Abstract
Building on farmer’s agroecological knowledge to design environmental-friendly agricultural systems is crucial given the environmental impact of industrial agriculture. We investigated the drivers of farmers’ knowledge of agrobiodiversity management and analyzed how farmers’ knowledge and their current farming contexts may guide future farming systems in sub-humid (Bassila) and semi-arid (Boukoumbé) areas of Benin. We conducted structured interviews with 180 farmers and used generalized linear models and correlation analyses to understand the spatio-temporal dynamics of farmers’ knowledge and perception. Land tenure, ecological conditions and sociolinguistic membership were the main drivers of farmers’ knowledge of agroforestry systems, practices, species diversity and current farming systems. Sociolinguistic membership also significantly predicted farmers’ knowledge of livestock management. Farmers in the semi-arid area were more involved in integrated crop-tree-livestock systems than those in the sub-humid area. However, all farmers indicated a willingness to adopt this integrated farming system regardless of socioeconomic and ecological factors. Farmer’s knowledge of agrobiodiversity (crops, agroforestry species and livestock diversity) management was correlated with the involvement in integrated crop-livestock-tree and agroforestry systems. These findings provide insights into how farmers’ knowledge can serve as basis in optimizing agricultural and livelihoods systems. Investigating the ecological, economic and social performance of the most desired integration/diversification options using a system approach involving a co-innovation process can further our mechanistic understanding of farmers decision making process.
1. Introduction
“Industrial or conventional” agriculture is a highly simplified ecosystem in which high productivity depends on a few improved high-yielding crop varieties and a heavy reliance on agrochemical inputs (e.g., fertilizers, pesticides) and fossil fuels [1,2,3,4]. This has contributed to the tremendous increase in food production over the past 50 years, although this achievement comes with heavy environmental costs [1,3,5,6,7,8]. Adverse effects of modern agriculture include loss of biodiversity and associated traditional knowledge that communities share about it, pest resistance, soil and water pollution, soil loss (along with soil fertility) and increased greenhouse gas emissions. Moreover, climate change is expected to further exacerbate food insecurity in areas currently vulnerable to hunger and undernutrition [9], such as the West African Sahel and dry savanna zones, where strong climatic variations and irregular rainfalls make the harvest of staple and cash crops highly uncertain [10].
Using agroecologically-based management strategies and diversified farming systems can increase agricultural systems’ sustainability, resilience and productivity, while reducing adverse environmental consequences associated with agricultural intensification [3,11,12,13,14]. Diversified farming systems promote and enhance ecosystems services that provide critical inputs to agricultural systems’ productivity and resilience amid a changing climate [14,15,16,17]. To develop culturally appropriate agroecological farming systems, it is crucial to include farmers’ agroecological knowledge and location-specific knowledge of production constraints [12,17,18,19]. Including this knowledge requires further understanding of the drivers of the spatio-temporal dynamics of farmers’ agroecological knowledge. Although it is commonly assumed that local people’s agroecological knowledge is used to develop more environmentally-friendly agricultural systems, this is often rarely demonstrated, especially in the West African Sahel and dry savanna zones.
In this paper, we: (i) investigated the drivers of farmers’ knowledge of agrobiodiversity management and current farming systems; and (ii) analyzed how farmers’ knowledge and their current farming context may guide their farming systems in the future in sub-humid and semi-arid areas of Benin (West Africa). Elucidating the link between current farming context and farmers’ intention is relevant for research and development policy orientations in the West African Sahel and dry savanna zones. In addition, this understanding will provide further insights into how farmers’ knowledge of agrobiodiversity serves as a basis for optimizing agricultural production and improving livelihoods. In this study, we specifically addressed the following major questions: (1) What is the influence of ecological differences between areas (semi-arid Sudanian vs. sub-humid Sudano-Guinean areas) and socioeconomic factors (ethnicity, age and land tenure) on farmers’ knowledge of agrobiodiversity management, on farmers’ current farming systems and on their future farming systems’ intention? (2) How does farmers’ knowledge of agrobiodiversity management affect current farming approaches? (3) How does farmers’ current farming context affect their farming systems in the future? We hypothesized that those ecological conditions in which farmers operated and their sociolinguistic and socioeconomic attributes are drivers of farmers’ knowledge of agrobiodiversity and current agricultural systems and that all farmers intend to apply diversified farming systems regardless of these drivers.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
This study was conducted in two ecological regions of Benin (West Africa): the Sudanian and the Sudano-Guinean regions. The Sudanian region is dominated by woodlands and savannas on ferruginous soils. The rainfall is unimodal with a mean annual rainfall of 1000 mm (Table 1). The temperature ranges from 24 to 31 °C [20,21]. The main sociolinguistic groups are Bariba, Fulani and Otamari and related sociolinguistic groups [22]. Farming systems are mainly based on cotton cultivation and livestock breeding. In the western part of the Sudanian region, farming systems are limited by the availability of land, leading to population migration into the Sudano-Guinean region [23]. The Sudano-Guinean region is a transitional zone with a mosaic of forest islands, gallery forests and savannas. The rainfall regime is also unimodal, but with a greater annual mean rainfall ranging from 1100 to 1300 mm (Table 1). The temperature varies from 25 °C to 29 °C [20,21]. The main sociolinguistic groups are Bariba, Yoruba and Fon and related sociolinguistic groups [22]. Otamari and Yom-Lokpa and sociolinguistic ethnics groups, two sociolinguistic groups forming the principal actors of migratory dynamics in Benin [24], are found in the Sudano-Guinean region. Fulani herders are also found in the Sudano-Guinean region because of their nomadic pastoralist lifestyle. Yam-based cropping systems are dominant [23], while rice cultivation is also important. Cotton and cashew nut cultivation are also of importance in the Sudano-Guinean region.

Table 1.
Comparative agroecological and socio-economic features of Bassila and Boukoumbé municipalities.
| Sub-Humid Area (Bassila) | Semi-Arid Area (Boukoumbé) | |
|---|---|---|
| Ecological region | Sudano-Guinean region (7°30′–9°30′N) | Sudanian region (9°30′–12°N) |
| Annual rainfall | 1100–1300 mm | 900–1100 mm |
| Active vegetation period | 200 days | 145 days |
| Forest cover | 50% of the total area of the municipality of Bassila is covered by forest reserves | Not available |
| Main cropping systems | Cereal- (maize and sorghum) and yam-based | Cereal-based (sorghum and pearl millet) |
| Food insecurity | Moderate food insecurity | Severe food insecurity |
| Poverty incidence | Low Less than 40% of poor households 20% of population living in extreme poverty | High 72% of poor households 51% of population living in extreme poverty |
| Total population | 71,511 habitants | 60,568 habitants |
| Total land area | 5661 km2 | 1,036 km2 |
| Population density | 13 habitants per km2 | 58 habitants per km2 |
Data assembled from Adomou [20], Akoègninou et al. [21], Bongi et al. [25], MAEP [26], INSAE [27].
2.2. Participants and Sampling
Based on the biophysical and socioeconomic gradients across the two ecological regions [20,21,25,26,27], we selected two municipality for our field investigations: Boukoumbé (10°10′36.1ʺN and 01°06′22.0ʺE) and Bassilla (09°01′00.1ʺN and 01°40′00.1ʺE; see Table 1 and Figure 1). Boukoumbé is located in the semi-arid Sudanian region. The total population of Boukoumbé is 60,568 with a population density of 58 habitants/km2 [27]. The total land area is 1,036 km2. About 72% of households are poor (the highest proportion at the national level), and 51% of its population live in extreme poverty [25]. To reduce this severe food insecurity, an emergency program of the Benin government was implemented from 2009 to 2011 through various projects [26]. Bassila is located in the sub-humid Sudano-Guinean region with a total population of 71,511 and a density of 13 habitants/km2 [27]. The total land area is 5661 km2. Nearly half of Bassila total land area is covered with forests. About 40% of households are poor with 20% of its population living in extreme poverty [25]. However, food insecurity is moderate and steady [26]. An in-depth description of the two municipalities can be found in Segnon and Achigan-Dako [28].
We conducted structured individual interviews with 180 farmers using a questionnaire (see Section 2.3), 90 in each municipality. Participants were randomly selected from a list provided by local extension service agents and included in the survey after informed consent. In Boukoumbé, eight villages (Dimatema, Dipokor 1, Ditchendia, Koukongou, Kounadogou, Koutchata, Okouaro and Tassayota) were surveyed, while in Bassila, four villages (Adjiro, Aoro-Lokpa, Camp pionier and Mondogui) were surveyed. Participants were mainly farmers, with an average of 3.67 ha farmland (ranging from 0.5 to 25 ha). The mean age is 37 years, and about 75% of participants were 25 to 50 years old (Table 2). The mean household size was 9. Most of the participants (73.33%) in Bassila were tenants, while all of them (100%) are landowners in Boukoumbé.

Table 2.
Socio-demographic characteristics of study participants (n = 180). Values are percentages.
| Characteristics | Bassila (n = 90) | Boukoumbé (n = 90) | Total (n = 180) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sociolinguistic groups | |||
| Ditamari | 33 | 77 | 55 |
| Lokpa | 27 | 0 | 13 |
| M’Bermé | 3 | 23 | 13 |
| Nagot | 27 | 0 | 13 |
| Fulani | 4 | 0 | 2 |
| Others | 6 | 0 | 3 |
| Land tenure | |||
| Landowner | 27 | 100 | 63 |
| Tenant | 73 | 0 | 37 |
| Age categories | |||
| <25 years | 9 | 14 | 12 |
| 25−34 years | 40 | 37 | 38 |
| 35−50 years | 37 | 31 | 34 |
| >50 years | 14 | 18 | 16 |
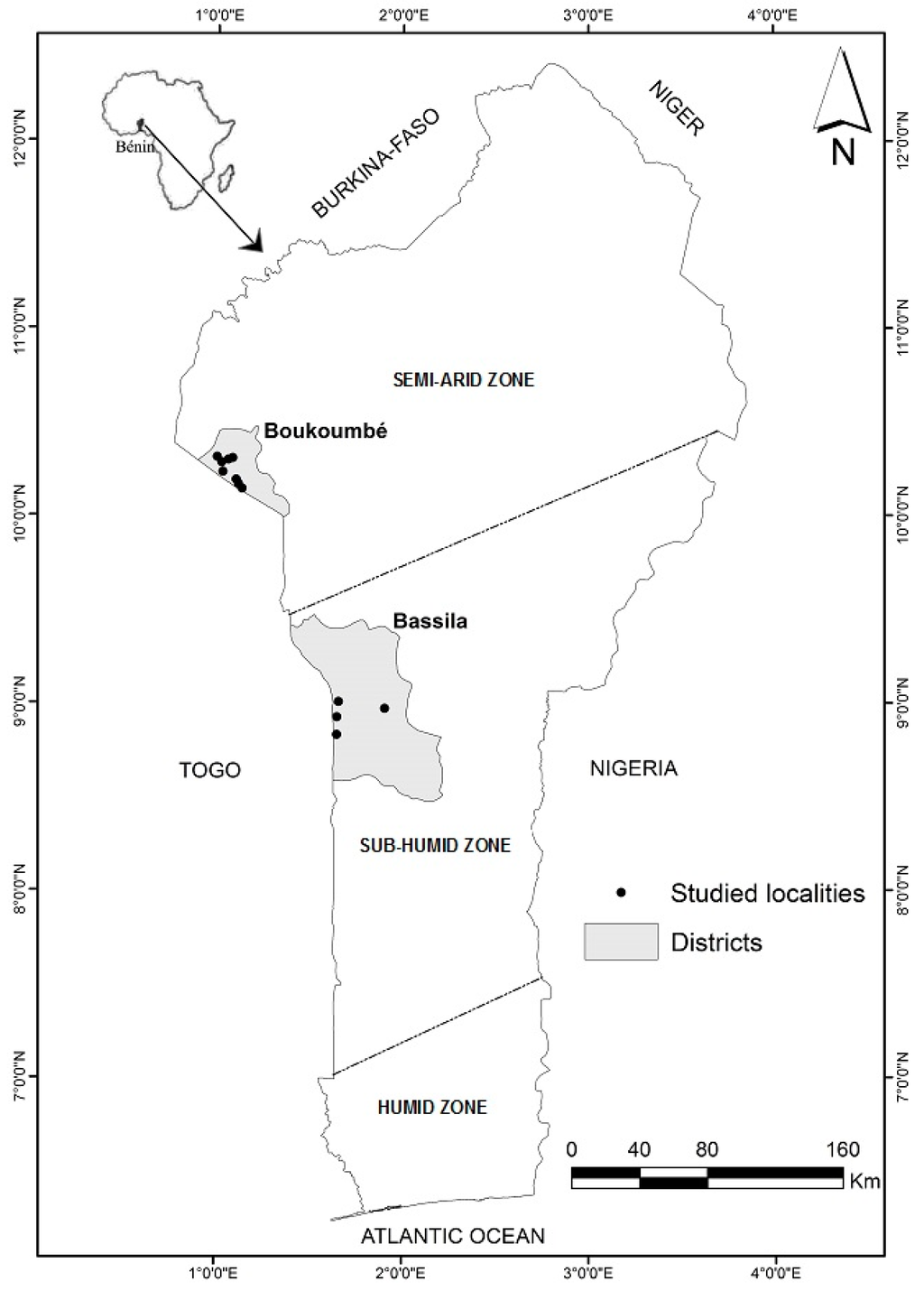
Figure 1.
Location of the study areas. Boukoumbe municipality is located in the Sudanian region, and Bassila municipality is located in the Sudano-Guinean region.
Figure 1.
Location of the study areas. Boukoumbe municipality is located in the Sudanian region, and Bassila municipality is located in the Sudano-Guinean region.
2.3. Questionnaire and Variable Measurements
In this study, agrobiodiversity is understood as “the variety and variability of living organisms that contribute to food and agriculture in the broadest sense, and that are associated with cultivating crops and rearing animals within ecological complexes” [29]. Spatial and temporal combinations or integrations of agrobiodiversity components formed diversified farming systems [12,13,14,15]. A diversified farming system includes: (i) genetic diversity within crop or livestock varieties; (ii) varietal diversity within a single crop or livestock species; (iii) multiple intercropped species and/or integration of fish or livestock species; and (iv) non-crop and wild plants and animals and semi-natural communities of plants and animals [12,13,15,17]. Diversified farming systems promote agrobiodiversity through practices that provide critical inputs (e.g., soil building, nitrogen fixation, nutrient cycling, water infiltration, pest or disease management and pollination) to farming systems’ productivity and resilience [13,15]. Components of agrobiodiversity considered in this study included crop and varietal diversity, tree (crop and wild useful trees) diversity and livestock resources. Diversified farming systems included crop-tree systems (agroforestry systems), crop-livestock systems, tree-livestock systems (pastoralism) and crop-tree-livestock systems (Figure 2).
The questionnaire consisted of 39 items identified by a literature search on smallholders’ farming and livelihoods systems, which are based on agrobiodiversity, in the West Africa Sahel and dry savannah zones (see Achigan-Dako et al. [19]). The items of the questionnaire were categorized into 13 constructs (see Table 3). Each item was presented as a statement, and participants were asked to indicate their level of agreement using a 5-point Likert response scale, ranging from strongly disagree to strongly agree [30]. Constructs measured farmers’ knowledge of the management of crop and varietal diversity in cropping systems, tree (cultivated and wild useful trees) diversity on farm and livestock resources, their current farming systems and their intention to implement diversified farming systems. Key subjects/issues addressed in each construct are listed in Table 3. The questionnaire was pre-tested with 10 farmers (who did not participate in this research) to ensure that the questions were understandable. Before each interview, we clarified the response scale using an example to ensure that participants understood the Likert scale. Socio-demographic characteristics of each participant were also recorded. For each item, a score ranging from 1 to 5 was assigned to responses ranging from strongly disagree to strongly agree. For each participant, we calculated a total score for each construct by adding the scores assigned to individual items within the construct [30,31,32].

Table 3.
Internal consistency and median scores of the constructs (n = 180).
| Constructs | Number of Items | Key Subjects/Issues | Cronbach α | Median | 25th–75th | Range a |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Farmers’ knowledge | ||||||
| Management of crop diversity | 13 | Food/commodity groups, crops, number of variety per crop cultivated in one cropping season; benefits and advantages of intercropping, mixed cropping and crop rotations (soil fertility management, pest and disease management, weed management, yield improvement) | 0.56 | 54 | 50–56 | 13, 65 |
| Agroforestry systems | 10 | Positive (soil fertility and microclimate improvement, soil and water conservation, weed and pest management, conservation of biodiversity, environmental protection, food security and poverty alleviation) and negative (shading effect, competition for resource, such as water, nutrients, rain, light, and allelopathy) effects of agroforestry systems | 0.64 | 38 | 36–41 | 10, 50 |
| Diversity of agroforestry species | 1 | Number of different agroforestry species on farm | - | 5 | 3–5 | 1, 5 |
| Agroforestry practices | 1 | Which crops and how to combine with trees in agroforestry system so as to reduce negative effects | - | 3 | 1–5 | 1, 5 |
| Management of livestock | 6 | Different animal types reared; benefits and utilities of animal rearing (source of income and manure for fertilization, indicators of wealth, traction for tillage and transportation) | 0.67 | 26 | 24–28 | 6, 30 |
| Current farming systems | ||||||
| Crop-tree-livestock systems | 1 | Involvement in crop-tree-livestock systems | - | 5 | 4–5 | 1, 5 |
| Agroforestry systems | 1 | Involvement in agroforestry systems | - | 1 | 1–3 | 1, 5 |
| Crop-livestock systems | 1 | Involvement in crop-livestock systems | - | 1 | 1-1 | 1, 5 |
| Pastoralism | 1 | Involvement in pastoral systems | - | 1 | 1-1 | 1, 5 |
| Farmers’ intention about diversified farming systems | ||||||
| Crop-tree-livestock systems | 1 | Intention to be involved in crop-tree-livestock systems in the future | - | 5 | 5-5 | 1, 5 |
| Agroforestry systems | 1 | Intention to be involved in agroforestry systems in the future | - | 1 | 1–3 | 1, 5 |
| Crop-livestock systems | 1 | Intention to be involved in crop-livestock systems in the future | - | 1 | 1-1 | 1, 5 |
| Pastoralism | 1 | Intention to be involved in pastoral systems in the future | - | 1 | 1-1 | 1, 5 |
a Range refers to the possible scores for each construct.
2.4. Data Analysis
To test the reliability and internal consistency of multiple item constructs, we calculated Cronbach’s alpha (α) [33] using the package psych [34] in R software Version 3.0.2 [35]. It determines the internal consistency or average correlation of items in a survey instrument and is used to gauge its reliability. Cronbach’s α coefficient ranged from 0.56 to 0.67, indicating acceptable reliability of the multiple item constructs (Table 3). We used generalized linear models with Poisson error structure [36] to test if farmers’ knowledge of crop diversity management, agroforestry systems, diversity of agroforestry species, agroforestry practices and management of livestock resources (each of these was considered as a dependent variable) is affected by sociolinguistic membership, age, land tenure and the ecological region in which farmer operates (independent variables). To test if farming systems adopted by farmers (each option considered as a dependent variable) and if farmers’ intention to implement these systems in the future (intention to implement each option considered as dependent variable) varied among sociolinguistic groups, age categories, land tenure and the ecological region in which farmer operates, we used generalized linear models with a Poisson error structure. We used Kendall’s rank correlation τ to test bivariate association between farmers’ knowledge and their current farming systems and between current farming systems and farmers’ willingness to implement various farming systems in the future (i.e., intention towards various farming systems in the future).
3. Results
3.1. Variation in Farmers’ Knowledge of Agrobiodiversity Management
Farmers’ knowledge of crop diversity management was not significantly different between ecological regions and was not influenced by sociolinguistic membership, age or land tenure (Table 4). Ninety three percent of farmers interviewed practiced intercropping and mixed cropping, while crop rotation was practiced by 94% of them. According to 84% of participants, crop diversification in cropping systems through intercropping and mixed cropping is a food security strategy. For instance, 90% of them cultivated at least one cereal, root and tuber, legume and vegetable crop in each cropping season. Furthermore, 89% of farmers interviewed indicated that, if adequately designed and applied, crop rotation could improve soil fertility and increase crop yield. However, farmers’ knowledge of agroforestry systems was significantly different between ecological regions (Z = 2.484, p < 0.05) and sociolinguistic groups (Z = 2.065, p < 0.05), though not significantly influenced by their age or land tenure (Table 4). Farmers from Nagot and Fulani sociolinguistic groups in the sub-humid area had the highest knowledge score for agroforestry systems. These farmers were more knowledgeable about the positive (e.g., soil fertility and microclimate improvement, soil and water conservation, conservation of biodiversity, food security and poverty alleviation) and negative (e.g., shading effect, competition for resource) effects of agroforestry systems compared to their counterparts. The diversity of agroforestry species on the farm varied significantly between ecological regions (Z = −4.537, p < 0.001) and was affected by sociolinguistic membership (Z = −2.910, p < 0.01) and land tenure (Z = −3.674, p < 0.001), but not by age. Farmers from Ditamari and M’Bermé sociolinguistic groups in the semi-arid area and landowners had the highest number of agroforestry species on the farm (on average, five different species). Farmers’ knowledge of agroforestry practices was significantly different between ecological regions (Z = −2.007, p < 0.01) and sociolinguistic groups (Z = −2.239, p < 0.05), but was not significantly influenced by their age or land tenure. Ditamari and M’Bermé farmers in the semi-arid area were most knowledgeable about which crops and how to combine with trees in agroforestry systems, so as to reduce negative effects. Similarly, farmers’ knowledge of management of livestock resources was only influenced by sociolinguistic membership (Z = −2.297, p < 0.05). Farmers from the Fulani sociolinguistic group had the highest mean score for livestock management.

Table 4.
Results of generalized linear models testing the effect of ecological region, ethnic affiliation, age and land tenure on farmers’ knowledge of the management of crop diversity in cropping systems, agroforestry systems, diversity of agroforestry species, agroforestry practices and management of livestock resources.
| Management of Crop Diversity | Agroforestry Systems | Diversity of Agroforestry Species | Agroforestry Practices | Management of Livestock Resources | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| z-value | p | z-value | p | z-value | p | z-value | p | z-value | p | |
| Region | −0.849 | 0.396 | 2.484 | 0.013 | −4.537 | <0.001 | −2.007 | 0.002 | −1.887 | 0.059 |
| Ethnicity | −0.974 | 0.330 | 2.065 | 0.039 | −2.910 | 0.003 | −2.239 | 0.025 | −2.297 | 0.021 |
| Age | 1.280 | 0.201 | 0.863 | 0.388 | 1.647 | 0.099 | 1.286 | 0.198 | 1.305 | 0.192 |
| Land tenure | −0.495 | 0.621 | 1.115 | 0.265 | −3.674 | <0.001 | −1.19 | 0.234 | −1.318 | 0.187 |
3.2. Difference in Current Farming Systems and Farmer’s Intention for the Future
The current implementation of crop-tree-livestock systems was significantly affected by land tenure (Z = −3.925, p < 0.001), ecological region (Z = −4.905, p < 0.001) and their sociolinguistic group (Z = −4.294, p < 0.001), but did not vary significantly according to their age (Table 5). Ninety-four percent of participants in the semi-arid area strongly agreed that their farming systems integrate crops, trees and livestock breeding, while in the sub-humid area, it was only 36% of participants. Furthermore, 32% of farmers interviewed in the sub-humid area strongly disagreed. Farmers from Ditamari and M’Bermé sociolinguistic groups in the semi-arid area who were landowners (see Table 2) were currently more involved in crop-tree-livestock systems than farmers from the other groups. Similarly, adoption of agroforestry systems was significantly affected by ecological region (Z = 6.280, p < 0.001), sociolinguistic membership (Z = 5.612, p < 0.001) and land tenure (Z = 3.927, p < 0.001), but did not vary significantly with their age (Z = −1.531, p = 0.126). Thirty-seven percent of farmers interviewed in the sub-humid area agreed that they were involved in agroforestry systems, while in the semi-arid area, only 2% agreed and 89% of them strongly disagreed. Farmers from Lokpa and Nagot sociolinguistic groups in the sub-humid area and tenants (who were mainly migrant farmers from Ditamari and M’Bermé sociolinguistic groups, but living in the sub-humid area) were currently more involved in agroforestry systems. However, farmers’ involvement in crop-livestock systems and pastoralism was not significantly affected by land tenure, age, the ecological region and sociolinguistic group to which they belong (Table 5).

Table 5.
Results of generalized linear models testing the effect of ecological region, ethnic affiliation, age and land tenure on current farming systems.
| Crop-Tree-Livestock Systems | Agroforestry Systems | Crop-Livestock Systems | Pastoralism | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| z-value | p | z-value | p | z-value | p | z-value | p | |
| Region | −4.905 | <0.001 | 6.280 | <0.001 | −0.916 | 0.359 | 0.074 | 0.941 |
| Ethnicity | −4.294 | <0.001 | 5.612 | <0.001 | −0.588 | 0.556 | −0.044 | 0.965 |
| Age | 0.810 | 0.418 | −1.531 | 0.126 | −0.471 | 0.638 | −0.165 | 0.869 |
| Land tenure | −3.925 | <0.001 | 3.927 | <0.001 | −0.541 | 0.588 | −0.280 | 0.78 |
Farmers were equally willing to consider the adoption of crop-tree-livestock systems regardless of the ecological region where they operated, their sociolinguistic group, age or land tenure (Table 6). Furthermore, farmers’ intention to adopt crop-tree-livestock systems in the future received a higher mean score compared to other farming systems. Indeed 90% of farmers interviewed stated that they strongly intended to integrate crops, trees and animal breeding in their farming systems in the future. However, intention to adopt agroforestry systems was significantly affected by the ecological region where farmers operated (Z = 6.488, p < 0.001), sociolinguistic membership (Z = 5.875, p < 0.001) and land tenure (Z = 4.764, p < 0.001). Forty-three percent of farmers interviewed in the sub-humid area stated that they intended to adopt agroforestry systems in the future. Lokpa and Nagot farmers from the sub-humid area and tenants (who were actually migrant farmers from Ditamari and M’Bermé sociolinguistic groups, but living in the sub-humid area) were more willing to adopt agroforestry systems in the future. Farmers’ intention to adopt crop-livestock systems was not significantly influenced by ecological region, sociolinguistic membership, land tenure or age (Table 5). Farmers’ intention to adopt pastoralism was not significantly influenced by ecological region, land tenure or age (Table 5), but varied significantly according to sociolinguistic membership (Z = 2.246, p < 0.05). Fulani farmers were more willing to adopt pastoralism.

Table 6.
Results of generalized linear models testing the effect of ecological region, ethnic affiliation, age and land tenure on farmers’ intention in the future.
| Crop-Tree-Livestock Systems | Agroforestry Systems | Crop-Livestock Systems | Pastoralism | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| z-value | p | z-value | p | z-value | p | z-value | p | |
| Region | −0.746 | 0.456 | 6.488 | <0.001 | 0.622 | 0.534 | 0.362 | 0.718 |
| Ethnicity | −0.947 | 0.344 | 5.875 | <0.001 | 0.839 | 0.402 | 2.246 | 0.0247 |
| Age | 0.224 | 0.823 | −0.751 | 0.453 | −1.241 | 0.215 | 0.351 | 0.726 |
| Land tenure | −0.914 | 0.36 | 4.764 | <0.001 | 1.984 | 0.0472 | 0.595 | 0.552 |
3.3. Farmers’ Knowledge of Agrobiodiversity Management and Current Farming Systems
Farmers’ knowledge of agrobiodiversity management was significantly correlated with the adoption of crop-tree-livestock systems and agroforestry systems, respectively (Figure 2). The other correlations were not significant (Figure 2). Farmers’ knowledge of crop diversity management in cropping systems was positively correlated with involvement in crop-tree-livestock systems (τ = 0.21, p < 0.001), but negatively correlated with the adoption of agroforestry systems (τ = −0.19, p < 0.001), although these correlations were weak. The diversity of agroforestry species on the farm was positively correlated with involvement in crop-tree-livestock systems (τ = 0.54, p < 0.001), but negatively correlated with the adoption of agroforestry systems (τ = −0.41, p < 0.001). Farmers’ knowledge of livestock management was positively correlated with involvement in crop-tree-livestock systems (τ = 0.46, p < 0.001), but negatively correlated with the adoption of agroforestry systems (τ = −0.39, p < 0.001).
3.4. Current Farming Systems and Farmer’s Intention for the Future
Farmers who were already involved in crop-tree-livestock systems were more willing to apply them in the future (τ = 0.41, p < 0.001, Figure 1), but did not intend to adopt agroforestry systems in the future (τ = −0.66, p < 0.001, Figure 2). This indicates that farmers that are harnessing crop diversity, tree diversity and livestock resources (three components of agrobiodiversity) through an integrated crop-tree-livestock systems do not want or strongly disagree to abandon animal breeding in the future and rely only on crop and tree diversity. Farmers who currently used agroforestry systems were strongly willing to maintain this system in the future (τ = 0.79, p < 0.001), but were not willing to apply crop-tree-livestock systems in the future (τ = −0.39, p < 0.001). Farmers whose current farming system integrates crop diversity and livestock resources were willing to maintain this system in the future (p < 0.01), although this correlation is weak (τ = 0.19). Pastoralists were not willing to maintain this livelihood system in the future (τ = −0.02, p = 0.793), indicating that they are willing to include crop diversity, tree resources or both in their production and livelihood systems.
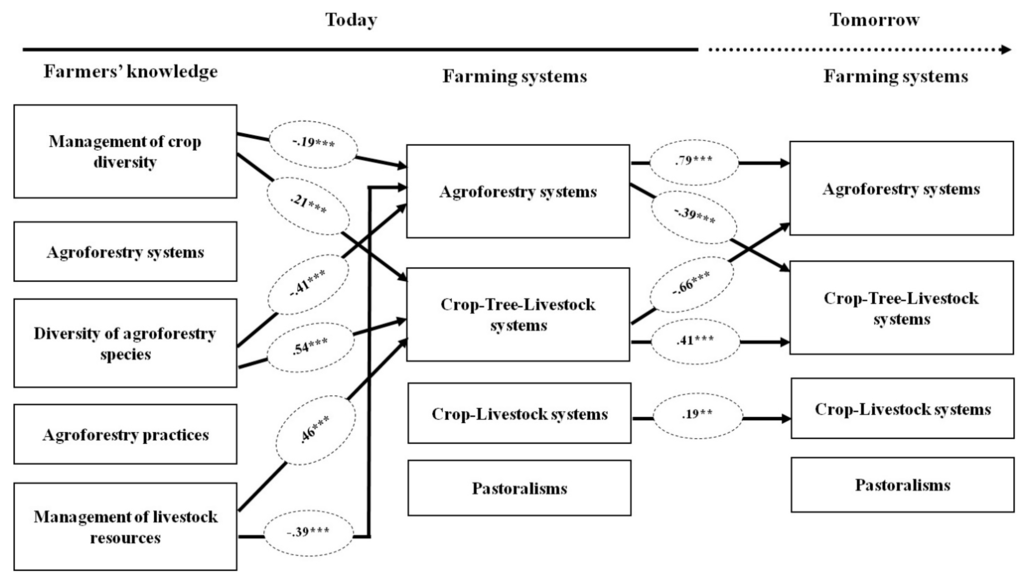
Figure 2.
Correlation between farmers’ knowledge and current farming systems and between current and future farming systems. *** p < 0.001; ** p < 0.01.
Figure 2.
Correlation between farmers’ knowledge and current farming systems and between current and future farming systems. *** p < 0.001; ** p < 0.01.
4. Discussion
4.1. Drivers of Farmers’ Knowledge of Agrobiodiversity Management in Agroecosystems
This study investigated farmers’ knowledge of agrobiodiversity management and analyzed their willingness to adopt diversified farming systems, which integrate crop diversity, trees and animal resources in sub-humid and semi-arid areas of Benin. We found that farmers’ knowledge was influenced by the ecological contexts in which they were living, sociolinguistic membership and socio-demographic factors. These results are consistent with previous findings on the drivers of local ecological knowledge [37,38,39,40]. However, similarly to Gaoue and Ticktin [38], we did not find significant support for age-dependent agroecological knowledge. Farmers’ knowledge of crop diversity management was not affected by ecological differences between regions, farmers’ sociolinguistic membership or land tenure. This indicated that farmers harness crop diversity in sub-humid and semi-arid region in a similar way regardless of their sociolinguistic membership. Indeed, there was no significant difference between the two areas regarding the cultivated species richness [28]. Population migration might play a role in the homogenization of farmers’ knowledge of crop diversity management between the two areas.
Farmers’ knowledge of on farm tree resources management was influenced by ecological differences between regions and sociolinguistic membership. Nagot and Fulani farmers from the Sudano-Guinean area had a higher mean knowledge score of agroforestry systems than farmers from the semi-arid Sudanian area. This suggest that farmers from the sub-humid Sudano-Guinean area were more knowledgeable of the ecosystem services and environmental benefits offered by agroforestry systems, including non-timber forest products (NTFPs) provisions, soil fertility improvement, soil and water conservation, biodiversity conservation, environmental protection by maintaining ecological stability and climate change mitigation through carbon sequestration on the farm [41,42,43], compared to their counterpart from the semi-arid Sudanian area. This may explain why farmers living in the Sudano-Guinean region were more involved in and more willing to adopt agroforestry systems. The ecosystem services and functions provided by agroforestry systems are at the center of the local ecological knowledge guiding the management options of the farmers [44]. However, the reverse was observed for knowledge of agroforestry practices. Ditamari and M’Bermé farmers from the semi-arid area had the highest knowledge score for agroforestry practices. That is, knowledge related to which crops to combine with tree species, how to combine species in agroforestry system and knowledge related to management techniques, so as to reduce negative effects (e.g., shading effect, competition for resources, such as water, nutrients, rain and light, and allelopathy [45,46]), are better handled by farmers of the semi-arid area. In addition, farmers in the semi-arid area had more agroforestry species on their farms than those in the sub-humid Sudano-Guinean region, although floristic diversity is known to be higher in Sudano-Guinean region than the Sudanian one [28,47,48]. This is consistent with the findings by Assogbadjo et al. [49] that traditional agroforestry systems in the Sudanian region of Benin are more diversified in terms of species richness than in the Sudano-Guinean region. This is due to the fact that farmers keep more tree species on the farm in the semi-arid Sudanian zone as an insurance policy against uncertainty in climate and food shortage. Similarly, Schroth and Ruf [50] highlighted the importance of tree species diversification on the farm as a means to reduce farmers’ vulnerability to environmental shocks. For instance, to cope with the effects of wind erosion, farmers in semi-arid West Africa developed and used various methods of integrating shrubs, trees and herbaceous vegetation in the cultivation systems [51].
Our study emphasizes the critical role of agroforestry systems in buffering climate risk [44]. Our results also highlighted the impact of sociolinguistic membership in the valuation NTFPs species (of which many are agroforestry species) [37,40,52,53,54]. However, not only cultural differences, but also environmental conditions, such as geographical contexts, might play a role in the use and the valuation of plant species by local communities [24,28,47]. The similarity exhibited between the Ditamari and M’Bermé may be explained by the fact that these two sociolinguistic groups have high linguistic and cultural affinities. They formed with other minor sociolinguistic groups the Otamari and related sociolinguistic groups [22]. Because Ditamari and M’Bermé sociolinguistic groups live in the Atacora region (a stony and mountainous environment in the northwestern part of Benin), they faced land shortage [23]. Consequently, they retained and valued agroforestry species more than other groups. Land tenure affected farmers’ practice of tree diversity conservation on the farm. Farmers who own their land had a higher number of agroforestry species on their farm compared to tenant farmers. In fact, in Benin, as well as in many West African countries, planting a tree on a land is an indication of land ownership [55,56]. Thus, tenant farmers are not allowed to plant trees on their farms.
Farmers’ knowledge of livestock management was influenced by sociolinguistic membership. Fulani, who are traditionally pastoralists, have the highest knowledge score. Unlike the other sociolinguistic groups, Fulani are very dependent on livestock for cultural and economic wealth, even though trees provide them a significant income through NTFPs [57]. The Fulani have detailed ecological knowledge of important tree species useful for their lifestyle (e.g., Khaya senegalensis), which is not always translated into sustainable practices [38].
4.2. Linking the Current with the Future Farming Contexts: Implications for Research and Development
Our results showed that farmers in sub-humid and semi-arid areas of Benin were involved in different forms of diversified farming systems. However, their implementation varied according to ecological region, sociolinguistic and socioeconomic factors. Evidence that farmers from the semi-arid Sudanian area and particularly Ditamari and M’Bermé were more involved in crop-tree-livestock systems may be explained by the fact that these farmers are living in harsh environmental conditions (e.g., droughts, rainfall variability in space and time, land degradation), lack of land access, food shortage and food insecurity; therefore, harnessing of agrobiodiversity through crop diversity, trees and livestock resources integration can be seen as adaptation and resiliency strategies that allow these farmers to cope with the severe environmental conditions. Results also indicated that there is, on the one hand, a strong positive correlation between the implementation of crop-tree-livestock systems in the present and the intention to do it in the future, and on the other hand, a strong negative correlation between the implementation of crop-tree-livestock systems and intention to adopt agroforestry systems. Furthermore, the implementation of crop-tree-livestock systems was significantly and positively correlated with farmers’ knowledge of agrobiodiversity (crops, trees and animal species) management. These results highlighted the critical role of farmers’ ecological knowledge in managing natural resources and local environment [51,58] and in enhancing the social-ecological resilience to hazards [59,60].
Farmers’ intention to apply crop-tree-livestock systems was not affected by ecological region, ethnic affiliation, age or land tenure. Here is a good signal from farmers for reaching more environmental-friendly farming systems regardless of ecological contexts, sociolinguistic attributes and socio-demographic factors. Although farmers intend to move towards diversified systems regardless of the drivers tested in this study, intervention strategies to improve productivity and conserve natural resources should be different and tailored according to regions. Indeed, farmers from the semi-arid area were more involved in crop-tree-livestock systems, while farmers from the sub-humid area were currently more involved in agroforestry systems and intended to maintain this in the future. Therefore, the entry point in the sub-humid area should be the agroforestry option, while in the semi-arid area, crop-tree-livestock systems should be promoted and strengthened. There is therefore a need to improve traditional agroforestry systems, so as to preserve their multi-functionality and environmental benefits provided to smallholder farmers. Research and development interventions should aim, among others, at strengthening integrated crop-livestock systems as a strategic entry point for achieving future food security and environmental sustainability [61]. National and regional conducive policies should take this into account, so as to efficiently support the implementation of more environmental-friendly farming systems in Benin, as well as in West African dry savanna zones.
Our results highlight the crucial role of farmers’ knowledge in diversified farming systems or more environmental-friendly farming systems. As shown by Eilola et al. [62], farmers’ local agroecological knowledge is critical for identifying potential management improvements to achieve healthy agroecosystems. Similarly, building on farmers’ knowledge and traditional local technologies, Lahmar et al. [63] developed alternative and tailored conservation agriculture technologies for West African semi-arid zones. We argued for a more farmer-centered approach in research and development policies in which farmers’ agroecological knowledge is recognized and effectively used. Sustainable or resource-conserving practices developed by farmers in less favorable areas need to be strengthened and supported and also promoted in more favorable areas, so as to preserve agroecosystems and natural resources for upcoming generations [28]. Training and capacity building on healthy agroecosystems and sustainable production practices are required to improve productivity and conserve natural resources in sub-humid and semi-arid areas. Many participatory approaches can be used, including the farmer-field-school (FFS) approach and information and communication technologies (ICT) tools. For instance, FFS methods have been used to enhance farmer’s knowledge of sustainable practices of chili cultivation and improve farmer cohesiveness and information sharing [64]. ITC tools, such as farmer-to-farmer videos, have great potential to enhance sustainable agriculture by encouraging local innovations [65]. Videos are cross-cultural diffusion tools that can help share knowledge between cultures [66]. Using videos can have more impact than conventional training, such as workshops, since they reach more farmers [67]. Moreover, an agricultural innovation platform can be used as a way of bringing farmers of the two areas together to enable knowledge exchange and learning from one another, so as to foster innovations based on their knowledge. Indeed, innovation platforms provide the social space in which opportunities can be created, tested and transformed into changes in institutional regimes [68].
In this paper, we quantified farmers’ knowledge of agrobiodiversity management and their perceptions and intentions regarding different farming systems. The next step is to evaluate the performance (e.g., ecological, economic and social) of the most desired farming systems, namely crop-tree-livestock systems and agroforestry systems. Achieving this is methodologically challenging, especially the study of crop-tree-livestock interactions in smallholders’ farming systems [44]. A system approach involving a co-innovation process, between farmers and researchers, that combines characterization, diagnosis and redesign of farming systems, social learning and dynamic monitoring and evaluation [69] can be a promising approach. Furthermore, the method employed did not account for farmers’ source of knowledge and the effect of farmers’ social networks on knowledge scores. Actually, social networks have been shown to play an important role in information acquisition and adoption of resource-conserving agriculture [70], in enhancing the adoption of natural resource management practices [71] and in shaping crop diversity among farmers [72]. Therefore, further investigations are required to better understand how social networks shape farmers’ ecological knowledge and intention towards diversified farming systems. Our measure of farmers’ intention regarding diversified farming systems in the future might be affected by a ‘wish to please’ behavior, which might obscure their true intention. However, constraints on real adoption did not affect these results, since farmers were already involved in diversified farming systems (e.g., 65% of farmers interviewed were involved in integrated crop-tree-livestock systems).
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, this paper illustrated spatio-temporal dynamics in farmers’ knowledge of agrobiodiversity management and famers’ intention to improve their farming systems towards more diversified farming systems in sub-humid and semi-arid areas of Benin. We found that: (i) drivers of farmers’ knowledge of agrobiodiversity management and current farming systems include ecological contexts, sociolinguistic attributes and land tenure; (ii) farmer’s knowledge of agrobiodiversity management is correlated with involvement in crop-tree-livestock systems and agroforestry systems; and (iii) farmer’s intention to upgrade to crop-tree-livestock integrated systems is independent of ecological regions, ethnicity and socioeconomic factors, such as land tenure. These findings are crucial for policy orientations and research and development to efficiently support the implementation of more environmental-friendly farming systems in Benin, as well as in West African dry savanna zones. More investigations are needed to better understand how social networks can shape farmers’ ecological knowledge of agrobiodiversity management, the adoption of more environmental-friendly farming systems and how their knowledge is transmitted through generations.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by New Alliance Trust (Grant No. NAT013/002 to the first author). We gratefully acknowledge the valuable technical and logistic assistance of Damien Coukpo during the fieldwork in Bassila. We are particularly indebted to Géraud N’Tia and his family for their support, linguistic assistance and collaboration in Boukoumbé. We are also grateful to all of the farmers interviewed during this work for their time and willingness to share their knowledge.
Author Contributions
Alcade C. Segnon and Enoch G. Achigan-Dako contributed to the conception and design of the study. Alcade C. Segnon collected and analyzed the data, contributed to the interpretation of the findings and prepared the first draft of the manuscript and improved it. Enoch G. Achigan-Dako supervised the data collection, contributed to the interpretation of the findings and improved the manuscript. Orou G. Gaoue contributed to the interpretation of the findings and improved the manuscript. Adam Ahanchédé supervised the study and gave conceptual advice. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The founding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; nor in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Altieri, M.A. The ecological role of biodiversity in agroecosystems. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 1999, 74, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malézieux, E. Designing cropping systems from nature. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2012, 32, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matson, P.A.; Parton, W.J.; Power, A.G.; Swift, M.J. Agricultural intensification and ecosystem properties. Science 1997, 277, 504–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaba, S.; Lescourret, F.; Boudsocq, S.; Enjalbert, J.; Hinsinger, P.; Journet, E.-P.; Navas, M.-L.; Wery, J.; Louarn, G.; Malézieux, E.; et al. Multiple cropping systems as drivers for providing multiple ecosystem services: From concepts to design. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2015, 35, 607–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomiero, T.; Pimentel, D.; Paoletti, M.G. Is there a need for a more sustainable agriculture? Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2011, 30, 6–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilman, D.; Cassman, K.G.; Matson, P.A.; Naylor, R.; Polasky, S. Agricultural sustainability and intensive production practices. Nature 2002, 418, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallinga, D. Today’s food system: How healthy is it? J. Hunger Environ. Nutr. 2009, 4, 251–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baudron, F.; Corbeels, M.; Monicat, F.; Giller, K. Cotton expansion and biodiversity loss in African savannahs, opportunities and challenges for conservation agriculture: A review paper based on two case studies. Biodivers. Conserv. 2009, 18, 2625–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, T.; von Braun, J. Climate change impacts on global food security. Science 2013, 341, 508–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hengsdijk, H.; van Keulen, H. The effect of temporal variation on inputs and outputs of future-oriented land use systems in West Africa. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2002, 91, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altieri, M.; Funes-Monzote, F.; Petersen, P. Agroecologically efficient agricultural systems for smallholder farmers: Contributions to food sovereignty. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2012, 32, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altieri, M.A.; Nicholls, C.I. An agroecological basis for designing diversified cropping systems in the tropics. J. Crop Improv. 2004, 11, 81–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremen, C.; Iles, A.; Bacon, C. Diversified farming systems: An agroecological, systems-based alternative to modern industrial agriculture. Ecol. Soc. 2012, 17, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koohafkan, P.; Altieri, M.A.; Gimenez, E.H. Green agriculture: Foundations for biodiverse, resilient and productive agricultural systems. Int. J. Agric. Sustain. 2011, 10, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremen, C.; Miles, A. Ecosystem services in biologically diversified versus conventional farming systems: Benefits, externalities, and trade-offs. Ecol. Soc. 2012, 17, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khumairoh, U.; Groot, J.C.J.; Lantinga, E.A. Complex agro-ecosystems for food security in a changing climate. Ecol. Evol. 2012, 2, 1696–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altieri, M.A. Linking ecologists and traditional farmers in the search for sustainable agriculture. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2004, 2, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Sanchez, D.; Kleine Koerkamp-Rabelista, J.; Navarro-Garza, H.; Lantinga, E.A.; Groot, J.C.J.; Kropff, M.J.; Rossing, W.A.H. Diagnosis for ecological intensification of maize-based smallholder farming systems in the Costa Chica, Mexico. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosystems 2011, 91, 185–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achigan-Dako, E.G.; Sogbohossou, O.D.; Segnon, A.C.; N’Danikou, S.; Sinsin, A.B.; Vodouhè, S.R. Agricultural Ecological Intensification Options in the West African Sahel and Dry Savannas: Current Knowledge and Possible Scenario; Bioversity International, West and Central Office: Cotonou, Benin, 2013; p. 84. [Google Scholar]
- Adomou, A.C. Phytogoegraphy of Benin. In Protection de la Nature en Afrique de l’Ouest: Une Liste Rouge Pour le Bénin. Nature Conservation in West Africa: Red List for Benin; Neuenschwander, P., Sinsin, B., Goergen, G., Eds.; International Institute of Tropical Agriculture: Ibadan, Nigeria, 2011; pp. 14–20. [Google Scholar]
- Akoègninou, A.; Van Der Burg, W.; van der Maesen, L. Flore Analytique du Bénin; Backhuys Publishers: Cotonou, Benin; Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- INSAE. Troisième Recensement General de la Population et de l’Habitat (RGPH3),Tome 3: Caractéristiques Socioculturelles et Economiques; Direction des Etudes Démographiques, Institue National de Statistique Appliquée et d’Economie (INSAE): Cotonou, Bénin, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Igué, A.M.; Floquet, A.; Stahr, K. Land use and farming systems in Benin. In Adapted Farming in West Africa: Issues, Potentials and Perspectives; Graef, F., Lawrence, P., von Oppen, M., Eds.; Verlag Ulrich E. Grauer: Stuttgart, Germany, 2000; pp. 219–230. [Google Scholar]
- Baco, M.N.; Biaou, G.; Lescure, J.-P. Complementarity between geographical and social patterns in the preservation of yam (Dioscorea sp.) diversity in northern Benin. Econ. Bot. 2007, 61, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongi, S.; Obama, G.; Le Dain, A.-S.; Cossi, A. République du Bénin: Analyse Globale de la Vulnérabilité,de la Sécurité Alimentaire et de la Nutrition; Programme Alimentaire Mondial (PAM): Rome, Italie, 2009; Available online: http://documents.wfp.org/stellent/groups/public/documents/ena/wfp203247.pdf (accessed on 15 April 2015).
- MAEP. Etude Préliminaire sur l’Etat des Lieux des Interventions en Matière de Sécurité Alimentaire au Bénin; Ministère de l’Agriculture, de l’Elevage et de la Pêche (MAEP): Cotonou, Bénin, 2013; p. 175. [Google Scholar]
- INSAE. Cahiers des Villages et Quartiers de Ville des Départements de l’Atacora et de la Donga; Direction des Etudes Démographiques, Institue National de Statistique Appliquée et d’Economie (INSAE): Cotonou, Bénin, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Segnon, A.C.; Achigan-Dako, E.G. Comparative analysis of diversity and utilization of edible plants in arid and semi-arid areas in Benin. J. Ethnobiol. Ethnomed. 2014, 10, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, L.E.; Brussaard, L.; de Ruiter, P.C.; Pascual, U.; Perrings, C.; Bawa, K. Agrobiodiversity. In Encyclopedia of Biodiversity, 2nd ed.; Levin, S.A., Ed.; Academic Press: Waltham, MA, USA, 2013; pp. 126–135. [Google Scholar]
- Babbie, E. The Practice of Social Research, 12th ed.; Wadsworth Publishing: Belmont, MA, USA, 2010; p. 625. [Google Scholar]
- Fanou-Fogny, N.; van Dam, B.; Koreissi, Y.; Dossa, R.A.M.; Brouwer, I.D. Factors predicting consumption of fonio grain (Digitaria exilis) among urban malian women of reproductive age. J. Nutr. Educ. Behav. 2011, 43, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knight, A.T.; Cowling, R.M.; Difford, M.; Campbell, B.M. Mapping human and social dimensions of conservation opportunity for the scheduling of conservation action on private land. Conserv. Biol. 2010, 24, 1348–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cronbach, L. Coefficient alpha and the internal structure of tests. Psychometrika 1951, 16, 297–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revelle, W. Psych: Procedures for Personality and Psychological Research; Version 1.4.2; Northwestern University: Evanston, IL, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2013; Available online: http://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 15 April 2015).
- Crawley, M.J. The R Book, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2013; p. 1076. [Google Scholar]
- Ayantunde, A.A.; Briejer, M.; Hiernaux, P.; Udo, H.J.; Tabo, R. Botanical knowledge and its differentiation by age, gender and ethnicity in southwestern Niger. Hum. Ecol. 2008, 36, 881–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaoue, O.G.; Ticktin, T. Fulani knowledge of the ecological impacts of Khaya senegalensis (Meliaceae) foliage harvest in Benin and its implications for sustainable harvest. Econ. Bot. 2009, 63, 256–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souto, T.; Ticktin, T. Understanding interrelationships among predictors (age, gender, and origin) of local ecological knowledge. Econ. Bot. 2012, 66, 149–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sop, T.K.; Oldeland, J.; Bognounou, F.; Schmiedel, U.; Thiombiano, A. Ethnobotanical knowledge and valuation of woody plants species: A comparative analysis of three ethnic groups from the sub-Sahel of Burkina Faso. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2012, 14, 627–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jose, S. Agroforestry for ecosystem services and environmental benefits: An overview. Agrofor. Syst. 2009, 76, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, A.; Kandji, S.T. Carbon sequestration in tropical agroforestry systems. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2003, 99, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verchot, L.; Van Noordwijk, M.; Kandji, S.; Tomich, T.; Ong, C.; Albrecht, A.; Mackensen, J.; Bantilan, C.; Anupama, K.V.; Palm, C. Climate change: Linking adaptation and mitigation through agroforestry. Mitig. Adapt. Strateg. Glob. Chang. 2007, 12, 901–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayala, J.; Sanou, J.; Teklehaimanot, Z.; Kalinganire, A.; Ouédraogo, S.J. Parklands for buffering climate risk and sustaining agricultural production in the Sahel of West Africa. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2014, 6, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atangana, A.; Khasa, D.; Chang, S.; Degrande, A. Ecological interactions and productivity in agroforestry systems. In Tropical Agroforestry; Atangana, A., Khasa, D., Chang, S., Degrande, A., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 151–172. [Google Scholar]
- Kohli, R.K.; Singh, H.P.; Batish, D.R.; Jose, S. Ecological interactions in agroforestry: An overview. In Ecological Basis of Agroforestry; Batish, D.R., Kohli, R.K., Jose, S., Singh, H.P., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008; pp. 3–14. [Google Scholar]
- Achigan-Dako, E.G.; N’Danikou, S.; Assogba-Komlan, F.; Ambrose-Oji, B.; Ahanchede, A.; Pasquini, M.W. Diversity, geographical, and consumption patterns of traditional vegetables in sociolinguistic communities in Benin: Implications for domestication and utilization. Econ. Bot. 2011, 65, 129–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salako, V.K.; Fandohan, B.; Kassa, B.; Assogbadjo, A.E.; Idohou, A.F.R.; Gbedomon, R.C.; Chakeredza, S.; Dulloo, M.E.; Glele Kakaï, R. Home gardens: An assessment of their biodiversity and potential contribution to conservation of threatened species and crop wild relatives in Benin. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2014, 61, 313–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assogbadjo, A.E.; Glèlè Kakaï, R.; Vodouhê, F.G.; Djagoun, C.A.M.S.; Codjia, J.T.C.; Sinsin, B. Biodiversity and socioeconomic factors supporting farmers’ choice of wild edible trees in the agroforestry systems of Benin (West Africa). Forest Policy Econ. 2012, 14, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroth, G.; Ruf, F. Farmer strategies for tree crop diversification in the humid tropics. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2014, 34, 139–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wezel, A.; Rath, T. Resource conservation strategies in agro-ecosystems of semi-arid West Africa. J. Arid Environ. 2002, 51, 383–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heubach, K.; Wittig, R.; Nuppenau, E.-A.; Hahn, K. Local values, social differentiation and conservation efforts: The impact of ethnic affiliation on the valuation of NTFP-species in northern Benin, West Africa. Hum. Ecol. 2013, 41, 513–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vodouhê, F.; Coulibaly, O.; Greene, C.; Sinsin, B. Estimating the local value of non-timber forest products to Pendjari biosphere reserve dwellers in Benin. Econ. Bot. 2009, 63, 397–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Caluwé, E.; De Smedt, S.; Assogbadjo, A.E.; Samson, R.; Sinsin, B.; van Damme, P. Ethnic differences in use value and use patterns of baobab (Adansonia digitata L.) in northern Benin. Afr. J. Ecol. 2009, 47, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saïdou, A.; Adjei-Nsiah, S.; Kossou, D.; Sakyi-Dawson, O.; Kuyper, T.W. Sécurité foncière et gestion de la fertilité des sols: Études de cas au Ghana et au Bénin. Cah. Agric. 2007, 16, 405–412. [Google Scholar]
- Saïdou, A.; Tossou, R.C.; Kossou, D.; Sambieni, S.; Richards, P.; Kuyper, T.W. Land tenure and sustainable soil fertility management in central Benin: Towards the establishment of a cooperation space among stakeholders. Int. J. Agric. Sustain. 2007, 5, 195–212. [Google Scholar]
- Heubach, K.; Wittig, R.; Nuppenau, E.-A.; Hahn, K. The economic importance of non-timber forest products (NTFPs) for livelihood maintenance of rural west African communities: A case study from northern Benin. Ecol. Econ. 2011, 70, 1991–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wezel, A.; Haigis, J. Fallow cultivation system and farmer’s resource management in Niger, West Africa. Land Degrad. Dev. 2002, 13, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Glasenapp, M.; Thornton, T.F. Traditional ecological knowledge of Swiss alpine farmers and their resilience to socioecological change. Hum. Ecol. 2011, 39, 769–781. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-Baggethun, E.; Reyes-García, V.; Olsson, P.; Montes, C. Traditional ecological knowledge and community resilience to environmental extremes: A case study in Doñana, SW Spain. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2012, 22, 640–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemaire, G.; Franzluebbers, A.; Carvalho, P.C.d.F.; Dedieu, B. Integrated crop–livestock systems: Strategies to achieve synergy between agricultural production and environmental quality. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 190, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eilola, S.; Käyhkö, N.; Fagerholm, N.; Kombo, Y.H. Linking farmers’ knowledge, farming strategies, and consequent cultivation patterns into the identification of healthy agroecosystem characteristics at local scales. Agroecol. Sustain. Food Syst. 2014, 38, 1047–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahmar, R.; Bationo, B.A.; Dan Lamso, N.; Guéro, Y.; Tittonell, P. Tailoring conservation agriculture technologies to West Africa semi-arid zones: Building on traditional local practices for soil restoration. Field Crops Res. 2012, 132, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariyono, J.; Luther, G.C.; Bhattarai, M.; Ferizal, M.; Jaya, R.; Fitriana, N. Farmer field schools on chili peppers in Aceh, Indonesia: Activities and impacts. Agroecol. Sustain. Food Syst. 2013, 37, 1063–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zossou, E.; Van Mele, P.; Vodouhe, S.D.; Wanvoeke, J. The power of video to trigger innovation: Rice processing in central Benin. Int. J. Agric. Sustain. 2009, 7, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentley, J.; Van Mele, P. Sharing ideas between cultures with videos. Int. J. Agric. Sustain. 2011, 9, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zossou, E.; Van Mele, P.; Vodouhe, S.D.; Wanvoeke, J. Comparing farmer-to-farmer video with workshops to train rural women in improved rice parboiling in central Benin. J. Agric. Educ. Ext. 2009, 15, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Röling, N.; Jiggins, J.; Hounkonnou, D.; van Huis, A. Agricultural research—From recommendation domains to arenas for interaction: Experiences from West Africa. Outlook Agric. 2014, 43, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogliotti, S.; García, M.C.; Peluffo, S.; Dieste, J.P.; Pedemonte, A.J.; Bacigalupe, G.F.; Scarlato, M.; Alliaume, F.; Alvarez, J.; Chiappe, M.; et al. Co-innovation of family farm systems: A systems approach to sustainable agriculture. Agric. Syst. 2014, 126, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matouš, P.; Todo, Y.; Mojo, D. Roles of extension and ethno-religious networks in acceptance of resource-conserving agriculture among Ethiopian farmers. Int. J. Agric. Sustain. 2013, 11, 301–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wossen, T.; Berger, T.; Mequaninte, T.; Alamirew, B. Social network effects on the adoption of sustainable natural resource management practices in Ethiopia. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Ecol. 2013, 20, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labeyrie, V.; Rono, B.; Leclerc, C. How social organization shapes crop diversity: An ecological anthropology approach among Tharaka farmers of mount Kenya. Agric. Hum. Values 2014, 31, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
