Abstract
The resilience of cities in response to natural disasters and long-term climate change has emerged as a focus of academic and policy attention. In particular, how to understand the interconnectedness of urban and natural systems is a key issue. This paper introduces an urban model that can be used to evaluate city resilience outcomes under different policy scenarios. The model is the Wellington Integrated Land Use-Transport-Environment Model (WILUTE). It considers the city (i.e., Wellington) as a complex system characterized by interactions between a variety of internal urban processes (social, economic and physical) and the natural environment. It is focused on exploring the dynamic relations between human activities (the geographic distribution of housing and employment, infrastructure layout, traffic flows and energy consumption), environmental effects (carbon emissions, influences on local natural and ecological systems) and potential natural disasters (e.g., inundation due to sea level rise and storm events) faced under different policy scenarios. The model gives insights that are potentially useful for policy to enhance the city’s resilience, by modelling outcomes, such as the potential for reduction in transportation energy use, and changes in the vulnerability of the city’s housing stock and transport system to sea level rise.
1. Introduction
Today, more than 95% of the world’s population lives in less than 10% of the Earth’s land area, mainly in cities and towns. The level of urbanization continues to rise, and it is forecast that by 2050, the urban population could be 6.29 billion, which will account for 69% of the total global population [1]. The most important influences of urbanization on the environment are energy use and the related increase in the emission of greenhouse gases, due to changes in land use and urban human activities [2,3]. The human population of the planet has increased four-fold over the last one hundred years, while—in the same time period—material and energy use has increased ten-fold [1]. With increasing urbanization, cities now consume about 75% of total global energy and produce 80% of its greenhouse gases [1].
Cities have become significant players in regard to policies, which are attempting to respond to peak oil and climate change. Recently, these policies have been focused on building resilient cities, which aim to enhance a city’s ability to respond to a natural resource shortage and the recognition of the human impact on climate change [4]. Resilient cities are believed to adapt better to change through adjusting inner systems, for example, by changing their transport-land use system to reduce energy consumption and exposure of the system to potential natural disasters (e.g., sea-level rise). A resilient city reduces its ecological footprint (e.g., energy consumption), while simultaneously improving its quality of life. Resilient city policies are concerned with strengthening a city’s capacity to adapt to shocks, such as natural disasters [5]. Such policies increase the degree of collaboration between urban subsystems (social, environmental-infrastructural, economic and institutional systems), while enhancing the robustness of each subsystem.
In particular, it is vital to build resilient urban futures for coastal cities. Coastal cities play a crucial role in human social and economic development in the world. Most global cities, such as London, New York, Sydney, Amsterdam, Tokyo, Hong Kong and Shanghai, are coastal cities. Thirteen of the world’s 20 megacities are situated along coastlines, and more than two-thirds of the world’s large cities are in coastal areas vulnerable to global warming and rising sea levels. In the 20th century, sea levels rose by an estimated average of 17 cm, and global mean projections for sea level rise between 1990 and 2080 range from 22 cm to 34 cm, according to reports by the IPCC (the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change) [6]. However, a recent research finding showed that sea-level rise was 3.2 ± 0.5 mm per year during the period from 1993 to 2011, which is 60% faster than the best IPCC estimate of 2.0 mm per year for the same period [7]. The sea level rise could range from 37 to 60 cm between 2000 and 2100, according to a high model scenario. The low elevation coastal zone—the continuous area along coastlines that is less than 10 m above sea level—represents 2% of the world’s land area, but contains 10% of its total population and 13% of its urban population [8]. There are 3351 cities in the low elevation coastal zones around the world [8]. Urban areas are most vulnerable to sea level rise, and few coastal cities are likely to be spared by climate change.
A transport system is a precondition for social and economic activities in a city, enabling passenger and goods movements. Transport systems have been attracting the attention of the public, politicians and planners in building resilient cities [9]. One reason for this is that transportation is the fastest growing contributor to global climate change and urban health problems in the past few decades. Global transport emissions contributed an estimated 22% of direct CO2 emissions in 2010, and 75% of global transport emissions were due to road transport [10]. The share is expected to continue growing at a rate of 1.7% per year up to 2030 [11]. In particular, total emissions have increased continuously for passenger transport (an increase of 27% between 1990 and 2004) [12]. Total vehicle miles travelled (VMT) is still growing globally, even though the growth seems to be slowing in several developed countries [13,14]. Motor vehicles can also cause the emissions of other environmentally harmful gases, such as NOx, SO2 and particulate matter [15]; so, abating carbon yields substantial co-benefits. Urban air pollution caused by transport and traffic injuries combined together kill about 2.5 million people every year [16,17]. The other reason why transport systems are important to sustainability and resilience is that transport systems are often criticized for having much less adaptive capacity than other city systems. Once transport infrastructures are built, in particular, airports, ports, railways, highways and main roads, they are hard to change. Transport emissions are affected by many factors in city systems, for example, land-use patterns, planning constraints, city and transport network design, public transit services, parking policies, vehicle and fuel technologies and other factors related to individual travel behaviours [18]. Accordingly, many policies have been used in an attempt to change these systems and reduce transport emissions. However, these policies are still often criticized for their inefficiencies. Apart from the limitations of individual policies, the lack of integration and misalignment between these individual policies is a major reason for the criticisms. Cities are complex systems [19,20]. A systemic solution, which takes all these factors into account, would, in principle, be a more efficient way of reducing emissions from transport [18].
In addition, many policies designed to reduce GHG (Greenhouse Gas) emissions from road transport are focused on vehicle and fuel technology. However, many transportation researchers argue that individual travel behaviour is a critical aspect of sustainable transportation and just as important as technical factors and infrastructure supply. Many empirical studies have already provided evidence for this [21]. Therefore, developing a model based on individuals’ travel behaviour is necessary in order to evaluate GHG emissions reduction policies.
This paper introduces an urban model that can be used to evaluate city resilience outcomes under a range of policy scenarios. The model is the Wellington Integrated Land Use-Transport-Environment Model (WILUTE), which is currently being developed by the New Zealand Centre for Sustainable City, University of Otago. The model is used to consider different policy scenarios and assess resilience. In the model, resilience is measured in three aspects. One is a city’s capacity to reduce energy consumption and GHG emissions, in particular, from transportation changes. Another is the vulnerability of a city’s land use and transport system to sea-level rise. The other is the costs related to reduce the vulnerability to a safe level with a consideration of its financial capacity. If the vulnerability and the costs are too high for its financial capacity, the city has a low resilience. Wellington is a typical small to medium-sized (city region population around 490,000) coastal city. It is the capital of New Zealand, which, with most cities being coastal, is vulnerable to sea-level rise, but resilient in terms of institutional, policy and human capacity. A model based on Wellington is useful in illustrating climate mitigation and resilience policies for other medium-sized coastal cities in New Zealand and in other countries.
The WILUTE model considers the city as a complex system characterized by interactions between a variety of internal urban processes (social, economic and physical) and the natural environment. It is focused on exploring the dynamic relations between human activities (the geographic distribution of housing and employment, infrastructure layout, traffic flows and energy consumption), environmental effects (carbon emissions, influences on local natural and ecological systems) and potential natural disasters (e.g., inundation due to sea level rise and storm events) faced under different policy scenarios. The model gives insights that are potentially useful for policy to enhance the city’s resilience, by modelling key outcomes, such as traffic flows, transport energy consumption, GHG emissions, distribution of houses and commercial areas and traffic links. These key outcomes of modelling are the main factors influencing the changes in a city’s resilience, as indicated by the aspects described above (transportation emissions response, etc.)
2. The City as a System
The city is a complex system characterized by nonlinear behaviour, self-organization and emergent properties [19,20]. It is permeated by uncertainty and discontinuities [22]. The city as a whole is far from equilibrium and is more than the sum of its subsystems. Urban development is a complex process, involving a wide range of activities, actors and policies on a variety of geographical and administrative scales (country, state, regional, municipal and community). The urban change process consists of many dynamic sub-processes, such as economic, social, spatial, cultural and institutional processes. It involves a variety of city activities and sectors. For example, the urban spatial change process involves urban development and redevelopment activities, urban planning and design, household residential location choice, urban governance, transport demand and supply, industrial and commercial firms’ location choice, changes in the technical sophistication of building and transport technology, etc. There is a high level of interaction between these sub-processes (Figure 1).
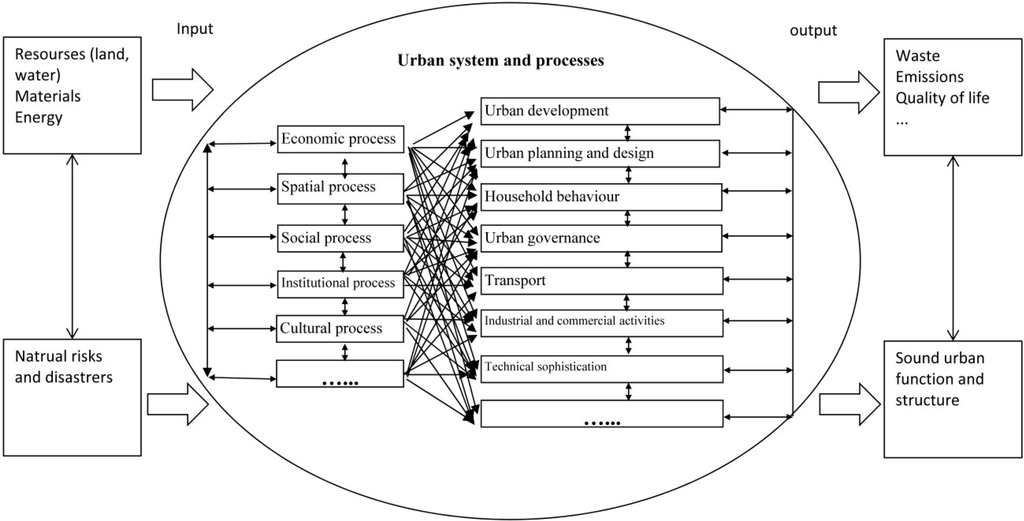
Figure 1.
The urban system and processes.
The urban change process has effects on urban sustainability through impacts on human well-being and ecosystems. As mentioned above, the major output of an urban system is the discharge of waste and emissions into the biosphere. Urban areas, in this sense, are primarily sites of consumption of water, energy, food, materials, land and other natural resources, and the discharges that reflect this consumption have many health effects. For example, urban outdoor air pollution contributes to approximately 5% of trachea, bronchus and lung cancer, 2% of cardiorespiratory mortality and about 1% of respiratory infections in the world in 2001 [23].
While the urban change process is too complex and organic to be fully optimized, the process can be reorganized and improved, for example, to reduce the discharge of waste and emissions into the biosphere and the consequent impacts on well-being. There are two strategies that are usually used to reduce the negative effects of urban development on emissions according to the ‘city as system’ theory. One strategy is to increase resource efficiency of the city system by means, such as enhancing motor vehicle engine technology or fuel to reduce resource use or waste and emissions. For example, electrical vehicles can reduce petrol consumption and, thus, reduce GHG emissions. The other strategy is managing or reorganizing the interaction between various urban sectors to minimise resource consumption, waste or emissions under a given sector’s technical conditions. For example, rather than motor vehicle efficiency being the focus, access or communication might be improved. The latter strategy involves the strengthening of the urban system using various policies, for example, land use planning, transport planning, increasing density at urban sub-centres, etc. A typical measure is increasing density and land use mix to reduce VMT (vehicle miles travelled) and, thus, reduce energy consumption and GHG emissions. This way of reorganizing a city system aims to optimise urban processes through redistributing activity within the land use and transport systems. It is focused on improving the sustainability and resilience of a city.
Resilience is allied to, but distinguishable from, sustainability. In both cases, meanings are clearer when the context is specific. For example, resilience can mean, in an engineering sense, the ability of a system to return to an equilibrium or steady-state after a disturbance [24]. In this sense, a city’s resilience is determined by its recovery from disturbance, its capacity to rebound [5]. A city’s vulnerability to natural hazards and disasters depends on both the magnitude of hazards and the city’s internal systems. To reduce the vulnerability of a city to hazards is often seen as one of the main goals of building a resilient city.
Ecological resilience is a broader concept and refers to the magnitude of the disturbance that can be absorbed before the system changes its structure [24]. A city system’s resilience in this sense is determined by its ability to persist and adapt to a new environment; a city’s resilience reflects its ability to remain within given ecological thresholds, either in the existing environment or in the new environment. A variant on this concept is socio-ecological resilience, which focuses on the changing nature of systems over time, with or without an external disturbance, and taking into account social processes [25,26]. Here, changes in resilience reflect the evolution of a city system. As its systems are strengthened, a city has a stronger ability to resist or adapt to new disturbances, for instance, natural disasters [25,27]. In this perspective, urban resilience is conceived of as the ability of a complex social-ecological system to adapt and, when necessary, transform in response to stresses and strains [28]. Resilient city policies help a city to be in a state of evolutionary resilience.
Effective and resilient urban transportation is a combined result of many effective sub-processes: for example, adaptable land use and an adaptable and diverse transport network respond to social processes (changes in income, ethnicity, lifestyle), economic processes (industrial and commercial development, oil price changes, the pricing of parking) and institutional processes (governance, urban planning, transport planning, road pricing). The association between land use and transport has been widely studied (see Handy, [29]; Crane, [30]; Stead and Marshall, [31]; Litman, [32]; Ewing and Cervero [21]). Most empirical studies find that changes in land use can result in changes in travel demand and, thus, induce changes in transport infrastructure systems. Transport infrastructures and traffic characteristics (congestion) affect location accessibility, which is a major factor influencing land use. When time is taken into account, the interactions between land use and transport become more complex. Wegener [33] summarised the land use-transport system as eight subsystems characterised in terms of time: transport networks and land use often have very slow changes; buildings of workplace and housing have slow changes; employment and population caused by economic development have fast change; and goods transport and passenger travel have immediate change.
In the field of transport, many studies have found that land use policies or transport planning do reduce the costs of transport and GHG emissions from transport. For example, Rodier and colleagues [34] found that more intensive or denser land use can yield a reduction of ~10% in US urban transport activity without reducing accessibility. Ewing and colleagues [35] estimated that shifting 60% of new growth to compact patterns would save 85 million metric tons of CO2 annually by 2030 in the USA. A recent study by Grazi and colleagues [36] shows a potential for changes in urban form to reduce average travel distance by 10% (25% when increasing density to its maximum degree), which, in turn, would lead to an 11% (31% under maximum density) reduction in GHG emissions.
For environment and planning research, system models have been widely used by researchers to simulate dynamics of the urban system and to evaluate the social and environmental effects of the urban system changes (see a review by [37]). System models are based on systems thinking, which considers individual and separate processes of a city as a connected whole. However, research about urban modelling is still being challenged by a diversity of methods, metrics, indicators and data. A proper estimation of uncertainty of a system is another challenge to the development of a system model. An urban system and its relationship with natural systems tend to be even more complex and uncertain, because of climate change and related unpredictable natural changes. This calls for new modelling tools and algorithms that can take into account phenomena, such as climate change. Recently, the topic has been attracting increasing attention from researchers, as the resilience of cities in response to natural disasters and long-term climate change has emerged as a focus of city policies [4,38].
3. Systemic Approach in WILUTE
3.1. Climate Adaptation and Mitigation in Wellington
The model is based on Wellington, a fairly compact city core confined by natural topographical features, in the centre of a city region that has sprawled significantly in recent decades. Sea levels in New Zealand rose by 17 cm last century, and they have risen on average 1.7 mm/year over the last 40 years. The city’s harbour has experienced an average rise in sea level of about 2 mm per year over the past century. Wellington, like other New Zealand cities, is on the coast and, thus, vulnerable to coastal hazards caused or aggravated by climate change, such as storms and sea-level rise. For example, in Wellington, waves could be 15% higher by 2050 and 30% higher by 2100 [39]. A recent report from the National Institute of Water and Atmospheric Research suggests that Wellington harbour’s relative sea level is tracking towards a 0.8 m rise by the 2090s [40], but that for planning purposes, a range of plausible sea-level rise estimates of up to 2.0 m should be considered.
Building resilient cities in New Zealand requires focusing on both mitigation and adaptation. One focus necessitates significant changes to transportation and land use systems in order to reduce carbon emissions. The other focus requires changes to enhance the city’s capacity to manage impacts of climate change, such as sea-level rise. In regards to mitigation, New Zealand is on track to meeting its Kyoto Protocol commitment for the period 2008–2012, but has achieved this through afforestation, not emission reduction. In fact, emissions have grown sharply since 1990, from 59.1 million tonnes of carbon dioxide equivalent (Mt CO2-e), to 70.6 Mt CO2-e in 2009, an increase of 19.4%. While agriculture was New Zealand’s largest emitting sector in 2009 (32 Mt CO2-e), the growth in emissions is largely attributed to growth in energy emissions, particularly from road transport and electricity generation [41]. New Zealand’s road transport emissions increased by 66% over the period, 1990–2009 [42]. Carbon emissions from transport are becoming an increasing concern for the New Zealand community and an embarrassment for the New Zealand government. In addition, traffic accidents and other traffic pollutants, such as NOx, SO2, other toxic waste, water pollution and noise pollution, are contributing factors in local environmental and public heath challenges [43].
3.2. Main Purpose of WILUTE
The objective of the Wellington Integrated Land Use-Transport-Environment Model (WILUTE) is to establish an archetypal projection and assessment system for land use and transport development in the Wellington Region. It is designed as a platform to test and evaluate transport or land-use policies and their interaction, with respect to transport-related environmental and public health effects. It can also be used to assess and forecast the vulnerability of the transport and land use system to sea-level rise. To do this, the model is designed to, firstly, measure current energy consumption and environmental pollutants arising from the transport system and forecast the effects of transport or land use policy options on energy consumption and environmental pollutants from transportation. Secondly, it is designed to assess the public health benefits from transport policies. Public health effects in relation to transport include traffic accidents on roads, pedestrians’ and cyclists’ exposure to pollutants from road traffic and active travel. According to a report by WHO, transport-related air pollution affects a number of health outcomes, including mortality, nonallergic respiratory morbidity, allergic illness and symptoms (such as asthma), cardiovascular morbidity, cancer, pregnancy, birth outcomes and male fertility. Transport-related air pollution increases the risk of death, particularly from cardiopulmonary causes, and of non-allergic respiratory symptoms and disease.
At the current stage, the WILUTE model is focused on the assessment of the impacts of the transport and land use system on carbon emissions, active travel (cycling and walking) and local residents’ exposure to pollutants from road traffic. In the next stage, the WILUTE model will be used to explore other transport-related air pollution impacts, such as health modelling progresses, and to collect health data. Thirdly, the model will be used to predict how the transport system is exposed to sea-level rise and project first-round socioeconomic outcomes of possible policies responding to sea-level rise.
At present, four key questions are being addressed by the model for the Wellington Region:
- (1)
- How does the existing transport and land use system influence carbon emissions and local air quality in the region?
- (2)
- How might future transport infrastructure (e.g., new light rail, new cycle lanes) change current transport mode choices and promote green transportation?
- (3)
- To what extent are current transport and settlements vulnerable to sea-level rise?
- (4)
- How can the capacity of the transport-land use system to respond to sea-level rise be strengthened in future?
The model measures short-term transport activities (e.g., mode choice, route choice, travel time), long-term transport activities (car ownership, travel distance), long-term transport effects caused by socioeconomic activities (e.g., household location and relocation choice and employment location and relocation choice) and the effects of sea-level rise on transport (transport links, passenger traffic), as well as possible transportation results of policies designed to respond to sea-level rise.
The model analyses land use at different scales: buildings, parcels, neighbourhoods and communities, since policies are usually concerned with issues at multiple geographical levels. At the buildings scale, the model uses information on individual properties, such as location, land area, floor area, age, use, site cover, etc. Parcel data, which includes information on boundary, size, land use and subdivision, are used at the parcels level. At the neighbourhood or community level, the model uses information on local facilities and infrastructure. These scales are interconnected in the analysis at the neighbourhood or community level. For example, information on land use at a community level is aggregated from information on individual parcels, which are, in turn, aggregated from individual building data.
WILUTE addresses four main aspects of urban sustainability: economic sustainability; social sustainability; environmental sustainability; and system sustainability. In the modelling process, WILUTE generates a number of indicators of urban sustainability from the perspective of the land use and transport system. The indicators cover the main aspects of urban sustainability (Figure 2). The indicators of travel costs in time and money and population and employment growth measure economic sustainability. The social sustainability indicators include housing affordability, which is indicated by housing price and the supply of houses in terms of types and locations, the factors influencing the risk of traffic accidents (traffic speed and volumes) and the percentage of walking and cycling. The environmental sustainability indicators include air pollution, energy consumption, CO2 emissions, etc., and people’s exposure to sea-level rise across different income and ethnic groups (environmental equity) and, particularly, their exposure in terms of residential location.
System sustainability is indicated in a stylised way by its financial capacity and the costs (time, resources and social costs) needed by the transport and land use system to recover to a “normal” situation in the event of a natural disaster associated with sea-level rise. These costs include the costs of relocating residents, industries and facilities. The costs also include the investment in new infrastructure to reduce the impacts of sea-level rise, for example, sea walls and new elevated highways in the most vulnerable areas. The assumption is made that these measures indicate the broad magnitude of cost for a likely response strategy; it is acknowledged that other response strategies are possible.
Table 1 shows how these indicators cover both the human and natural systems in a city. The indicators measure two-way interactions between human and natural systems in a city, as emphasised in writing on social-ecological resilience. The ability of a city system to reduce energy consumption from transport and buildings affects natural systems. Conversely, the vulnerability of the transport and land use system to natural hazards, such as sea-level rise, shows the impact of the natural environment on the city.
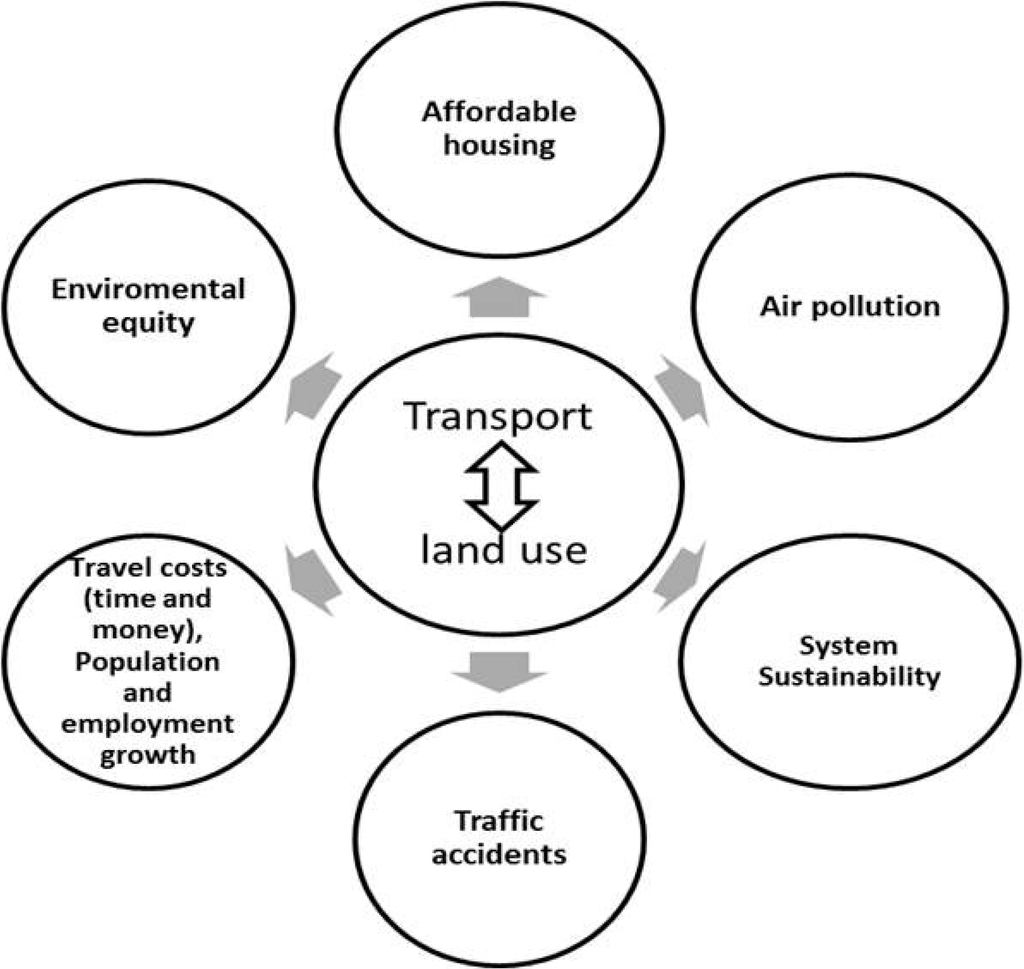
Figure 2.
Urban sustainability indicators.

Table 1.
Human and natural system interactions and resilience indicators.
| Indicators | Natural system | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Air | Land | Environment and other resources | Natural disasters and hazards | ||
| Human system | Transport | Air pollution | City resilience (ability to reduce energy use and emissions; vulnerability of transport and land use to sea-level rise; costs related to reducing the vulnerability) | ||
| Housing | Housing affordability | Environmental equity related to residential location | |||
| Economic growth | Population and employment growth | ||||
3.3. Systemic Methodology in WILUTE
As noted above, city system theory is applied in the WILUTE model. The model treats land use, transport and the environment in an integrated way. The model attempts to take full account of the complex interactions and synergies that occur between urban processes (economic, social and spatial process), including household location choice, firm location choice, transportation choices and land use decisions. In the model, environmental factors (e.g., energy use) are treated as endogenous elements in the transportation distribution and mode choice. The environmental effects of land use-transport polices are measured at different levels, including areas, links and sites.
The core of the WILUTE model is derived from the IELT model [44]. IELT refers to an integrated economy, land use and transport system model. It can be used to forecast regional economic growth and changes in land use and transport. An IELT model has already been validated using data from Beijing. The WILUTE model extends the IELT model in three ways. First, land use is modelled in a more precise way, at a parcel level based on individual properties. Secondly, a health impact sub-model is added. Thirdly, a resilience analysis is included. The architecture of the model consists of six sub-models: a regional economic growth model, growth distribution model, land market model, land use and building distribution model, transport and environmental model and environmental and health impacts model (Figure 3).
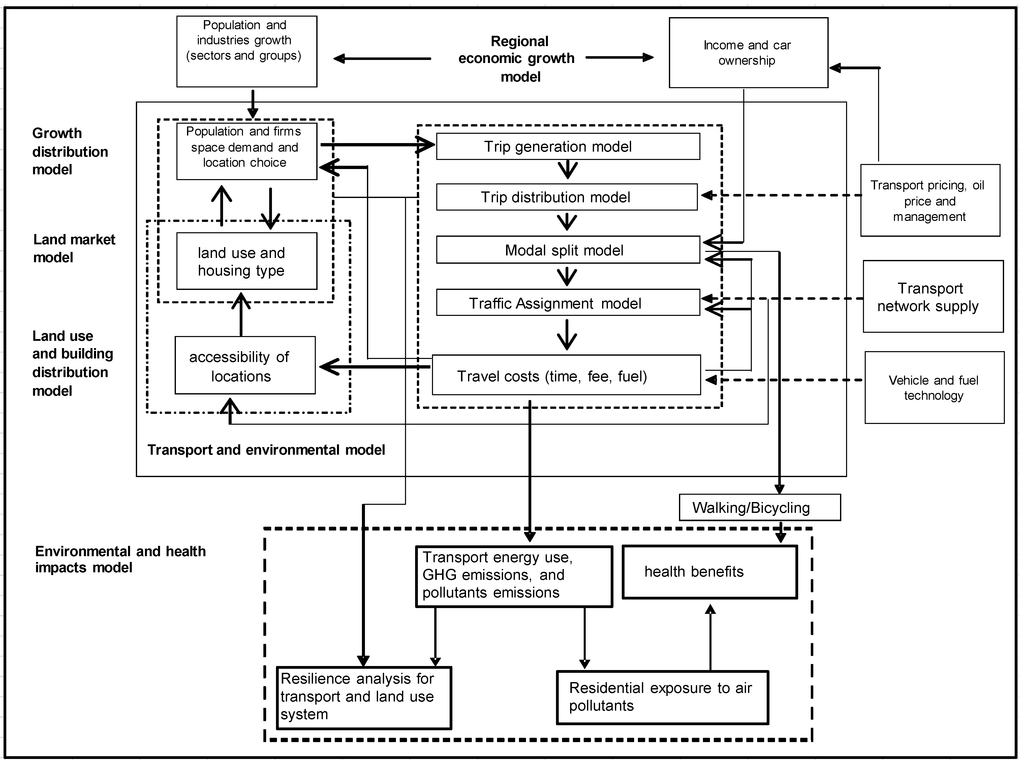
Figure 3.
Architecture of the Wellington Integrated Land Use-Transport-Environment Model (WILUTE).
The regional economic growth model forecasts the growth (or decline) of firms by sector, population by group and the increase of household incomes and car ownership. An input-output function is applied. The growth distribution model distributes the growth (or decline) of population to the local level (land parcel) across the whole region. A multinomial logit (MNL) function is applied for household location choice and employment location choice. The land market model transfers the economic growth into land demand and estimates the land price according to land demand and supply. A dynamic market equilibrium rule is applied in the land market model. The land use and building distribution model distributes space and housing demand to local levels. It is also based on a discrete choice model. The transport and environmental model is derived from the traditional ‘four-step’ transport demand model and a transport energy and carbon dioxide emissions estimation. In the model, travel costs are transferred into area-based accessibilities, which are major factors in the distribution of economic growth and the land market. The air quality and health benefits model utilizes the estimates of trips and transport energy consumption to measure the transport links’ emissions. Transport energy consumption measurement takes into account energy intensity, calculated in litres per 100 km (L/100 km), by different vehicles at different speeds. GHG emissions in transport links are measured from energy consumed in the links. Emission factors are used to quantify GHG emissions per litre of energy consumption. To allow calculation, vehicles are classified in terms of their emission level, such as Euro 3 or 4. The transport links’ emissions are transferred into site- and area-based ambient air quality. Public health impacts are simulated by changes in active travel trips (walking and bicycling) and concentrations of air pollutants.
The resilience analysis aims to evaluate how resilient a city’s transport and land use system is. WILUTE uses three types of indicators to measure city resilience. The first is a city’s capacity to reduce energy consumption from urban transportation in particular. The second is the exposure of the land use and transport system in a city to natural disasters, sea-level rise, in particular. This is measured as the vulnerability of residents, traffic links and traffic flows to sea-level rise. In the analysis, local topography, weather and infrastructure conditions (e.g., flood-proof dikes) are taken into account. The third indicator is the costs related to reducing exposure of the land use and transport system to potential nature disasters to an acceptable level. These costs include the costs of relocation of residents and economic activities and building new infrastructure to reduce the impacts of natural disasters, such as sea walls and dikes, etc.
3.4. The Merits of the System Approach in WILUTE
The WILUTE model has several advantages, compared to the current most widely used integrated transport-land use models in the world, for example, LTLUP (The Integrated Transportation and Land Use Package), IRPUD (The Institute of Spatial Planning of the University of Dortmund), LILT (The Integrated Land-use Transport model), MEPLAN (The Marcial Echenique Plan), TRANUS (Transporte y Uso del Suelo), DELTA (The Land-use/Economic Modelling Package), POLIS (Projective Optimization Land-Use Information System), MASTER (Micro-Analytical Simulation of Transport, Employment and Residence), etc. [33]. Firstly, while most of the previous models integrate land use and transport, and some partly integrate economic development with land use and transport, none integrates environmental effects with economic development, land use and transport. The WILUTE model integrates economic development, land use and the transport system with transportation energy consumption, greenhouse gas emissions, local air quality and public health co-benefits. In particular, the interactions between environmental effects and transport and land use are considered in the WILUTE model in two ways. One is that exposure to traffic pollutants due to housing location and traffic flows can affect residential location choices, which, in turn, shape new patterns of traffic flows. The other is that residents’ consideration of vulnerability of their houses to sea-level rise affects their location choice and traffic flows, which influence new property development and infrastructure investments.
Secondly, in the model, land use and transport is simulated by a discrete choice approach, which is based on utility theory and has advantages in better modelling individuals’ behaviour. Land use modelling runs four calculation processes: the residential location choice model, the firm location choice model, the developer’s development location choice model and the developer’s land use choice model. These calculation processes are based at a census area unit level, which approximates a community neighbourhood, and is aggregated up from individual buildings and, then, from parcels.
Thirdly, as noted above, many empirical studies have found that individual travel behaviour is the key to more sustainable transportation and more important than technical factors and infrastructure supply. The WILUTE model forecasts travel demand in a disaggregated way based on individuals’ travel behaviour data. Therefore, WILUTE has the potential to evaluate GHG emission reduction policies more accurately than previous models, which are based on aggregated travel patterns. Fourthly, the model has a transparent architecture, which can be easily understood by policy-makers and the public. Most of the previous models have been criticised, as they have an architecture that is often seen as “black box” to local government officers [33]. During the development of WILUTE, the model was demonstrated to and discussed with City and Greater Wellington Regional Council officers. Some scenarios were presented, and ongoing discussions are proceeding to utilize and further test the model.
Currently, cellular automata (CA) models are not uncommon. Compared with a CA land use model, the WILUTE model has at least three merits: (1) it achieves a greater integration between land use and transportation, as it can estimate traffic flow, pattern and accessibility and involve traffic outcomes in forecasting the changes in housing location or employment location and, thus, land use; (2) it treats land use as a complex process, which is affected not only by transport accessibility, but also by individual households’ choices of location and travel mode; and (3) it can directly quantify the environmental effects of transport and land use policies through a group of indicators: land consumption, transport energy use, emissions and local air quality impacts. To the extent that a CA model has a comparative advantage in simulating land use changes, the WILUTE model could integrate a CA model within its sub-model of land use and building distribution.
Land use or transport policy options are accessed as input variables relating to the district plans, the urban design framework and “design upgrades”, the urban growth boundary, transport infrastructure provision (e.g., new light rail), public transit service (e.g., service quality), travel demand management (transport pricing, oil price, parking management), vehicle and fuel technology, etc. These options are amenable to modelling with the WILUTE model, which can be used at different geographical scales—from individual building sites, to neighbourhoods, communities and cities.
3.5. The Operation of WILUTE
The WILUTE model is organized as a dynamic GIS (Geography Information System)-based operational model (Figure 4, Figure 5). It runs in annual time steps, progressing through the regional economic growth model, growth distribution model, land market model, land use and building distribution model, transport and environmental model and air quality and health benefits model. The transport model simulates travel for an average working day for transport zones for one year. It also estimates a traffic equilibrium incorporating congestion effects. It provides outputs of accessibility to land uses for the model for the subsequent year. Traffic changes and location changes in housing and employment often do not occur simultaneously. Location changes usually lag behind the traffic changes. The model takes this into account. In the model, the interactions from the transport model to land use are simulated less frequently than both land use and transport model changes. A five-year time lag is used to reflect the features of interaction between transport and land use.
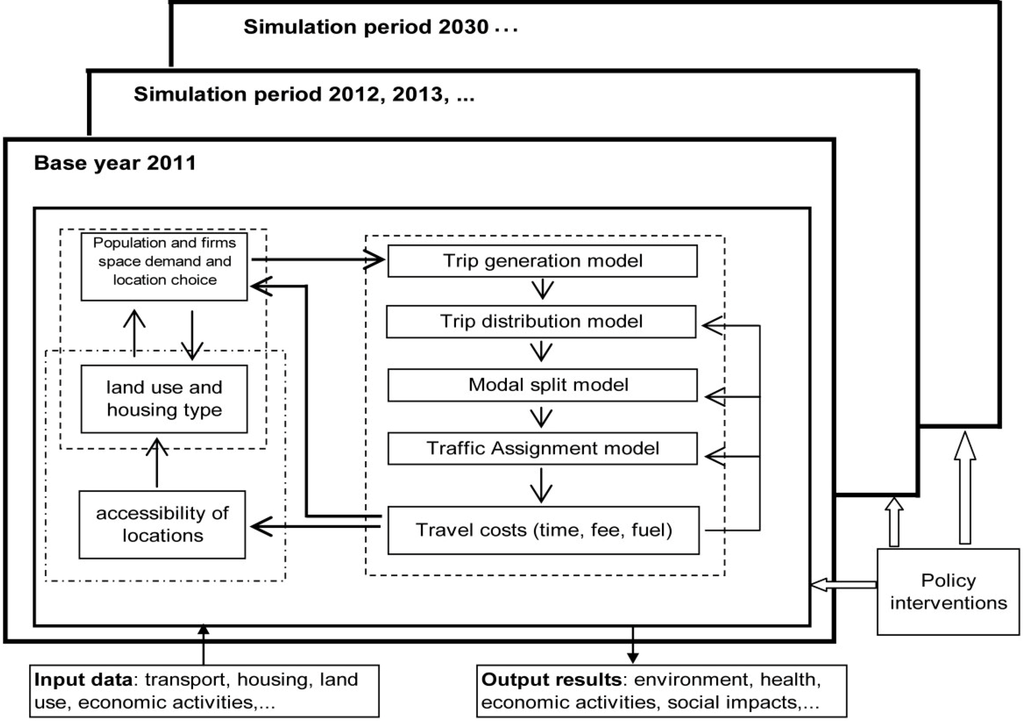
Figure 4.
The operation of WILUTE.
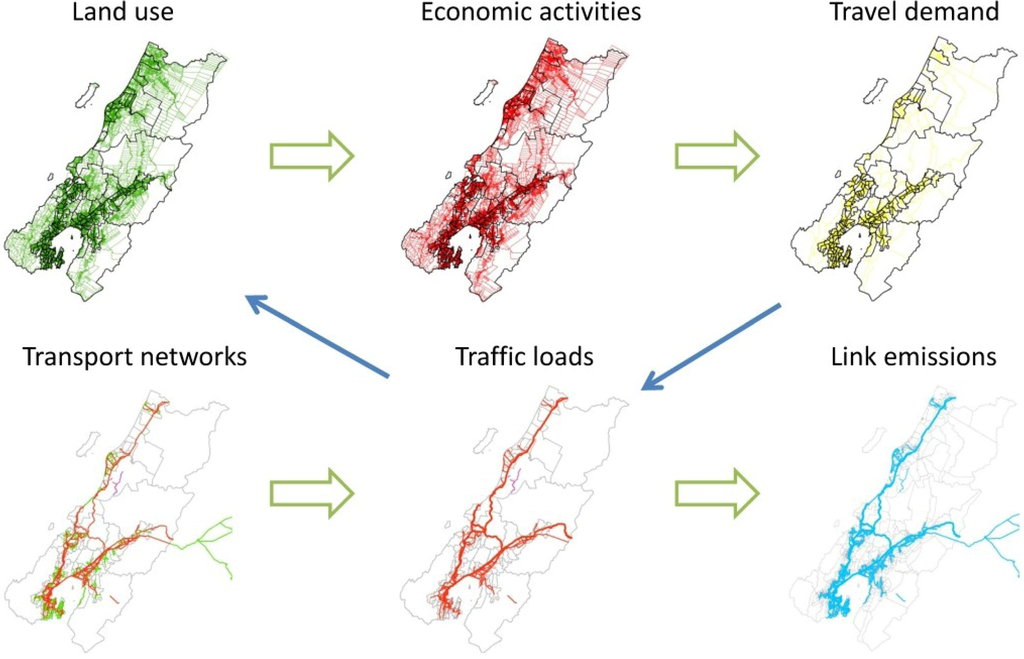
Figure 5.
The GIS data process in WILUTE.
There are two types of input data in the modelling process. One is base year data, including data on transport (traffic survey, transport network, fares, etc.), housing or property, land use, demographics, employment, topographic, etc. The other input comprises policy intervention data, for example, on land use planning, transport planning, road pricing, fuel taxes and behaviour change education—each of which is designed to change personal travel behaviour. The output data show the values of the indicators for urban sustainability that are estimated in the model. The output data also include two important indicators measuring city resilience, as noted earlier. The costs related to reducing vulnerability to climate impacts are not considered in WILUTE at the current stage.
4. Application Examples
4.1. Transport Results of Scenarios
Several transport and land use scenarios were composed to reflect transport and environmental effects of different transport-land use policy scenarios, including intensification scenarios, an urban limit scenario, a transit-oriented development scenario, a transport infrastructure scenario and a fuel and traffic pricing scenario. The environmental effects, in particular, energy consumption and carbon emissions, are estimated in each transport-land use scenario. Meanwhile, several sea-level rise scenarios are estimated for each transport-land use scenario. The base year of the model is 2006, and the scenario final year is 2031. This paper focuses on introducing two intensification scenarios to illustrate the model. One is a high intensification scenario; the other is a low intensification scenario.
In the low intensification scenario; the current pattern of low dwelling and population density are assumed to continue at the business as usual level; for new incremental houses; the floor area: land area ratios were changed to the average value measured in 10 minimum traffic zones (at the 2006 business as usual level).
To create the high intensification scenario, four changes to “business as usual” were made to indicate increases of urban intensification. Firstly, for new incremental developments, the land per person for each of the land use types was reduced to the average of the 10 lowest (non-zero) land areas per person for all traffic zones. This proxies intensification policies, such as limits on land supply and a growth boundary. This change also altered the population densities of each traffic zone.
Secondly, we changed the ratio of houses to apartments from 9:1 in base year 2006 to 1:9 (houses: apartments) in 2031 in high traffic zones. This measures the urban infill development policies and policies of building high density apartments in transit areas.
Thirdly, we changed the land per apartment and land per house to the minimum value in 2006 for all traffic zones. The smaller the section, the greater the intensification.
Finally, for individual parcels, the floor area:land area ratios (FARs) were changed from being the average of the 10 lowest FARs to being the average of the 10 highest FARs. This would simulate individual houses or apartments having more base (floor) area for buildings and leave less space for non-building functions, for example, green yards or open spaces.
In the modelling process, individuals were grouped by age and income into five categories: people of aged 0–10 years old; 11–19 years; 20–64 years with no or low income; 20–64 years with medium or high income; and above 64 years old. Each trip was categorized into five groups based on the purpose of the trip, the purpose of the overall journey and the starting place of the trip. These categories were: home-based work trips, for trips that started at home and had the overall journey purpose of going to work; “home-based non-work” for trips that started at home, but were not for the purpose of getting to work; “non-home based trips home”, for all trips returning home from any other location; “non-home based trips to work”, for trips to work that did not start at the home address; and “non-home trips other”, for all trips that did not go to work and did not start at, or return to, the home address.
Figure 6, Figure 7 show the population and transport results of the low intensification scenario and the high intensification scenario, respectively. The modelling results suggest that the high intensification scenario could save about 20,600 trips per day, compared to the low intensification scenario. The exact energy savings and the reduction of social costs of transport are not reported here. However, it is clear that policies designed to enhance urban intensification would reduce the carbon footprint of the city in the future.
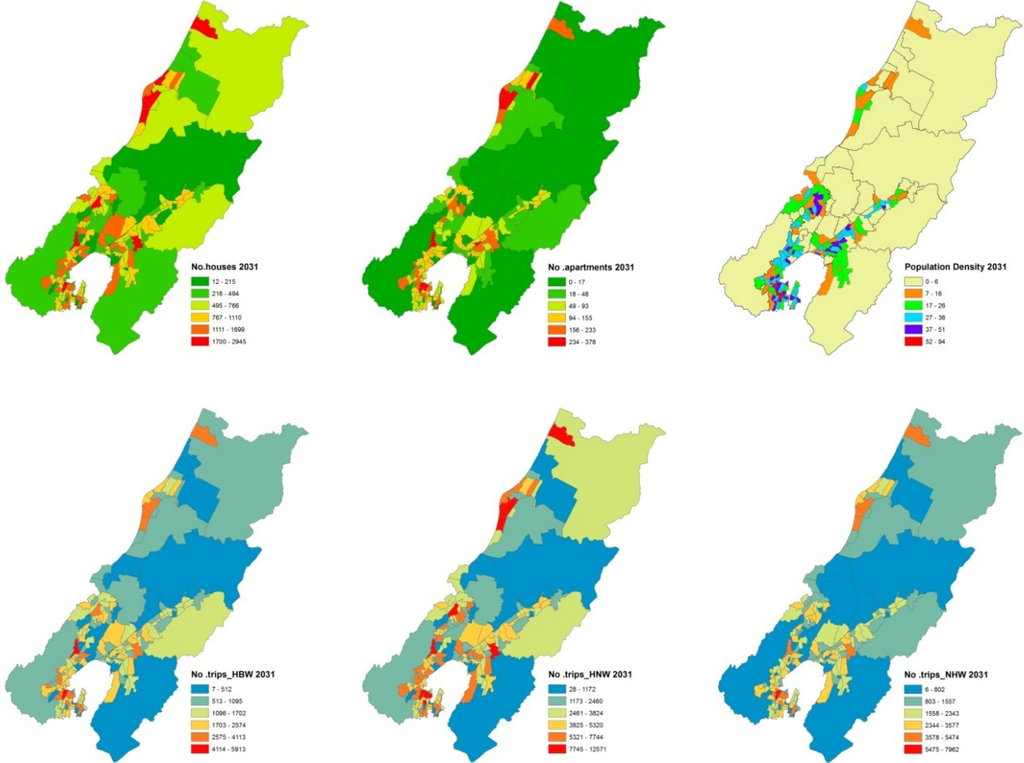
Figure 6.
Population, houses and transport in the low intensification scenario.
4.2. Transport Vulnerability to Sea-Level Rise
The section provides an example of the application of WILUTE for forecasting transport vulnerability to sea-level rise. In the WILUTE model, the vulnerability of people, houses and transport are calculated in different ways. Firstly, vulnerability of people and houses to sea-level rise in an area in a given period (e.g., 2030) is calculated from the distribution of residents, land development and houses through a spatial analysis. The sea-level rise in this given period is measured with consideration of sea-wall and flood protection. Secondly, the vulnerability of transport to sea-level rise is calculated through two indicators. One is the transport network vulnerability to sea-level rise in an area in a given period. It calculates how transport infrastructure is vulnerable to sea-level rise through spatial analysis. The other is the vulnerability of traffic flows by population group. This is calculated from the outcomes of the transport model in WILUTE.
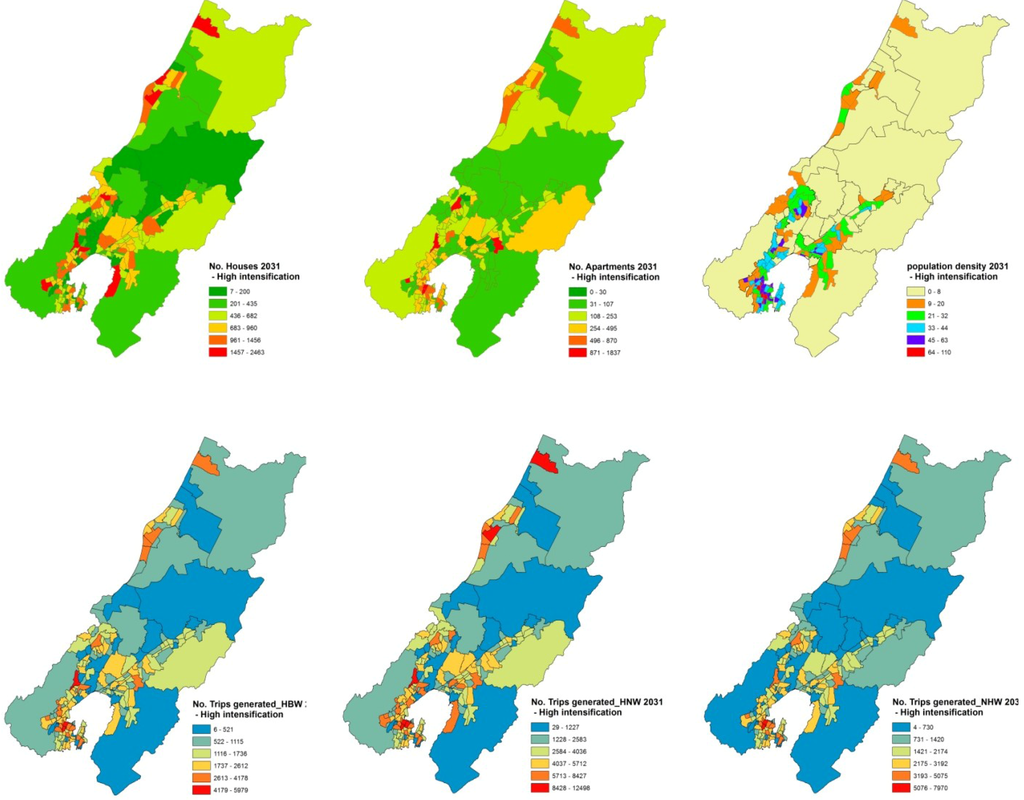
Figure 7.
Population, houses and transport in the high intensification scenario.
Figure 8 shows the vulnerability of traffic links and flows (standard cars per hour) to sea-level rise, based on transport patterns in 2006. Many major roads in the city are at risk of being flooded, depending on the extent of sea-level rise. We underline that the higher sea-level rise scenarios (above 2 m) are extremely unlikely in the projection period to 2031. Wellington International Airport and its major connection roads would be seriously affected if sea level rise were 3 m. The scenario analysis suggests that nearly 11,000 home-based work trips per day would be affected by a three-metre sea-level rise. Over 42,000 residents would need to be evacuated and 8,000 houses would, in theory, be under the sea if sea level rose by 3 m (2006) (Figure 9). Nearly 60,000 residents would need to be evacuated by 2031 if sea level rose by 3 m.
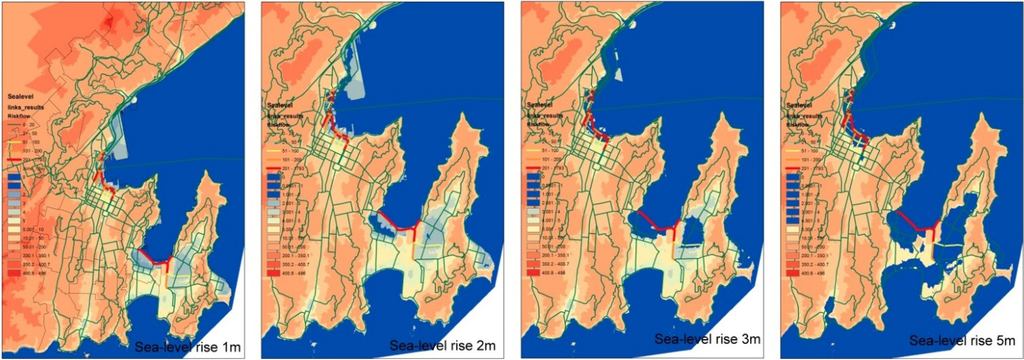
Figure 8.
Vulnerability of traffic links and flows to sea-level rise.
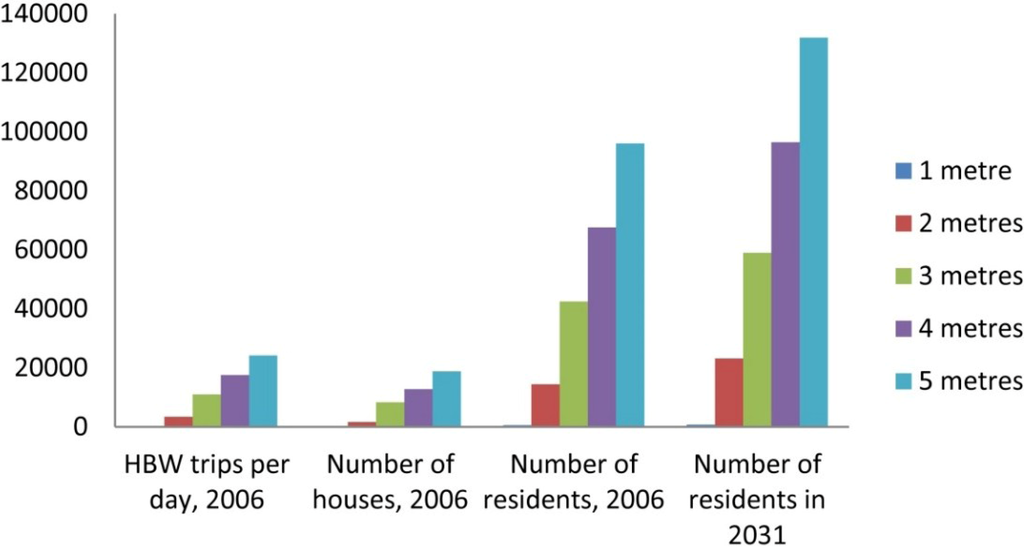
Figure 9.
Vulnerability of people, houses and transport to sea-level rise.
The effects of sea-level rise may not be equitably distributed between places and between different groups in terms of income or ethnicity, since the transport-land use system has high spatial heterogeneity features. Vulnerability in this context is interpreted specifically as living in a dwelling vulnerable to sea-level rise (it excludes, for example, impacts on people’s trips to work or other forms of vulnerability). This underlines the environmental inequity regarding the impacts of climate change and sea-level rise. Figure 10 shows that of those people below 10, on low or no incomes, or over 65 years old, 54% are vulnerable. Only 24% of those on medium to high incomes aged 20–64 are vulnerable. And of those aged 11–19, only 22% are vulnerable.
5. Discussion and Conclusion
Making cities more resilient has become one of the most important goals of urban sustainability in many countries. How to build a resilient city in order to respond to climate change and other possible disasters, such as earthquakes and tsunamis, is of major interest to planners, politicians and the public. For researchers, great efforts have been made to contribute to resilience policies, but there are still major gaps in the existing literature on urban resilience. In particular, we lack a sound method through which to properly evaluate alternative resilience policies.
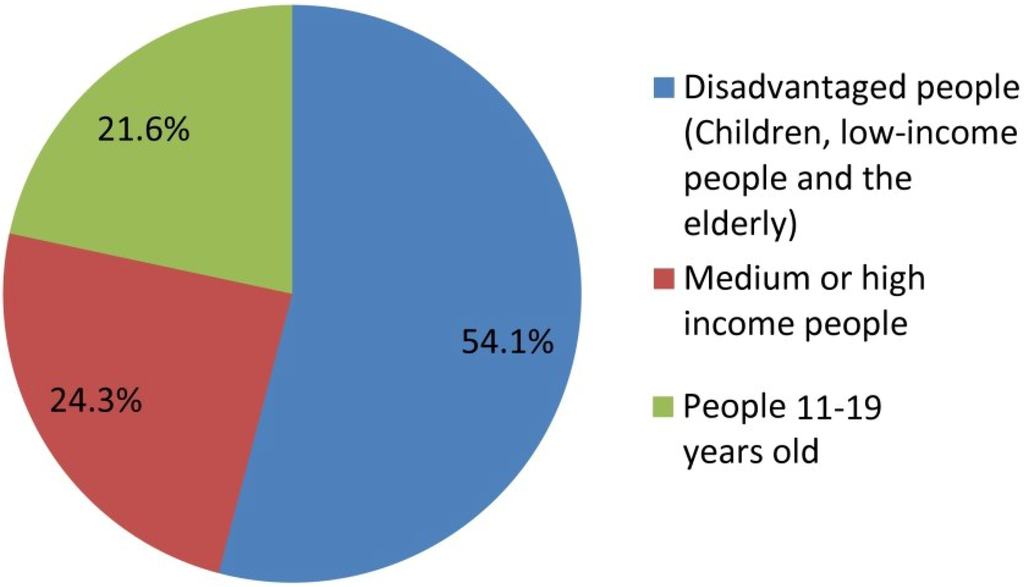
Figure 10.
Vulnerability of different groups to sea-level rise (5 m).
Policies for resilient cities are interpreted here as those strengthening the urban system’s capacity to change in response to economic and natural shocks to the system [26]. The various human-built systems of a city and the natural system are complex. In particular, the complexity of urban systems presents a major challenge for identifying environmental impacts of urban processes and for evaluating the efficiency of policies in reducing environmental and health impacts. Recently, simulation tools have seen significant developments in relation to transport emissions and other health-related effects. The approaches range from operations research (OR) to system dynamics (SD) and discrete-event or discrete-agent system simulation approaches (DS). This paper has introduced an integrated land use-transport-environment model, which can be used to evaluate city resilience outcomes under different policy scenarios. City resilience is measured by its capacity to reduce energy consumption and GHG emissions, the vulnerability of its transport and land use system to sea-level rise and the costs related to reducing the vulnerability to a safe level by taking into account its financial capacity. The model is designed to estimate the complex links between urban economic activities, household and firms’ location choices, transportation and land use, building on accepted theories of urban systems. The design of the model can enhance our existing knowledge of a systemic approach to study urban transport and land use policies and effects on urban sustainability.
Future modelling of urban systems still faces challenges, including the application of models in practice. The approach to treating “dynamic” issues within a model needs further attention. Most models, including the WILUTE model, project the state of the urban system and its effects on the environment in the future, relative to a base year. The future year is seen as a user-specified horizon year for the model. The dynamic features of the urban system are treated as the evolution of the system state from one point in time (the base year) to another (e.g., horizon year). Many models assume that the system equilibrium (within land use system, transport system or both) can be achieved by the evolutionary process of the system.
A model is able to simulate the dynamic processes of the system through appealing to the mathematical conditions for equilibrium to represent the system situation at a given point in time. In fact, urban system dynamics will be much more complicated than we can simulate using such processes across different time-frames. For example, in the WILUTE model, it is assumed that there is a five-year time lag between changes in land use and transport, and a five-year time lag is used to reflect such features of dynamics in the transport and land use system. However, some fast-acting dynamics in transport (e.g., departure time, travel path choice) may not be reflected well. Some very slow dynamics (e.g., urban land use patterns) may only be partly included in a model’s time scale. Combining various dynamic processes within one overall model is still a big challenge to a system approach when it is applied to evaluate urban sustainability.
Secondly, a proper estimation of the uncertainties in any urban system is another challenge to the development of such models. Uncertain interactions between urban processes and between human activities and environmental processes are typical features of the urban system. Uncertainty of an urban system is an on-going topic of discussion of integrated modelling. How to enhance the capacity of a model to respond to uncertainties in urban systems has become a new challenge to systemic modelling. There are various possible ways to approach this. One is to increase the comprehensiveness of the policy alternatives or scenarios. Another is to increase the flexibility of the model regarding the calculation process and data needed.
When it comes to policy practice, individual policies designed to build a resilient city or enhance a city’s resilience need to be integrated; overall resilience is more than the sum of the parts. In the transportation field, transport infrastructure projects, land use planning, housing policies and travel demand policies should be integrated in order to reduce transport-related energy consumption and GHG emissions. Different aspects of city sustainability should be included in resilient city policies. In particular, environmental justice across different income and ethnic groups is often ignored. As Newman and colleagues [4] argued, a resilient city will reduce its ecological footprint, while simultaneously improving the quality of life it provides to the population. Improving social and environmental equity is also one of the objectives of building a resilient city [45,46]. Integrated solutions, which can be explored by models, such as the WILUTE model, need to be addressed in future policy-making to create resilient cities.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- United Nations, World Urbanization Prospects, the 2009 Revision: Highlights; Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division: New York, NY, USA, 2010.
- IPCC (Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change), Climate Change 2001: The Scientific Basis; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2001.
- Pielke, R.A., Sr.; Marlans, G.; Betts, R.A.; Chase, T.N.; Eastman, J.L.; Niles, J.O. The influence of land-use change and landscape dynamics on the climate system: Relevance to climate-change policy beyond the radiative effects of greenhouse gases. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. A 2002, 360, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Newman, P.; Beatley, T.; Boyer, H. Resilient Cities: Responding to Peak Oil and Climate Change; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Vale, B.; Campanella, T.J. The Resilient City: How Modern Cities Recover from Disaster; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC (Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change), Fourth Assessment Report: Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007.
- Rahmstorf, S.; Foster, G.; Cazenave, A. Comparing climate projections to observations up to 2011. Environ. Res. Lett. 2012, 7, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- UN-HABITAT. State of the World’s Cities Report 2008/2009: Harmonious Cities. Available online: http://www.unhabitat.org/pmss/listItemDetails.aspx?publicationID=2562 (accessed on 12 March 2013).
- World Health Organization, Health in the Green Economy: Health Co-Benefits of Climate Change Mitigation-Transport Sector; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011.
- IEA, CO2 Emissions from Fuel Combustion Highlights; International Energy Agency: Paris, France, 2012.
- IEA, World Energy Outlook; International Energy Agency: Paris, France, 2006.
- IEA, Energy Technologies for a Sustainable Future: Transport; International Energy Agency: Paris, France, 2004.
- Puentes, R.; Tomer, A. The Road Less Traveled: An Analysis of Vehicle Miles Traveled Trends in the U.S.; Brookings Institution: Washington, DC, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Newman, P.; Kenworhy, J.R. Peak Car Use: Understanding the Demise of Automobile Dependence. WTPP 2011, 17, 31–42. [Google Scholar]
- Ekins, P. How large a carbon tax is justified by secondary benefits of the CO2 abatement? Resour. Energy Econo. 1996, 18, 161–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization, The Global Burden of Disease: 2004; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008.
- World Health Organization, Global Health Risks: Mortality and Burden of Disease Attributable to Selected Major Risks; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009.
- Banister, D.; Button, K. (Eds.) Transport, the Environment, and Sustainable Development; Spon Press: London, UK, 1993.
- Batty, M. Cities and Complexity: Understanding Cities with Cellular Automata, Agent-Based Models, and Fractals; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Forrester, J.W. Urban Dynamics; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Ewing, R.; Cervero, R. Travel and the Built Environment—A Meta-Analysis. J. Am. Plann. Assoc. 2010, 76, 265–294. [Google Scholar]
- Berkes, F.; Folke, C. Linking Social and Ecological Systems: Management Practices and Social Mechanisms for Building Resilience; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- WHO, World Health Report 2002: Reducing Risk, Promoting Healthy Life; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2002.
- Holling, C.S. Engineering resileince versus ecological resilience. In Engineering Within Ecological Constraints; Schulze, P.C., Ed.; National Academy Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1996; pp. 31–44. [Google Scholar]
- Scheffer, M. Critical Transitions in Nature and Society; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Folke, C.; Carpenter, S.T.; Walker, B.; Scheffer, M.; Chapin, T.; Rockström, J. Resilience thinking: Integrating resilience, adaptability and transformability. Ecol. Soc. 2010, 15, 20–28. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, D.R.; Adger, W.N.; Brown, K. Adaptation to Environmental Change: Contributions of a Resilience Framework. Annu. Rev. Env. Resour. 2007, 32, 395–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, S.R.; Westley, F.; Turner, G. Surrogates for resilience of social-ecological systems. Ecosystems 2005, 8, 941–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handy, S. Critical Assessment of the Literature on the Relationships Among Transportation, Land Use, and Physical Activity; TRB Special Report 2821996; Transportation Research Board: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Crane, R. The Influence of Urban Form on Travel: An Interpretive Review. J. Plan. Lit. 2000, 15, 3–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stead, D.; Marshall, S. The Relationships between Urban Form and Travel Patterns: An International Review and Evaluation. EJTIR 2001, 1, 113–141. [Google Scholar]
- Litman, T. Land Use Impacts on Transport:: How Land Use Factors Affect Travel Behavior; Victoria Transport Policy Institute: Victoria, BC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wegener, M. Overview of land-use transport models. In Handbook of Transport Geography and Spatial Systems; Hensher, D.A., Button, K.J., Eds.; Pergamon/Elsevier Science: Kidlington, UK, 2004; Volume 5, pp. 127–146. [Google Scholar]
- Rodier, C.J.; Johnston, R.A.; Abraham, J.E. Heuristic policy analysis of regional land use, transit and travel pricing scenarios using two urban models. Transport. Res. D 2002, 7, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewing, R.; Bartholomew, K.; Winkelman, S.; Walters, J.; Chen, D. Growing Cooler: The Evidence on Urban Development and Climate Change; Urban Land Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Grazi, F.; van den Bergh, J.C.J.; van Ommeren, J. An Empirical Analysis of Urban Form, Transport, and Global Warming. Energ. J. 2008, 29, 97–122. [Google Scholar]
- Albeverio, S.; Andrey, D.; Giordano, P.; Vancheri, A. (Eds.) The Dynamics of Complex Urban Systems: An Interdisciplinary Approach; Physica-Verlag Heidelberg: New York, NY, USA, 2008.
- Hickman, R.; Ashiru, O.; Banister, D. Transport and climate change: Simulating the options for carbon reduction in London. Transp. Policy 2010, 17, 110–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry for the Environment of New Zealand. Adapting to climate change. Available online: http://www.mfe.govt.nz/issues/climate/adaptation/index.html (accessed on 18 Feburay 2013).
- Bell, R.; Hannah, J. Sea-Level Variability and Trends-Wellington Region: Prepared for GWRC; NIWA: Wellington, New Zealand, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- The Ministry of Environment, New Zealand’s Greenhouse Gas Inventory 1990–2009, Environmental Snapshot; The Ministry of Environment: Wellington, New Zealand, 2011.
- The Ministry of Environment, New Zealand Climate Change; The Ministry of Environment: Wellington, New Zealand, 2006.
- The Ministry of Environment, Health Effects due to Motor Vehicle Air Pollution in New Zealand; The Ministry of Environment: Wellington, New Zealand, 2002.
- Zhao, P. Urban Form and Transport Energy Use in Beijing: A Long-Term Prospective Analysis; Peking University: Beijing, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Boone, C.G. Environmental justice, sustainability and vulnerability. Int. J. Urban Sustain. Dev. 2010, 2, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, J.C.; Budd, W.W.; Lovrich, N.P., Jr. Resilience and sustainability in US urban areas. Environ. Polit. 2011, 20, 566–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).