Leadership and Sustainable Development in Tabuk’s Nonprofits: A Moderated Mediation of Organizational Commitment and Strategic Planning Capability
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review and Hypotheses
2.1. Organizational Sustainable Development
2.2. Leadership and Organizational Sustainable Development
2.3. Leadership and Organizational Commitment
2.4. Organizational Commitment and Organizational Sustainable Development
2.5. The Mediating Role of Organizational Commitment
2.6. The Moderating Role of Strategic Planning Capability
3. Methodology
3.1. Ethical Approval and Participants
3.2. Measures
3.3. Endogeneity and Fixed Effects Considerations
3.4. Sample Size and Biased Regression Coefficients
4. Results
4.1. Descriptive Statistics and Reliability
4.2. Correlations and Discriminant Validity
4.3. Confirmatory Factor Analysis (CFA)
4.4. Direct Effects Testing (H1–H3)
4.5. Mediation Analysis (H4)
4.6. Moderation and Moderated Mediation Analysis (H5)
4.7. Conditional Indirect Effects and Simple Slopes Analysis
4.8. Simple Slopes Analysis for Interaction Effect
4.9. Model Summary
4.10. Hypothesis Testing Summary
5. Discussion
5.1. Theoretical Implications
5.2. Practical Implications
5.3. Limitations and Future Research
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Montiel, I.; Delgado-Ceballos, J. Defining and Measuring Corporate Sustainability: Are We There Yet? Organ. Environ. 2014, 27, 113–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyllick, T.; Muff, K. Clarifying the Meaning of Sustainable Business: Introducing a Typology from Business-as-Usual to True Business Sustainability. Organ. Environ. 2016, 29, 156–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vision 2030. (2023/2025). Vision 2030 Portal and Annual Report. Available online: https://www.vision2030.gov.sa/media/xi2jlj0y/english_vision2030_annual_report_2023.pdf (accessed on 24 April 2025).
- Bryson, J.M. Strategic Planning for Public and Nonprofit Organizations: A Guide to Strengthening and Sustaining Organizational Achievement; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Dinh, J.E.; Lord, R.G.; Gardner, W.L.; Meuser, J.D.; Liden, R.C.; Hu, J. Leadership theory and research in the new millennium: Current theoretical trends and changing perspectives. Leadersh. Q. 2014, 25, 36–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maak, T.; Pless, N.M.; Voegtlin, C. Business statesman or shareholder advocate? CEO responsible leadership styles and the micro-foundations of political CSR. J. Manag. Stud. 2016, 53, 463–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UN General Assembly. Transforming our world: The 2030 agenda for sustainable development. In Division for Sustainable Development Goals; World Health Organization: New York, NY, USA, 2015; Available online: https://sdgs.un.org/2030agenda (accessed on 24 April 2025).
- Haque, A.; Fernando, M.; Caputi, P. How is responsible leadership related to the three-component model of organizational commitment? Int. J. Product. Perform. Manag. 2021, 70, 1137–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afsar, B.; Umrani, W.A. Transformational leadership and innovative work behavior: The role of motivation to learn, task complexity and innovation climate. Eur. J. Innov. Manag. 2020, 23, 402–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, B.; Walker, R.M.; Monster, J. Does strategic planning improve organizational performance? A meta-analysis. Public Adm. Rev. 2019, 79, 810–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bass, B.M.; Riggio, R.E. Transformational Leadership; Psychology Press: Hove, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, R.E. Strategic Management: A Stakeholder Approach; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano, R. Towards better embedding sustainability into companies’ systems: An analysis of voluntary corporate initiatives. J. Clean. Prod. 2012, 25, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barney, J. Firm resources and sustained competitive advantage. J. Manag. 1991, 17, 99–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teece, D.J.; Pisano, G.; Shuen, A. Dynamic capabilities and strategic management. Strateg. Manag. J. 1997, 18, 509–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiMaggio, P.J.; Powell, W.W. The iron cage revisited: Institutional isomorphism and collective rationality in organizational fields. Am. Sociol. Rev. 1983, 48, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaltegger, S.; Burritt, R.L.; Petersen, H. An Introduction to Corporate Environmental Management, 2nd ed.; Routledge: Oxfordshire, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loviscek, V. Triple bottom line toward a holistic framework for sustainability: A systematic review. Rev. Adm. Contemp. 2020, 25, e200017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eccles, R.G.; Ioannou, I.; Serafeim, G. The Impact of Corporate Sustainability on Organizational Processes and Performance. Manag. Sci. 2014, 60, 2835–2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piwowar-Sulej, K.; Iqbal, Q. Leadership styles and sustainable performance: A systematic literature review. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 382, 134600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y. Sustainable leadership: A literature review and prospects for future research. Front. Psychol. 2022, 13, 1045570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammed, R.Y.M. Sustainability Leadership in Saudi Non-profit Organizations: A Qualitative Insight Governance. Public Adm. Res. 2024, 13, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alnamlah, A.A.; Nalband, N.A. A Study on the Role of Leaders in Achieving Sustainable Competitiveness and Sustainability During Change. Sustainability 2024, 16, 9978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ba, Y.; Nair, S.; Kedia, M. Cross-sector collaboration, nonprofit readiness, and sustainability transitions. Environ. Innov. Soc. Transit. 2024, 53, 100933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King Khalid Foundation. Nonprofit Sector Outlook 2025—Flagship Report Highlights Growth Trajectory of Saudi’s Nonprofit Sector. Available online: https://kkf.org.sa/ (accessed on 24 April 2025).
- Eva, N.; Robin, M.; Sendjaya, S.; Van Dierendonck, D.; Liden, R.C. Servant leadership: A systematic review and call for future research. Leadersh. Q. 2019, 30, 111–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, Q.; Ahmad, N.H. Sustainable development: The colors of sustainable leadership in learning organization. Sustain. Dev. 2021, 29, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smilevski, C. Sustainable leadership and organizational sustainability through organizational change. J. Bus. Paradig. 2017, 2, 1–33. [Google Scholar]
- Paulen, K. The Role of Leadership Within Nonprofits. 2021. Available online: https://digitalcommons.coastal.edu/goal-17-partnerships/2 (accessed on 24 April 2025).
- Abdullah, H.O.; Atshan, N.; Al-Abrrow, H.; Alnoor, A.; Valeri, M.; Erkol Bayram, G. Leadership styles and sustainable organizational energy in family business: Modeling non-compensatory and nonlinear relationships. J. Fam. Bus. Manag. 2023, 13, 1104–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboramadan, M.; Dahleez, K.A. Leadership styles and employees’ work outcomes in nonprofit organizations: The role of work engagement. J. Manag. Dev. 2020, 39, 869–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, C.; Safdar, M.A.; Ahmed, M. Impact of responsible leadership on sustainable performance: A moderated mediation model. Kybernetes 2024, 53, 5263–5284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang’ana, G.A.; Ongeti, W.J.; Chiroma, J.A. Collaborative leadership and performance: Does environmental dynamism matter. Strateg. J. Bus. Change Manag. 2023, 10, 1472–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiatong, W.; Wang, Z.; Alam, M.; Murad, M.; Gul, F.; Gill, S.A. The impact of transformational leadership on affective organizational commitment and job performance: The mediating role of employee engagement. Front. Psychol. 2022, 13, 831060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aunin, J.; Lüde, P.; Sander, I.; Vogel, R.; Wiesner, J. Perceived Ethical Leadership and Follower Outcomes in the Public Sector: The Moderating Effect of Followers’ Need for Autonomy. Public Perform. Manag. Rev. 2024, 47, 986–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahim, M.G.A. Strategic human resource management and public employee retention. Rev. Econ. Political Sci. 2018, 3, 20–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkahtani, A.H. The influence of leadership styles on organizational commitment: The moderating effect of emotional intelligence. Bus. Manag. Stud. 2016, 2, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R. Organizational Commitment in the Nonprofit Sector and the Underlying Impact of Stakeholders and Organizational Support. Voluntas 2022, 33, 538–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saudi Green Initiative. About SGI. Available online: https://www.vision2030.gov.sa/en/explore/projects/saudi-green-initiative (accessed on 24 April 2025).
- Katz, I.M.; Rauvola, R.S.; Rudolph, C.W.; Zacher, H. Employee green behavior: A meta-analysis. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2022, 29, 1146–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, A.F. Introduction to Mediation, Moderation, and Conditional Process Analysis: A Regression-Based Approach; Guilford publications: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Krejcie, R.V.; Morgan, D.W. Determining sample size for research activities. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 1970, 30, 607–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J.F. A Primer on Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM); Sage: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Rupprecht, E.A.; Waldrop, J.S.; Grawitch, M.J. Initial validation of a new measure of leadership. Consult. Psychol. J. Pract. Res. 2013, 65, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na-Nan, K.; Phanniphong, K.; Niangchaem, L.; Ouppara, N. Validation of an organizational sustainable development questionnaire: Exploring dimensions and implications. Sustain. Futures 2024, 7, 100221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mowday, R.T.; Steers, R.M.; Porter, L.W. The measurement of organizational commitment. J. Vocat. Behav. 1979, 14, 224–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydın, E.; Karakulle, İ.; Polat, H. Strategic Plan Perception Scale; A Scale Development Study. Dumlupınar Üniversitesi Sos. Bilim. Derg. 2022, 72, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences; Routledge: Oxfordshire, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]




| Characteristic | Category | Frequency | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Male | 98 | 63.6% |
| Female | 56 | 36.4% | |
| Age (Years) | 25 and less | 45 | 29.2% |
| 26–40 | 71 | 46.1% | |
| 41–55 | 32 | 20.8% | |
| 56 and above | 6 | 3.9% | |
| Education | Secondary School | - | 0% |
| Bachelor’s Degree | 102 | 66.2% | |
| Master’s Degree | 48 | 31.2% | |
| PhD | 4 | 2.6% |
| Variable | Description | Sample Item | Source | No. of Items | Cronbach’s α |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leadership | The extent to which leaders exhibit transformational behaviors. | “My supervisor communicates a compelling vision for the future.” | Rupprecht et al. (2013) [44] | 15 | 0.941 |
| Organizational Sustainable Development | The organization’s capacity to integrate economic, social, and environmental objectives into its core activities. | “The organization encourages employees to share their environmental experiences.” | Na-Nan et al. (2024) [45] | 15 | 0.937 |
| Organizational Commitment | The employee’s emotional attachment to, identification with, and involvement in the organization. | “I am willing to put in a great deal of effort beyond what is normally expected in order to help this organization be successful.” | Mowday et al. (1979) [46] | 10 | 0.926 |
| Strategic Planning Capability | The organization’s ability appling strategic planning in a systematic manner. | “Our organization has a clear and regularly updated strategic plan.” | Aydın et al. (2022) [47] | 10 | 0.953 |
| Construct | No. of Items | Mean | SD | Cronbach’s α | Skewness | Kurtosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leadership | 15 | 4.15 | 0.82 | 0.941 | −0.45 | 0.32 |
| Organizational Commitment | 10 | 4.12 | 0.87 | 0.926 | −0.38 | 0.28 |
| Sustainable Development | 15 | 4.08 | 0.84 | 0.953 | −0.42 | 0.35 |
| Strategic Planning | 10 | 4.18 | 0.79 | 0.937 | −0.41 | 0.31 |
| Variable | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Leadership | 1.00 | |||
| 2. Organizational Commitment | 0.684 ** | 1.00 | ||
| 3. Sustainable Development | 0.716 ** | 0.648 ** | 1.00 | |
| 4. Strategic Planning | 0.623 ** | 0.587 ** | 0.661 ** | 1.00 |
| Model | χ2/df | CFI | TLI | RMSEA | SRMR | AIC | BIC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4-Factor | 2.38 | 0.943 | 0.935 | 0.067 | 0.054 | 8452.3 | 8721.6 |
| 1-Factor | 5.72 | 0.782 | 0.765 | 0.142 | 0.113 | 9214.8 | 9452.1 |
| Difference | −3.34 | +0.161 | +0.170 | −0.075 | −0.059 | −762.5 | −730.5 |
| Hypothesis | Path | β | SE | t- Value | p- Value | 95% CI Lower | 95% CI Upper | Supported |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H1 | Leadership → Sustainable Dev | 0.592 | 0.048 | 12.333 | <0.001 | 0.497 | 0.687 | Yes |
| H2 | Leadership → Org.Comitment | 0.634 | 0.051 | 12.431 | <0.001 | 0.533 | 0.735 | Yes |
| H3 | Org.Commitment → Sust. Dev | 0.308 | 0.058 | 5.310 | <0.001 | 0.193 | 0.423 | Yes |
| Main Relationship | Without Control Variables | With Control Variables | Change in Coefficient (Δβ) | Significance Stability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leadership → Sustainable Development | β = 0.592 | β = 0.587 | −0.005 | Remained significant (p < 0.001) |
| Leadership → Organizational Commitment | β = 0.634 | β = 0.628 | −0.006 | Remained significant (p < 0.001) |
| Commitment → Sustainable Development | β = 0.308 | β = 0.302 | −0.006 | Remained significant (p < 0.001) |
| Strategic Planning → Commitment | β = 0.385 | β = 0.379 | −0.006 | Remained significant (p < 0.001) |
| Effect Type | Path | Effect | Boot SE | Boot LLCI | Boot ULCI | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Direct | Leadership → Sustainable Development | 0.392 | 0.061 | 0.272 | 0.512 | Significant |
| Indirect | Leadership → Commitment → Sust. Dev | 0.195 | 0.042 | 0.118 | 0.283 | Significant |
| Total | Leadership → Sustainable Development | 0.587 | 0.048 | 0.492 | 0.682 | Significant |
| Predictor | β | SE | t-Value | p-Value | LLCI | ULCI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Constant | 4.121 | 0.069 | 59.725 | <0.001 | 3.985 | 4.257 |
| Leadership (X) | 0.427 | 0.062 | 6.887 | <0.001 | 0.305 | 0.549 |
| Strategic Planning (W) | 0.385 | 0.064 | 6.016 | <0.001 | 0.259 | 0.511 |
| X × W (Interaction) | 0.176 | 0.041 | 4.293 | <0.001 | 0.095 | 0.257 |
| R2 | 0.512 | |||||
| F-value | 52.67 | <0.001 |
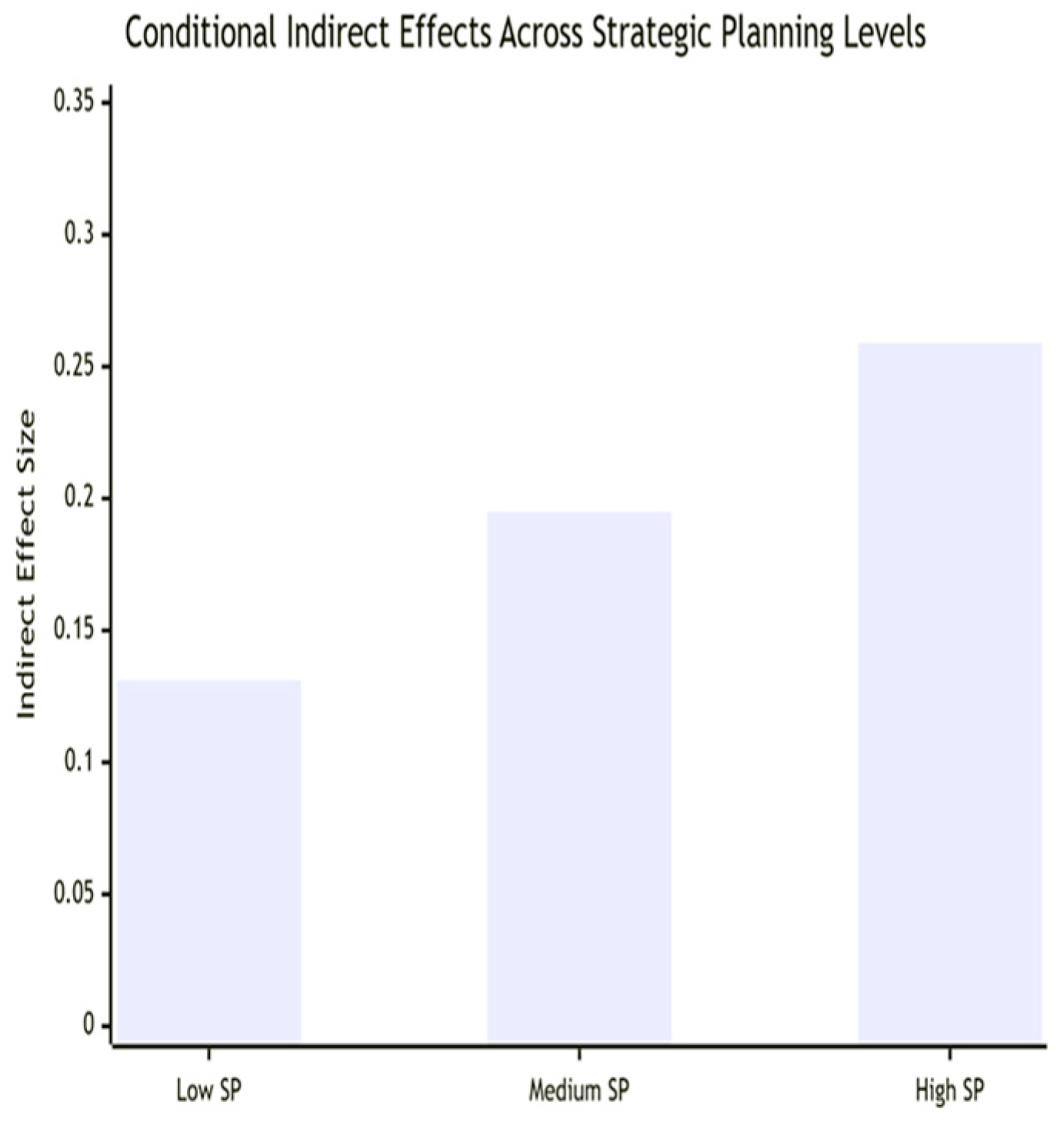
| Strategic Planning Level | Indirect Effect | Boot SE | Boot LLCI | Boot ULCI | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low (Mean − 1SD) | 0.131 | 0.035 | 0.068 | 0.205 | Significant |
| Medium (Mean) | 0.195 | 0.042 | 0.118 | 0.283 | Significant |
| High (Mean + 1SD) | 0.259 | 0.051 | 0.164 | 0.365 | Significant |
| Index of Moderated Mediation | 0.054 | 0.017 | 0.023 | 0.091 | Significant |
| Strategic Planning Level | Simple Slope | SE | t-Value | p-Value | LLCI | ULCI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low (Mean − 1SD) | 0.251 | 0.072 | 3.486 | <0.001 | 0.109 | 0.393 |
| Medium (Mean) | 0.427 | 0.062 | 6.887 | <0.001 | 0.305 | 0.549 |
| High (Mean + 1SD) | 0.603 | 0.075 | 8.040 | <0.001 | 0.455 | 0.751 |
| Component | Value | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Total R2 (Full Model) | 0.638 | Large effect size |
| Direct Effect Size | 0.392 | Medium to large effect |
| Indirect Effect Size | 0.195 | Small to medium effect |
| Moderation Effect Size | 0.176 | Small to medium interaction |
| Index of Mod. Mediation | 0.054 | Significant conditional process |
| Statistical Power | >0.95 | Adequate for detecting effects |
| Hypothesis | Description | Statistical Evidence | Supported |
|---|---|---|---|
| H1 | Leadership → Sustainable Development | β = 0.592, p < 0.001, CI [0.497, 0.687] | Yes |
| H2 | Leadership → Org Commitment | β = 0.634, p < 0.001, CI [0.533, 0.735] | Yes |
| H3 | Commitment → Sustainable Development | β = 0.308, p < 0.001, CI [0.193, 0.423] | Yes |
| H4 | Commitment mediates Leadership → Sustainable Dev | Indirect effect = 0.195, CI [0.118, 0.283] | Yes |
| H5 | Strategic Planning moderates Leadership → Commitment | Interaction β = 0.176, p < 0.001, Index = 0.054, CI [0.023, 0.091] | Yes |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Ahmed, N.; Arabi, N. Leadership and Sustainable Development in Tabuk’s Nonprofits: A Moderated Mediation of Organizational Commitment and Strategic Planning Capability. Sustainability 2026, 18, 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/su18010111
Ahmed N, Arabi N. Leadership and Sustainable Development in Tabuk’s Nonprofits: A Moderated Mediation of Organizational Commitment and Strategic Planning Capability. Sustainability. 2026; 18(1):111. https://doi.org/10.3390/su18010111
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhmed, Noha, and Nahla Arabi. 2026. "Leadership and Sustainable Development in Tabuk’s Nonprofits: A Moderated Mediation of Organizational Commitment and Strategic Planning Capability" Sustainability 18, no. 1: 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/su18010111
APA StyleAhmed, N., & Arabi, N. (2026). Leadership and Sustainable Development in Tabuk’s Nonprofits: A Moderated Mediation of Organizational Commitment and Strategic Planning Capability. Sustainability, 18(1), 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/su18010111






