Abstract
Sustainability reporting is the process by which companies describe how they deal with their own economic, environmental, and social impacts, thus making stakeholders able to recognize the value of sustainable practices. As stressed in the Global Reporting Initiative guidelines, which act as a de facto standard for sustainability reporting, sustainable reports should take into account the stakeholders’ view. In particular, engaging stakeholders is essential to carry out the materiality analysis, by which organizations can identify their own more relevant sustainability aspects. Yet, on the one hand, the existing guidelines do not provide specific indications on how to get stakeholders actually engaged; on the other hand, research on quantitative techniques to support stakeholder engagement in materiality analysis is scarce. Therefore, the purpose of this paper is the development of a quantitative structured approach based on multi-attribute group decision-making techniques to effectively and reliably support stakeholder engagement during materiality analysis in sustainability reporting. As it more strictly guides the reporting process, the proposed approach at the same time simplifies materiality analysis and makes it more reliable. Though any company can adopt the approach, small- and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) are expected to particularly benefit from it, due to the quite limited implementation effort that is required. With this respect, the approach has been validated on a sample of Italian SMEs belonging to different sectors.
1. Introduction
The last few decades have seen a growing debate on the role of business in society and the need for companies to take sustainability issues into account (e.g., [1,2]). In 2011, the European Union (EU) [3] defined corporate social responsibility as “the responsibility of enterprises for their impacts on society”. With this respect, EU underlines the need for companies to implement a “close collaboration with their stakeholders”. Such concepts are central to stakeholder theory [4], based on which (i) a company has to be considered as a network of stakeholders and (ii) social responsibility needs to be integrated within the business strategy. Several scholars (e.g., [5,6,7,8]), indeed, agree on the need to involve stakeholders in the definition of the corporate strategy as well as in the management of a company. Stakeholder engagement, in some cases referred to as stakeholder management, encompasses the practices that companies undertake to actively involve stakeholders in organizational activities [9]. The engagement is a fundamental accountability mechanism, which must have a “clear purpose” and be aimed at achieving “agreed outcomes” [10].
This paper deals with stakeholder engagement in sustainability reporting. The latter is the process by which an organization communicates how it deals with sustainability issues. In particular, the purpose of this paper is the development of a structured quantitative approach to support organizations in the assessment of the stakeholders’ view during the materiality analysis, i.e. the identification of the sustainability aspects most relevant for the organization itself and its stakeholders. The proposed approach fills a gap in the literature (e.g., [11]), as it is expected to support firms, especially small- and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) [12,13], in effectively and reliably managing stakeholder engagement. Furthermore, an extensive adoption of the proposed approach would make it more difficult for companies pursuing opportunistic behaviors during sustainability reporting [14].
The paper is organized as follows. Section 2 presents an overview of the literature on stakeholder engagement and sustainability reporting, with emphasis on materiality analysis. In Section 3, the importance of stakeholder engagement for materiality analysis is illustrated and the main gaps associated to existing approaches discussed. Section 4 presents and discusses the structured quantitative approach to support organizations in the assessment of the stakeholders’ view during the materiality analysis. Section 5 describes the results of a test of the approach carried out on a sample of Italian SMEs. Additionally, some considerations on the comparative analyses that could be carried out if the approach would be adopted by a significant number of firms are reported. Final remarks and further research avenues are reported in the Conclusions section.
2. Background
In this Section an overview of the literature on stakeholder engagement and sustainability reporting is discussed.
2.1. Stakeholder Engagement
In 1963, the Stanford Research Institute introduced the term stakeholder to refer to “those groups without whose support the organization would cease to exist” [4]. Such definition was successively revised by Freeman [15], who defined stakeholder as “any group or individual who can affect or is affected by” the firm’s objective. Since the Stanford Research Institute’s seminal work, stakeholder related research was carried out in the field of organization theory, corporate planning, corporate social responsibility, and system theory [16]. Particularly relevant to the development of stakeholder theory were the studies carried out by Freeman [15], who stressed the importance of the strategic dimension of the relationships with stakeholders, and Donaldson and Preston [6], who justified the essential content and significance of the theory and discussed it under a managerial perspective. Other important studies examined the issues of stakeholder analysis and legitimacy (e.g., [17]). Potential company stakeholders include groups such as customers, investors, employees and managers, local communities, future generations, government, competitors, media, natural environment, suppliers, and business partners [18]. Such groups have been classified in different ways, e.g., primary vs. secondary [19], further classified as social vs. non-social [18], external vs. internal [15], and voluntary vs. involuntary (e.g., [20]). Mitchell, Agle, and Wood [17] stressed that stakeholders are not all equally salient and, based on stakeholder’s power, urgency and legitimacy, classified them into latent, expectant, and definitive stakeholders.
Each stakeholder should be engaged in the firm’s organizational activities with a specific and clear goal. Stakeholder engagement is indeed a central theme in stakeholder theory. Depending on the stakeholder type and saliency, the organizational activities may deal with public relations, customer service, supplier relations, management accounting, and human resource management. Hence, based on the specific activity, engagement may be thus seen as a mechanism for achieving consent or co-operating, a form of involvement and participation, a method for enhancing trust, a substitute for true trust, a discourse to enhance fairness, or a mechanism of corporate governance [14].
According to [21], the stakeholder engagement process involves five main iterative stages, namely: (i) strategic thinking about engagement, which includes stakeholder mapping, setting of strategic objectives for engagement, identification of issues, and the prioritization of stakeholders and issues; (ii) engagement analysis and planning, which includes reviewing and learning, assessment, learning about stakeholder, resource identification, and plan definition; (iii) maintenance and strengthening of the capacities needed to engage effectively, which includes the development of internal skills to address engagement; (iv) engagement; and (v) definition of actions based on the output of the engagement process and reviewing of the engagement process. Similar activities are also reported in the AA1000 Stakeholder Engagement Standard [10]. The engagement stage involves the identification of the engagements methods. Level of engagement and methods must be selected based on the specific stakeholder profile, the specific issue to be examined, the relationship context, and the organization’s as well as stakeholders’ objectives and needs [21,22]. The level of engagement may vary from simple information to empowerment. Engagement methods include: inviting written responses from stakeholders, e.g., via reply slips in reports, telephone hotlines, meetings, online engagement mechanisms, focus groups, surveys, stakeholder advisory or assurance panels, multi-stakeholder forums, multi-stakeholder alliances, partnerships, voluntary initiatives, and joint-projects. For small and large group meetings, different facilitating techniques are also proposed in the literature, e.g., appreciative inquires, consensus building, nominal group techniques, open space technology, scenario planning, and a world café. In most cases, the techniques are qualitative; furthermore, when quantitative approaches are proposed, the issue of integrating different stakeholders’ opinion remains unsatisfactorily addressed.
2.2. Sustainability Reporting
A sustainability report is a document that describes how an organization deals with its economic, environmental, and social impacts. Sustainability reporting has undergone several development stages [23]. The first social reports were written in the seventies. In the late 1980s, environmental reports were published by companies operating in environmentally sensitive industries. In the mid-1990s, the social and environmental dimensions were jointly discussed with the economic one in the first sustainability reports.
In the last decade, companies have increasingly adopted sustainability reporting all over the world [24]. Sustainability reporting indeed becomes crucial for companies to manage sustainability issues and communicate to stakeholders how they deal with them but also to address specific norms on the compulsory release of non-financial disclosures (e.g., Directive 2014/95/EU) introduced by countries as well as stock exchanges (with respect to their own listed companies). Sustainability reporting is also crucial for embracing sustainable strategies. As stated by GRI-G4 [25], which acts as a de facto standard for sustainability reporting [26], “reporting is not only a matter of communication nor ‘a mere data gathering or compliance exercise’. It helps organizations to set goals, measure performance, and manage change”. Yet, communication to stakeholders itself and—before that—stakeholder engagement in the reporting process allow an organization to better align performance along the three sustainability dimensions, namely, economic, environmental, and social. Stakeholder engagement not only requires informing stakeholders on company’s decisions, but also having them contributing to the decision-making process, often recurring to negotiation so as to trade-off conflicting objectives.
In this paper, we focus on stakeholder engagement during materiality analysis, a crucial task in the reporting process [25]. The output of materiality analysis is the so-called materiality matrix. To develop it, an organization must identify and prioritize its own material aspects, namely, the sustainability topics that result as the most relevant for its processes. Even though the GRI-G4 guidelines require stakeholder engagement for materiality analysis, e.g., [27], they only give general suggestions rather than specific indications or tools to actually engage stakeholders. This paper presents a novel structured quantitative approach that can be used for that purpose.
3. Stakeholder Engagement in Materiality Analysis
Materiality analysis within the sustainability reporting process is the specific activity by which an organization identifies and prioritizes its own material aspects, thus determining the materiality matrix (Figure 1).
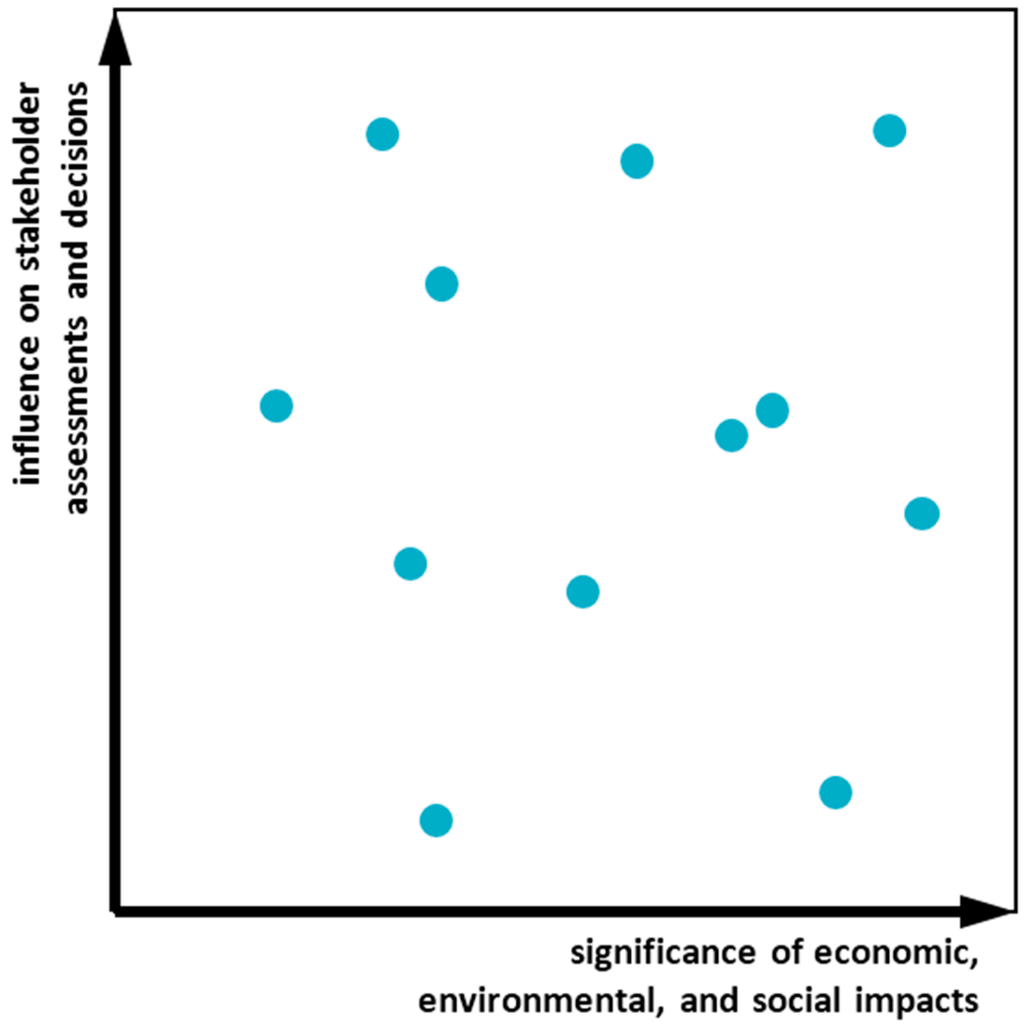
Figure 1.
The materiality matrix (adapted from: [25]).
The matrix depicts every sustainability aspect as a dot properly positioned within it. Any aspect has to be characterized in terms of “significance of economic, environmental, and social impacts” (x-axis) and “influence on stakeholder assessments and decisions” (y-axis) [25]. Positioning the dots by assessing x and y values, allows the material aspects to be actually identified. This is a critical step as it heavily impacts on the sustainability report: The report should indeed analytically discuss exactly those sustainability aspects identified as material.
The x-value may come from an “objective” evaluation, which often is in practice provided by the organization itself through the entrepreneur or a manager, as long as they are experts about the given aspect. On the contrary, assessing the y-value is more complex (not only due to the fact that—in our opinion—the guidelines do not give much help for it): GRI-G4 guidelines do not discuss in detail how to identify which stakeholders should express the evaluation, in which way the evaluation should be expressed, nor how to synthesize the evaluations by different stakeholders, which might not be coherent among each other.
As already mentioned, despite the relevance of materiality analysis, the guidelines do not provide anything but general, principle-based suggestions. Specifically, they lack any indication of structured approaches to address this task.
Similarly, the extant literature seems not to help with this respect. As discussed in Calabrese et al. [11], “few studies have inquired into quantitative methods for assessing the materiality of sustainability aspects […] and existing studies do not deal effectively with the issues of subjectivity” inherent in materiality analysis. In most cases, scholars suggest qualitative approaches, which render the need for an objective procedure essentially unsolved. Moreover, there is a lack of methods that, to address the problem of SMEs’ shortage of resources (human, temporal and financial ones), indicate the appropriate levels of completeness for materiality analysis and, in general, sustainability reporting.
Two studies have recently proposed quantitative approaches to support materiality assessment in sustainability reporting. A method based on a fuzzy Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) [28] is suggested in [11], which converts the decision-makers’ relative judgments into priorities for aspects. A materiality analysis model based on the failure modes and effects analysis (FMEA) [29] combined with Analytic Network Process (ANP) [30] is presented in [24]. A drawback of the former method is that every decision is made by a unique decision-maker; thus, that approach is prevented from actually capturing a multiple stakeholders’ view and engaging stakeholders. The latter model derives priorities by considering more decision-makers, which, however, are all managers internal to the organization. Therefore, doing it fails to take the opinions of most stakeholders into account, irrespective of their salience.
The next section describes a novel structured approach that we developed, building on the previous studies, in an attempt to overcome their criticalities. In particular, we address the issue of effectively involving all stakeholders, internal as well as external, in assessing sustainability aspects.
4. An Approach to Model the Stakeholders’ View
This section presents a structured approach to help an organization engage stakeholders during the materiality analysis in the sustainability reporting process.
To address the criticalities mentioned in Section 3, the approach leverages on multi-attribute group decision-making (MAGDM) techniques. This family of techniques extends the scope of multi-attribute decision-making (MADM) techniques [31,32], which aim at making judgments on (or sorting) a given, finite set of feasible alternatives over a set of attributes or decision criteria, both quantitative and qualitative. In MADM techniques, the unique decision-maker is asked to provide her preference on each alternative with respect to each attribute, based on a suitable scale of judgment, expressed in terms of numerical values (e.g., exact values or intervals, or fuzzy numbers) or non-numerical values (e.g., verbal labels). Compared to the MADM techniques, the MAGDM ones differ as they take into account the diverse opinions of two or more independent decision-makers, e.g., group members or experts [33], each possibly having his own importance. As stakeholders do not have the same salience, such an aspect makes those techniques particularly suitable for stakeholder engagement.
The Approach
The approach is composed of six steps. Steps 1 and 2 drive the organization respectively in pointing the aspects that will be considered for inclusion in the sustainability report and identifying the stakeholders to be engaged in materiality analysis. Step 3 involves the choice and assessment of verbal labels to be used in evaluating sustainability aspects. The assessment of aspects is carried out in accordance with Step 4, and individual judgments are aggregated according to Step 5. Finally, through Step 6, the organization can identify material aspects.
(1) Identify sustainability aspects. At first, the organization identifies all the aspects that could be included in the sustainability report. In accordance with the precautionary principle, all the sustainability aspects that may (i) reflect the organization’s relevant economic, environmental, or social impact, or (ii) affect the assessments and decisions of stakeholders, should be listed. GRI Sustainability reporting guidelines provide a broad list of prospective aspects, classified into three categories, i.e. economic, environmental, and social, the latter being in turn partitioned into sub-categories (human rights, labor practices, product responsibility, and society). For each aspect, some indicators are also provided. Such a list could be possibly complemented with other aspects that are specific to that organization.
(2) Identify stakeholders and prioritize them. The organization identifies its stakeholders, so as to engage them in evaluating to which extent every sustainability aspect affects their assessments and decisions. Nonetheless, since the stakeholders are not equally relevant, it is crucial to prioritize them. To this end, stakeholders might be distinguished between primary and secondary, the latter being essential for the organization’s survival [34]. Stakeholders may also be characterized based on their importance, or salience, which, in turn, as already mentioned, depends on three drivers, i.e., urgency, power, and legitimacy [17]. A stakeholder’s salience may vary with respect to the considered sustainability aspect. For example, should corruption be used as a way to win competitive tender, the salience of shareholders could be considered as lower than the salience they have with respect to other aspects, e.g., economic performance; at the opposite, the salience of customers or competitors could be considered higher. For the sake of simplicity, we suggest providing stakeholders with a salience that is specific for each category to which the sustainability aspects belong, i.e., economic, social, and environmental. To assess such a salience, the organization has to compare stakeholders pairwise as for their importance within each category of sustainability aspects. The pairwise comparison procedure, indeed, combines a rigorous mathematical approach with observations based on psychology, and has been extensively adopted to solve different types of weighing problems, even in the field of sustainability [35]. The comparison should be expressed in terms of the dominance index, according to the Saaty’s fundamental scale of judgments [36]. The salience of the k-th stakeholder with reference to the c-th category of aspect, denoted as ukc, can be easily derived by the logarithmic least squares method [37]:
where akjc denotes the dominance index of the k-th stakeholder compared to the j-th one as for the c-th category of sustainability aspect. Based on the characteristics of the organization, e.g., its dimension, the comparisons should be dealt with by the entrepreneur(s), top manager(s), or other professional(s), as long as they possess a comprehensive vision of the organization. To check the consistency of pairwise comparisons, it is suggested that the geometric consistency index is used, as proposed by [38]. Possible inconsistencies can be amended by the procedure presented in [39].
(3) Adopt and calibrate a set of verbal labels. The set should include all the adjectives, or adverbs, that will be potentially used to assess sustainability aspects by a company representative as well as every stakeholder (comprehensively henceforth referred to as “decision-makers”). In [40], a moderate granularity for the set of adopted labels (adjectives, or adverbs) is suggested: not too few so as to allow for a reliable assessment, but not too many so as to make it easy to discriminate among labels. For instance five-label scales could be {extremely, much, neither much nor little, little, very little}, {excellent, very good, good, fair, poor} or {crucial, substantial, valuable, marginal, negligible}.
It should be observed, however, that stakeholders are likely to differ in terms of cultural background (they might even speak diverse languages). Thus, meanings attributed to the same label may vary: In general, the way to rank labels in a set could be disputed, and the distance (i.e. the difference of meaning) between two consecutive labels could vary (e.g., the distance between first and second labels compared to the one between the third and fourth ones).
To mitigate this problem, a preliminary procedure to calibrate the set of verbal labels is needed: We propose the adoption of a pairwise comparison procedure. In return for the additional effort that it requires of each decision-maker, this calibration enhances the evaluation reliability for all the aspects he/she will have to consider. Specifically, each decision-maker asked to evaluate the sustainability aspects should assess the relative importance of every i-th label compared with the j-th one. Such a relative importance, denoted as aijk (k referring to the decision-maker), is expressed in terms of dominance index derived by the so-called Saaty’s fundamental scale of judgment. Once all the pairwise comparisons have been carried out, the weight of the i-th label according to the k-th decision-maker can be calculated by the logarithmic least squares method:
where n is the granularity of the set (typically, n = 5 or 7). Consistency of pairwise comparisons made by a given decision-maker can be assessed and possibly amended.
(4) Assess sustainability aspects. The organization, on the one hand, and all stakeholders, on the other hand, should assess every sustainability aspects by means of a label picked out of the set. Specifically, in accordance with the GRI-G4 guidelines, the organization should assess any aspect with regard to the significance of its economic, environmental, and social impacts, whereas stakeholders should do that as for the influence that the considered aspect has on their assessments and decisions.
All these verbal assessments should be then converted into quantitative assessments. To this aim, the weights that are associated to the attendant labels of the set for each decision-maker are adopted. The assessment of the organization as for the i-th sustainability aspect is denoted as xi, whereas the evaluation of the k-th stakeholder for the i-th aspect is denoted as yik.
(5) Combine the stakeholders’ assessments. A multi-attribute group decision-making methodology is proposed hereafter to aggregate the diverse opinions of the several stakeholders. This is a typical problem wherein the focus is the aggregation of individual priorities [41]: Stakeholders’ opinions are indeed related to their thoughts about the influence that an aspect has on their own assessments and decisions. To aggregate such opinions, i.e., the weights of the attendant labels, both geometric and arithmetic means are allowed, as neither method violates the unanimity rule (if individuals unanimously prefer an alternative A to another alternative B, then the group as a whole must also prefer A to B).
We suggest the arithmetic weighted mean, wherein weights are the stakeholders’ salience. Therefore, the aggregate assessment of the i-th sustainability aspect, belonging to the c-th category, is given by the additive weighted aggregation operator [42]:
(6) Determine the material aspects. The determined xi (Step 4) and yi (Step 5) are the coordinates representing the associated aspects as points in the materiality matrix. Determining which aspects are material requires the definition of appropriate thresholds θx and θy along both axes: Aspects above both thresholds are certainly material. Furthermore, the GRI-G4 guidelines stress that “significance within one viewpoint is more important than convergence between the different viewpoints” [25]. With this regard, we suggest using a rule of thumb, based on the Euclidean norm, and considering also material any aspect i such that:
where .
5. Application
The proposed approach is general in that it can be adopted by large companies as well as SMEs. It is designed so as not to require a high organizational effort nor specific competencies. For that reason the approach can be particularly useful for, and easily implemented by, SMEs, which in general struggle more than larger organizations in allocating resources for sustainability reporting. In this section, we discuss the possible applications of the proposed approach. To this end, we first present the results of a testing phase carried out on a sample of SMEs. Additionally, based on that, we discuss the possible applications, the strengths, and the limitations of the proposed approach.
We selected a sample of 17 SMEs located in Apulia (Southern Italy) and belonging to various sectors (8 mechanics, 4 food & tourism, 3 ICT, 2 others). The companies have been selected through three Apulian networks, caring for diverse reasons for sustainability: “Forum RSI”, a group of firms sensitive to CSR within Confindustria (the largest association of Italian Employers); “Costellazione Apulia”, which comprises companies specifically focused on leveraging positive externalities of their activities; and “UCID”, an association of entrepreneurs and managers inspired to Catholic social teaching [43].
The testing phase was aimed at checking whether organizations might find some criticalities in implementing the proposed approach, and providing feedback to improve it [44,45]. At this stage of the research, we limited the analysis to only three stakeholder categories, which the literature generally qualifies as primary [46]: customers, employees, and suppliers. Note that we did not consider the important category of company shareholders (or owners), given that their voice is taken into account when evaluating the aspect’s impact along the x-axis. A large part of the SMEs included in the sample are indeed family businesses, so their management and ownership often correspond.
To support the SMEs in the adoption of the proposed approach, we collected the required information included in the sample. In particular, we conducted several interviews with a manager or executive for each company, as well as with the attendant stakeholders. The first interview was made by meeting in person a company representative, and lasted around two hours. Its aim was twofold: (i) to identify a list of sustainability aspects possibly relevant for that organization, by complementing the list included in [25] with other aspects that reflect the peculiarities of their company (Step 1); and (ii) to identify and prioritize stakeholders (Step 2). To increase the effectiveness of the meetings, a few days before we contacted the company representative by e-mail so as to make him/her informed on the goal of the research and the main concepts useful to effectively carry on the required activities. Subsequently, we contacted one by one the stakeholders indicated by the company representative—in person when possible (e.g., for employees and local customers and suppliers), otherwise by telephone or e-mail—so as to ask them to (i) preliminarily calibrate the set of verbal labels to be used in assessing the sustainability aspects (Step 3) and (ii) assess the sustainability aspects in the list defined by the company representative (Step 4). A similar activity was done with the stakeholder representative. Finally, the stakeholders’ assessments were combined and the material aspects determined according to the proposed approach (Step 5). The resulting materiality matrices were illustrated to the companies’ representatives, and compared with the ones of other companies in the sample that belong to the same sector.
With respect to the organizations’ feedback, companies included in the sample did not find any particular difficulty in following the steps to implement the proposed approach. In particular, the small size of all the companies in the sample allowed for a relatively simple assessment of the impacts (x-axis): The interviewed person as representative of the company (either the entrepreneur or a top manager) possessed an adequate understanding of the whole business and its related sustainability aspects. On the contrary, some problems emerged to gather feedback from stakeholders: Identifying the proper representative/s for a given stakeholder category was not always straightforward. For example, in some cases, the company had several diverse product lines and attendant customer segments. The adopted solution was to interview one customer representative for every segment, and compute the feedback of the stakeholder category as a weighted mean of the assessments given by such representatives (thus applying what was described in Step 5, although with reference to combining the assessments given by the diverse stakeholder categories). Similar considerations apply to the management of other stakeholder categories (e.g., suppliers).
The approach represents a first attempt to define a standardized procedure to carry out materiality analysis so as to address the subjectivity and completeness problems discussed in Section 3. It can be easily adopted by SMEs, which usually do not have adequate resources to deal with sustainability reporting.
Furthermore, it could be used to ease comparative analyses among companies involved in materiality analysis. Below, we report an example of comparative analysis carried out on the selected companies. Due to the limited number of organizations included in the sample, the analysis is in no way aimed at deriving insights, which is beyond the scope of this paper. Rather, the following might be an example of the kind of information that the proposed approach, if extensively adopted, lets us derive.
Stakeholders’ prioritization has shown that, on average, customers’ relevance is the highest (45%), whereas both suppliers and employees weigh 27%. Nonetheless, differences emerge among sectors: For example, suppliers’ relevance varies from 18% (mechanics) to 46% (food & tourism), whereas customers’ from 31% (ICT) to 51% (mechanics). Material aspects have been identified adopting θx = θy = 0.5 as threshold values (Step 6). Table 1 shows the most recurrent aspects.

Table 1.
Materiality analysis: most recurrent material aspects in the sample.
Another interesting further result would be associated to the assessment of the average number of identified material aspects. In each case, though such results are by no way generalizable due to the limited dimension of the sample, they were 12.7, with no substantial difference among sectors. Specifically, the average number of material aspects in the economic, environmental, and social categories are 2.2, 4.4, and 6.1, respectively. Differences across sectors emerge in the environmental and social categories: Moving from ICT to food & tourism, in the environmental (social) category, material aspects on average go from 2.3 to 5.0 (from 7.3 to 4.3). In both cases mechanics is intermediate, as material aspects resulted 4.0 in the environmental category and 5.4 in the social one.
Yet, at least for the environmental category, the result seems consistent with the fact that companies producing mostly services (the ICT sector encompasses firms, whose main products is software) are expected to involve a lower environmental impact in terms of materials, emissions, wastes, and physical transportations requirements.
6. Conclusions
This paper has addressed the issue of stakeholder engagement for materiality analysis within sustainability reporting. Its aim was to propose a novel structured approach to take into account the stakeholders’ view during the identification of the organization’s material aspects. The approach has been tested on a sample of Italian SMEs concerned with sustainability issues, operating in different sectors. The empirical test has shown that the approach is relatively easy to be understood and adopted by practitioners, irrespective of the firm sector.
Rooted in existing techniques, mostly developed in the field of multi-attribute group decision-making (MAGDM), our approach is innovative in that it (i) is specifically designed for supporting stakeholder engagement during materiality analysis and (ii) allows all the relevant stakeholders’ view on any aspect to be captured and then synthesized into a unique evaluation. To our knowledge, there are only two studies [11,24] that propose quantitative approaches to support materiality assessment in sustainability reporting. The former approach is quite sophisticated in that it uses fuzzy numbers to deal with linguistic attributes, yet it does not actually model group decisions. On the contrary, the approach developed by [24] does propose a form of multi-attribute group decision-making (MAGDM) techniques, yet very simplified. As a result, both approaches show limits in successfully engaging, capturing, and synthesizing stakeholders’ views.
We have also looked at the resource and capability scarcity that often affects SMEs, and defined an approach that is easily scalable: For instance, the number of involved stakeholders may vary as well as every stakeholder may be associated with one or several different weights (being each specific weight related to the importance of the given stakeholder for a certain aspect or aspect category).
From a managerial perspective, the approach not only complements the existing guidelines for sustainability reporting, but also enhances the quality of sustainability reporting. In particular, it codifies one of its key activities—materiality analysis (which is likely to be the most important)—thus ensuring a higher reliability of a sustainability report as well as its comparability to other reports. A further implication concerns stakeholder engagement: As stakeholders’ opinions are more reliably described and taken into account, stakeholders are expected to develop a higher trust towards the company, which in turn improves their engagement. Finally, the adoption of a structured approach would make it more difficult for companies to adopt opportunistic behaviors and/or misunderstand stakeholders’ opinions when capturing and then synthesizing their view into a unique evaluation.
This paper presents some limitations. First, the approach applies to materiality analysis as described by GRI G4 sustainability reporting guidelines. However, this potential problem for the generality of our research might be less relevant than expected. Stakeholder management, i.e. the specific topic we address, is indeed relevant for almost any framework. Second, through the empirical test we have identified some implementation criticalities. We have addressed such criticalities, but we cannot exclude that others might emerge.
Additional research would be necessary to further test the entire approach. In particular, still focusing on the specific needs of SMEs, firms located in other geographic areas should be considered to examine whether such a variable might have an impact on the generality of the approach. Another promising research avenue concerns the outcomes of materiality analysis, which are actually beyond the scope of this paper. For example, the influences of a sector, as well as of a country or firm size, could be among the topics worth investigating in future research.
Author Contributions
All authors contributed substantially to the work presented in this paper. Barbara Scozzi is the main author of Section 1, Section 2, and Section 3, Nicola Bellantuono the main author of Section 4 and Section 5, and Pierpaolo Pontrandolfo the main author of Section 6. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Waddock, S.A. Parallel Universes: Companies, Academics, and the Progress of Corporate Citizenship. Bus. Soc. Rev. 2004, 109, 5–42. [Google Scholar]
- Amini, M.; Bienstock, C.C. Corporate sustainability: An integrative definition and framework to evaluate corporate practice and guide academic research. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 76, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Union. A renewed EU strategy 2011–14 for Corporate Social Responsibility. 2011. Available online: eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=COM:2011:0681:FIN:en:PDF (accessed on 14 April 2016).
- Freeman, R.E. Strategic Management: A Stakeholder Approach; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, R.; Menichini, T. A multidimensional approach for CSR assessment: The importance of the stakeholder perception. Expert Syst. Appl. 2013, 40, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donaldson, T.; Preston, L.E. The Stakeholder Theory of the Corporation: Concepts, Evidence, and Implications. Acad. Manag. Rev. 1995, 20, 65–91. [Google Scholar]
- Freeman, R.E.; Harrison, J.S.; Wicks, A.C.; Parmar, B.L.; DeColle, S. Stakeholder Theory: The State of the Art; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler, D.; Sillanpaa, M. Including the Stakeholders: The Business Case. Long Range Plan. 1998, 31, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, A.L.; Miles, S. Stakeholders: Theory and Practice; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- AccountAbility. AA1000 Stakeholder Engagement Standard. Available online: http://www.accountability.org/standards/aa1000ses.html (accessed on 14 April 2016).
- Calabrese, A.; Costa, R.; Levialdi, N.; Menichini, T. A fuzzy Analytic Hierarchy Process method to support materiality assessment in sustainability reporting. J. Clean. Prod. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battisti, M.; Perry, M. Walking the talk? Environmental responsibility from the perspective of small-business owners. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2011, 18, 172–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann-Pauly, D.; Wickert, C.; Spence, L.; Scherer, A.G. Organizing Corporate Social Responsibility in Small and Large Firms: Size Matters. J. Bus. Ethics 2013, 115, 693–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwood, M. Stakeholder Engagement: Beyond the Myth of Corporate Responsibility. J. Bus. Ethics 2007, 74, 315–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, R.E. Strategic Management: A Stakeholder Perspective; Pitman: Boston, MA, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Elias, A.A.; Cavana, R.Y.; Jackson, L.S. Stakeholder analysis for R&D project management. R D Manag. 2002, 32, 301–310. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell, R.K.; Agle, B.R.; Wood, D.J. Toward a theory of stakeholder identification and salience: Defining the principle of who and what really. Acad. Manag. Rev. 1997, 22, 853–886. [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler, D.; Sillanpää, M. The Stakeholder Corporation; Pitman: London, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Carroll, A.B. Business and Society: Ethics and Stakeholder Management; South-Western College Pub: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Post, J.E.; Preston, L.E.; Sachs, S. Managing the extended enterprise: The new stakeholder view. Calif. Manag. Rev. 2002, 45, 6–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AccountAbility; the United Nations Environment Programme; Stakeholder Research Associates. The Stakeholder Engagement Manual; Beacon Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2005; Volume 2, Available online: http://www.accountability.org/images/content/2/0/208.pdf (accessed on 14 April 2016).
- Reed, M.S. Stakeholder participation for environmental management: A literature review. Biol. Conserv. 2008, 141, 2417–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzig, C.; Ghosh, B. Sustainability Reporting. In The Business Student’s Guide to Sustainable Management; Molthan-Hill, P., Ed.; Greenleaf Publishing Limited: Austin, TX, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, C.-W.; Lee, W.-H.; Chao, W.-C. Materiality analysis model in sustainability reporting: A case study at Lite-On Technology Corporation. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 57, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global reporting initiative. Gri-g4 Sustainability Reporting Guidelines—Reporting Principles and Standard Disclosures. 2013. Available online: http://www.globalreporting.org/resourcelibrary/GRIG4-Part2-Implementation-Manual.pdf (accessed on 14 April 2016).
- KPMG. Survey of Corporate Responsibility Reporting. 2013. Available online: https://assets.kpmg.com/content/dam/kpmg/pdf/2015/08/kpmg-survey-of-corporate-responsibility-reporting-2013.pdf (accessed on 14 April 2016).
- Manetti, G. The quality of stakeholder engagement in sustainability reporting: Empirical evidence and critical points. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2011, 18, 110–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, D.Y. Applications of the extent analysis method on fuzzy AHP. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1996, 95, 649–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatis, D.H. Failure Mode and Effect Analysis: FMEA from Theory to Execution; ASQ Quality Press: Milwaukee, WI, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Saaty, T.L. The Analytic Network Process; Springer US: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Arrow, K.J. Social Choice and Individual Values; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1963. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z. Uncertain Multi-Attribute Decision Making: Methods and Applications; Springer-Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, Z. Developing a straightforward approach for group decision making based on determining weights of decision makers. Appl. Math. Model. 2012, 36, 4106–4117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarkson, M.B.E. A stakeholder framework for analyzing and evaluating corporate social performance. Acad. Manag. J. 1995, 20, 92–118. [Google Scholar]
- Ruf, B.M.; Muralidhar, K.; Paul, K. The development of a systematic, aggregate measure of corporate social performance. J. Manag. 1998, 24, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaty, T.L. How to make a decision: The Analytic Hierarchy Process. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1990, 48, 9–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, G.; Williams, C. A note on the analysis of subjective judgment matrices. J. Math. Psychol. 1985, 29, 387–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguarón, J.; Moreno-Jiménez, J.M. The geometric consistency index: Approximated thresholds. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2003, 147, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Xu, J. A consistency and consensus based decision support model for group decision making with multiplicative preference relations. Decis. Support. Syst. 2012, 52, 757–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.C.; Xu, Y.F.; Yu, S. Linguistic multiperson decision making based on the use of multiple preference relations. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 2009, 160, 603–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forman, E.; Peniwati, K. Aggregating individual judgments and priorities with the analytic hierarchy process. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1998, 108, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z. An automatic approach to reaching consensus in multiple attribute group decision making. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2009, 56, 1369–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massaro, T. Living Justice: Catholic Social Teaching in Action; Rowman & Littlefield: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Lynham, S.A. The general method of theory-building research in applied disciplines. Adv. Dev. Hum. Resour. 2002, 4, 221–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanson, R.A.; Chermack, T.J. Theory Building in Applied Disciplines; Berrett-Koehler Publishers: Oakland, CA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, T.; Schermerhorn, J.R.; Dienhart, J.W. Strategic leadership of ethical behavior in business. Acad. Manag. Exec. 2004, 18, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).