Low-Carbon Based Multi-Objective Bi-Level Power Dispatching under Uncertainty
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- We establish a bi-level multi-objective model for a power dispatch problem which better reflects the real world. In the proposed model, the upper decision-maker is the regional power grid company and the lower decision-makers are the power generation groups.
- We consider a hybrid uncertain environment, so use random and fuzzy variables to describe the imprecise information in the power dispatch problem.
- We set the quoted power price and the power generation quantities as the decision variables to more accurately reflect the current power dispatch systems in many countries.
2. Problem Statement
3. Modeling
3.1. Notations
3.2. Upper Level Dispatch Model
3.2.1. Upper Level Objectives
3.2.2. Upper Level Constraints
3.3. Lower Level Generation Model
3.3.1. Lower Level Objective
3.3.2. Lower Level Constraints
4. Model Processing
- (1)
- ;
- (2)
- ;
- (3)
- .
- (1)
- ;
- (2)
- ;
- (3)
- ;
4.1. Chance Constrained Model
4.2. Expected Value Model
5. Solution Method
5.1. Eliciting the Satisfaction Degree Functions
5.2. Evaluating the Satisfactorysolution
6. Case Study
6.1. Related Data
6.2. Results
6.2.1. Results of the Chance Constrained Model
6.2.2. Results of the Expected Value Model
6.3. Comparison and Discussion
7. Conclusions
- (1)
- As all action is based on the power demand estimation, the power grid company needs to have enhanced forecasting abilities.
- (2)
- The chance constrained model and the expected value model are suitable for different decision making scenarios. The expected value model can give a reference solution for an average situation and the chance constrained model can suggest a range of plans depending on the confidence levels.
- (3)
- Upper level decision makers need to carefully consider all factors to determine the satisfaction degree so as to balance the interests between all decision making levels.
- (4)
- Severe carbon allowance and carbon trading will have a great significance in realizing sustainable development of power industry.
Acknowledgements
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gao, C.; Li, Y. Evolution of China’s power dispatch principle and the new energy saving power dispatch policy. Energy Policy 2010, 38, 7346–7357. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Cheng, H.; Zhu, J.; Liang, H.; Li, P. The optimal dispatch of a power system containing virtual power plants under fog and haze weather. Sustainability 2016, 8, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niknam, T.; Firouzi, B.B.; Mojarrad, H.D. A new evolutionary algorithm for non-linear economic dispatch. Expert Syst. Appl. 2011, 38, 13301–13309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruitt, K.A.; Leyffer, S.; Newman, A.M.; Braun, R.J. A mixed-integer nonlinear program for the optimal design and dispatch of distributed generation systems. Optim. Eng. 2014, 15, 167–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barcelo, W.R.; Rastgoufard, P. Dynamic economic dispatch using the extend security constrained economic dispatch algorithm. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 1997, 12, 961–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panigrahi, C.K.; Chattopadhyay, P.K.; Chakrabarti, R.N.; Basu, M. Simulated annealing technique for dynamic economic dispatch. Electr. Power Compon. Syst. 2006, 34, 577–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, C.L.; Mariani, V.C. Combining of chaotic differential evolution and quadratic programming for economic dispatch optimization with valve-point effect. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2006, 21, 989–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faísca, N.P.; Rustem, B.; Dua, V. Bilevel and multilevel programming; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, German, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Hetzer, J.; Yu, D.C.; Bhattarai, K. An economic dispatch model incorporating wind power. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2008, 23, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wierzbowski, M.; Lyzwa, W.; Musial, I. MILP model for long-term energy mix planning with consideration of power system reserves. Appl. Energy 2016, 169, 93–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Q.; Huang, G.H.; Cai, Y.P. A fuzzy evacuation management model oriented toward the mitigation of emissions. J. Environ. Inform. 2015, 25, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.Y.; Chen, L.; Liao, Q. Effect of rainfall measurement errors on nonpoint-source pollution model uncertainty. J. Environ. Inform. 2015, 26, 14–26. [Google Scholar]
- Kockar, I.; Conejo, A.J.; Mcdonald, J.R. Influence of the emissions trading scheme on generation scheduling. Int. J. Electr. Power 2009, 31, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhou, J.; Mo, L.; Ouyang, S.; Liao, X. Economic environmental dispatch using an enhanced multi-objective cultural algorithm. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2013, 99, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Huang, G.H.; Fan, Y.R.; Liao, R.F. A nonlinear fractional programming approach for environmental–economic power dispatch. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2016, 78, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ren, X.; Zhong, J. The Comprehensive Evaluation Model of Low Carbon Benefits of the Power Planning and Its Application; Atlantis Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Yang, X.; Tao, Z. A tripartite equilibrium for carbon emission allowance allocation in the power-supply industry. Energy Policy 2015, 82, 62–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Li, Y.P.; Huang, G.H.; Fan, Y.R.; Nie, S. A dynamic model to optimize municipal electric power systems by considering carbon emission trading under uncertainty. Energy 2015, 88, 636–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinricha, G.; Howellsb, M.; Bassona, L.; Petrie, J. Electricity supply industry modeling for multiple objectives under demand growth uncertainty. Energy 2007, 32, 2210–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.Y.; Lin, J.K. Interactive multi-objective active power scheduling considering uncertain renewable energies using adaptive chaos clonal evolutionary programming. Energy 2013, 53, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Nasri, E.; Chini, A.; Ries, R.; Xu, J. A multiple objective decision making model for energy generation portfolio under fuzzy uncertainty: Case study of large scale investor-owned utilities in Florida. Renew. Energy 2015, 75, 224–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, Y.P.; Huang, G.H. A robust possibilistic mixed-integer programming method for planning municipal electric power systems. Int. J. Electr. Power 2015, 73, 757–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Yao, L. Random-Like Multiple Objective Decision Making; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, German, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Zhou, X. Fuzzy-Like Multiple Objective Decision Making; Springer: Berlin, German, 2011. [Google Scholar]

| Parameter | Installed Capacity | Variable Costs | Carbon Emissions | Government Subsidies | Government Controlled Price | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Index | ||||||
| g = 1 | i = 1 | 158,760 | (0.24,0.037,0.01) | (0.98,0.1,0.1) | 0.01 | 0.3346 |
| i = 3 | 12,408 | 0.5 | 0 | 0.38 | 0.6 | |
| i = 4 | 450 | 0.8 | 0 | 0.42 | 0.88 | |
| g = 2 | i = 1 | 136,080 | (0.24,0.037,0.01) | (0.98,0.1,0.1) | 0.01 | 0.3346 |
| i = 2 | 8560.5 | 0.09 | 0 | 0 | 0.27 | |
| i = 3 | 14,256 | 0.5 | 0 | 0.38 | 0.6 | |
| i = 4 | 75 | 0.8 | 0 | 0.42 | 0.88 | |
| g = 3 | i = 1 | 386,370 | (0.23,0.047,0.01) | (0.98,0.26,0.26) | 0.01 | 0.3346 |
| i = 2 | 26,325 | 0.09 | 0 | 0 | 0.27 | |
| i = 3 | 4752 | 0.5 | 0 | 0.38 | 0.6 | |
| g = 4 | i = 1 | 238,680 | (0.23,0.037,0.01) | (0.98,0.2,0.2) | 0.01 | 0.3346 |
| i = 3 | 4800 | 0.5 | 0 | 0.38 | 0.6 | |
| i = 4 | 75 | 0.8 | 0 | 0.42 | 0.88 | |
| g = 5 | i = 1 | 116,910 | (0.24,0.037,0.01) | (0.98,0.1,0.1) | 0.01 | 0.3346 |
| i = 2 | 108,868.5 | 0.09 | 0 | 0 | 0.27 | |
| i = 3 | 2376 | 0.5 | 0 | 0.38 | 0.6 | |
| i = 4 | 6000 | 0.8 | 0 | 0.42 | 0.88 |
| Parameter | Demand | Lowest Power Price | Highest Power Price | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Index | ||||
| u = 1 | t = 1 | N(27,900, 3800) | 0.41 | 0.5088 |
| t = 2 | N(30,350, 1850) | 0.41 | 0.5088 | |
| t = 3 | N(35,200, 3600) | 0.41 | 0.5088 | |
| u = 2 | t = 1 | N(748,650, 11,250) | 0.41 | 0.5539 |
| t = 2 | N(518,900, 8700) | 0.41 | 0.5539 | |
| t = 3 | N(636,700, 14,800) | 0.41 | 0.5539 | |
| u = 3 | t = 1 | N(208,250, 4650) | 0.41 | 0.7934 |
| t = 2 | N(164,750, 9850) | 0.41 | 0.7934 | |
| t = 3 | N(158,550, 7150) | 0.41 | 0.7934 | |
| u = 4 | t = 1 | N(195,050, 4500) | 0.41 | 0.4983 |
| t = 2 | N(164,850, 16,850) | 0.41 | 0.4983 | |
| t = 3 | N(175,350, 4250) | 0.41 | 0.4983 |
| Parameter | Carbon Emissions Allowances | Storage Ratio | Stabilized Power Ratio | Price of Carbon Emissions Rights | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Index | g = 1 | g = 2 | g = 3 | g = 4 | g = 5 | ||||
| T | t = 1 | 177,367 | 152,028 | 431,653 | 266,653 | 130,612 | 0.02 | 0.7 | 0.03 |
| t = 2 | 130,691 | 112,021 | 318,060 | 196,481 | 96,240 | 0.02 | 0.7 | 0.03 | |
| t = 3 | 154,029 | 132,025 | 374,856 | 231,567 | 113,426 | 0.02 | 0.7 | 0.03 | |
| Results | Minimum Values | Maximum Values | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Objective | |||
| Power grid company’s profit | 16.10664 | 1053.504 | |
| Power surplus | 106.3082 | 578.523 | |
| Total carbon emissions | 2,461,995 | 2,991,382 | |
| Power generation group No.1’s profit | 0.002862 | 55.98099 | |
| Power generation group No.2’s profit | 0.002436 | 57.35391 | |
| Power generation group No.3’s profit | 0.563342 | 125.478 | |
| Power generation group No.4’s profit | 0.219078 | 70.68472 | |
| Power generation group No.5’s profit | 0.002097 | 98.7799 | |
| Results | Power Generation | Quoted Price | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Index | |||||||||
| i = 1 | i = 2 | i = 3 | i = 4 | i = 1 | i = 2 | i = 3 | i = 4 | ||
| g = 1 | t = 1 | 158.760 | - | 12.408 | 0 | 0.256 | - | 0.600 | 0 |
| t = 2 | 100.9774 | - | 10.33929 | 0 | 0.256 | - | 0.600 | 0 | |
| t = 3 | 93.41928 | - | 12.408 | 0 | 0.256 | - | 0.500 | 0 | |
| g = 2 | t = 1 | 136.080 | 8.560500 | 14.256 | 0 | 0.256 | 0.09 | 0.500 | 0 |
| t = 2 | 0 | 8.560500 | 14.256 | 0 | 0 | 0.09 | 0.500 | 0 | |
| t = 3 | 136.080 | 8.560500 | 5.374715 | 0 | 0.256 | 0.09 | 0.500 | 0 | |
| g = 3 | t = 1 | 386.370 | 26.325 | 4.752 | - | 0.249 | 0.268 | 0.598 | - |
| t = 2 | 386.370 | 26.325 | 4.752 | - | 0.296 | 0.268 | 0.598 | - | |
| t = 3 | 386.370 | 26.325 | 4.752 | - | 0.247 | 0.268 | 0.598 | - | |
| g = 4 | t = 1 | 238.680 | - | 4.800 | 0 | 0.252 | - | 0.598 | 0 |
| t = 2 | 238.680 | - | 4.800 | 0 | 0.251 | - | 0.598 | 0 | |
| t = 3 | 238.680 | - | 4.800 | 0 | 0.307 | - | 0.598 | 0 | |
| g = 5 | t = 1 | 94.9236 | 108.8685 | 2.376 | 0 | 0.256 | 0.09 | 0.596 | 0 |
| t = 2 | 0 | 108.8685 | 2.376 | 0 | 0 | 0.207 | 0.596 | 0 | |
| t = 3 | 0 | 108.8685 | 2.376 | 0 | 0 | 0.184 | 0.596 | 0 | |
| Results | Power Generation Quota | Power Selling Price | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Index | ||||||||||
| g = 1 | g = 2 | g = 3 | g = 4 | g = 5 | u = 1 | u = 2 | u = 3 | u = 4 | ||
| t = 1 | 171.168 | 158.8965 | 417.447 | 243.48 | 206.1681 | 0.509 | 0.554 | 0.793 | 0.498 | |
| t = 2 | 111.3167 | 22.81650 | 417.447 | 243.48 | 111.2445 | 0.509 | 0.554 | 0.793 | 0.498 | |
| t = 3 | 105.8273 | 150.0152 | 417.447 | 243.48 | 111.2445 | 0.509 | 0.554 | 0.793 | 0.498 | |
| Results | Objective Values | |
|---|---|---|
| Objective Function | ||
| Lower level SD | 0.343 | |
| Satisfaction ratio | 0.381 | |
| Power grid company’s profit | 949.7642 | |
| Power surplus | 106.3082 | |
| Total carbon emissions | 2491822 | |
| Power generation group No.1’s profit | 19.21949 | |
| Power generation group No.2’s profit | 19.69052 | |
| Power generation group No.3’s profit | 43.44508 | |
| Power generation group No.4’s profit | 24.4091 | |
| Power generation group No.5’s profit | 33.91169 | |
| Results | Objective Values | |
|---|---|---|
| Objective Function | ||
| Lower level SD | 0.343 | |
| Satisfaction ratio | 0.381 | |
| Power grid company’s profit | 990.390 | |
| Power surplus | −0.00008 | |
| Total carbon emissions | 2,467,113 | |
| Power generation group No.1’s profit | 18.903 | |
| Power generation group No.2’s profit | 19.41753 | |
| Power generation group No.3’s profit | 42.71704 | |
| Power generation group No.4’s profit | 23.72096 | |
| Power generation group No.5’s profit | 33.6678 | |
| Results | Power Generation | Quoted Price | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Index | |||||||||
| i = 1 | i = 2 | i = 3 | i = 4 | i = 1 | i = 2 | i = 3 | i = 4 | ||
| g = 1 | t = 1 | 135.3847 | - | 12.408 | 0 | 0.326 | - | 0.598 | 0 |
| t = 2 | 45.97597 | - | 12.408 | 0 | 0.332 | - | 0.598 | 0 | |
| t = 3 | 37.83506 | - | 12.408 | 0 | 0.332 | - | 0.598 | 0 | |
| g = 2 | t = 1 | 126.6169 | 8.56050 | 14.256 | 0 | 0.303 | 0.268 | 0.600 | 0 |
| t = 2 | 0 | 8.56050 | 14.256 | 0 | 0 | 0.268 | 0.600 | 0 | |
| t = 3 | 64.24969 | 8.56050 | 14.256 | 0 | 0.331 | 0.268 | 0.600 | 0 | |
| g = 3 | t = 1 | 386.370 | 26.325 | 4.752 | - | 0.255 | 0.268 | 0.598 | - |
| t = 2 | 386.370 | 26.325 | 4.752 | - | 0.332 | 0.268 | 0.598 | - | |
| t = 3 | 386.370 | 26.325 | 4.752 | - | 0.332 | 0.268 | 0.598 | - | |
| g = 4 | t = 1 | 238.680 | - | 4.800 | 0 | 0.335 | - | 0.600 | 0 |
| t = 2 | 238.680 | - | 4.800 | 0 | 0.335 | - | 0.600 | 0 | |
| t = 3 | 238.680 | - | 4.800 | 0 | 0.258 | - | 0.600 | 0 | |
| g = 5 | t = 1 | 110.4524 | 108.8685 | 2.376 | 0 | 0.314 | 0.27 | 0.600 | 0 |
| t = 2 | 25.47803 | 108.8685 | 2.376 | 0 | 0.260 | 0.27 | 0.600 | 0 | |
| t = 3 | 96.31924 | 108.8685 | 2.376 | 0 | 0.262 | 0.27 | 0.600 | 0 | |
| Results | Power Generation Quota | Power Selling Price | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Index | ||||||||||
| g = 1 | g = 2 | g = 3 | g = 4 | g = 5 | u = 1 | u = 2 | u = 3 | u = 4 | ||
| t = 1 | 147.7927 | 149.4334 | 417.447 | 243.480 | 221.6969 | 0.509 | 0.554 | 0.793 | 0.498 | |
| t = 2 | 58.38397 | 22.81650 | 417.447 | 243.480 | 136.7225 | 0.509 | 0.554 | 0.793 | 0.498 | |
| t = 3 | 50.24306 | 87.06619 | 417.447 | 243.480 | 207.5637 | 0.509 | 0.554 | 0.793 | 0.498 | |
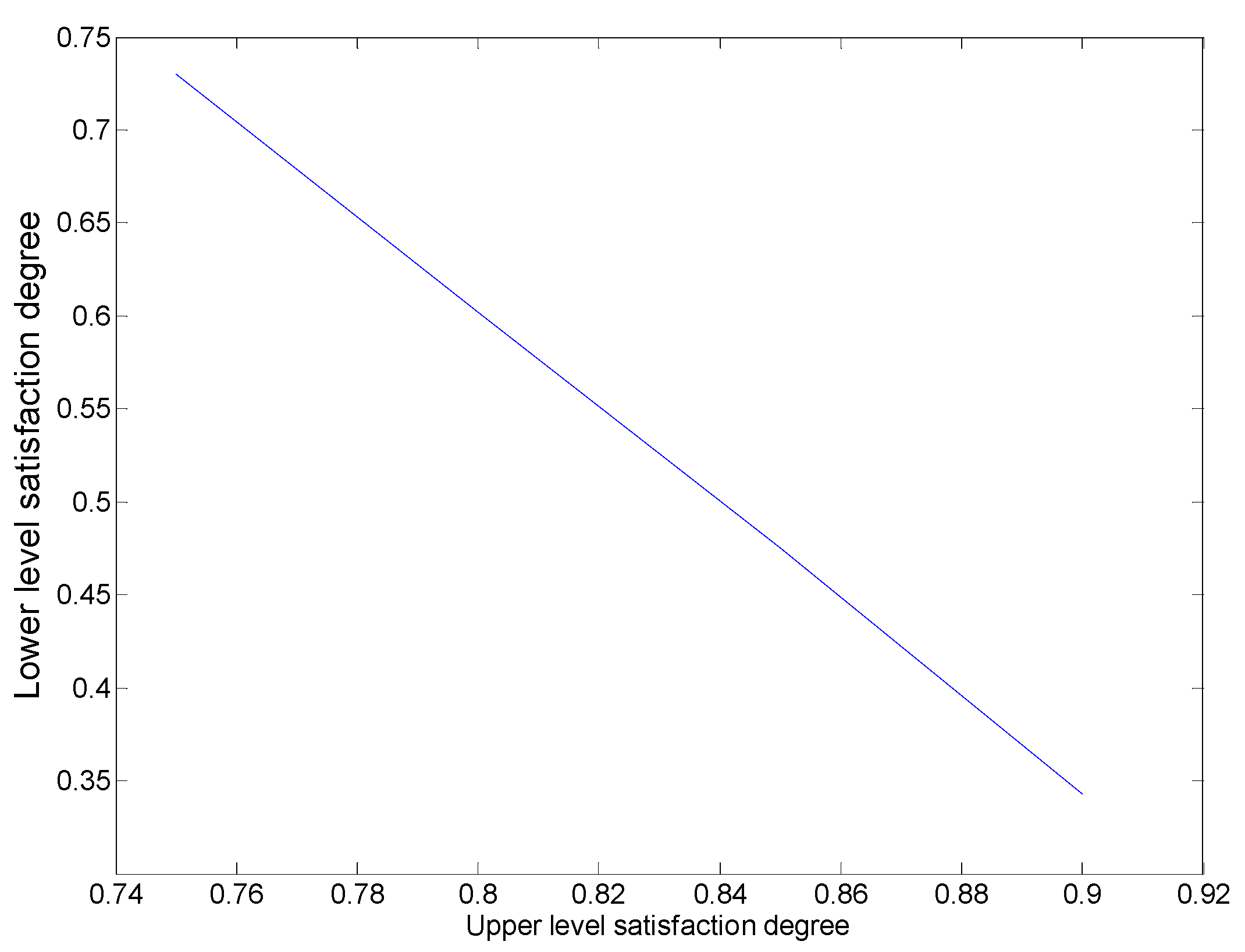
| Upper Level SD | 0.9 | 0.85 | 0.8 | 0.75 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Objective | |||||
| Lower level SD | 0.343 | 0.475 | 0.602 | 0.730 | |
| Satisfaction ratio | 0.381 | 0.559 | 0.753 | 0.973 | |
| Power grid company’s profit | 949.7642 | 897.8944 | 846.0245 | 794.1546 | |
| Power surplus | 106.3082 | 106.3082 | 106.3082 | 106.3081 | |
| Total carbon emissions | 2,491,822 | 2,481,201 | 2,481,201 | 2,481,201 | |
| Power generation group No.1’s profit | 19.21949 | 26.59339 | 33.71892 | 40.84447 | |
| Power generation group No.2’s profit | 19.69052 | 27.24531 | 34.54567 | 41.84603 | |
| Power generation group No.3’s profit | 43.44508 | 59.89982 | 75.80038 | 91.70099 | |
| Power generation group No.4’s profit | 24.4091 | 33.69139 | 42.6611 | 51.63078 | |
| Power generation group No.5’s profit | 33.91169 | 46.92364 | 59.49734 | 72.07104 | |
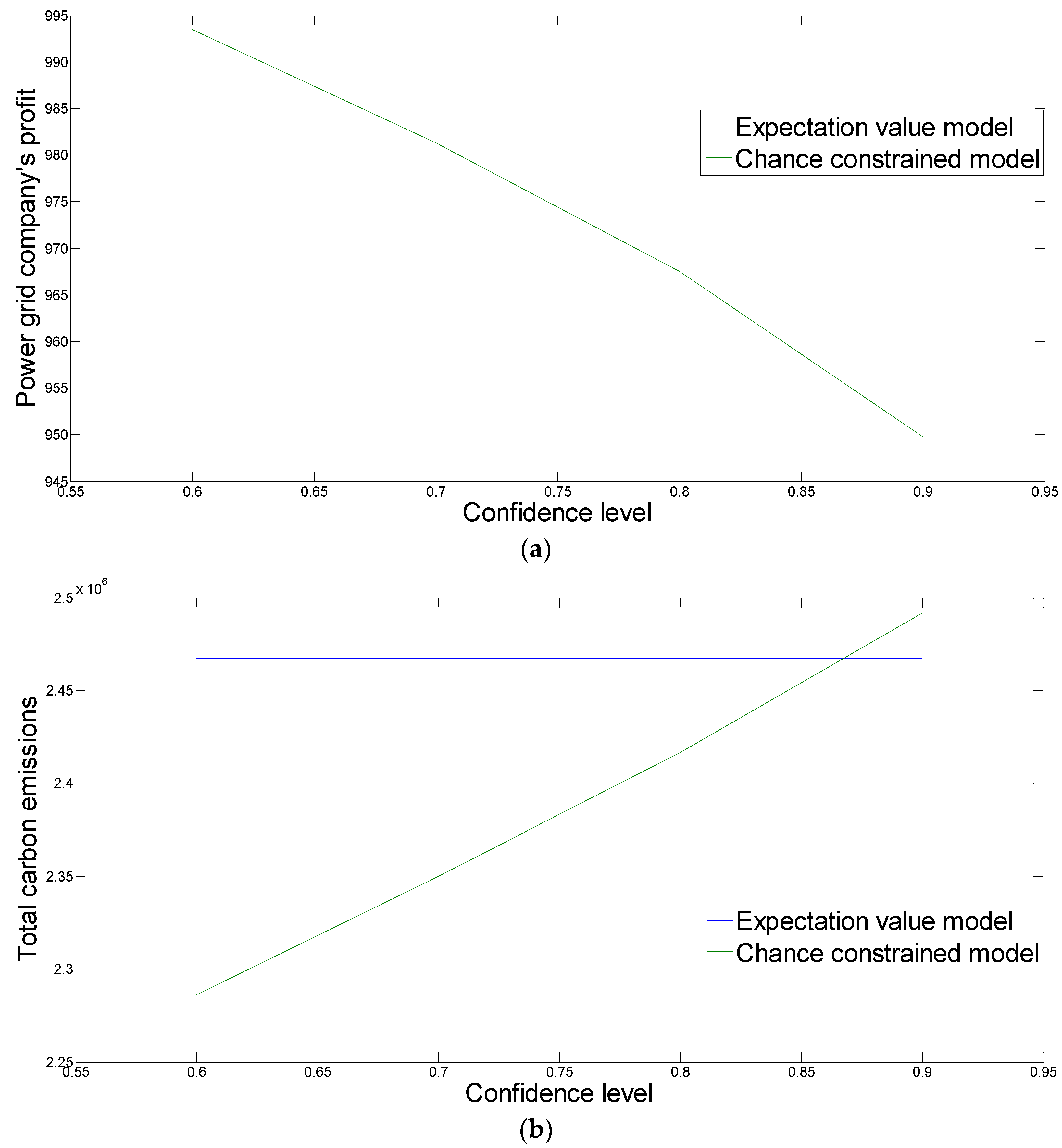
| Confidence Level | 0.9 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.6 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Objective | |||||
| Lower level SD | 0.343 | 0.341 | 0.338 | 0.334 | |
| Satisfaction ratio | 0.381 | 0.379 | 0.376 | 0.371 | |
| Power grid company’s profit | 949.7642 | 967.5023 | 981.319 | 993.495 | |
| Power surplus | 106.3082 | 69.76466 | 43.18765 | 20.7633 | |
| Total carbon emissions | 2,491,822 | 2,416,525 | 2,349,838 | 2,286,018 | |
| Power generation group No.1’s profit | 19.21949 | 19.38729 | 19.50868 | 19.62742 | |
| Power generation group No.2’s profit | 19.69052 | 19.81135 | 19.88514 | 19.95673 | |
| Power generation group No.3’s profit | 43.44508 | 44.83267 | 46.10858 | 47.37054 | |
| Power generation group No.4’s profit | 24.4091 | 24.9098 | 25.35132 | 25.78875 | |
| Power generation group No.5’s profit | 33.91169 | 33.89363 | 33.79718 | 33.69921 | |
| Carbon Emission Policy | Carbon Limit Policy | Carbon Trading Policy | Rate of Change | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Objective | ||||
| Total carbon emissions | 2,487,498 | 2,491,822 | 0.174% | |
| Power generation group No.1’s profit | 16.6101 | 19.21949 | 15.71% | |
| Power generation group No.2’s profit | 17.11469 | 19.69052 | 15.05% | |
| Power generation group No.3’s profit | 36.90187 | 43.44508 | 17.731% | |
| Power generation group No.4’s profit | 20.71354 | 24.4091 | 17.841% | |
| Power generation group No.5’s profit | 29.90611 | 33.91169 | 13.394% | |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, X.; Zhao, C.; Chai, J.; Lev, B.; Lai, K.K. Low-Carbon Based Multi-Objective Bi-Level Power Dispatching under Uncertainty. Sustainability 2016, 8, 533. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8060533
Zhou X, Zhao C, Chai J, Lev B, Lai KK. Low-Carbon Based Multi-Objective Bi-Level Power Dispatching under Uncertainty. Sustainability. 2016; 8(6):533. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8060533
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Xiaoyang, Canhui Zhao, Jian Chai, Benjamin Lev, and Kin Keung Lai. 2016. "Low-Carbon Based Multi-Objective Bi-Level Power Dispatching under Uncertainty" Sustainability 8, no. 6: 533. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8060533
APA StyleZhou, X., Zhao, C., Chai, J., Lev, B., & Lai, K. K. (2016). Low-Carbon Based Multi-Objective Bi-Level Power Dispatching under Uncertainty. Sustainability, 8(6), 533. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8060533








