Dynamics of Multi-Scale Intra-Provincial Regional Inequality in Zhejiang, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review, Research Areas and Methods
2.1. Literature Review
| Authors | Spatial Scales |
|---|---|
| Ye and Chen[13] | District |
| Luo[14] | Municipality |
| Wei and Ye[1] | County and Municipality |
2.2. Research Areas and Research Unit Division
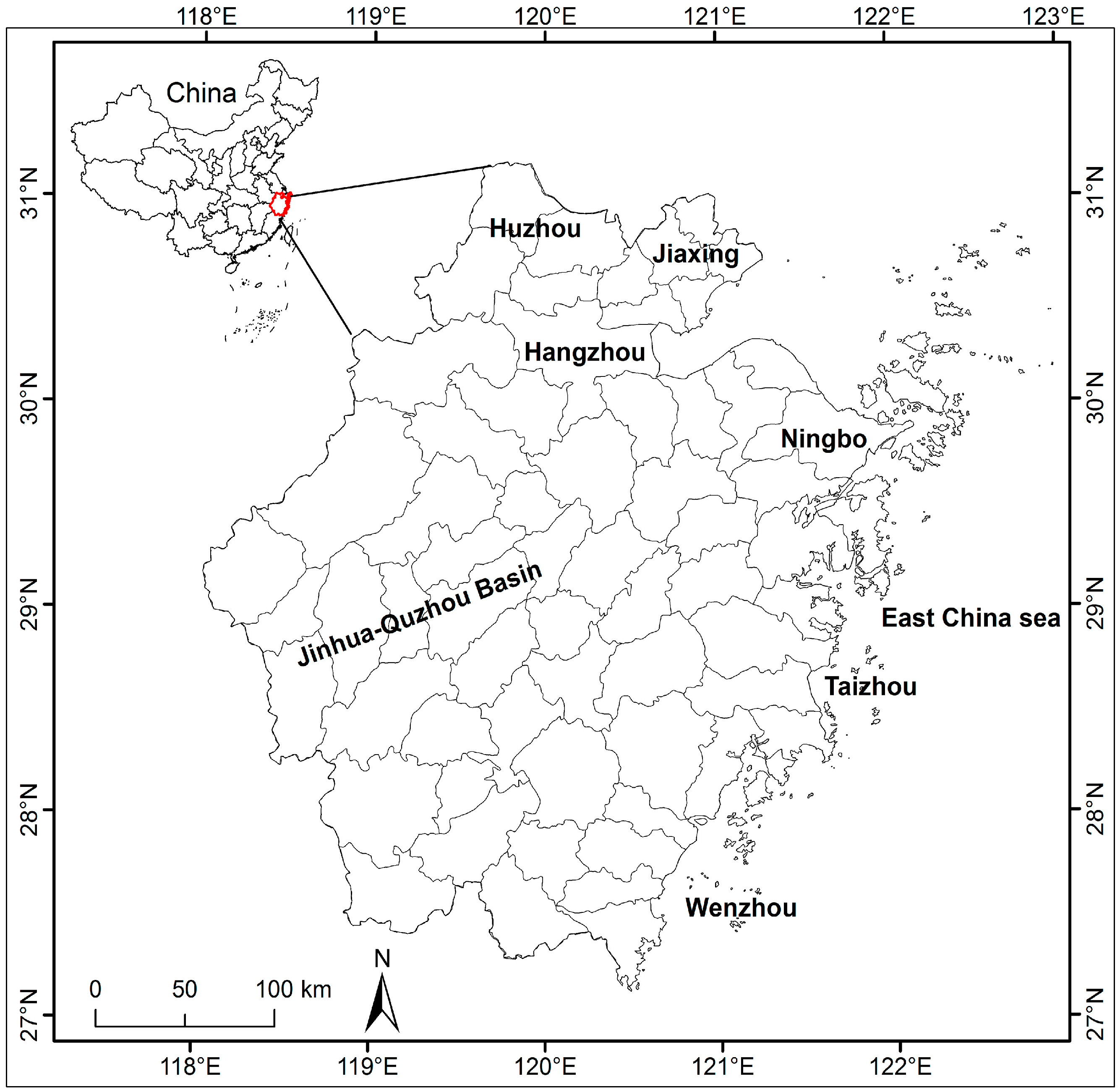
| ZJ | % of China | Northeast | % of ZJ | Southeast | % of ZJ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Population (million) | 47.4795 | 3.54 | 24.0046 | 50.56 | 23.4748 | 49.44 |
| Land area (km2) | 104,141 | 1.08 | 45,864 | 44.04 | 58,277 | 55.96 |
| GDP (billion yuan) | 2772.231 | 6.91 | 1815.362 | 67.97 | 888.03 | 32.03 |
| Investment in fixed assets (billion yuan) | 1237.604 | 4.45 | 881.406 | 71.22 | 345.121 | 28.78 |
| Exports (U.S. $billion) | 180.465 | 11.44 | 137.233 | 76.04 | 43.247 | 23.96 |
| FDI (U.S. $billion) | 11.00175 | 10.41 | 10.22908 | 92.98 | 0.76031 | 7.02 |
| Local fiscal expenditure (billion yuan) | 2857.83 | 3.87 | 1870.49 | 65.45 | 987.34 | 34.55 |
| Local fiscal revenue (billion yuan) | 2371.85 | 5.84 | 1730.63 | 72.97 | 641.22 | 27.03 |

3. Methods
3.1. Theil Index
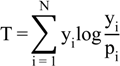
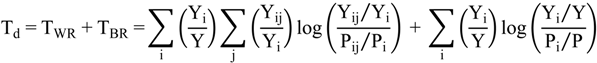
3.2. Moran’ I
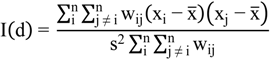
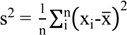 , xi is the observation at spatial unit i, x is the arithmetic mean value of xi, wij is the spatial weighting value. The value of the Global Moran’ I ranges from −1 to 1. A positive value for I(d) indicates spatial clustering of similar values (high or low), whereas a negative value indicates spatial clustering of dissimilar values between a region and its neighbors.
, xi is the observation at spatial unit i, x is the arithmetic mean value of xi, wij is the spatial weighting value. The value of the Global Moran’ I ranges from −1 to 1. A positive value for I(d) indicates spatial clustering of similar values (high or low), whereas a negative value indicates spatial clustering of dissimilar values between a region and its neighbors.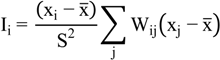
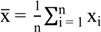 ,
, 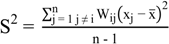 . If Ii is significantly greater than 0, it indicates that spatial inequality between region i and its surrounding regions is significantly small and vice versa.
. If Ii is significantly greater than 0, it indicates that spatial inequality between region i and its surrounding regions is significantly small and vice versa.3.3. Spatial Markov Chains
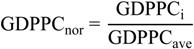
4. Findings
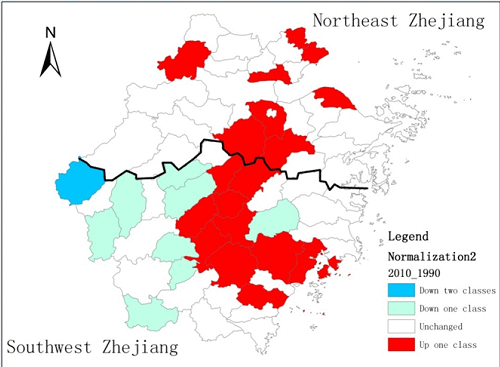
4.1. Multi-Scale Regional Inequality in Zhejiang
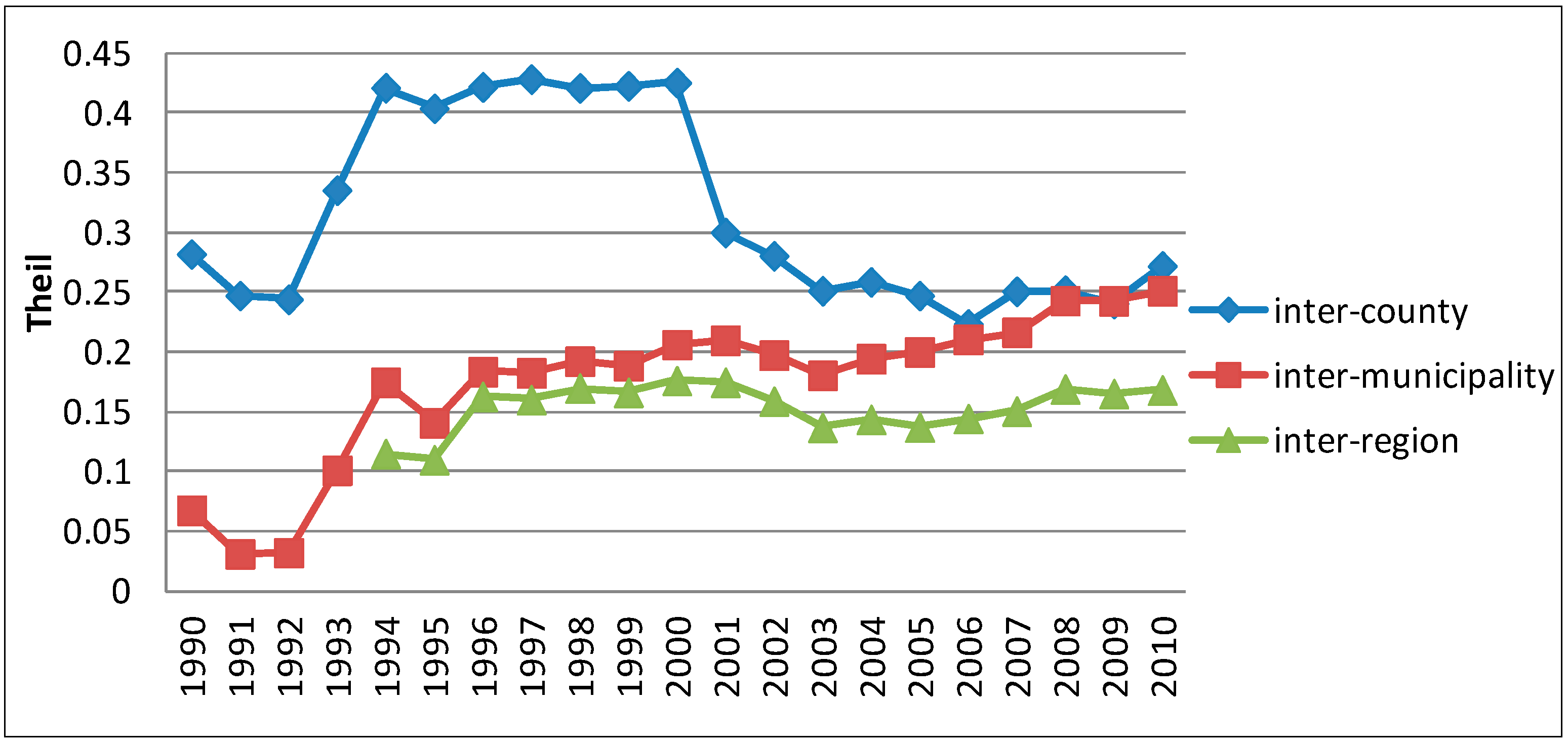
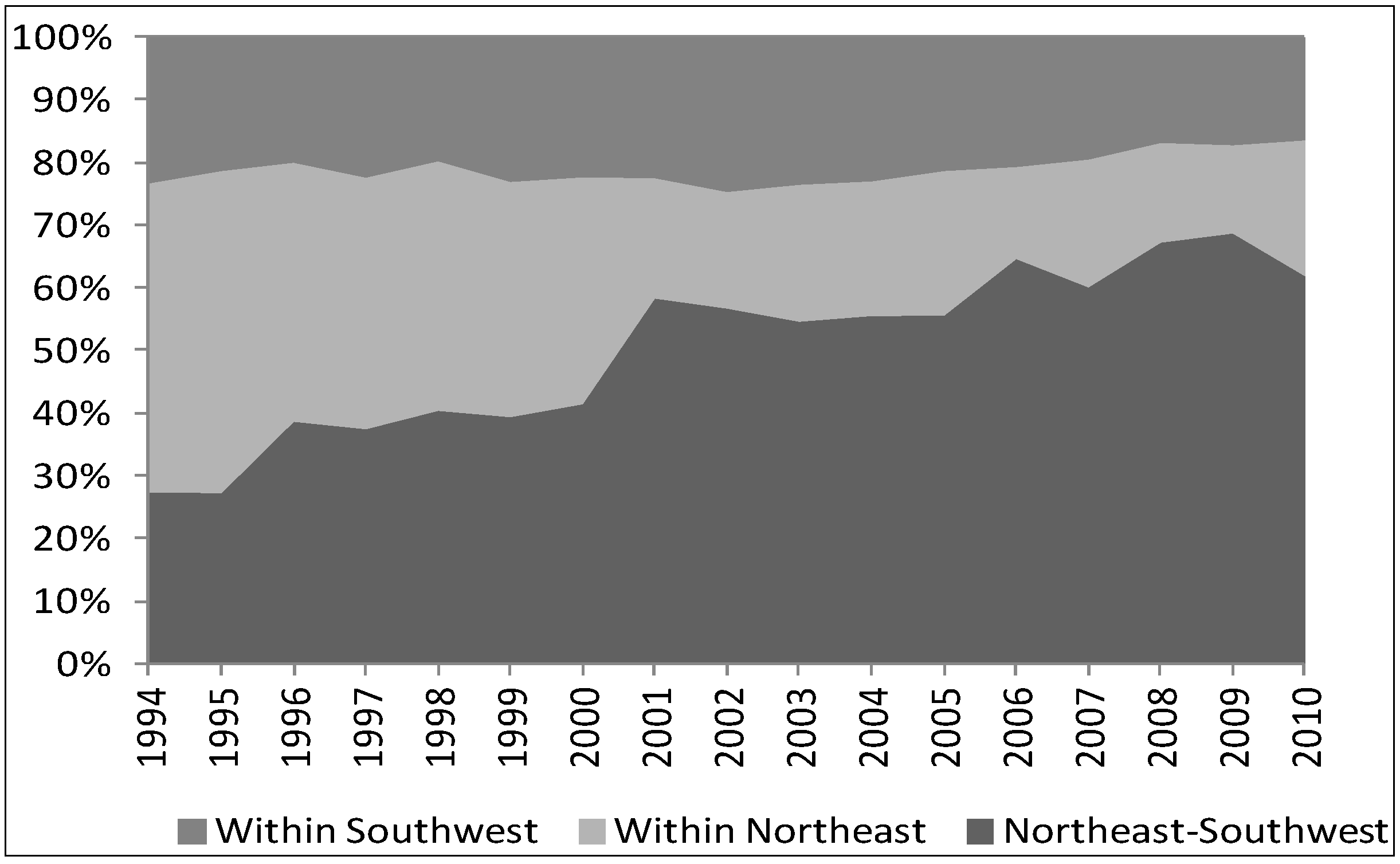
4.2. Spatial Aggregation and the Dynamics of Inter-County Equality in Zhejiang Province
4.2.1. Global Spatial Autocorrelation

4.2.2. Local Spatial Aggregation
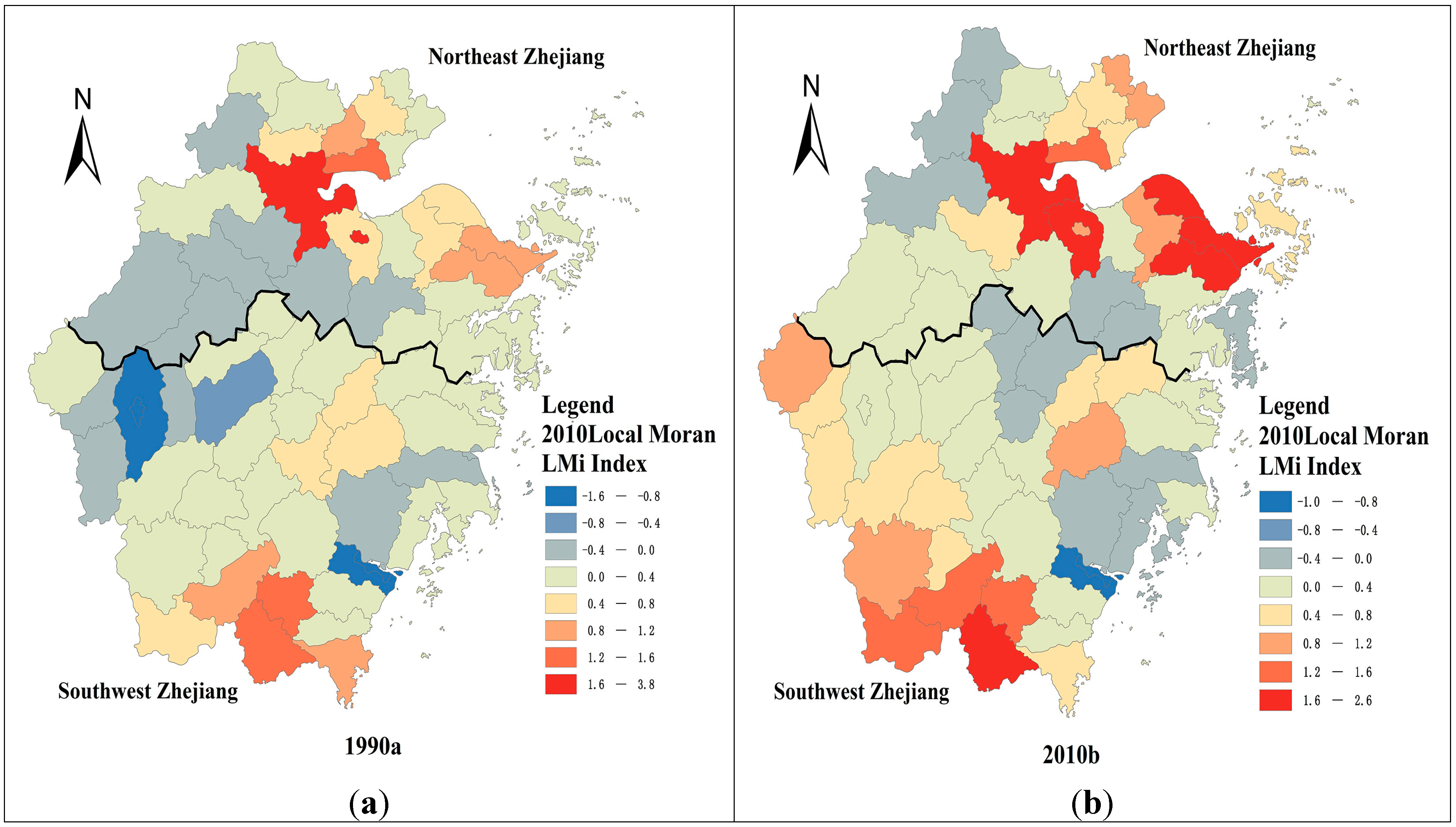

4.3. The Spatial-Temporal Dynamics of County Level Regional Inequality in Zhejiang
4.3.1. Spatial Patterns of Regional Development in Zhejiang Province
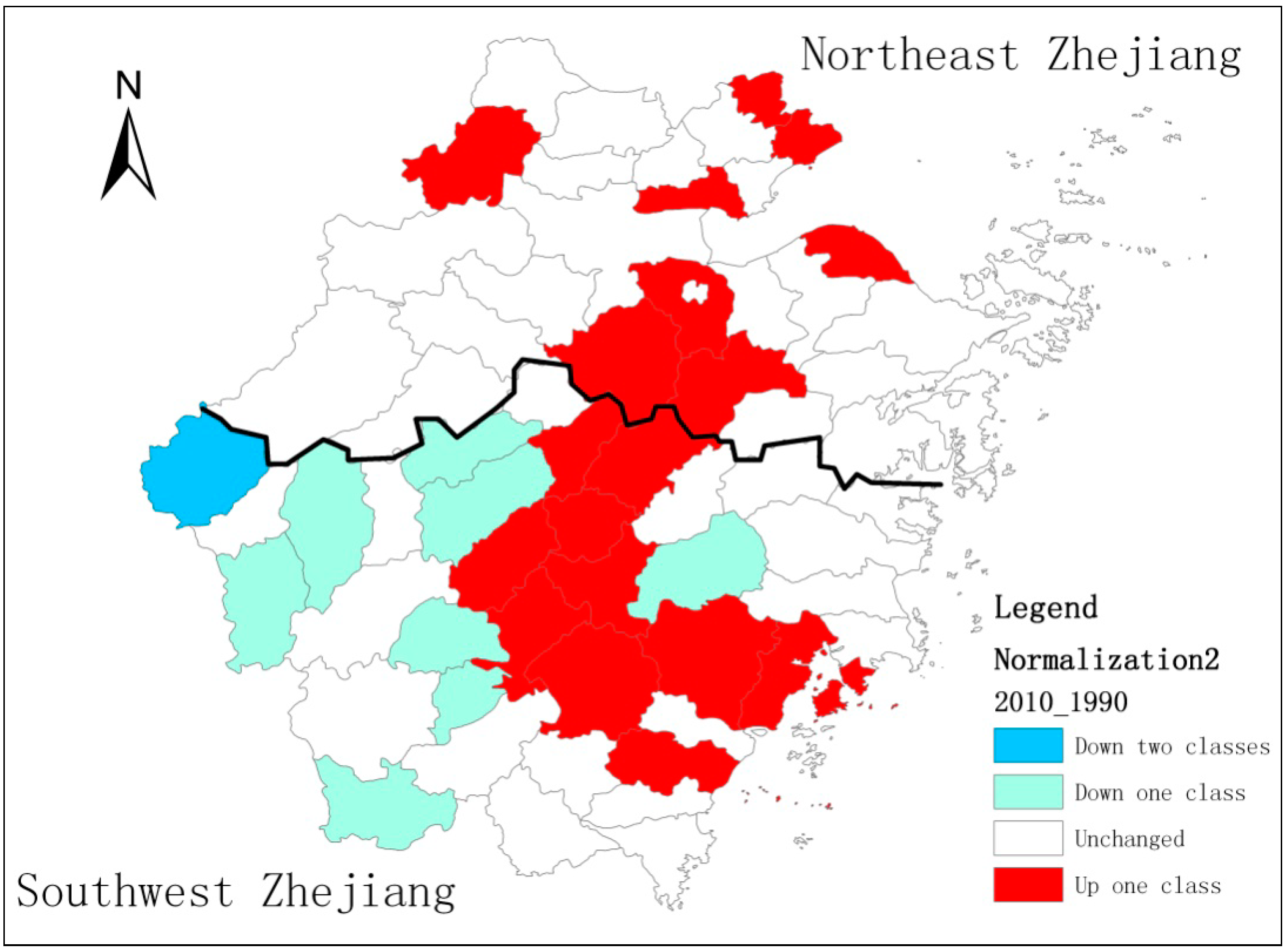
4.3.2. Markov Chains Analysis of Regional Inequality
| Transition Probability | P | L | D | R |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1990–2010 | ||||
| P(131) | 0.9313 | 0.0687 | 0 | 0 |
| L(372) | 0.0269 | 0.9247 | 0.0484 | 0 |
| D(609) | 0 | 0.0213 | 0.9376 | 0.0411 |
| R(199) | 0 | 0 | 0.1005 | 0.8995 |
| Ergodic distribution | 8.54% | 21.81% | 49.45% | 20.20% |
| 1990–2000 | ||||
| P(57) | 0.9123 | 0.0877 | 0 | 0 |
| L(181) | 0.0221 | 0.9061 | 0.0718 | 0 |
| D(303) | 0 | 0.0297 | 0.9274 | 0.0429 |
| R(80) | 0 | 0 | 0.1375 | 0.8625 |
| Ergodic distribution | 5.69% | 22.60% | 54.65% | 17.05% |
| 2001–2010 | ||||
| P(68) | 0.9412 | 0.0588 | 0 | 0 |
| L(170) | 0.0353 | 0.9353 | 0.0294 | 0 |
| D(274) | 0 | 0.0146 | 0.9489 | 0.0365 |
| R(109) | 0 | 0 | 0.0826 | 0.9174 |
| Ergodic distribution | 13.32% | 22.20% | 44.72% | 19.76% |
4.3.3. Spatial Markov Chains of Regional Inequality
| 2010 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spatial lag | 1990 | P | L | D | R |
| P | P | 0.962 | 0.038 | 0 | 0 |
| L | 0.0312 | 0.9167 | 0.0521 | 0 | |
| D | 0 | 0.018 | 0.9459 | 0.036 | |
| R | 0 | 0 | 0.075 | 0.925 | |
| L | P | 0.8846 | 0.1154 | 0 | 0 |
| L | 0.0287 | 0.9522 | 0.0191 | 0 | |
| D | 0 | 0.1304 | 0.8696 | 0 | |
| R | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| D | P | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| L | 0.0167 | 0.85 | 0.1333 | 0 | |
| D | 0 | 0.0125 | 0.9467 | 0.0408 | |
| R | 0 | 0 | 0.0952 | 0.9048 | |
| R | P | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| L | 0 | 0.8571 | 0.1429 | 0 | |
| D | 0 | 0.0075 | 0.9323 | 0.0602 | |
| R | 0 | 0 | 0.1299 | 0.8701 | |
4.3.4. The Trend of Spatial-Temporal Dynamics of Regional Inequality in Zhejiang
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wei, Y.D.; Ye, X. Beyond convergence: Space, scale, and regional inequality in China. J. Econ. Soc. Geogr. 2009, 100, 59–80. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y.D.; Yu, D.; Chen, X. Scale, agglomeration, and regional inequality in provincial China. J. Econ. Soc. Geogr. 2011, 102, 406–425. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, C.C.; Sun, M. Regional inequality in China, 1978–2006. Eurasian Geogr. Econ. 2008, 49, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Wei, Y.D. Analyzing regional inequality in post-Mao China in a GIS Environment. Geogr. Econ. 2003, 44, 514–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Bureau of Statistics of China. China Statistical Yearbook, 2011; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations Development Program (UNDP). Human Development Report 2014; United Nations Development Program: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y.D.; Ye, X. Regional inequality in China: A case study of Zhejiang Province. J. Econ. Soc. Geogr. 2004, 95, 44–60. [Google Scholar]
- Barro, R.J.; Sala-I-Martin, X. Convergence across states and regions. Brook. Papers Econ. Act. 1991, 22, 107–182. [Google Scholar]
- Barro, R.J.; Sala-i-Martin, X. Convergence. J. Political Econ. 1992, 100, 223–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wei, Y.D. The spatial-temporal hierarchy of regional inequality of China. Appl. Geogr. 2010, 30, 303–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Q. Local impacts of the post-Mao development strategy: The case of the Zhujiang Delta, southern China. Int. J. Urban Reg. Res. 1998, 22, 425–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.D. Regional development in China: Transitional institutions, embedded globalization, and hybrid economies. Eurasian Geogr. Econ. 2007, 48, 16–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Chen, X. The analysis of the regional economic inequality in Zhejiang in recent 16 years. Explor. Econ. Probl. 2008, 2, 59–65. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, D. The analysis of regional inequality of economic development in Zhejiang. Econ. Res. Guide 2009, 42, 102–103. [Google Scholar]
- Rey, S.J.; Murray, A.T.; Anselin, L. Visualizing regional income distribution dynamics. Lett. Spat. Resour. Sci. 2011, 4, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey, S.J.; Anselin, L. PySAL: A Python library of spatial analytical methods. In Handbook of Applied Spatial Analysis; Fischer, M., Getis, A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 175–193. [Google Scholar]
- Anselin, L.; Syabri, I.; Kho, Y. GeoDa: An introduction to spatial data analysis. Geogr. Anal. 2006, 38, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celebioglu, F.; Dall’erba, S. Spatial disparities across the regions of Turkey: An exploratory spatial data analysis. Anna. Reg. Sci. 2010, 45, 379–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Gallo, J.; Ertur, C. Exploratory spatial data analysis of the distribution of regional per capita GDP in Europe, 1980–1995. Papers Reg. Sci. 2003, 82, 175–201. [Google Scholar]
- Rey, S.J.; Janikas, M. 2005 Regional convergence, inequality, and space. J. Econ. Geogr. 2005, 5, 155–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey, S.J. Spatial empirics for economic growth and convergence. Geogr. Anal. 2001, 33, 195–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey, S.J. Rank-based Markov chains for regional income distribution dynamics. J. Geogr. Syst. 2014, 16, 115–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, J. Space-time analysis of GDP disparities among European regions: A Markov chains approach. Int. Reg. Sci. Rev. 2004, 27, 138–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Pose, A.; Vassilis, T. Mapping regional personal income distribution in Western Europe: Income per capita and inequality. Financ. Uver-Czech J. Econ. Financ. 2009, 59, 41–70. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Pose, A.; Vassilis, T. Mapping the European regional educational distribution. Eur. Urban Reg. Stud. 2011, 18, 358–374. [Google Scholar]
- Zhejiang Province Statistics Bureau. Zhejiang Statistical Yearbook, 2011; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, X.; Wei, Y.D. Geospatial analysis of regional development in China: The case of Zhejiang Province and the Wenzhou model. Eurasian Geogr. Econ. 2005, 46, 445–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey, S.J. Show me the code: Spatial analysis and open source. J. Geogr. Syst. 2009, 11, 191–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselin, L. Local indicators of spatial association-LISA. Geogr. Anal. 1995, 27, 93–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Yue, W.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, X.; Cheng, Y.; Leipnik, M.R. Dynamics of Multi-Scale Intra-Provincial Regional Inequality in Zhejiang, China. Sustainability 2014, 6, 5763-5784. https://doi.org/10.3390/su6095763
Yue W, Zhang Y, Ye X, Cheng Y, Leipnik MR. Dynamics of Multi-Scale Intra-Provincial Regional Inequality in Zhejiang, China. Sustainability. 2014; 6(9):5763-5784. https://doi.org/10.3390/su6095763
Chicago/Turabian StyleYue, Wenze, Yuntang Zhang, Xinyue Ye, Yeqing Cheng, and Mark R. Leipnik. 2014. "Dynamics of Multi-Scale Intra-Provincial Regional Inequality in Zhejiang, China" Sustainability 6, no. 9: 5763-5784. https://doi.org/10.3390/su6095763
APA StyleYue, W., Zhang, Y., Ye, X., Cheng, Y., & Leipnik, M. R. (2014). Dynamics of Multi-Scale Intra-Provincial Regional Inequality in Zhejiang, China. Sustainability, 6(9), 5763-5784. https://doi.org/10.3390/su6095763