Game Behavior Analysis between the Local Government and Land-Lost Peasants in the Urbanization Process
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Interest Game Analysis between the Local Government and Peasant
2.1. Hypothesis
2.2. The Establishment of the Bargaining Game Model between the Local Government and Land-Lost Peasants
3. Analysis of the Static Game Model between the Local Government and Land-Lost Peasants
3.1. Establishing the Dual Game Matrix
3.2. Instructions for Building the Game Model
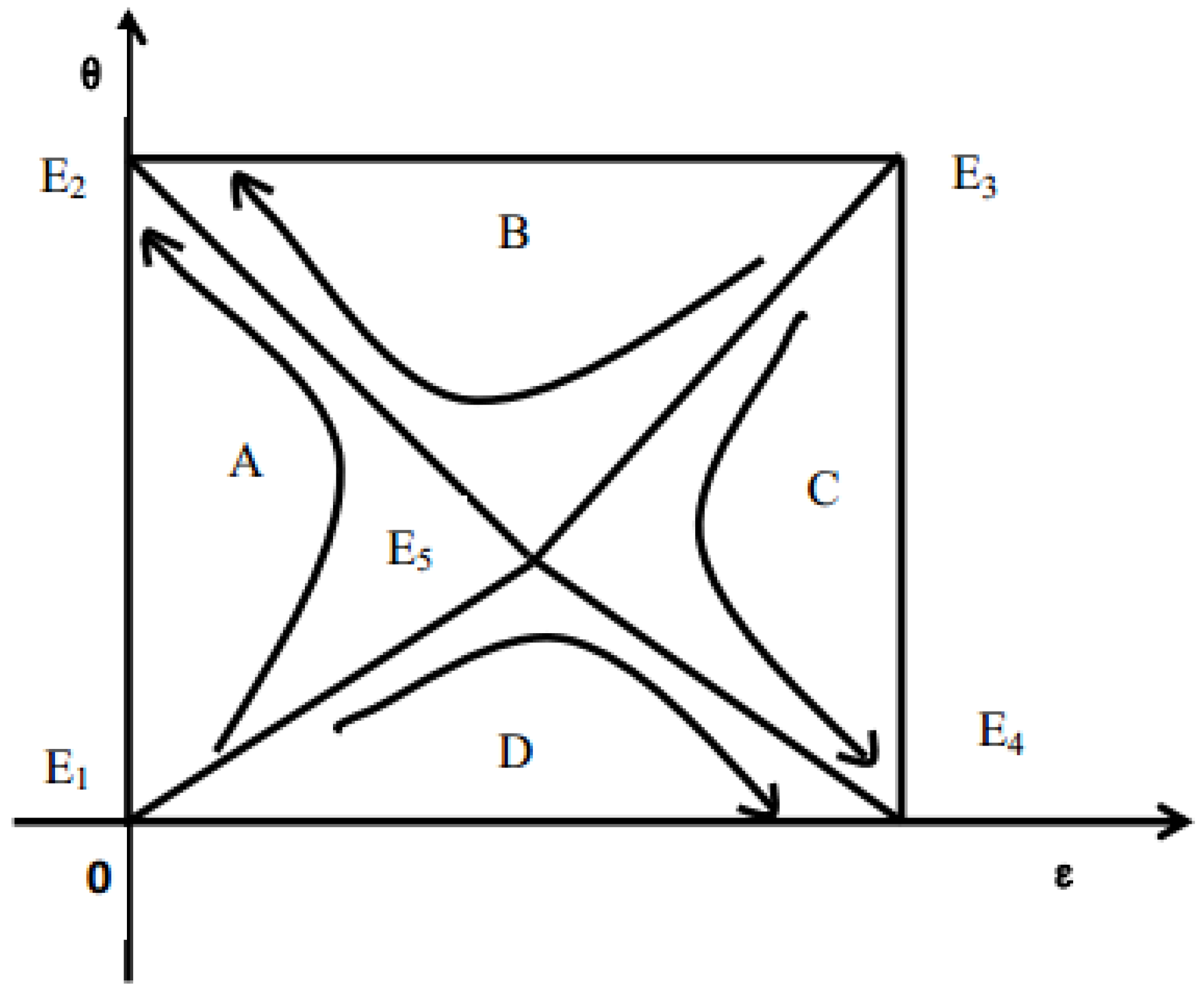
3.3. Stability Analysis of the Equilibrium Point
3.4. The Interactive Evolution Process of the Game Strategy
3.5. The Improving Measure
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Long, H. Spatio-temporal analysis of land-use conversion in the eastern coastal China during 1996–2005. J. Geogr. Sci. 2008, 18, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.; Peng, Y.; Luo, C.; Wu, C.; Du, Q. Urban Land Expansion and Sustainable Land Use Policy in Shenzhen: A Case Study of China’s Rapid Urbanization. Sustainability 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China Statistics Press. China Statistical Yearbook. 2016. Available online: http://www.stats.gov.cn/tjsj/ndsj/ (accessed on 22 November 2016). [Google Scholar]
- National Bureau of Statistics of China. Statistical Communiqué of the People’s Republic of China on the 2015 National Economic and Social Development. 2015. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2016–02/29/content_5047274.htm (accessed on 22 November 2016). [Google Scholar]
- Mayors, C.A.O. Annual Report on Urban Development of China; China City Press: Beijing, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, G.Z.; Liu, T. Dynamic Mechanism of Urbanization and Its Evolution in Post-reform China. China Soft Sci. 2010, 46, 86–95. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Xu, X.-Q. Spatial Evolvement and Its Affecting Factors of Urbanization in China after Reforming and Open-up. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2007, 27, 142–148. [Google Scholar]
- Friedmann, J. Four Theses in the Study of China’s Urbanization. Int. J. Urban Regional Res. 2008, 30, 440–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.J.C. Urban Transformation in China, 1949–2000: A Review and Research Agenda. Environ. Plan. A 2002, 34, 1545–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Wang, X.; Xiao, G. A remote sensing and GIS integrated study on urbanization with its impact on arable lands: Fuqing City, Fujian Province, China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2000, 11, 301–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y. Land cover changes during agrarian restructuring in Northeast China. Appl. Geogr. 2006, 26, 312–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Wang, R.C.; Wu, J.P.; Zhou, B.; Shi, Z.; Ding, L.X. Quantifying Land Use Change in Zhejiang Coastal Region, China Using Multi-Temporal Landsat TM/ETM+ Images. Pedosphere 2007, 17, 712–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Li, X.; Lu, C. Urban land expansion and arable land loss of the major cities in China in the 1990s. Sci. China 2005, 48, 1492–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. China National Human Development Report 2013—Sustainable and Liveable Cities: Towards Ecological Civilization. Available online: http://www.cn.undp.org/content/dam/china/docs/Publications/UNDP-CH_2013%20NHDR_EN.pdf (accessed on 22 November 2016).
- Long, H.; Gerhard, K.H.; Li, X.; Zhang, M. Socio-economic development and land-use change: Analysis of rural housing land transition in the Transect of the Yangtse River, China. Land Use Policy 2007, 24, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, H.L.; Liu, Y.S.; Li, X.B.; Chen, Y.F. Building new countryside in China: A geographical perspective. Land Use Policy 2010, 27, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrow, K.J.; Fisher, A.C. Environmental Preservation, Uncertainty, and Irreversibility. Q. J. Econ. 1974, 88, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodge, I. Uncertainty, irreversibility and the loss of agricultural land. J. Agric. Econ. 1984, 35, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, J.O.S. Uncertainty, irreversibility and the loss of agricultural land: A reconsideration. J. Agric. Econ. 1987, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.A.; Tong, X. Self-identity of the Passive-urbanized Group in the Process of Obtaining Urban Adaptability and Modernity: An empirical study on 561 land-displaced peasants in Nanjing. Sociol. Stud. 2006, 2, 86–106. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Zhen, F.; Wei, Z.; Guo, S.; Chen, T. A theoretical framework and methodology for urban activity spatial structure in e-society: Empirical evidence for Nanjing City, China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2015, 25, 672–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.K. Study of the Remodeling Characteristics of Traditional Urban Housing for Lease (cases of an Open-rectangular plan in the Traditional Urban Housing Neighborhood of Bukchon). J. Korea Acad.-Ind. Cooperation Soc. 2014, 15, 6906–6914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Yao, Z.Y. Identification of the New Peasant-workers and the Hindrances Concerned—Based on a Sample Survey of the Peasant-workers in Changsha City. J. Hunan Agric. Univ. 2009, 164, 55–71. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, J. Farmer’s Citizenship: The Role Transition from Farmers to Townspeople. J. East China Norm. Univ. 2004, 36, 55–61. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tang, G.N.; Xu, W.X.; Jia, L.Y.; Shigeru, K.; Zheng, J.C. A research on the relationship between the economic threshold of Chinese farmers’ citizen and urbanization: Theory and demonstration. Econ. Geogr. 2006, 26, 118–121. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Z.P. Five obstacles on the way of urbanization of rural population. City Plan. Rev. 2003, 27, 68–70. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Huang, K. Empirical Analysis of the Impact on the Citizenization of Rural Migrant Workers from Urban-rural Dual Institution. China Popul. Today 2011, 5. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Feng, C. From Fake Urbanization to Residentialization: Actual Route of Chinese Peasant-labors’ Urbanization. J. Soc. Sci. 2007, 2, 110–120. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, M.J.; Wei, L.Z. Analysis on system restricting factors of peasant’s citizenship in China. J. Qiqihar Univ. Philos. (Soc. Sci. Ed.) 2003, 4, 49–52. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tan, B.; Luo, W.Y. Deepen System of Household Registration Reform to Promote the Urbanization Development of Chuxiong Yi Nationality Autonomous Prefecture. J. Chuxiong Norm. Univ. 2007, 22, 75–79. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lou, Y.-G.; Jin, H. The Support System to the Land Being T aken Peasant in the Process of Vrbanize. Northwest Popul. J. 2002, 23, 27–30. [Google Scholar]
- Zen, S.-S.; Zhang, Y.Z. On Gambling Relation Between Peasants and Government in the Process of Peasants’ Being Citizen. Sichuan Commer. Coll. J. 2004, 12, 7–9. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.N. Game Analysis of the Benefits between the Lost Land Farmer and the Government during Urbanization. 2010, 5, 61–64. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Fuchun, M. Complete Compensation for the Rational Benefits of Land—Losing Farmers. Issues Agric. Econ. 2007, 3, 82–85. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Feng, L.W.Y. The Obstruction Analysis on the Farmer-to-citizen Process. J. Shanghai Polytech. Coll. Urban Manag. 2005, 4, 50–52. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.B. Farmland Grabs by Urban Sprawl and Their Impacts on Peasants’ Livelihood in China: An Overview. Available online: https://www.mendeley.com/catalog/farmland-grabs-urban-sprawl-impacts-peasants-livelihood-china-overview/ (accessed on 22 November 2016). (In Chinese)
- Dang, G.Y. Current Situation and Problems of the Reform of Rural Land System in China. J. Cent. China Norm. Univ. 2005, 44, 8–18. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tan, R.; Qu, F.; Heerink, N.; Mettepenningen, E. Rural to urban land conversion in China—How large is the over-conversion and what are its welfare implications? China Econ. Rev. 2011, 22, 474–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.J.; Liu, Y.T.; Webster, C.; Wu, F.L. Property Rights Redistribution, Entitlement Failure and the Impoverishment of Landless Farmers in China. Urban Stud. 2009, 46, 1925–1949. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, D.; Wang, D. Urbanization and a Moderate Conversion of Farmland: Institutional Obstacles and Policy. Issues Agric. Econ. 2006, 27, 60–65. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, C. Policy and praxis of land acquisition in China. Land Use Policy 2007, 24, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, E.C.M.; Bao, H.J.; Zhang, X.L. The policy and praxis of compensation for land expropriations in China: An appraisal from the perspective of social exclusion. Land Use Policy 2013, 32, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X. Research on the Society Security of the Landless Peasants of Henan Province; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 69–74. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Y.; Lu, W.; Wu, W. Are social security policies for Chinese landless farmers really effective on health in the process of Chinese rapid urbanization? A study on the effect of social security policies for Chinese landless farmers on their health-related quality of life. Int. J. Equity Health 2014, 13, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.-L.; Qu, F.-T. Research on Increment Income Configuration Mechanism & Distribution of Farmland Requisition during the Period of Economic Transition. China Land Sci. 2006, 20, 2–12. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, P.X.; Qu, F.-T. Distribution of land benefit and land allocation between agricultural and non-agricultural uses: A case study of N City of Jiangsu Province. J. Nanjing Agric. Univ. 2006, 6, 1–6. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Hong, Y.M.; Peng, W.Y. Revenue Realization and Distribution in the Transfer of Rural Collective Construction Land Leasehold. China Land Sci. 2009, 23, 20–23. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chinese Premier Stresses Human-Centered Urbanization. 2014. Available online: http://news.xinhuanet.com/english/2016–01/24/c_135041010.htm (accessed on 22 November 2016).
- Daily, S.M. 300 Million of the Real Urbanization Is the Difficulty of Household Registration Reform. 2013. Available online: http://www.sina.com.cn (accessed on 22 November 2016).
- Von Neumann, J.; Morgenstern, O. Theory of Games and Economic Behavior; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1944; pp. 2–14. [Google Scholar]
- Nash, J.F., Jr. The Bargaining Problem. Econometrica 1950, 18, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrow, J.D. Game Theory for Political Scientists; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1994; pp. 331–333. [Google Scholar]
- Hofbauer, J.; Sigmund, K. Evolutionary Games and Population Dynamics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1998; pp. 2565–2570. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, P.L.; Geckil, I.K. Applied Game Theory and Strategic Behavior; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010; pp. 407–410. [Google Scholar]
- Shoham, Y.; Leyton-Brown, K. Multiagent Systems: Algorithmic, Game-Theoretic, and Logical Foundations; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2012; pp. 5929–5934. [Google Scholar]
- Petrosi︠a︡n, L.A.; Donetz, J.M. Game Theory; World Scientific: Jurong East, Singapore, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Chankong, V.; Haimes, Y.Y. Optimization-Based Methods for Multiobjective Decision-Making: An Overview. Large Scale Syst. 1983, 5, 1–33. [Google Scholar]
- Kreps, D.M. Game Theory and Economic Modelling. J. Econ. Educ. 1990, 30, 895–896. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L. Social Security Right and Orientation for City-people. J. Guangdong Polytechn. Norm. Univ. 2008, 5, 62–65. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.C. Analysis of the Influence of Social Capital Factor on the Urbanization of Land-expropriated Farmers. Econ. Surv. 2007, 5, 118–121. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.; Jiang, K. A Study on the Family Life and Cultural Consumption of Peasants during the Process of Urbanization—The Analysis and Countermeasures Based on the Investigations of 208 Peasant Households in Shanghai Outskirts. J. East China Univ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 4, 100–111. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Auvachez, É. Supranational Citizenship Building and the United Nations: Is the UN Engaged in a “Citizenization” Process? Glob. Gov. 2009, 15, 43–66. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, E.F. Reconsidering US Immigration Reform: The Temporal Principle of Citizenship. Perspect. Politics 2011, 9, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorob’ev, N.N.; Kotz, S. Game Theory: Lectures for Economists and Systems Scientists; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Christopher, C.; Devlin, J. A note on the Replicator Equations of dynamical game theory. Appl. Math. Lett. 1993, 6, 31–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhaidari, A.D.; Heller, E.J.; Yamani, H.A.; Abdelmonem, M.S. The J Matrix Method; Springer-Verlag GmbH: Berlin, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Nasser, I.; Abdelmonem, M.S.; Bahlouli, H.; Alhaidari, A.D. The rotating Morse potential model for diatomic molecules in the tridiagonal J-matrix representation: I. Bound states. J. Phys. B Atom. Mol. Opt. Phys. 2007, 40, 4245–4257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maquet, A.; Chu, S.; Reinhardt, W.P. Stark ionization in dc and ac fields: An L2 complex-coordinate approach. Phys. Rev. A 1983, 27, 2946–2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| The Local Government | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Resist (G1) | Accept (G2) | ||
| Peasants | Resist (P1) | m − F1, B − m − G1 | M + I − F2, B − m − G2 − I |
| Accept (P2) | m, B − m | M + (1 − r)L + T − C, B − m − (1 − r)L − T | |
| Equilibrium Point | Determinant of Matrix J | Positive or Negative | Trace of Matrix J | Positive or Negative | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E1(0,0) | [(1 − r)L + T] × [I + C − F2 − (1 − r)L − T] | + | I + C − F2 | + | Instable |
| E2(0,1) | F1 × [(1 − r)L + T] | + | −F1 − T − (1 − r)L | − | Stable |
| E3(1,1) | F1(G1 − G2 − I) | + | F1 + G1 − G2 − I | + | Instable |
| E4(1,0) | (I + C − F2 − (1 − r)L − T)[(1 − r)L + T](G1− G2 − I) | + | F2 + T + (1 − r)L + G2 − G1 − C | − | Stable |
| E5 (, ) | 0 | Saddle Point |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, L.; Du, H.; Zhao, Y. Game Behavior Analysis between the Local Government and Land-Lost Peasants in the Urbanization Process. Sustainability 2016, 8, 1213. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8121213
Zhang L, Du H, Zhao Y. Game Behavior Analysis between the Local Government and Land-Lost Peasants in the Urbanization Process. Sustainability. 2016; 8(12):1213. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8121213
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Lu, Hongru Du, and Yannan Zhao. 2016. "Game Behavior Analysis between the Local Government and Land-Lost Peasants in the Urbanization Process" Sustainability 8, no. 12: 1213. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8121213
APA StyleZhang, L., Du, H., & Zhao, Y. (2016). Game Behavior Analysis between the Local Government and Land-Lost Peasants in the Urbanization Process. Sustainability, 8(12), 1213. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8121213





