Field Evaluation of Rice Husk Biochar and Pine Tree Woodchips for Removal of Tire Wear Particles from Urban Stormwater Runoff in Oxford, Mississippi (USA)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
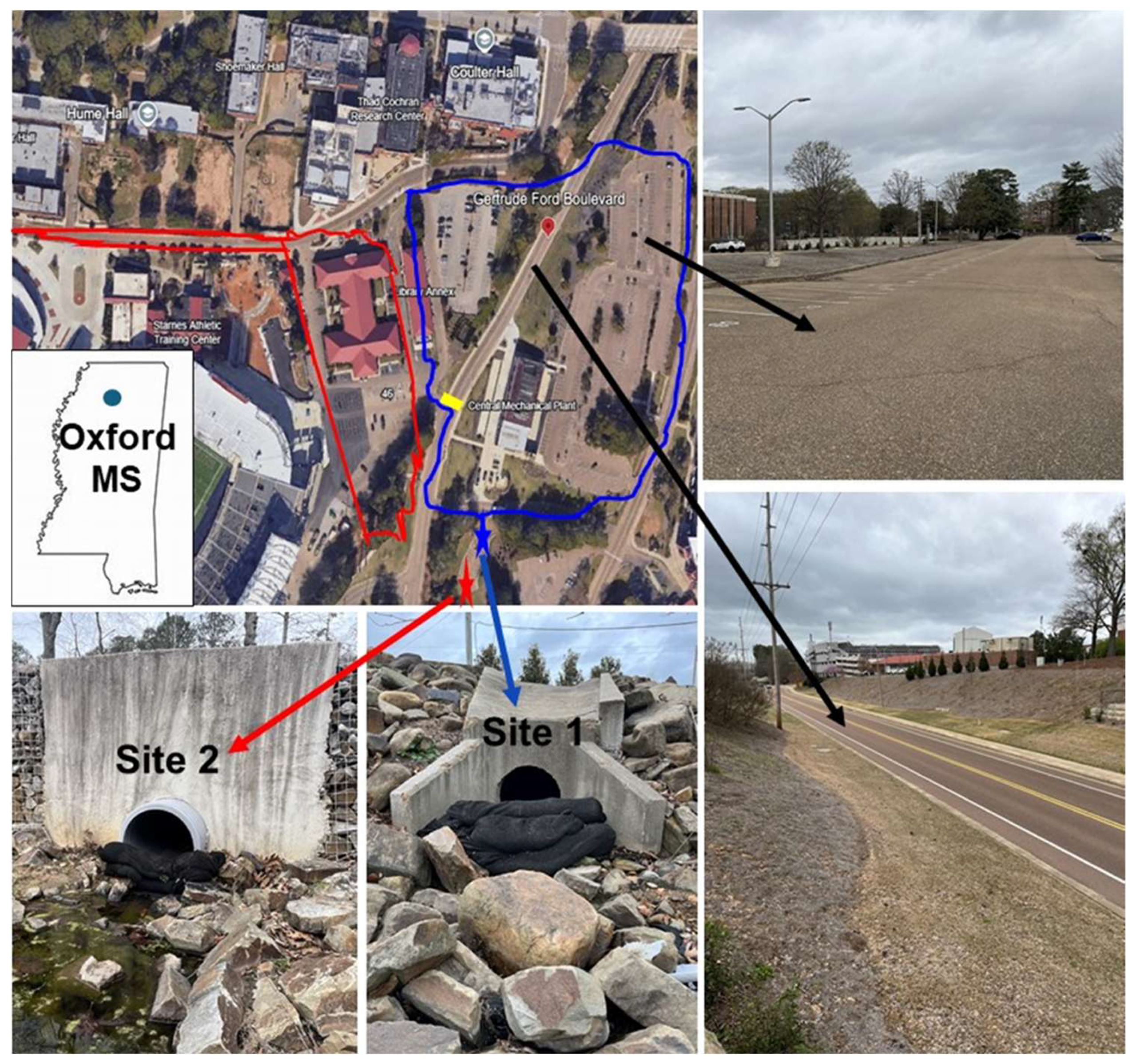
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Biofilter Preparation and Sample Collection
2.3. Isolation and Preconcentration of TWPs
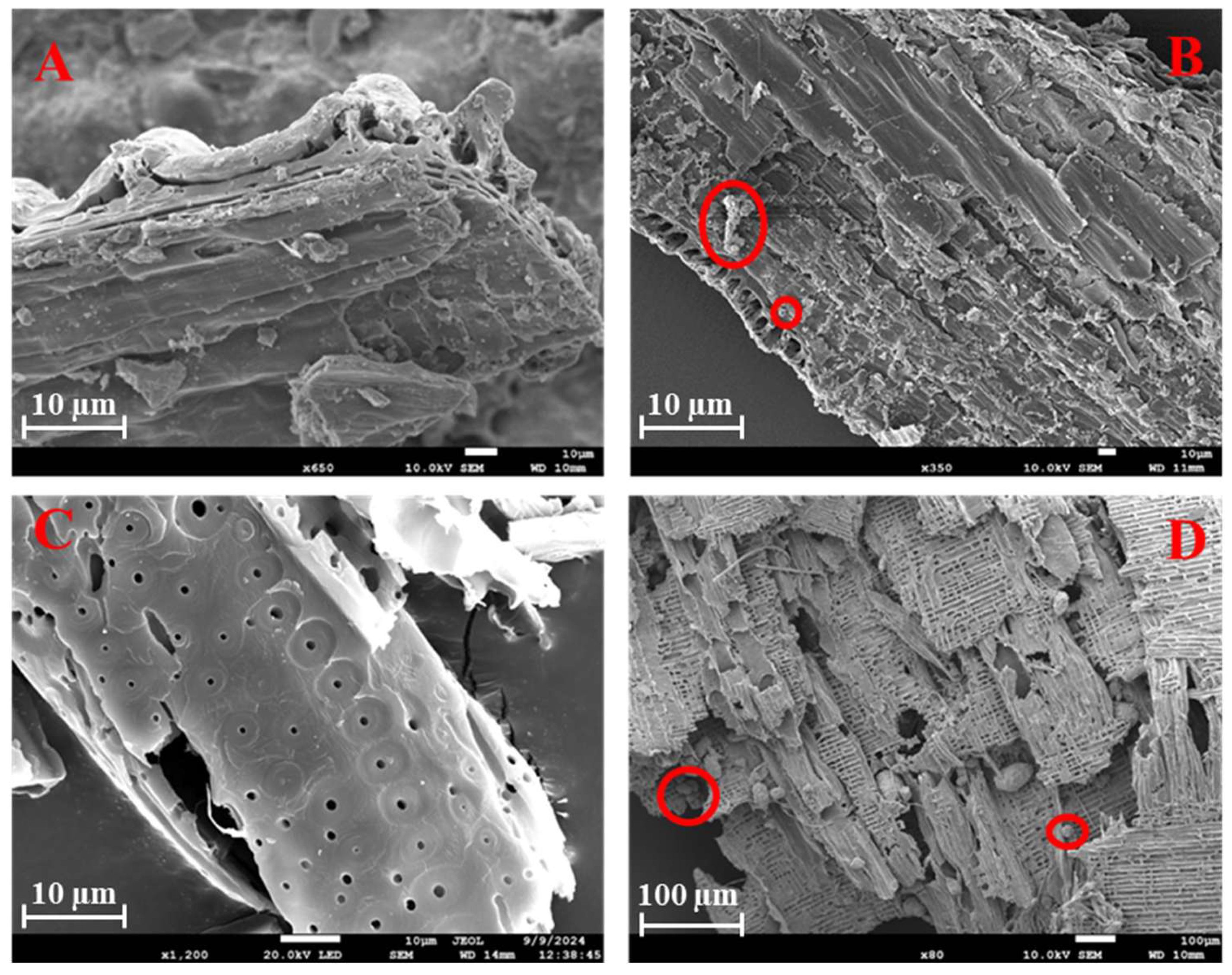
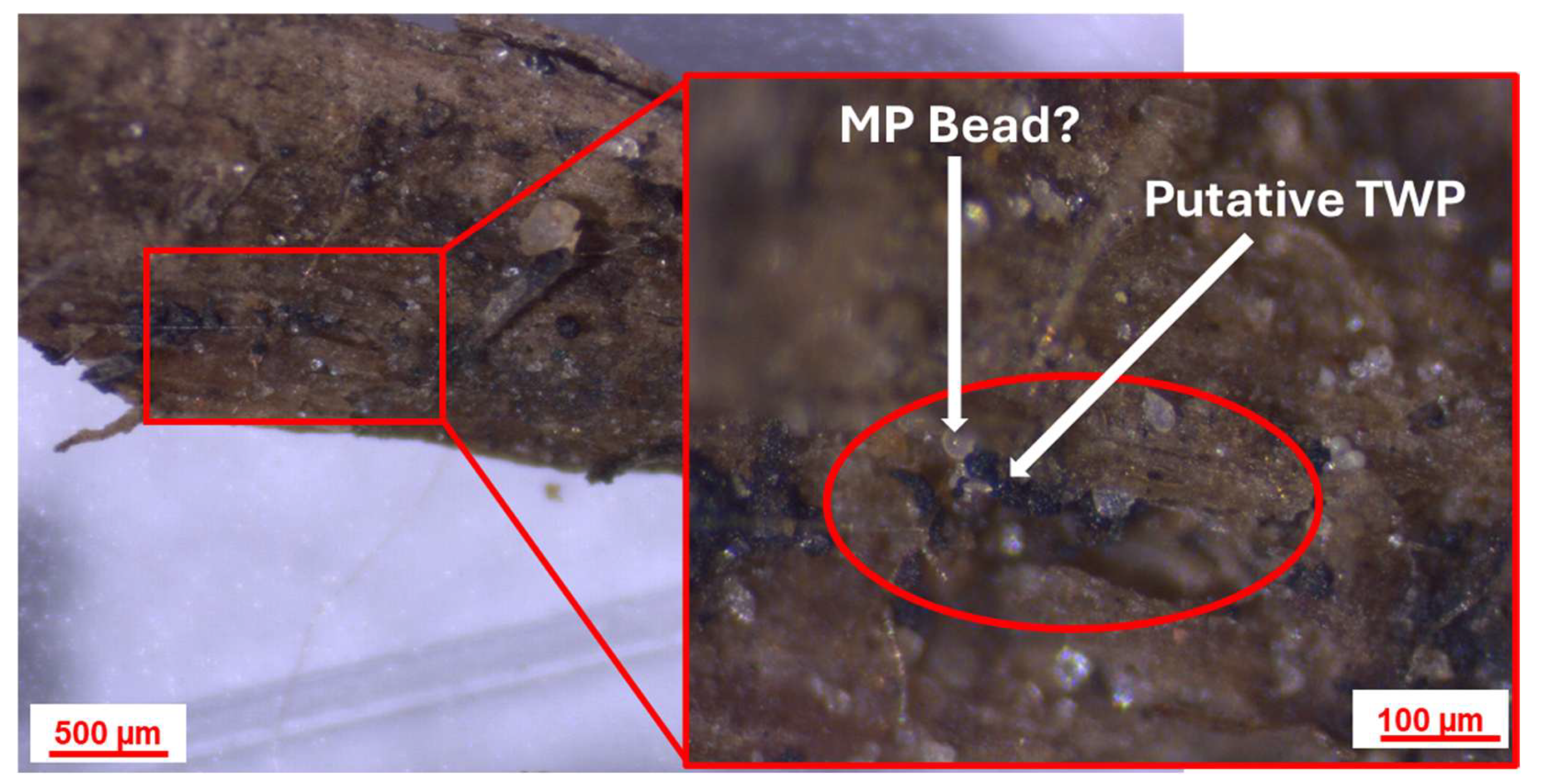
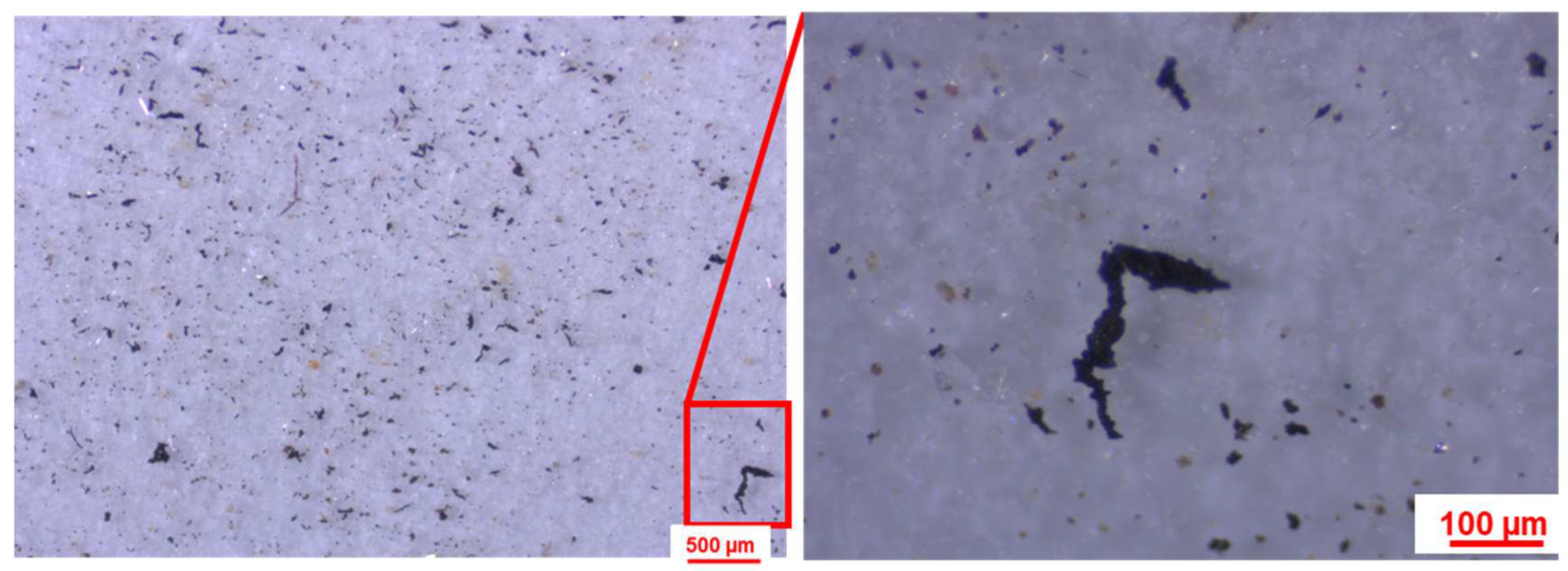
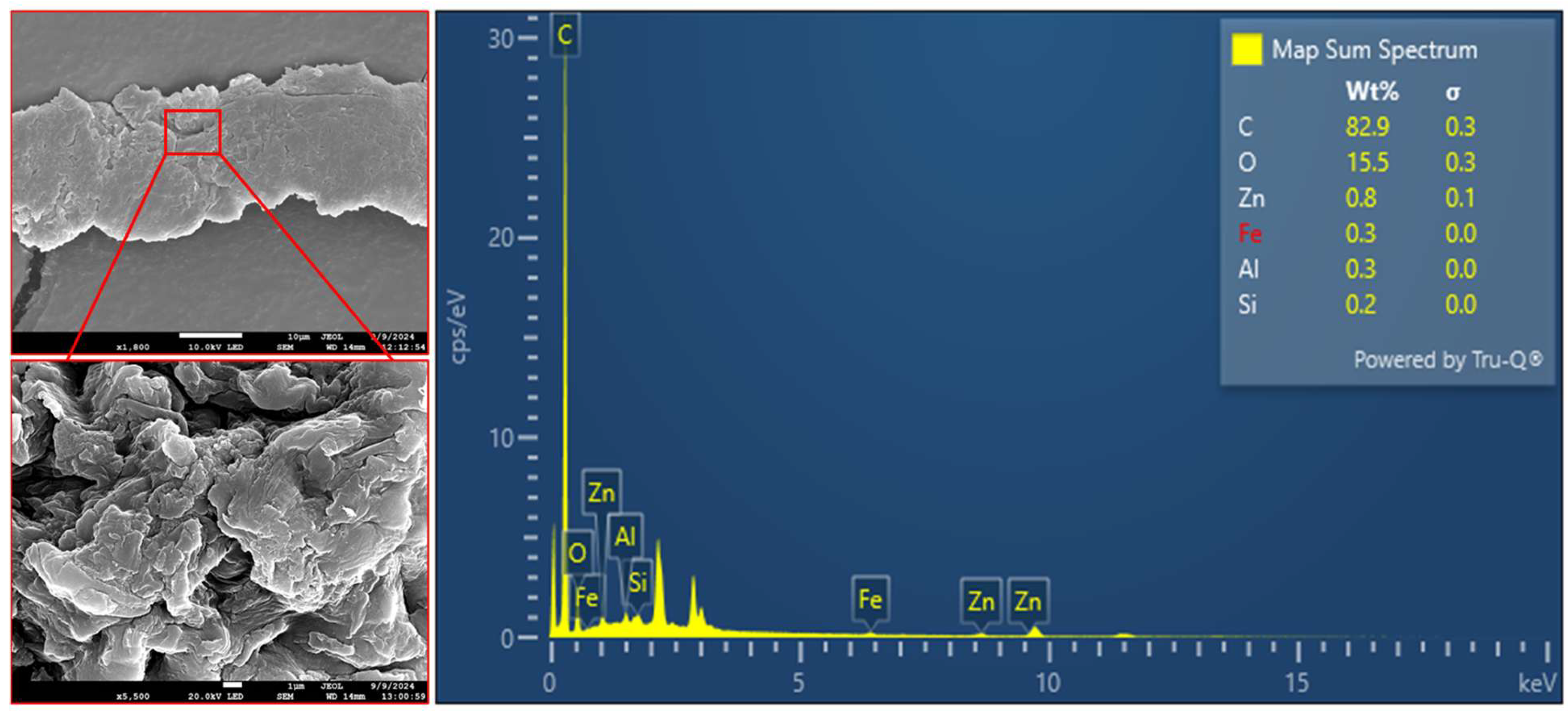
2.4. Analysis of TWPs by Stereomicroscopy, µ-ATR-FTIR, and SEM-EDX
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Quality Assurance and Control Measures
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Abundance of TWPs in Stormwater Runoff
3.2. Reduction in TWPs in Stormwater Runoff
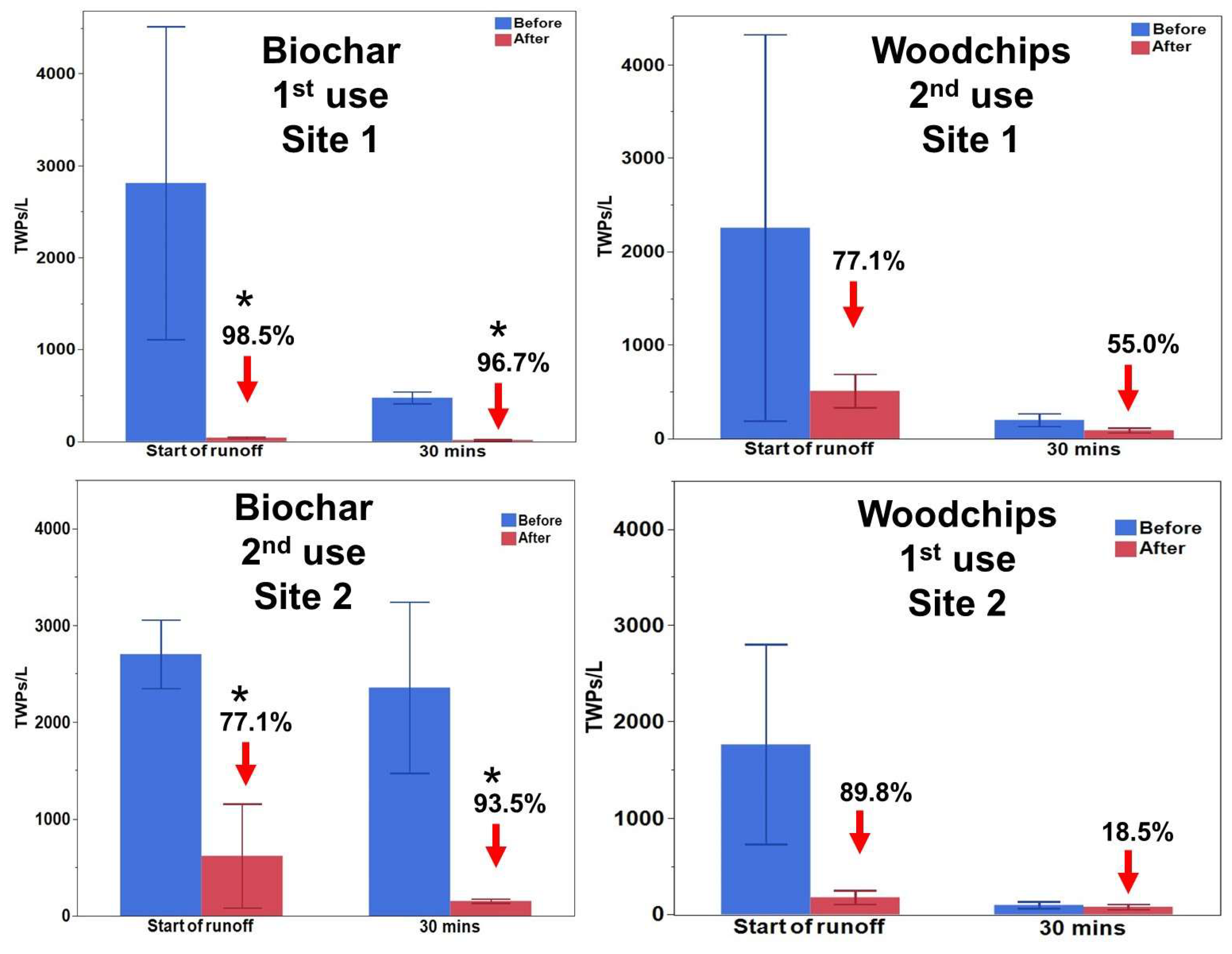
3.2.1. Removal of TWPs with the Biochar Filter Sock
3.2.2. Removal of TWPs with the Woodchips Filter Sock
3.2.3. Biochar vs. Woodchips
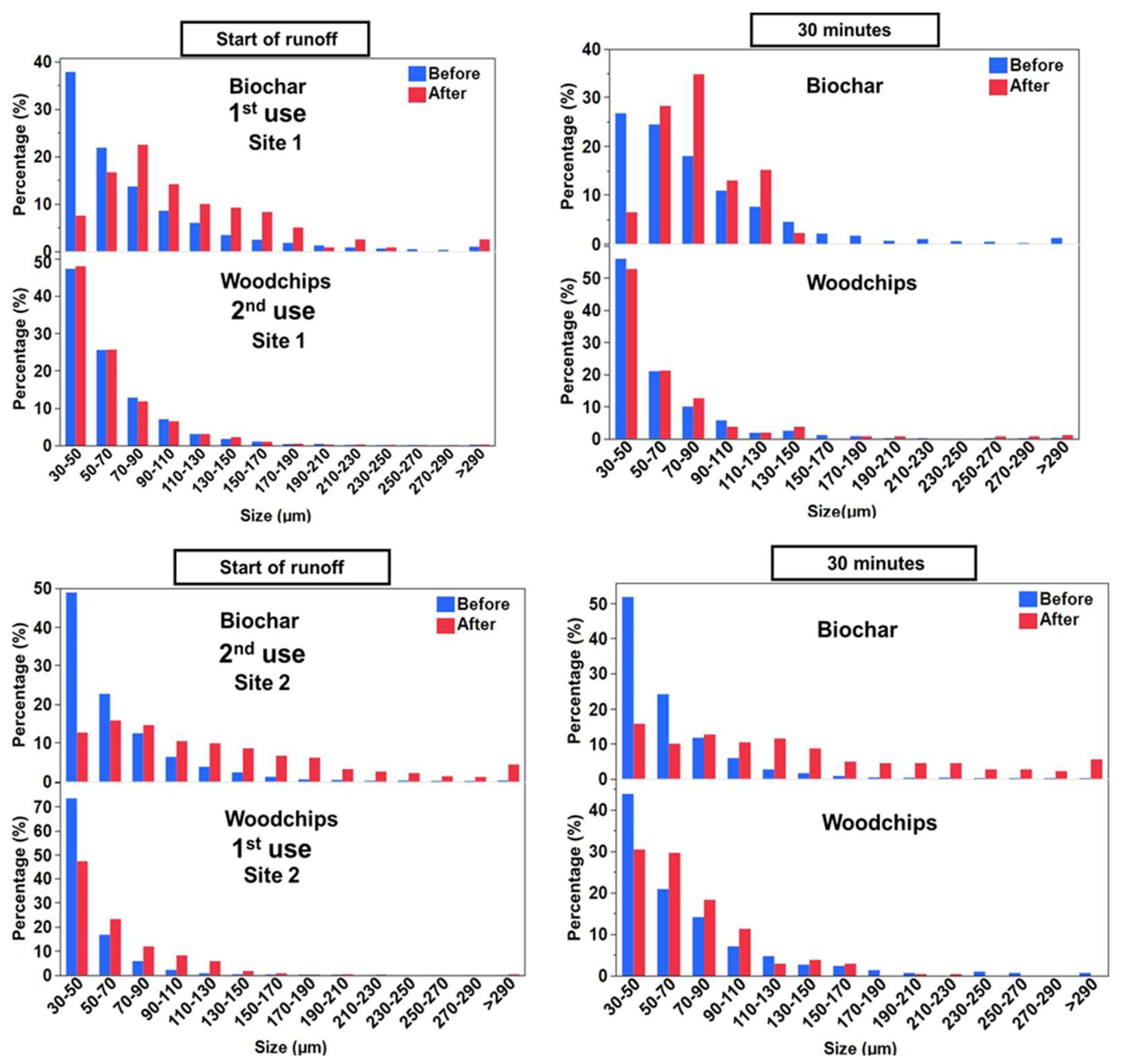
3.3. Particle Size Distribution (PSD) of TWPs in Urban Stormwater Runoff
3.4. Study Limitations
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peng, G.; Xu, P.; Zhu, B.; Bai, M.; Li, D. Microplastics in freshwater river sediments in Shanghai, China: A case study of risk assessment in mega-cities. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 234, 448–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Olesen, K.; Borregaard, A.R.; Vollertsen, J. Microplastics in urban and highway stormwater retention ponds. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 671, 992–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Cai, L.; Sun, F.; Li, G.; Che, Y. Public attitudes towards microplastics: Perceptions, behaviors and policy implications. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 163, 105096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unice, K.; Weeber, M.; Abramson, M.; Reid, R.; van Gils, J.; Markus, A.; Vethaak, A.; Panko, J. Characterizing export of land-based microplastics to the estuary—Part I: Application of integrated geospatial microplastic transport models to assess tire and road wear particles in the Seine watershed. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 646, 1639–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieber, R.; Kawecki, D.; Nowack, B. Dynamic probabilistic material flow analysis of rubber release from tires into the environment. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 258, 113573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leifheit, E.F.; Kissener, H.L.; Faltin, E.; Ryo, M.; Rillig, M.C. Tire abrasion particles negatively affect plant growth even at low concentrations and alter soil biogeochemical cycling. Soil Ecol. Lett. 2021, 4, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Zhou, X.; Su, Y.; Wang, H.; Yu, R.; Zhou, S.; Xu, E.G.; Xing, B. Environmental occurrence, fate, impact, and potential solution of tire microplastics: Similarities and differences with tire wear particles. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 795, 148902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baensch-Baltruschat, B.; Kocher, B.; Kochleus, C.; Stock, F.; Reifferscheid, G. Tire and road wear particles—A calculation of generation, transport and release to water and soil with special regard to German roads. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 752, 141939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.S.; Billah, M.M.; Ali, M.M.; Bhuiyan, M.K.A.; Guo, L.; Mohinuzzaman, M.; Cai, W. Microplastics in Aquatic Environments: A Comprehensive Review of Toxicity, Removal, and Remediation Strategies. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 876, 162414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kole, P.J.; Löhr, A.J.; Van Belleghem, F.G.A.J.; Ragas, A.M.J. Wear and tear of tyres: A stealthy source of microplastics in the environment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2017, 14, 1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hann, S.; Sherrington, C.; Jamieson, O.; Hickman, M.; Kershaw, P.; Bapasola, A.; Cole, G. Investigating Options for Reducing Releases in the Aquatic Environment of Microplastics Emitted by (but Not Intentionally Added in) Products; Report for DG Environment of the European Commission; ICF: London, UK, 2018; 335p, Available online: https://bmbf-plastik.de/sites/default/files/2018-04/microplastics_final_report_v5_full.pdf (accessed on 24 March 2025).
- Järlskog, I.; Jaramillo-Vogel, D.; Rausch, J.; Gustafsson, M.; Strömvall, A.M.; Andersson-Sköld, Y. Concentrations of tire wear microplastics and other traffic-derived non-exhaust particles in the road environment. Environ. Int. 2022, 170, 107618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreider, M.L.; Panko, J.M.; McAtee, B.L.; Sweet, L.I.; Finley, B.L. Physical and chemical characterization of tire-related particles: Comparison of particles generated using different methodologies. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verschoor, A.; Poorter, L.; Dröge, R.; Kuenen, J.; Valk, E. Emission of Microplastics and Potential Mitigation Measures; Institute for Public Health and the Environment: Bilthoven, The Netherlands, 2016; Volume 26, pp. 1–73. Available online: https://rivm.openrepository.com/entities/publication/90afb531-c31c-4224-aa1d-ae0f04966478 (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- Siegfried, M.; Koelmans, A.A.; Besseling, E.; Kroeze, C. Export of microplastics from land to sea. A modelling approach. Water Res. 2017, 127, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wik, A.; Dave, G. Occurrence and effects of tire wear particles in the environment—A critical review and an initial risk assessment. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, S.; Hüffer, T.; Klöckner, P.; Wehrhahn, M.; Hofmann, T.; Reemtsma, T. Tire wear particles in the aquatic environment—A review on generation, analysis, occurrence, fate and effects. Water Res. 2018, 139, 83–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, F.; Dietze, V.; Baum, A.; Sauer, J.; Gilge, S.; Maschowski, C.; Gieré, R. Tire Abrasion as a Major Source of Microplastics in the Environment. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2018, 18, 2014–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goehler, L.O.; Moruzzi, R.B.; da Conceição, F.T.; Júnior, A.A.C.; Speranza, L.G.; Busquets, R.; Campos, L.C. Relevance of tyre wear particles to the total content of microplastics transported by runoff in a high-imperviousness and intense vehicle traffic urban area. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 314, 120200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.; Lee, S. Characteristics of tire wear particles generated by a tire simulator under various driving conditions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 12153–12161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neupert, J.W.; Venghaus, D.; Barjenbruch, M. Measures to Reduce the Discharge of tire Wear into the Environment. Microplastics 2024, 3, 305–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitchcock, J.N. Storm events as key moments of microplastic contamination in aquatic ecosystems. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 734, 139436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Cizdziel, J.V.; Wontor, K.; Clisham, C.; Focia, K.; Rausch, J.; Jaramillo-Vogel, D. On airborne tire wear particles along roads with different traffic characteristics using passive sampling and optical microscopy, single particle SEM/EDX, and µ-ATR-FTIR analyses. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olubusoye, B.S.; Cizdziel, J.V.; Bee, M.; Moore, M.T.; Pineda, M.; Yargeau, V.; Bennett, E.R. Toxic tire wear compounds (6PPD-Q and 4-ADPA) detected in airborne particulate matter along a highway in Mississippi, USA. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2023, 111, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rødland, E.S.; Heier, L.S.; Lind, O.C.; Meland, S. High levels of tire wear particles in soils along low traffic roads. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 903, 166470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leads, R.R.; Weinstein, J.E. Occurrence of tire wear particles and other microplastics within the tributaries of the Charleston Harbor Estuary, South Carolina, USA. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 145, 569–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauert, C.; Charlton, N.; Okoffo, E.D.; Stanton, R.S.; Agua, A.R.; Pirrung, M.C.; Thomas, K.V. Concentrations of tire additive chemicals and tire road wear particles in an Australian urban tributary. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 2421–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rødland, E.S.; Lind, O.C.; Reid, M.J.; Heier, L.S.; Okoffo, E.D.; Rauert, C.; Thomas, K.V.; Meland, S. Occurrence of tire and road wear particles in urban and peri-urban snowbanks, and their potential environmental implications. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 824, 153785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson-Sköld, Y.; Johanesson, M.; Gustafsson, M.; Järlskog, I.; Lithner, D.; Polukarova, M.; Strömvall, A.M. Microplastics from Tyre and Road Wear—A Literature Review; Swedish National Road and Transport Research Institute: Linköping, Sweden, 2020; Available online: https://www.diva-portal.org/smash/get/diva2:1430623/FULLTEXT02 (accessed on 23 March 2025).
- Li, J.; Xu, J.; Jiang, X. Urban runoff mortality syndrome in zooplankton caused by tire wear particles. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 329, 121721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redondo-Hasselerharm, P.E.; De Ruijter, V.N.; Mintenig, S.M.; Verschoor, A.; Koelmans, A.A. Ingestion and chronic effects of car tire tread particles on freshwater benthic macroinvertebrates. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 13986–13994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Zhao, H.; Peter, K.T.; Gonzalez, M.; Wetzel, J.; Wu, C.; Hu, X.; Prat, J.; Mudrock, E.; Hettinger, R.; et al. A ubiquitous tire rubber–derived chemical induces acute mortality in coho salmon. Science 2021, 371, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamis, J.E.; Koelmans, A.A.; Dröge, R.; Kaag, N.H.; Keur, M.C.; Tromp, P.C.; Jongbloed, R.H. Environmental risks of car tire microplastic particles and other road runoff pollutants. Micropl. Nanopl. 2021, 1, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arole, K.; Velhal, M.; Tajedini, M.; Xavier, P.G.; Bardasz, E.; Green, M.J.; Liang, H. Impacts of particles released from vehicles on environment and health. Tribol. Int. 2023, 184, 108417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, X.; Wang, D. Tire-rubber related pollutant 6-PPD quinone: A review of its transformation, environmental distribution, bioavailability, and toxicity. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 459, 132265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johannessen, C.; Helm, P.; Metcalfe, C.D. Detection of selected tire wear compounds in urban receiving waters. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 287, 117659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Challis, J.K.; Popick, H.; Prajapati, S.; Harder, P.; Giesy, J.P.; McPhedran, K.; Brinkmann, M. Occurrences of tire rubber-derived contaminants in cold-climate urban runoff. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2021, 8, 961–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seiwert, B.; Nihemaiti, M.; Troussier, M.; Weyrauch, S.; Reemtsma, T. Abiotic oxidative transformation of 6-PPD and 6-PPD quinone from tires and occurrence of their products in snow from urban roads and in municipal wastewater. Water Res. 2022, 212, 118122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkmann, M.; Montgomery, D.; Selinger, S.; Miller, J.G.P.; Stock, E.; Alcaraz, A.J.; Challis, J.K.; Weber, L.; Janz, D.; Hecker, M.; et al. Acute toxicity of the tire rubber-derived chemical 6PPD-quinone to four fishes of commercial, cultural, and ecological importance. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2022, 9, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyth, K.; Drake, J.; Li, Y.; Rochman, C.; Van Seters, T.; Passeport, E. Bioretention cells remove microplastics from urban stormwater. Water Res. 2021, 191, 116785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rullander, G.; Lorenz, C.; Herbert, R.B.; Strömvall, A.M.; Vollertsen, J.; Dalahmeh, S.S. How effective is the retention of microplastics in horizontal flow sand filters treating stormwater? J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 344, 118690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rullander, G.; Lorenz, C.; Strömvall, A.M.; Vollertsen, J.; Dalahmeh, S.S. Bark and Biochar in Horizontal Flow Filters Effectively Remove Microplastics from Stormwater. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 356, 124335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olubusoye, B.S.; Cizdziel, J.V.; Wontor, K.; Heinen, E.; Grandberry, T.; Bennett, E.R.; Moore, M.T. Removal of microplastics from agricultural runoff using biochar: A column feasibility study. Front. Environ. Sci. 2024, 12, 1388606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbreath, A.; Mckee, L.; Shimabuku, I.; Lin, D. Multiyear Water Quality Performance and Mass Accumulation of PCBs, Mercury, Methylmercury, Copper, and Microplastics in a Bioretention Rain Garden. J. Sustain. Water Built Environ. 2019, 5, 04019004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, K.; Magnusson, K.; Viklander, M.; Blecken, G.T. Removal of rubber, bitumen and other microplastic particles from stormwater by a gross pollutant trap—Bioretention treatment train. Water Res. 2021, 202, 117457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klöckner, P.; Seiwert, B.; Weyrauch, S.; Escher, B.I.; Reemtsma, T.; Wagner, S. Comprehensive characterization of tire and road wear particles in highway tunnel road dust by use of size and density fractionation. Chemosphere 2021, 279, 130530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gwenzi, W.; Chaukura, N.; Noubactep, C.; Mukome, F.N. Biochar-based water treatment systems as a potential low-cost and sustainable technology for clean water provision. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 197, 732–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, M.; He, L.; Jiang, M.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, J.; Gustave, W.; Wang, S.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z. Biochar for the removal of emerging pollutants from aquatic systems: A review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Verma, A.; Rakib, M.R.J.; Gupta, P.K.; Sharma, P.; Garg, A.; Girard, P.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Adsorptive behavior of micro (nano) plastics through biochar: Co-existence, consequences, and challenges in contaminated ecosystems. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 856, 159097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, L.J.; Xiong, Q.; Yang, L.H.; Li, H.; Zhou, Y.Y.; Zhang, W.J.; Jiang, S.J.; Li, H.L.; Huang, H.J. An overview on engineering the surface area and porosity of biochar. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 763, 144204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Zhou, D.; Zhu, L. Transitional adsorption and partition of nonpolar and polar aromatic contaminants by biochars of pine needles with different pyrolytic temperatures. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 5137–5143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Xing, Y.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, D.; Tang, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, B. The Removal and Mitigation Effects of Biochar on Microplastics in Water and Soils: Application and Mechanism Analysis. Sustainability 2024, 16, 9749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Sedighi, M.; Lea-Langton, A. Filtration of microplastic spheres by biochar: Removal efficiency and immobilisation mechanisms. Water Res. 2020, 184, 116165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganie, Z.A.; Khandelwal, N.; Tiwari, E.; Singh, N.; Darbha, G.K. Biochar facilitated remediation of nanoplastic contaminated water: Effect of pyrolysis temperature induced surface modifications. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 417, 126096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siipola, V.; Pflugmacher, S.; Romar, H.; Wendling, L.; Koukkari, P. Low-cost biochar adsorbents for water purification including microplastics removal. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, B.; Zhu, L. Enhanced sorption of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from aqueous solution by modified pine bark. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 7307–7313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Björklund, K.; Li, L. Evaluation of low-cost materials for sorption of hydrophobic organic pollutants in stormwater. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 159, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, M.; Wang, Q.; Wang, T.; Zhou, Z.; Mehling, M.; Guo, T.; Zou, H.; Xiao, X.; He, Y.; et al. Flowthrough capture of microplastics through polyphenol-mediated interfacial interactions on wood sawdust. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2301531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, L.J.; Parker-Jurd, F.N.; Al-Sid-Cheikh, M.; Thompson, R.C. Tyre wear particles: An abundant yet widely unreported microplastic? Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 18345–18354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Sarswat, A.; Pittman Jr, C.U.; Mlsna, T.; Mohan, D. Sustainable low-concentration arsenite [As (III)] removal in single and multicomponent systems using hybrid iron oxide–biochar nanocomposite adsorbents—A mechanistic study. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 2575–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scircle, A.; Cizdziel, J.V.; Missling, K.; Li, L.; Vianello, A. Single-pot method for the collection and preparation of natural water for microplastic analyses: Microplastics in the Mississippi River system during and after historic flooding. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2020, 39, 986–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, E.; Ren, Z.; Mays, D. Zinc leaching from rubber tire crumb. Envrion. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 12856–12863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klöckner, P.; Seiwert, B.; Eisentraut, P.; Braun, U.; Reemtsma, T.; Wagner, S. Characterization of Tire and Road Wear Particles from Road Runoff Indicates Highly Dynamic Particle Properties. Water Res. 2020, 185, 116262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rausch, J.; Jaramillo-Vogel, D.; Perseguers, S.; Schnidrig, N.; Grobéty, B.; Yajan, P. Automated identification and quantification of tire wear particles (TWP) in airborne dust: SEM/EDX single particle analysis coupled to a machine learning classifier. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 803, 149832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wontor, K.; Olubusoye, B.S.; Cizdziel, J.V. Microplastics in the Mississippi River System during Flash Drought Conditions. Environments 2024, 11, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, E.Y.; Tran, K.; Young, D. Evaluation of potential molecular markers for urban stormwater runoff. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2004, 90, 23–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goonetilleke, A.; Wijesirierick, B.; Bandala Erick, R. Water and soil pollution Implications of road traffic. In Environmental Impacts of Road Vehicles: Past, Present and Future; Hester, R.E., Harrison, R.M., Eds.; Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2017; pp. 86–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.; Shim, W.J.; Ha, S.Y.; Han, G.M.; Jang, M.; Hong, S.H. Microplastic emission characteristics of stormwater runoff in an urban area: Intra-event variability and influencing factors. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 866, 161318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumata, H.; Sanada, Y.; Takada, H.; Ueno, T. Historical trends of N-Cyclohexyl2-benzothiazolamine, 2-(4-morpholinyl)benzothiazole, and other anthropogenic contaminants in the urban reservoir sediment core. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaze, J.; Chiew, F.H. Experimental study of pollutant accumulation on an urban road surface. Urban Water J. 2002, 4, 379–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagström, S. Fate and Transport of Microplastic Particles in Small Highway-Adjacent Streams—A Case Study in Gothenburg Region. Master’s Thesis, Chalmers University of Technology, Göteborg, Sweden, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.H.; Bang, K.W. Characterization of urban stormwater runoff. Water Res. 2000, 34, 1773–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, H.G.; Lu, F.H.; Luo, X.L.; Tian, H.Y.; Zeng, E.Y. Occurrence, phase distribution, and mass loadings of benzothiazoles in riverine runoff of the Pearl River Delta, China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 1892–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertrand-Krajewski, J.L.; Chebbo, G.; Saget, A. Distribution of pollutant mass vs volume in stormwater discharges and the first flush phenomenon. Water Res. 1998, 32, 2341–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, A.; Österlund, H.; Marsalek, J.; Viklander, M. The pollution conveyed by urban runoff: A review of sources. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 709, 136125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Sun, C.; Huang, Q.-X.; Chi, Y.; Yan, J.-H. Adsorption and thermal degradation of microplastics from aqueous solutions by Mg/Zn modified magnetic biochars. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 419, 126486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, L.; Harindintwali, J.D.; Wang, F.; Redmile-Gordon, M.; Chang, S.X.; Fu, Y.; He, C.; Muhoza, B.; Brahushi, F.; Bolan, N.; et al. Integrating Biochar, Bacteria, and Plants for Sustainable Remediation of Soils Contaminated with Organic Pollutants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 16546–16566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Z.; Yao, B.; Yang, X.; Wang, L.; Xu, Z.; Yan, X.; Tian, L.; Zhou, H.; Zhou, Y. Novel insights into the adsorption of organic contaminants by biochar: A review. Chemosphere 2022, 287, 132113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, M.; Lubis, N.M.A.; Usama, M.; Ahmad, J.; Al-Wabel, M.I.; Al-Swadi, H.A.; Rafique, M.I.; Al-Farraj, A.S.F. Scavenging microplastics and heavy metals from water using jujube waste-derived biochar in fixed-bed column trials. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 335, 122319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brás, I.; Teixeira Lemos, L.; Alves, A.; Fernando, R.; Pereira, M. Application of pine bark as a sorbent for organic pollutants in effluents. Manag. Environ. Qual. 2004, 15, 491–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentín, L.; Kluczek-Turpeinen, B.; Willför, S.; Hemming, J.; Hatakka, A.; Steffen, K.; Tuomela, M. Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris) bark composition and degradation by fungi: Potential substrate for bioremediation. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 2203–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlachos, D.; Voutsa, D. Adsorption of emerging micropollutants on tire wear particles. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 971, 179068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loganathan, P.; Vigneswaran, S.; Kandasamy, J. Road-deposited sediment pollutants: A critical review of their characteristics, source apportionment, and management. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 43, 1315–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovochich, M.; Parker, J.A.; Oh, S.C.; Lee, J.P.; Wagner, S.; Reemtsma, T.; Unice, K.M. Characterization of individual tire and road wear particles in environmental road dust, tunnel dust, and sediment. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2021, 8, 1057–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piscitello, A.; Bianco, C.; Casasso, A.; Sethi, R. Non-exhaust traffic emissions: Sources, characterization, and mitigation measures. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 766, 144440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, S.; Keshavarzi, B.; Moore, F.; Turner, A.; Kelly, F.J.; Dominguez, A.O.; Jaafarzadeh, N. Distribution and potential health impacts of microplastics and microrubbers in air and street dusts from Asaluyeh County, Iran. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 244, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarlskog, I.; Stromvall, A.-M.; Magnusson, K.; Gustafsson, M.; Polukarova, M.; Galfi, H.; Aronsson, M.; Andersson-Skold, Y. Occurrence of tire and bitumen wear microplastics on urban streets and in sweepsand and washwater. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 729, 138950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ihenetu, C.; Hao, Y.; Ma, J.; Li, J.; Li, G. Effects of Biochar on Tire Wear Particle-Derived 6PPD, 6PPD-Q, and Antimony Levels and Microbial Community in Soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 491, 137951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, M.; Liu, M.; Hossain, K.B.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Yan, M.; Leung, K.M. Current status and emerging techniques for sampling, separating, and identifying microplastics in freshwater environments. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2025, 184, 118151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Pyrolysis temperature | 600 °C |
| Carbon (weight %) | 38.4% |
| Ash (weight %) | 53.5% |
| SBET (m2 g−1) | 300 |
| External surface area (m2 g−1) | 12.71 |
| Micropore volume W0 (cm3 g−1) | 18.07 |
| Average pore diameter (Å) | 0.12 |
| Sampling Date | Prior Dry Days | Biofilter | Flow Rate (L/min) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Site 1 | Site 2 | Site 1 | Site 2 | ||
| 26 June 2024 | 22 | Biochar | Woodchip | 24 ± 1.8 | 14 ± 0.3 |
| 25 July 2024 | 28 | Woodchip | Biochar | 32 ± 0.2 | 15 ± 0.5 |
| Biofilter | Parameters | Sampling Site 1 | Sampling Site 2 | ||||||
| Event 1 | Event 2 | ||||||||
| Start of runoff | 30 min | Start of runoff | 30 min | ||||||
| Before | After | Before | After | Before | After | Before | After | ||
| Biochar | Total TWPs | 8433 | 120 | 1429 | 46 | 8104 | 1454 | 7068 | 452 |
| Mean ± SD | 2811 ± 1700 | 40 ± 9.6 | 476 ± 63 | 15 ± 6 | 2702 ± 353 | 619 ± 536 | 2356 ± 884 | 153 ± 22 | |
| p-value | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.02 | |||||
| % reduction | 98.5% | 96.7% | 77.3% | 93.5% | |||||
| Woodchip | Parameters | Event 2 | Event 1 | ||||||
| Start of runoff | 30 min | Start of runoff | 30 min | ||||||
| Before | After | Before | After | Before | After | Before | After | ||
| Total TWPs | 6765 | 1532 | 600 | 269 | 5296 | 537 | 297 | 240 | |
| Mean ± SD | 2255 ± 2064 | 511 ± 176 | 200 ± 67 | 90 ± 24 | 1765 ± 1037 | 179 ± 71 | 99 ± 36 | 81 ± 26 | |
| p-value | 0.13 | 0.08 | 0.10 | 0.10 | |||||
| % reduction | 77.1% | 55.0% | 89.8% | 18.5% | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Olubusoye, B.S.; Cizdziel, J.V.; Wontor, K.; Li, R.; Hambuchen, R.; Aminone, V.T.; Moore, M.T.; Bennett, E.R. Field Evaluation of Rice Husk Biochar and Pine Tree Woodchips for Removal of Tire Wear Particles from Urban Stormwater Runoff in Oxford, Mississippi (USA). Sustainability 2025, 17, 4080. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17094080
Olubusoye BS, Cizdziel JV, Wontor K, Li R, Hambuchen R, Aminone VT, Moore MT, Bennett ER. Field Evaluation of Rice Husk Biochar and Pine Tree Woodchips for Removal of Tire Wear Particles from Urban Stormwater Runoff in Oxford, Mississippi (USA). Sustainability. 2025; 17(9):4080. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17094080
Chicago/Turabian StyleOlubusoye, Boluwatife S., James V. Cizdziel, Kendall Wontor, Ruojia Li, Rachel Hambuchen, Voke Tonia Aminone, Matthew T. Moore, and Erin R. Bennett. 2025. "Field Evaluation of Rice Husk Biochar and Pine Tree Woodchips for Removal of Tire Wear Particles from Urban Stormwater Runoff in Oxford, Mississippi (USA)" Sustainability 17, no. 9: 4080. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17094080
APA StyleOlubusoye, B. S., Cizdziel, J. V., Wontor, K., Li, R., Hambuchen, R., Aminone, V. T., Moore, M. T., & Bennett, E. R. (2025). Field Evaluation of Rice Husk Biochar and Pine Tree Woodchips for Removal of Tire Wear Particles from Urban Stormwater Runoff in Oxford, Mississippi (USA). Sustainability, 17(9), 4080. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17094080








