Analysis of Local Settlements Due to Operational EPB Tunneling Driving Parameters: A Case Study of the Barcelona Metro Line 9 Tunnel
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Assessing the impact of TBM pressures, including face pressure (P1), shield pressure (P2), and shield tail pressure (P3), on settlement magnitudes.
- Evaluating the influence of grouting volumes injected into the shield (Vshield) and segment tails (Vtail) on settlement mitigation.
- Identifying sources of increased ground volume loss, particularly at geological transitions, station entrances/exits, and hyperbaric maintenance stops.
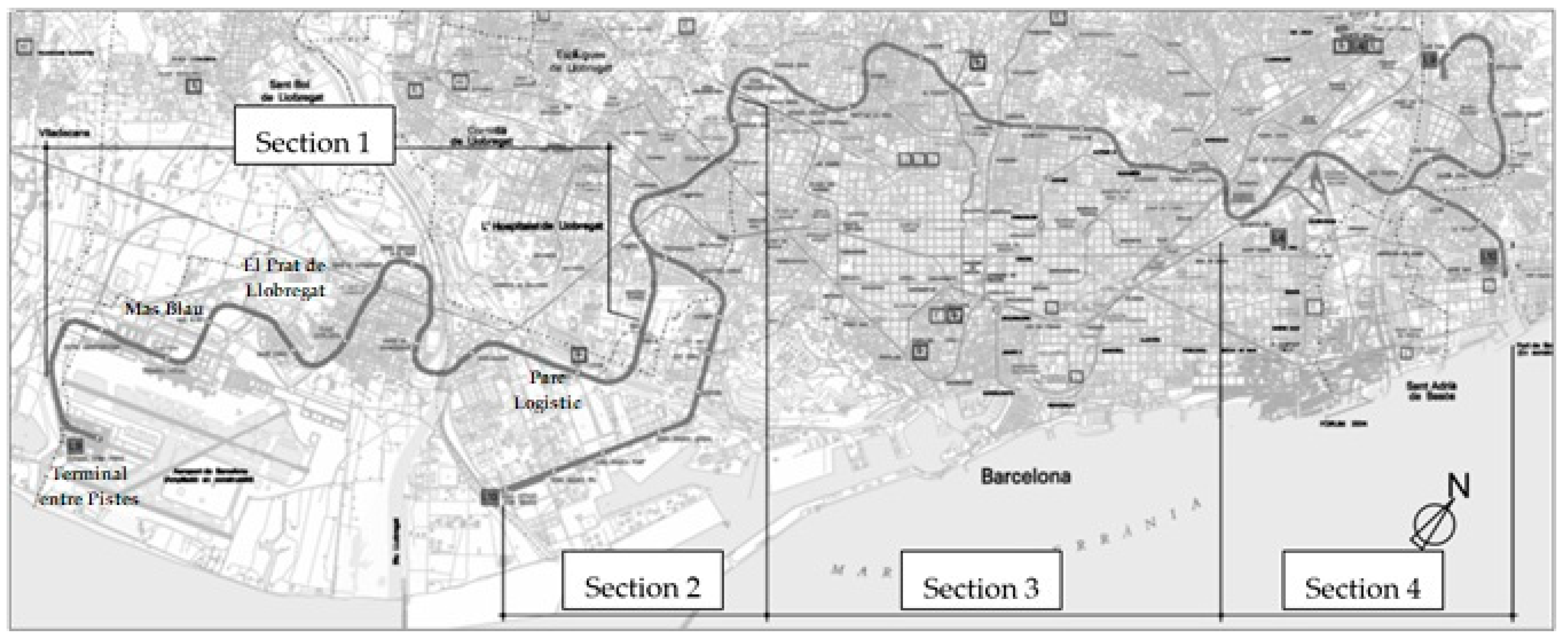
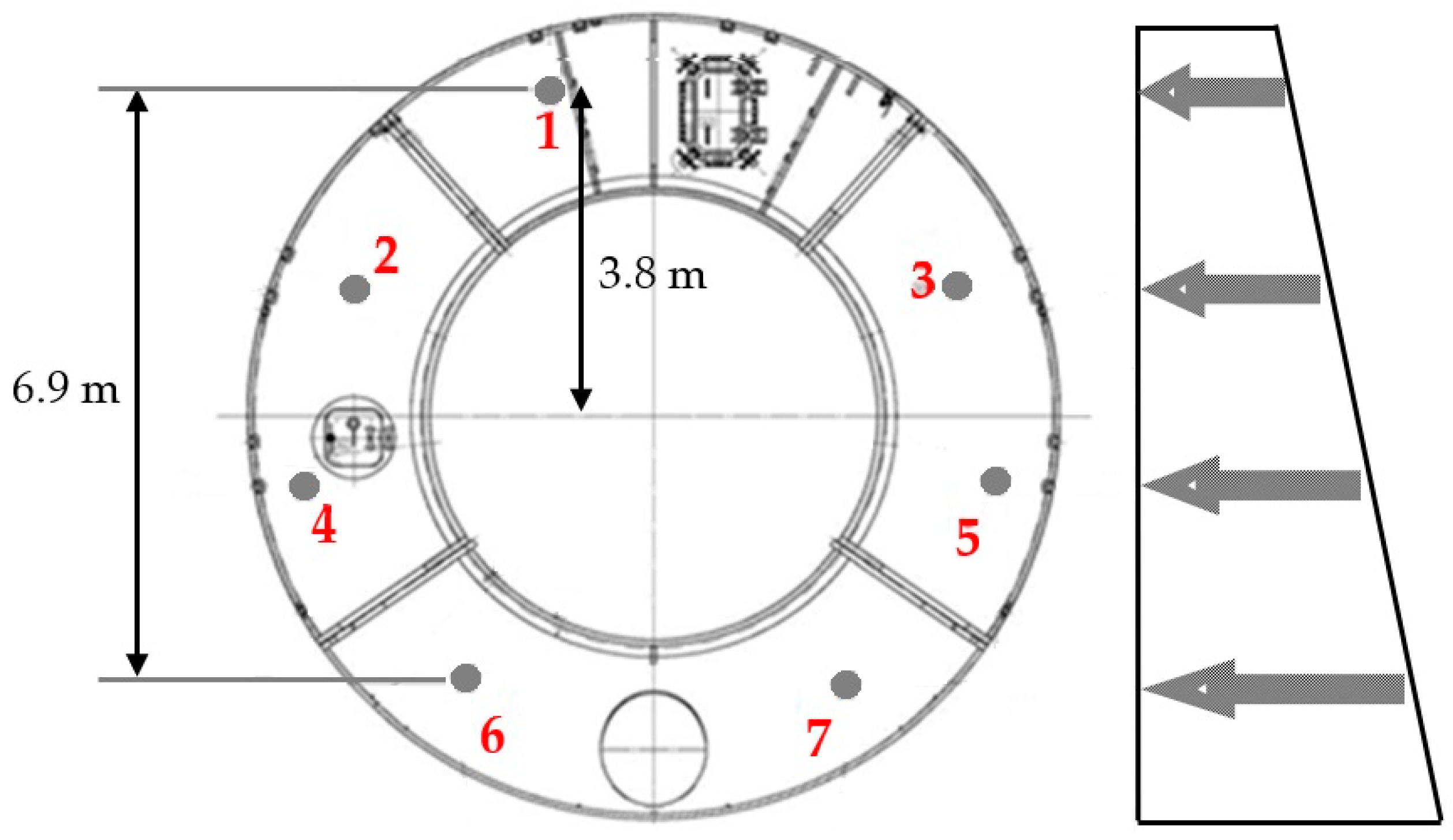
2. Geological Conditions and Instrumentation Layout
3. Tunneling Details
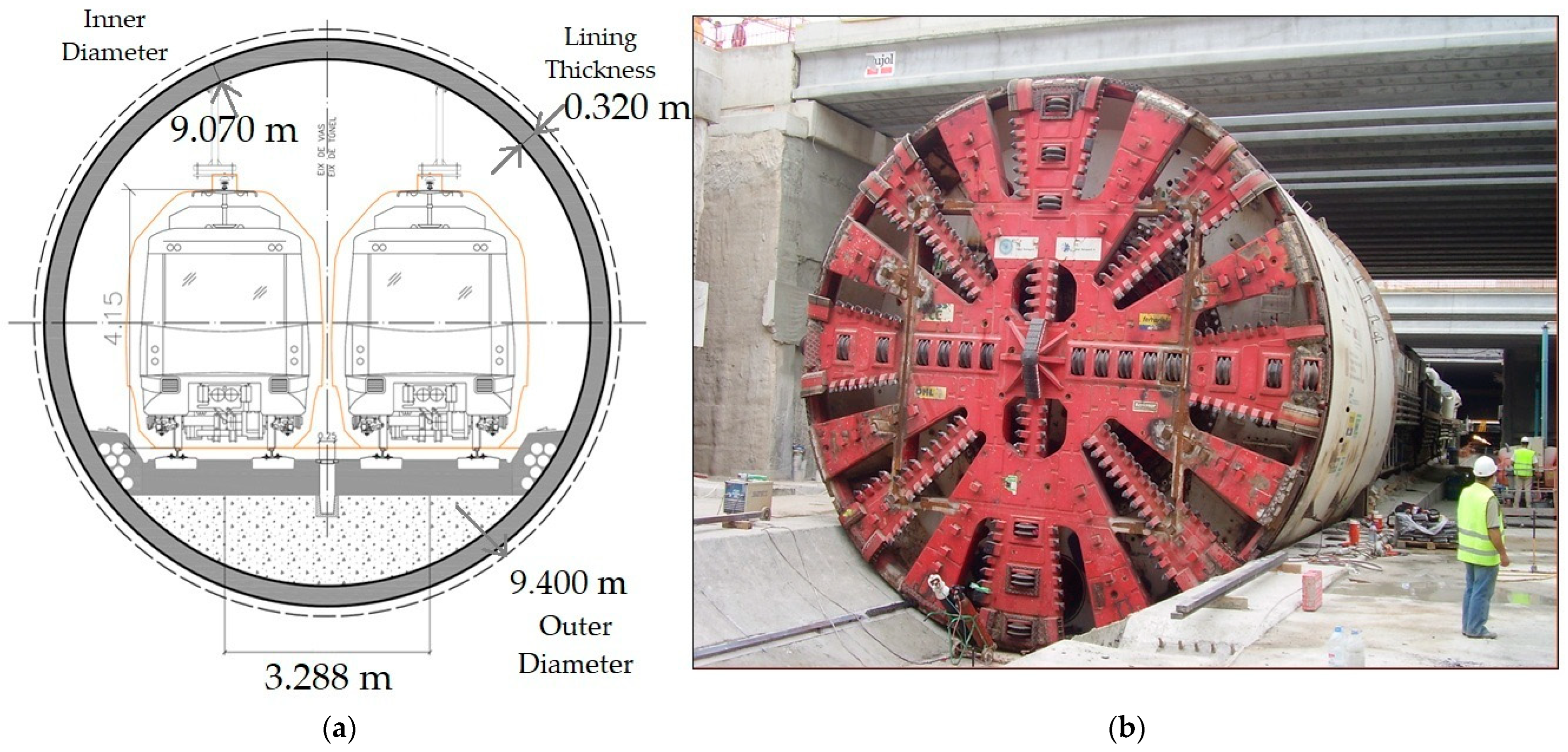
3.1. Earth Pressure Machines (EPBs)
3.2. Main Factors Associated with Ground Movements Due to EPB Excavation
3.3. Operational Control Parameters Used in Hades and Guster
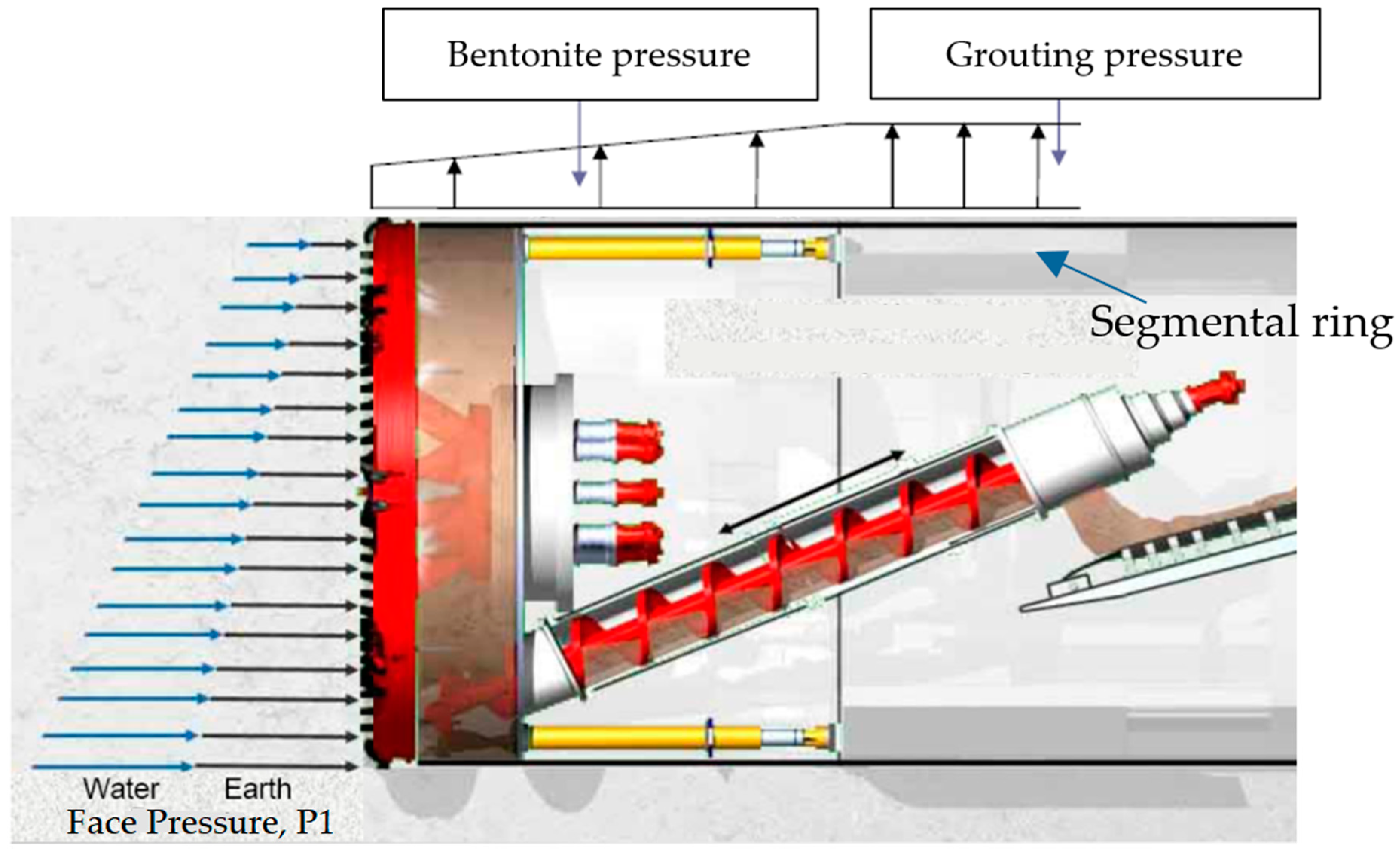
3.3.1. Face Pressure (P1)
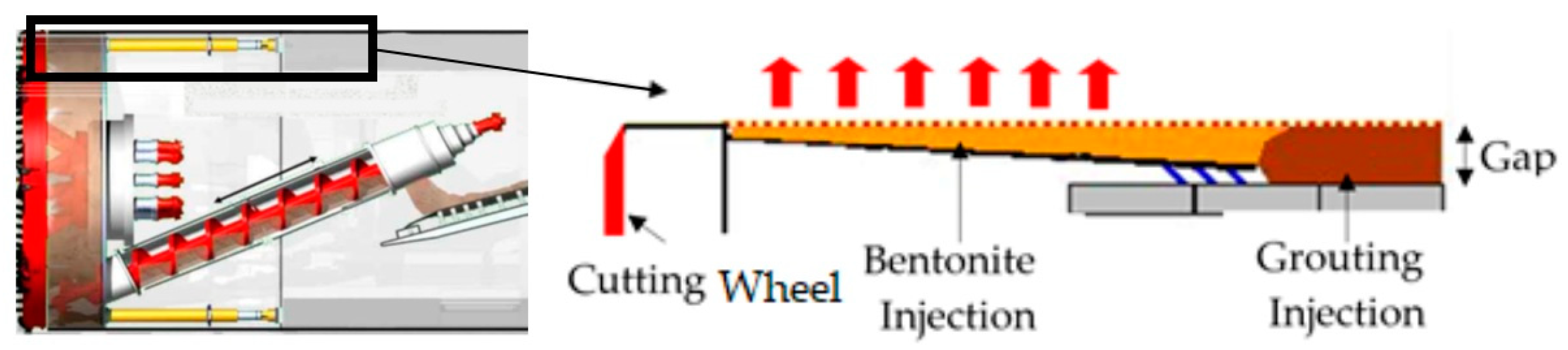
3.3.2. Bentonite Slurry Pressure Around the Shield (P2) and (V2)
3.3.3. Pressure and Volume of Grouting Injected into the Shield Tail (P3) and (V3)
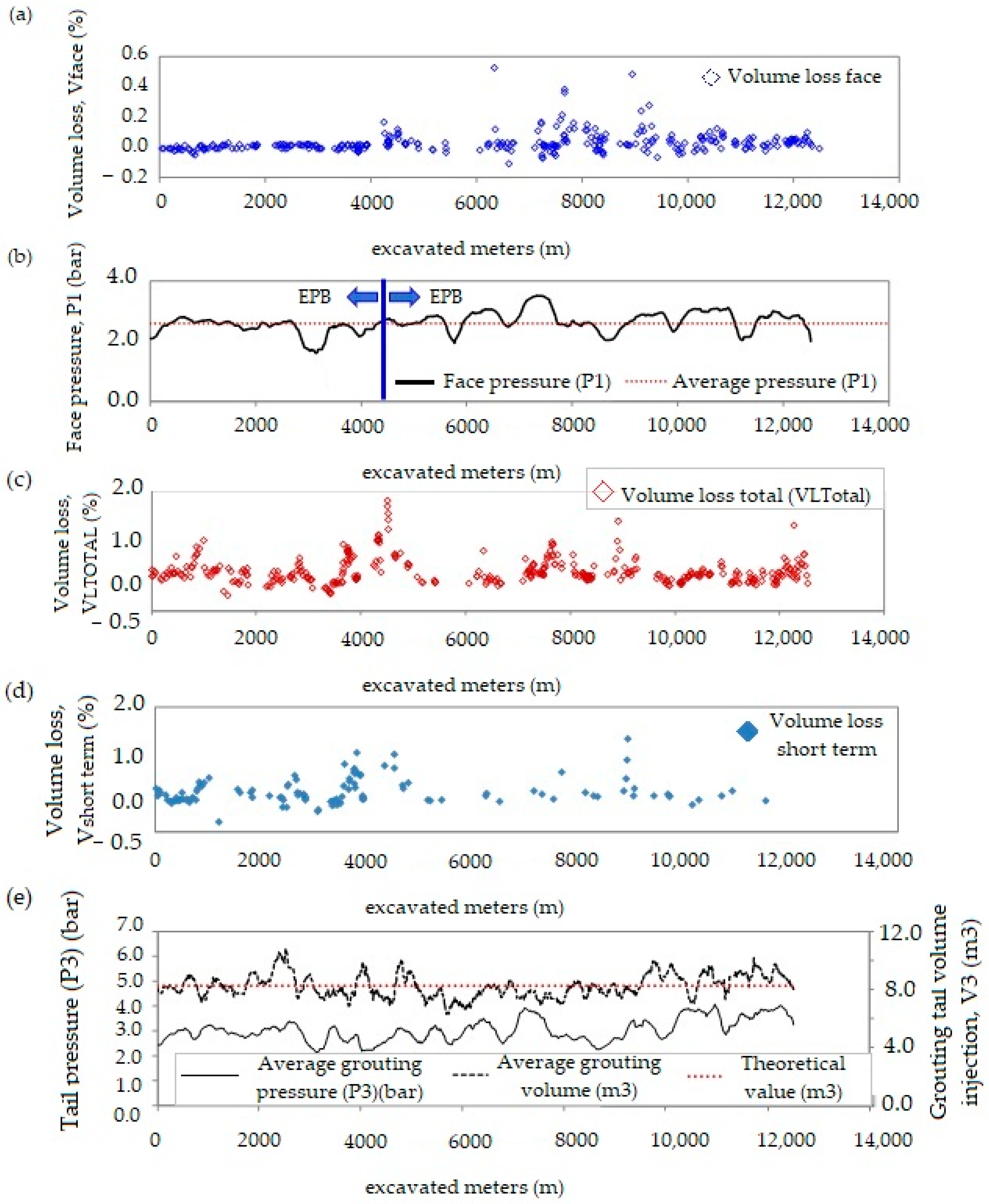
4. Surface Ground Movements
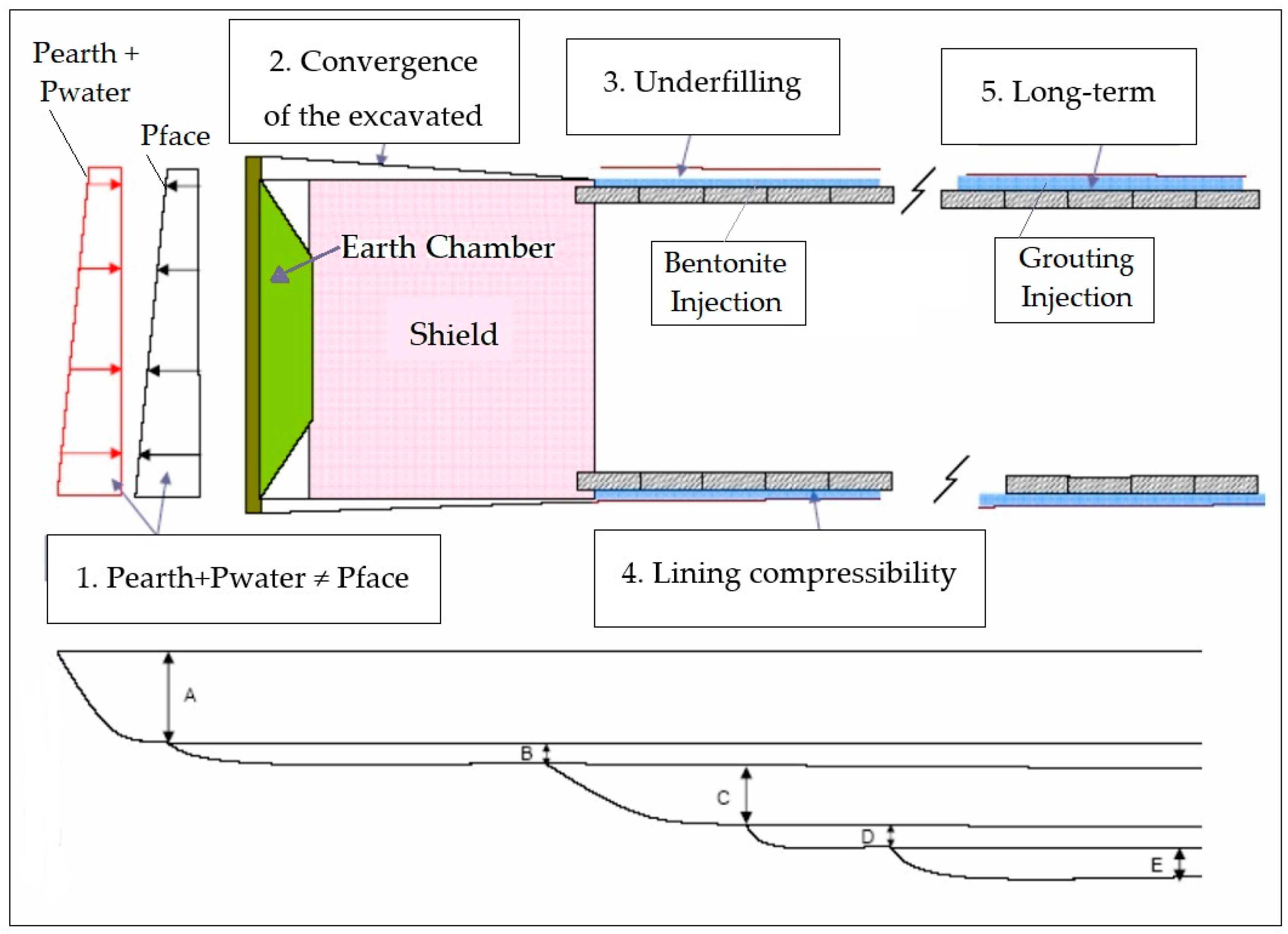
4.1. Components of Ground Settlement Due to EPB Tunneling
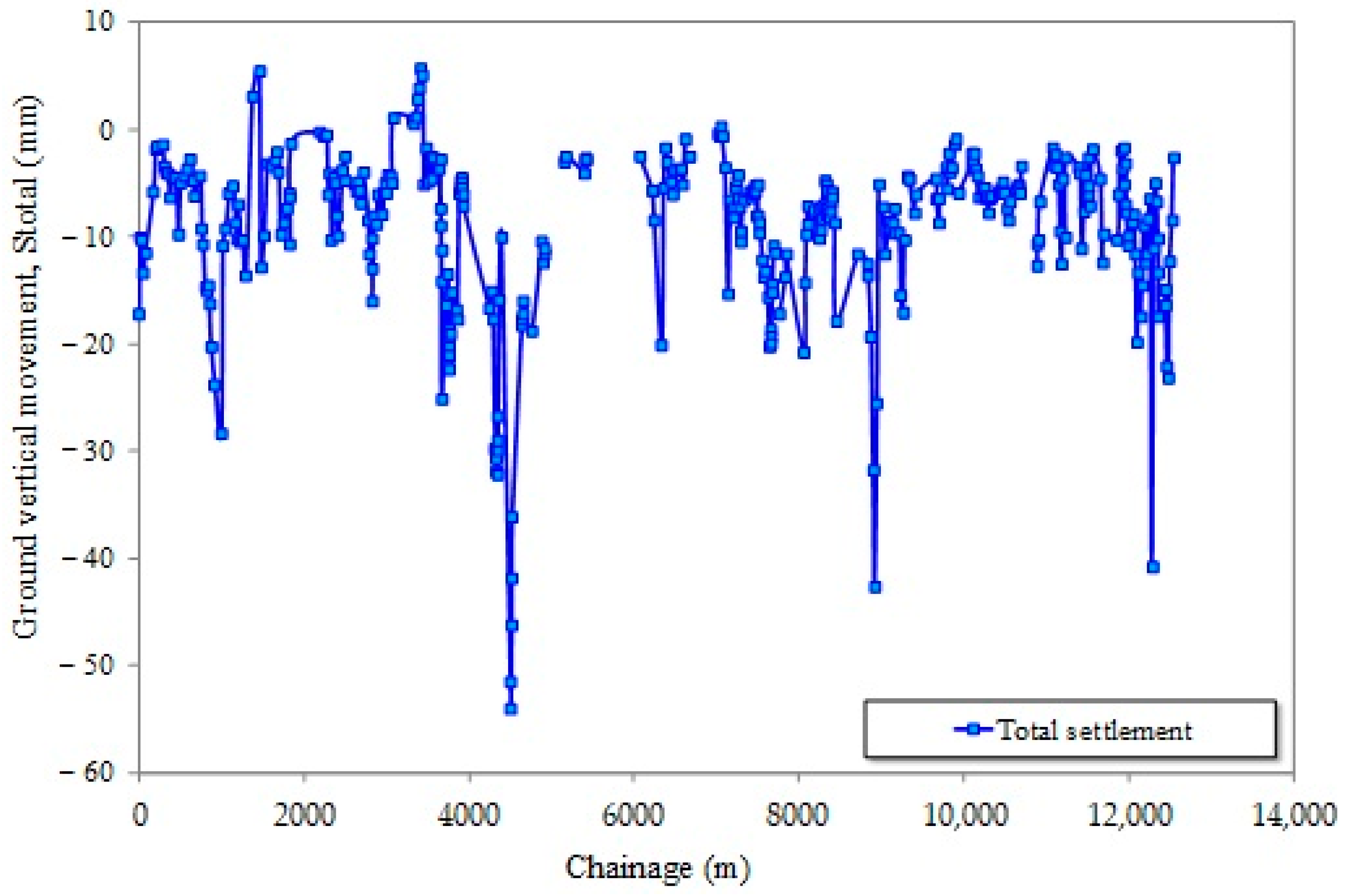
4.2. Ground Movement in Section 1
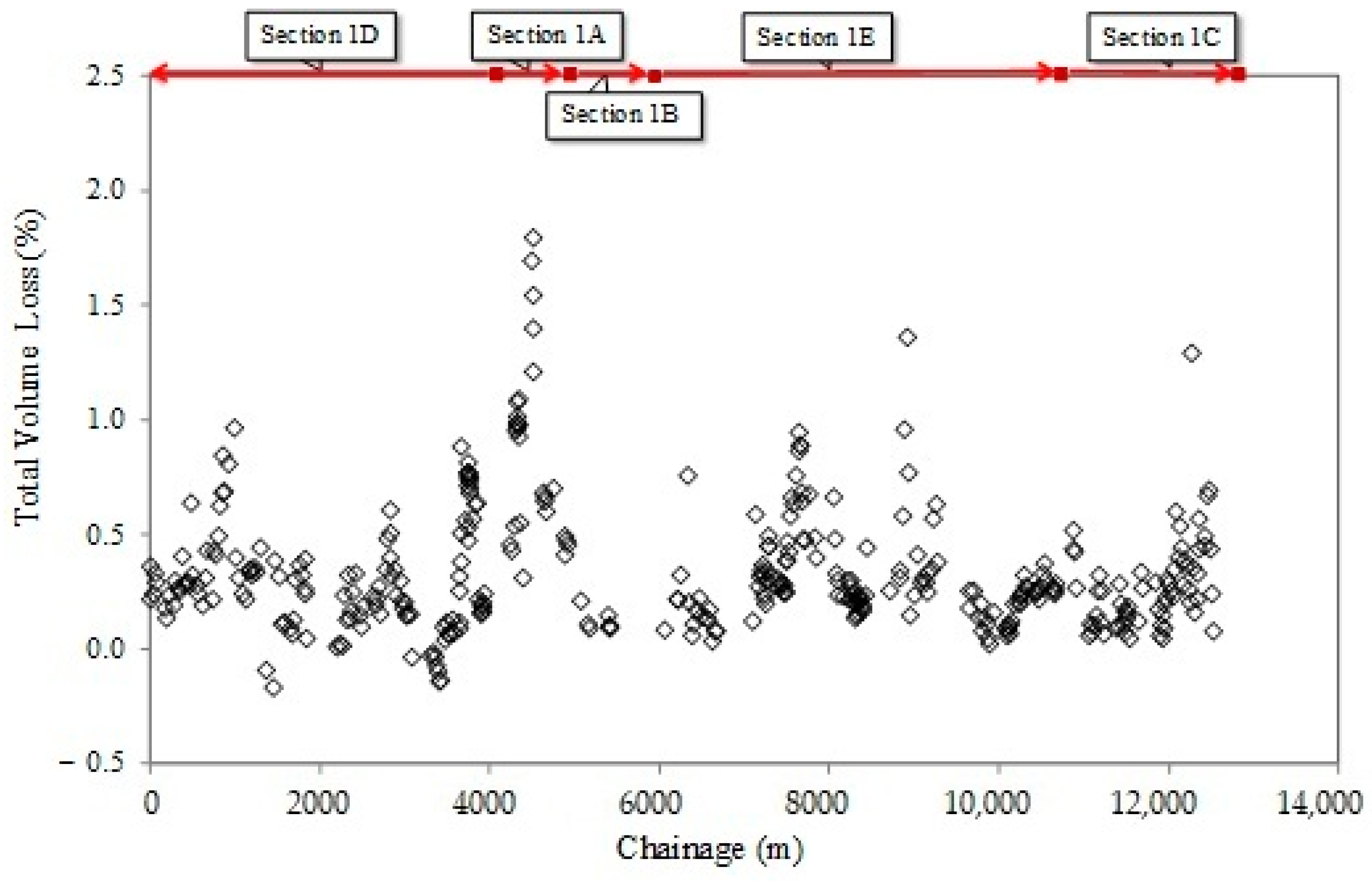
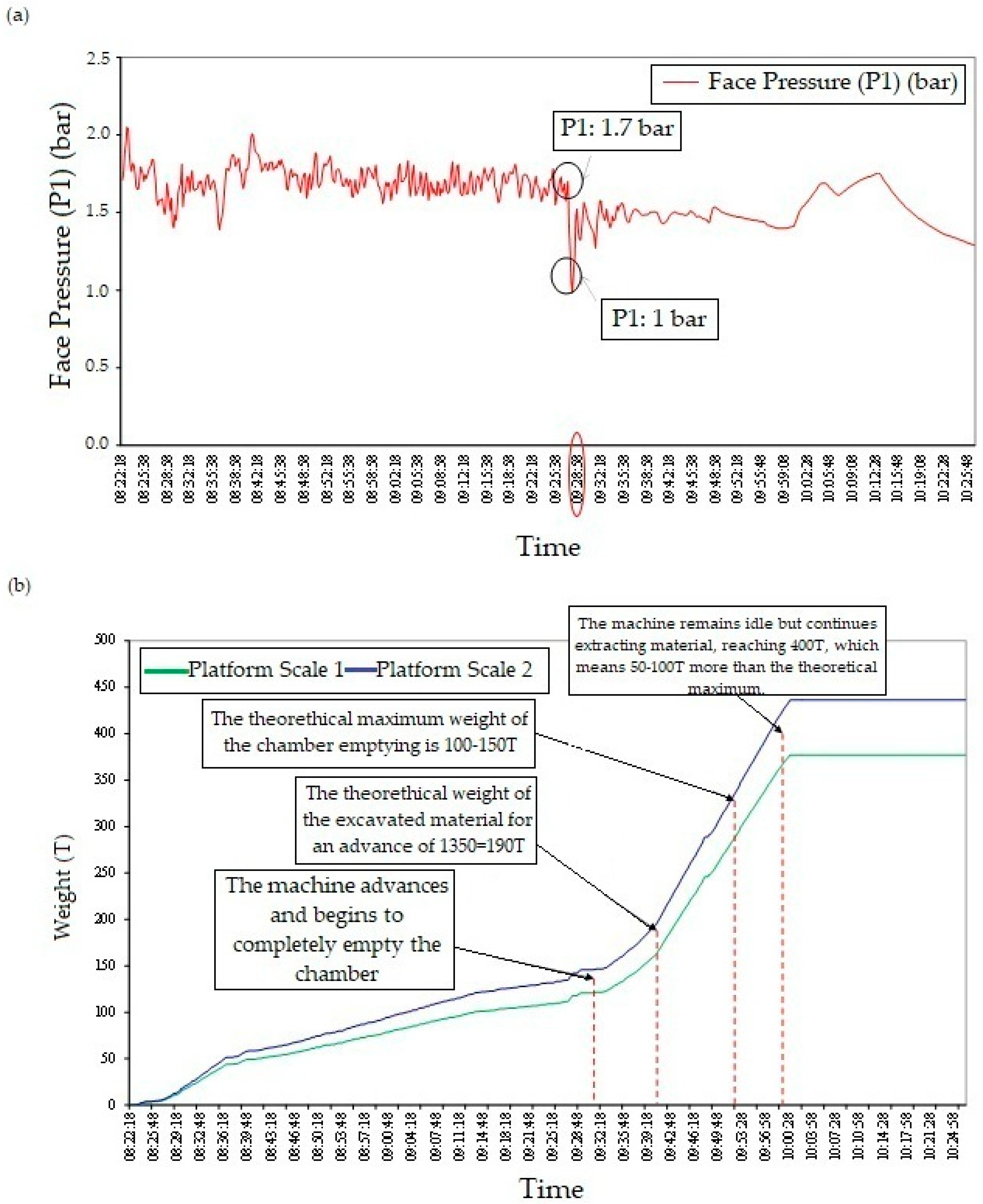
4.3. Measurement of Volume Loss Above the EPB Crown
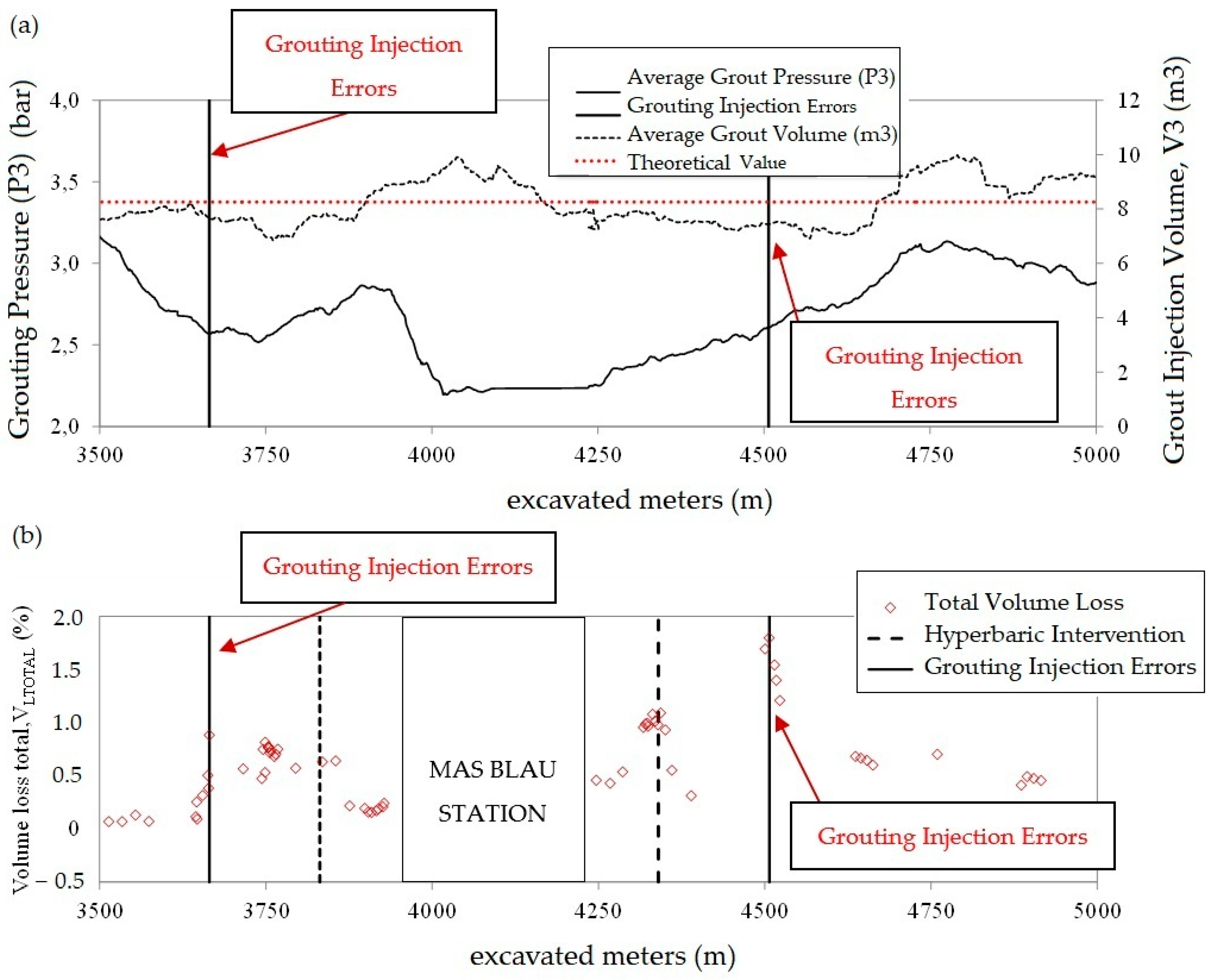
4.4. Correlation Between Ground Volume Loss and EPB Operation Variables
- Homogeneous Geological Conditions: Study sections with similar geological characteristics within the deltaic terrain were selected to ensure that observed variations in ground response were not due to stratigraphic or groundwater level differences.
- Control of Operational Parameters: When analyzing the impact of injection techniques, key TBM variables were maintained within restricted operational ranges. Specifically, face pressure (1.0–3.5 bar), advance speed (80 mm/min suggests a relatively controlled advance), and soil extraction rates (50 m3/h, indicating the maximum capacity for evacuating the excavated material) were regulated to prevent cross-effects influencing the results.
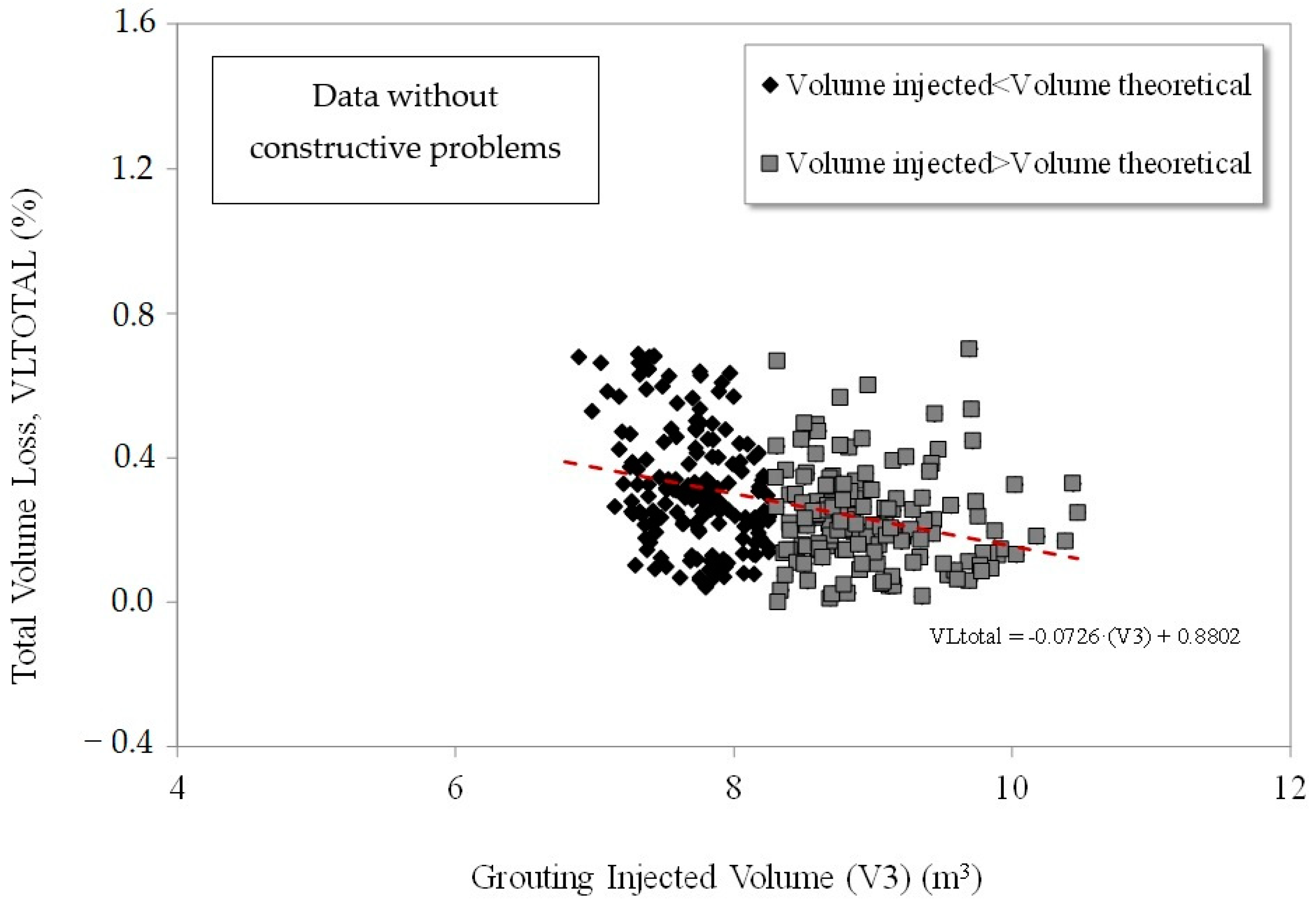
- Distinction Between Injection Techniques: Two primary injection methods were evaluated:
- ○
- Bentonite injection around the TBM shield: Implemented to fill over-excavation voids and enhance ground stability during TBM passage. This technique was innovative, and its effectiveness was analyzed by comparing sections with and without its application while keeping other parameters constant.
- ○
- Tail void grouting: Used to fill the annular gap between the tunnel lining and the surrounding ground. Various grout formulations and injection pressures were tested to assess their influence on settlement mitigation, ensuring consistency in application time and materials.
- Back-Analysis of Significant Settlements: In cases where settlements exceeded expected values, a retrospective analysis was conducted, considering TBM parameter records and injection conditions. This allowed for identifying correlations between operational variables and ground response, further validating the applied control methods.
Influence of Injection Volumes
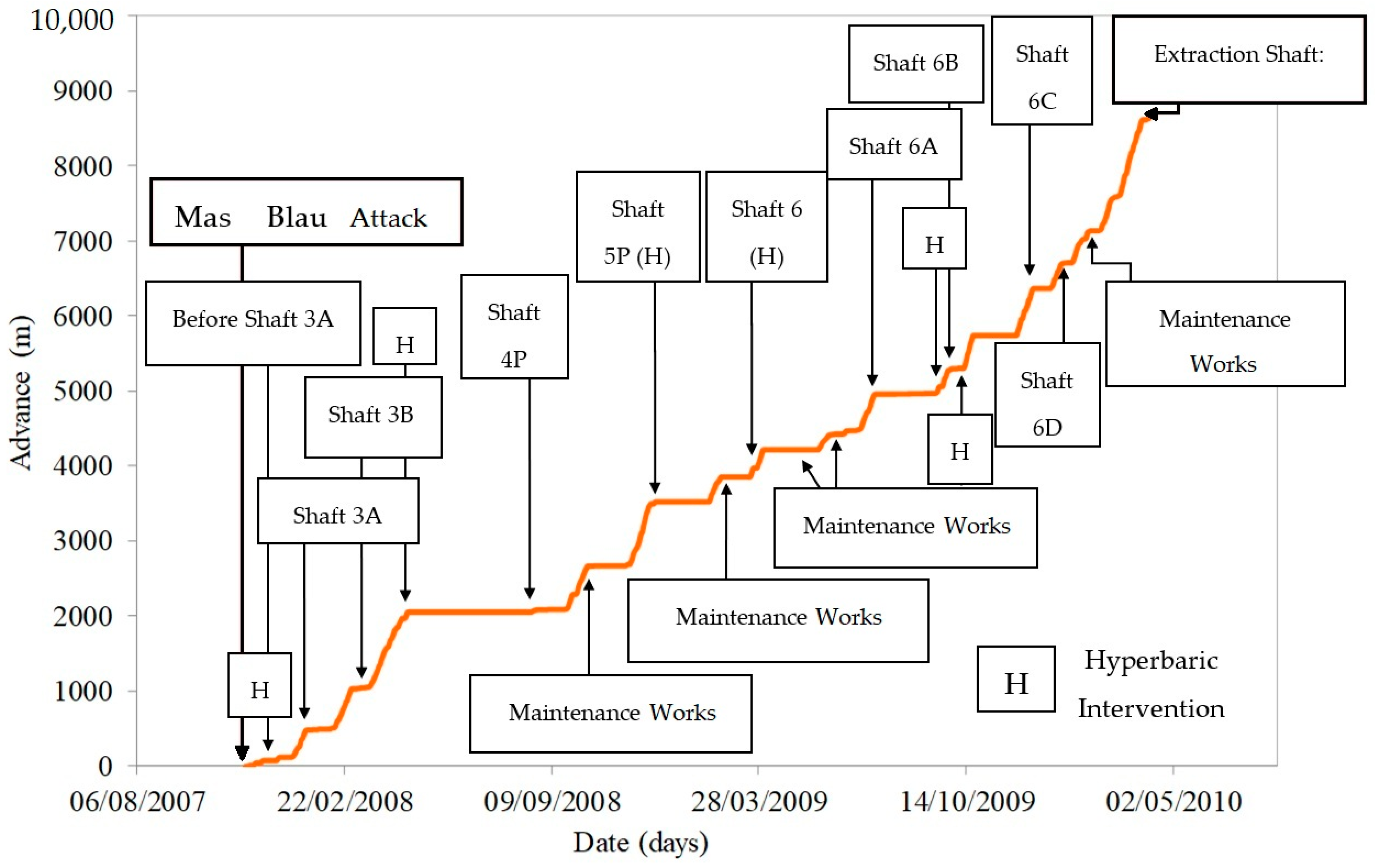
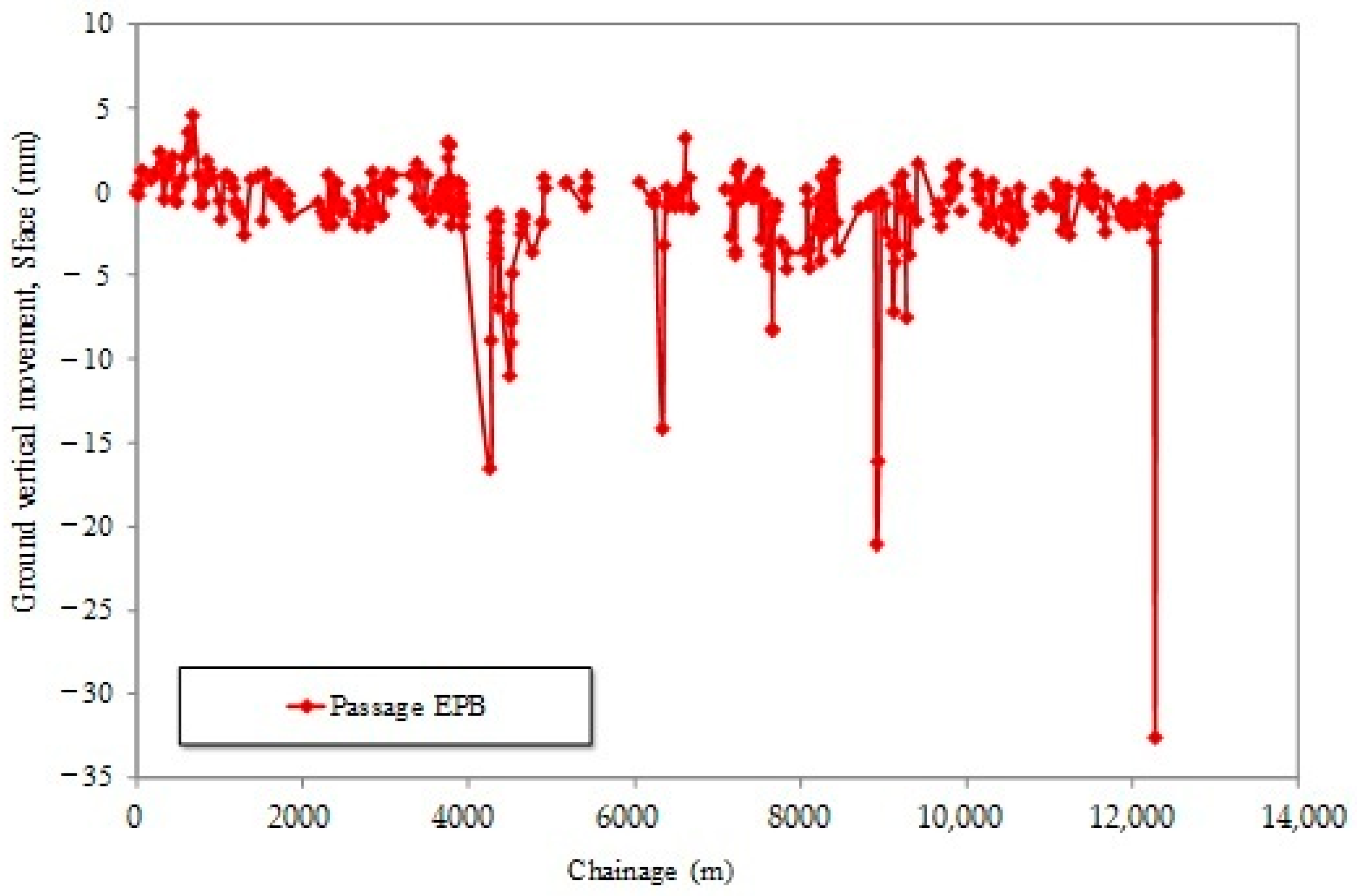
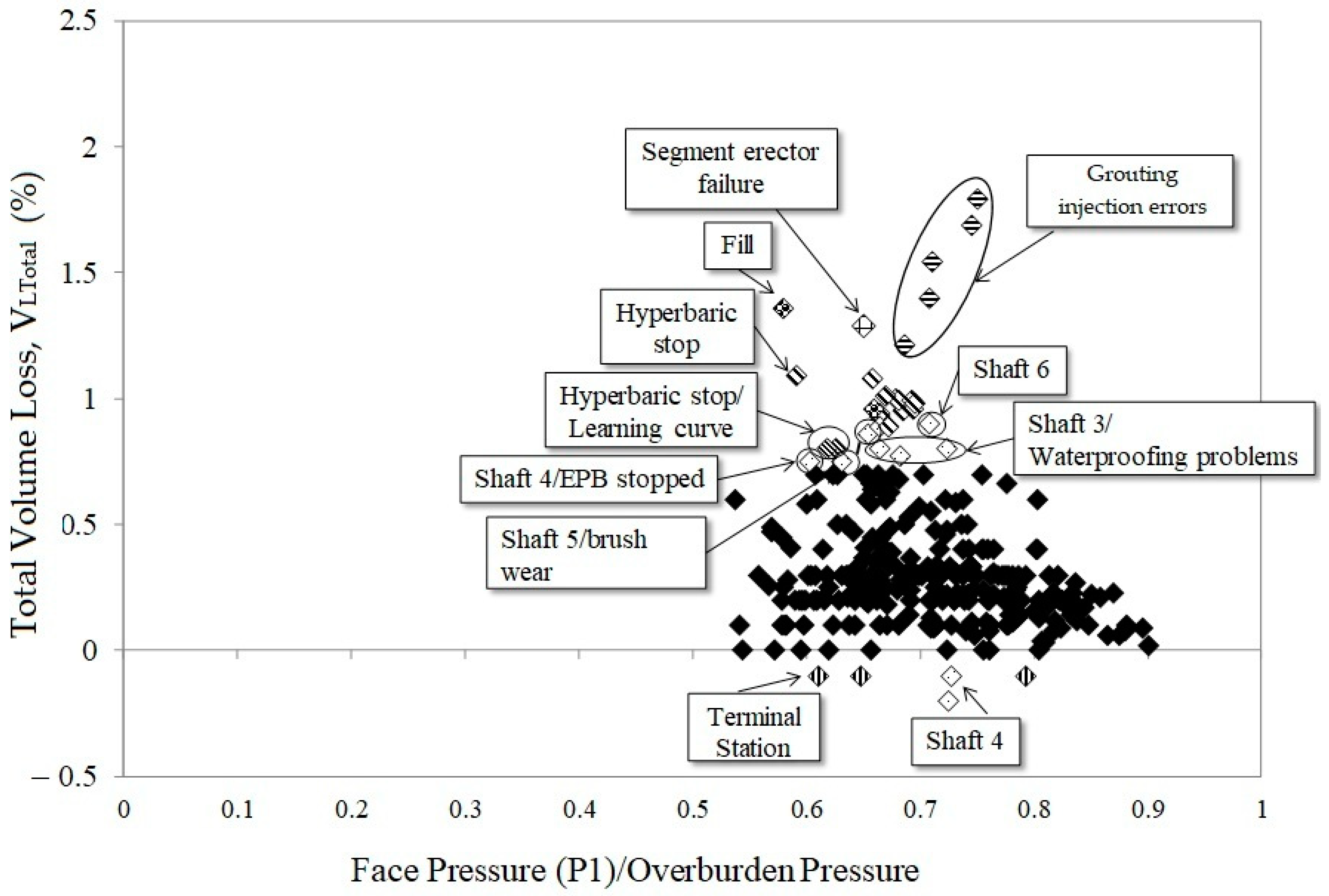
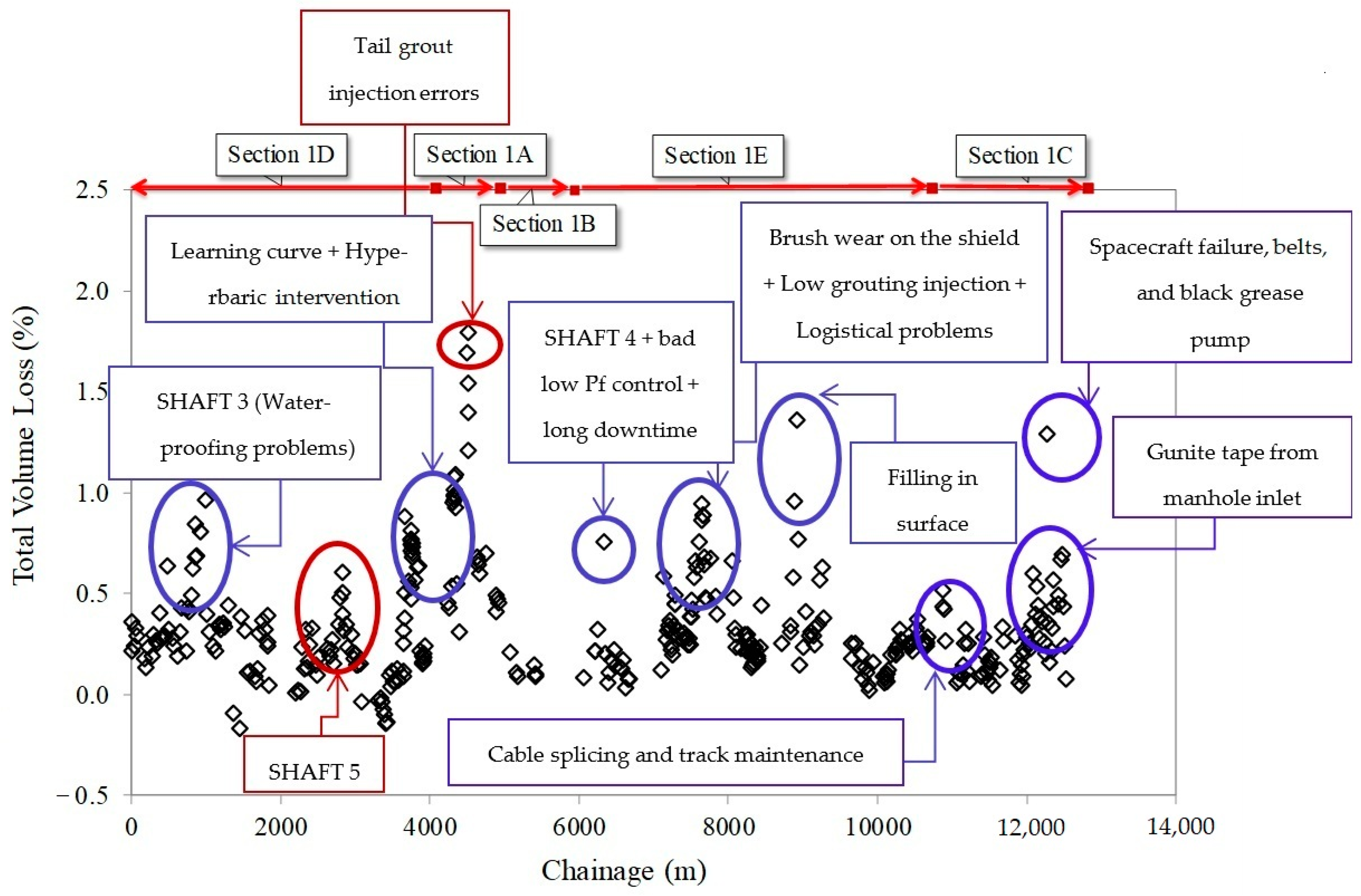
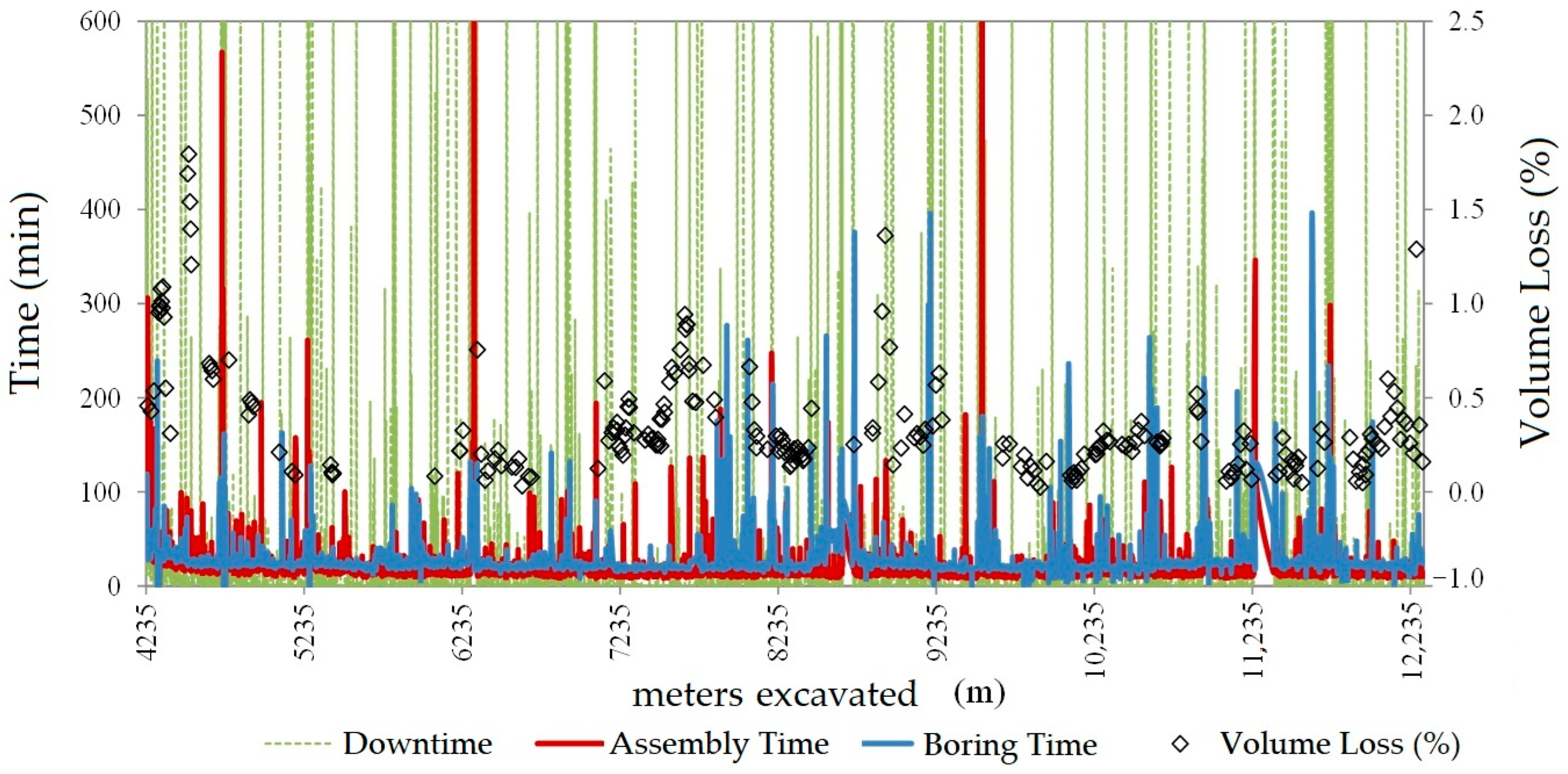
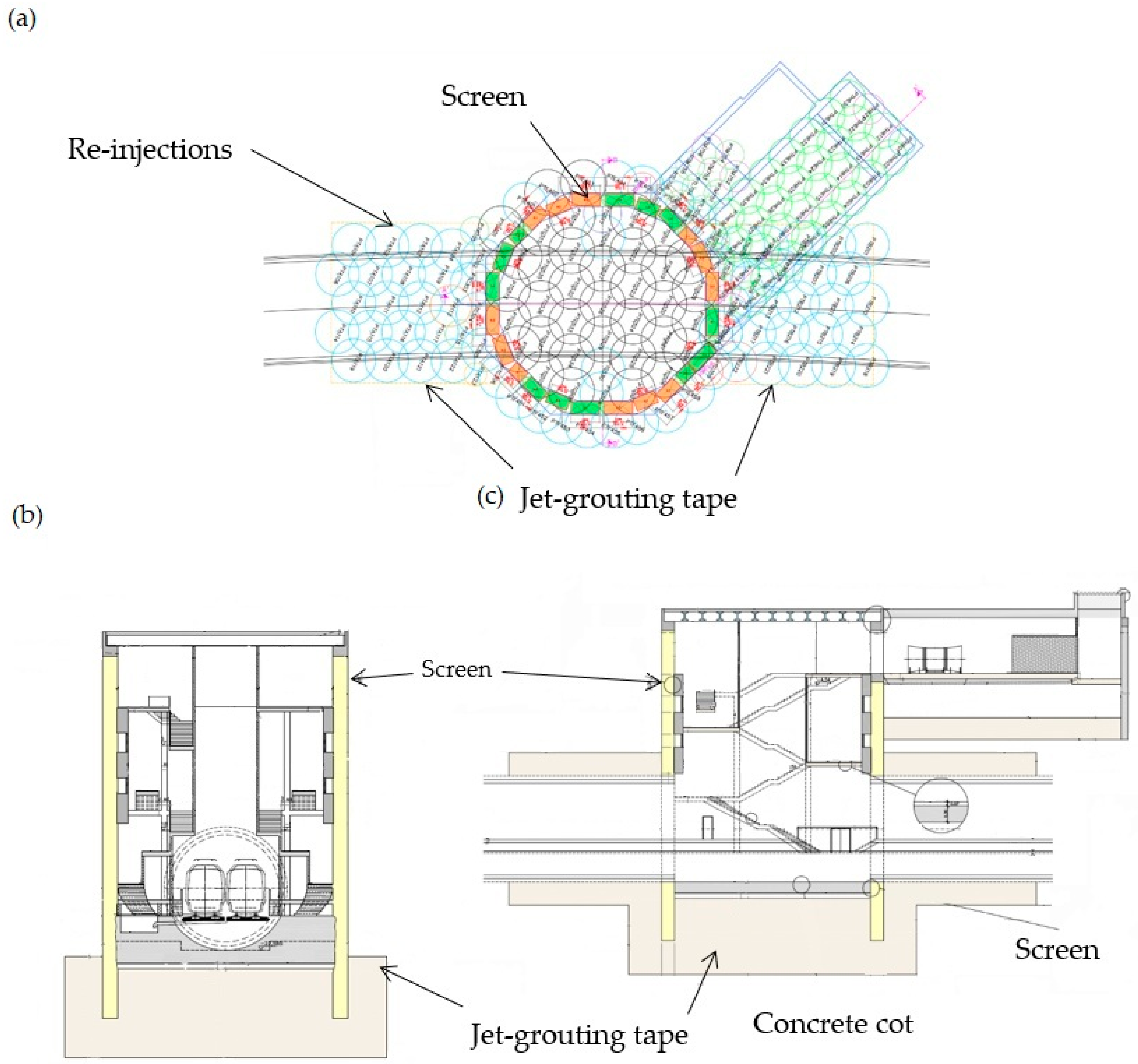
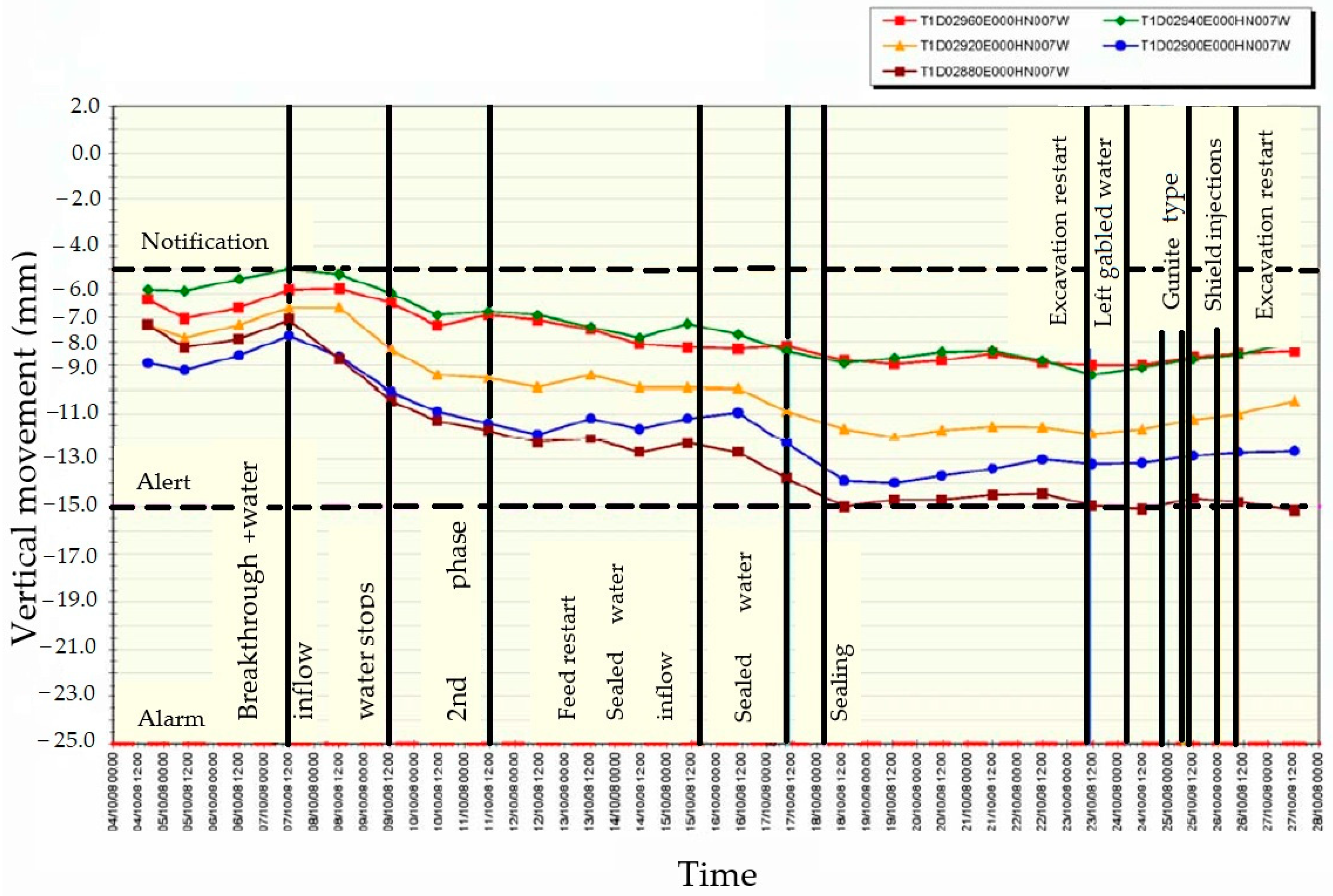
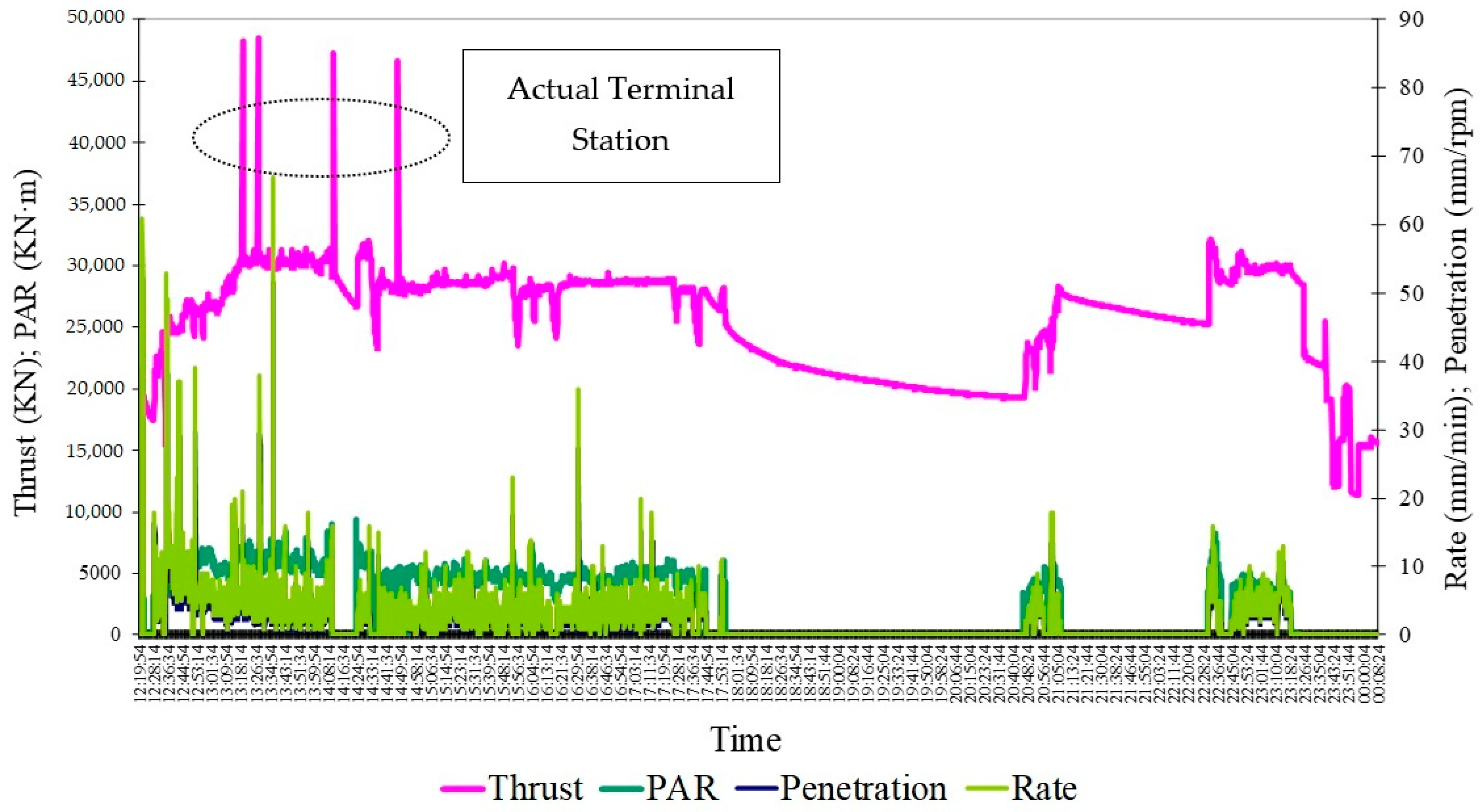
5. Study of the Singular Points
6. Conclusions
6.1. Ground Response and Settlement Control
6.2. Impact of Operational Parameters
6.3. Challenges in Excavation and Gap Filling
6.4. Future Research and Practical Applications
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Clough, G.W.; Sweeney, B.P.; Finno, R.J. Measured Soil Response to EPB Shield Tunneling. J. Geotech. Eng. 1983, 109, 131–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leca, E.; Leblais, Y.; Kuhnhenn, K. Underground works in soils and soft rock tunneling. Int. J. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2000, 1, 220–268. [Google Scholar]
- Mair, R.J.; Taylor, R.N. Theme Lecture: Bored tunnelling in the urban environment. Plenar Session 4. In Proceedings of the Fourteenth International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering, Hamburg, Germany, 6–12 September 1997; Volume 4, pp. 2353–2385. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, S.; Yubero, M.T.; Tarragó, D. Análisis en 3D de los Movimientos del Terreno Causados por la Excavación Mecanizada de túneles (EPB). Master’s Thesis, Universidad Politécnica de Catalunya, Barcelona, Spain, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Antiga, A.; Chiorboli, M. Tunnel face stability and settlement control using earth pressure balance shield in cohesionless soil. In Geotechnical Aspects Underground Construction in Soft Ground; Ng, C.W.W., Huang, H.W., Liu, G.B., Eds.; Taylor & Francis Group: Shanghai, China, 2009; pp. 365–371. [Google Scholar]
- Do, N.A.; Dias, D.; Oreste, P.; Djeran-Maigre, I. Three-dimensional numerical simulation of a mechanized twin tunnels in soft ground. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2014, 42, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollon, G.; Dias, D.; Soubra, A.H. Probabilistic analysis of tunneling-induced ground movements. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2013, 37, 181–199. [Google Scholar]
- Pelizza, S.; Peila, D.; Grasso, P. TBM tunneling in difficult ground conditions. Geol. Soc. Lond. Eng. Geol. Spec. Publ. 2010, 25, 213–218. [Google Scholar]
- Sirivachiraporn, A.; Phienwej, N. Ground movements in EPB shield tunneling of Bangkok subway project and impacts on adjacent buildings. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2012, 30, 10–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwansawat, S. Earth Pressure Balance (EPB) Shield Tunneling in Bangkok: Ground Response and Prediction of Surface Settlements Using Artificial Neural Networks; Massachusetts Institute of Technology: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Ng, C.W.W. Effects of stress-induced anisotropy and structure on undrained behavior of reconstituted and intact soft clay. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2015, 141, 04015012. [Google Scholar]
- Dimmock, P.S. Tunnelling-Induced Ground and Building Movement on the Jubilee Line Extension. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Fargnoli, V.; Boldini, D.; Amorosi, A. TBM tunnelling-induced settlements in coarse-grained soils: The case of the new Milan underground line 5. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2013, 38, 336–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gens, A.; Mariano, A.D.i.; Yubero, M.T. EPB tunneling in deltaic deposits: Observations of ground movements. In Geotechnical Aspects of Underground Construction in Soft Ground; Viggiani, G., Ed.; Taylor & Francis Group: Abingdon, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Yubero, M.T. Ejecución De Túneles En Terreno Deltaico Mediante Tuneladora EPB. El Caso De La Línea 9. Ph.D. Thesis, Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya, Barcelona, Spain, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Yubero, M.T.; Bonet, E. Ground Surface Effect of Earth Pressure Balance Tunnelling in Deltaic Deposits: A Case Study of Line 9 of the Barcelona Metro. Sustainability 2024, 16, 8275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Reilly, M.P.; New, B.M. Settlements above tunnels in the U.K—Their magnitude and prediction. Tunneling 1992, 82, 173–181. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.G.; Zhang, Z.M.; Wu, S.M.; Yu, F. Key techniques and important issues for slurry shield under-passing embankments: A case study of Hangzhou Qiantang River Tunnel. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2013, 38, 306–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phienwej, N.; Sirivachiraporn, A.; Timpong, S.; Tavaranum, S. Characteristics of Ground Movements from Shield Tunnelling of the First Bangkok Subway Line. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Underground Excavation and Tunnelling, Bangkok, Thailand, 2–4 February 2006; pp. 319–330. [Google Scholar]
- Cording, E.J. Control of ground movements around tunnels in soil. In Proceedings of the Ninth Pan American Conference, Vina del Mar, Chile, 5–9 August 1991; pp. 2195–2244. [Google Scholar]
- Wongsaroj, J. Three-Dimensional Finite Element Analysis of Short and Long-Term Ground Response to open-Face Tunnelling in Stiff Clay. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Wongsaroj, J.; Borghi, F.X.; Soga, K.; Mair, R.J.; Sugiyama, T.; Hagiwara, T.; Bowers, K.J. Effect of TBM driving parameters on ground surface movements: Channel Tunnel Rail Link Contract 220. In Geotechnical Aspects of Underground Construction in Soft Ground; Taylor & Francis Group: London, UK, 2006; pp. 335–341. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.M.; Ji, H.W.; Shen, C.K.; Liu, J.H.; Bai, T.H. Ground response to the construction of Shanghai Metro Tunnel-Line 2. Soil Found. 1999, 39, 113–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Choi, H.; Choi, S.-W.; Chang, S.-H.; Kang, T.-H.; Lee, C. Numerical Simulation of EPB Shield Tunnelling with TBM Operational Condition Control Using Coupled DEM–FDM. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushita, Y.; Iwasaki, Y.; Ashimoto, T.; Imanishi, H. Behaviour of subway tunnel driven by large slurry shield. In Underground Construction in Soft Ground; Taylor & Francis Group: Abingdon, UK, 1995; pp. 253–256. [Google Scholar]
- Medina, L. Estudio de los Movimientos Originados por la Excavación de Túneles con Escudos de Presión de Tierras en los Suelos Tosquizos de Madrid. Ph.D. Thesis, University of La Coruña, A Coruña, Spain, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Bono, R.; Ortu, M.; Valdemarin, F. Surface Settlement Minimization in Soft Soil When Excavating with an Earth Pressure Balance Shield; Jornada Técnica Túneles con EPB, UPC: Barcelona, Spain, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Mair, R.J. Tunnelling and geotechnics: New horizons. Géotechnique 2008, 58, 695–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gens, A.; Persio, R.; Di Mariano, A.; Castellanza, R.; Arroyo, M. Relación enre parámetros de una tuneladora EPB y los movimientos del terreno. In Geotecnia, 3as Jornadas Hispano-Portuguesas de; Cedex: Madrid, Spain, 2009; pp. 433–441. [Google Scholar]
- Di Mariano, A.; Gesto, J.M.; Gens, A.; Schwarz, H. Ground deformation and mitigating measures associated with the excavation of a new Metro line. In Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, Madrid, Spain, 24–27 September 2007; pp. 1901–1906. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, C.; Ding, W.; Xie, D. Twin EPB tunneling-induced deformation and assessment of a historical masonry building on Shanghai soft clay. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2020, 98, 103300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, X.; Lu, H.; Wang, M.; Wen, Z.; Rong, X. Cutter wear evaluation from operational parameters in EPB tunneling of Chengdu Metro. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2019, 93, 103043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Xu, K.; Guo, P.; Lei, G.; Cheng, K.; Gong, X. Ground deformation characteristics induced by mechanized shield twin tunneling along curved alignments. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2021, 2021, 6640072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendaña, F. La construcción de túneles en terrenos mixtos con tuneladoras de gran diámetro. Experiencias recientes de algunas obras. Rev. Obras Públicas 2009, 15, 65–78. [Google Scholar]
- Bel, J.; Branque, D.; Camus, T. Physical modelling of EPB TBM in dry sand and greenfield conditions. Eur. J. Environ. Civ. Eng. 2022, 27, 3236–3259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, D.; Kastner, R. Movements caused by the excavation of tunnels using face pressurized shields—Analysis of monitoring and numerical modeling results. Eng. Geol. 2013, 152, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirlaw, J.N.; Ong JC, W.; Rosser, H.B.; Tan, C.G.; Osborne, N.H.; Heslop, P.E. Local settlements and sinkholes due to EPB tunnelling. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng. Geotech. Eng. 2003, 156, 193–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talmon, A.M.; Bezuijen, A. Backfill grouting research at Groene Hart Tunne. In International Symposium on Geotechnical Aspects of Undergroung Construction in Soft Ground; Ng, G.B., Huang, C.C.W., Lui, H.W., Eds.; Taylor & Francis Group: Shanghai, China; London, UK, 2009; pp. 349–356. [Google Scholar]
- Kasper, T.; Meschke, G. On the influence of face pressure, grouting pressure and TBM design in soft ground tunnelling. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2006, 21, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franza, A.; Marshall, A.M.; Zhou, B. Greenfield tunnelling in sands: The effects of soil density and relative depth. Geotechnique 2019, 69, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthoz, N.; Branque, D.; Wong, H.; Subrin, D. TBM soft ground interaction: Experimental study on a 1 g reduced-scale EPBS model. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2018, 72, 189–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melis, M.; Medina, L. Predicted versus measured soil movements induced by shield tunnelling in the Madrid Metro extension. Can. Geotech. J. 2005, 42, 1160–1172. [Google Scholar]
- Melis, M.; Medina, L.; Rodriguez, J.M. Prediction and analysis of subsidence induced by shield tunnelling in the Madrid Metro extension. Can. Geotech. J. 2002, 39, 1273–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, A.M.; Farrell, R.P.; Klar, A.; Mair, R.J. Tunnels in sands: The effect of size, depth, and volume loss on greenfield displacements. Geotechnique 2012, 62, 385–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Zhu, H.; Ding, W.; Ge, X. Laboratory model tests and field investigations of EPB shield machine tunneling in soft ground in Shanghai. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2011, 26, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasper, T.; Meschke, G. A 3D finite element simulation model for TBM tunnelling in soft ground. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 2004, 28, 1441–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





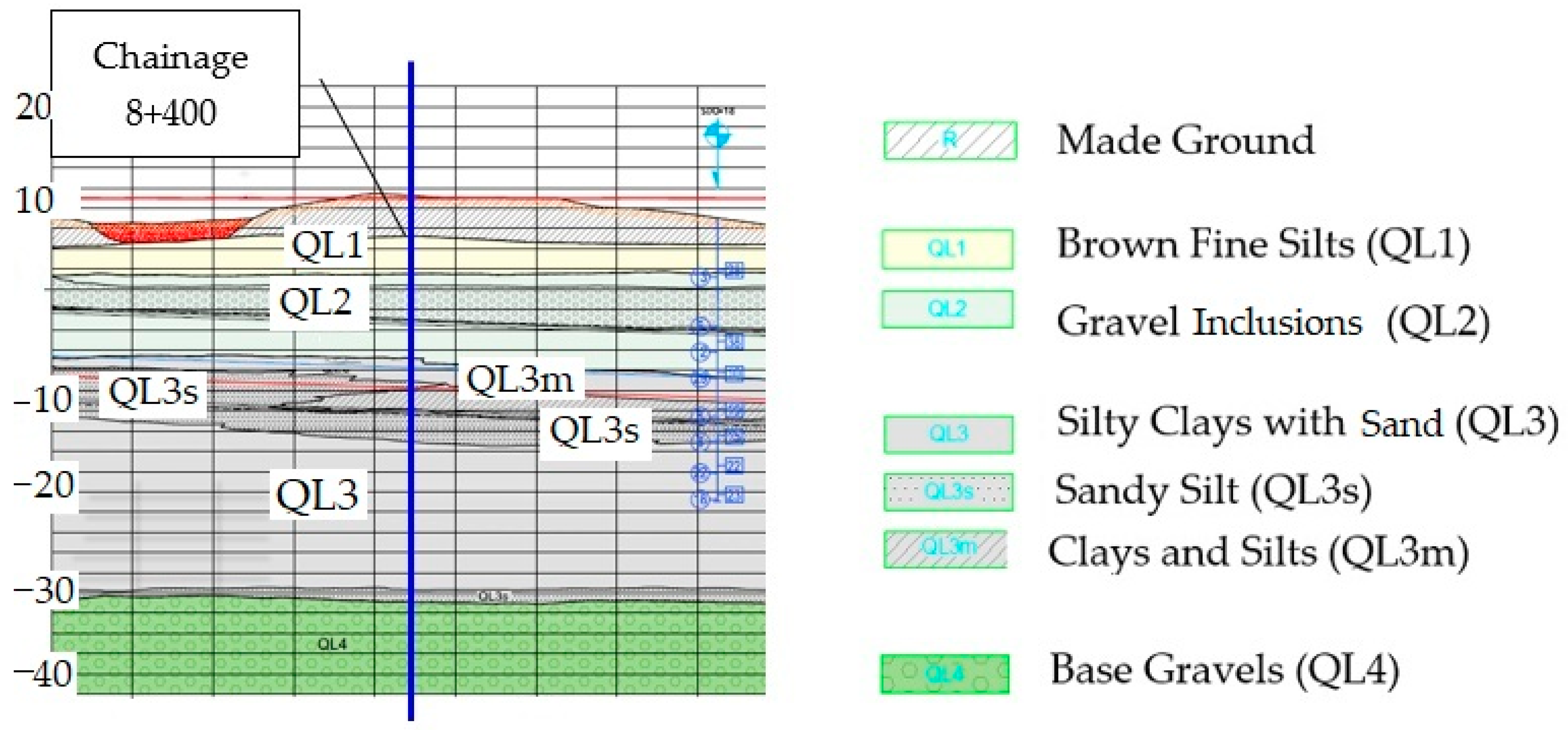

| Geological Unit | R | QL1 | QL2 | QL3 | QL3s | QL3m | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Granulometry | % Fines | 91.35 | 28.55 | 28.61 | 90.81 | 81.5 | 91.62 |
| % Sands | 8.61 | 67.67 | 63.54 | 9.14 | 18.39 | 8.36 | |
| % Gravel | 0.04 | 3.78 | 7.85 | 0.05 | 0.11 | 0.03 | |
| Limits | LL | 30.1 | 39 | 25.9 | 25.8 | 33–21.6 | 23.7 |
| LP | 19–23 | 21.4 | 18.72 | 16.2–25 | 12.4–21.9 | 17.9 | |
| Humidity | % | 18 | 18 | 21 | 26 | 25 | 27 |
| Density (γn) | g/cm3 | 2.06 | 1.95 | 2.53 | 1.9 | 1.6 | 1.83 |
| Dry density (γd) | g/cm3 | 1.75 | 1.47 | 1.75 | 1.54 | 1.47 | 1.44 |
| NSPT | Medio | 14.44 | 8.16 | 13.5 | 12.76 | 9.8 | 11.55 |
| Simple Compression | qu (Kg/cm2) | 0.84 | 1.05 | 0.24 | 0.65 | 0.35 | 0.25 |
| Direct Cutting | c (Kg/cm2) | 0.13–0.37 | 0.15–0.20 | 0.15–0.40 | 0.3 | 0–0.07 | 0.2 |
| φ (°) | 26 | 38.1 | 34.7 | 28.5 | 28 | 26.7 | |
| Oedometer | e0 | 0.5 | 0.65 | 0.7 | 0.67 | 0.73 | 0.62 |
| Cc | 0.09 | 0.08 | 0.15 | 0.12 | 0.09 | 0.09 | |
| Mv | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.002 | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.01 | |
| Triaxial | C | 0–1.50 | 0.47 | 0.38 | 0.32 | ||
| φ (°) | 31–39.00 | 17.19 | 24.8 | 21.01 | |||
| Sulphates | % | 0.12 | <0.1 | 0.1–0.48 | 0.1–0.26 | 0.19–0.59 | 0.1–0.26 |
| Organic material | % | 0.12 | 0.1–0.33 | 0.22–0.40 | 0.29–1.2 | 0.07–0.91 | 0.74 |
| Pressure meter | MPa | 10.3 | 14.2 | 15.2 | 11.9 | 15.1 | |
| Permeability | cm/s | 5.71 × 10−5 | 2.29 × 10−4 | 1.29 × 10−8 | 4.27 × 10−6 | 2.79 × 10−7 |
| Category | Details |
|---|---|
| Composition |
|
| Properties |
|
| Functions in EPB |
|
| Category | Details |
|---|---|
| Composition |
|
| Properties |
|
| Excavation Parameter | Average Value |
|---|---|
| Pressure at the Excavation Face (bar) | 2.6 |
| Bentonite Injection Pressure (bar) | 2.0 |
| Bentonite Injection Volume (m3) | 1.0–2.5 |
| Tail Pressure (bar) | 3.1 |
| Grouting Injection Volume (m3) | 8.23 |
| Machine Stops/Ring (min) | 178 |
| Installation Ring Time (min) | 19 |
| Drilling Time/Ring (min) | 28 |
| Cycle Time/Ring (min) | 225 |
| Wheel Thrust Force (kN) | 6217.57 |
| Propulsion Force (kN) | 25,600 |
| PAR (kNm) | 4475 |
| Ratio Advance (mm/min) | 63 |
| Penetration (mm/rpm) | 53 |
| Excavation Chamber Temperature (ºC) | 29.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yubero, M.T.; Bonet, E.; Gens, A. Analysis of Local Settlements Due to Operational EPB Tunneling Driving Parameters: A Case Study of the Barcelona Metro Line 9 Tunnel. Sustainability 2025, 17, 3966. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17093966
Yubero MT, Bonet E, Gens A. Analysis of Local Settlements Due to Operational EPB Tunneling Driving Parameters: A Case Study of the Barcelona Metro Line 9 Tunnel. Sustainability. 2025; 17(9):3966. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17093966
Chicago/Turabian StyleYubero, Maria Teresa, Enrique Bonet, and Antonio Gens. 2025. "Analysis of Local Settlements Due to Operational EPB Tunneling Driving Parameters: A Case Study of the Barcelona Metro Line 9 Tunnel" Sustainability 17, no. 9: 3966. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17093966
APA StyleYubero, M. T., Bonet, E., & Gens, A. (2025). Analysis of Local Settlements Due to Operational EPB Tunneling Driving Parameters: A Case Study of the Barcelona Metro Line 9 Tunnel. Sustainability, 17(9), 3966. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17093966





