An Index of Human Well-Being for the U.S.: A TRIO Approach
Abstract
:1. Introduction

| Index | Scale | Economic
Well-Being | Basic Needs | Environmental
Well-Being | Subjective
Well-Being |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The Economic Intelligence Unit’s
Quality of Life [13] | N | X | X | ||
| Australian Unity Wellbeing Index [14] | N | X | X | X | |
| Human Development Index [15] | N | X | X | ||
| Quality of Life Index for Developing Countries [16] | N | X | X | (X) | X |
| The Well-being of Nations [17] | N | X | X | X | |
| Sustainable Society Index [18] | N | X | X | X | |
| Hong Kong Quality of Life [19] | R | X | X | X | X |
| Well-being in EU Countries—Multidimensional Index of Sustainability [20] | N | X | X | X | |
| National Well-being Index—Life Satisfaction [21] | N | X | X | X | (X) |
| Child and Youth Well-being Index [22] | N | X | X | ||
| Canadian Index of Well-being [23] | N | X | X | X | |
| Happy Planet Index [9] | N | X | X | X | |
| Index of Child Well-Being in Europe [24] | N | X | X | X | |
| Index of Social Health [25] | N | X | X | ||
| Gallup-Healthways Well-Being Index [26] | M | X | X | ||
| The State of the Commonwealth Index [27] | S | X | X | X | X |
| QOL 2007 in Twelve of New Zealand’s Cities [28] | L | X | X | X | X |
| Nova Scotia 2008 GPI [29] | R | X | X | X | |
| Gross National Happiness [30] | N | X | X | X | X |
| Human Well-Being Index [this manuscript] | M | X | X | X | X |
2. Index Development, Application and Discussion
2.1. Characterizing Well-Being
2.1.1. Index Description



| Domain | Indicator | Metrics |
|---|---|---|
| Connection to Nature | Biophilia | Connection to Life |
| Spiritual Fulfillment | ||
| Cultural Fulfillment | Activity Participation | Performing Arts Attendance |
| Rate of Congregational Adherence | ||
| Education | Basic Educational Knowledge and Skills of Youth | Mathematics Skills |
| Reading Skills | ||
| Science Skills | ||
| Participation and Attainment | Adult Literacy | |
| High School Completion | ||
| Participation | ||
| Post-Secondary Attainment | ||
| Social, Emotional and Developmental Aspects | Bullying | |
| Contextual Factors | ||
| Physical Health | ||
| Social Relationships and Emotional Well-being | ||
| Health | Healthcare | Population with a Regular Family Doctor |
| Satisfaction with Healthcare | ||
| Life Expectancy and Mortality | Asthma Mortality | |
| Cancer Mortality | ||
| Diabetes Mortality | ||
| Heart Disease Mortality | ||
| Infant Mortality | ||
| Life Expectancy | ||
| Suicide Mortality | ||
| Lifestyle and Behavior | Alcohol Consumption | |
| Healthy Behaviors Index | ||
| Teen Pregnancy | ||
| Teen Smoking Rate | ||
| Personal Well-being | Happiness | |
| Life Satisfaction | ||
| Perceived Health | ||
| Physical and Mental Health Conditions | Adult Asthma Prevalence | |
| Cancer Prevalence | ||
| Childhood Asthma Prevalence | ||
| Coronary Heart Disease Prevalence | ||
| Depression Prevalence | ||
| Diabetes Prevalence | ||
| Heart Attack Prevalence | ||
| Obesity Prevalence | ||
| Stroke Prevalence | ||
| Leisure Time | Activity Participation | Average Nights on Vacation |
| Physical Activity | ||
| Time Spent | Leisure Activities | |
| Working Age Adults | Adults who Provide Care to Seniors | |
| Adults Working Long Hours | ||
| Adults Working Standard Hours | ||
| Living Standards | Basic Necessities | Food Security |
| Housing Affordability | ||
| Income | Incidence of Low Income | |
| Median Household Income | ||
| Persistence of Low Income | ||
| Wealth | Median Home Value | |
| Mortgage Debt | ||
| Work | Job Quality | |
| Job Satisfaction | ||
| Safety and Security | Actual Safety | Accidental Morbidity and Mortality |
| Loss of Human Life | ||
| Property Crime | ||
| Violent Crime | ||
| Perceived Safety | Community Safety | |
| Risk | Social Vulnerability Index | |
| Social Cohesion | Attitude toward Others and the Community | Belonging to Community |
| City Satisfaction | ||
| Discrimination | ||
| Helping Others | ||
| Trust | ||
| Democratic Engagement | Interest in Politics | |
| Registered Voters | ||
| Satisfaction with Democracy | ||
| Trust in Government | ||
| Voice in Government Decisions | ||
| Voter Turnout | ||
| Family Bonding | Exceeded Screen Time Guidelines | |
| Frequency of Meals at Home | ||
| Parent-child Reading Activities | ||
| Social Engagement | Participation in Group Activities | |
| Participation in Organized, Extracurricular Activities | ||
| Volunteering | ||
| Social Support | Close Friends and Family | |
| Emotional Support |
2.1.2. Indicators and Data Source Selection
| Service Type | Service | Indicator | Number of Metrics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Economic | Capital Investment | Capital Formation | 1 |
| Commercial Durables | 1 | ||
| New Housing Starts | 1 | ||
| New Infrastructure Investments | 4 | ||
| Consumption | Cost of Living | 1 | |
| Discretionary Spending | 1 | ||
| Goods and Services | 3 | ||
| Sustainable Consumption | 1 | ||
| Employment | Employment | 3 | |
| Employment Diversity | 1 | ||
| Underemployment | 1 | ||
| Unemployment | 1 | ||
| Finance | Governance | 2 | |
| Loans | 4 | ||
| Savings | 1 | ||
| Innovation | Investment | 2 | |
| Patents and Products | 1 | ||
| Production | Exports | 1 | |
| Household Services | 1 | ||
| Market goods and services | 2 | ||
| Sustainable Production | 1 | ||
| Redistribution | Inequality | 1 | |
| Public Support | 5 | ||
| Ecosystem | Air Quality | Usable Air | 1 |
| Food and Fiber Provisioning | Energy | 4 | |
| Food and Fiber | 3 | ||
| Raw Materials | 5 | ||
| Green Space | Natural Areas | 4 | |
| Recreation and Aesthetics | 3 | ||
| Natural Hazard Protection | Natural Hazard Exposure | 4 | |
| Water Quality | Usable Water | 2 | |
| Water Quantity | Available Water | 2 | |
| Social | Activism | Participation | 4 |
| Communication | Accessibility | 3 | |
| Industry Infrastructure | 3 | ||
| Providers | 1 | ||
| Public Service Communication | 1 | ||
| Quality | 2 | ||
| Community and Faith-based Initiatives | Investment | 1 | |
| Providers | 1 | ||
| Education (services) | Accessibility | 3 | |
| Confidence | 1 | ||
| Investment | 2 | ||
| Providers | 2 | ||
| Emergency Preparedness | Post-Disaster Response | 1 | |
| Pre-Disaster Planning | 1 | ||
| Responders | 1 | ||
| Family Services | Accessibility | 2 | |
| Effectiveness | 3 | ||
| Investment | 1 | ||
| Providers | 1 | ||
| Healthcare | Accessibility | 5 | |
| Investment | 3 | ||
| Providers | 1 | ||
| Quality | 1 | ||
| Justice | Accessibility | 2 | |
| Confidence | 1 | ||
| Environmental | 4 | ||
| Investment | 2 | ||
| Providers | 1 | ||
| Quality | 1 | ||
| Labor | Confidence | 1 | |
| Effectiveness | 1 | ||
| Employee Rights | 2 | ||
| Public Works | Accessibility | 2 | |
| Investment | 4 | ||
| Providers | 1 | ||
| Quality | 5 | ||
| Quantity | 5 |
2.1.3. Data Imputation, Outliers and Standardization
2.1.4. Calculating the HWBI

2.2. Uncertainty and Sensitivity

| Time Period | Scale | Average Error | Standard Deviation | Minimum | Maximum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annual | National | 0.40 | 0.03 | 0.33 | 0.43 |
| GSS Region | 1.09 | 0.36 | 0.54 | 1.83 | |
| State | 2.34 | 1.31 | 0.98 | 8.10 | |
| County | 9.51 | 2.99 | 5.93 | 24.09 | |
| 2000–2010 | National | 0.122 | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| GSS Region | 0.33 | 0.11 | 0.19 | 0.51 | |
| State | 0.70 | 0.38 | 0.33 | 2.09 | |
| County | 2.64 | 0.90 | 1.83 | 6.93 |
| Domain | Indicator | Metric |
|---|---|---|
| Connection to Nature | Biophilia | Spiritual Fulfillment |
| Connection to Life | ||
| Cultural Fulfillment | Activity Participation | Performance Arts Attendance |
| Rate of Congregational Adherence | ||
| Safety and Security | Actual Safety | Loss from Natural Hazards |
| Perceived Safety | Community Safety | |
| Social Cohesion | Attitude Toward Others and the Community | City Satisfaction |
2.3. Index Performance
| Source | Index Name |
|---|---|
| Gallup-Healthways | Well-Being Index |
| Social Science Research Council | American Human Development Index |
| Sustainable Society Foundation | Sustainable Society Index |
| United Nations Development Programme | Human Development Index |

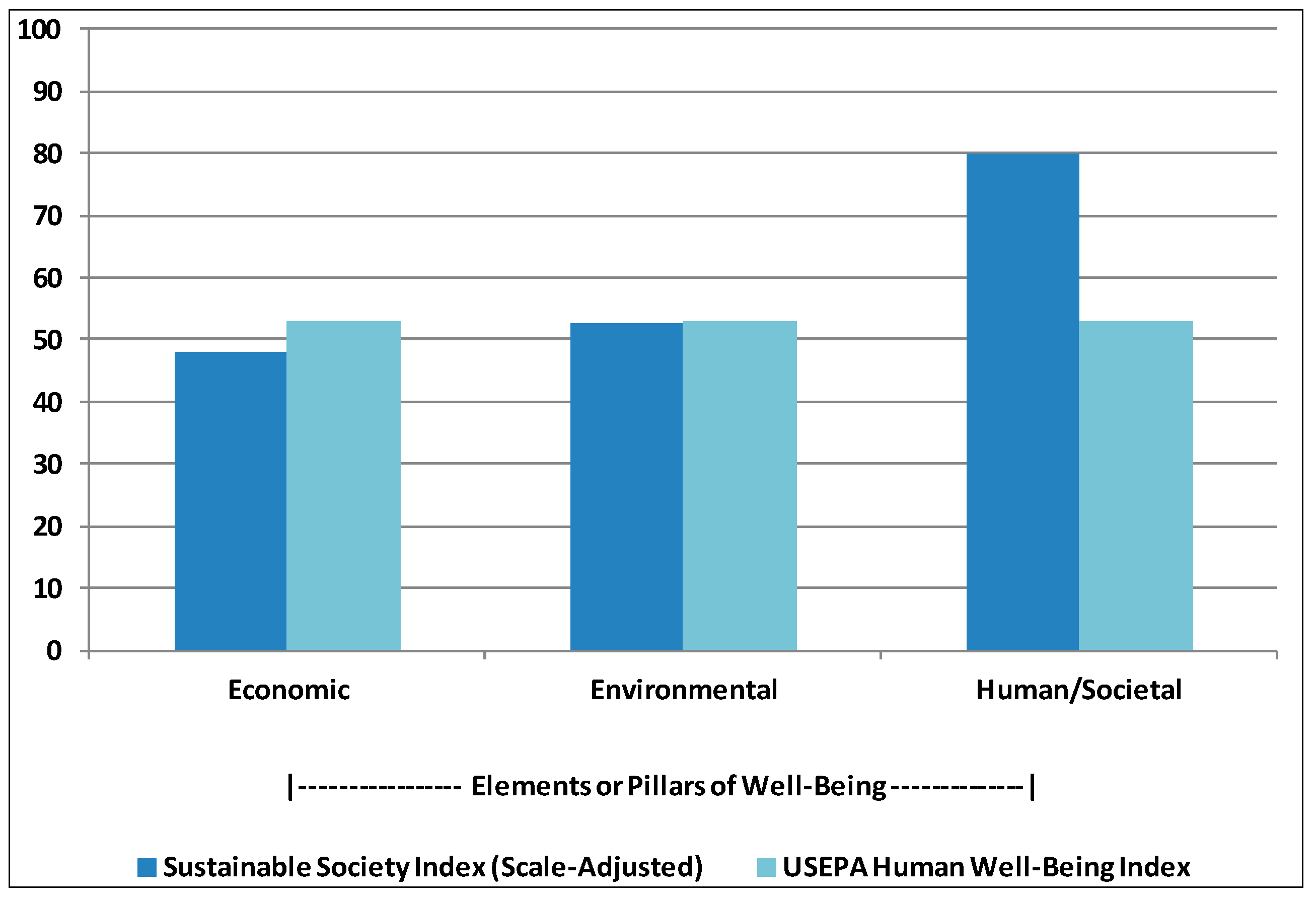
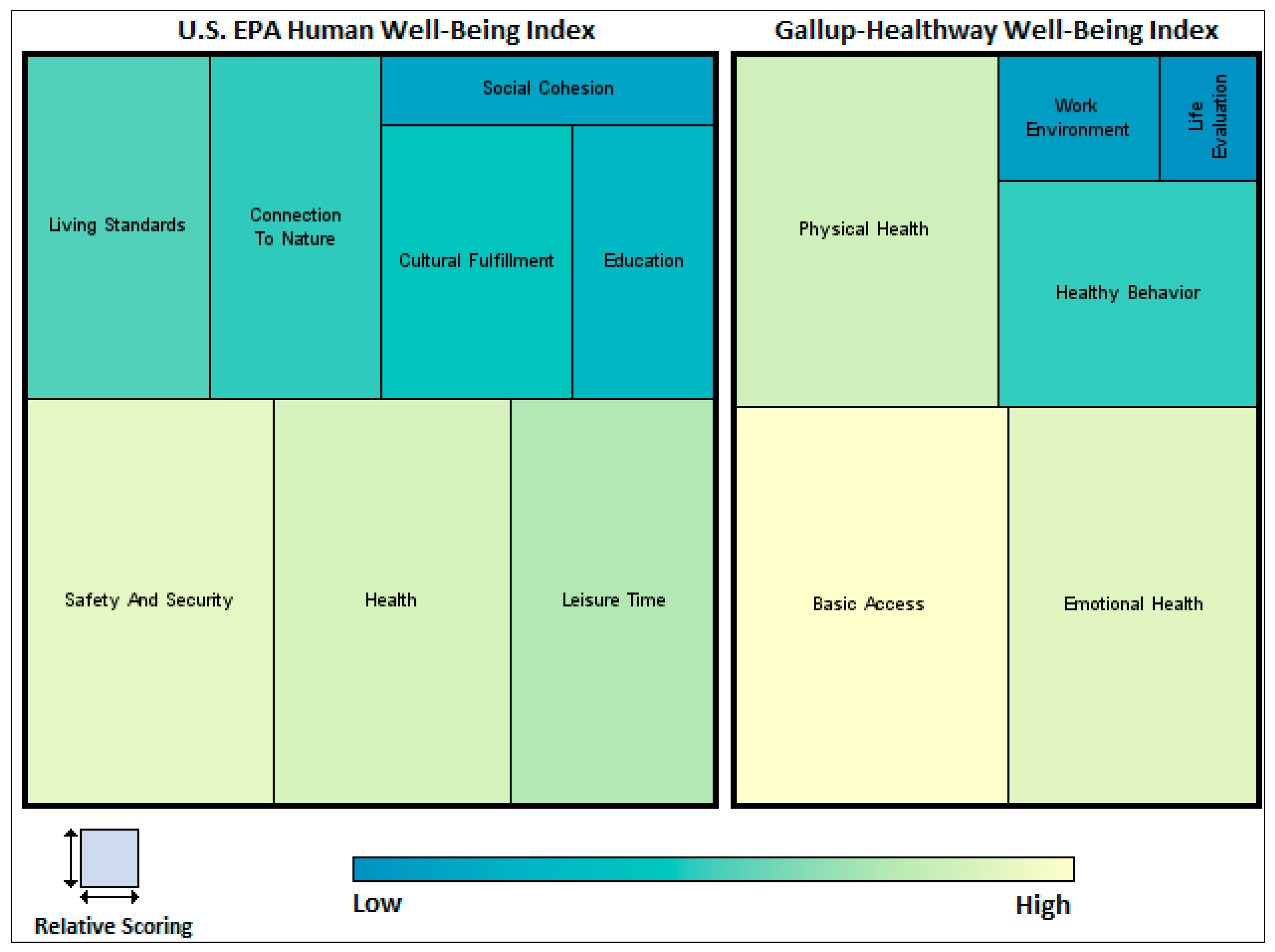
2.4. Well-Being in the Context of TRIO
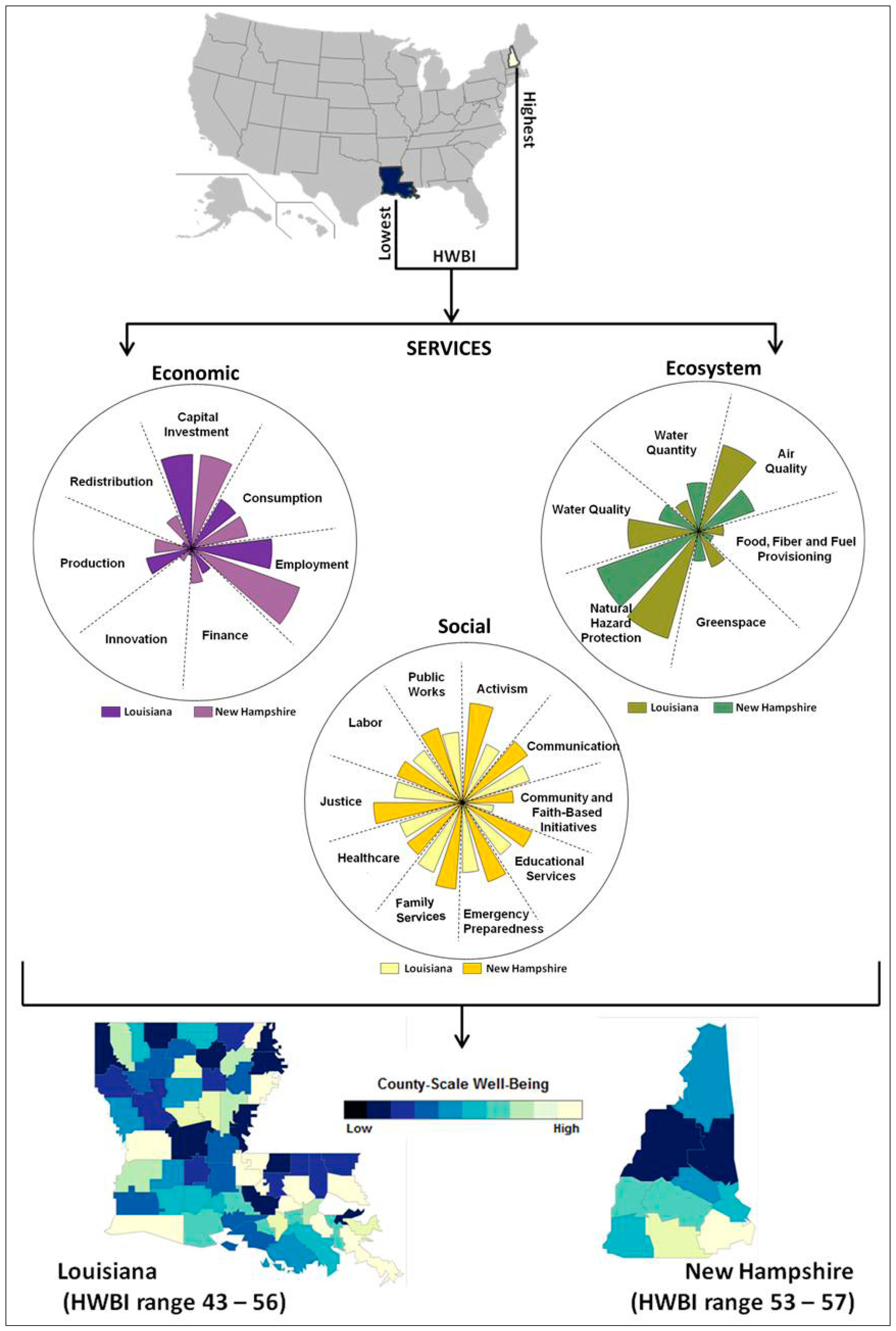
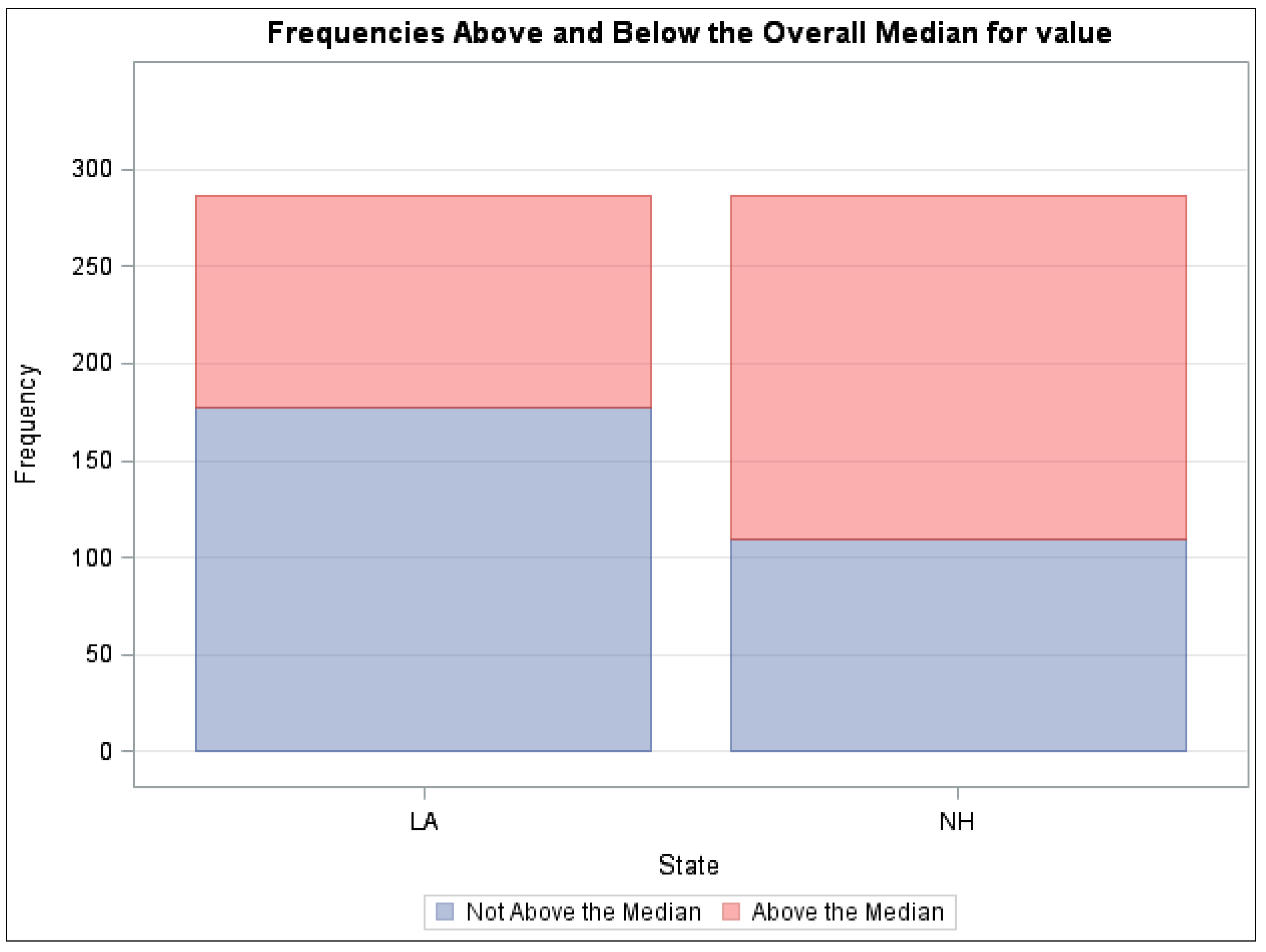
3. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). Indicators and Methods for Constructing a U.S. Human Well-being Index (HWBI) for Ecosystem Services Research; EPA/600/R-12/023; USEPA/ORD/NHEERL: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; p. 120. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). Indicators and Methods for Constructing a U.S. Tribal Well-being Index for Sustainable and Healthy Communities Research; Supplement 1 to EPA/600/R-12-023; USEPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2014; p. 24. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). Indicators and Methods for Evaluating Ecosystem, Economic and Social Services Provisioning; draft; USEPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2014; p. 115. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). Sustainable and Healthy Communities: Strategic Research Action Plan 2012–2016; EPA 601/R-12/005; USEPA/Office of Research and Development: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Elkington, J. The triple bottom line for 21st century business. In The Earthscan Reader in Business and Sustainable Development; Sterling Publishers: London, UK, 2001; pp. 20–43. [Google Scholar]
- Willard, B. The Sustainability Advantage: Seven Business Case Benefits of a Triple Bottom Line; New Society Publishers: Gabriola Island, BC, Canada, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Savitz, A.W.; Weber, K. The Triple Bottom Line: How Today’s Best-Run Companies Are Achieving Economic, Social and Environmental Success—And How You Can Too; Jossey-Bass Publishing Company: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Phillips, P.P.; Phillips, J.J. The Green Scorecard; Nicholas Beasley Publishing: Boston, MA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Marks, N.; Simms, A.; Thompson, S.; Abdallah, S. The Happy Planet Index: An Index of Human Well-Being and Environmental Impact; New Economics Foundation: London, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Ecosystems and Human Well-Being: Health Synthesis; WHO Press: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Wackernagel, M.; Schultz, N.; Deumling, D.; Linares, A.; Kapos, V.; Montfredo, C.; Loh, J.; Myers, N.; Norgaard, R.; Rardis, J. Tracking the ecological overshoot of the human economy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 9266–9271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.M.; Case, J.L.; Smith, H.M.; Harwell, L.C.; Summers, J.K. Relating ecosystem services to domains of human well-being: Foundation for a U.S. index. Ecol. Indic. 2013, 28, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Economist Intelligence Unit (EIU). The Economist Intelligence Unit’s quality-of-Life Index. Available online: http://www.economist.com/media/pdf/QUALITY_OF_LIFE.pdf (accessed on 20 February 2014).
- Cummins, R.A.; Eckersley, R.; Pallant, J.; van Vugt, J.; Msagon, R. Developing a national index of subjective well-being: The Australian Unity Wellbeing Index. Soc. Indic. Res. 2003, 64, 159–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations Development Programme. Human Development Index. In Human Development Reports: Indices & Data. Available online: http://hdr.undp.org/en/statistics/hdi/ (accessed on 3 December 2013).
- Diener, E.D. A value based index for measuring national quality of life. Soc. Indic. Res. 1995, 36, 107–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prescott-Allen, R. The Wellbeing of Nations: A Country-by-Country Index of Quality of Life and the Environment; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Van de Kerk, G.; Manuel, A.R. A comprehensive index for a sustainable society: The SSI—The Sustainable Society Index. Ecol. Econ. 2008, 66, 228–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, Y.; Kwan, C.; Shek, T. Quality of life in Hong Kong: The CUHK Kong Kong quality of life index. Soc. Indic. Res. 2005, 71, 259–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Distaso, A. Well-being and/or quality of life in EU countries through a multi-dimensional index of sustainability. Ecol. Econ. 2007, 64, 163–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vemuri, A.W.; Costanza, R. The role of human, social, built, and natural capital in explaining life satisfaction at the country level: Towards a National Well-Being Index (NWI). Ecol. Econ. 2006, 58, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Land, K.C.; Lamb, V.L.; Mustillo, S.K. Child and youth well-being in the United States 1975–1998: Some findings from a new index. Soc. Indic. Res. 2001, 56, 241–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Institute of Well-Being. How Are Canadians Really Doing? The First Report of the Institute of Well-Being. Available online: http://www.ciw.ca/en/TheCanadianIndexofWellbeing.aspx (accessed on 20 February 2014).
- Bradshaw, G.A.; Richardson, D. An index of child well-being in Europe. Child Indic. Res. 2009, 2, 319–351. [Google Scholar]
- Miringoff, M.; Miringoff, M.L. The Social Health of the Nation: How America is Really Doing; Oxford Press: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Gallup-Healthways. Well-Being Index. In Gallup Well-Being. Available online: http://www.gallup.com/poll/125066/State-States.aspx (accessed on 9 April 2014).
- Watts, A. New Index Measures Well-Being and Ranks Kentucky. Foresight 11 2004. Available online: http://kltprc.info/foresight/Vol11no1.pdf (accessed on 20 February 2014).
- Jamieson, K. Quality of Life 07 in Twelve of New Zealand Cities. The Quality of Life Project. Available online: http://www.qualityoflifeproject.govt.nz (accessed on 20 February 2014).
- Pannozzo, L.; Colman, R.; Ayer, N.; Charles, T.; Burbridge, C.; Sawyer, D.; Stiebert, S.; Savelson, A.; Dodds, C. The 2008 Nova Scotia GPI Accounts: Indicators of Genuine Progress GPI Atlantic; GPI Atlantic: Glen Haven, NS, Canada, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ura, K. Explanation of GNH Index. Gross National Happiness. The Centre for Bhutan Studies. Available online: http://www.grossnationalhappiness.com/gnhindex/introductionGNH.aspx#_ftn1 (accessed on 20 February 2014).
- Zhang, S.; Liao, J.; Zhu, Z. A SAS® Macro for Single Imputation. In Proceedings of the Annual Pharmaceutical Industry SAS Users Group, Atlanta, GA, USA, 1–4 June 2008.
- USDA. Rural-Urban Continuum Codes: Documentation. USDA Economic Research Services. Available online: http://www.ers.usda.gov/data-products/rural-urban-continuum-codes/documentation.aspx#.Ufpo49LVCfU (accessed on 20 February 2014).
- US Census Bureau. Household Income Inequality within U.S. Counties: 2006–2010 American Community Survey Briefs; ACSBR/10-18; US Census Bureau: Suitland, MD, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- OECD. Compendium of OECD Well-Being Indicators. Paris, France. Available online: http://www.oecd.org/document/28/0,3746,en.2649.201185.47916764.1.1.1,00.html (accessed on 20 February 2014).
- Smith, L.M.; Case, J.L.; Harwell, L.C.; Smith, H.M.; Summers, J.K. Development of relative importance values as contribution weights for evaluating human wellbeing: An ecosystem services example. Hum. Ecol. 2013, 41, 631–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tampa’s Well-Being: A Demonstration of a Human Well-Being Index. Available online: http://www.epa.gov/ged/tbes/tampaswellbeing.html (accessed on 11 June 2014).
- Social Science Research Council. About Human Development. In Measure of America. Available online: http://www.measureofamerica.org/human-development/ (accessed on 3 December 2013).
- Sustainable Society Foundation. Sustainable Society Index. In Sustainable Society Index—Your Compass to Sustainability. Available online: http://www.ssfindex.com/about-ssf/ (accessed on 2 December 2013).
- Summers, J.K.; Smith, L.M.; Case, J.; Linthurst, R.A. A review of the elements of human wellbeing with an emphasis on the contributions of ecosystem services. AMBIO 2012, 41, 327–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summers, J.K.; Smith, L.M. The role of social and intergenerational equity in making changes in human well-being sustainable. AMBIO 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Summers, J.K.; Smith, L.M.; Harwell, L.C.; Case, J.L.; Wade, C.M.; Straub, K.R.; Smith, H.M. An Index of Human Well-Being for the U.S.: A TRIO Approach. Sustainability 2014, 6, 3915-3935. https://doi.org/10.3390/su6063915
Summers JK, Smith LM, Harwell LC, Case JL, Wade CM, Straub KR, Smith HM. An Index of Human Well-Being for the U.S.: A TRIO Approach. Sustainability. 2014; 6(6):3915-3935. https://doi.org/10.3390/su6063915
Chicago/Turabian StyleSummers, J. Kevin, Lisa M. Smith, Linda C. Harwell, Jason L. Case, Christina M. Wade, Kendra R. Straub, and Heather M. Smith. 2014. "An Index of Human Well-Being for the U.S.: A TRIO Approach" Sustainability 6, no. 6: 3915-3935. https://doi.org/10.3390/su6063915
APA StyleSummers, J. K., Smith, L. M., Harwell, L. C., Case, J. L., Wade, C. M., Straub, K. R., & Smith, H. M. (2014). An Index of Human Well-Being for the U.S.: A TRIO Approach. Sustainability, 6(6), 3915-3935. https://doi.org/10.3390/su6063915





