The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Green Innovation Resilience: Evidence from China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review and Research Hypotheses
2.1. Literature Review
2.1.1. Green Innovation Resilience
2.1.2. Artificial Intelligence
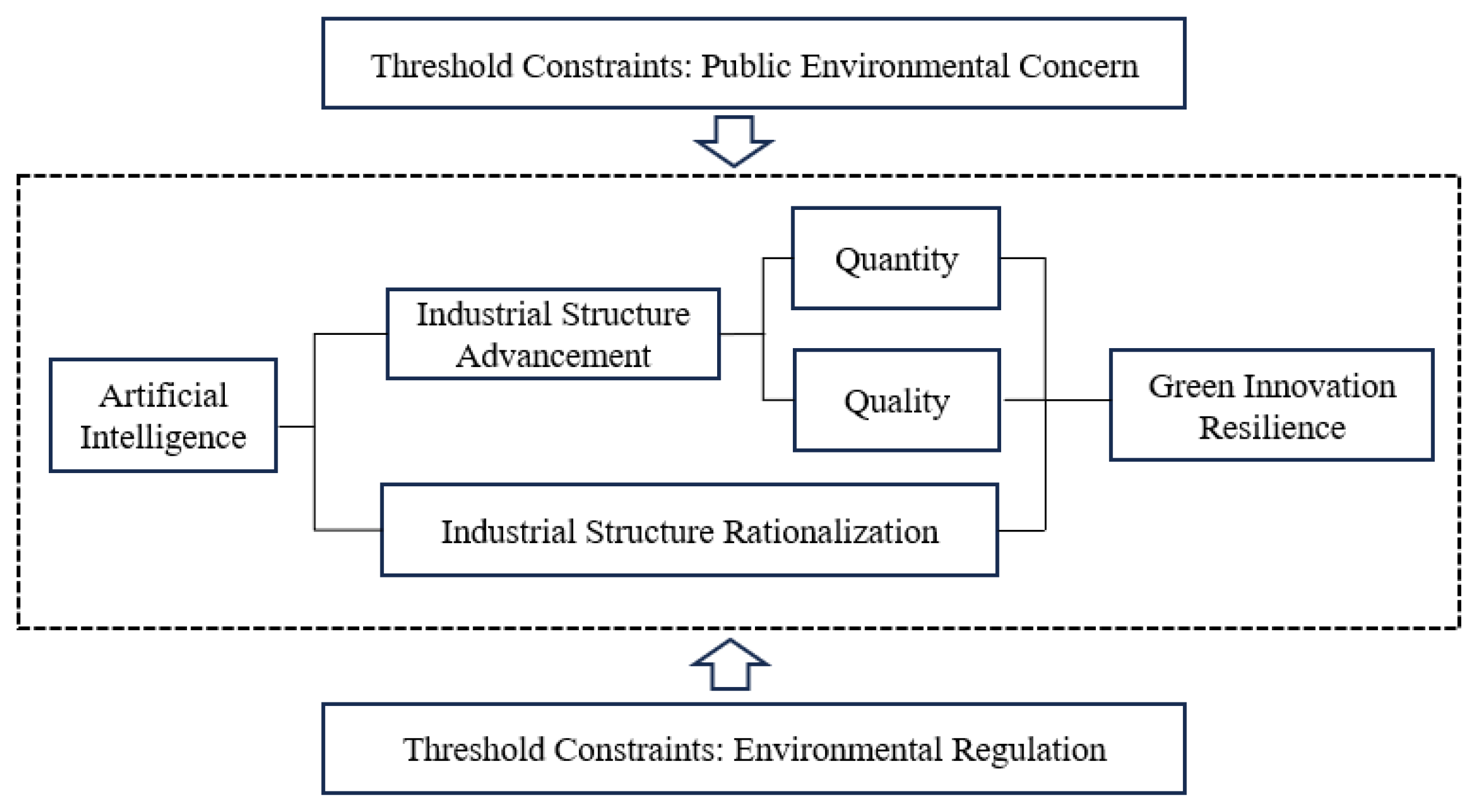
2.2. Research Hypotheses
2.2.1. The Impact of AI on Green Innovation Resilience
2.2.2. The Mediating Role of Industrial Structure Upgrading
2.2.3. Threshold Effect of Public Environmental Concern
2.2.4. Threshold Effect of Environmental Regulation
3. Research Design
3.1. Variable Measurement and Data Source
3.1.1. Explained Variable
- Ri denotes the green innovation resilience of region in year .
- and represent the number of granted green invention patents in region in years and , respectively.
- measures the observed change in granted green invention patents in region from year to year .
- and denote the number of granted green invention patents in the reference region in years and , respectively.
- ∆E captures the change in granted green invention patents in the reference region from year to year , and it is used as the benchmark for predicting the expected patent change for the research object.
3.1.2. Explanatory Variable
3.1.3. Mediating Variables
3.1.4. Threshold Variables
3.1.5. Control Variables
3.2. Selection of Econometric Models
4. Empirical Analysis
4.1. Descriptive Statistical Analysis
4.2. Baseline Regression Analysis
4.2.1. Baseline Regression
4.2.2. Robustness Test
4.3. Mediation Effect Regression Results Analysis
4.3.1. The Mediation Effect of Industrial Structure Advancement
4.3.2. The Mediation Effect of Industrial Structure Rationalization
4.4. Threshold Effect Analysis
4.4.1. Threshold Effect Test
4.4.2. Threshold Regression Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions and Recommendations
6.1. Conclusions
6.2. Recommendations
6.3. Limitations and Future Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| GIR | Green Innovation Resilience |
| R&D | Research and Development |
| ISA | Industrial Structure Advancement |
| ISR | Industrial Structure Rationalization |
| PEC | Public Environmental Concern |
| ER | Environmental Regulation |
| RI | R&D Intensity |
| IL | Industrialization Level |
| HCL | Human Capital Level |
| TML | Technology Market Level |
| TBL | Tax Burden Level |
Appendix A
| Province | DE | Province | DE | Province | DE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing | 0.586 | Zhejiang | 0.442 | Hainan | 0.051 |
| Tianjin | 0.144 | Anhui | 0.208 | Chongqing | 0.165 |
| Hebei | 0.190 | Fujian | 0.206 | Sichuan | 0.308 |
| Shanxi | 0.082 | Jiangxi | 0.167 | Guizhou | 0.095 |
| Inner Mongolia | 0.115 | Shandong | 0.399 | Yunnan | 0.131 |
| Liaoning | 0.150 | Henan | 0.234 | Shaanxi | 0.197 |
| Jilin | 0.087 | Hubei | 0.241 | Gansu | 0.071 |
| Heilongjiang | 0.096 | Hunan | 0.246 | Qinghai | 0.089 |
| Shanghai | 0.312 | Guangdong | 0.817 | Ningxia | 0.074 |
| Jiangsu | 0.610 | Guangxi | 0.125 | Xinjiang | 0.069 |
| Province | DE | Province | DE | Province | DE |
| Beijing | 0.586 | Zhejiang | 0.442 | Hainan | 0.051 |
| Province | DE | Province | DE | Province | DE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing | 0.871 | Zhejiang | 0.496 | Hainan | 0.773 |
| Tianjin | 0.027 | Anhui | 0.761 | Chongqing | 0.540 |
| Hebei | 0.579 | Fujian | 0.754 | Sichuan | 0.418 |
| Shanxi | 0.313 | Jiangxi | 0.000 | Guizhou | 0.202 |
| Inner Mongolia | 0.830 | Shandong | 0.742 | Yunnan | 0.726 |
| Liaoning | 0.579 | Henan | 0.171 | Shaanxi | 0.497 |
| Jilin | 1.000 | Hubei | 0.841 | Gansu | 0.404 |
| Heilongjiang | 0.671 | Hunan | 0.663 | Qinghai | 0.491 |
| Shanghai | 0.863 | Guangdong | 0.520 | Ningxia | 0.584 |
| Jiangsu | 0.504 | Guangxi | 0.548 | Xinjiang | 0.761 |
| Province | DE | Province | DE | Province | DE |
| Beijing | 0.871 | Zhejiang | 0.496 | Hainan | 0.773 |
| Variables | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GIR | 0.254 | 0.482 | 0.162 | 0.528 | 0.425 | 0.539 | 0.349 | 0.543 | 0.510 | 0.571 |
| AI | 0.099 | 0.107 | 0.111 | 0.119 | 0.131 | 0.140 | 0.151 | 0.165 | 0.181 | 0.223 |
| RI | 0.016 | 0.016 | 0.016 | 0.017 | 0.017 | 0.018 | 0.019 | 0.020 | 0.020 | 0.012 |
| IL | 0.345 | 0.337 | 0.317 | 0.303 | 0.305 | 0.303 | 0.298 | 0.288 | 0.308 | 0.319 |
| HCL | 0.019 | 0.019 | 0.020 | 0.020 | 0.020 | 0.021 | 0.022 | 0.024 | 0.025 | 0.027 |
| TML | 0.012 | 0.012 | 0.013 | 0.015 | 0.016 | 0.019 | 0.021 | 0.025 | 0.029 | 0.035 |
| TBL | 0.087 | 0.089 | 0.088 | 0.083 | 0.081 | 0.083 | 0.079 | 0.073 | 0.073 | 0.064 |
| ISA1 | 2.350 | 2.363 | 2.389 | 2.410 | 2.427 | 2.443 | 2.448 | 2.443 | 2.435 | 2.425 |
| ISA2 | 1.125 | 1.172 | 1.300 | 1.404 | 1.459 | 1.517 | 1.577 | 1.619 | 1.512 | 1.486 |
| ISR | 0.186 | 0.174 | 0.155 | 0.144 | 0.140 | 0.133 | 0.120 | 0.100 | 0.109 | 0.128 |
| PEC | 4.436 | 4.714 | 4.688 | 4.689 | 4.821 | 4.775 | 4.628 | 4.619 | 4.638 | 4.617 |
| ER | 51.984 | 62.180 | 41.324 | 46.325 | 30.571 | 23.777 | 22.965 | 15.531 | 12.661 | 9.450 |
References
- BloombergNEF. Clean Energy Investment Trends Q1 2024; Bloomberg Finance LP: London, UK, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.; Zhu, C.; Wang, G. The impact of green innovation resilience on energy efficiency: A perspective based on the development of the digital economy. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 355, 120424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Halbusi, H.; Al-Sulaiti, K.I.; Alalwan, A.A.; Al-Busaidi, A.S. AI capability and green innovation impact on sustainable performance: Moderating role of big data and knowledge management. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2025, 210, 123897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Sahut, J.M. Artificial intelligence, digital finance, and green innovation. Glob. Financ. J. 2025, 64, 101072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, T.; Qiu, Z.; Yang, X.; Li, Z. The impact of artificial intelligence on green technology cycles in China. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2024, 209, 123821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akram, R.; Li, Q.; Srivastava, M.; Zheng, Y.; Irfan, M. Nexus between green technology innovation and climate policy uncertainty: Unleashing the role of artificial intelligence in an emerging economy. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2024, 209, 123820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, F.; Li, J.; Zhang, F.; Sun, J. The impact of artificial intelligence on green innovation efficiency: Moderating role of dynamic capability. Int. Rev. Econ. Financ. 2024, 96, 103649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Zhao, L.; Li, Y.; Wang, W. Can enterprise green technology innovation performance achieve “corner overtaking” by using artificial intelligence? Evidence from Chinese manufacturing enterprises. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2023, 194, 122732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.J.; Zhu, N. Online public opinion attention, digital transformation, and green investment: A deep learning model based on artificial intelligence. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 371, 123294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nepal, R.; Zhao, X.; Dong, K.; Wang, J.; Sharif, A. Can artificial intelligence technology innovation boost energy resilience? The role of green finance. Energy Econ. 2025, 142, 108159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, M.; Zhang, W. Green finance: The catalyst for artificial intelligence and energy efficiency in Chinese urban sustainable development. Energy Econ. 2024, 139, 107883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Mariz, F. Finance with a Purpose: FinTech, Development and Financial Inclusion in the Global Economy; World Scientific: Singapore, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Taghizadeh-Hesary, F.; Mohsin, M. Role of artificial intelligence on green economic development: Joint determinates of natural resources and green total factor productivity. Resour. Policy 2023, 82, 103508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumayli, A.; Mahdi, W.A.; Alamoudi, J.A. Analysis of nanomedicine production via green processing: Modeling and simulation of pharmaceutical solubility using artificial intelligence. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2023, 51, 103587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.C.; Hussain, J.; Abass, Q. An integrated analysis of AI-driven green financing, subsidies, and knowledge to enhance CO2 reduction efficiency. Econ. Anal. Policy 2025, 85, 675–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Xu, S.; Zhang, J. How does industrial intelligence affect carbon intensity in China? Empirical analysis based on Chinese provincial panel data. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 376, 134273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javaid, M.; Haleem, A.; Singh, R.P.; Suman, R.; Gonzalez, E.S. Understanding the adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies in improving environmental sustainability. Sustain. Oper. Comput. 2022, 3, 203–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Zhu, Q. Innovation in emerging economies: Research on the digital economy driving high-quality green development. J. Bus. Res. 2022, 145, 801–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Shao, X.; Liu, W.; Kong, J.; Zuo, G. The impact of the pilot program on industrial structure upgrading in low-carbon cities. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 290, 125868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramezani, J.; Camarinha-Matos, L.M. Approaches for resilience and antifragility in collaborative business ecosystems. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2020, 151, 119846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, B.; Holling, C.S.; Carpenter, S.R.; Kinzig, A. Resilience, adaptability and transformability in social–ecological systems. Ecol. Soc. 2004, 9, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Deng, L.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, H. The impact of digital transformation on green innovation: Novel evidence from firm resilience perspective. Financ. Res. Lett. 2025, 74, 106767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanveer, A.; de Oliveira, R.T.; Rizvi, S. How sector fluidity (knowledge-intensiveness and innovation) shapes startups’ resilience during crises. J. Bus. Ventur. Insights 2024, 22, e00500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chin, J.Y.T.; Wang, X.; Yuen, K.F. Building maritime organisational competitiveness through resource, innovation, and resilience: A resource orchestration approach. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2024, 252, 107092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido-Moreno, A.; Martín-Rojas, R.; García-Morales, V.J. The key role of innovation and organizational resilience in improving business performance: A mixed-methods approach. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2024, 77, 102777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Yu, L. Research on the influence mechanism and characteristics of innovation resilience on high-tech industry innovation. Sci. Technol. Prog. Policy 2022, 39, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gama, F.; Magistretti, S. Artificial intelligence in innovation management: A review of innovation capabilities and a taxonomy of AI applications. J. Prod. Innov. Manag. 2025, 42, 76–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariani, M.M.; Machado, I.; Magrelli, V.; Dwivedi, Y.K. Artificial intelligence in innovation research: A systematic review, conceptual framework, and future research directions. Technovation 2023, 122, 102623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhao, J.; Yang, Y.; Ma, D. Artificial intelligence and green development well-being: Effects and mechanisms in China. Energy Econ. 2025, 141, 108094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y. Intelligent energy management and operation efficiency of electric vehicles based on artificial intelligence algorithms and thermal energy optimization. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2024, 55, 102900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurthy, S.; Adewuyi, O.B.; Luwaca, E.; Ratshitanga, M.; Moodley, P. Artificial intelligence-based forecasting models for integrated energy system management planning: An exploration of the prospects for South Africa. Energy Convers. Manag. X 2024, 24, 100772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladosu, T.L.; Pasupuleti, J.; Kiong, T.S.; Koh, S.P.J.; Yusaf, T. Energy management strategies, control systems, and artificial intelligence-based algorithms development for hydrogen fuel cell-powered vehicles: A review. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 61, 1380–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, T.; Feng, S.; Li, K.; Chang, R.; Huang, R. Unveiling the effects of artificial intelligence and green technology convergence on carbon emissions: An explainable machine learning-based approach. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 373, 123657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Chin, T.; Papa, A.; Pisano, P. Artificial intelligence augmenting human intelligence for manufacturing firms to create green value: Towards a technology adoption perspective. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2025, 213, 124013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, K.; Song, L. Artificial intelligence adoption and corporate green innovation capability. Financ. Res. Lett. 2025, 72, 106480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Shen, F.; Guo, J.; Hu, G.; Song, Y. Can artificial intelligence technology improve companies’ capacity for green innovation? Evidence from listed companies in China. Energy Econ. 2025, 143, 108280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumpeter, J.A. Capitalism, Socialism and Democracy; Routledge: London, UK, 1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Zhu, C. Do national high-tech zones promote the transformation and upgrading of China’s industrial structure? China Ind. Econ. 2018, 8, 60–77. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holling, C.S. Resilience and Stability of Ecological Systems; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Han, Q.; Yu, S. Industrial intelligence and industrial structure change: Effect and mechanism. Int. Rev. Econ. Financ. 2024, 93, 1494–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhai, Y. Can the application of artificial intelligence in industry cut China’s industrial carbon intensity? Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 79571–79586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, P.C.; Laurell, C.; Ots, M.; Sandström, C. Digital innovation and the effects of artificial intelligence on firms’ research and development: Automation or augmentation, exploration or exploitation? Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2022, 179, 121636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Jie, W.; He, H.; Alsubih, M.; Arnone, G.; Makhmudov, S. From resources to resilience: How green innovation, fintech and natural resources shape sustainability in OECD countries. Resour. Policy 2024, 91, 104856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Yuan, W.; Jiang, J.; Ma, T.; Zhu, S. Asymmetric effects of industrial structure rationalization on carbon emissions: Evidence from thirty Chinese provinces. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 428, 139347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, T.; Zhang, D.; Huang, C.; Zhang, H.; Dai, N.; Song, Y.; Chen, H. Artificial intelligence in sustainable energy industry: Status quo, challenges and opportunities. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 289, 125834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Yang, Q.; Pu, Y.; Taghizadeh-Hesary, F. Employing artificial intelligence and enhancing resource efficiency to achieve carbon neutrality. Resour. Policy 2024, 88, 104510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Li, J.; Zhao, Z.; Boamah, V.; Lansana, D.D. The influence of industrial structure transformation on urban resilience based on 110 prefecture-level cities in the Yangtze River. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 96, 104621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, M.R.; Carvalho, L.C. AI-driven participatory environmental management: Innovations, applications, and future prospects. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 373, 123864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, A.; Lu, J.; Ren, H.; Wei, J. The role of AI capabilities in environmental management: Evidence from USA firms. Energy Econ. 2024, 134, 107653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Li, S. Artificial intelligence and public environmental concern: Impacts on green innovation transformation in energy-intensive enterprises. Energy Policy 2025, 198, 114469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Yang, L.; Hossain, M.E.; Haseeb, M.; Ran, Q. Unveiling the trajectory of corporate green innovation: The roles of the public attention and government. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 444, 141119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Feng, X.; Tian, L.G.; Tu, Y. Environmental regulation, green technology innovation and enterprise performance. Financ. Res. Lett. 2024, 68, 105983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, Y.; Dong, H.; Cao, H. The effect of digital economy and environmental regulation on green total factor productivity: Evidence from China. Glob. Financ. J. 2024, 62, 101010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wu, T.; Liu, B.; Zhou, M. Can digital transformation enhance corporate ESG performance? The moderating role of dual environmental regulations. Financ. Res. Lett. 2024, 62, 105241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Du, K.; Sun, R.; Wang, T. Can strict environmental regulation reduce firm cost stickiness? Evidence from the new environmental protection law in China. Energy Econ. 2025, 142, 108218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhang, J.; Chen, C. Digital technology innovation and corporate resilience. Glob. Financ. J. 2024, 63, 101042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Liu, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, N.; Li, J. A novel multi-criteria decision making method to evaluate green innovation ecosystem resilience. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2025, 139, 109528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Chen, D.; Xia, N. Green development effects of artificial intelligence: Technological empowerment and structural optimization. Mod. Econ. Sci. 2023, 45, 30–45. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Wang, M.; Li, M. Low-carbon policy and industrial structure upgrading: Based on the perspective of strategic interaction among local governments. Energy Policy 2023, 183, 113794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Ding, H. How public attention drives corporate environmental protection: Effects and channels. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2023, 191, 122486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, P.H.; Wang, X.Q.; Meng, X.R. U-shaped relationship between environmental regulation and the digital transformation of the Chinese coal industry: Mechanism and moderating effects. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 373, 123641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Wang, J. Digital finance and green technology innovation: A dual path test based on market and government. Financ. Res. Lett. 2024, 70, 106283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.; Zhang, X.; Zeng, G.; Cao, Z.; Zhou, S. The spatial distribution and synergistic effect of different innovation activities in Chinese cities: An analysis based on technology, design, and market activities. Appl. Geogr. 2025, 176, 103527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, S.; Wu, K.; Zhai, C.; Li, Y. Environmental protection tax and enterprises’ green technology innovation: Evidence from China. Int. Rev. Econ. Financ. 2024, 96, 103617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtaruzzaman, M.; Banerjee, A.K.; Boubaker, S. Government intervention and green innovation in renewable energy. Energy Econ. 2025, 145, 108185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, B.E. Threshold effects in non-dynamic panels: Estimation, testing, and inference. J. Econom. 1999, 93, 345–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanoie, P.; Laurent-Lucchetti, J.; Johnstone, N.; Ambec, S. Environmental policy, innovation and performance: New insights on the Porter hypothesis. J. Econ. Manag. Strategy 2011, 20, 803–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calel, R.; Dechezleprêtre, A. Environmental policy and directed technological change: Evidence from the European carbon market. Rev. Econ. Stat. 2016, 98, 173–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Gao, Y.; Liu, X. The impact of environmental regulation on industrial structure upgrading: A case study of low carbon city pilot policy. Energy Policy 2025, 197, 114432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Primary Indicator | Secondary Index | Specific Measures |
|---|---|---|
| Intelligent Environmental Foundation | Research Foundation Conditions | Number of Research Projects |
| Number of Legal Entities in Research and Technical Services | ||
| Talent Support Conditions | Urban Employment in Research and Technical Services | |
| Urban Employment in Information Transmission, Software, and Information Technology Services | ||
| Average Number of Employees in High-tech Industries | ||
| Infrastructure Conditions | Internal R&D Funding Expenditure | |
| Regional Average Fiber-optic Cable Length | ||
| Fixed Asset Investment in Information Transmission, Computer Services, and Software | ||
| Intelligent Technology Creation | Knowledge Creation Achievements | Regional Average Number of Published Scientific Papers |
| Number of Invention Patents in Regional Research Institutions | ||
| Material Creation Achievements | Software Business Revenue | |
| Number of High-tech New Product Development Projects | ||
| Intelligent Industry Competitiveness | Business Operation Ability | Average Profit of High-tech Enterprises |
| Ratio of Main Business Revenue to Employees in High-tech Industries | ||
| Capital Operation Ability | Average Investment in High-tech Enterprises | |
| R&D Investment Intensity |
| Variables | Obs | Mean | SD | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GIR | 300 | 0.436 | 0.252 | 0.000 | 1.000 |
| AI | 300 | 0.143 | 0.118 | 0.020 | 0.817 |
| RI | 300 | 0.017 | 0.011 | 0.002 | 0.065 |
| IL | 300 | 0.312 | 0.077 | 0.101 | 0.498 |
| HCL | 300 | 0.022 | 0.006 | 0.009 | 0.044 |
| TML | 300 | 0.020 | 0.031 | 0.001 | 0.191 |
| TBL | 300 | 0.080 | 0.029 | 0.035 | 0.200 |
| ISA1 | 300 | 2.413 | 0.118 | 2.132 | 2.836 |
| ISA2 | 300 | 1.417 | 0.757 | 0.665 | 5.283 |
| ISR | 300 | 0.139 | 0.085 | 0.007 | 0.404 |
| PEC | 300 | 4.660 | 0.398 | 3.154 | 5.372 |
| ER | 300 | 31.677 | 36.204 | 0.624 | 309.837 |
| Variables | Model 1-1 | Model 1-2 |
|---|---|---|
| AI | 0.486 *** (3.09) | |
| RI | −6.479 *** (−3.08) | −9.707 *** (−4.18) |
| IL | −0.187 (−0.88) | −0.320 (−1.50) |
| HCL | 2.028 (0.66) | 4.202 (1.36) |
| TML | 0.986 (1.30) | 0.530 (0.70) |
| TBL | 0.228 (0.36) | 0.771 (1.19) |
| Cons | 0.524 *** (4.70) | 0.470 *** (4.23) |
| Wald | 15.41 | 25.46 |
| p | 0.009 | 0.000 |
| Variables | Instrumental Variables Method | DID | Sample Deletion | Winsorizing | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L.AI | 1.169 *** (47.59) | ||||
| AI | 0.320 ** (2.54) | 0.134 *** (3.46) | 0.394 ** (2.00) | 0.487 *** (3.11) | |
| RI | −0.934 *** (−5.01) | −8.836 *** (−4.12) | −8.021 *** (−3.80) | −7.025 * (−1.73) | −9.882 *** (−4.16) |
| IL | 0.0118 (0.96) | −0.107 (−0.44) | −0.138 (−0.66) | −0.487 * (−1.93) | −0.304 (−1.40) |
| HCL | 0.0119 (0.06) | 1.252 (0.35) | 1.371 (0.46) | 5.612 (1.35) | 4.468 (1.42) |
| TML | 0.252 *** (4.68) | 0.786 (1.09) | 0.975 (1.31) | 2.153 (1.59) | 0.544 (0.69) |
| TBL | −0.007 (−0.15) | 0.677 (0.98) | 0.244 (0.39) | 1.009 (1.10) | 0.808 (1.23) |
| Cons | −0.001 (−0.16) | 0.497 *** (4.04) | 0.523 *** (4.79) | 0.420 *** (2.94) | 0.458 *** (4.03) |
| Wald | 1098.00 | 25.25 | 27.97 | 19.82 | 25.26 |
| p | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.003 | 0.000 |
| Variables | ISA1 | GIR | GIR | ISA2 | GIR | GIR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model 2-1 | Model 2-2 | Model 2-3 | Model 3-1 | Model 3-2 | Model 3-3 | |
| AI | 0.192 *** (5.57) | 0.356 ** (2.18) | 0.539 *** (3.58) | 0.427 *** (2.68) | ||
| ISA1 | 0.852 *** (3.41) | 0.678 *** (2.60) | ||||
| ISA2 | 0.142 ** (2.39) | 0.109 * (1.82) | ||||
| RI | 4.079 *** (8.01) | −11.037 *** (−4.48) | −12.471 *** (−4.93) | 3.896 * (1.75) | −7.538 *** (−3.53) | −10.132 *** (−4.37) |
| IL | −0.247 *** (−5.28) | −0.021 (−0.10) | −0.153 (−0.69) | −5.121 *** (−25.01) | 0.517 (1.43) | 0.239 (0.64) |
| HCL | 2.385 *** (3.53) | 0.727 (0.24) | 2.585 (0.83) | −6.414 ** (−2.17) | 3.278 (1.07) | 4.902 (1.59) |
| TML | 0.505 *** (3.03) | 0.403 (0.53) | 0.187 (0.25) | 10.103 *** (13.85) | −0.516 (−0.53) | −0.573 (−0.59) |
| TBL | 1.262 *** (8.86) | −0.664 (−0.98) | −0.084 (−0.12) | 6.878 *** (11.05) | −0.660 (−0.90) | 0.021 (0.03) |
| Cons | 2.231 *** (91.57) | −1.394 ** (−2.43) | −1.043 * (−1.76) | 2.263 *** (21.25) | 0.195 (1.10) | 0.223 (1.27) |
| Wald | 1194.40 | 27.62 | 32.81 | 2895.43 | 21.39 | 29.06 |
| p | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.002 | 0.000 |
| Variables | Model 4-1 | Model 4-2 | Model 4-3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| ISR | GIR | GIR | |
| AI | −0.311 *** (−7.69) | 0.476 *** (2.77) | |
| ISR | −0.283 (−1.36) | −0.031 (−0.14) | |
| RI | −3.303 *** (−5.52) | −7.997 *** (−3.36) | −9.808 *** (−4.03) |
| IL | 0.307 *** (5.59) | −0.124 (−0.57) | −0.311 (−1.38) |
| HCL | −3.815 *** (−4.80) | 1.342 (0.44) | 4.084 (1.28) |
| TML | 1.197 *** (6.11) | 1.242 (1.59) | 0.567 (0.70) |
| TBL | −0.404 ** (−2.41) | 0.212 (0.34) | 0.759 (1.16) |
| Cons | 0.235 *** (8.21) | 0.580 *** (4.89) | 0.477 *** (3.88) |
| Wald | 263.18 | 17.36 | 25.48 |
| p | 0.000 | 0.008 | 0.001 |
| Variables | Threshold | Threshold Value | F | p | 10% | 5% | 1% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PEC | Single Threshold | 4.600 | 14.96 | 0.022 | 11.861 | 13.363 | 16.534 |
| Double Threshold | 4.404 | 5.41 | 0.586 | 11.419 | 13.340 | 16.845 | |
| ER | Single Threshold | 10.344 | 14.43 | 0.020 | 9.519 | 11.431 | 15.729 |
| Double Threshold | 11.084 | 5.02 | 0.514 | 9.299 | 10.938 | 14.744 |
| Variables | Model 5-1 | Model 5-2 |
|---|---|---|
| PEC | ER | |
| AI < threshold | 1.718 ** (2.20) | 1.267 *** (2.85) |
| AI > threshold | 0.568 (1.42) | 2.077 *** (3.56) |
| RI | −3.967 (−1.04) | −2.479 (−0.64) |
| IL | 0.472 (0.92) | 0.089 (0.18) |
| HCL | 17.484 ** (2.41) | 12.065 * (1.68) |
| TML | 1.607 (0.92) | 0.870 (0.50) |
| TBL | 0.180 (0.10) | 0.157 (0.09) |
| Cons | −0.101 (−0.38) | −0.093 (−0.36) |
| F | 5.60 | 5.71 |
| p | 0.000 | 0.000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Yan, L.; Li, W.; Tan, S.; Liu, X. The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Green Innovation Resilience: Evidence from China. Sustainability 2026, 18, 167. https://doi.org/10.3390/su18010167
Yan L, Li W, Tan S, Liu X. The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Green Innovation Resilience: Evidence from China. Sustainability. 2026; 18(1):167. https://doi.org/10.3390/su18010167
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Le, Wei Li, Shizheng Tan, and Xiaoguang Liu. 2026. "The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Green Innovation Resilience: Evidence from China" Sustainability 18, no. 1: 167. https://doi.org/10.3390/su18010167
APA StyleYan, L., Li, W., Tan, S., & Liu, X. (2026). The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Green Innovation Resilience: Evidence from China. Sustainability, 18(1), 167. https://doi.org/10.3390/su18010167






