Analysis of Factors that Influence the Willingness to Pay for Irrigation Water in the Kurdistan Regional Government, Iraq
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
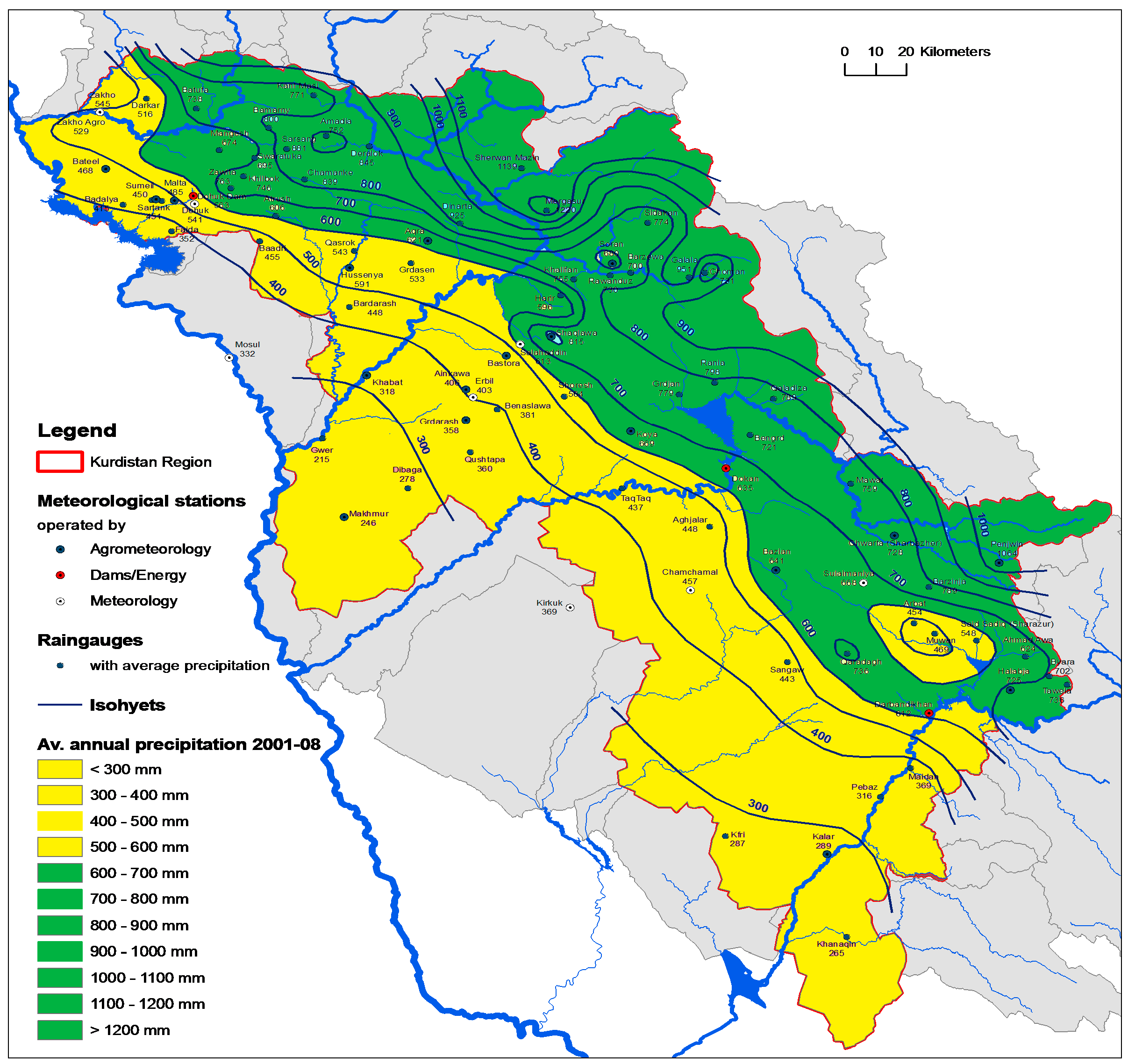
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Estimation of Willingness to Pay for Water in Zone A
| Variable | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | Model 4 | Model 5 | Model 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Constant | 10.6596 (0.5912) a | 6.6024 (1.5937) a | 6.7636 (1.5555) a | −0.2522 (4.1614) | ||
| Bid | −0.4888 (0.0696) a | −0.7364 (0.1017) a | −0.7199 (0.0971) a | −0.7907 (0.1399) b | −0.7791 (0.1388) a | −0.7809 (0.1137) a |
| Water deficit | 0.8187 (0.3964) b | 0.8721 (0.3915) b | 1.6289 (0.6592) b | 1.6097 (0.5410) a | 1.7449 (0.5975) a | |
| Ground water | 7.9958 (0.9667) a | 7.5713 (0.9401) a | 11.8681 (1.8644) a | 10.7821 (1.6498) a | 8.7986 (1.2671) a | |
| Cultivated area in 2011 | 0.0155 (0.0742) | |||||
| Education | −2.6008 (0.5419) a | −2.5843 (0.6408) a | −1.9421 (0.5461) a | |||
| Age | 0.2047 (0.0614) a | 0.1959 (0.0464) a | 0.1529 (0.0423) a | |||
| Main activity agriculture | −3.1387 (1.8731) c | −2.2212 (1.6677) | ||||
| Ln (L) | −99.3227 | −95.1258 | −94.2720 | −91.9522 | −91.8657 | −92.3971 |
| ρ | 0.9851 | 0.9912 | 0.9910 | 0.9908 | 0.9903 | 0.9897 |
| No. of observations (No. of groups) | 590 (118) | 590 (118) | 590 (118) | 590 (118) | 590 (118) | 590 (118) |
| Source of water | Ground water | Other types of sources | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type of respondents | |||
| All farmers | 20.28 | 11.49 | |
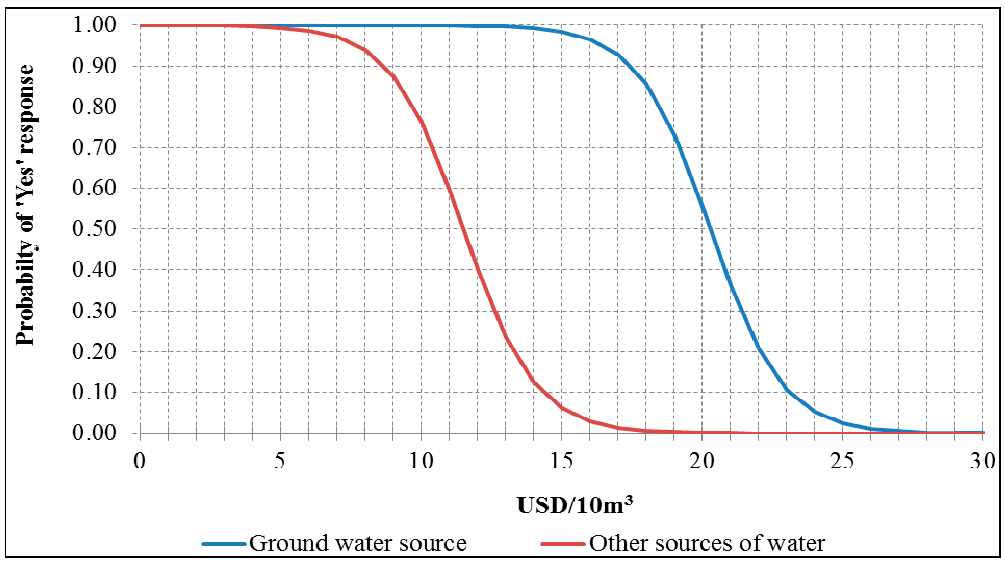
3.2. The Estimation of Willingness to Pay for Water in Zone B
| Variable | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | Model 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Constant | 7.4649 (0.5426) a | −44.4277 (5.8659) a | −23.9513 (7.0296) a | −27.8759 (6.8600) a |
| Bid | −0.1517 (0.0652) b | −0.8713 (0.1791) a | −0.3822 (0.1452) a | −0.4097 (0.1525) a |
| Water deficit | 18.1843 (2.6099) a | 8.2777 (1.6574) a | 9.5600 (1.9178) a | |
| Ground water | −9.7616 (1.6223) a | −1.3220 (0.9704) | ||
| Cultivated area in 2011 | 0.0281 (0.0505) | 0.0137 (0.0279) | ||
| Education | −0.1793 (0.6193) | |||
| Age | 0.0249 (0.0461) | |||
| Main activity agriculture | −0.5213 (1.0879) | |||
| Ln(L) | −73.6322 | −34.3754 | −36.5469 | −38.1397 |
| ρ | 0.9792 | 0.9895 | 0.9286 | 0.9439 |
| No. of observations (No. of groups) | 590 (118) | 590 (118) | 590 (118) | 585 (117) |
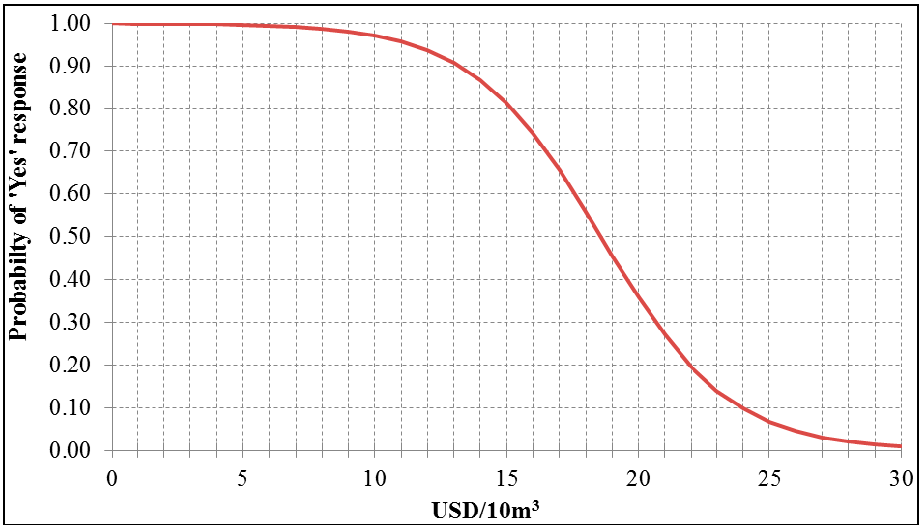
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bardini, M.D. The Water Policy Reform Program of the Economic Development Institute: Tracer Evaluation Report; EDI Evaluation Studies, No. ES98-10; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Moldan, D. Water for Food, Water for Life: A Comprehensive Assessment of Water Management in Agriculture; Earthscan: London, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Solanes, M.; Villarreal, F.G. The Dublin Principles for Water as Reflected in a Comparative Assessment of Institutional and Legal Arrangements for Integrated Water Resources Management; Global Water Partnership Technical Advisory Committee (TAC): Stockholm, Sweden; Global Water Partnership: Stockholm, Sweden, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Rogers, P.; de Silva, R.; Bhatia, R. Water is an economic good: How to use prices to promote equity, efficiency, and sustainability. Water Policy 2002, 4, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, P.; Bhatia, R.; Huber, A. Water as a Social and Economic Good: How to Put the Principle into Practice; Global Water Partnership: Stockholm, Sweden, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Briscoe, J. Water as an Economic Good, The Idea and what it means in practice. Available online: http://jzjz.tripod.com/icid16.html (accessed on 1 May 2015).
- Freeman, A.M., III. Economic Valuation: What and Why. In A Primer on Non-market Valuation; Champ, P.A., Boyle, K.J., Brown, T.C., Eds.; Kluwer Academic Publisher: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003; pp. 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Agudelo, J.I. The Economic Valuation of Water Principles and methods. In Value of Water Reasearch Report; IHE: Delft, The Netherlands, 2001; Volume 5. [Google Scholar]
- Champ, P.A.; Boyle, K.J.; Brown, T.C. A Primer on Non-market Valuation; Kluwer Academic Publisher: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Russo, T.; Alfedro, K.; Fisher, J. Sustainable Water Management in Urban, Agricultural, and Natural System. Water 2014, 6, 3934–3956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsur, Y.; Terry, R.; Doukkali, R.; Dinar, A. Pricing Irrigation Water, Principles and Cases, from Developing Countries; Resources for the Future: Washington, DC, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Hanemann, W.M. The economic conception of water. In Water Crisis: Myth or Reality? Taylor & Francis Plc.: London, UK, 2004; pp. 61–92. [Google Scholar]
- Marques, G.F.; Lund, J.R.; Howitt, R.E. Modeling irrigated agricultural production and water use decisions under water supply uncertainty. Water Resourc. Res. 2005, 41, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baerlaine, T.; Kasymov, U.; Zikos, D. Self-Governance and Sustainable Common Pool Resource Management in Kyrgyzstan. Sustainability 2015, 7, 496–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsur, Y. Economic Aspects of Irrigation Water Pricing. Can. Water Resour. J. 2005, 30, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, R.C. Micro and Macro-Level Approaches for Assessing the Value of Irrigation Water. Available online: http://elibrary.worldbank.org/doi/pdf/10.1596/1813-9450-3778 (accessed on 1 May 2015).
- Al Saadi, H.A. Aquatic Environment; Yazori: Amman, Jordan, 2005. (In Arabic) [Google Scholar]
- Al Salhi, S.A.; Al Ghureiri, A.A.F. Environment and Water; Dar Al Safa: Amman, Jordan, 2008; p. 9. (In Arabic) [Google Scholar]
- Young, R.A. Nonmarket Economic Valuation for Irrigation Water Policy Decisions: Some Methodological Issues. J. Contemp. Water Res. Educ. 2005, 131, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, D.N. Determining Economic Value of Irrigation Water: Comparison of Willingness to Pay and Indirect Valuation Approaches as a Measure of Sustainable Resource Use. Available online: http://www.cserge.ac.uk/sites/default/files/gec_1998_05.pdf (accessed on 1 April 2014).
- Abu Madi, M.; Braadbaart, O.; Al-Sa’ed, R.; Alaerts, G. Willingness of farmers to pay for reclaimed wastewater in Jordan and Tunisia. Neth. Water Sci. Technol. 2003, 3, 115–122. [Google Scholar]
- Akter, S. Farmers’ Willingness to Pay for Irrigation Water under Government Managed Small Scale Irrigation Projects in Bangladesh. J. Bangladesh Stud. 2007, 9, 21–31. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Z.; Nan, Z.; Liu, J. The Willingness to Pay for Irrigation Water: A Case Study in Northwest China. Global NEST J. 2013, 15, 76–84. [Google Scholar]
- Mallios, Z.; Latinopoulos, P. Willingness to pay for irrigation water: A case study in Greece Chalkidiki. In Proceedings of the 7th the International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology Ermoupolis, Syros Island, Greece, 3–6 September 2001.
- Allan, J.A.; Chibli, M.; Shai, W.; Wild, J. Water in the Middle East, Legal, Political and Commercial Implications; I.B. Tauris: London, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Weinthal, E.; Sowers, J.; Vengosh, A. Climate change, water resources, and the politics of human security in the Middle East and North Africa. In In Proceeding of the Climate Change and Security Conference, Trondheim, Norway, 21–24 June 2010.
- Frenken, K. Irrigation in the Middle East region in figures. Available online: ftp://ftp.fao.org/docrep/fao/012/i0936e/i0936e01.pdf (accessed on 1 May 2014).
- Ismael, S.A. Water policy for the countries of the Tigris and Euphrates basins and their impact on the Kurdish issue. 2004. Available online: http://www.k-css.org/Content.aspx?LinkID=45&Action=3 (accessed on 1 June 2015). (In Arabic)
- Ramadhan, H.M. The Impact of the Man Activity in Duhok Dam Watershed on the Future of Duhok Dam Lake North-Iraq. In In Proceeding of the first International Applied Geological Congress, Department of Geology, Mashhad Branch, Iran, 26–28 April 2010.
- Ministry of Planning (MoP). Regional Development Strategy for Kurdistan Region 2012-2016. Available online: http://www.mop.krg.org/resources/MoP%20Files/PDF%20Files/gd_ps/regional_development_strategy.pdf (accessed on 1 April 2014).
- United States Agency for International Development. Kurdistan Region Economic Development Assessment. Local Governance Project. RTI-International; 2008. Available online: http://www.mop.krg.org/resources/MoP%20Files/PDF%20Files/DCC/Studies/EDA%20Report_English.pdf (accessed on 1 May 2015). [Google Scholar]
- The review Kurdistan Region of Iraq. March 2013. Available online: http://www.investingroup.org/files/the_review-kurdistan_region_of_iraq-march_2013.pdf (accessed on 1 April 2014).
- Mohamed-Ali, J.J. Water Resources and its Sustainability for Agricultural Development in Sulaimani Governorate. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Suleimani, Sulaymaniyah, Iraq, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- The Ministry of Municipalities and Tourism (MoMT). Kurdistan Region Infrastructure Water Sector Master Plan Water Balance and Management Report, KRG. 2011. Available online: http://www.mop.krg.org/index.jsp?sid=1&id=275&pid=109 (accessed on 1 April 2014). [Google Scholar]
- Hoyos, D.; Mariel, P. Contingent Valuation: Past, Present and Future. Prague Econ. Papers 2010, 4, 329–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J. A Review of Stated Choice Method Discussion Paper 05-27. Available online: http://www2.econ.osaka-u.ac.jp/library/global/dp/0527.pdf (accessed on 1 May 2014).
- Hanemann, W.M. Welfare evaluations in contingent valuation experiments with discrete responses. Am. J. Agric. Econ. 1984, 66, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rollins, K.; Dumitras, D.; Castledine, A. An Analysis of Congestion Effects Across and within Multiple Recreation Activities. Can. J. Agric. Econ. 2008, 56, 95–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, W.H. Econometric Analysis, 5th ed.; Prentice-Hall: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Harun, R.; Muresan, I.C.; Arion, F.H.; Dumitras, D.E.; Lile, R. Analysis of Factors that Influence the Willingness to Pay for Irrigation Water in the Kurdistan Regional Government, Iraq. Sustainability 2015, 7, 9574-9586. https://doi.org/10.3390/su7079574
Harun R, Muresan IC, Arion FH, Dumitras DE, Lile R. Analysis of Factors that Influence the Willingness to Pay for Irrigation Water in the Kurdistan Regional Government, Iraq. Sustainability. 2015; 7(7):9574-9586. https://doi.org/10.3390/su7079574
Chicago/Turabian StyleHarun, Rezhen, Iulia C. Muresan, Felix H. Arion, Diana E. Dumitras, and Ramona Lile. 2015. "Analysis of Factors that Influence the Willingness to Pay for Irrigation Water in the Kurdistan Regional Government, Iraq" Sustainability 7, no. 7: 9574-9586. https://doi.org/10.3390/su7079574
APA StyleHarun, R., Muresan, I. C., Arion, F. H., Dumitras, D. E., & Lile, R. (2015). Analysis of Factors that Influence the Willingness to Pay for Irrigation Water in the Kurdistan Regional Government, Iraq. Sustainability, 7(7), 9574-9586. https://doi.org/10.3390/su7079574








