Environmental Education as a Fundamental Tool for Preventing the Ingestion of Chemical Contaminants in Spain
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Limitations
2.2. Survey
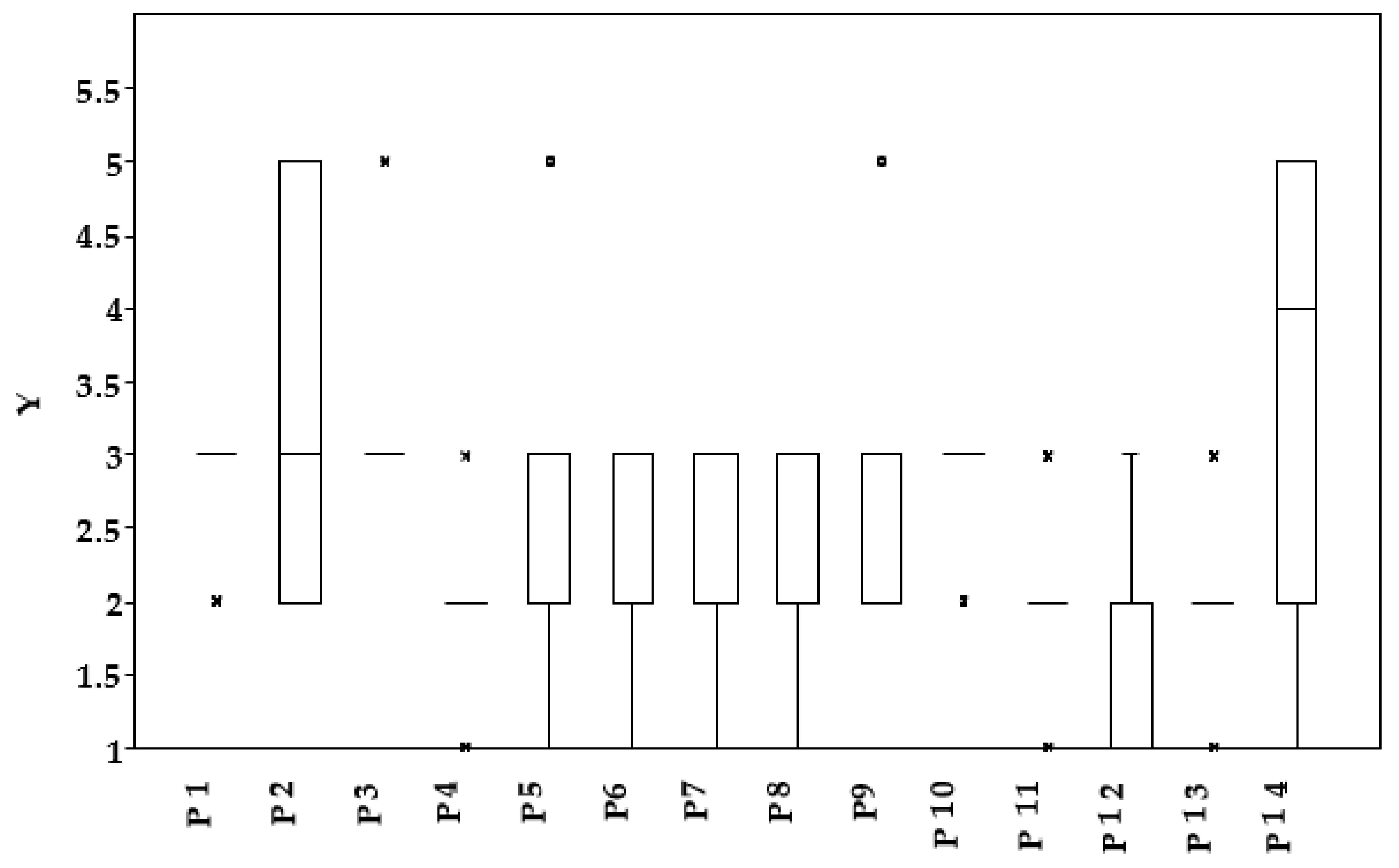
- P1: Should a well-maintained soil have a horizon A rich in plant residues?
- P2: Do you believe a well-maintained soil should have vegetation cover or not?
- P3: Do you think there is competition for water between vegetation cover and cultivated species?
- P4: Do you think this competition for water depends on the type of crop?
- P5: Do you believe that without vegetation cover, insects disappear?
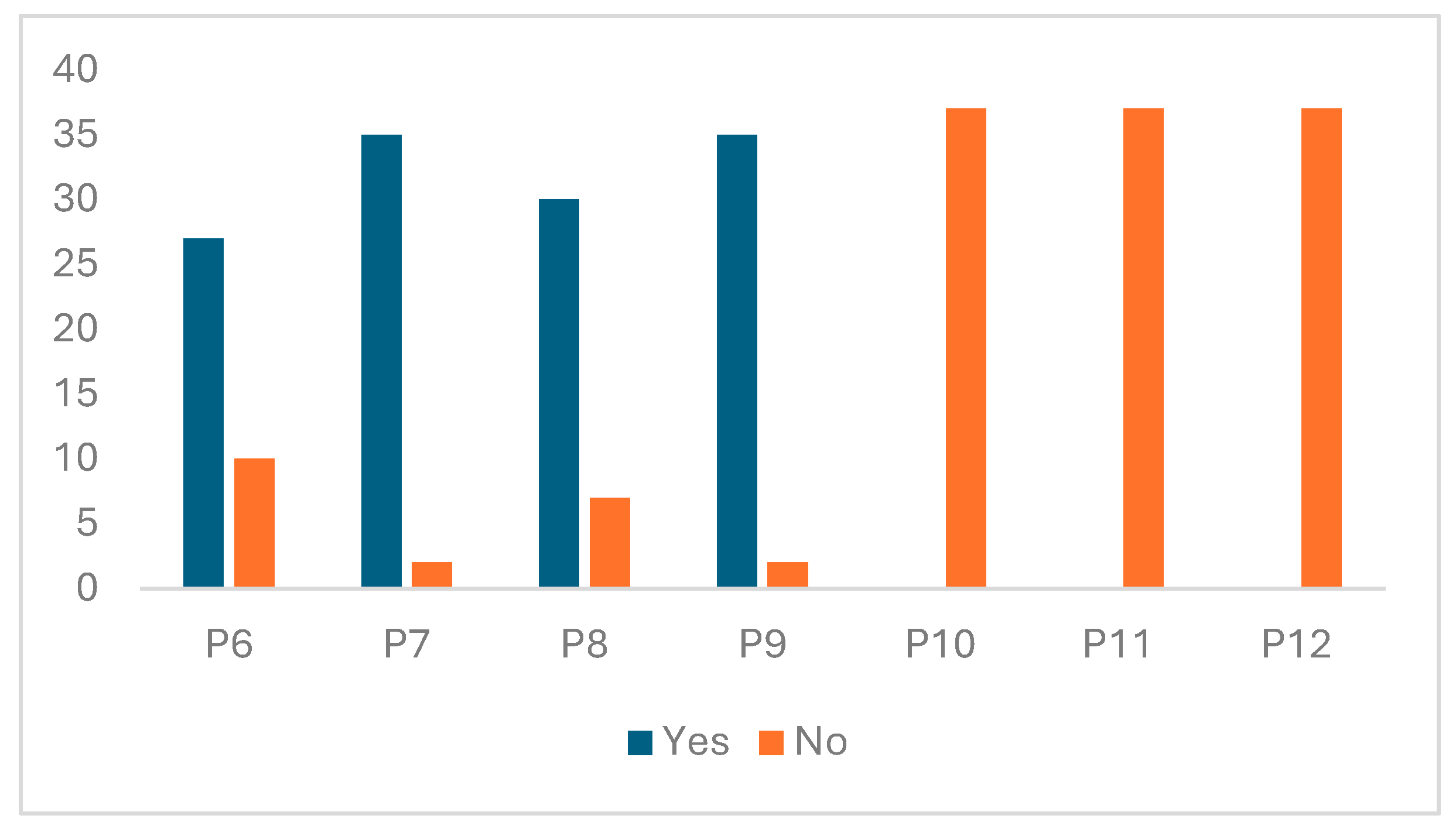
- P6: Do you consider it appropriate to eliminate vegetation from a crop using herbicides?
- P7: Do you believe herbicides are harmful to health?
- P8: Could herbicides reach groundwater?
- P9: Could herbicides reach the fruits or vegetables we eat?
- P10: Do you know of any diseases caused by food contamination?
- P11: Do you know how agrochemical products should be used and in what concentrations?
- P12: Do you think you have received sufficient knowledge about agriculture and sustainability in school?
- P13: Do you consider sustainability a relevant topic for you?
- P14: Would you propose to include their study in initial levels in education?
- a = Cronbach’s alpha coefficient;
- n = number of items;
- p = average of all item correlations.
3. Results and Discussion
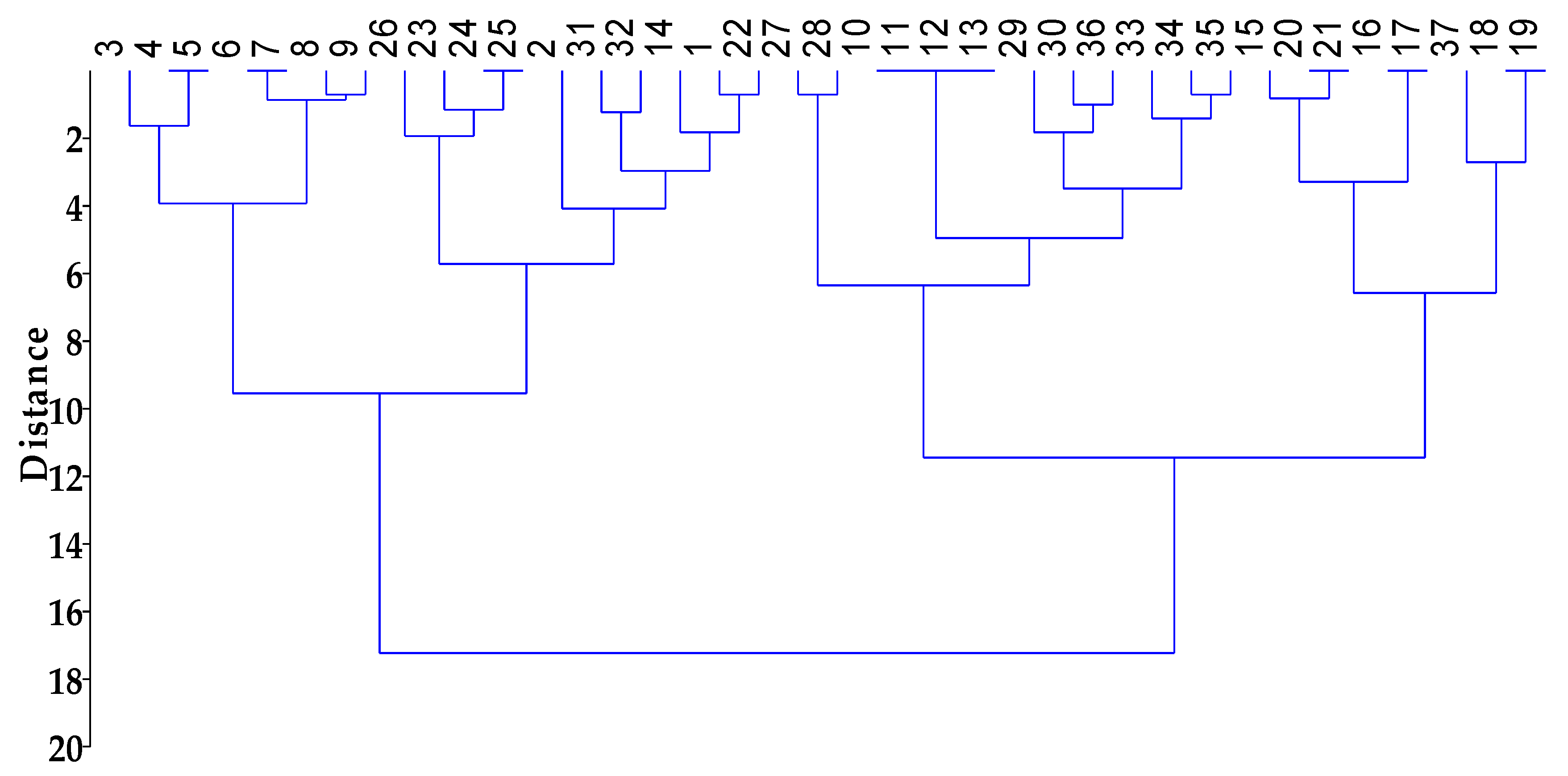
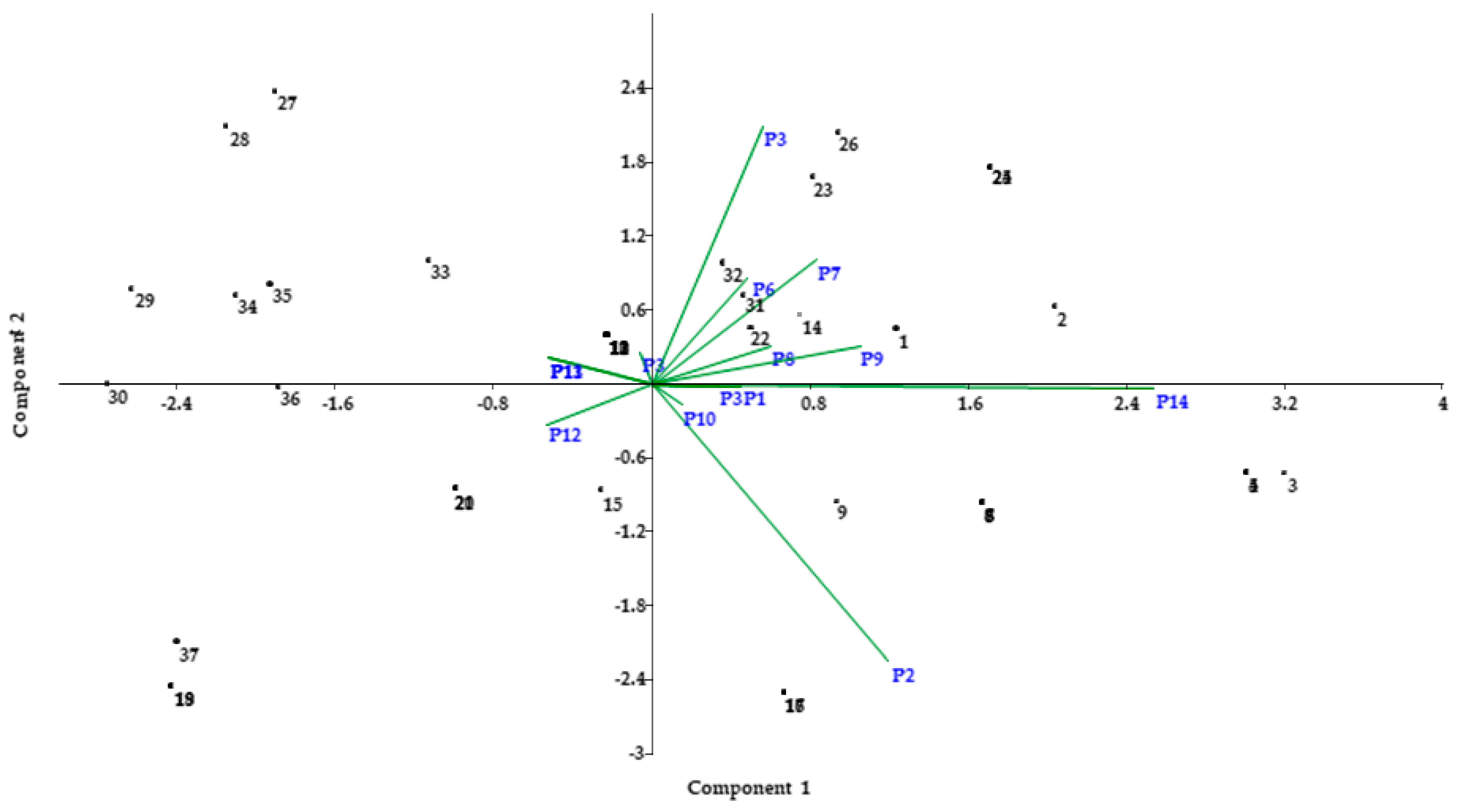
3.1. Results Analysis
3.2. Discussion Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- García-Vinuesa, A.; Meira Cartea, P.Á.; Caride Gómez, J.A.; Bachiorri, A. El cambio climático en la educación secundaria: Conocimientos, creencias y percepciones. Enseñanza De Las Ciencias 2022, 40, 25–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez Aznar, M.M.; Martín del Pozo, R.; Rodrigo Vega, M.; Varela Nieto, M.P.; Fernández Lozano, M.P.; Guerrero Serón, A. Estudio comparativo sobre el pensamiento profesional y la “acción docente” de los profesores de Ciencias de Educación Secundaria Parte II. Enseñanza De Las Ciencias 2002, 20, 243–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez Aznar, M.M.; Ibañez Orcajo, M.T. Resolver situaciones problemáticas en Genética para modificar las actitudes relacionadas con la ciencia. Enseñanza De Las Ciencias 2006, 24, 193–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano Ortiz, A. Bioindicadores y Cubiertas Vegetales en el Olivar in Nuevas Tendencias en Olivicultura; Service Publishing University Jaén: Jaén, Spain, 2016; pp. 70–117. [Google Scholar]
- Cano-Ortiz, A.; Piñar Fuentes, J.C.; Cano, E. Analysis of Toxic Contaminants in Agriculture: Educational Strategies to Avoid Their Influence on Food. Res. J. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2024, 4, 1–15. Available online: https://www.scipublications.com/journal/index.php/rjees/article/view/718 (accessed on 20 January 2025). [CrossRef]
- Zocchi, D.M.; Bondioli, C.; Hamzeh Hosseini, S.; Miara, M.D.; Musarella, C.M.; Mohammadi, D.; Khan Manduzai, A.; Dilawer Issa, K.; Sulaiman, N.; Khatib, C.; et al. Food Security beyond Cereals: A Cross-Geographical Comparative Study on Acorn Bread Heritage in the Mediterranean and the Middle East. Foods 2022, 11, 3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, J.A.; Lacasaña, M. Pesticides; exposure classification, use, toxicology and medicine. Arch Prev. Labor Risks 2001, 4, 67–75. [Google Scholar]
- Arroyare, S.M.S.; Correa Restrepo, F.J. Análisis de la contaminación del suelo: Revisión de la normativa y posibilidad de regulación económica. Semest. Económico 2009, 12, 13–34. Available online: https://www.redalyc.org/pdf/1650/165013122001.pdf (accessed on 20 January 2025).
- Castillo, B.; Ruiz, J.O.; Manrique, M.A.L.; Pozo, C. Contaminación por plaguicidas agrícolas en los campos de cultivo de Cañete (Perú). Revista Espacios 2020, 41, 11. Available online: https://www.revistaespacios.com/a20v41n10/20411011.html (accessed on 20 January 2025).
- Leiva Gea, F. Influencia de la Bioclimatología y Técnicas de Cultivo Sobre la Diversidad Florística en Olivares Andaluces. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Jaén, Jaén, Spain, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Martín Molero, F. Bases teóricas de la educación ambiental: Un modelo interdisciplinar. Rev. Complut. Educ. 1995, 6, 95–120. Available online: https://produccioncientifica.ucm.es/documentos/619ca488a08dbd1b8f9fd52d (accessed on 20 January 2025).
- Vega Marcote, P.; Álvarez Suárez, P. Planteamiento de un marco teórico de la Educación Ambiental para un desarrollo sostenible. Rev. Electrónica Enseñanza Las Cienc. 2005, 4, 1–16. Available online: https://www.academia.edu/96311604/ (accessed on 25 January 2025).
- CONED. Modelo de Creencias en Salud: Un Modelo Para el Cambio de Comportamiento en Personas con Diabetes. 2025. Available online: https://coned.org.mx/modelo-de-creencias-en-salud-un-modelo-para-el-cambio-de-comportamiento-en-personas-con-diabetes/ (accessed on 4 March 2025).
- Torres, D.; Capote, J. Agroquímicos un problema ambiental global: Uso del análisis químico como herramienta para el monitoreo ambiental. Ecosistema 2004, 13, 2–6. Available online: https://www.revistaecosistemas.net/index.php/ecosistemas/article/view/201 (accessed on 15 January 2025).
- Programa de las Naciones Unidas para el Medio Ambiente (PNUMA). Nueva guía de Educación Ambiental Para ALC se Enfoca en Acciones por la Naturaleza y el Clima y Contra la Contaminación. 2021. Available online: https://www.unep.org/es/noticias-y-reportajes/comunicado-de-prensa/nueva-guia-de-educacion-ambiental-para-alc-se-enfoca-en (accessed on 10 February 2025).
- Organización Mundial de la Salud (OMS). El mundo debe luchar contra el peligro inminente de la contaminación química. 2019. Available online: https://news.un.org/es/story/2019/03/1452621 (accessed on 10 February 2025).
- Naciones Unidas. La Contaminación Mata Nueve Millones de Personas al Año, el Doble Que el COVID-19. 2022. Available online: https://news.un.org/es/story/2022/02/1504162 (accessed on 24 November 2024).
- Organización Mundial de la Salud (OMS). Casi el 99% de la Población Mundial Respira Aire que Supera los Límites de Contaminación Recomendados. 2022. Available online: https://news.un.org/es/story/2022/04/1506592 (accessed on 15 January 2025).
- Lara Calderón, A.M. La educación ambiental en sociedades agrícolas: El caso de Pueblo Llano, Mérida. Educere. La Rev. Venez. Educ. 2014, 19, 143–152. Available online: https://www.redalyc.org/pdf/356/35631103016.pdf (accessed on 15 February 2025).
- Köpeczi-Bócz, T. The Impact of a Combination of Flipped Classroom and Project-Based Learning on the Learning Motivation of University Students. Educ. Sci. 2024, 14, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caraballo Vidal, I.; Pezelj, L.; Ramos-Álvarez, J.J.; Guillen-Gamez, F.D. Level of Satisfaction with the Application of the Collaborative Model of the Flipped Classroom in the Sport of Sailing. Educ. Sci. 2024, 14, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magaji, A.; Adjani, M.; Coombes, S. A Systematic Review of Preservice Science Teachers’ Experience of Problem-Based Learning and Implementing It in the Classroom. Educ. Sci. 2024, 14, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, L. The Grass Ceiling: Hidden Educational Barriers in Rural England. Educ. Sci. 2024, 14, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criado-Del Rey, J.; Portela-Pino, L.; Domínguez-Alonso, J.; Pino-Juste, M. Assessment of Teacher Motivation, Psychometric Properties of the Work Tasks Motivation Scale for Teachers (WTMST) in Spanish Teachers. Educ. Sci. 2024, 14, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano-Ortiz, A.; Piñar Fuentes, J.C.; Rodrigues Meireles, C.; Cano, E. Urban Natural Spaces as Laboratories for Learning and Social Awareness. Sustainability 2024, 16, 3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monroe, M.C.; Krasny, M.E. Across the spectrum: Resources for environmental education. North Am. Assoc. Environ. Educ. 2015, 2, 1–102. Available online: https://www.academia.edu/27500674/Foundation_of_Environmental_Education (accessed on 15 February 2025).
- Guerrero, E.M.; Suarez, M.R. Integración de valores económicos y sociales de los servicios ecosistémicos del parque Migel Lillo (Necochea, Argentina). Rev. Latinoam. Estud. Socioambientales 2019, 26, 69–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Wang, M.; Yang, S.; Zhang, F.; Wang, Y.; Li, P.; Ma, W.; Sui, S.; Liu, T.; Wang, M. Analysis of Agricultural Carbon Emissions and Carbon Sinks in the Yellow River Basin Based on LMDI and Tapio Decoupling Models. Sustainability 2024, 16, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machete, K.C.; Senyolo, M.P.; Gidi, L.S. Adaptation through Climate-Smart Agriculture: Examining the Socioeconomic Factors Influencing the Willingness to Adopt Climate-Smart Agriculture among Smallholder Maize Farmers in the Limpopo Province, South Africa. Climate 2024, 12, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.; Xiong, K.; Zhu, D.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, W. Ecosystem Services Value Realization and Ecological Industry Design in Scenic Areas of Karst in South China. Forests 2024, 15, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilches, A.; Gil-Pérez, D. The transition to Sustainability as an urgent objective for overcoming the current systemic crisis. Eureka J. Sci. Educ. Dissem. 2016, 13, 395–407. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/10498/18296 (accessed on 15 February 2025).
- Palacios, J.; Amud, N.; Mendoza, D. Implementación de huertas escolares como estrategia de enseñanza-aprendizaje de la biología de grado sexto en la Institución Educativa Agrícola de Urabá del municipio de Chigorodó y de grado séptimo de la Institución Educativa Rural Zapata, de Necoclí, departamento de Antioquia. (Tesis magistral Universidad Pontificia Bolivariana, Medellín). 2016. Available online: https://repository.upb.edu.co/bitstream/handle/20.500.11912/2950/T.G.%20JULIO%20%C3%89DINSON%20PALACIOS%20Y%20OTROS.pdf (accessed on 25 November 2024).
- Reglamento de Ejecución (UE) Nº 543/2011 de la Comisión Europea, de 7 Junio. 2011. Por el Que se Establecen Disposiciones de Aplicación del Reglamento (CE) nº 1234/2007 del Consejo, en los Sectores de Frutas y Hortalizas y de las Frutas y Hortalizas Transformadas. Available online: https://www.boe.es/doue/2011/157/L00001-00163.pdf (accessed on 25 November 2024).
- BOE. Real Decreto 830/2010, de 25 Junio por el Que se Establece la Normativa Reguladora de la Capacitación Para Realizar Tratamientos Con Biocidas. BOE nº 170 del 14 Julio. 2010. Available online: https://www.boe.es/eli/es/rd/2010/06/25/830/con (accessed on 25 November 2024).
- BOE. Real Decreto 1105/2014, de 26 de Diciembre por el Que se Establece el Currículo Básico de la Educación Secundaria Obligatoria y del Bachillerato. BOE nº 3, del 3 de Enero. 2014. Available online: https://www.boe.es/eli/es/rd/2014/12/26/1105/con (accessed on 25 November 2024).
- BOE. Real Decreto 387/2021, de 1 Junio por el que se Regula el Régimen de Certificación Fitosanitaria Oficial). BOE nº 151 del 25 Junio. 2021. Available online: https://www.boe.es/eli/es/rd/2021/06/01/387 (accessed on 25 November 2024).
- Montaner-Villalba, S.; Santiago, R.; Bergmann, J. Aprender al revés. Flipped Learning 3.0 y metodologías activas en el aula. Rev. Interuniv. Investig. Tecnol. Educ. (RIITE) 2018, 7, 98–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero Fernández, A.; Rodríguez Marín, F.; López Lozano, L.; Solís Ramírez, E. Alfabetización ambiental en la formación inicial docente: Diseño y validación de un cuestionario. Enseñanza Las Cienc. 2022, 40, 25–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magwegwe, E.; Zivengwa, T.; Zenda, M. Adaptation and Coping Strategies of Women to Reduce Food Insecurity in an Era of Climate Change: A Case of Chireya District, Zimbabwe. Climate 2024, 12, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodson, D. Time for action: Science education for an alternative future. Int. J. Sci. Educ. 2003, 25, 645–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furtak, E.M.; Seidel, T.; Iverson, H.; Briggs, D.C. Experimental and quasi-experimental studies of inquiry-based science teaching: A meta-analysis. Rev. Educ. Res. 2012, 82, 300–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perochena González, P.; Torrecilla Sánchez, E.M.; Torrijos Fincias, P.; Rodríguez Conde, M.J. Estrategias de Selección de Participantes Para Diseños Experimentales en Investigación Evaluativa en Educación: Reflexión a Partir de Tres Estudios; En Investigar con y para la sociedad; Asociación Interuniversitaria de Investigación Pedagógica (AIDIPE): Barcelona, Spain, 2015; Volume 1, pp. 125–134. Available online: https://portalcientifico.uned.es/documentos/5e4fc35d29995245c6b28bc8 (accessed on 15 February 2025).
- Pozo, J.I.; Gómez Crespo, M.Á. Aprender y Enseñar Ciencia: Del Conocimiento Cotidiano al Conocimiento Científico. Morata. 1998, p. 329. Available online: https://dialnet.unirioja.es/servlet/articulo?codigo=7383752 (accessed on 15 February 2025).
- Hodson, D. Teaching and Learning about Science: Language, Theories, Methods, History, Traditions and Values; Sense Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2009; Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/347784433_Teaching_and_Learning_about_Science_Language_Theories_Methods_History_Traditions_and_Values (accessed on 15 February 2025).
- Oviedo, H.C.; Campo-Arias, A. Aproximación al uso del coeficiente alfa de Cronbach. Rev. Colomb. Psiquiatr. 2005, 34, 572–580. Available online: http://www.scielo.org.co/pdf/rcp/v34n4/v34n4a09.pdf (accessed on 20 November 2024).
- Vygotsky, L.S. Pensamiento y Lenguaje; Paidós: Barcelona, Spain, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Dewey, J. Experience and Education; Touchstone: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Piaget, J. La teoría de Piaget. Infanc. Y Aprendiz. 1981, 4, 13–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, L.; Chard, S.C. Engaging Children’s Minds: The Project Approach; Greenwood Publishing Group: Westport, CP, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Caruso, G. Calabrian Native Project: Botanical Education Applied to Conservation and Valorization of Autochthonous Woody Plants. Res. J. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2022, 2, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Olvera, W.; Esquivel-Gámez, I. Using the flipped learning model in a public high school. Rev. Educ. A Distancia RED 2018, 58, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez Rodríguez, F.J.; Palomares Ruiz, A. El “aula invertida” como metodología activa para fomentar la centralidad en el estudiante como protagonista de su aprendizaje. Contextos Educ. 2020, 26, 261–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano-Ortiz, A. Bioindicadores Ecológicos y Manejo de Cubiertas Vegetales como Herramienta para la Implantación de una Agricultura Sostenible. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad de Jaén, Jaén, Spain, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Villarias, J.L. Guía de Aplicaciones de los Herbicidas; Prensa, M., Ed.; 1981; p. 850. Available online: https://www.iberlibro.com/9788471141071/GUIA-APLICACION-HERBICIDAS-VILLARIAS-MORADILLO-8471141078/plp (accessed on 15 February 2025).
- Villarias, J.L. Atlas de Malas Hierbas. Prensa, M., Ed.; 2006, p. 632. Available online: https://www.mundiprensa.com/catalogo/9788484762881/atlas-de-malas-hierbas (accessed on 15 February 2025).
- Elliott, J. La Investigación-Acción en Educación; Ediciones Morata. 2007. Available online: https://edmorata.es/producto/la-investigacion-accion-en-educacion/ (accessed on 15 February 2025).
- Stufflebeam, D.L.; Shinkfield, A.J. Evaluation Theory, Models, and Applications; Jossey-Bass: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2007; p. 803. Available online: https://mp-pasca.unpak.ac.id/pdf/Bahan_Ajar/28_(Research%20Methods%20for%20the%20Social%20Sciences)%20Daniel%20L.%20Stufflebeam,%20Chris%20L.%20S.%20Coryn%20-%20Evaluation%20Theory,%20Models,%20and%20Applications-Jossey-Bass%20(2014).pdf (accessed on 15 February 2025).
- Quijano-López, R.; Chocano Óscar, G.; Pérez-Ferra, M. A Interdisciplinaridade no ensino das ciências experimentais: O estado atual da questão. Roteiro 2022, 47, e30105. Available online: https://periodicos.unoesc.edu.br/roteiro/article/view/30105 (accessed on 7 March 2025). [CrossRef]
- Diaz Linares, G.L. Aprendizaje basado en indagación (ABI): Una estrategia para mejorar la enseñanza—Aprendizaje de la química. Cienc. Lat. Rev. Científica Multidiscip. 2023, 7, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbes Scott, H. Holistic Education: An Analysis of Its Ideas and Nature; Foundation for Educational Renewal: Brandon, MB, USA, 2003; p. 408. [Google Scholar]
- Añez de Bravo, M.A. Modelo de aprendizaje holístico del ser: Una propuesta pedagógica en orientación. Rev. Estilos Aprendiz. 2009, 3, 177–195. Available online: https://revistaestilosdeaprendizaje.com/article/view/884/1572 (accessed on 20 November 2024). [CrossRef]
- Hare, J. La Educación Holística: Una Interpretación para los Profesores de los Programas del IB; Organización del Bachillerato Internacional: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010; pp. 1–8. Available online: https://es.scribd.com/document/177983712/La-educacion-holistica-John-HareMaría (accessed on 20 November 2024).
- Reyes-Cárdenas, F.; Padilla, K. La indagación y la enseñanza de las ciencias. Educ. Química 2012, 23, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.T.T. Implementing Feedforward-based Collaborative Assessment at Higher Education. Athens J. Educ. 2024, 11, 335–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Peiteado, M. Los estilos de enseñanza y aprendizaje como soporte de la actividad docente. Rev. Estilos Aprendiz. 2013, 11, 51–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perlado Lamo de Espinosa, I.; Barroso Tristán, J.M.; Trujillo Vargas, J.J. Evaluación por competencias y estilos de aprendizaje. Rev. Estilos Aprendiz. 2023, 16, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos Bernal, P. Métodos Alternativos a la Enseñanza Tradicional de las Ciencias Naturales: El Aprendizaje Basado en Proyectos. 2020, pp. 1–52. Available online: https://uvadoc.uva.es/handle/10324/58861 (accessed on 26 November 2024).
- Da Silva Siltori, P.F.; Lourenzani, W.L.; Satolo, E.G.; Ferreira Caldana, A.C.; Salati Marcondes de Moraes, G.H.; Batista Martins, V.W.; Simon Rampasso, I. Training Future Managers to Address the Challenges of Sustainable Development: An Innovative, Interdisciplinary, and Multiregional Experience on Corporate Sustainability Education. World 2024, 5, 155–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez Verdera, V.; Escámez Sánchez, J. Universidad y sostenibilidad social desde la ética del cuidado. Teoría La Educ. Rev. Interuniv. 2022, 34, 141–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banet, E. Finalidades de la educación científica en secundaria: Opinión del profesorado sobre la situación actual. Enseñanza Las Cienc. 2007, 25, 005–020. [Google Scholar]
- Cantó Doménech, J.; Hurtado Soler, A.; Vilches Peña, A. Educación científica más allá del aula. Alambique Didáctica Las Cienc. Exp. 2013, 74, 76–83. [Google Scholar]
- Gutiérrez-Pérez, B.M.; Ruedas-Caletrio, J.; Caballero Franco, D.; Murciano-Hueso, A. La conexión de la naturaleza como factor clave en la formación de las identidades infantiles: Una revisión sistemática. Teoría La Educación. Rev. Interuniv. 2024, 36, 31–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domíguez, S. Del holismo al constructivismo. Los grandes maestros. Rev. Postgrado FACE-UC 2014, 6, 39–51. Available online: http://www.arje.bc.uc.edu.ve/arj15/art03.pdf (accessed on 25 January 2025).


| Method | Objective | Data Source | Conclusion |
|---|---|---|---|
| Assessment of students’ knowledge. | Measure the level of understanding regarding chemical and environmental risks. | Questionnaires, response analysis. | Identification of knowledge gaps and areas for improvement. |
| Effectiveness of teaching methods (PBL, IBL, flipped classroom). | Evaluate the effectiveness of pedagogical methods in promoting students’ critical understanding. | Classroom observation, interviews, grade analysis. | Significant improvement in critical understanding and knowledge application. |
| Analysis of educational curricula. | Assess the inclusion of environmental and health topics in curricula. | Curriculum documents, teacher interviews. | Need to integrate more content related to sustainability and health. |
| Environmental and health impacts of chemical risks in agriculture. | Evaluate the effects of chemical pollution on health and the environment. | International reports, expert interviews. | Chemical pollution in agriculture poses a serious risk to human health. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cano-Ortiz, A.; Peña-Martínez, J.; Cano, E. Environmental Education as a Fundamental Tool for Preventing the Ingestion of Chemical Contaminants in Spain. Sustainability 2025, 17, 4052. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17094052
Cano-Ortiz A, Peña-Martínez J, Cano E. Environmental Education as a Fundamental Tool for Preventing the Ingestion of Chemical Contaminants in Spain. Sustainability. 2025; 17(9):4052. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17094052
Chicago/Turabian StyleCano-Ortiz, Ana, Juan Peña-Martínez, and Eusebio Cano. 2025. "Environmental Education as a Fundamental Tool for Preventing the Ingestion of Chemical Contaminants in Spain" Sustainability 17, no. 9: 4052. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17094052
APA StyleCano-Ortiz, A., Peña-Martínez, J., & Cano, E. (2025). Environmental Education as a Fundamental Tool for Preventing the Ingestion of Chemical Contaminants in Spain. Sustainability, 17(9), 4052. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17094052








