Using System Dynamics to Analyze Influencing Factors and Emission Reduction Potential of Geothermal Resources Development and Utilization in Tianjin
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Contextual Background
1.2. Literature Review
1.3. Research Objectives
2. Study Area, Historical Background Related to Geothermal Development, and Status
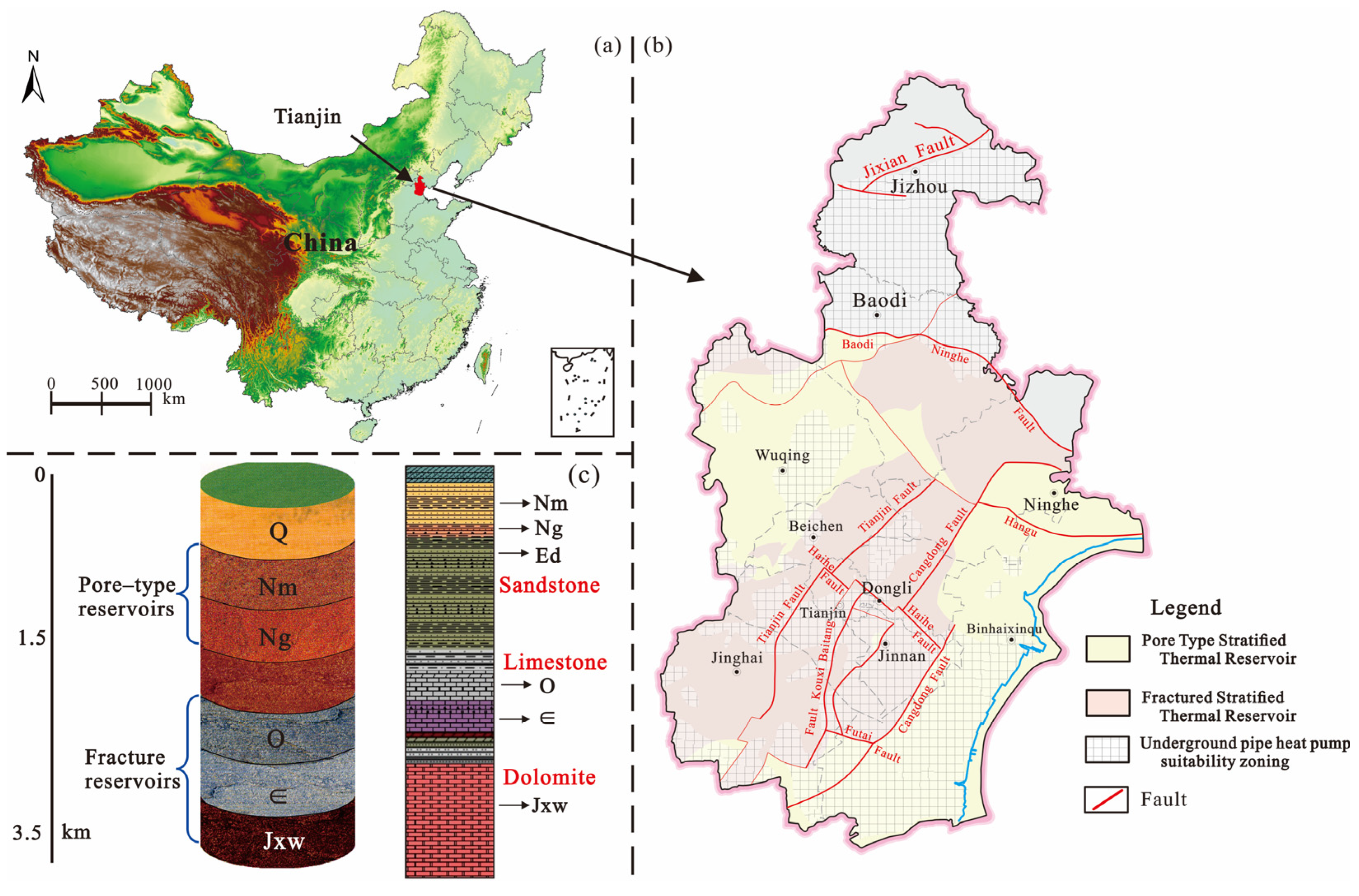
2.1. Study Area
2.2. History and Current Status of Geothermal Energy in Tianjin
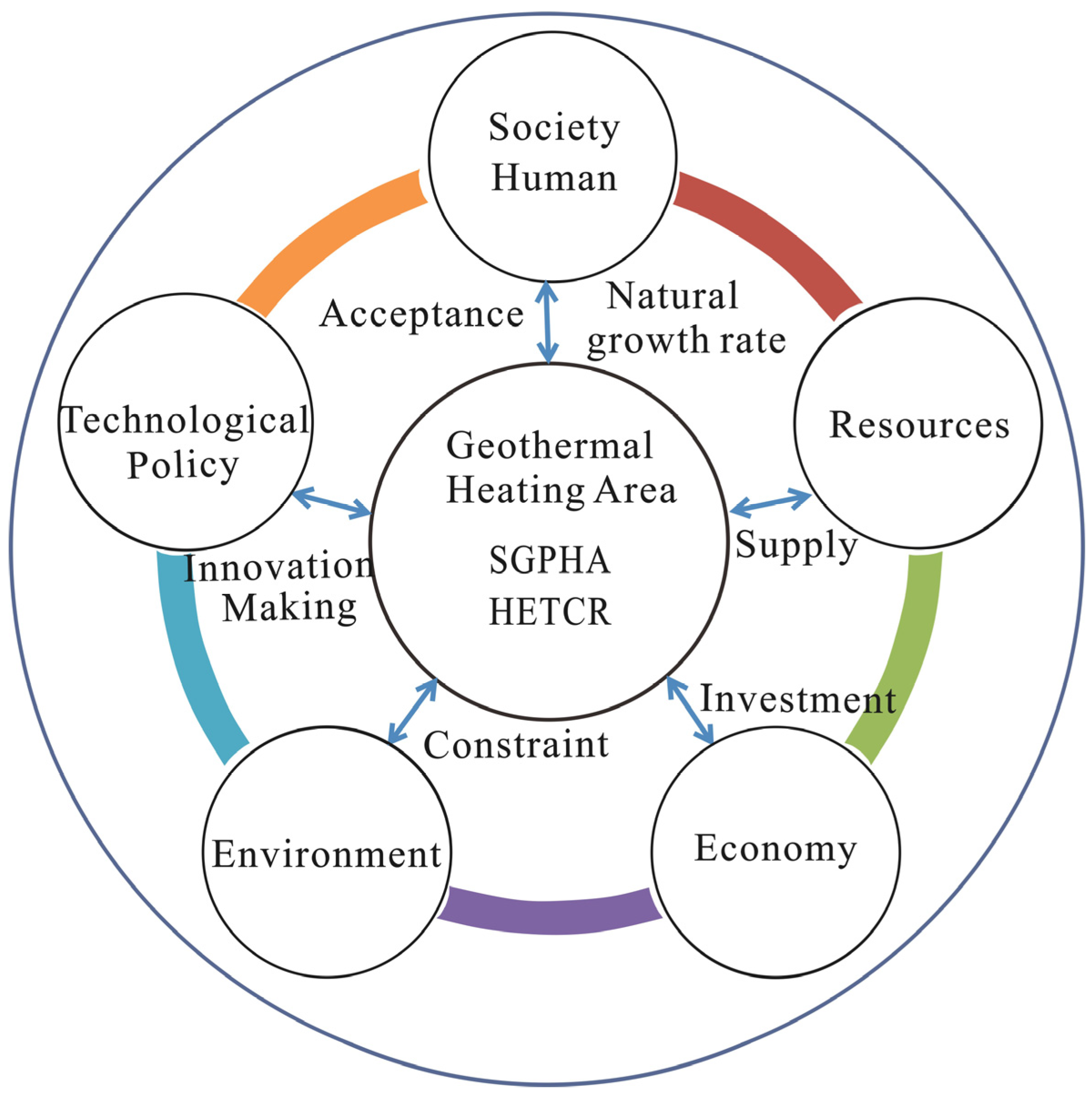
2.3. Influence Mechanism of Geothermal Development in Tianjin
3. Methodology
3.1. SD Model Boundaries
3.2. A Framework Based on the System Dynamics Model
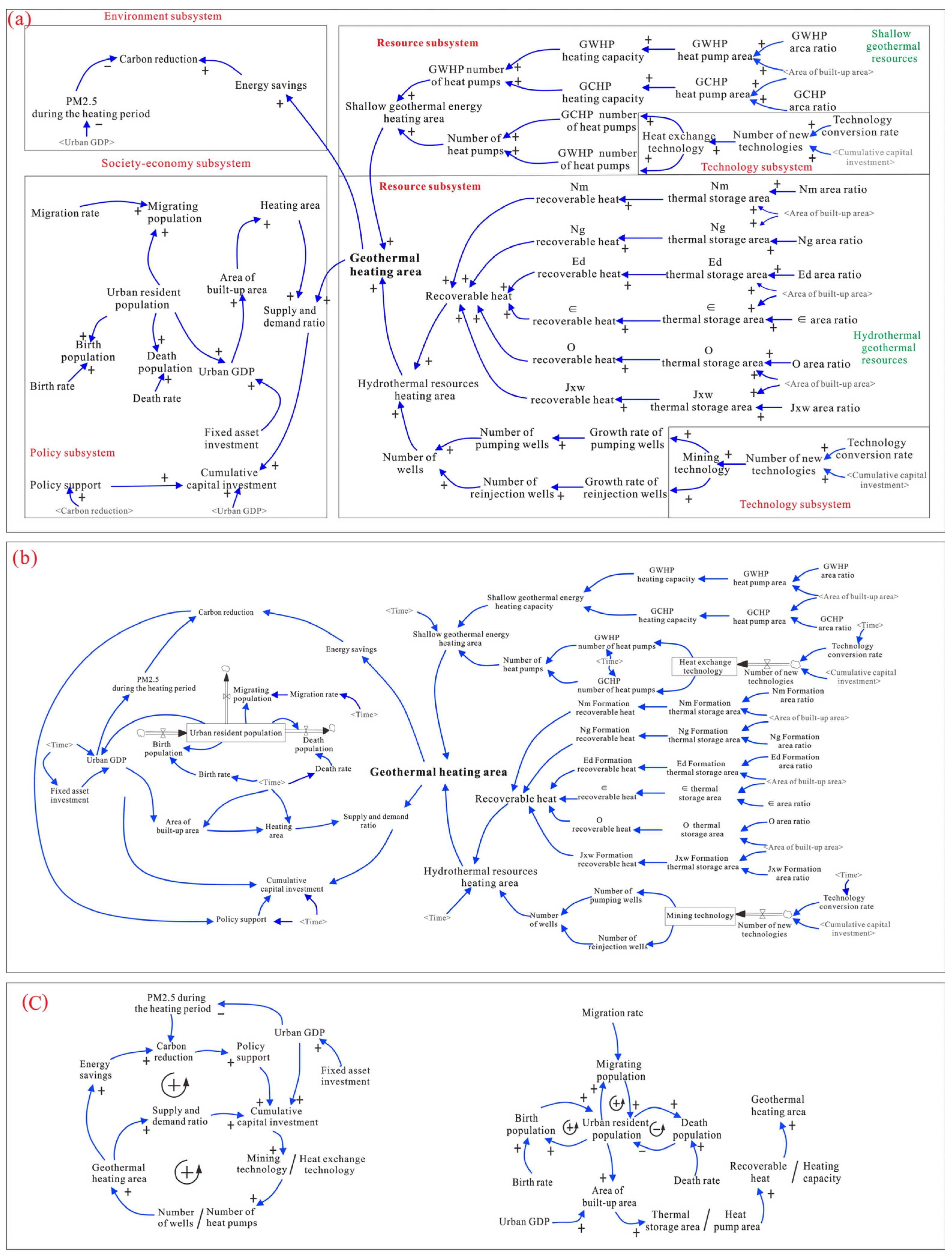
3.2.1. Causal Loop Diagrams (CLD) Analysis
3.2.2. Socioeconomic Subsystem
3.2.3. Geothermal Resource Subsystem
3.2.4. Environment Subsystem
3.2.5. Policy and Technology Subsystem
3.3. Model Tests
3.3.1. History Test
3.3.2. Sensitivity Test
3.4. Scenario Setting and Parameter Assumptions
3.4.1. Scenario Setting
3.4.2. Parameter Assumptions
4. Results
4.1. Sensitivity Analysis Results and Main Influencing Factors
4.2. Comparative Analysis of Multiscenario Results
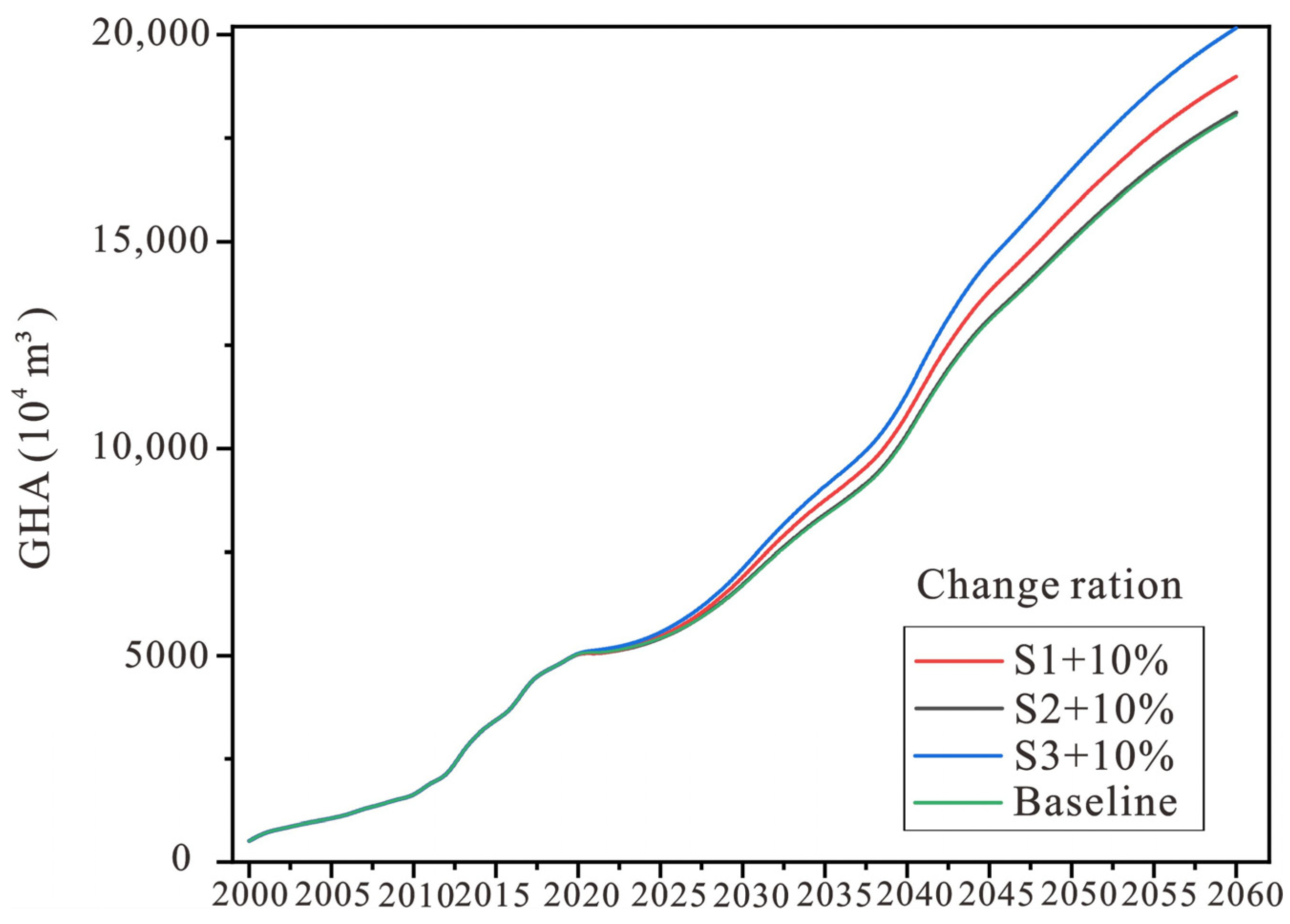
4.2.1. Multiscenario Prediction Results of GHA
4.2.2. Multiscenario Prediction Results of HRHA and SGEHA
4.2.3. Multiscenario Prediction Results of CER
5. Discussion
5.1. Improve the Policy Mechanism
5.2. Improve Economic Investment
5.3. Promote Technological Progress
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CER | Carbon emissions reduction; |
| CO2 | Carbon dioxide; |
| EPDS | Economic Priority Development Scenario; |
| FAI | Fixed asset investment; |
| GCHP | Ground-coupled heat pumps; |
| GDP | Gross domestic product; |
| GHA | Geothermal heating area; |
| GWHP | Groundwater heat pumps; |
| HETCR | Heat exchange technology conversion rate; |
| HRHA | Hydrothermal resources heating area; |
| MTCR | Mining technology conversion rate; |
| PGR | Population growth rate; |
| PSS | Policy-Strengthening Scenario; |
| SCS | Status Continuation Scenario; |
| SD | System dynamics; |
| SGEHA | Shallow geothermal energy heating area; |
| TPS | Technological Progress Scenario; |
| Nm | Minghuazhen group; |
| Ng | Guantao group; |
| Ed | Paleogene formation Dongying group; |
| O | Paleozoic Ordovician group; |
| ∈ | Cambrian group; |
| Jxw | Mesoproterozoic Jixian Wumishan group. |
References
- Zhu, X.; Zhang, Q.L.; Wang, W.L.; Liu, Y.G. Study on the influencing factors of rock-soil thermophysical parameters in shallow geothermal energy. J. Groundw. Sci. Eng. 2015, 3, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhang, W.; Liang, J.; Lin, W.; Liu, Z.; Wang, W. Evaluation of geothermal resources potential in China. Acta Geosci. Sin. 2017, 38, 448–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Cao, M.; Liu, P. Development and utilization of geothermal energy in China: Current practices and future strategies. Renew. Energy 2018, 125, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Lu, X. Characteristics and prospect of geothermal industry in China under the “dual carbon” target. Energy Geosci. 2023, 4, 100199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wan, G. Current situation and prospect of China’s geothermal resources. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 32, 651–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Lu, C.; Li, Y. Genetic model and exploration target area of geothermal resources in Hongtang Area, Xiamen, China. J. Groundw. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y. Deep geothermal resources in China: Potential, distribution, exploitation, and utilization. Energy Geosci. 2023, 4, 100209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Z.; Hu, S.; Wang, J. A roadmap to geothermal energy development in China. Sci. Technol. Rev. 2012, 30, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, J.W.; Huttrer, G.W.; Toth, A.N. Characteristics and trends in geothermal development and use, 1995 to 2020. Geothermics 2022, 105, 102522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Jia, L.; Yu, Y.; Wang, H. The development and utilization of geothermal energy in the world. Geol. Chin. 2021, 48, 1734–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toth, A.N. 7.11—Geothermal Utilization Statistics 2019. In Comprehensive Renewable Energy, 2nd ed.; Letcher, T.M., Ed.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2022; pp. 220–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, R.; Zhou, P.; Tang, J. Current status and enlightenments of geothermal development in Europe. Chin. Min. Mag. 2017, 26, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milanović Pešić, A.; Brankov, J.; Denda, S.; Bjeljac, Ž.; Micić, J. Geothermal energy in Serbia—Current state, utilization and perspectives. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 162, 112442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebbihiat, N.; Atia, A.; Arıcı, M.; Meneceur, N. Geothermal energy use in Algeria: A review on the current status compared to the worldwide, utilization opportunities and countermeasures. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 302, 126950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benti, N.E.; Woldegiyorgis, T.A.; Geffe, C.A.; Gurmesa, G.S.; Chaka, M.D.; Mekonnen, Y.S. Overview of geothermal resources utilization in Ethiopia: Potentials, opportunities, and challenges. Sci. Afr. 2023, 19, e01562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X. Study on Method and Application of Economic Evaluation of Geothermal Resources. Ph.D. Thesis, China University of Geosciences, Beijing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Zhang, Q.; Li, H.; Mclellan, B.; Zhang, T.; Tan, Z. Investment decision on shallow geothermal heating & cooling based on compound options model: A case study of China. Appl. Energy 2019, 254, 113655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Zwaan, B.; Dalla Longa, F. Integrated assessment projections for global geothermal energy use. Geothermics 2019, 82, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitch, A.; Haley, B.; Hastings-Simon, S. Can the oil and gas sector enable geothermal technologies? Socio-technical opportunities and complementarity failures in Alberta, Canada. Energy Policy 2019, 125, 384–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebri, M. Use renewables to be cleaner: Meta-analysis of the renewable energy consumption–economic growth nexus. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 42, 657–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzella, A.; Bonciani, R.; Allansdottir, A.; Botteghi, S.; Donato, A.; Giamberini, S.; Lenzi, A.; Paci, M.; Pellizzone, A.; Scrocca, D. Environmental and social aspects of geothermal energy in Italy. Geothermics 2018, 72, 232–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanbury, O.; Vasquez, V.R. Life cycle analysis of geothermal energy for power and transportation: A stochastic approach. Renew. Energy 2018, 115, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, H.; Roumi, S.; Ármannsson, H.; Noorollahi, Y. Cascading uses of geothermal energy for a sustainable energy supply for Meshkinshahr City, Northwest, Iran. Geothermics 2019, 79, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, W. The statis and development trend of geothermal resources in China. Earth Sci. Front. 2020, 27, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Lei, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, L. Examination of the relationship between the exploitation of geothermal sources and regional economies: A Beijing case study. Water Environ. J. 2020, 34, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hähnlein, S.; Bayer, P.; Ferguson, G.; Blum, P. Sustainability and policy for the thermal use of shallow geothermal energy. Energy Policy 2013, 59, 914–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L. Study on the Industry Investment Fund under the Exploitation of Geothermal Resources. Ph.D. Thesis, Jilin University, Changchun, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, W. Study on Economic Evaluation of Geothermal Energy Developing and Utilizing. Ph.D. Thesis, China University of Geosciences, Beijing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Noorollahi, Y.; Gholami Arjenaki, H.; Ghasempour, R. Thermo-economic modeling and GIS-based spatial data analysis of ground source heat pump systems for regional shallow geothermal mapping. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 72, 648–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L. The Asian Geothermal Map and the Evaluation on Geothermal Potential. Master’s Thesis, Jilin University, Changchun, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Li, X.; Ma, L.; Li, Z. Using system dynamics to analyse key factors influencing China’s energy-related CO2 emissions and emission reduction scenarios. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 320, 128811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Y.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, Y. Research on the Sustainable Development of an Economic-Energy-Environment (3E) System Based on System Dynamics (SD): A Case Study of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region in China. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, G.B.; Levine, R.; Miller, R.L. Using system dynamics modeling to understand the impact of social change initiatives. Am. J. Community Psychol. 2007, 39, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Niu, D.; Wang, K.; Xu, X. Sustainable development pathways of hydropower in China: Interdisciplinary qualitative analysis and scenario-based system dynamics quantitative modeling. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 287, 125528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yue, D.; Feng, Z.; Song, J.; Liu, D.; Song, Z. Sinoprobe and parameters study on deep karst geothermal reservoir in the Donglihu Area, Tianjin and its exploitable potential analysis. Geol. Chin. 2022, 49, 1732–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zheng, R.; Yi, L.; Yuan, J. A system dynamics modeling on wind grid parity in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 247, 119170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y. Simulation and selection of fiscal and taxation policy in geothermal industry development based on system dynamics. Ph.D. Thesis, China University of Geosciences, Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, H.; Wang, G.; Zhang, W.; Ma, F.; Lin, W.; Ji, M. Predicting the Potential of China’s Geothermal Energy in Industrial Development and Carbon Emission Reduction. Sustainability 2023, 15, 7508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Zhao, S.; Cai, Y.; Yan, J.; Xu, L. Dynamic evolution of geothermal reservoir characteristics in Tianjin in the last three decades of large-scale development. Acta Geol. Sin. 2023, 97, 297–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Song, M.; Tian, G. Development situation of the geothermal resources and suggestion on sustainable development utilization in Tianjin. North Chin. Geol. 2012, 35, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Lin, L.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, W.; Zhao, S. Discussion on the sustainable exploitation and utilization of geothermal resources in Tianjin. North Chin. Geol. 2006, 29, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Wang, W.; Zhang, W.; Ma, F.; Liu, F. The status quo and prospect of geothermal resources exploration and development in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region in China. Chin. Geol. 2020, 3, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Hao, Y.; Zhang, P.; Xiong, X.; Shi, Z. System dynamics modeling of food-energy-water resource security in a megacity of China: Insights from the case of Beijing. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 355, 131773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minissale, A.; Borrini, D.; Montegrossi, G.; Orlando, A.; Tassi, F.; Vaselli, O.; Huertas, A.D.; Yang, J.; Cheng, W.; Tedesco, D.; et al. The Tianjin geothermal field (north-eastern China): Water chemistry and possible reservoir permeability reduction phenomena. Geothermics 2008, 37, 400–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Feng, J.; Luo, J.; Zeng, Y. Distribution, exploitation, and utilization of intermediate-to-deep geothermal resources in eastern China. Energy Geosci. 2023, 4, 100187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, R.; Wang, G.; Feng, L.; Zhang, W.; Wan, W.; Cao, S. Evaluation of shallow geothermal energy resources in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Plain based on land use. J. Groundw. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, G.; Zhu, X.; Liu, Z. Characteristics and potential of shallow geothermal resources in provincial capital cities of China. Geol. Chin. 2017, 44, 1062–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, G.; Lin, L.; Cheng, W.; Zeng, M.; Liu, D.; Song, M. The construction of dynamic monitoring network for the development and utilization of shallow geothermal energy in Tianjin. Geol. Chin. 2011, 38, 1660–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Luo, C.; Wang, Y. Direct utilization status and power generation potential of low-medium temperature hydrothermal geothermal resources in Tianjin, China: A review. Geothermics 2016, 64, 426–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, D.; Niu, W.; Xiang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Z. Prospects and problems of geothermal resources exploitation and utilization in Tianjin. North Chin. Geol. 2022, 45, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Z.; Huang, S.; Hu, S.; Zhao, P.; He, L. Geothermal studies in China: Progress and prospects 1995–2014. Chin. J. Geol. 2014, 49, 719–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Dou, J.; Li, M.; Zeng, M. Geothermal energy in China: Status, challenges, and policy recommendations. Util. Policy 2020, 64, 101020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, H.; Zhu, Q.; Tian, P.; Hu, W. Technologies and Applications of Geophysical Exploration in Deep Geothermal Resources in China. In Proceedings of the World Geothermal Congress, Melbourne, Australia, 19–25 April 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Alsaleh, M.; Yang, Z.; Chen, T.; Wang, X.; Abdul-Rahim, A.S.; Mahmood, H. Moving toward environmental sustainability: Assessing the influence of geothermal power on carbon dioxide emissions. Renew. Energy 2023, 202, 880–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laimon, M.; Mai, T.; Goh, S.; Yusaf, T. System dynamics modelling to assess the impact of renewable energy systems and energy efficiency on the performance of the energy sector. Renew. Energy 2022, 193, 1041–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apergis, N.; Payne, J.E. Renewable energy consumption and economic growth: Evidence from a panel of OECD countries. Energy Policy 2010, 38, 656–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T11615-2010; Geological Exploration Specification for Geothermal Resources. Standardization Administration of China, Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2010.
- Rehan, R.; Knight, M.A.; Haas, C.T.; Unger, A.J.A. Application of system dynamics for developing financially self-sustaining management policies for water and wastewater systems. Water Res. 2011, 45, 4737–4750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China Geological Survey; Ministry of Natural Resources. China Geothermal Energy Development Report; China Petrochemical Press: Beijing, China, 2018.
- Daniilidis, A.; Alpsoy, B.; Herber, R. Impact of technical and economic uncertainties on the economic performance of a deep geothermal heat system. Renew. Energy 2017, 114, 805–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorsteinsson, H.H.; Tester, J.W. Barriers and enablers to geothermal district heating system development in the United States. Energy Policy 2010, 38, 803–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huculak, M.; Jarczewski, W.; Dej, M. Economic aspects of the use of deep geothermal heat in district heating in Poland. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 49, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

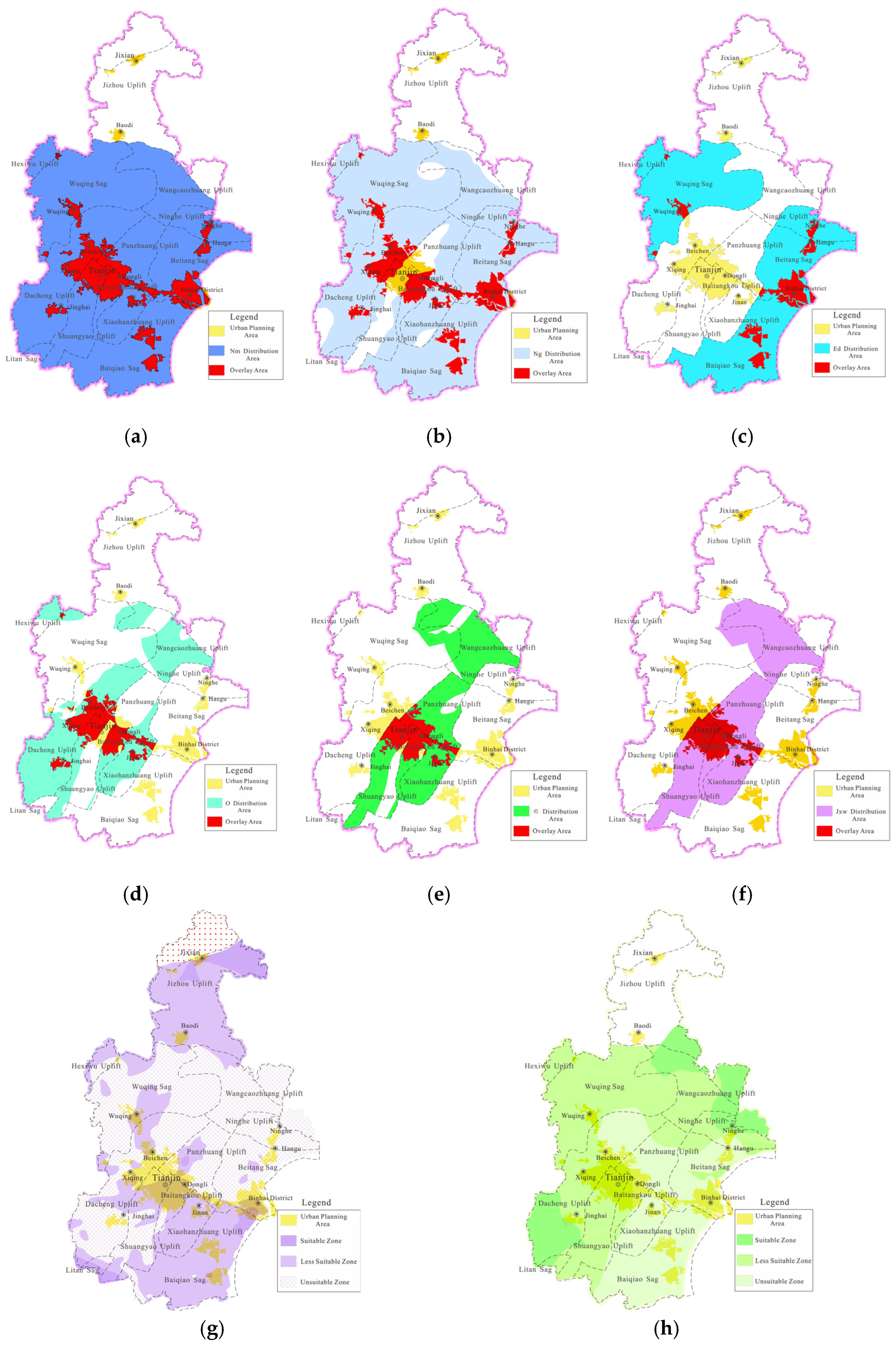




| Thermal Reservoir | Distribution Area/km2 | Geothermal Resources/1018 J | Equivalent Standard Coal/108 J |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nm | 9467.44 | 260.377 | 88.843 |
| Ng | 8451.97 | 126.932 | 43.308 |
| Ed | 4882.85 | 39.16 | 13.362 |
| O | 3548.86 | 125.372 | 42.778 |
| ∈ | 2753.83 | 54.734 | 18.675 |
| Jxw | 3440.78 | 259.966 | 99.604 |
| Scenarios | Parameters |
|---|---|
| Economic Priority Development Scenario (EPDS) | According to the “Fourteenth Five-Year Plan for National Economic and Social Development of Tianjin City” and the outline of the 2035 Visionary Goals, the growth rate of the GDP in Tianjin will adjust to 6% from 2021 to 2025, 4% from 2026 to 2035, 3% from 2036 to 2050, and 2% from 2051 to 2060. |
| Technological Progress Scenario (TPS) | The increase in heat exchange technology conversion rate (HETCR) and mining technology conversion rate (MTCR) in Tianjin will be 5% from 2021 to 2030. After carbon peaking, the increase in HETCR and MTCR will be 2% from 2031 to 2050. In consideration of the carbon neutrality goal, the increase in HETCR and MTCR will be 1% from 2051 to 2060. |
| Policy-Strengthening Scenario (PSS) | Tianjin City Territorial Spatial Master Plan (2021–2035): Tianjin’s resident population will reach 15 million in 2025. The planned population of Tianjin City in 2035 is controlled at about 20 million. Under the above the EPDS and TPS scenarios, the proportion of the urban population in 2035 will be 85%. |
| Year | 2025 | 2030 | 2060 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline (104 m2) | GHA | 5413.13 | 6688.92 | 18,055.1 |
| HRHA | 4106.39 | 5185.24 | 15,330.9 | |
| SGEHA | 1306.74 | 1503.68 | 2724.14 | |
| CER | 292.43 | 361.35 | 975.38 | |
| EPDS (104 m2) | GHA | 5554.8 | 7248.52 | 22,739.2 |
| HRHA | 4152.85 | 5578.55 | 19,420.6 | |
| SGEHA | 1401.94 | 1670.97 | 3318.56 | |
| CER | 300.08 | 391.64 | 1228.43 | |
| TPS (104 m2) | GHA | 5472.35 | 6859.92 | 18,952.5 |
| HRHA | 4153.15 | 5316.85 | 16,087.1 | |
| SGEHA | 1319.20 | 1543.07 | 2865.41 | |
| CER | 295.63 | 370.59 | 1023.86 | |
| PSS (104 m2) | GHA | 5850.49 | 9101.01 | 32,031.4 |
| HRHA | 4418.18 | 7318.47 | 28,362 | |
| SGEHA | 1432.31 | 1782.54 | 3369.37 | |
| CER | 316.06 | 491.66 | 1730.41 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuan, R.; Wang, G.; Xu, B.; Zhao, S.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, W.; Lin, W.; Shi, H. Using System Dynamics to Analyze Influencing Factors and Emission Reduction Potential of Geothermal Resources Development and Utilization in Tianjin. Sustainability 2025, 17, 4005. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17094005
Yuan R, Wang G, Xu B, Zhao S, Zhu X, Zhang W, Lin W, Shi H. Using System Dynamics to Analyze Influencing Factors and Emission Reduction Potential of Geothermal Resources Development and Utilization in Tianjin. Sustainability. 2025; 17(9):4005. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17094005
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, Ruoxi, Guiling Wang, Bowen Xu, Sumin Zhao, Xi Zhu, Wei Zhang, Wenjing Lin, and Honglei Shi. 2025. "Using System Dynamics to Analyze Influencing Factors and Emission Reduction Potential of Geothermal Resources Development and Utilization in Tianjin" Sustainability 17, no. 9: 4005. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17094005
APA StyleYuan, R., Wang, G., Xu, B., Zhao, S., Zhu, X., Zhang, W., Lin, W., & Shi, H. (2025). Using System Dynamics to Analyze Influencing Factors and Emission Reduction Potential of Geothermal Resources Development and Utilization in Tianjin. Sustainability, 17(9), 4005. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17094005







