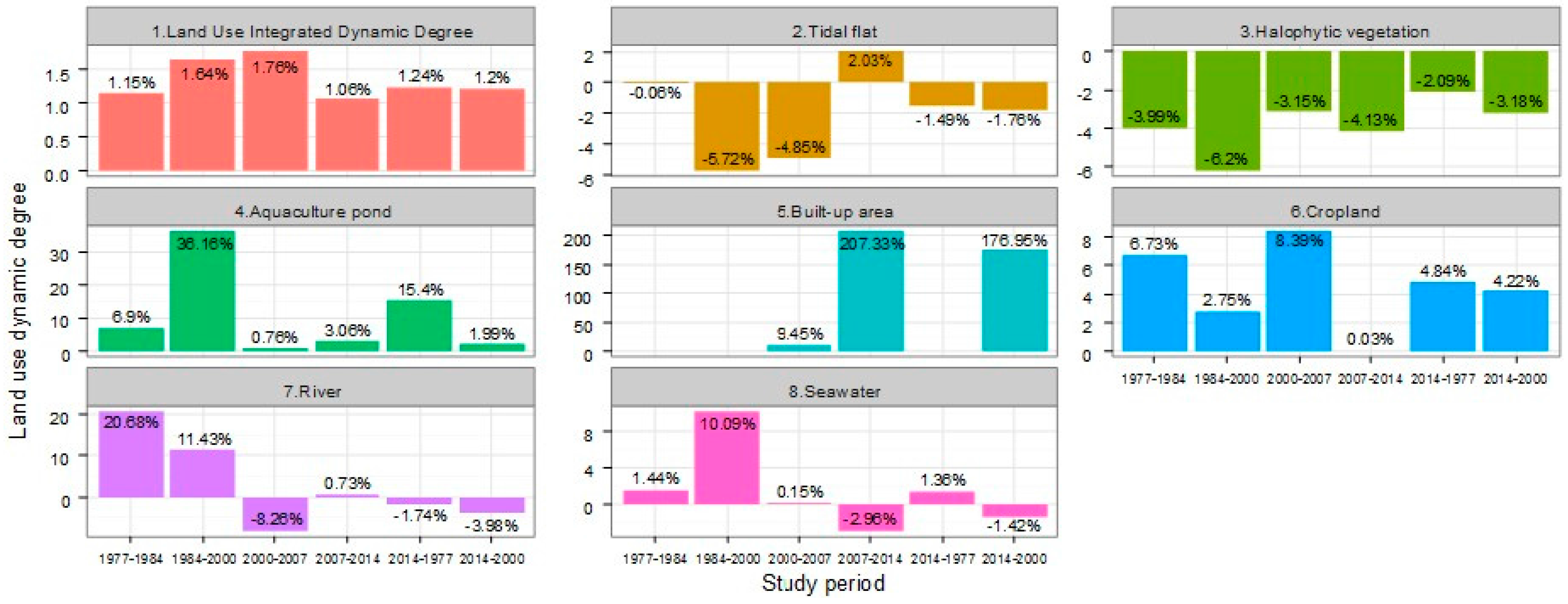
2.4.1. Land Use Dynamic Degree Models
2.4.2. Landscape Ecological Security (LES)
2.4.3. Ecosystem Service Value (ESV)
2.4.4. Changing of the Gravity Center of LES and ESV
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
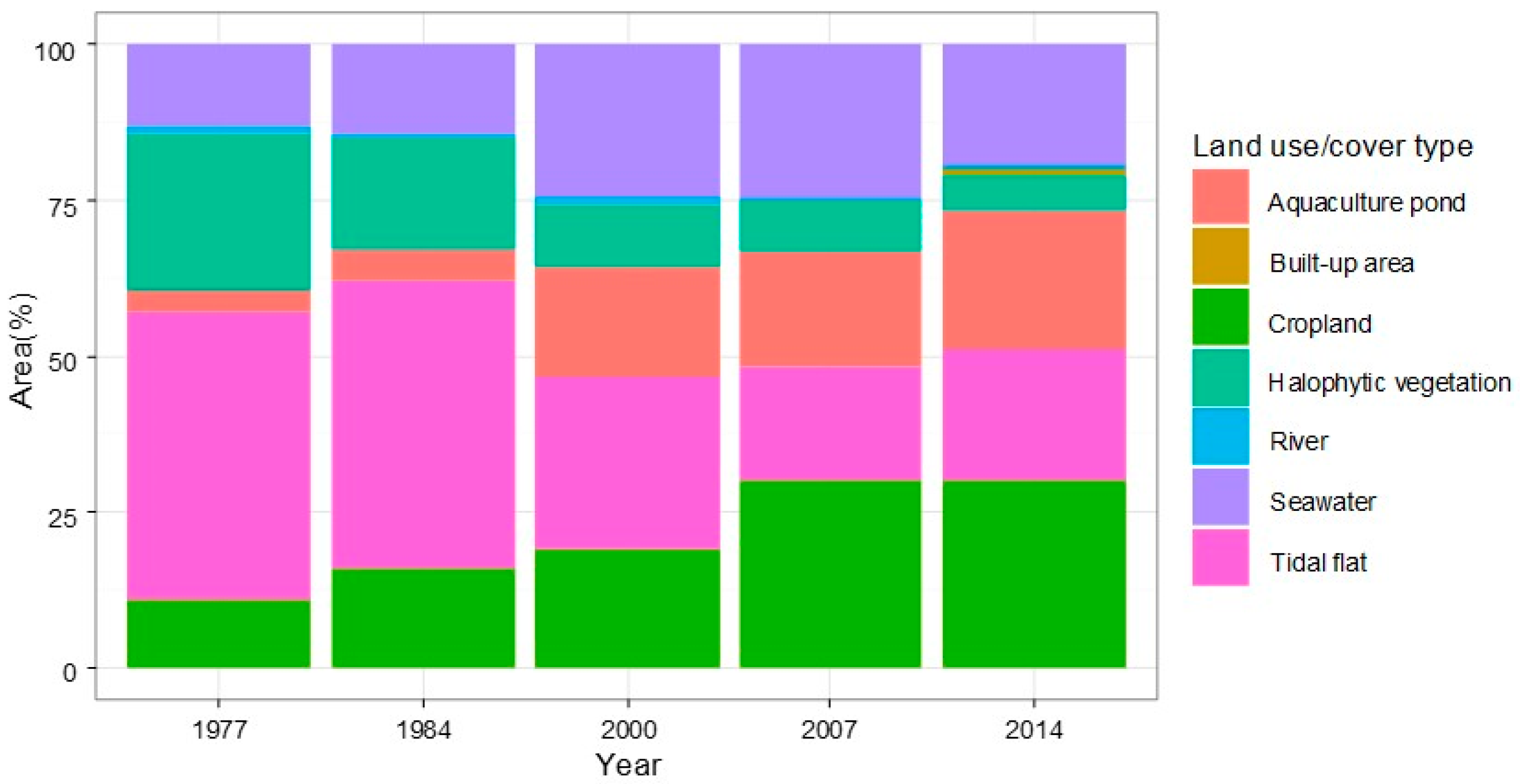
3.1. Changes in Land Use and Land Cover
3.2. Analysis of Ecoenvironment Response to Land Use Change
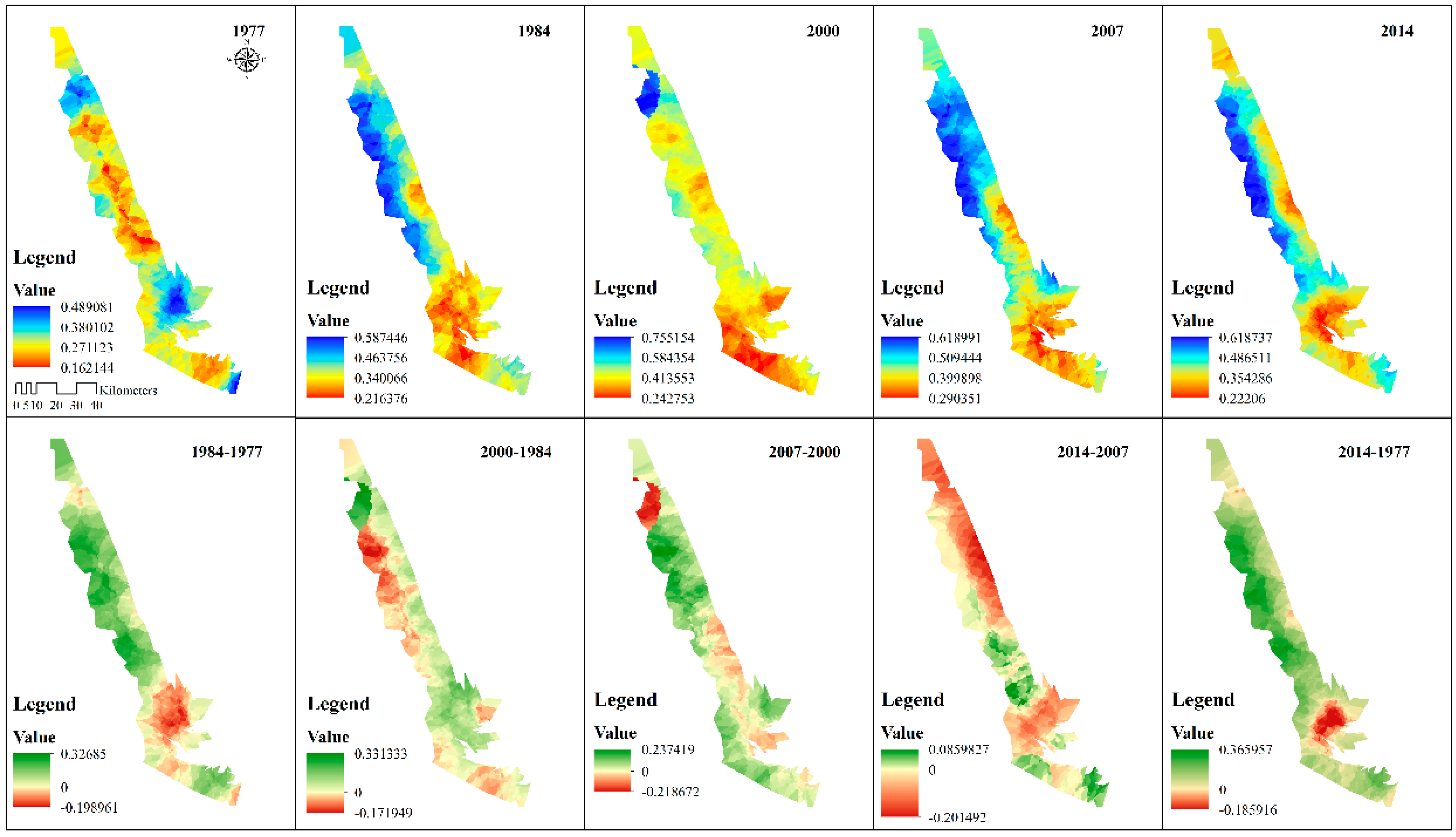
3.2.1. The Features of Landscape Ecological Security
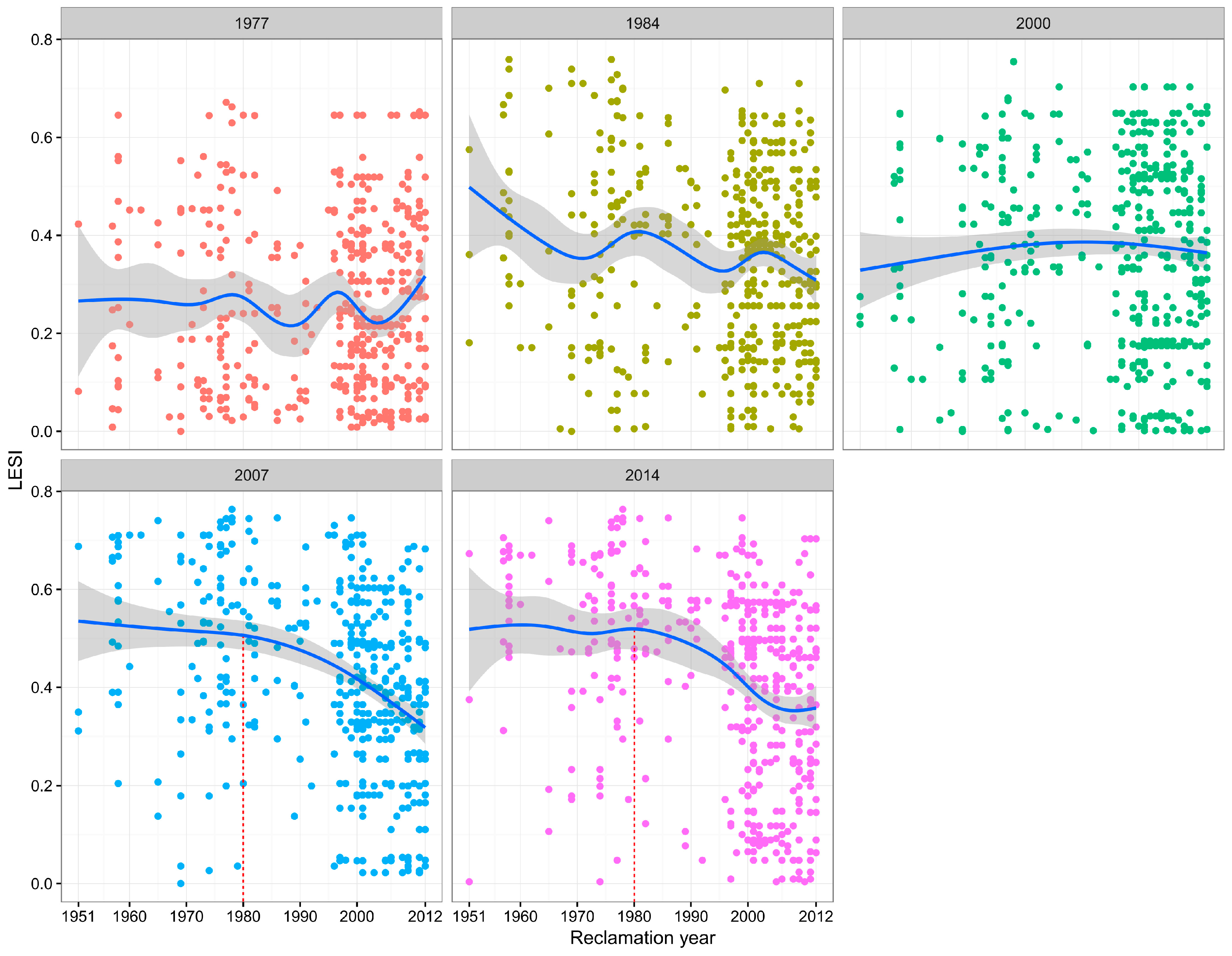
3.2.2. Relationship between LESI and Reclamation Year
3.3. Changes in Ecosystem Services Values
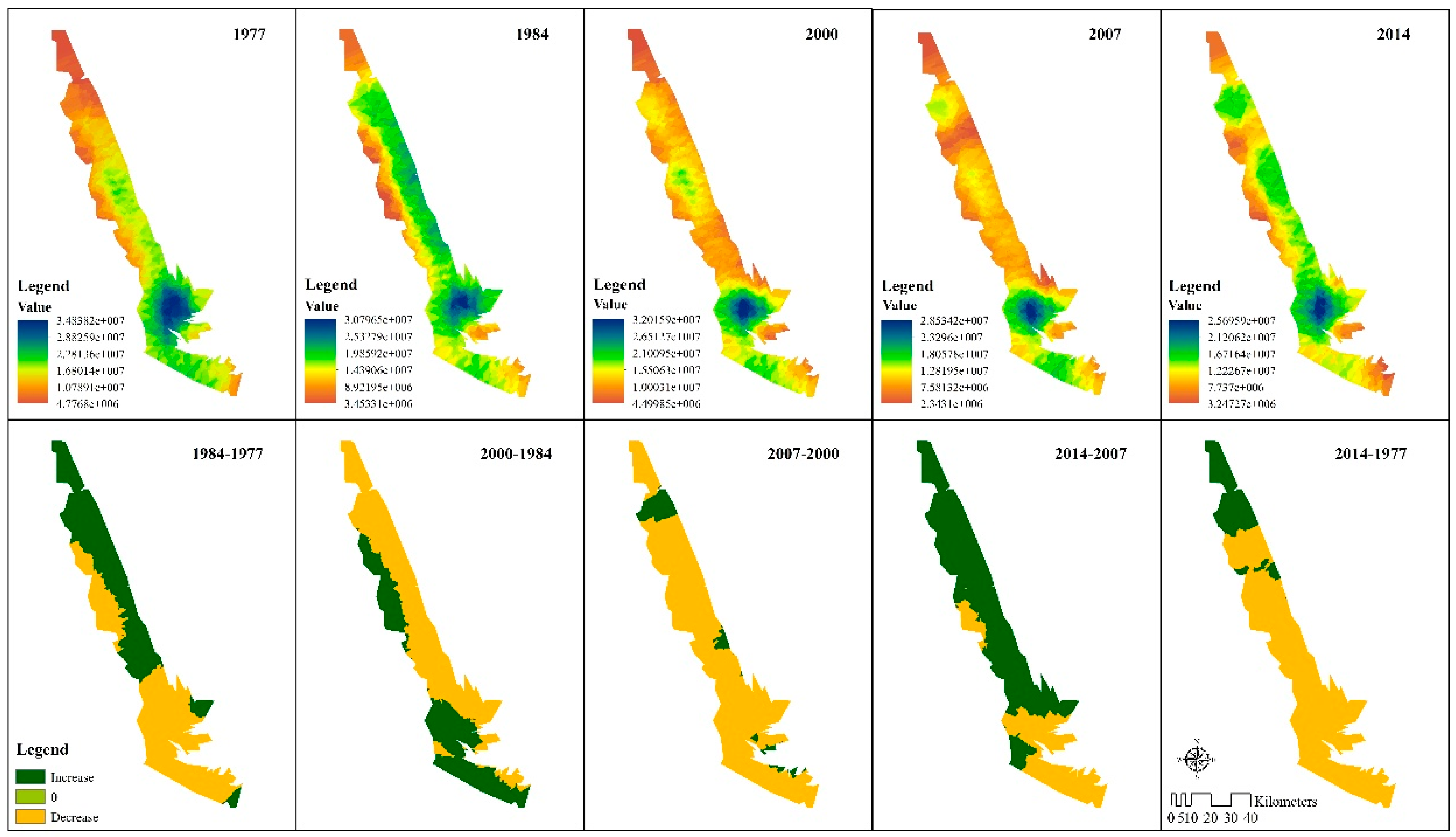
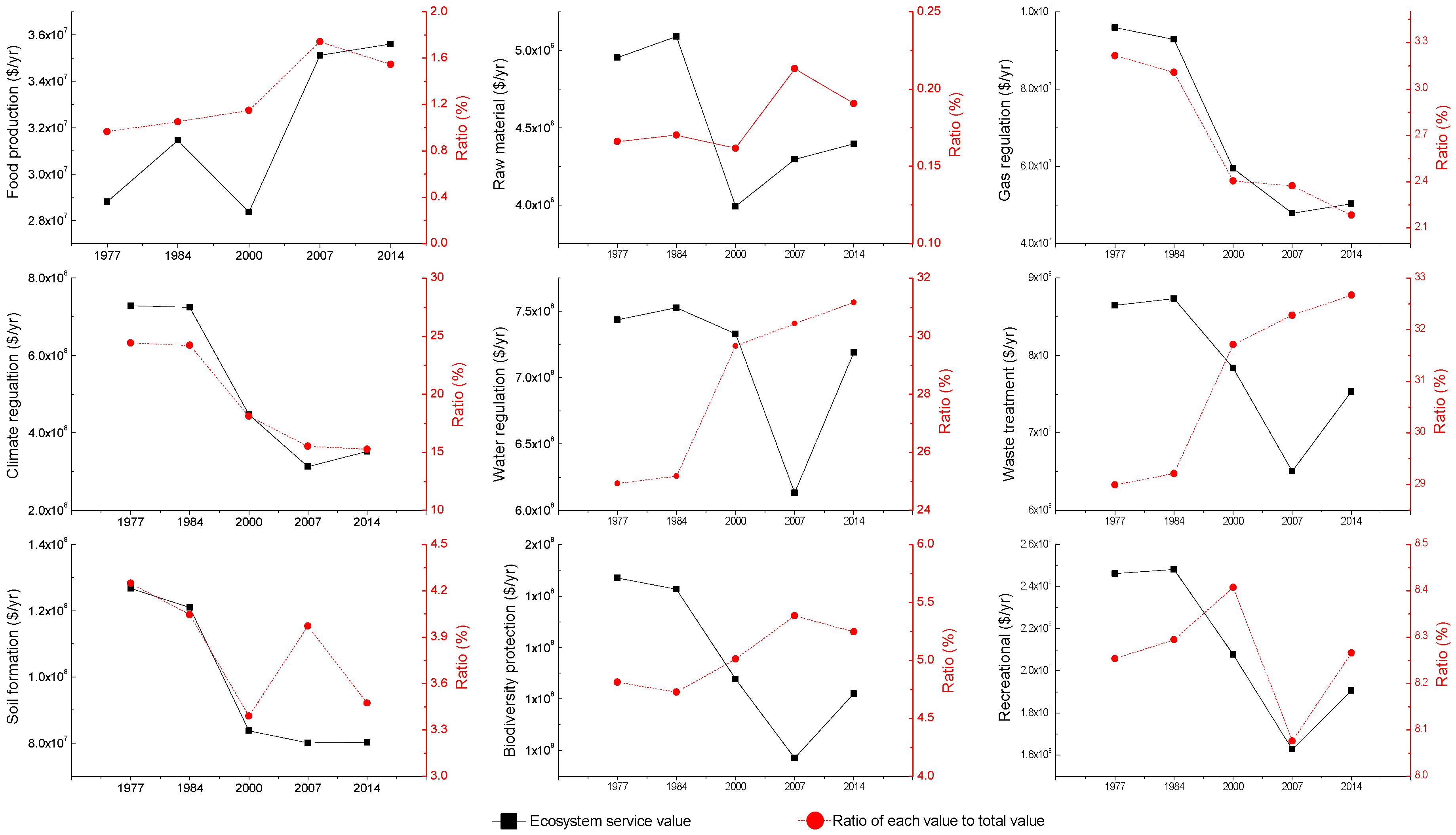
3.3.1. Spatiotemporal Features of Ecosystem Services Values
3.3.2. Ecosystem Service Functions
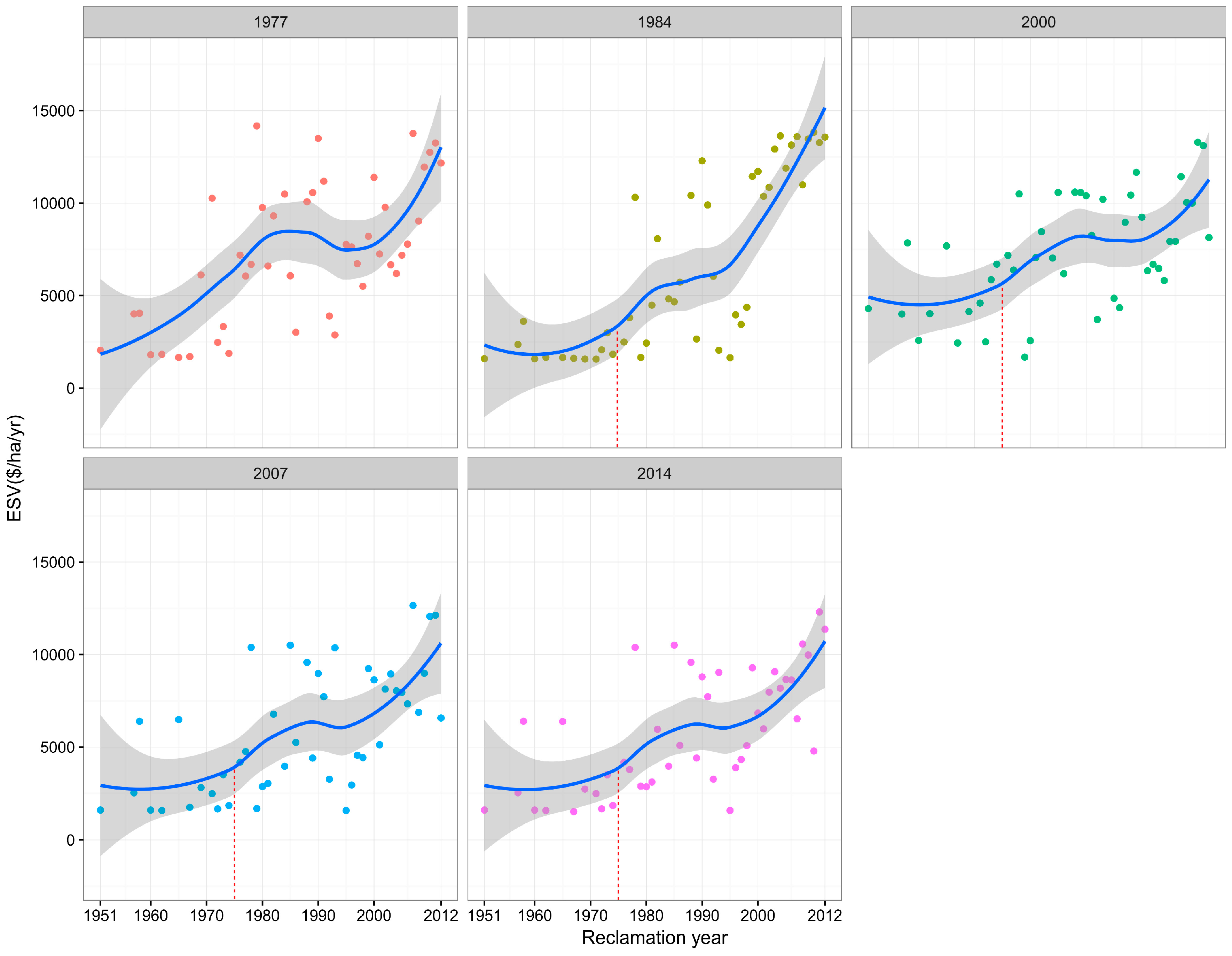
3.3.3. Relationship between ESV and Reclamation Year
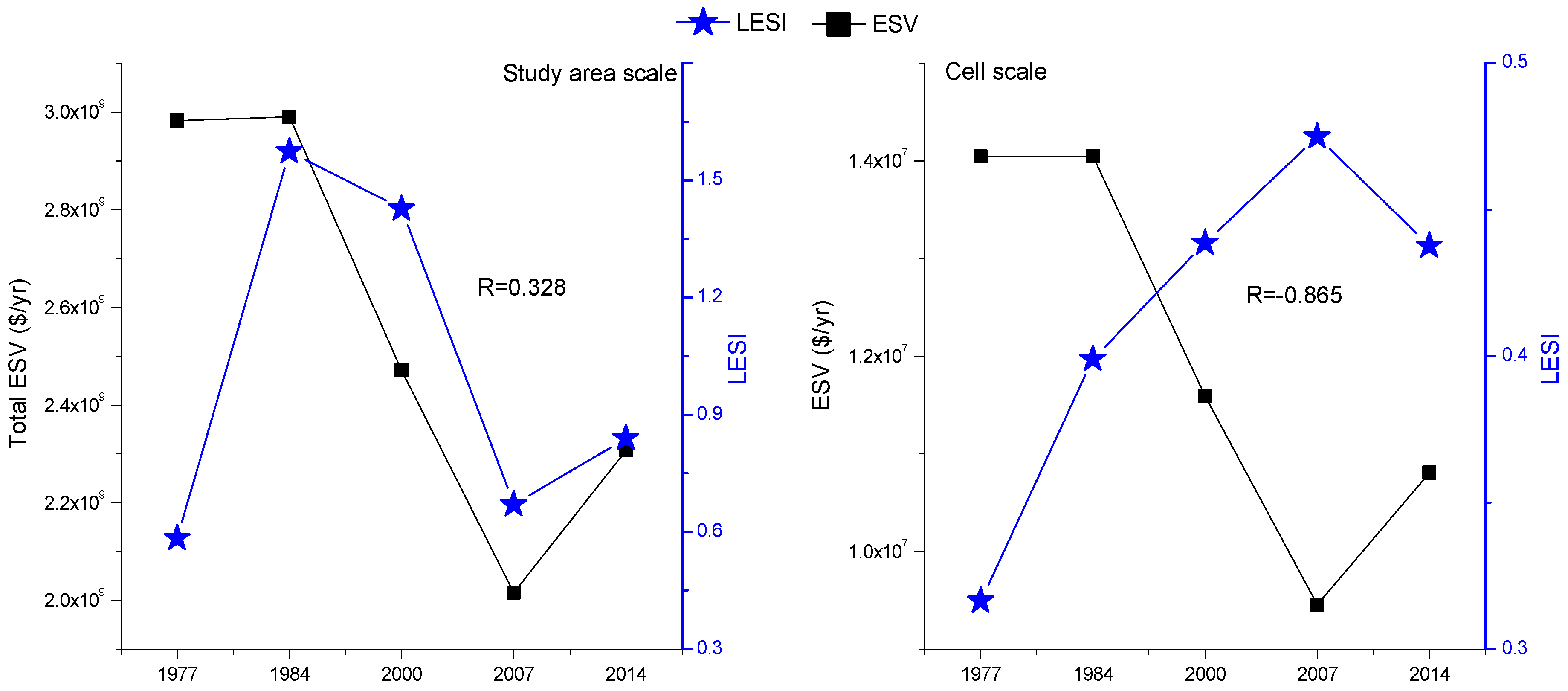
3.4. LESI and ESV
3.4.1. Relationship between LESI and ESV
3.4.2. Changing Track of the Gravity Center of LESI and ESV
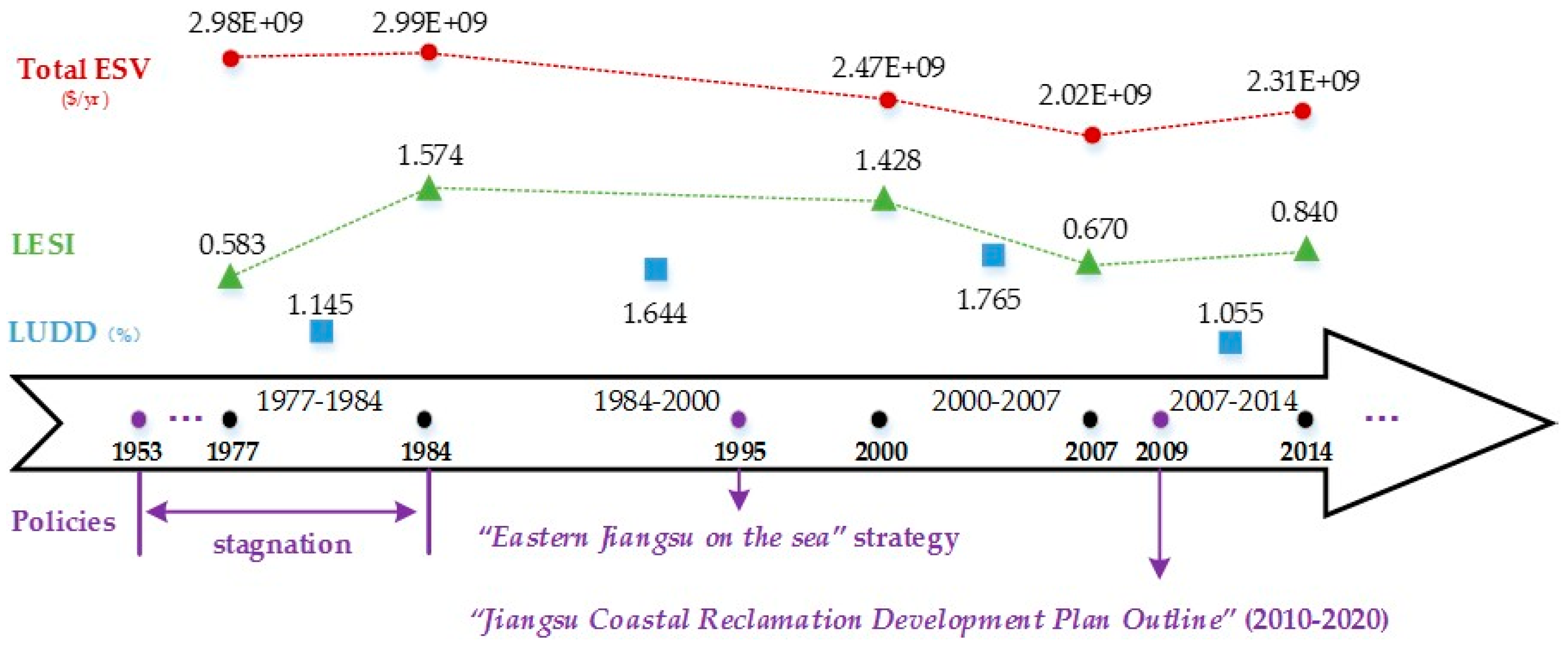
3.5. Comprehensive Analysis with Policy
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LES | landscape ecological security |
| LESI | landscape ecological security index |
| ESV | ecosystem service value |
| LUCC | land use and cover change |
| LUDD | land use dynamic degree |
| PD | patch density |
| SPLIT | splitting index |
| FRAC | fractal dimension |
| SHDI | Shannon’s diversity index |
| SHEI | Shannon’s evenness index |
| LVI | landscape vulnerability index |
| LDI | landscape disturbance index |
| LOWESS/LOESS | locally weighted scatterplot smoothing |
References
- Lee, S.Y.; Dunn, R.J.K.; Young, R.A.; Connolly, R.M.; Dale, P.; Dehayr, R.; Lemckert, C.J.; McKinnon, S.; Powell, B.; Teasdale, P. Impact of urbanization on coastal wetland structure and function. Austral Ecol. 2006, 31, 149–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonnell, M.J.; Pickett, S.T.A.; Groffman, P.; Bohlen, P.; Pouyat, R.V.; Zipperer, W.C.; Parmelee, R.W.; Carreiro, M.M.; Medley, K. Ecosystem processes along an urban-to-rural gradient. Urban Ecosyst. 1997, 1, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimm, N.B.; Grove, J.G.; Pickett, S.T.A.; Redman, C.L. Integrated approaches to long-term studies of urban ecological systems: Urban ecological systems present multiple challenges to ecologists—Pervasive human impact and extreme heterogeneity of cities, and the need to integrate social and ecological approaches, concepts, and theory. BioScience 2000, 50, 571–584. [Google Scholar]
- Pickett, S.T.A.; Cadenasso, M.L.; Grove, J.M.; Nilon, C.H.; Pouyat, R.V.; Zipperer, W.C.; Costanza, R. Urban ecological systems: Linking terrestrial ecological, physical, and socioeconomic components of metropolitan areas. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 2001, 32, 127–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinney, M.L. Urbanization, biodiversity, and conservation: The impacts of urbanization on native species are poorly studied, but educating a highly urbanized human population about these impacts can greatly improve species conservation in all ecosystems. BioScience 2002, 52, 883–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, R.K.; Subak, S.; Adger, W.N. Pressures, trends, and impacts in coastal zones: Interactions between socioeconomic and natural systems. Environ. Manag. 1996, 20, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, R.S.; Deluca, W.V.; Whigham, D.F.; Marra, P.P. Threshold effects of coastal urbanization on phragmites australis (common reed) abundance and foliar nitrogen in chesapeake bay. Estuar. Coasts 2007, 30, 469–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, W.F.; Charlier, R.H. Sustainability of subtropical coastal zones in southeastern florida: Challenges for urbanized coastal environments threatened by development, pollution, water supply, and storm hazards. J. Coast. Res. 2003, 19, 934–943. [Google Scholar]
- Zedler, J.B.; Kercher, S. Causes and consequences of invasive plants in wetlands: Opportunities, opportunists, and outcomes. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2004, 23, 431–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.-X.; Liu, J.-E.; Qin, P. Impacts of an alien species (Spartina alterniflora) on the macrobenthos community of Jiangsu coastal inter-tidal ecosystem. Ecol. Eng. 2009, 35, 521–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambin, E.F.; Turner, B.L.; Geist, H.J.; Agbola, S.B.; Angelsen, A.; Bruce, J.W.; Coomes, O.T.; Dirzo, R.; Fischer, G.; Folke, C. The causes of land-use and land-cover change: Moving beyond the myths. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2001, 11, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worrall, F.; Burt, T. The impact of land-use change on water quality at the catchment scale: The use of export coefficient and structural models. J. Hydrol. 1999, 221, 75–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, K.; Weil, R. Land use effects on soil quality in a tropical forest ecosystem of Bangladesh. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2000, 79, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremen, C.; Williams, N.M.; Aizen, M.A.; Gemmill-Herren, B.; LeBuhn, G.; Minckley, R.; Packer, L.; Potts, S.G.; Steffan-Dewenter, I.; Vazquez, D.P. Pollination and other ecosystem services produced by mobile organisms: A conceptual framework for the effects of land-use change. Ecol. Lett. 2007, 10, 299–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metzger, M.; Rounsevell, M.; Acosta-Michlik, L.; Leemans, R.; Schröter, D. The vulnerability of ecosystem services to land use change. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2006, 114, 69–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, B.L. Local faces, global flows: The role of land use and land cover in global environmental change. Land Degrad. Dev. 1994, 5, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalnay, E.; Cai, M. Impact of urbanization and land-use change on climate. Nature 2003, 423, 528–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2001: The Scientific Basis; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2014: Synthesis Report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Jeanson, M.; Dolique, F.; Anthony, E.J. A GIS-based coastal monitoring and surveillance observatory on tropical islands exposed to climate change and extreme events: The example of Mayotte Island, Indian ocean. J. Coast. Conserv. 2014, 18, 567–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parthasarathy, A.; Natesan, U. Coastal vulnerability assessment: A case study on erosion and coastal change along Tuticorin, Gulf of Mannar. Nat. Hazards 2015, 75, 1713–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, A.M.; Mitra, D.; Dewan, A.; Akhter, S.H. Coastal multi-hazard vulnerability assessment along the ganges deltaic coast of Bangladesh—A geospatial approach. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2016, 127, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hereher, M.E. Assessment of Egypt’s red sea coastal sensitivity to climate change. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 2831–2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boruff, B.J.; Emrich, C.; Cutter, S.L. Erosion hazard vulnerability of US coastal counties. J. Coast. Res. 2005, 21, 932–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, S.; Li, H.; Guan, B.; Zhou, C.; Wang, Z.; Deng, Z.; Zhi, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xu, C.; Fang, S.; et al. China’s natural wetlands: Past problems, current status, and future challenges. Ambio 2007, 36, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, W.J. The end of a tradition: 1000 years of embankment and reclamation of wetlands in the Netherlands. Ambio 1992, 21, 287–291. [Google Scholar]
- Ohkura, Y. The roles and limitations of newspapers in environmental reporting. Case study: Isahaya Bay land reclamation project issue. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2003, 47, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lie, H.-J.; Cho, C.-H.; Lee, S.; Kim, E.-S.; Koo, B.-J.; Noh, J.-H. Changes in marine environment by a large coastal development of the saemangeum reclamation project in Korea. Ocean Polar Res. 2008, 30, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Liu, H.; Li, Y.; Su, J. Development and management of land reclamation in China. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2014, 102, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Melville, D.S.; Liu, J.; Chen, Y.; Yang, H.; Ren, W.; Zhang, Z.; Piersma, T.; Li, B. Rethinking China’s new Great Wall. Science 2014, 346, 912–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The People’s Government of Jiangsu Province. Jiangsu Beach Reclamation Development Planning Outline. Available online: http://govinfo.nlc.gov.cn/jssfz/jszb/201020/201104/t20110414_696110.shtml?classid=416# (accessed on 16 August 2016). (In Chinese)
- Gao, J.; Bai, F.; Yang, Y.; Gao, S.; Liu, Z.; Li, J. Influence of spartina colonization on the supply and accumulation of organic carbon in tidal salt marshes of northern Jiangsu Province, China. J. Coast. Res. 2012, 486–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H. Characterizing landuse changes in 1990–2010 in the coastal zone of Nantong, Jiangsu Province, China. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2013, 71, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.; Li, G.; Cui, L.; Ouyang, N.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S. Study on evolution features and spatial distribution patterns of coastal wetlands in north Jiangsu Province, China. Wetlands 2014, 34, 877–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.J.; Gao, S.; Wang, Y.P. Modeling the deposition system evolution of accreting tidal flats: A case study from the coastal plain of central Jiangsu, China. J. Coast. Res. 2015, 31, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Zou, X.; Liu, X.; Liu, P.; Zhamangulova, N.; Xu, X.; Zhao, Y. Integrated ecosystem health assessment based on eco-exergy theory: A case study of the Jiangsu coastal area. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 48, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveh, Z.; Lieberman, A.S. Landscape Ecology: Theory and Application; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.G. Landscape ecology, cross-disciplinarity, and sustainability science. Landsc. Ecol. 2006, 21, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, R.V.; Krummel, J.R.; Gardner, R.H.; Sugihara, G.; Jackson, B.; DeAngelis, D.L.; Milne, B.T.; Turner, M.G.; Zygmunt, B.; Christensen, S.W.; et al. Indices of landscape pattern. Landsc. Ecol. 1988, 1, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGarigal, K.; Marks, B.J. Fragstats: Spatial Pattern Analysis Program for Quantifying Landscape Structure; Gen. Tech. Rep. PNW-GTR-351; US Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Pacific Northwest Research Station: Portland, OR, USA, 1995.
- Hargis, C.D.; Bissonette, J.A.; David, J.L. The behavior of landscape metrics commonly used in the study of habitat fragmentation. Lands. Ecol. 1998, 13, 167–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, R.V.; Riitters, K.H.; Wickham, J.D.; Jones, K.B. Landscape pattern metrics and regional assessment. Ecosyst. Health 1999, 5, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luck, M.; Wu, J.G. A gradient analysis of urban landscape pattern: A case study from the Phoenix metropolitan region, Arizona, USA. Landsc. Ecol. 2002, 17, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzanopoulos, J.; Vogiatzakis, I.N. Processes and patterns of landscape change on a small Aegean island: The case of Sifnos, Greece. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2011, 99, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewan, A.M.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Ziaur Rahman, M. Dynamics of land use/cover changes and the analysis of landscape fragmentation in Dhaka metropolitan, Bangladesh. GeoJournal 2012, 77, 315–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.S.; Pu, L.J.; Li, J.G.; Zhang, J.; Xu, Y. Landscape ecological security response to land use change in the tidal flat reclamation zone, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Wu, Z.; Lou, Q.; Huang, H.; Cheng, J.; Chen, Z. Landscape ecological security assessment based on projection pursuit in Pearl River Delta. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2012, 184, 2307–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Wang, R.; Zhang, H. Analysis of patterns and ecological security trend of modern oasis landscapes in Xinjiang, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 134, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botequilha Leitão, A.; Ahern, J. Applying landscape ecological concepts and metrics in sustainable landscape planning. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2002, 59, 65–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, J. Guidelines for landscape synthesis: Some directions—Old and new. Landsc. Urban Plan. 1987, 14, 295–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Xu, L.; Duan, X.; Xu, X. Analysis of boundary adjustments and land use policy change—A case study of Tianjin Palaeocoast and Wetland National Natural Reserve, China. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2012, 56, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Lu, L.; Wang, Y. The mechanism and trend of coastal erosion of Jiangsu Province in China. Geogr. Res. 2002, 21, 469–478. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.-S.; Liu, Y.-X.; Li, M.-C.; Sun, C.; Zhou, M.-X.; Zhang, H.-X. Analysis of Jiangsu tidal flats reclamation from 1974 to 2012 using remote sensing. China Ocean Eng. 2015, 29, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Pu, L.; Zhu, M.; Dai, X.; Xu, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, R. Monitoring soil salt content using HJ-1A hyperspectral data: A case study of coastal areas in Rudong County, eastern China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2015, 25, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatch, L.K.; Mallawatantri, A.; Wheeler, D.; Gleason, A.; Mulla, D.; Perry, J.; Easter, K.W.; Smith, R.; Gerlach, L.; Brezonik, P. Land management at the major watershed—Agroecoregion intersection. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2001, 56, 44–51. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Li, X.; Mander, Ü.; He, Y.; Jia, Y.; Ma, Z.; Guo, W.; Xin, Z. Effect of reclamation time and land use on soil properties in Changjiang River estuary, China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2011, 21, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China Centre for Resources Satellite Data and Application. Available online: http://www.cresda.com/CN/ (accessed on 16 August 2016). (In Chinese)
- Chinese Academy of Sciences Computer Network Information Center. Geospatial Data Cloud. Available online: http://www.gscloud.cn/ (accessed on 16 August 2016). (In Chinese)
- Yang, S.; Yan, H.; Guo, L. The land use change and its eco-environmental effects in transitional agro-pastoral region—A case study of Yulin City in northern Shaanxi Province. Prog. Geogr. 2004, 23, 49–55. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Bao, Y. Study on the methods of land use dynamic change research. Prog. Geogr. 1999, 18, 83–89. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Z.; Li, J.; Yin, H.; Yajin, S.; Xu, C. Analysis of ecological security of wetland in Liaohe River Delta based on the landscape pattern. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2010, 19, 701–705. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Huang, H.; Wu, Z. Landscape ecological security assessment based on projection pursuit: A case study of nine cities in the Pearl River Delta. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2010, 30, 5894–5903. [Google Scholar]
- Juan, W.; BaoShan, C.U.I.; HuaRong, Y.A.; ShiLiang, L.I.U. The temporal and spatial characteristic of landscape ecological security at lancang river watershed of longitudinal range gorge region in southwest China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2008, 28, 1681–1690. [Google Scholar]
- McGarigal, K.; Cushman, S.; Maile, N.; Ene, E. FRAGSTATS v4: Spatial Pattern Analysis Program for Categorical and Continuous Maps; Department of Environmental Conservation, University of Massachusetts: Amherst, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, G.; Lu, C.; Leng, Y.; Zheng, D.; Li, S. Ecological assets valuation of the Tibetan Plateau. J. Nat. Resour. 2003, 18, 189–196. [Google Scholar]
- Jiangsu Province’s Bureau of Statistics. Jiangsu Statistical Yearbook. Available online: http://www.jssb.gov.cn/ (accessed on 16 August 2016). (In Chinese)
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Available online: http://faostat3.fao.org/download/P/PP/E (accessed on 16 August 2016).
- Kreuter, U.P.; Harris, H.G.; Matlock, M.D.; Lacey, R.E. Change in ecosystem service values in the San Antonio area, Texas. Ecol. Econ. 2001, 39, 333–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Chen, Y.; Tang, H.; Yao, Y.; Yang, P.; Chen, Z. Exploring spatial change and gravity center movement for ecosystem services value using a spatially explicit ecosystem services value index and gravity model. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 175, 563–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen, A.; Smith, T. Gravity Models of Spatial Interaction Behavior; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, D.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, C.; Hu, Y.; Zhou, L. An assessment of China’s ecological environment quality change and its spatial variation. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2012, 67, 1599–1610. [Google Scholar]
- Earls, J.; Dixon, B. Spatial interpolation of rainfall data using ArcGIS: A comparative study. In Proceedings of the 27th Annual ESRI International User Conference, San Diego, CA, USA, 18–22 June 2007.
- Mishra, U.; Lal, R.; Slater, B.; Calhoun, F.; Liu, D.; van Meirvenne, M. Predicting soil organic carbon stock using profile depth distribution functions and ordinary kriging. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2009, 73, 614–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Childs, C. Interpolating Surfaces in ArcGIS Spatial Analyst. Available online: http://www.esri.com/news/arcuser/0704/files/interpolating.pdf (accessed on 17 July 2016).
- Dubrule, O. Two methods with different objectives: Splines and kriging. J. Int. Assoc. Math. Geol. 1983, 15, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubrule, O. Comparing splines and kriging. Comput. Geosci. 1984, 10, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laslett, G.; McBratney, A.; Pahl, P.J.; Hutchinson, M. Comparison of several spatial prediction methods for soil pH. J. Soil Sci. 1987, 38, 325–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, M.A.; Webster, R. Kriging: A method of interpolation for geographical information systems. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Syst. 1990, 4, 313–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laslett, G.M. Kriging and splines: An empirical comparison of their predictive performance in some applications. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1994, 89, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Lin, H.S. Comparing ordinary kriging and regression kriging for soil properties in contrasting landscapes. Pedosphere 2010, 20, 594–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleveland, W.S.; Devlin, S.J. Locally weighted regression: An approach to regression analysis by local fitting. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1988, 83, 596–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleveland, W.S. Lowess: A program for smoothing scatterplots by robust locally weighted regression. Am. Stat. 1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleveland, W.S. Robust locally weighted regression and smoothing scatterplots. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1979, 74, 829–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McArthur, J.; Howarth, R.; Bailey, T. Strontium isotope stratigraphy: LOWESS version 3: Best fit to the marine Sr-isotope curve for 0–509 ma and accompanying look-up table for deriving numerical age. J. Geol. 2001, 109, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.-G. On history and status of costal economic development in Jiangsu Province. J. Jiangsu Polytech. Univ. (Soc. Sci. Ed.) 2008, 9, 37–41. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Alphan, H. Land-use change and urbanization of Adana, Turkey. Land Degrad. Dev. 2003, 14, 575–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, E.; Bocco, G.; Mendoza, M.; Duhau, E. Predicting land-cover and land-use change in the urban fringe a case in Morelia city, Mexico. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2001, 55, 271–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, J.; Zhang, X. The landscape pattern characteristics of coastal wetlands in Jiaozhou Bay under the impact of human activities. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 124, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewan, A.M.; Yamaguchi, Y. Using remote sensing and gis to detect and monitor land use and land cover change in Dhaka metropolitan of Bangladesh during 1960–2005. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2008, 150, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dabelko, G.D.; Dabelko, D.D. Environmental security: Issues of conflict and redefinition. Environ. Chang. Secur. Proj. Rep. 1995, 1, 3–13. [Google Scholar]
- Levy, M.A. Is the environment a national security issue? Int. Secur. 1995, 20, 35–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, K.S. Ecological security and multinational corporations. Environ. Chang. Secur. Proj. Rep. 1997, 3, 29–36. [Google Scholar]
- Solovjova, N.V. Synthesis of ecosystemic and ecoscreening modelling in solving problems of ecological safety. Ecol. Model. 1999, 124, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezeonu, I.C.; Ezeonu, F.C. The environment and global security. Environmentalist 2000, 20, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalby, S. Security and ecology in the age of globalization. Environ. Chang. Secur. Proj. Rep. 2002, 8, 95–108. [Google Scholar]
- Kullenberg, G. Regional co-development and security: A comprehensive approach. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2002, 45, 761–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ma, K.; Fu, B.; Niu, S. The regional pattern for ecological security (RPES): Designing principles and method. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2004, 24, 1055–1062. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, M.G. Landscape ecology: The effect of pattern on process. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1989, 20, 171–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, M.G.; O’Neill, R.V.; Gardner, R.H.; Milne, B.T. Effects of changing spatial scale on the analysis of landscape pattern. Landsc. Ecol. 1989, 3, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J. Effects of changing scale on landscape pattern analysis: Scaling relations. Landsc. Ecol. 2004, 19, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickett, S.T.; Cadenasso, M.L. Landscape ecology: Spatial heterogeneity in ecological systems. Science 1995, 269, 331–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daily, G. Nature’s Services: Societal Dependence on Natural Ecosystems; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Costanza, R.; d’Arge, R.; de Groot, R.; Farber, S.; Grasso, M.; Hannon, B.; Limburg, K.; Naeem, S.; O’Neill, R.V.; Paruelo, J.; et al. The value of the world’s ecosystem services and natural capital. Nature 1997, 387, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Liu, W.; Cao, M. Impact of land use and land cover changes on ecosystem services in Menglun, Xishuangbanna, southwest China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2008, 146, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewan, A.M.; Kabir, M.H.; Nahar, K.; Rahman, M.Z. Urbanisation and environmental degradation in Dhaka metropolitan area of Bangladesh. Int. J. Environ. Sustain. Dev. 2012, 11, 118–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Pu, L. The variation of land use pattern in tidal flat reclamation zones in Jiangsu coastal area: A case study of Rudong County of Jiangsu Province. J. Nat. Resour. 2014, 29, 643–652. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Pu, L.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, J.; Li, P.; Dai, X.; Xu, Y.; Liu, L. Evolution of soil properties following reclamation in coastal areas: A review. Geoderma 2014, 226–227, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Sun, W.; Tong, C.; Zeng, C.; Yu, X.; Mou, X. China’s coastal wetlands: Conservation history, implementation efforts, existing issues and strategies for future improvement. Environ. Int. 2015, 79, 25–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascual-Aguilar, J.; Andreu, V.; Gimeno-García, E.; Picó, Y. Current anthropogenic pressures on agro-ecological protected coastal wetlands. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 503–504, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

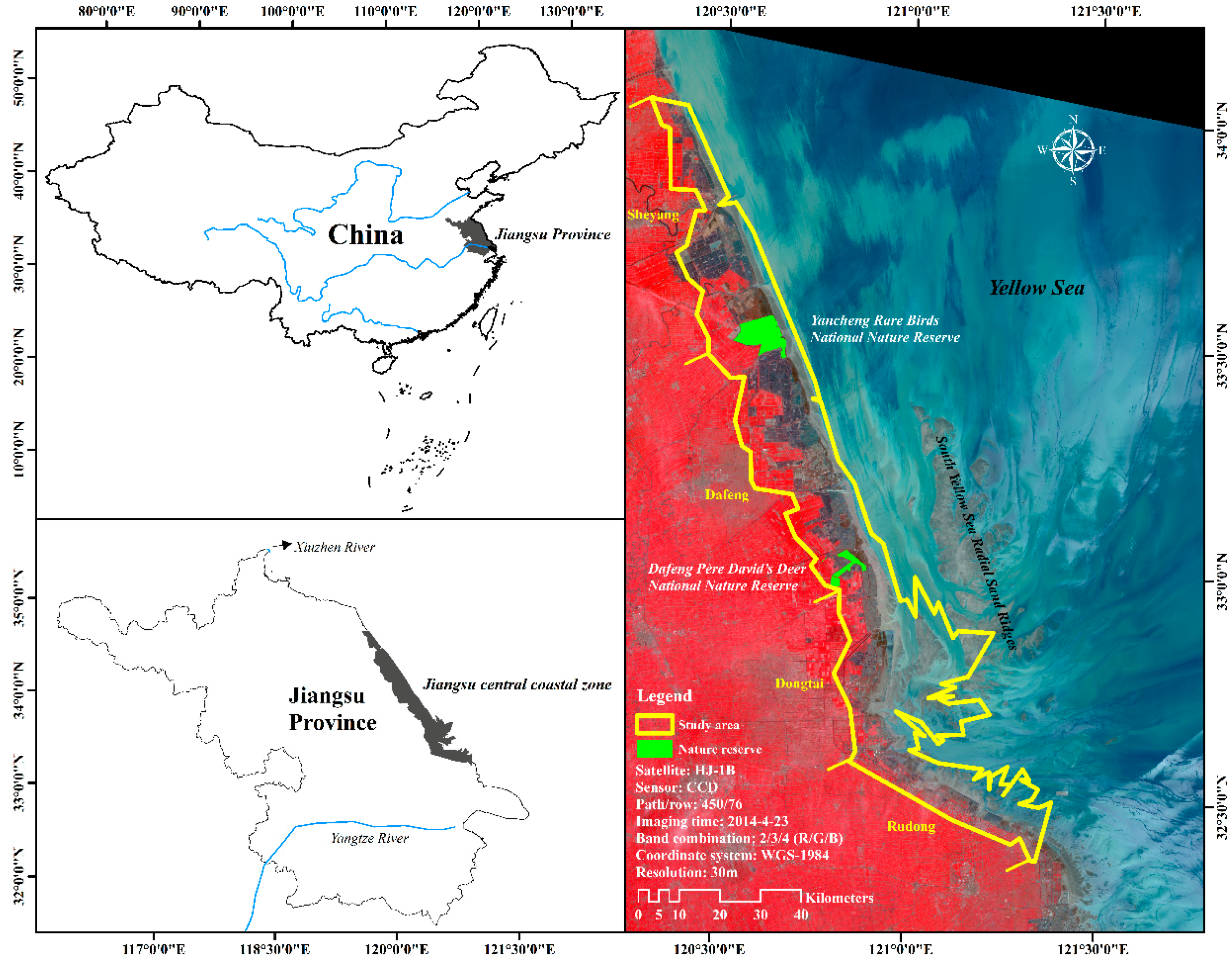
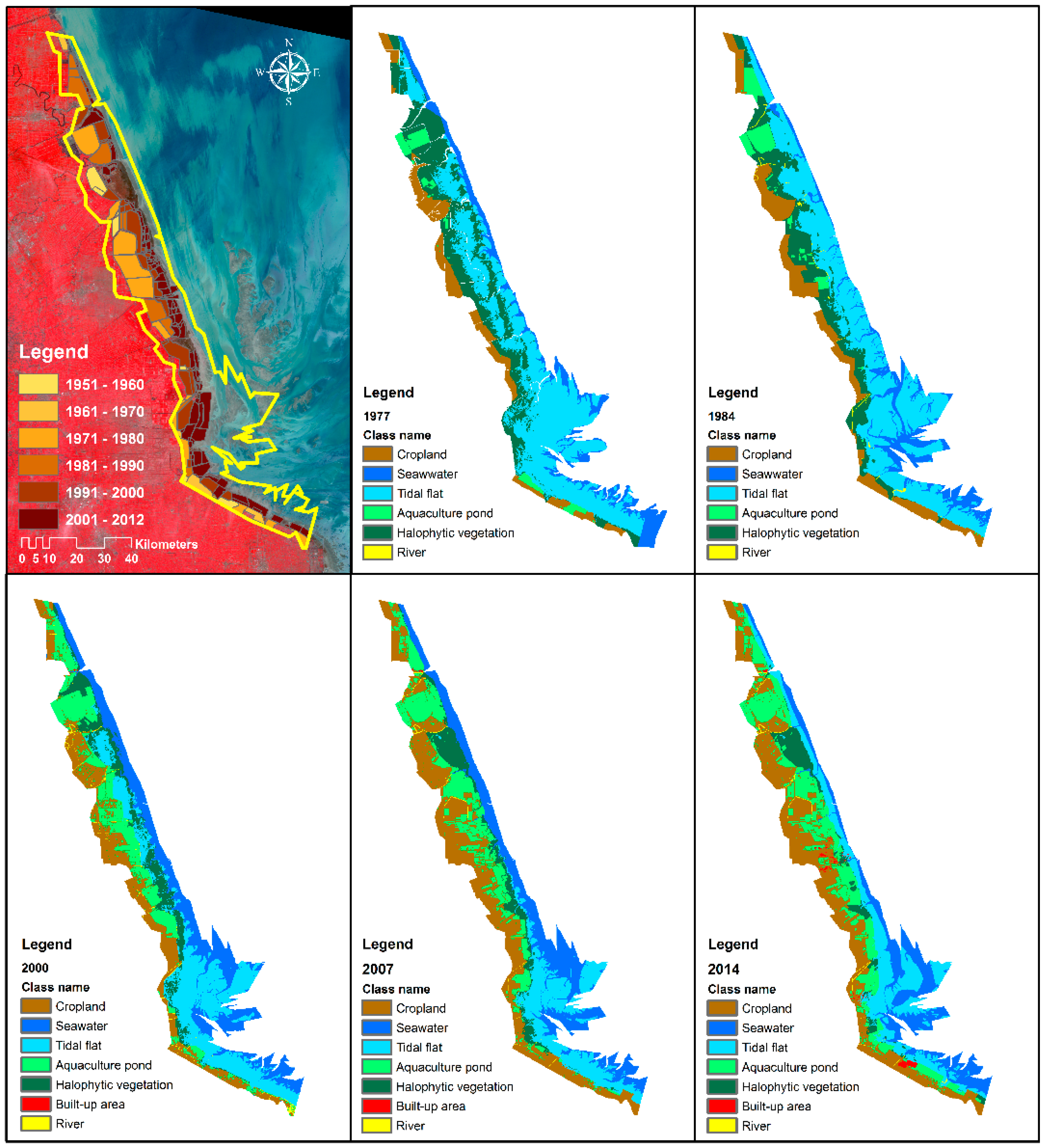

| Satellite | Sensor | Path/Row | Acquisition Date | Resolution/m |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HJ-1B | CCD | 450/76 | 23 April 2014 | 30 |
| Landsat 5 | TM | 119/37 | 17 June 2007 | 30 |
| Landsat 7 | ETM | 119/37 | 20 May 2000 | 30 |
| Landsat 5 | TM | 119/37 | 4 August 1984 | 30 |
| Landsat 2 | TM | 128/37 | 20 April 1977 | 79 |
| No. | LUCC Class | Description | wi |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Cropland | Land in either a vegetated or nonvegetated state used for the production of food and oil, including cultivated and uncultivated croplands | 0.6 |
| 2 | Seawater | Part of Yellow Sea | 0.7 |
| 3 | Tidal flat | Tidal flats are common along shallow-water coastlines and estuaries worldwide, accumulating fine-grained sediments on gently sloping beds, forming the basic structure upon which coastal wetlands built | 1 |
| 4 | Aquaculture pond | The farming of fish and other aquatic life in regular ponds | 0.5 |
| 5 | Halophytic vegetation | Grow in salt-affected habitats with many species | 0.8 |
| 6 | Built-up area | Rural residential land | 0.2 |
| 7 | River | A large amount of fresh water flowing continuously in a long line across the land | 0.8 |
| Ecosystem Service | Farmland | Forest | Grassland | Wetland | Water Body | Barren Land | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Provisioning | Food production | 1 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.01 |
| Raw material | 0.1 | 2.6 | 0.05 | 0.07 | 0.01 | 0 | |
| Regulating | Gas regulation | 0.5 | 3.5 | 0.8 | 1.8 | 0 | 0 |
| Climate regulation | 0.89 | 2.7 | 0.9 | 17.1 | 0.46 | 0 | |
| Water regulation | 0.6 | 3.2 | 0.8 | 15.5 | 20.38 | 0.03 | |
| Waste treatment | 1.64 | 1.31 | 1.31 | 18.18 | 18.18 | 0.01 | |
| Supporting | Soil formation | 1.46 | 3.9 | 1.95 | 1.71 | 0.01 | 0.02 |
| Biodiversity protection | 0.71 | 3.26 | 1.09 | 2.5 | 2.49 | 0.34 | |
| Cultural | Recreational | 0.01 | 1.28 | 0.04 | 5.55 | 4.34 | 0.01 |
| Total | 6.91 | 21.85 | 7.24 | 62.71 | 45.97 | 0.42 | |
| Ecosystem Service | Cropland | Tidal Flat | Aquaculture Pond | Halophytic Vegetation | Built-up Area | River/Ditch | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Provisioning | Food production | 230.58 | 69.17 | 23.06 | 69.17 | 2.31 | 23.06 |
| Raw material | 23.06 | 16.14 | 2.31 | 11.53 | 0.00 | 2.31 | |
| Regulating | Gas regulation | 115.29 | 415.05 | 0.00 | 184.47 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Climate regulation | 205.22 | 3942.96 | 106.07 | 207.52 | 0.00 | 106.07 | |
| Water regulation | 138.35 | 3574.03 | 4699.27 | 184.47 | 6.92 | 4699.27 | |
| Waste treatment | 378.15 | 4191.99 | 4191.99 | 302.06 | 2.31 | 4191.99 | |
| Supporting | Soil formation | 336.65 | 394.30 | 2.31 | 449.64 | 4.61 | 2.31 |
| Biodiversity protection | 163.71 | 576.46 | 574.15 | 251.33 | 78.40 | 574.15 | |
| Cultural | Recreational | 2.31 | 1279.73 | 1000.73 | 9.22 | 2.31 | 1000.73 |
| Total | 1593.32 | 14,459.83 | 10,599.89 | 1669.41 | 96.86 | 10,599.89 | |
| Correlation Coefficient R | ESV | |
|---|---|---|
| LESI | 1977 | −0.134 |
| 1984 | −0.179 * | |
| 2000 | −0.364 *** | |
| 2007 | −0.353 *** | |
| 2014 | −0.375 *** | |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, C.; Pu, L.; Zhu, M.; Li, J.; Chen, X.; Wang, X.; Xie, X. Ecological Security and Ecosystem Services in Response to Land Use Change in the Coastal Area of Jiangsu, China. Sustainability 2016, 8, 816. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8080816
Xu C, Pu L, Zhu M, Li J, Chen X, Wang X, Xie X. Ecological Security and Ecosystem Services in Response to Land Use Change in the Coastal Area of Jiangsu, China. Sustainability. 2016; 8(8):816. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8080816
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Caiyao, Lijie Pu, Ming Zhu, Jianguo Li, Xinjian Chen, Xiaohan Wang, and Xuefeng Xie. 2016. "Ecological Security and Ecosystem Services in Response to Land Use Change in the Coastal Area of Jiangsu, China" Sustainability 8, no. 8: 816. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8080816
APA StyleXu, C., Pu, L., Zhu, M., Li, J., Chen, X., Wang, X., & Xie, X. (2016). Ecological Security and Ecosystem Services in Response to Land Use Change in the Coastal Area of Jiangsu, China. Sustainability, 8(8), 816. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8080816