A Global Perspective on the Sustainable Performance of Urbanization
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Research Methods
- Maturity: The indicator system should be able to guide the practice of sustainable urbanization. Selected indicators in this study are from international practices and authoritative studies.
- Measurability: The difficulty of collecting and quantifying the indicator data should be as low as possible to allow the effective use of the indicator. Data for all the indicators in use in this study can be collected through the UN Database or World Bank Database.
- Independence: Indicators should be independent of each other, and overlap and autocorrelation between indicators should be avoided. Correlation analysis is therefore adopted to identify and remove those strongly correlated indicators.
- Operability: The indicator system can be used for supporting calculation analysis of the sustainable performance of urbanization.
2.1. Correlation Analysis
2.2. Establishing Weighting Values between Indicators
- (a)
- Normalization for All Indicators
- (b)
- Standardization of Indicator Value
- (c)
- Entropy Value for Indicators
- (d)
- Establishment of Weighting Values for All Indicators
2.3. Evaluation of Sustainable Performance of Urbanization
3. Indicators for Measuring Sustainable Urbanization Performance
3.1. Candidate Indicators
- Sample 1(S1): Urban indicator database [58]. The Urban Indicators Program of the United Nations Human Settlements Program (UN-Habitat) was established in 1988. The database helps individual countries design, collect, and apply policy-oriented urban indicators.
- Sample 2(S2): United Nations Millennium Development Goals of Indicators [59]. In order to develop a more equal, healthy, sustainable world, leaders from 189 nations issued Millennium Development Goals (MDG); 60 indicators are defined in order to achieve these goals.
- Sample 3(S3): Indicators of Sustainable Development [36]. The United Nations issued the indicators of Sustainable Development for guiding nations to better sustainable development.
- Sample 4(S4): Shen et al. [60] developed a set of 115 indicators for examining the variations between different sustainable urbanization practices at an international level.
- Sample 5(S5): The World Bank issued the World Development Indicators in 2012 [61]. These indicators are grouped under six themes: worldview, people, the environment, the economy, states and markets, and global links.
3.2. Selection of Indicators
4. Analysis Results of Sustainable Urbanization Performance among the Selected Countries
5. Discussion
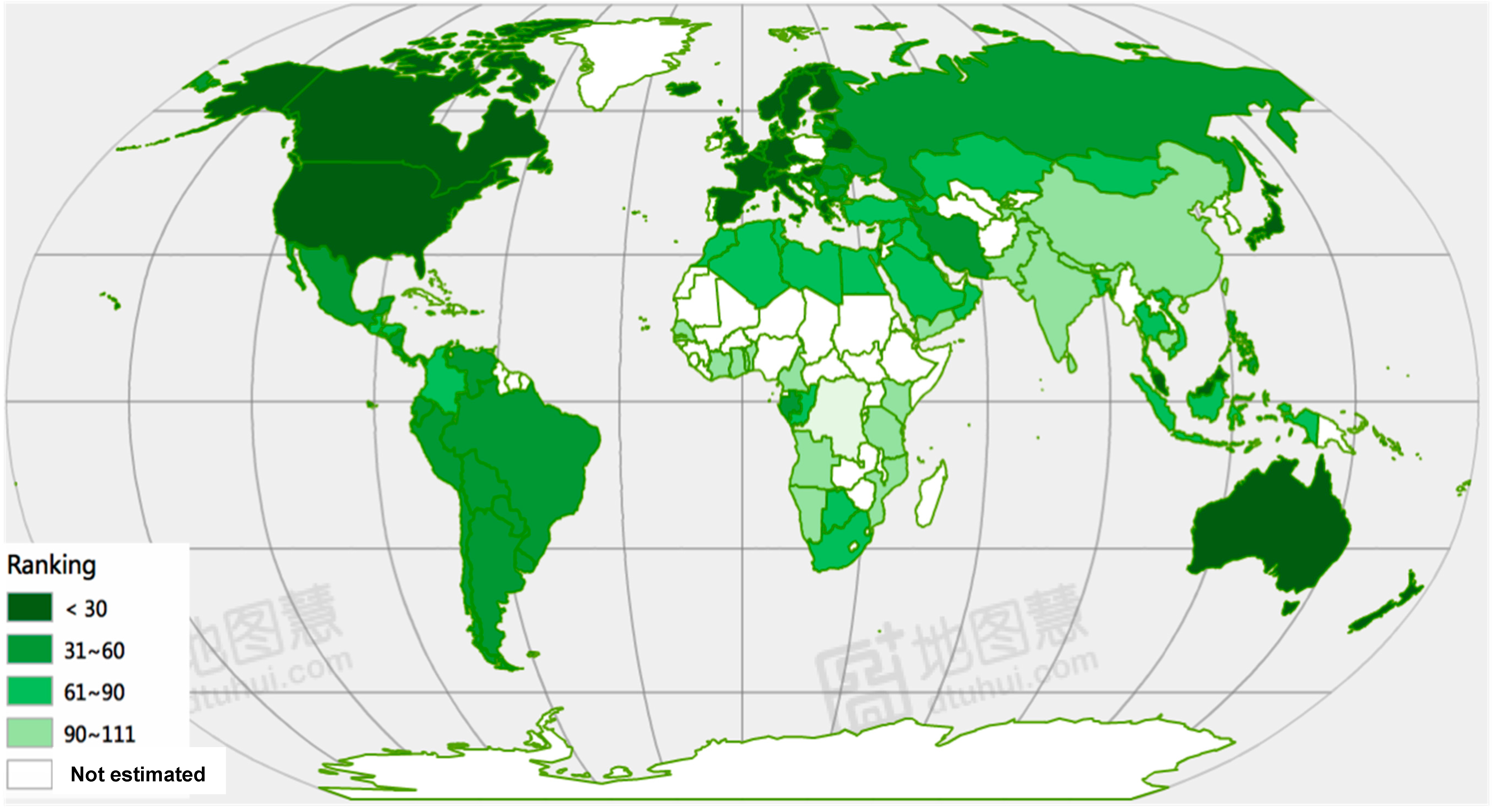
5.1. The Ranking on Sustainable Urbanization Performance
5.2. A Global Perspective on the Sustainable Performance of Urbanization
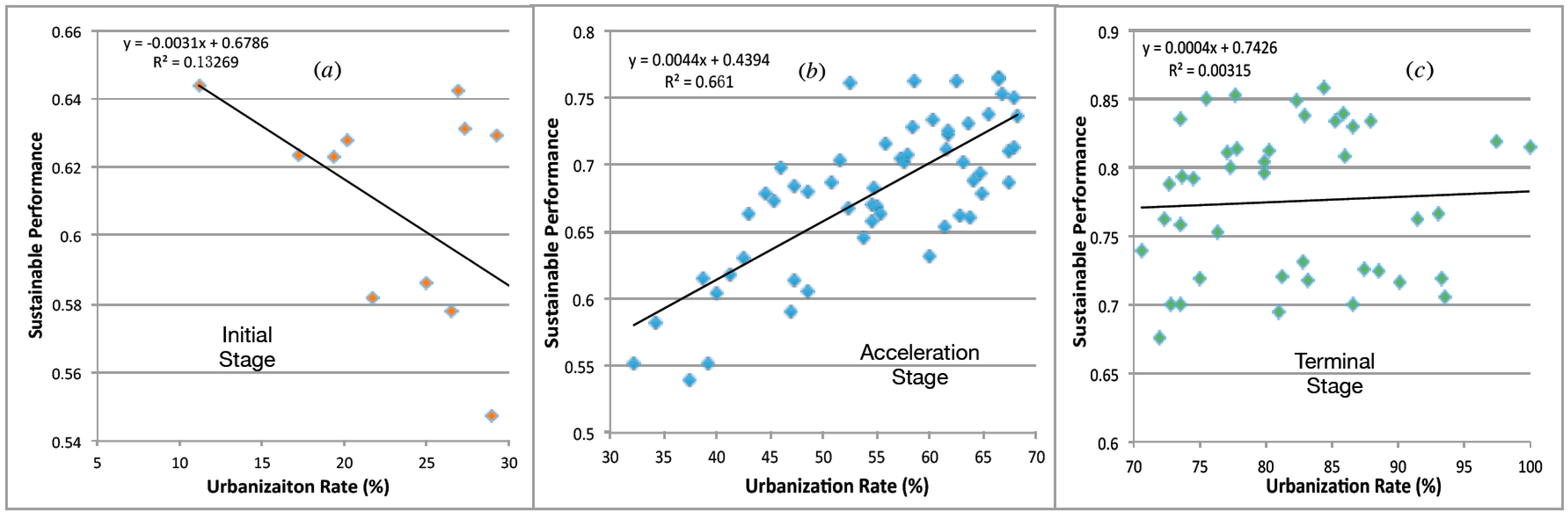
5.3. Relationship between Sustainable Performance and Urbanization Rate
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shen, L.; Zhou, J. Examining the effectiveness of indicators for guiding sustainable urbanization in China. Habitat Int. 2014, 44, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Bank. Available online: http://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SP.URB.TOTL.IN.ZS/countries/1W?display=graph (accessed on 2 June 2015).
- Northam, R.M. Urban Geography; John Wiley & Sons: London, UK, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Zhang, X.; Shen, L. Urbanization bubble: Four quadrants measurement model. Cities 2015, 46, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, K.L.; White, D.D.; Gober, P.; Wutich, A. Decision-Making under Uncertainty for Water Sustainability and Urban Climate Change Adaptation. Sustainability 2015, 7, 14761–14784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Childers, D.L.; Cadenasso, M.L.; Grove, J.M.; Marshall, V.; McGrath, B.; Pickett, S.T.A. An ecology for cities: A transformational nexus of design and ecology to advance climate change resilience and urban sustainability. Sustainability 2015, 7, 3774–3791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewan, A.M.; Kabir, M.H.; Nahar, K.; Rahman, M.Z. Urbanisation and environmental degradation in Dhaka Metropolitan Area of Bangladesh. Int. J. Environ. Sustain. Dev. 2012, 11, 118–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squires, G.D. Urban Sprawl: Causes, Consequences, & Policy Responses; The Urban Insitute: Washington, DC, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, M.P. Environmental impacts of urban sprawl: A survey of the literature and proposed research agenda. Environ. Plan. A 2001, 33, 717–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yigitcanlar, T.; Teriman, S. Rethinking sustainable urban development: towards an integrated planning and development process. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 12, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Zhou, J.; Skitmore, M.; Xia, B. Application of a hybrid Entropy–McKinsey Matrix method in evaluating sustainable urbanization: A China case study. Cities 2015, 42, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, B. Flood management under rapid urbanisation and industrialisation in flood-prone areas: A need for serious consideration. Irrig. Drain. 2006, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swan, A. How increased urbanisation has induced flooding problems in the UK: A lesson for African cities? Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2010, 35, 643–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewan, A.M.; Yamaguchi, Y. Effect of Land Cover Changes on Flooding: Example from Greater Dhaka of Bangladesh. Int. J. Geoinform. 2008, 4, 11–12. [Google Scholar]
- Dewan, A.M.; Islam, M.M.; Kumamoto, T.; Nishigaki, M. Evaluating flood hazard for land-use planning in Greater Dhaka of Bangladesh using remote sensing and GIS techniques. Water Resour. Manag. 2007, 21, 1601–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewan, A.M.; Kumamoto, T.; Nishigaki, M. Flood hazard delineation in greater Dhaka, Bangladesh using an integrated GIS and remote sensing approach. Geocarto Int. 2006, 21, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewan, A.M.; Humayun Kabir, M.; Monirul Islam, M.; Kumamoto, T.; Nishigaki, M. Delineating flood risk areas in Greater Dhaka of Bangladesh using geoinformatics. Georisk 2007, 1, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yigitcanlar, T. Smart cities: an effective urban development and management model? Aust. Plan. 2015, 52, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Shen, L.; Song, X.; Zhang, X. Selection and modeling sustainable urbanization indicators: A responsibility-based method. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 56, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UN-Habitat, Urban Management Programme (UMP). Available online: http://www.unhabitat.org/categories.asp?catid=374 (accessed on 5 October 2012).
- United Nations. United Nations Millennium Declaration: Resolution; UN: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), 2004 Istanbul Summit. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/2004_Istanbul_summit (accessed on 8 August 2016).
- Hong Kong Planning Department, Hong Kong 2030—Planning Vision and Strategy, 2007. Available online: http://www.epd.gov.hk/epd/SEA/eng/file/ExecutiveSummary(Eng).pdf (accessed on 8 August 2016).
- Melbourne City Council, City Plan 2010—Towards a Thriving and Sustainable City. Available online: http://www.melbourne.vic.gov.au/rsrc/PDFs/Publications/CityPlan2010_part1.pdf (accessed on 18 July 2015).
- Plan, S.G. Beyond Clean and Green towards Environmental Sustainability; Ministry of the Environment and Water Resources: Singapore, 2012.
- Mexico City Government, Green Plan “Plan Verde”. Available online: http://www.dac.dk/en/dac-cities/sustainable-cities/all-cases/social-city/mexico-city-successful-environmental-management/ (accessed on 8 August 2016).
- Iskandar Regional Development Authority, Comprehensive Development Plan for Iskandar Malaysia. Avaialbe online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Iskandar_Malaysia#Comprehensive_Development_Plan_.28CDP.29 (accessed on 8 August 2016).
- Shen, L.-Y.; Ochoa, J.J.; Zhang, X.; Yi, P. Experience mining for decision making on implementing sustainable urbanization—An innovative approach. Autom. Constr. 2013, 29, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussiopoulos, N.; Achillas, C.; Vlachokostas, C.; Spyridi, D.; Nikolaou, K. Environmental, social and economic information management for the evaluation of sustainability in urban areas: A system of indicators for Thessaloniki, Greece. Cities 2010, 27, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X. Sustainable urbanization: A bi-dimensional matrix model. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 134, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Y. An alternative model for evaluating sustainable urbanization. Cities 2012, 29, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, K.; Yamashita, T. Methodological framework of sustainability assessment in City Sustainability Index (CSI): A concept of constraint and maximisation indicators. Habitat Int. 2015, 45, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewan, A.M.; Corner, R.J. Spatiotemporal analysis of urban growth, sprawl and structure. In Dhaka Megacity; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2014; pp. 99–121. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; Coors, V. Combining system dynamics model, GIS and 3D visualization in sustainability assessment of urban residential development. Build. Environ. 2012, 47, 272–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.Y.; Shen, L.Y.; Ren, W.J.; Rong, W. Comparative study on sustainable urban development indicator systems in China. Jian She Guan Li Guo Ji Xue Bao 2013, 1, 29–48. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations. Indicators of Sustainable Development: Guidelines and Methodologies; United Nations Publications: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Ramos, T.B.; Caeiro, S. Meta-performance evaluation of sustainability indicators. Ecol. Indic. 2010, 10, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Jiao, L.; He, B.; Li, L. Evaluation on the utility efficiency of metro infrastructure projects in China from sustainable development perspective. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2015, 33, 528–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, C.; Puissant, A. Urbanization pressure and modeling of urban growth: Example of the Tunis Metropolitan Area. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 86, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewan, A.M.; Yamaguchi, Y. Land use and land cover change in Greater Dhaka, Bangladesh: Using remote sensing to promote sustainable urbanization. Appl. Geogr. 2009, 29, 390–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiland, U.; Kindler, A.; Banzhaf, E.; Ebert, A.; Reyes-Paecke, S. Indicators for sustainable land use management in Santiago de Chile. Ecol. Indic. 2011, 11, 1074–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, Y.; Skitmore, M.; Jiang, S. Sustainable infrastructure projects in balancing urban-rural development: Towards the goal of efficiency and equity. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 107, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Moreno, S.; De Hoyos-Martínez, J. Indicators of urban sustainability in Mexico. Theor. Empir. Res. Urban Manag. 2010, 7, 46–60. [Google Scholar]
- Yigitcanlar, T.; Dur, F.; Dizdaroglu, D. Towards prosperous sustainable cities: A multiscalar urban sustainability assessment approach. Habitat Int. 2015, 45, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewan, A.M.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Rahman, M.Z. Dynamics of land use/cover changes and the analysis of landscape fragmentation in Dhaka Metropolitan, Bangladesh. GeoJournal 2012, 77, 315–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, J.O. Sustainability profile for urban districts in Copenhagen. In Proceedings of the Sustainable Cities and Regions: Enabling Vision or Empty Talk? Örebro, Sweden, 11–13 March 2009.
- Reddy, B.S.; Balachandra, P. Benchmarking Urban Sustainability—A Composite Index for Mumbai and Bangalore; Indira Gandhi Institute of Development Research: Mumbai, India, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Byomkesh, T.; Nakagoshi, N.; Dewan, A.M. Urbanization and green space dynamics in Greater Dhaka, Bangladesh. Landsc. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 8, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghshenas, H.; Vaziri, M. Urban sustainable transportation indicators for global comparison. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 15, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Liu, X.; Hu, D.; Wang, R.; Yang, W.; Li, D.; Zhao, D. Measurement indicators and an evaluation approach for assessing urban sustainable development: A case study for China’s Jining City. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2009, 90, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, N. Urban form revisited—Selecting indicators for characterising European cities. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2010, 96, 29–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recanatesi, F.; Clemente, M.; Grigoriadis, E.; Ranalli, F.; Zitti, M.; Salvati, L. A Fifty-Year Sustainability Assessment of Italian Agro-Forest Districts. Sustainability 2015, 8, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasage, R.; Muis, S.; Sardella, C.S.E.; van Drunen, M.A.; Verburg, P.H.; Aerts, J.C.J.H. A Stepwise, Participatory Approach to Design and Implement Community Based Adaptation to Drought in the Peruvian Andes. Sustainability 2015, 7, 1742–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, W.W.; Pitcher, T.J.; Pauly, D. A fuzzy logic expert system to estimate intrinsic extinction vulnerabilities of marine fishes to fishing. Biol. Conserv. 2005, 124, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Li, N. Performance Evaluation for Sustainability of Strong Smart Grid by Using Stochastic AHP and Fuzzy TOPSIS Methods. Sustainability 2016, 8, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, E.-S.; Won, K.; Kim, Y.; Lee, H. Water resource vulnerability characteristics by district’s population size in a changing climate using subjective and objective weights. Sustainability 2014, 6, 6141–6157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Fang, C.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Ma, H. Quantifying the relationship between urban development intensity and carbon dioxide emissions using a panel data analysis. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 49, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UN-Habitat, Global Urban Indicators Database. Available online: http://unhabitat.org/books/global-urban-indicators-database (accessed on 11 October 2015).
- DESA, UN-DESA. Official list of MDG Indicators; UN Department of Economic and Social Affairs—Statistics Division: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, L.-Y.; Ochoa, J.J.; Shah, M.N.; Zhang, X. The application of urban sustainability indicators—A comparison between various practices. Habitat Int. 2011, 35, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Bank. World Development Indicators 2012; World Bank Publications: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, M. Planning for sustainable urbanisation in fast growing cities: Mitigation and adaptation issues addressed in Dhaka, Bangladesh. Habitat Int. 2009, 33, 276–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dizdaroglu, D.; Yigitcanlar, T.; Dawes, L.A. Sustainable urban futures: An ecological approach to sustainable urban development. In Proceedings of the Second Infrastructure Theme Postgraduate Conference 2009: Rethinking Sustainable Development-Planning, Infrastructure Engineering, Design and Managing Urban Infrastructure, Queensland University of Technology, Brisbane, Queensland, Australia, 9 July 2010; pp. 187–195.
- Yigitcanlar, T.; Dizdaroglu, D. Assessing Urban Ecosystem Sustainability: An Indexing Approach. Available online: http://s3.amazonaws.com/academia.edu.documents/30968394/Assessing-urban-ecosystem-sustainability-an-indexing-approach.pdf?AWSAccessKeyId=AKIAJ56TQJRTWSMTNPEA&Expires=1468819753&Signature=dqbGGXjzNGsfUhgrzvlV3FYqR7w%3D&response-content-disposition=inline%3B%20filename%3DAssessing_urban_ecosystem_sustainability.pdf (accessed on 23 May 2014).
- Scipioni, A.; Mazzi, A.; Mason, M.; Manzardo, A. The Dashboard of Sustainability to measure the local urban sustainable development: The case study of Padua Municipality. Ecol. Indic. 2009, 9, 364–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, C.; Jiao, L.; Song, X.; Shen, L. Decoupling Analysis on the Relationship between Economic Development and Environment Degradation in China. In Proceedings of the 20th International Symposium on Advancement of Construction Management and Real Estate; Springer: Singapore, Singapore, 2017; pp. 1207–1216. [Google Scholar]
- Yigitcanlar, T.; Dur, F. Developing a sustainability assessment model: The sustainable infrastructure, land-use, environment and transport model. Sustainability 2010, 2, 321–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mason, A. Saving, economic growth, and demographic change. Popul. Dev. Rev. 1988, 14, 113–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickell, S. Unemployment and labor market rigidities: Europe versus North America. J. Econ. Perspect. 1997, 11, 55–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, R.P.; Arvin, M.B.; Bahmani, S. Causal nexus between economic growth, inflation, and stock market development: The case of OECD countries. Glob. Financ. J. 2015, 27, 98–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M. Education: A Challange for Women with Special Reference to South Central Asian Countries. Int. J. Sci. Res. 2016, 4, 674–675. [Google Scholar]
- Semyonov, M.; Gorodzeisky, A.; Glikman, A. Neighborhood ethnic composition and resident perceptions of safety in European countries. Soc. Probl. 2012, 59, 117–135. [Google Scholar]
- United Nation. Databases. Available online: http://data.un.org/ (accessed on 18 July 2016).
- Constantin, D. Tourism and environmentally sustainable regional development: The case of Romania. In Proceedings of the 40th Congress of the European Regional Science Association, Vienna, Austria, 29 August–1 September 2000; Volume 29.
- Teodorescu, G. Climate change impact on urban ecosystems and sustainable development of cities in Romania. WSEAS Trans. Environ. Dev. 2010, 6, 103–112. [Google Scholar]
- Nistoreanu, P. The Ecotourism-Element of the Sustainable Development of the Local Rural Communities in Romania. Amfiteatru Econ. J. 2005, 7, 42–47. [Google Scholar]
- Rotmans, J.; van Asselt, M.; Anastasi, C.; Greeuw, S.; Mellors, J.; Peters, S.; Rothman, D.; Rijkens, N. Visions for a sustainable Europe. Futures 2000, 32, 809–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, V. The urbanization process and economic growth: The so-what question. J. Econ. Growth 2003, 8, 47–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyson, T. The role of the demographic transition in the process of urbanization. Popul. Dev. Rev. 2011, 37, 34–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Dimension | Indicators |
|---|---|
| Environment (En) | En1-CO2 emissions per capita (kt per capita) |
| En2-Consumption of ozone-depleting CFCs in ODP metric tons per capita | |
| En3-Forest area (% of land area) | |
| En4-Marine protected areas (% of territorial waters) | |
| En5-Electric power consumption (kWh per capita) | |
| En6-Population growth (annual %) | |
| En7-Population Density (%) | |
| Economic (Ec) | Ec1-GDP per capita |
| Ec2-Gross savings (% of GDP) | |
| Ec3-Employment-population ratio (annual %) | |
| Ec4-Adjusted net savings as percentage of gross national income (GNI) | |
| Ec5-Inflation Rate (annual %) | |
| Ec6-Internet users (per 100 population) | |
| Ec7-Fixed telephone lines (per 100 population) | |
| Ec8-Mobile cellular telephone subscribers (per 100 population) | |
| Social (So) | So1-School enrollment, primary (% net) |
| So2-Ratio of female to male primary enrollment (%) | |
| So3-Life expectancy at birth, total (years) | |
| So4-Incidence of tuberculosis (per 100,000 people) | |
| So5-Mortality rate, under-5 (per 1000 live births) | |
| So6-Intertional homicide, number and rate per 100,000 population | |
| So7-Improved water source (% of population with access) | |
| So8-Improved sanitation facilities (% of population with access) |
| Dimension | Indicators | Data Source |
|---|---|---|
| Environment (En) | En1-CO2 emissions per capita (kt per capita) | World Bank |
| En2-Consumption of ozone-depleting CFCs in ODP metric tons per capita | United Nation | |
| En3-Forest area (% of land area) | World Bank | |
| En4-Marine protected areas (% of territorial waters) | United Nation | |
| En5-Electric power consumption (kWh per capita) | World Bank | |
| En6-Population growth (annual %) | World Bank | |
| En7-Density (%) | World Bank | |
| Economic (Ec) | Ec1-GDP per capita | World Bank |
| Ec2-Gross savings (% of GDP) | United Nation | |
| Ec3-Employment-population ratio (annual %) | World Bank | |
| Ec4-Inflation Rate (annual %) | United Nation | |
| Ec5-Mobile cellular telephone subscribers( per 100 population) | World Bank | |
| Social (So) | So1-School enrollment, primary (% net) | World Bank |
| So2-Ratio of female to male primary enrollment (%) | United Nation | |
| So3-Life expectancy at birth, total (years) | World Bank | |
| So4-Intentional homicide, number and rate per 100,000 population | United Nation | |
| So5-Improved water source (% of population with access) | World Bank |
| Indicator (En) | Weight (%) | Indicator (Ec) | Weight (%) | Indicator (So) | Weight (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| En-1 | 5.043 | Ec-1 | 8.045 | So-1 | 6.684 |
| En-2 | 4.914 | Ec-2 | 5.757 | So-2 | 6.542 |
| En-3 | 4.986 | Ec-3 | 5.934 | So-3 | 6.341 |
| En-4 | 6.756 | Ec-4 | 5.359 | So-4 | 5.635 |
| En-5 | 5.732 | Ec-5 | 6.486 | So-5 | 4.179 |
| En-6 | 5.362 | ||||
| En-7 | 6.245 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shen, L.; Shuai, C.; Jiao, L.; Tan, Y.; Song, X. A Global Perspective on the Sustainable Performance of Urbanization. Sustainability 2016, 8, 783. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8080783
Shen L, Shuai C, Jiao L, Tan Y, Song X. A Global Perspective on the Sustainable Performance of Urbanization. Sustainability. 2016; 8(8):783. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8080783
Chicago/Turabian StyleShen, Liyin, Chenyang Shuai, Liudan Jiao, Yongtao Tan, and Xiangnan Song. 2016. "A Global Perspective on the Sustainable Performance of Urbanization" Sustainability 8, no. 8: 783. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8080783
APA StyleShen, L., Shuai, C., Jiao, L., Tan, Y., & Song, X. (2016). A Global Perspective on the Sustainable Performance of Urbanization. Sustainability, 8(8), 783. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8080783






