Hydrogen Production from Water by Photolysis, Sonolysis and Sonophotolysis with Solid Solutions of Rare Earth, Gallium and Indium Oxides as Heterogeneous Catalysts
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Preparation and Characterization of Photocatalysts
2.3. Sonophotocatalytic Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
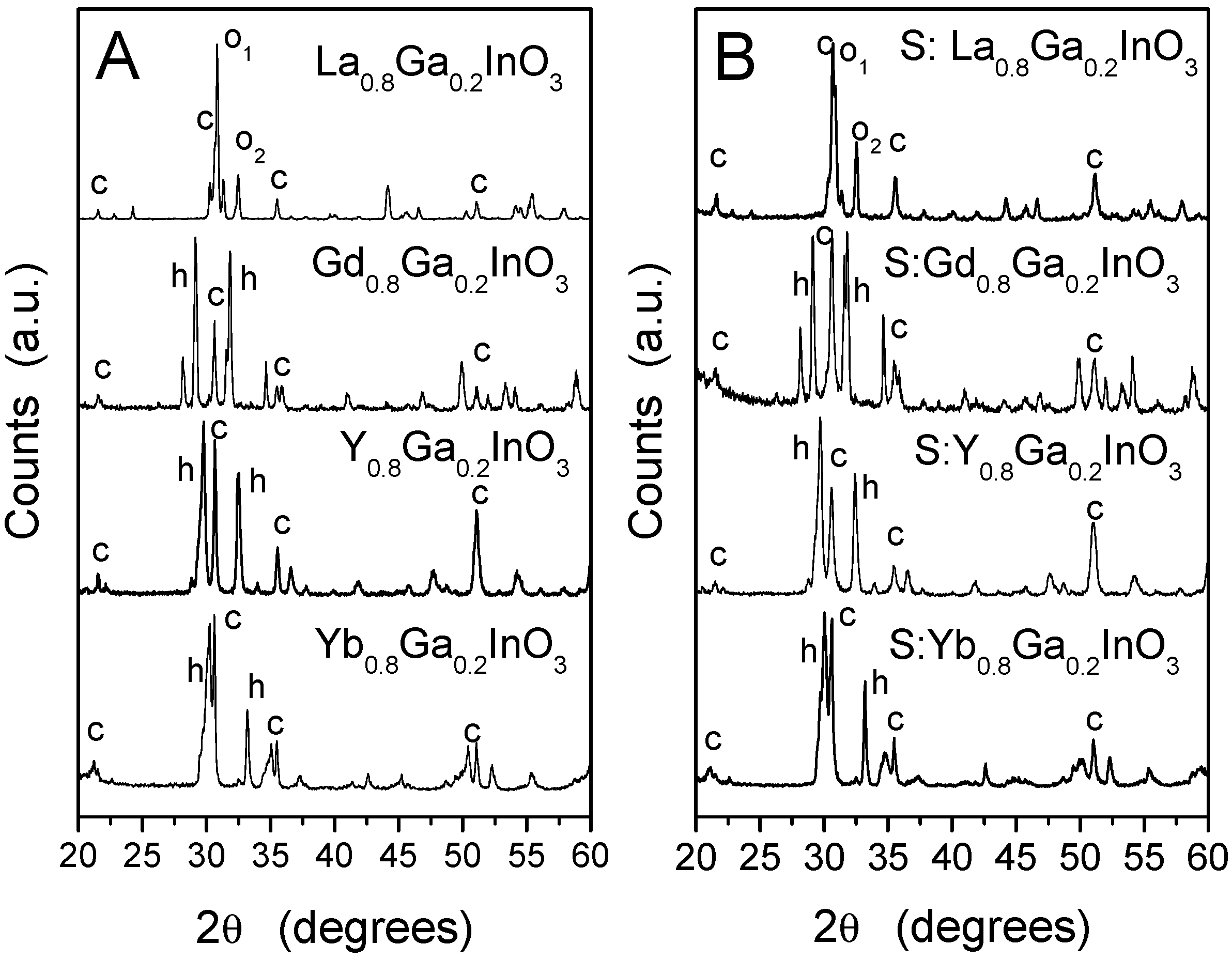
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of the Photocatalysts

| Sample | BG, eV (nm) |
|---|---|
| La0.8Ga0.2InO3 | 2.93 (423) |
| Gd0.8Ga0.2InO3 | 2.92 (425) |
| Y0.8Ga0.2InO3 | 2.95 (420) |
| Yb0.8Ga0.2InO3 | 2.96 (419) |
3.2. Hydrogen Production by Photocatalysis

| Undoped Solid Solutions | Sufur-Doped Solid Solutions | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | µmoles (H2)/h | Sample | µmoles (H2)/h |
| La0.8Ga0.2InO3 | 0.08 ± 0.03 | S:La0.8Ga0.2InO3 | 0.36 ± 0.10 |
| Gd0.8Ga0.2InO3 | 0.015 ± 0.006 | S:Gd0.8Ga0.2InO3 | 0.045 ± 0.02 |
| Y0.8Ga0.2InO3 | 0.14 ± 0.05 | S:Y0.8Ga0.2InO3 | 1.0 ± 0.4 |
| Yb0.8Ga0.2InO3 | 0.008 ± 0.003 | S:Yb0.8Ga0.2InO3 | 0.014 ± 0.005 |
3.3. Hydrogen Production by Sonolysis in Absence of Photocatalysts
3.3.1. Effect of the Chemical Composition of the Solution
| Solution | μmoles(H2)/h |
|---|---|
| Water | 80 ± 2 |
| Ethanol | 5.5 ± 0.2 |
| Ethanol/water (20% vol) | 112 ± 3 |
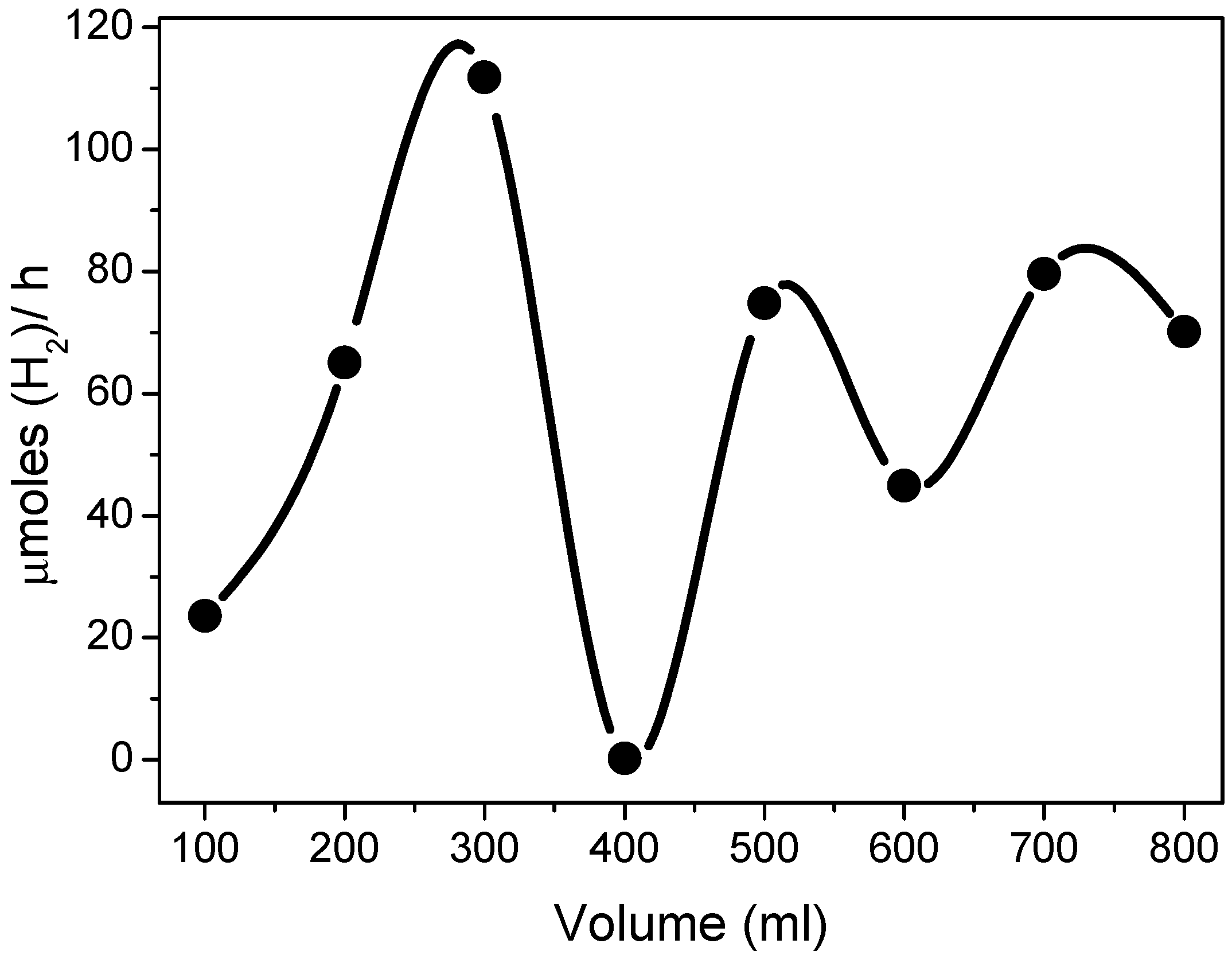
3.3.2. Effect of the Volume of the Solution
3.3.3. The Effect of the Intensity of Ultrasounds
| Power | μmoles(H2)/h |
|---|---|
| Minimum | 0 |
| Medium | 18.3 ± 0.5 |
| Maximum | 112 ± 3 |
3.4. Hydrogen Production by Sonolysis and Sonophotolysis in the Presence of S:Y0.8Ga0.2InO3
| Sample | Photolysis μmol/h | Sonolysis μmol/h | Sonophotolysis μmol/h | Synergy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S:Y0.8Ga0.2InO3 | 1.0 ± 0.4 | 107 ± 3 | 125 ± 4 | 0.13 ± 0.05 |
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bockris, J.O’M. The hydrogen economy: Its history. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2013, 38, 2579–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hema Krishna, R. Review of research on production methods of hydrogen: Future fuel. Eur. J. Biotechnol. Biosci. 2013, 1, 84–93. [Google Scholar]
- Rossi, F.; Nicolini, A. Experimental investigation on a novel electrolyte configuration for cylindrical Molten Carbonate Fuel Cells. J. Fuel Cell Sci. Technol. 2011, 8, 051012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotana, F.; Rossi, F.; Nicolini, A. A new geometry high performance small power MCFC. J. Fuel Cell Sci. Technol. 2004, 1, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, F.; Nicolini, A. A cylindrical small size Molten Carbonate Fuel Cell: Experimental investigation on materials and improving performance solutions. Fuel Cells 2009, 9, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, F.; Nicolini, A. Ethanol reforming for supplying Molten Carbonate Fuel Cells. Int. J. Low-Carbon Technol. 2013, 8, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, F.; Nicolini, A.; di Profio, P. Small size cylindrical Molten Carbonate Fuel Cells and future approaches for decreasing working temperature. ECS Trans. 2008, 12, 455–466. [Google Scholar]
- Kudo, A.; Miseki, Y. Heterogeneous photocatalyst materials for water splitting. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 253–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, R. Recent progress on photocatalytic and photoelectrochemical water splitting under visible light irradiation. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C 2010, 11, 179–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Shen, S.; Guo, L.; Mao, S.S. Semiconductor-based photocatalytic hydrogen generation. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 6503–6570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, K. Photocatalytic water splitting using semiconductor particles: History and recent developments. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C 2011, 12, 237–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, A.A.; Bahnemann, D.W. Photochemical splitting of water for hydrogen production by photocatalysis: A review. Sol. Energy Mater. Solar Cells 2014, 128, 85–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakata, T.; Kawai, T. Heterogeneous photocatalytic production of hydrogen and methane from ethanol and water. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1981, 80, 341–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentili, P.L.; Rossi, F.; Penconi, M.; Ortica, F.; Elisei, F. Hydrogen production through sono-photolysis of water in the presence of solid solutions of metal oxides as photocatalysts. Expert Commentary. In Hydrogen Production: Prospects and Processes; Honnery, D.R., Moriarty, P., Eds.; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 413–422. [Google Scholar]
- Kudo, A.; Mikami, I. Photocatalytic activities and photophysical properties of Ga2-xInxO3 solid solution. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1998, 94, 2929–2932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, K.; Domen, K. Solid solution of GaN and ZnO as a stable photocatalyst for overall water splitting under visible light. Chem. Mater. 2010, 22, 612–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, S.; Ye, J. β-AgAl1-xGaxO2 solid-solution photocatalysts: continuous modulation of electronic structure toward high-performance visible-light photoactivity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 7757–7763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Zai, J.; Yuan, Y.; Qian, X. Band gap-tunable (CuIn)xZn2(1−x)S2 solid solutions: Preparation and efficient photocatalytic hydrogen production from water under visible light without noble metals. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 23929–23934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asahi, R.; Morikawa, T.; Ohwaki, T.; Aoki, K.; Taga, Y. Visible-light photocatalysis in nitrogen-doped titanium oxides. Science 2001, 293, 269–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umebayashi, T.; Yamaki, T.; Itoh, V.; Asai, K. Band gap narrowing of titanium dioxide by sulfur doping. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2002, 81, 454–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, T.; Tsubota, T.; Toyofuku, M.; Inaba, R. Photocatalytic activity of a TiO2 photocatalyst doped with C4+ and S4+ ions having a rutile phase under visible light. Catal. Lett. 2004, 98, 255–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Sark, W.G.J.H.M.; de Wild, J.; Rath, J.K.; Meijerink, A.; Schropp, R.E.I. Upconversion in solar cells. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.Y.; Fückel, B.; MacQueen, R.W.; Khoury, T.; Clady, R.G.C.R.; Schulze, T.F.; Ekins-Daukes, N.J.; Crossley, M.J.; Stannowski, B.; Lips, K.; et al. Improving the light-harvesting of amorphous silicon solar cells with photochemical upconversion. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 6953–6959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penconi, M.; Ortica, F.; Elisei, F.; Gentili, P.L. New molecular pairs for low power non-coherent triplet-triplet annihilation based upconversion: Dependence on the triplet energies of sensitizer and emitter. J. Lumin. 2013, 135, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penconi, M.; Gentili, P.L.; Massaro, G.; Elisei, F.; Ortica, F. A triplet-triplet annihilation based up-conversion process investigated in homogeneous solutions and oil-in-water microemulsions of a surfactant. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2014, 13, 48–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suslick, K.S. Sonocatalysis. Available online: http://www.scs.illinois.edu/suslick/documents/HBHetCat.pdf (accessed on 10 July 2015).
- Joseph, C.G.; Li Puma, G.; Bono, A.; Krishnaiah, D. Sonophotocatalysis in advanced oxidation process: A short review. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2009, 16, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, H. Sonophotocatalytic decomposition of water using TiO2 photocatalyst. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2001, 8, 55–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentili, P.L.; Penconi, M.; Ortica, F.; Cotana, F.; Rossi, F.; Elisei, F. Synergistic effects in hydrogen production through water sonophotolysis catalyzed by new La2xGa2yIn2(1-x-y)O3 solid solutions. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2009, 34, 9042–9049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán, A.; Monteagudo, J.M.; Sanmartín, I.; García-Díaz, A. Sonophotocatalytic mineralization of antipyrine in aqueous solution. Appl. Catal. B 2013, 138–139, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagannathan, M.; Grieser, F.; Ashokkumar, M. Sonophotocatalytic degradation of paracetamol using TiO2 and Fe3+. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 103, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anju, S.G.; Yesodharan, S.; Yesodharan, E.P. Zinc oxide mediated sonophotocatalytic degradation of phenol in water. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 189–190, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Quan, X.; Xiong, Y.; Yang, L.; Huang, Y. Synergistic degradation of methyl orange in an ultrasound intensified photocatalytic reactor. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2012, 19, 1027–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekiguchi, K.; Sasaki, C.; Sakamoto, K. Synergistic effects of high-frequency ultrasound on photocatalytic degradation of aldehydes and their intermediates using TiO2 suspension in water. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2011, 18, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.C.; Vorontsov, A.V.; Smirniotis, P.G. Enhanced photocatalytic degradation of dimethyl methylphosphonate in the presence of low-frequency ultrasound. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2003, 2, 694–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mrowetz, M.; Pirola, C.; Selli, E. Degradation of organic water pollutants through sonophotocatalysis in the presence of TiO2. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2003, 10, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentili, P.L.; Penconi, M.; Costantino, F.; Sassi, P.; Ortica, F.; Rossi, F.; Elisei, F. Structural and photophysical characterization of some La2xGa2yIn2zO3 solid solutions, to be used as photocatalysts for H2 production from water/ethanol solutions. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2010, 94, 2265–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentili, P.L.; Clementi, C.; Romani, A. Ultraviolet-Visible Absorption and Luminescence Properties of Quinacridone-Barium Sulfate Solid Mixtures. Appl. Spectrosc. 2010, 64, 923–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koda, S.; Kimura, T.; Kondo, T.; Mitome, H. A standard method to calibrate sonochemical efficiency of an individual reaction system. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2003, 10, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Trejo, E.; Tavizón, G.; Arroyo-Landeros, A. Structure, point defects and ion migration in LaInO3. J. Phys. Chem. Solid 2003, 64, 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.M.; Lee, H.J.; Park, S.H.; Yoo, H.I. Lanthanum indium oxide from X-ray powder diffraction. Acta Cryst. 2003, C59, i131–i132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.E.; Mizoguchi, H.; Delaney, K.; Spaldin, N.A.; Sleight, A.W.; Subramanian, M.A. Mn3+ in trigonal bipyramidal coordination: A new blue chromophore. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 17084–17086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, D.H.; Huang, K.C. Phase composition and properties of solid solutions of GdFeO3–GdInO3 bulks. Ceram. Int. 2008, 34, 1503–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pistorius, C.W.F.T.; Kruger, G.J. Stability and structure of noncentrosymmetric hexagonal LnInO3 (Ln = Eu, Gd, Tb, Dy, Ho, Y). J. Inorg. Nucl. Chem. 1976, 38, 1471–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uno, M.; Kosuga, A.; Okui, M.; Horisaka, K.; Muta, H.; Kurosaki, K.; Yamanaka, S. Photoelectrochemical study of lanthanide zirconium oxides, Ln2Zr2O7 (Ln = La, Ce, Nd and Sm). J. Alloys Compd. 2006, 420, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machida, M.; Murakami, S.; Kijima, T.; Matsushima, S.; Arai, M. Photocatalytic property and electronic structure of lanthanide tantalates, LnTaO4 (Ln = La, Ce, Pr, Nd, and Sm). J. Phys. Chem. B 2001, 105, 3289–3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutkar, V.S.; Gogate, P.R. Design aspects of sonochemical reactors: Techniques for understanding cavitational activity distribution and effect of operating parameters. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 155, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, L.H.; Doraiswamy, L.K. Sonochemistry: Science and engineering. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1999, 38, 1215–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misik, V.; Riesz, P. Recent applications of EPR and spin trapping to sonochemical studies of organic liquids and aqueous solutions. Ultrason. Sonochem. 1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasikala, R.; Jayakumar, O.D.; Kulshreshtha, S.K. Enhanced hydrogen generation by particles during sonochemical decomposition of water. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2007, 14, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asakura, Y.; Nishida, T.; Matsuoka, T.; Koda, S. Effects of ultrasonic frequency and liquid height on sonochemical efficiency of large-scale sonochemical reactors. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2008, 15, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Nakagawa, N.; Sekiguchi, Y. Observation of multibubble phenomena in an ultrasonic reactor. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2007, 31, 1083–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivakumar, M.; Pandit, A.B. Ultrasound enhanced degradation of Rhodamine B: optimization with power density. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2001, 8, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ondruschka, B.; Lifka, J.; Hofmann, J. Aquasonolysis of Ether–Effect of Frequency and Acoustic Power of Ultrasound. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2000, 23, 588–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, M.; Henglein, A. Chemical action of pulsed ultrasound: observation of an unprecedented intensity effect. J. Phys. Chem. 1990, 94, 3625–3628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, N.; Ghosh, S.K.; Bannerjee, S.; Aikat, K. Bioethanol production from agricultural wastes: An overview. Renew. Energy 2012, 37, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotana, F.; Cavalaglio, G.; Gelosia, M.; Nicolini, A.; Coccia, V.; Petrozzi, A. Production of bioethanol in a second generation prototype from pine wood chips. Energy Procedia 2014, 45, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Penconi, M.; Rossi, F.; Ortica, F.; Elisei, F.; Gentili, P.L. Hydrogen Production from Water by Photolysis, Sonolysis and Sonophotolysis with Solid Solutions of Rare Earth, Gallium and Indium Oxides as Heterogeneous Catalysts. Sustainability 2015, 7, 9310-9325. https://doi.org/10.3390/su7079310
Penconi M, Rossi F, Ortica F, Elisei F, Gentili PL. Hydrogen Production from Water by Photolysis, Sonolysis and Sonophotolysis with Solid Solutions of Rare Earth, Gallium and Indium Oxides as Heterogeneous Catalysts. Sustainability. 2015; 7(7):9310-9325. https://doi.org/10.3390/su7079310
Chicago/Turabian StylePenconi, Marta, Federico Rossi, Fausto Ortica, Fausto Elisei, and Pier Luigi Gentili. 2015. "Hydrogen Production from Water by Photolysis, Sonolysis and Sonophotolysis with Solid Solutions of Rare Earth, Gallium and Indium Oxides as Heterogeneous Catalysts" Sustainability 7, no. 7: 9310-9325. https://doi.org/10.3390/su7079310
APA StylePenconi, M., Rossi, F., Ortica, F., Elisei, F., & Gentili, P. L. (2015). Hydrogen Production from Water by Photolysis, Sonolysis and Sonophotolysis with Solid Solutions of Rare Earth, Gallium and Indium Oxides as Heterogeneous Catalysts. Sustainability, 7(7), 9310-9325. https://doi.org/10.3390/su7079310