Abstract
TiSi2 and Ti5Si3 were synthesized through a simple and cost-effective process, providing a sustainable way to recycle titanium oxide and silicon wastes from industry. The reaction process was investigated at 1500 °C under various slag/silicon ratios and slag compositions. TiSi2 was synthesized successfully under all experimental conditions, with nearly complete extraction of titanium oxide from the slag within 5 h under optimized conditions. TiSi2 initially formed at the slag/silicon interface, followed by the formation of Ti5Si3 as TiSi2 droplets fell through the slag. The production rate of TiSi2 was higher than that of Ti5Si3. Kinetic analysis showed that the reaction rate constant ranged from 1.2 × 10−5 to 4.3 × 10−4 s−1. Viscosity and basicity were not the limiting factors of the kinetics in this work. The amount of TiO2 in the slag significantly influenced the reaction process, with slag containing less than 30 mol% TiO2 identified as optimal for efficient titanium extraction and a high synthesis rate.
1. Introduction
Titanium silicides, particularly Ti5Si3 and TiSi2, are promising structural materials, with good oxidation resistance, excellent creep resistance and low specific weight [1]. Ti5Si3 is known for its high melting point (~2130 °C), excellent oxidation resistance, and high-temperature mechanical strength, making it suitable for aerospace, gas turbine, and protective coating applications [2]. TiSi2 is widely used in the microelectronics industry as a contact material and interconnecting layer because of its low electrical resistivity, thermal stability, and good compatibility with silicon-based devices [3]. In addition, TiSi2 is an attractive anode material for lithium ion batteries, offering high gravimetric and volumetric capacity [4]. There are plenty of production processes for titanium silicides that have been developed in recent decades, which are summarized in Table 1. Most processes employ the powder metallurgy method [3,4,5]. However, the purity of the titanium silicide products depends on the raw materials, whilst purification with powder metallurgical processes is difficult. Therefore, high-purity elementary substances are in high demand for combustion synthesis and mechanical alloying processes. This, however, increases the material cost of the product.

Table 1.
Production process of titanium silicides.
Oxides have been adopted to replace pure elementary substances during process development to reduce the costs. Mg was proposed to be introduced into the process to reduce the oxides [6,7]. However, considering the high partial pressure of Mg at high temperatures, a special high-pressure vessel is required. This could raise the production costs and the need for safety measures.
Electrochemical reduction was proposed as a low-temperature process to reduce oxides by green electricity [8,9]. Although it is a sustainable process, its industrialization still needs significant work. Moreover, the titanium silicides produced from the aforementioned methods still highly depend on the purity of the raw materials. Therefore, the silicothermic method was proposed for the production of titanium silicides because the refining process can be combined with the synthesis process to improve the purity of the products.
The silicothermic method was initially developed to reduce titanium-bearing blast furnace slag and produce ferroalloys [10]. In 2015, Morita et al. [13,14] adapted this method to synthesize titanium silicides from TiO2-bearing slag and silicon. In this process, titanium oxide-bearing melts were reacted with molten silicon, providing a sustainable recycling method for both silicon waste and titanium-bearing blast furnace slag [15]. It also provides a sustainable way to recycle titanium oxide from the waste catalysts, such as spent SCR denitration catalysts. The huge amount of these three types of solid waste from the chemical and energy industries increases the importance of such urgently needed recycling technologies. Furthermore, the silicothermic method can completely extract the titanium from the oxide phase. Therefore, the TiO2-free slag as a by-product can be used for the production of construction material, making this method a zero-solid-waste production process.
This method extracts the silicon oxide content from the molten oxide system while allowing silicon (or silicon alloys) to be converted into titanium silicides. Reaction conditions, such as the weight ratio of silicon to slag, influence the composition of the alloy product [16]. Our previous work [13] suggested that Ti5Si3 formation from slag proceeds via the intermediate phase TiSi2. There are Ti5Si4 and TiSi between Ti5Si3 and TiSi2, but Ti5Si4 was only reported with stabilization by TiAl3 alloying [17]. This may be because of thermodynamical compatibility [18], but it still needs further investigation. Normally, Ti5Si3 could not react further with molten silicon because of the difficulties of silicon diffusion in a solid.
In most cases, titanium in the slag can be effectively extracted into the intermetallic phases, resulting in a high recovery rate of valuable resources. Consequently, research efforts have mainly focused on optimizing reaction kinetics and phase separation efficiency.
Kinetic analysis of the reaction process has shown that silicon diffusion in the slag is the rate-determining step, meaning that slag properties significantly influence the reaction kinetics. A higher slag basicity may increase the value of the silicon diffusion coefficient and benefit the reaction kinetics [15]. Ion diffusion is generally influenced by the slag viscosity: the replacement of Si4+ with Al3+ increases the slag viscosity, whereas increasing the MgO content in the CaO-SiO2-MgO-Al2O3 slag decreases its viscosity. Correspondingly, Zhang et al. [19] observed the opposite effects of the Al and Mg concentrations in the slag on the reaction kinetics.
To improve phase separation and purification, several additional approaches have been applied, such as the directional solidification method [20], electromagnetic separation [21] and electroslag remelting refining [22]. It has been proven by experiments that titanium silicides can be successfully separated from other solid products. However, regarding the reaction process itself, it has been observed that the separation of slag and the intermetallic products can benefit from a long reaction time and high temperature [23]. This highlights the need for further studies on kinetics and phase separation.
In this study, we investigated the reaction process in the reduction, focusing on the effect of slag compositions and the slag-to-silicon ratio on the synthesis of titanium silicides. An artificial slag was applied in this work to simplify the study of the principal slag composition effect on the kinetics. The TiO2 content was varied to investigate the potential for titanium extraction from the slag resource. The typical TiO2 concentration is approximately 20 mass% in TiO2-bearing slag, while the titanium can be enriched to 40 mass% [24]. Additionally, slag with higher TiO2 compositions was investigated to explore the potential of the process for waste catalyst recycling, as the catalyst can contain more than 80 mass% TiO2 [25].
2. Experimental
The slag was pre-melted at 1500 °C from reagent grade TiO2, SiO2 and CaO. The CaO precursor was prepared by calcining CaCO3 at 1000 °C for 10 h in air. A 0.5 g semiconductor-grade silicon sample was melted in a graphite crucible (inner diameter: 8 mm) at 1500 °C. The reaction considerations are summarized in Table 2. The mass ratio of slag to silicon, denoted as rs, was controlled, as it influences the composition of the final product. Additionally, variations in the TiO2 content of the slag alter the reactant activity, thereby affecting the reduction process.

Table 2.
Compositions and weights of slags used in the experiments.
The slag was allowed to react with silicon for 2 h at 1500 °C in an induction furnace under a deoxidized argon atmosphere. After the reaction, the sample was withdrawn from the furnace, quenched in argon gas, and then subjected to metallographic examination and microstructural analysis using a scanning electron microscope (SEM, JSM6510LA, JEOL Ltd., Tokyo, Japan) equipped with an energy dispersive spectrum (EDS) system. The slag phase was mechanically separated from the alloy phase, and its composition was analyzed using inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy (ICP-AES, SPS 7700, SII Nano Technology, Chiba, Japan). For ICP-AES sample preparation, 0.1 g of crushed slag was digested in a platinum crucible using 0.5 g of Na2CO3 and 0.5 g of Na2B4O7 at 1000 °C for 20 min. The alkaline-fused sample was then dissolved in a 1:3 HCl/H2O acid solution and immediately analyzed.
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Different Slag/Silicon Ratios
The alloy phase, which mainly contained elemental silicon, floated on the slag in the reaction. SEM graphs of the alloy phase in the reacted samples are shown in Figure 1. SEM/EDS measurements revealed that the alloy consisted of three different phases (Figure 2). The light-colored phase was identified to be TiSi2, with an EDS-determined Ti:Si molar ratio of approximately 64:36. The dark-colored phase in the gaps between the TiSi2 grains was a Ti solution in Si, with the Ti content varying between 2.6~8.6 mol%. The other dark-colored phase in larger pieces was identified as pure silicon. No alloy phase containing more than 67 mol% titanium was detected, indicating that Ti5Si3 did not form within 2 h under these experimental conditions.
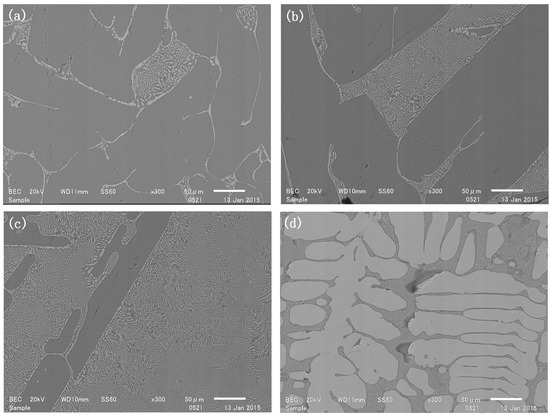
Figure 1.
Sample reduced for 2 h with a mass ratio of slag to silicon rs of (a) 1; (b) 2; (c) 3; (d) 4.
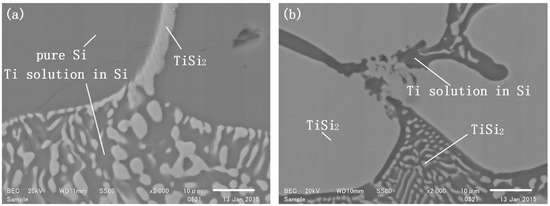
Figure 2.
Phase compositions of the sample reduced for 2 h with a mass ratio of slag to silicon rs of (a) 1; (b) 4.
The cross-sections of the reacted samples (Figure 1) showed that the ratio of the TiSi2 phase in the reduction increased with an increasing rs. The TiSi2 phase area fractions in these cross-sections were measured to be 6%, 13%, 39% and 78% in samples 1 to 4, respectively. It is well known that the TiSi2–Si binary system exhibits eutectic behavior, and the alloy in sample 4 was located on the TiSi2 rich side of the binary system. The image analysis indicated that the TiSi2 phase area fraction increased as a cubic function of increasing rs. For samples with a lower rs, most of the TiSi2 phase was aggregated at the boundaries of the pure silicon grains. As rs increased, the proportion of TiSi2–Ti solution mixture increased, while the pure silicon phase decreased. When rs reached four, the principal phase transitioned to pure TiSi2 dendritic crystals, the pure silicon phase disappeared, and the Ti solution phase segregated into the interdendritic regions, accompanied by some TiSi2 fine grains.
Pure bulk TiSi2 could be produced when the reaction time was prolonged. As shown in Figure 3a, the area fraction of TiSi2 in sample 3 increased from 39% to 61% when the reaction time was extended from 2 h to 5 h. After 12 h, the Si matrix was almost completely transformed into bulk TiSi2 (Figure 3b). Similarly, bulk TiSi2 phase was observed in sample 4 after 5 h of reaction.
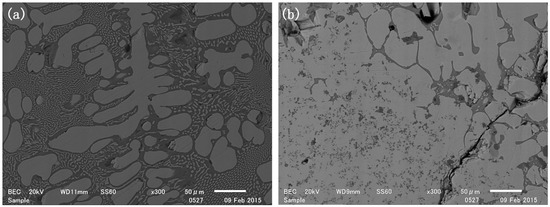
Figure 3.
Sample 3 reduced at 1500 °C for (a) 5 h; (b) 12 h.
During the reaction, alloy drops were also observed within the slag. This was due to the higher density of titanium silicides compared to slag. TiSi2 formed in the molten silicon and subsequently separated from the molten silicon phase as droplets in the reaction (Figure 4). The elemental mapping in Figure 4 demonstrated that the titanium content in the slag was significantly lower than in the alloy phase, indicating that the formation of intermetallics in the molten silicon facilitated the extraction of Ti from the slag. Additionally, the titanium-to-silicon ratio in the droplets was higher than that in the floating alloy, suggesting that these droplets were denser and continued to form additional titanium silicide phases as the reaction progressed.
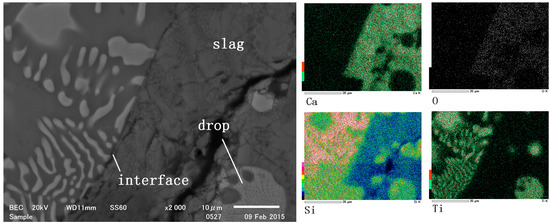
Figure 4.
SEM photo and elements map of the slag/silicon reaction interface and drops.
The variation of slag components during the reaction was measured and is presented in Figure 5. It shows that the TiO2 content decreased and SiO2 content increased during the reaction. Because of the lower molar mass of SiO2 compared to TiO2, the synthesis of titanium silicides led to a reduction in total slag mass, which consequently resulted in an increase in the CaO mass ratio in the slag. This shows that most of the TiO2 in the slag could be extracted out when the value of rs was no greater than two in the synthesis of TiSi2. According to the overall chemical reaction, thermodynamically, for complete TiO2 reduction, the rs value must be less than 2.38:
(TiO2) + 3[Si] = TiSi2 + (SiO2)
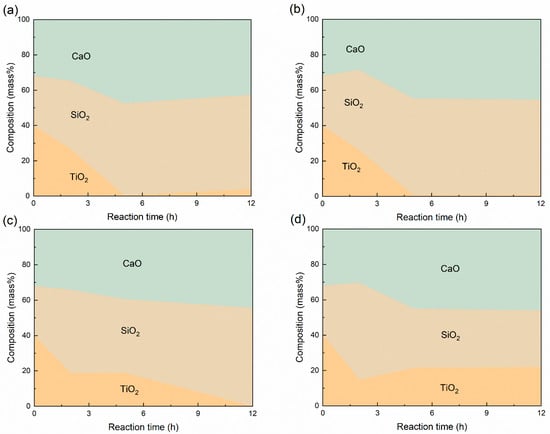
Figure 5.
Variation of slag compositions during the reaction at different reaction times with a mass ratio of slag to silicon rs of (a) 1; (b) 2; (c) 3; (d) 4.
As shown in Figure 5, the reaction rate of the TiSi2 synthesis appeared to be consistent across samples with rs ≤ 2, implying that the TiSi2 formation rate was not significantly affected by the slag-to-silicon mass ratio.
In the sample with rs = 3, a further reduction of TiO2 was observed, suggesting the formation of Ti5Si3, which is thermodynamically predicted by the following reaction:
5(TiO2) + 8[Si] = Ti5Si3 + 5(SiO2)
Figure 5 shows that the slag composition changed more slowly in the samples with rs = 3 and 4, particularly in the rs = 4 samples, where the reaction eventually stopped. This implies that the titanium extraction ratio was affected by the slag-to-silicon mass ratio. It could be related to the Ti5Si3 formation mechanism. According to our previous work [15], Ti5Si3 formed in the dropping alloy phase as it passed through the slag, via two potential reaction pathways:
Reaction within falling alloy particles:
7[Ti] + 3TiSi2 = 2Ti5Si3
Reaction at the interface between falling droplets and slag:
8TiSi2 + 7(TiO2) = 3Ti5Si3 + 7(SiO2)
Thermodynamic calculations indicate that the formation of Ti5Si3 is more energetically favorable than TiSi2, with a Gibbs free energy decrease of approximately −475 kJ·mol−1 at 1500 °C, compared to −104 kJ·mol−1 for TiSi2 formation. However, despite this thermodynamic advantage, the experimental results demonstrated that the reaction kinetics of Ti5Si3 synthesis were significantly slower than that of TiSi2. Once the titanium-saturated silicon phase was mostly converted into TiSi2, Equation (4) became the dominant reaction pathway. In this case, effective contact between TiSi2 and the titanium-bearing slag was crucial for the reaction to proceed. However, as Ti5Si3 formed, it developed a network-like structure (Figure 6). When this network reached a critical content, it hindered diffusion within the slag, ultimately retarding or even blocking the reaction in the sample with rs = 4.
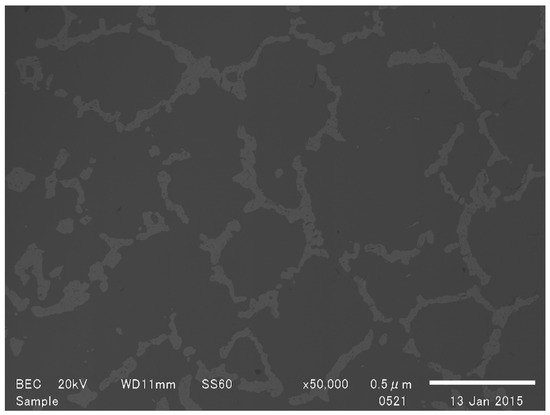
Figure 6.
SEM photo of the slag in the Ti5Si3 network.
3.2. Effect of Slag Compositions
The SEM graphs of samples with varying slag compositions reacted for 2 h at 1500 °C are shown in Figure 7. The light-colored phase was identified as TiSi2, where the Ti content was detected to be around 36 mol%. The dark phase surrounding TiSi2 was a silicon solution, containing about 2.7~8.7 mol% titanium. The solidified intermetallic phase primarily grew as dendritic crystals, with a significant number of fine intermetallic crystals dispersed within the silicon matrix. The statistical analysis of the cross-section images of the four samples indicated that the TiSi2 phase area fraction increased from 38% to 60% as the initial content of TiO2 in the slag increased. Additionally, some of the intermetallic dendritic crystals detached from the polished sample surface, suggesting that the pure TiSi2 particles could be separated by mechanical methods after crushing.
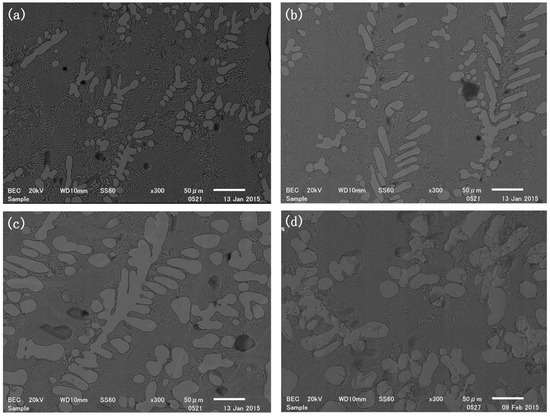
Figure 7.
SEM photo of sample (a) 5; (b) 6; (c) 7; (d) 8 reduced at 1500 °C for 2 h.
Ti5Si3 precipitation was observed at the bottom of the crucible in sample 5, which reacted for 12 h. The SEM image of the cross-section of sample 5 (Figure 8a) revealed that the morphology of the Ti5Si3 phase differed from that of TiSi2. Unlike the dendritic growth of TiSi2, bulk Ti5Si3 formed due to the aggregation of solid particles rather than dendritic overgrowth. This is attributed to the fact that the melting point of Ti5Si3 is much higher than the reaction temperature, allowing solid-state diffusion to cause particle coalescence. In contrast, the melting point of TiSi2 is below 1500 °C, so it remained in the liquid phase during the reaction. The TiO2-to-Si mole ratio in Sample 5 was approximately 5:8, which matches the stoichiometry ratio for Ti5Si3 formation in reaction (2). This explains why bulk Ti5Si3 was observed in this sample. Interestingly, Ti5Si3 particles were also detected in sample 1, despite its low Ti to Si mole ratio of only 2.6:10. In sample 1, the excess Si reactant was expected to yield a TiSi2/Si mixture. However, the presence of Ti5Si3 could be explained by variations in reaction interface locations. While the primary reaction occurred at the floating Si/slag interface, additional reactions took place at droplet/slag interfaces. The droplets located far from the floating silicon phase, along with the surrounding slag, could be considered as an isolated system within a limited reaction time, which was not in equilibrium with the floating silicon phase. Consequently, TiSi2 droplets reacted with the slag, leading to the formation of solid Ti5Si3.
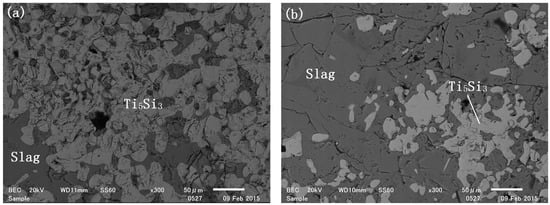
Figure 8.
Sample (a) 5; (b) 1 reduced at 1500 °C for 12 h.
The slag composition after the reaction is shown in Figure 9. Notably, the Ti extraction ratio does not decrease monotonically with the increase of initial TiO2 content in the slag. In samples with no more than 40 mass% TiO2, titanium was almost completely extracted from the slag. The samples with higher TiO2 content should lead to the production of titanium silicides with higher titanium ratios. For instance, in the sample with the highest TiO2 content, all the TiO2 in the slag was extracted out, with the final products consisting of 47 mol% TiSi2 and 53 mol% Ti5Si3 in view of thermodynamics. However, the reaction in the high TiO2-containing samples was highly retarded. The possible physicochemical factors that could reduce the reaction rate include the high melting point of slag, the high viscosity of slag, and the low basicity. However, there is no obvious consistency of change for the melting point of the slag or the reaction rate, so it is unlikely that melting temperature was the limiting factor for the low reaction rate in Samples 5 and 6. The viscosity of the slag was predicted by the Urbain model [26]. The details of the model and evaluation of the modeling results are given in the Supplementary Information. The results in Figure 10 indicate that the viscosity of the slag in Sample 8 is the highest, followed by Sample 7. The viscosity of the slag in Samples 6 and 5 is the lowest. Surprisingly, the high-viscosity slag reacted fast. This indicates that the viscosity of the slag has a negligible effect on the synthesis reaction rate in the slag–silicon reaction in this work. Although the literature [13] indicates that basicity has a positive effect on the reaction kinetics, the optical basicity of the slag only varied from 0.66 to 0.68 for all the five slag compositions. Therefore, the basicity would not affect the reaction kinetics in this condition.
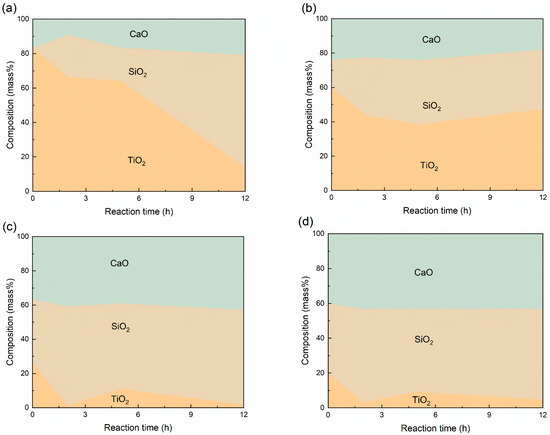
Figure 9.
Variation of slag compositions during the reaction at different reaction times with sample numbers (a) 5; (b) 6; (c) 7; (d) 8.
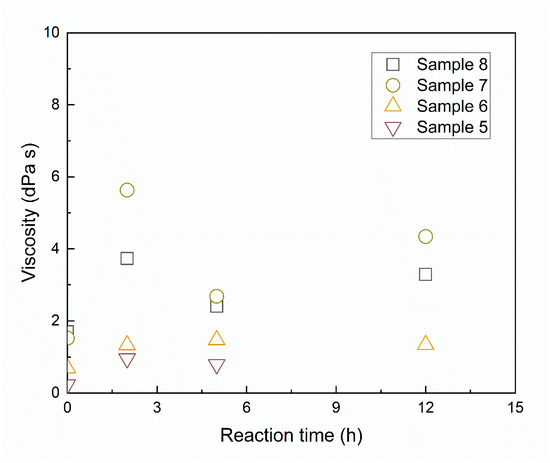
Figure 10.
Prediction of slag viscosity during the reaction at different reaction times with sample numbers from 5 to 8.
There is a hypothesis that the reaction rate may be principally determined by the amount of extracted TiO2 [15]. It is known from the experimental results that the consumption of a certain mass ratio of TiO2 in the slag (which could be 20 mass% of TiO2 in this work for a slag/Si mass ratio of three) resulted in the formation of a sufficient amount of TiSi2 in the silicon alloy. Since the melting point of TiSi2 is very close to the reaction temperature, a potential high viscosity of the TiSi2 may block the reaction. Furthermore, the formation of a relatively dense Ti5Si3 network in samples with a high TiO2 content could block the mass transfer in the slag, further slowing down the reaction.
3.3. Kinetic Analysis
The reduction process of titanium-bearing slag by molten silicon is proposed to be rate-determined by the silicon diffusion in the slag [13], where the reaction kinetics can be described by the following:
where is the mole fraction of the oxide in the slag and is the area of the reaction interface. The area of the reaction interface varies in the reaction due to the formation of droplets and the surface tension changes. It was assumed to be a constant value in this work to simplify the analysis. is the volume of the slag, is the diffusion coefficient of silicon in the slag, of which the magnitude is around 10−7 cm2·s−1. is the effective film thickness near the reaction interface, of which the value is approximately 10−3 cm. can be defined as the reaction rate constant, .
where is a constant with an estimated value of 5.3 × 104 at 1500 °C, and is the reaction equilibrium constant of the following reaction equation at 1500 °C, with a value of 2.88:
(TiO2) + 7[Si] = [Ti] + (SiO2)
This model was employed to analyze the synthesis reaction kinetics, and the results are shown in Figure 11. The values of all the reactions are within the range from 1.2 × 10−5 to 4.3 × 10−4 s−1. This is consistent with a previous report [13]. The volume fraction of TiSi2 in the alloy after reaction for 2 h increased with the increasing rs value, and the kinetic parameter () showed no significant change. This confirms that the value of the in the synthesis increased linearly with decreasing according to a reciprocal function relationship. Moreover, Figure 11d implies that the reaction is significantly accelerated when the content of TiO2 decreased below 30 mol% in the slag. The decrease of () could be because of the formation of an excess amount of titanium silicides in the high-titanium-containing reaction system.
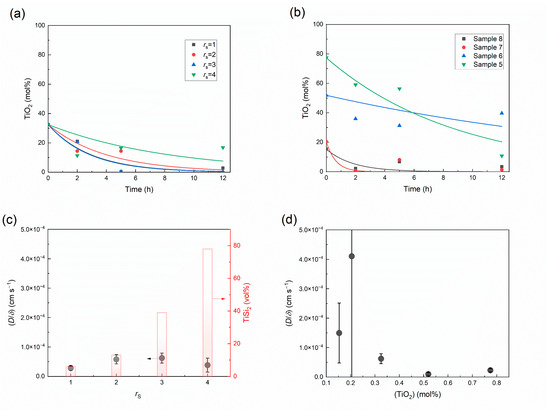
Figure 11.
Experimental and modeling curves with (a) various rs and (b) various slag compositions; (c) kinetic parameters of the titanium silicide synthesis process with variation of the slag/silicon ratio, where the volume fraction of TiSi2 in the alloy after reaction for 2 h is also shown; and (d) TiO2 mole fraction in the slag.
4. Conclusions
The synthesis of titanium silicides was studied at 1500 °C under an Ar atmosphere, focusing on the effect of the titanium-bearing-slag/silicon ratio and the slag composition on the formation mechanisms and kinetics of TiSi2 and Ti5Si3. Using a model slag system, the sequential formation of TiSi2 and Ti5Si3 was examined to gain fundamental insights into intermetallic phase evolution under controlled conditions.
The key findings of this study are:
- (1)
- TiSi2 can be synthesized across a broad range of slag compositions, but the formation of bulk TiSi2 requires a longer reaction time to facilitate the agglomeration of the intermetallic phases. A slag/silicon mass ratio increase from 1 to 4 can promote the production rate of TiSi2. However, rs no greater than 3 is suggested for the complete extraction of titanium sources from the slag and to avoid excessive dilution of silicon.
- (2)
- Ti5Si3 forms in a later stage of the reaction via further interaction of TiSi2 with the slag. Its formation is kinetically slower due to both the high melting point of TiSi2 and the diffusion barrier created by the development of a continuous Ti5Si3 network within the slag. The influence of slag viscosity, basicity, and melting point was found to be negligible under the current experimental conditions. The formation of the Ti5Si3 network may limit further reaction progression, and future work could explore mitigation strategies such as decreasing the slag viscosity, applying a supergravity field, and introducing low-melting point additives into the product.
- (3)
- From a kinetics perspective, the TiO2 content in the slag is suggested to be below 30 mol% to optimize reaction efficiency. The optimal reaction rate constant identified in this study is above 1 × 10−4 s−1 under the experimental conditions.
The findings provide practical guidance for the design and control of titanium silicide synthesis processes, particularly for metallurgical applications that aim to recover titanium from slags and waste catalysts, or develop intermetallic alloys. Controlling the slag/silicon ratio and phase evolution is key to improving process efficiency and product quality in TiSi-based systems.
This work was conducted using model slag systems to isolate specific parameters. However, industrial slags typically contain various impurity compounds (e.g., MgO, CaO, Al2O3, P2O5, CaF2) that can influence phase formation, reaction kinetics, and thermodynamic stability. Future studies should incorporate representative industrial slag compositions and combine experimental validation with thermodynamic modeling to assess scalability and real-world applicability.
This study contributes to the field of titanium silicide synthesis by elucidating the sequential reaction mechanism and kinetic behavior of TiSi2 and Ti5Si3 in controlled slag–silicon systems. The identification of the Ti5Si3 network as a kinetic barrier introduces a new perspective on controlling intermetallic phase evolution, which may support the development of optimized synthesis routes for high-performance Ti–Si materials.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/su17093994/s1, References [26,27,28,29] are citied in the Supplementary Materials.
Author Contributions
Z.Y.: Writing—review and editing, Writing—original draft, Methodology, Formal analysis, Data curation, Conceptualization. J.D.: Writing—review and editing, Supervision, Formal analysis, Conceptualization. Z.C.: Methodology, Investigation, Supervision, Data curation, Conceptualization. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Kazuki Morita of the University of Tokyo for his kind support and discussion of the experiments and mechanisms.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Frommeyer, G.; Rosenkranz, R. Structures and Properties of the Refractory Silicides Ti5Si3 and TiSi2 and Ti-Si-(Al) Eutectic Alloys. In Metallic Materials with High Structural Efficiency, NATO Science Series II: Mathematics, Physics and Chemistry; Senkov, O., Miracle, D., Firstov, S., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2004; Volume 146, pp. 287–308. [Google Scholar]
- Chumakova, L.S.; Bakulin, A.V.; Kulkova, S.E. Electronic Structure and Mechanical Properties of Ti5Si3. J. Exp. Theor. Phys. 2022, 134, 743–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.S.; Hwang, S.H.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, J.H.; Park, E.; Han, K.H.; Yu, H.Y. Excellent Improvement of Contact Resistivity and Thermal Stability for High Temperature Process After Silicidation of TiSi2 Through Ta Interlayer for Diffusion Barrier. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2023, 44, 1040–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, M.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, S.; Duan, P.; Zhong, Y.; Wu, Z.; Guo, X.; Yan, Z.; et al. Constructing cycle-stable Si/TiSi2 composites as anode materials for lithium ion batteries through direct utilization of low-purity Si and Ti-bearing blast furnace slag. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 876, 160125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, C.L.; Chen, W.H.; Hsu, C.C. Formation of titanium silicides Ti5Si3 and TiSi2 by self-propagating combustion synthesis. J. Alloys Compd. 2007, 432, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trambukis, J.; Munir, Z.A. Effect of Particle Dispersion on the Mechanism of Combustion Synthesis of Titanium Silicide. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1990, 73, 1240–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.M.; Lee, Y.S.; Kim, Y.W.; Sun, Y.K.; Lee, S.M. Electrochemical characterization of Ti–Si and Ti–Si–Al alloy anodes for Li-ion batteries produced by mechanical ball milling. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 472, 461–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.S.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, Y.W.; Sun, Y.K.; Lee, S.M. Rapidly solidified Ti–Si alloys/carbon composites as anode for Li-ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2006, 52, 1523–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Thom, A.J.; Akinc, M. Role of nitrogen on the oxidative stability of Ti5Si3 based alloys at elevated temperature. Intermetallics 2006, 14, 537–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Lu, X.; Zhou, Z.; Li, C.; Ding, W. Direct selective extraction of titanium silicide Ti5Si3 from multi-component Ti-bearing compounds in molten salt by an electrochemical process. Electrochim. Acta 2011, 56, 8430–8437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, H.; Wang, Q.; Ge, J.; Sun, H.; Jiao, S. Electrochemical synthesis of Ti5Si3 in CaCl2 melt. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 582, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zushu, L.; Chushao, X. The smelting process of titanium-silicon ferroalloy using blast furnace titaniferrous slag. ISIJ Int. 1996, 36, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chen, Z.; Li, Y.; Tan, Y.; Morita, K. Reduction of Titanium Oxide by Molten Silicon to Synthesize Titanium Silicide. Mater. Trans. 2015, 56, 1919–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Morita, K. Reduction of titanium bearing slag to titanium silicide. In Proceedings of the 170th ISIJ Conference, Fukuoka, Japan, 16–18 September 2015; pp. 16–18. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; You, Y.; Morita, K. Synthesis and kinetics of titanium silicides from photovoltaic industry waste and steelmaking slag for silicon and titanium recovery. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 7078–7085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Lei, Y.; Ma, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Ren, Y.; Lv, G. An approach to prepare high-purity TiSi2 for clean utilization of Ti-bearing blast furnace slag. Green Chem. 2022, 24, 3344–3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lei, Y.; Ma, W.; Shi, Z.; Chen, Q.; Li, Z.; Wang, C. A green approach for simultaneously preparing Ti5Si3 and Ti5Si4-TiAl3 alloys using spent SCR catalyst, Ti-bearing blast furnace slag, and Al alloy scrap. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 430, 132916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.; Wang, Y.X.; Yin, S.D.; Li, B.Q.; Ji, M.R.; Wu, J.X. Formation of silicides in the Ti, Ti(Ox)/Si (111), and Ti/SiO2/Si (111) systems. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A Vac. Surf. Films 1987, 5, 1402–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lei, Y.; Ma, W.; Ren, Y. Simultaneous recycling of Si and Ti from diamond wire saw silicon powder and Ti–bearing blast furnace slag via reduction smelting: An investigation of the effects of refractories on recycling. Waste Manag. 2023, 157, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhong, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wang, X. Study on the Reaction Process of Si/TiSi2 Composite Prepared by Induction Melting-Directional Solidification Method. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2025, 56, 1352–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Lv, G.; Lei, Y.; Li, S.; Chen, Z.; Ma, W. Preparation of Low-Oxygen Ti–Si Alloys by Electromagnetic Separation. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2025, 56, 852–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, G.; Wang, H.; Pang, S.; Sun, Y.; Guo, J.; Wang, D.; Zhou, J.; Sheng, Z.; Wang, Z. New insights into the application of non consumable electrode electroslag remelting refining: Enhanced removal of inclusions in Ti-Si alloy based the reduction of Ti-bearing blast furnace slag by SoG-Si scraps. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 490, 144684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.-H.; Wang, K.-F. Preparation of Ti5Si3 by silicothermic reduction of titanium-bearing blast furnace slag. Can. Metall. Q. 2018, 57, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Lü, H.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Ran, S.; Chen, Z.; Yang, Y.; Wu, X.; Li, L. Conversion of CaTi1−xMnxO3−δ-Based Photocatalyst for Photocatalytic Reduction of NO via Structure-Reforming of Ti-Bearing Blast Furnace Slag. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 10299–10309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Shang, X.; Wan, H.; Che, Y.; Yang, B.; He, J.; Song, J. Sustainable recycling of titanium from TiO2 in spent SCR denitration catalyst via molten salt electrolysis. J. Energy Chem. 2021, 58, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, K.; Yuan, L.; Jones, R. Estimating the physical properties of slags. J. South. Afr. Inst. Min. Metall. 2011, 111, 649–658. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Sun, H.Y.; She, X.F.; Wang, J.S.; Xue, Q.G. Influence of TiO2 on the viscosity of the molten slag and the confirmation of the acid–base property on TiO2. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2021, 48, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, L.; Wang, X. Investigation of the Viscosity and Structural Properties of CaO-SiO2-TiO2 Slags. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2014, 45, 1389–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Reddy, R.G.; Lv, X.; Pang, Z.; He, W. Structure-based viscosity model development for titania aluminosilicate slags. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2020, 47, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).