Risk-Based Identification of Priority Control Factors of Soil Potentially Toxic Elements (PTEs) in Typical Agricultural Areas of Pengzhou, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
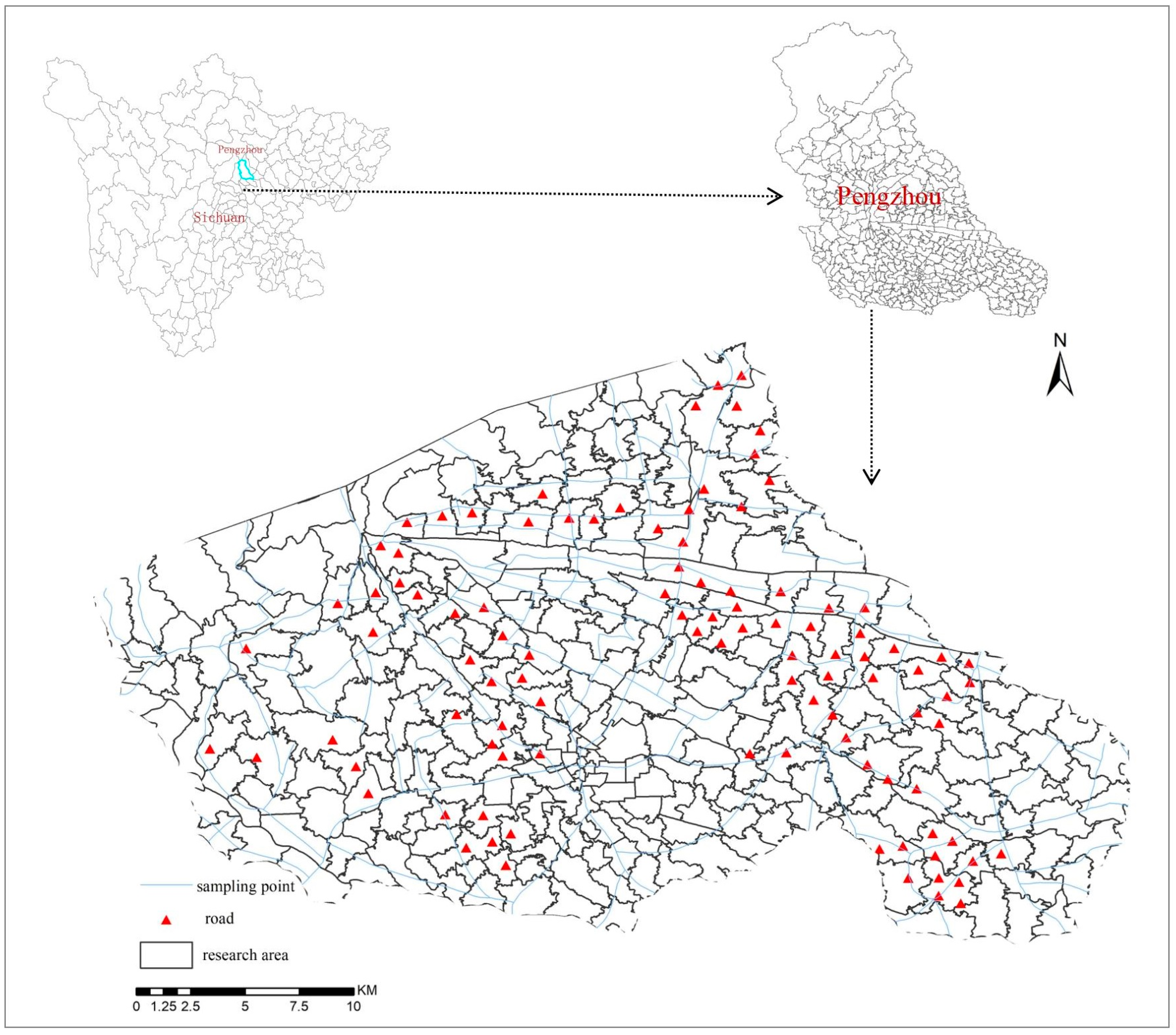
2.1. Study Region and Soil Sampling
2.2. Chemical Analysis, Quality Assurance, and Quality Control
2.3. Source Apportionment and Quantification Model
2.4. Risk Assessment
2.4.1. Potential Ecological Risk Assessment
2.4.2. Human Health Risk Assessment
2.4.3. Specific Source-Oriented Ecological Risk Assessment
2.4.4. Specific Source-Oriented Human Health Risk Assessment
2.5. Data Analysis Tool
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Concentration Characteristics and Contamination Status of Soil PTEs
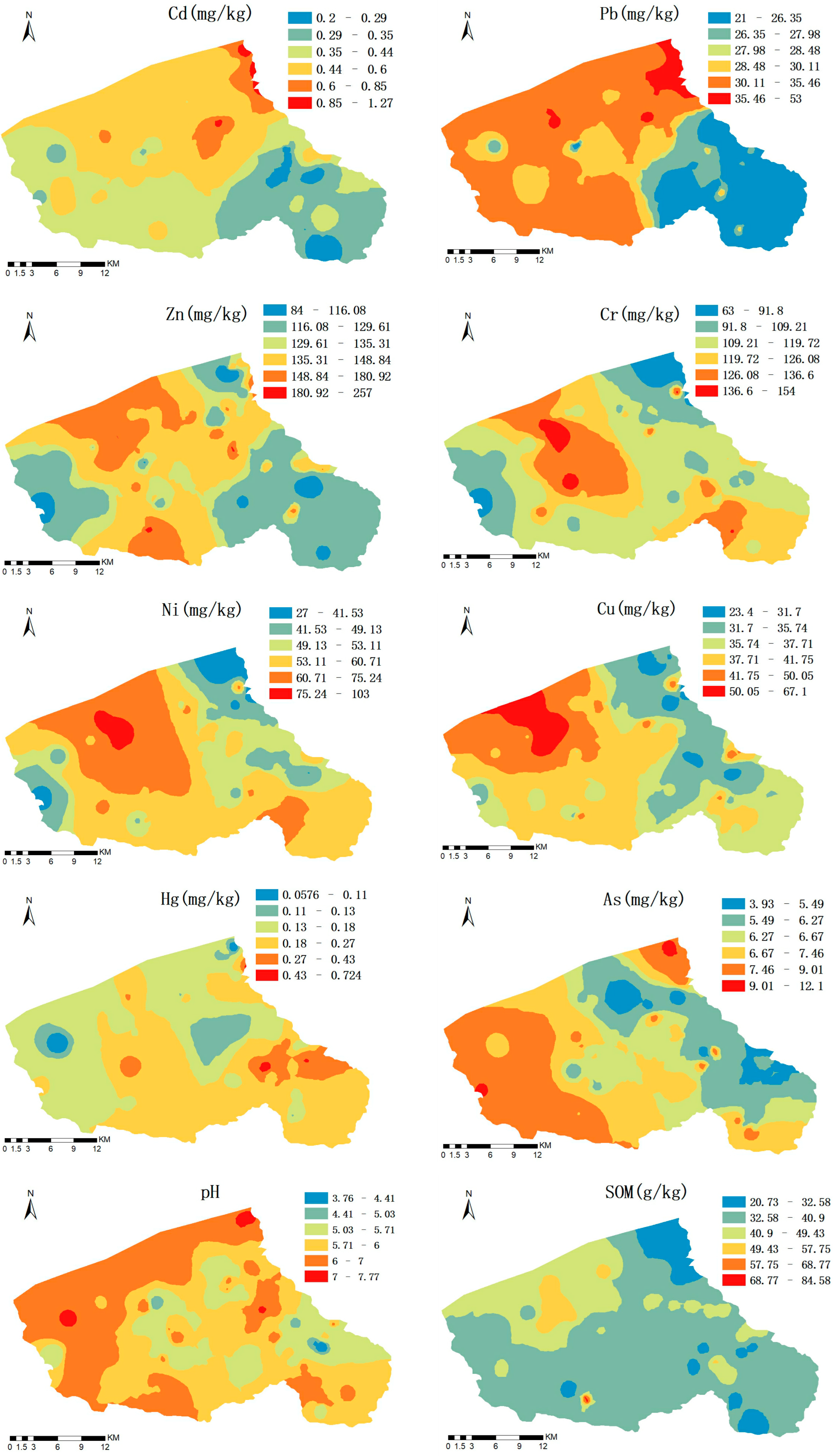
3.2. Spatial Distribution Pattern of Multiple Soil PTEs and Soil Properties
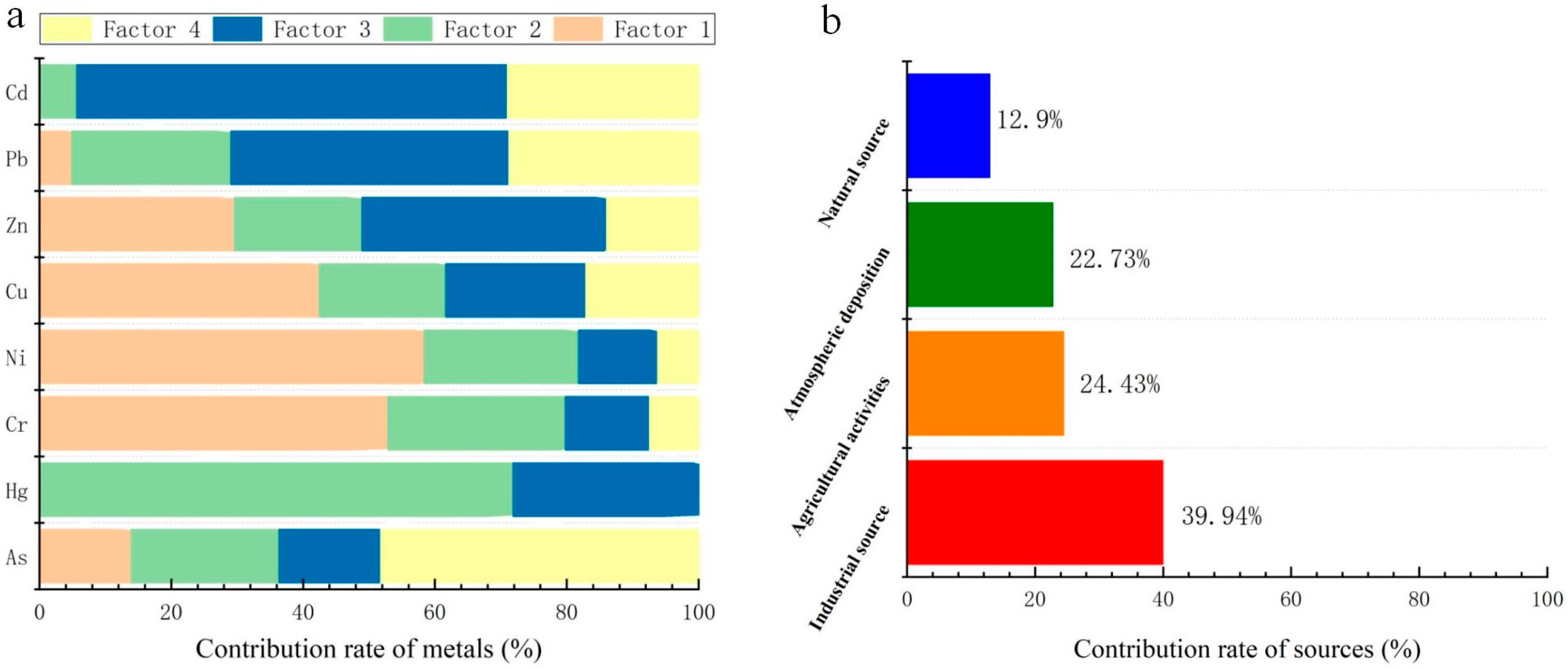
3.3. Pollution Source Identification and Quantification of Soil PTEs
3.3.1. Correlation Analysis Between Soil PTEs and Soil Properties
3.3.2. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
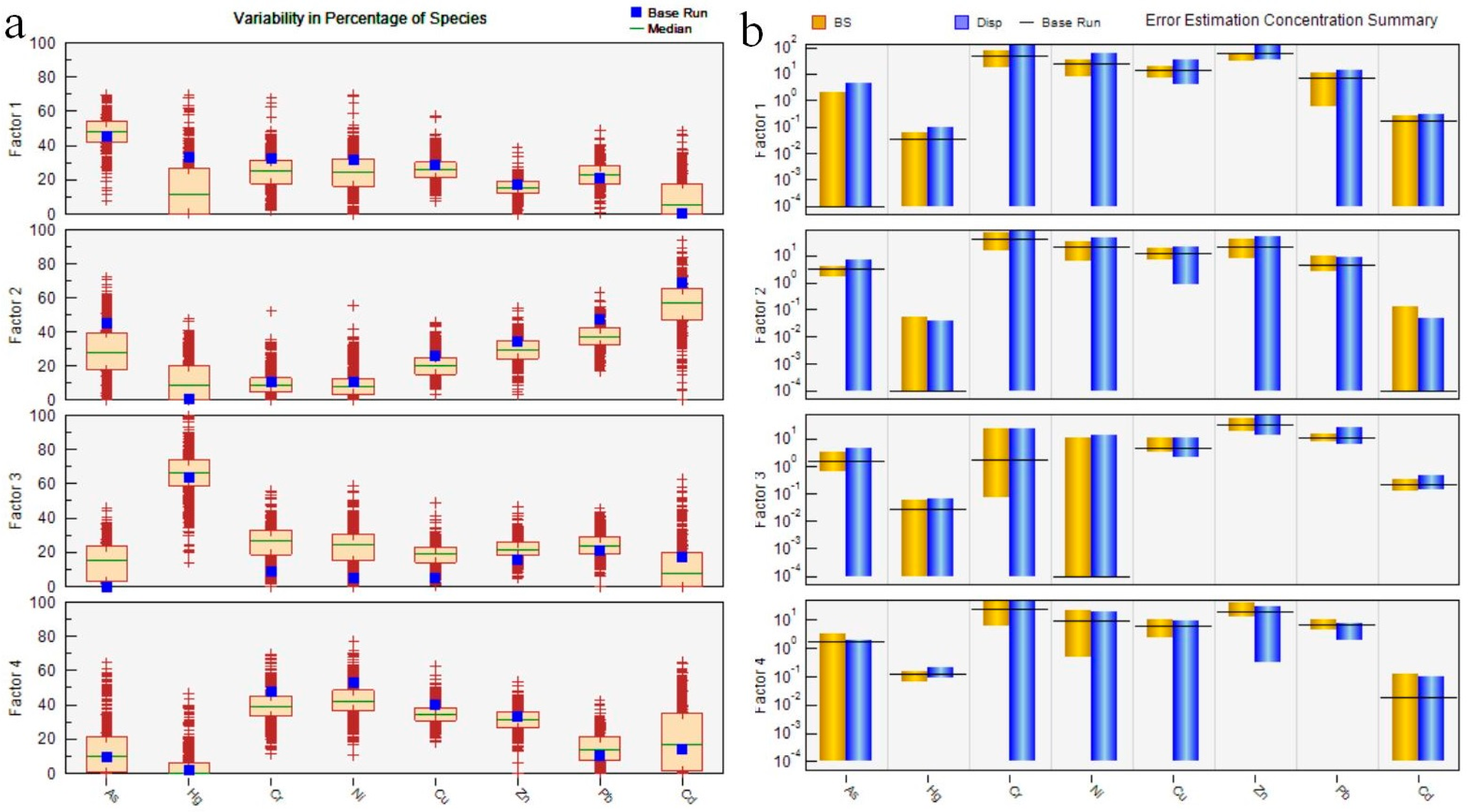
3.3.3. Analysis of Pollution Sources of Soil PTEs by PMF
3.4. Risk Assessment of Soil PTEs
3.4.1. Concentration-Oriented Ecological and Human Health Risks of Soil PTEs
3.4.2. Source-Oriented Ecological and Human Health Risks of Soil PTEs
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Deng, M.; Zhu, Y.; Shao, K.; Zhang, Q.; Ye, G.; Shen, J. Metals source apportionment in farmland soil and the prediction of metal transfer in the soil-rice-human chain. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 260, 110092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Luo, M.; Jiang, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, P.; Niu, Y. Research on the characteristics of heavy metal pollution in lake and reservoir sediments in China based on meta-analysis. Sustainability 2025, 17, 5489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghani, J.; Nawab, J.; Ullah, Z.; Rafiq, N.; Hasan, S.Z.; Khan, S.; Shah, M.; Almutairi, M.H. Multivariate Statistical Methods and GIS-Based Evaluation of Potable Water in Urban Children’s Parks Due to Potentially Toxic Elements Contamination: A Children’s Health Risk Assessment Study in a Developing Country. Sustainability 2023, 15, 13177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, D.; Jia, X.; Wang, L.; McGrath, S.; Zhu, Y.; Hu, Q.; Zhao, F.; Bank, M.S.; O’Connor, D.; Nriagu, J. Global soil pollution by heavy metals threatens agriculture and human health. Science 2025, 388, 316–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Q.; Liu, Y.; Feng, X.; Mao, P.; Sun, A.; Wang, M.; Wang, M. Pollution effect assessment of industrial activities on potentially heavy metal distribution in windowsill dust and surface soil in central China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 759, 144023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Li, W.; Song, S.; Wang, C.C.; Khan, K. Source apportionment and risk assessment of soil heavy metals around a key drinking water source area in northern China: Multivariate statistical analysis approach. Environ. Geochem. Health 2023, 45, 343–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Li, X.; Yang, J.; Zhou, R.; Hong, Z.J.; Liu, C.; Li, S.Y.; Zhao, Y.G.; Fu, D.G.; Pan, Y.; et al. Heavy metal soil speciation, corn accumulation and health risk assessment in acidic red soil farmland in mineral industry area. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2024, 235, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Li, X.; Dong, J.; Zheng, X.; Jiang, Y.; Jin, P.; Kui, X.; Liu, H.; Zhang, X.; Yan, X.Y. Risk assessment based on Cr, Mn, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, Ba, Pb, and Sc contents in soils and blood Pb levels in children: Seasonable variations and Monte Carlo simulations. Soil Environ. Health 2025, 3, 100131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zheng, L.; Xu, L.; Liu, B.; Liu, J.; Wang, X. Identification of dissolved metal contamination of major rivers in the southeastern hilly area, China: Distribution, source apportionment, and health risk assessment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 3908–3922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Wang, M.; Wang, M.; Xiong, Q.; Jia, L.; Ma, W.; Sui, S.B.; Wu, W.; Guo, X.M. Identification of the primary pollution sources and dominant influencing factors of soil heavy metals using a random forest model optimized by genetic algorithm coupled with geodetector. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2025, 290, 117731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.J.; Shen, H.R.; Li, Z.T.; Wang, L.; Wang, F.; Zhao, K.L.; Liu, X.M.; Wendroth, O.; Xu, J.M. Ten-year regional monitoring of soil-rice grain contamination by heavy metals with implications for target remediation and food safety. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 244, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y.; Sun, J.; Xie, Y.; Fan, Z. Do trace metal(loid)s in road soils pose health risks to tourists? A case of a highly-visited national park in China. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 111, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, A.; Gupta, B.S.; Patidar, S.; Hernández-Martínez, J.L.; Martín-Romero, F.; Meza-Figueroa, D. A comprehensive study of source apportionment, spatial distribution, and health risks assessment of heavy metal(loid)s in the surface soils of a semi-arid mining region in Matehuala, Mexico. Environ. Res. 2024, 260, 119619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.H.; Li, Y.; Gu, X.; Xavier-Supe-Tulcan, R.; Yan, L.; Lin, C.; Pan, J. Priority sources identification and risks assessment of heavy metal(loid)s in agricultural soils of a typical antimony mining watershed. J. Environ. Sci. 2024, 147, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proshad, R.; Asha, S.M.A.A.; Abedin, M.A.; Chen, G.; Li, Z.; Zhang, S.; Tan, R.; Lu, Y.N.; Zhang, Z.J.; Zhao, Z.J. Pollution area identification, receptor model-oriented sources and probabilistic health hazards to prioritize control measures for heavy metal management in soil. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 369, 122322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wu, Y.; Sun, J.; Li, X.; Geng, X.; Zhao, M.; Sun, T.; Fan, Z.Q. Health risk assessment of heavy metal(loid)s in park soils of the largest megacity in China by using Monte Carlo simulation coupled with Positive matrix factorization model. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 415, 125629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, Z.; Liu, E.; Yao, D.; Xiao, T.; Ma, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Liu, C.S. Contamination, oral bioaccessibility and human health risk assessment of thallium and other elements in farmland soils around a historic Tl-Hg mining area. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 758, 143577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Hu, B.; Shi, H.; Yi, L.; Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Cheng, J.L.; Huang, M.X.; Yu, W.; Shi, Z. Pollution and risk assessment of potentially toxic elements in soils from industrial and mining sites across China. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 336, 117672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Jiang, D.D.; Ding, D.; Wu, Y.J.; Wei, J.; Kong, L.Y.; Long, T.; Fan, T.T.; Deng, S.P. Ecological-health risks assessment and source apportionment of heavy metals in agricultural soils around a super-sized lead-zinc smelter with a long production history, in China. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 307, 119487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Wang, P.; Wang, M.G.; Liu, J.W.; Gong, L.; Xia, S.B. Spatial distribution, source identification, and risk assessment of heavy metals in riparian soils of the Tibetan plateau. Environ. Res. 2023, 237, 116977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, T.; Cao, B.; Yang, M.; Gan, X.; Chen, L.; Wang, X.; Li, M.; Lu, Y.; Xu, J. Heavy Metals Distribution and Source Identification in Contaminated Agricultural Soils: Isotopic and Multi-Model Analysis. Agronomy 2025, 15, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nour, H.E.; Ramadan, F.; Abdelwahed, N.; Rakha, A. Spatial distribution and contamination of specific heavy metals in the sediment of Bahr Mouse, Egypt. Egypt. J. Chem. 2024, 67, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Guo, W.; Wu, Y. Source-oriented health risk assessment of heavy metals in soil and dust at coal resource-based urban parks in northern China based on bioaccessibilities. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2025, 297, 118252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, P.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Zhu, X.; Sun, S.; Xu, J.L. Quantification of an integrated approach to heavy metal source apportionment and probabilistic health risk assessment in the black soil region of central Jilin Province, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2025, 299, 118358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.K. Analytical Methods for Soil and Agricultural Chemistry; China Agricultural Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2000. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Anaman, R.; Peng, C.; Jiang, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhou, Z.; Guo, Z.; Xiao, X. Identifying sources and transport routes of heavy metals in soil with different land uses around a smelting site by GIS based PCA and PMF. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 823, 153759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control: A sedimentological approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USEPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency). EPA Positive Matrix Factorization (PMF) 5.0 Fundamentals and User Guide; EPA/600/R-14/108 (NTIS PB2015-105147); Norris, G., Duvall, R., Brown, S., Bai, S., Eds.; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Research and Development: Washington, DC, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- USEPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency). EPA ExpoBox: A Toolbox for Exposure Assessors. Exposure Assessment Tools by Routes; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2016. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/expobox/exposure-assessment-tools-routes (accessed on 29 September 2025).
- GB 15618-2018; Soil Environmental Quality Risk Control Standard for Soil Contamination of Agricultural Land. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2018.
- Peng, Y.; Yu, G.I. Assessment of toxic metal pollution on agricultural land in Chengdu city under different anthropogenic pressures based on APCS-MLR modelling. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 165, 112183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.; Wang, L.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Dong, H.; Liu, J. Analysis of spatial differentiation and influencing factors of heavy metal content in soil at the town scale based on geographic detectors. Environ. Sci. 2022, 43, 4566–4577. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, Y.; Chen, W.; Li, J.; Yan, B.; He, H.; Zhang, Y.S. Influencing factors, risk assessment, and source identification of heavy metals in Purple soil in the eastern region of Guang’an city, Sichuan Province, China. Minerals 2024, 14, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Y.; Fan, X.; Wang, L.; Yu, B.; Lei, K.; Zuo, L.; Fan, P.; et al. Source–specific probabilistic risk evaluation of potentially toxic metal(loid)s in fine dust of college campuses based on positive matrix factorization and Monte Carlo simulation. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 347, 119056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.C.; Yang, Y.; Shen, Z.J.; Lin, Z.; Mei, N.; Luo, C.Z.; Wang, Y.M.; Zhang, C.; Wang, D.Y. Identifying heavy metal sources and health risks in soil-vegetable systems of fragmented vegetable fields based on machine learning, positive matrix factorization model and Monte Carlo simulation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 478, 135481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.H.; Wang, J.W.; Chen, Z.W.; Meng, J.; Yin, G.C.; Zhou, Y.Q.; Wang, T. Sources and health risks of heavy metals in soils and vegetables from intensive human intervention areas in South China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 857, 159389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, G.; Zhu, H.; Chen, Z.; Su, C.; He, Z.; Chen, X.; Qiu, J.; Wang, T. Spatial distribution and source apportionment of soil heavy metals in Pearl River Delta, China. Sustainability 2021, 13, 9651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Qu, Y.; Ma, J.; Liu, L.; Wu, Y. Comparison of the concentrations, sources, and distributions of heavy metal(loid)s in agricultural soils of two provinces in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 264, 114688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, F.; Zhao, Z.; Niu, X.; Wang, Z. Integrated pollution analysis, pollution area identification and source apportionment of heavy metal contamination in agricultural soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 465, 133215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Deng, M.; Japenga, J.; Li, T.; Yang, X.; He, Z.L. Heavy metal pollution and health risk assessment of agricultural soils in a typical peri-urban area in southeast China. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 207, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, D.; O’Connor, D.; Nathanail, P.; Tian, L.; Ma, Y. Integrated GIS and multivariate statistical analysis for regional scale assessment of heavy metal soil contamination: A critical review. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231, 1188–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Cao, H.; Du, P.; Ren, J.; Chen, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, H. Source-oriented probabilistic health risk assessment of soil potentially toxic elements in a typical mining city. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 443, 130222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Lu, N.; Wei, Y.; Zhu, D. Relationship between heavy metal content in polluted soil and soil organic matter and pH in mining areas. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 394, 52081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.F.; Zhao, X.L.; Meng, Y.B.; Fei, Y.; Teng, M.; Song, F.H.; Wu, F.C. Identification priority source of soil heavy metals pollution based on source-specific ecological and human health risk analysis in a typical smelting and mining region of South China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 242, 113864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Men, C.; Liu, R.; Xu, L.; Wang, Q.; Guo, L.; Miao, Y.; Shen, Z.Y. Source-specific ecological risk analysis and critical source identification of heavy metals in road dust in Beijing, China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 388, 121763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borah, G.; Deka, H. Crude oil associated heavy metals (HMs) contamination in agricultural land: Understanding risk factors and changes in soil biological properties. Chemosphere 2023, 310, 136890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Dai, H.; Skuza, L.; Xu, J.M.; Shi, J.C.; Wang, Y.J.; Shentu, J.L.; Wei, S. Integrated survey on the heavy metal distribution, sources and risk assessment of soil in a commonly developed industrial area. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 236, 113462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Q.; Wang, F.; Xu, C.; Pan, N.H.; Lin, J.K.; Zhao, R.; Yang, Y.Y.; Luo, H.P. Source apportionment of heavy metals in agricultural soil based on PMF: A case study in Hexi Corridor, northwest China. Chemosphere 2018, 193, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Peng, Z.; Zeng, J.; Li, C.; Tang, L.; Jiang, J.; Luo, X.; Gao, W.; Guo, J.; Shao, B.; et al. Source apportionment and quantitative risk assessment of heavy metals at an abandoned zinc smelting site based on GIS and PMF models. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 336, 117565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Q.; Liu, X.M.; Wu, H.; Tian, M.; Li, R.H.; Sheng, Z.C. Interpretations of Hg anomalous sources in drainage sediments and soils in China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2021, 224, 106711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, L. Concentration, risk assessment, and source identification of heavy metals in surface sediments in Yinghai: A shellfish cultivation zone in Jiaozhou Bay, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 121, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, B.; O’Connor, D.; Huang, Y.; Hou, R.; Cai, L.; Jin, Y.; Wang, P.; Zhang, H. An integrated framework for source apportionment and spatial distribution of mercury in agricultural soil near a primary ore mining site. Chemosphere 2024, 353, 141556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Xiao, J.; Yang, J.; Cai, S.; Liang, M.; Zhou, P. Quantitatively disentangling the geographical impacts of topography on PM2.5 pollution in China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 6309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, B.; Meng, Y.; Hao, J. Mitigation potential of mercury emissions from coal-fired power plants in China. Energy Fuels 2012, 26, 4635–4642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.R.; Zhang, J.R.; Shen, W.J.; Wang, J.; Li, X.Y. Machine learning can identify the sources of heavy metals in agricultural soil: A case study in northern Guangdong Province, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 245, 114107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Chen, Y.; Weng, L.; Ma, J.; Ma, Y.; Li, Y.; Islam, M.S. Comparisons of heavy metal input inventory in agricultural soils in North and South China: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 660, 776–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Feng, C.; Zeng, G.; Gao, X.; Zhong, M.; Li, X.; He, X.Y.; Fang, Y.L. Spatial distribution and source identification of heavy metals in surface soils in a typical coal mine city, Lianyuan, China. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 225, 681–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.W.; Zhang, S.K.; Gao, F.; Chen, Z.; Jiang, J.; Sun, G.X. Spatial distribution, sources apportionment and risk assessment of heavy metals in the Changchun black soil area, China. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2024, 13, 100402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q.; Tian, K.; Li, L.; He, Y.; Zhao, T.; Liu, B.; Wu, Q.M.; Huang, B.; Zhao, L.; Teng, Y. Ecological and human health risk assessment of heavy metals based on their source apportionment in cropland soils around an e-waste dismantling site, Southeast China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 242, 113929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.Y.; He, M.J.; Zhi, Y.Y.; Chang, S.X.; Gu, B.J.; Liu, X.M.; Xu, J.M. An integrated analysis on source-exposure risk of heavy metals in agricultural soils near intense electronic waste recycling activities. Environ. Int. 2019, 133, 105239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.H.; Cai, L.M.; Wen, H.H.; Hu, G.C.; Chen, L.G.; Luo, J. An integrated approach to quantifying ecological and human health risks from different sources of soil heavy metals. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 701, 134466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Yu, R.; Guo, F.; Shen, C.; Liu, Y.; Huang, Y. Source apportionment and risk assessment of soil heavy metals in the Huangshui River Basin using a hybrid model. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 160, 111906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolan, N.; Kumar, M.; Singh, E.; Kumar, A.; Singh, L.; Kumar, S.; Keerthanan, S.; Hoang, S.A.; El-Naggar, A.; Vithanage, M.; et al. Antimony contamination and its risk management in complex environmental settings: A review. Environ. Int. 2022, 158, 106908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, Y.J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, A.N. Quantitative contributions of the major sources of heavy metals in soils to ecosystem and human health risks: A case study of Yulin, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 164, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Ma, Z.; Kuijp, T.J.V.D.; Yuan, Z.; Huang, L. A review of soil heavy metal pollution from mines in China: Pollution and health risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 468–469, 843–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Guan, Q.Y.; Shao, W.Y.; Liu, Z.; Ma, Y.R.; Li, H.C. A joint method to quantify source contributions of toxic metals to ecological and human health risks in oasis farmland soil. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2021, 85, 1600–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Chen, Y.; Yue, X.; Ren, D.; Liu, Y.; Yang, K. Identification and hazard analysis of heavy metal sources in agricultural soils in ancient mining areas: A quantitative method based on the receptor model and risk assessment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 445, 130528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhao, M.; Huang, J.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Cai, B.; Han, Z.W.; Huang, H.H.; Fan, Z.Q. Determination of priority control factors for the management of soil trace metal(loid)s based on source-oriented health risk assessment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 127116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.; Liu, Z.; Tian, Y.; Shi, H.; Fei, Y.; Qi, J.; Mo, L. Research on health risk assessment of heavy metals in soil based on multi-factor source apportionment: A case study in Guangdong Province, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 159991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US EPA. Exposure Factors Handbook, 2011th ed.; EPA/600/R-09/052F; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- US EPA. Supplemental Guidance for Developing Soil Screening Levels for Superfund Sites; OSWER9355.4-24; Office of SOILD Waste and Emergency Response: Washington, DC, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, J.; Yu, M.; Liu, L.; Chen, Y.; Hu, R.; Gong, W. Study on the dietary nutrition intake level in Zhejiang Province. Dis. Surveill. 2006, 21, 670–672. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, S.Q.; Chen, X.M.; Liu, C.Y. Estimates of the exposed dermal surface area of Chinese in view of human health risk assessment. J. Safe. Environ. 2008, 8, 152–156. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Duan, X.L.; Nie, J.; Wang, Z.S. Human Exposure Factors in Health Risk Assessment. J. Environ. Health 2009, 26, 370–373. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China (MEPC). Exposure Factors Handbook of Chinese Population; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Teng, Y.; Lu, S.; Wang, Y.; Wu, J.; Wang, J. Source apportionment and health risk assessment of trace metals in surface soils of Beijing metropolitan, China. Chemosphere 2016, 144, 1002–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, H.; Chen, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Qiao, L.; Men, Y. Heavy metals in rice and garden vegetables and their potential health risks to inhabitants in the vicinity of an industrial zone in Jiangsu, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2010, 22, 1792–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Zhou, Q.; Liu, J.; Liu, W.; Wang, T.; Zhang, Q. High levels of heavy metalsin rice (oryza sativa l) from a typical e-waste recycling area in southeast china and its potential risk to human health. Chemosphere 2008, 71, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawut, R.; Kasim, N.; Maihemuti, B.; Li, H.; Abliz, A.; Abdujappar, A. Pollution characteristics and health risk assessment of heavy metals in the vegetable bases of northwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 642, 864–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Cd (mg kg−1) | As (mg kg−1) | Hg (mg kg−1) | Cr (mg kg−1) | Ni (mg kg−1) | Cu (mg kg−1) | Zn (mg kg−1) | Pb (mg kg−1) | pH | SOM (g kg−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | 0.202 | 3.925 | 0.058 | 63.302 | 26.849 | 23.358 | 83.566 | 20.595 | 3.76 | 20.73 |
| Max | 1.266 | 12.141 | 0.724 | 154.486 | 103.280 | 67.065 | 256.762 | 53.014 | 7.77 | 84.58 |
| Mean | 0.451 | 6.684 | 0.198 | 116.648 | 56.066 | 38.376 | 135.402 | 29.861 | 5.88 | 38.18 |
| Median | 0.431 | 6.525 | 0.168 | 117.821 | 56.053 | 37.359 | 132.003 | 28.940 | 5.97 | 35.66 |
| SD | 0.200 | 1.496 | 0.110 | 19.188 | 13.013 | 7.734 | 27.012 | 5.633 | 0.70 | 9.64 |
| CV | 44.23 | 22.38 | 55.40 | 16.45 | 23.21 | 20.15 | 19.95 | 18.86 | 11.91 | 25.24 |
| Number (RSV) a | 82 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 17 | 6 | 1 | 0 | \ | \ |
| Percentage (RSV) b | 80.39 | 0 | 0 | 2.94 | 16.67 | 5.88 | 0.98 | 0 | \ | \ |
| Number (BGV) c | 102 | 1 | 101 | 96 | 97 | 91 | 101 | 37 | \ | \ |
| Percentage (BGV) d | 100.00 | 0.98 | 99.02 | 94.12 | 95.10 | 89.22 | 99.02 | 36.27 | \ | \ |
| Factor 1 | Factor 2 | Factor 3 | Factor 4 | Total Factors | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-carcinogenic risk (THI) | As | 2.48 × 10−3 | 4.02 × 10−3 | 2.75 × 10−3 | 8.61 × 10−3 | 1.79 × 10−2 |
| Hg | 6.06 × 10−7 | 3.68 × 10−4 | 1.44 × 10−4 | 0.00E+00 | 5.12 × 10−4 | |
| Cr | 3.05 × 10−2 | 1.56 × 10−2 | 7.36 × 10−3 | 4.30 × 10−3 | 5.78 × 10−2 | |
| Ni | 1.31 × 10−3 | 5.27 × 10−4 | 2.68 × 10−4 | 1.39 × 10−4 | 2.24 × 10−3 | |
| Cu | 3.24 × 10−4 | 1.47 × 10−4 | 1.62 × 10−4 | 1.31 × 10−4 | 7.64 × 10−4 | |
| Zn | 1.06 × 10−4 | 7.00 × 10−5 | 1.34 × 10−4 | 5.03 × 10−5 | 3.60 × 10−4 | |
| Pb | 3.35 × 10−4 | 1.67 × 10−3 | 2.90 × 10−3 | 1.98 × 10−3 | 6.89 × 10−3 | |
| Cd | 0.00 × 100 | 2.38 × 10−5 | 2.73 × 10−4 | 1.22 × 10−4 | 4.19 × 10−4 | |
| HI | 3.51 × 10−2 | 2.25 × 10−2 | 1.40 × 10−2 | 1.53 × 10−2 | 8.69 × 10−2 | |
| Carcinogenic risk (CR) | As | 1.12 × 10−6 | 1.82 × 10−6 | 1.24 × 10−6 | 3.89 × 10−6 | 8.08 × 10−6 |
| Cr | 3.93 × 10−5 | 2.01 × 10−5 | 9.46 × 10−6 | 5.53 × 10−6 | 7.43 × 10−5 | |
| Pb | 9.81 × 10−9 | 4.89 × 10−8 | 8.50 × 10−8 | 5.80 × 10−8 | 2.02 × 10−7 | |
| Cd | 0.00 × 100 | 1.18 × 10−7 | 1.35 × 10−6 | 6.01 × 10−7 | 2.07 × 10−6 | |
| TCR | 4.04 × 10−5 | 2.21 × 10−5 | 1.21 × 10−5 | 1.01 × 10−5 | 8.47 × 10−5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
He, M.; Yu, H.; Guo, S.; Huang, D.; Shangguan, Y.; Zeng, X.; Luo, X.; Ouyang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, K.; et al. Risk-Based Identification of Priority Control Factors of Soil Potentially Toxic Elements (PTEs) in Typical Agricultural Areas of Pengzhou, China. Sustainability 2026, 18, 1519. https://doi.org/10.3390/su18031519
He M, Yu H, Guo S, Huang D, Shangguan Y, Zeng X, Luo X, Ouyang Y, Zhou Z, Chen K, et al. Risk-Based Identification of Priority Control Factors of Soil Potentially Toxic Elements (PTEs) in Typical Agricultural Areas of Pengzhou, China. Sustainability. 2026; 18(3):1519. https://doi.org/10.3390/su18031519
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Mingjiang, Hua Yu, Song Guo, Dan Huang, Yuxian Shangguan, Xiangzhong Zeng, Xing Luo, Yiting Ouyang, Zijun Zhou, Kun Chen, and et al. 2026. "Risk-Based Identification of Priority Control Factors of Soil Potentially Toxic Elements (PTEs) in Typical Agricultural Areas of Pengzhou, China" Sustainability 18, no. 3: 1519. https://doi.org/10.3390/su18031519
APA StyleHe, M., Yu, H., Guo, S., Huang, D., Shangguan, Y., Zeng, X., Luo, X., Ouyang, Y., Zhou, Z., Chen, K., & Qin, Y. (2026). Risk-Based Identification of Priority Control Factors of Soil Potentially Toxic Elements (PTEs) in Typical Agricultural Areas of Pengzhou, China. Sustainability, 18(3), 1519. https://doi.org/10.3390/su18031519





