Abstract
Commercial organic fertilizers (COFs), as an alternative to chemical fertilizers, have been widely promoted and applied to agricultural soils to improve soil fertility and develop green agriculture. However, the residues of veterinary antimicrobials in COFs could be transferred to agricultural soils and pose ecological risk that should not be ignored. This study quantified the occurrence of fifty-seven veterinary antimicrobials, covering five classes (i.e., twenty-three sulfonamides, nineteen quinolones, seven macrolides, six tetracyclines, and two lincosamides) in ninety-three COFs collected from five provinces in China. Twenty-two veterinary antimicrobials, including eleven quinolones, six sulfonamides, four macrolides, and one lincosamide, were detected in the COFs with total contents up to 3870 ng/g. The contents of individual antimicrobials ranged from 0.66 to 3310 ng/g, and their detection frequencies were between 2% and 49%. The composition and contents of antimicrobials in the COFs varied significantly, depending on their raw materials, production processes, and source regions. Seven antimicrobials, including ciprofloxacin, enrofloxacin, and tilmicosin, could pose low to medium potential ecological risk to soil organisms in the amended soils. The wide occurrence of antimicrobials in COFs and their potential ecological risk indicate the urgent need to establish regulatory limits of antimicrobial residues in COFs to control and prevent antimicrobial pollution in agricultural soils brought by their amendment.
1. Introduction
With the intensification of livestock farming, antimicrobials have been widely used for disease treatment and prevention, as well as growth promotion on animals. The total consumption of veterinary antimicrobials used in livestock farms was approximately 84,240 tons in China in 2013 [1]. The majority of these antimicrobials are not degraded in animal bodies and are mostly excreted with urine and feces [2]. When livestock manure containing antimicrobial residues is composted and processed into commercial organic fertilizers (COFs), the antimicrobials are not fully degraded and may even become concentrated due to the partial breakdown of organic matter [3]. Consequently, COFs frequently contain elevated levels of antimicrobials.
Studies have reported high levels of quinolones, sulfonamides, and tetracyclines in COFs, with contents and composition varying significantly with the raw materials and source regions. Analysis of 143 livestock manure samples covering chicken manure, cow manure, and pig manure in China revealed that the residue levels of most antimicrobials (e.g., sulfonamides and quinolones) were significantly different among different provinces and animal species [4]. For example, the levels of enrofloxacin detected in chicken manure (up to 1420 mg/kg) were two orders of magnitude higher than those detected in pig manure (up to 33.3 mg/kg) and cow manure (up to 46.7 mg/kg) [4]. The composition and contents of antimicrobials also differed greatly among the COFs collected in China, Malaysia, and Austria [5,6]. Despite the fact that COFs often contain high levels of antimicrobials, regulations on their contents in COFs are lacking worldwide. Although some countries have begun to develop relevant standards and regulations regarding antimicrobial residues, most of them focus on meat and dairy products [7].
The Chinese government has implemented a series of policies to encourage the use of organic fertilizers instead of chemical fertilizers to improve soil fertility and promote sustainable agricultural practices. As a result, the production and application of COFs to agricultural soils have reached 18.3 and 9.47 million tons in China, respectively [8]. Despite the benefits on soil quality and crop yields, the application of COFs could input substantial amounts of antimicrobials into farmland soils. The antimicrobials transferred into agricultural soils and their subsequent uptake by crops pose potential risk to ecosystems and human health.
While antimicrobial pollution has become a major environmental and agricultural concern in China, the residues of antimicrobials in COFs have not received significant attention yet. This study investigated the levels of antimicrobial residues in 93 COFs collected from five provinces in China. The composition and contents of antimicrobials in the COFs made from various raw materials and by different processes were compared, and their potential ecological risk on soil organisms was assessed. These findings demonstrate the urgent need to improve antimicrobial degradation in composting and reduce veterinary antimicrobial use in animal husbandry to significantly lower the contents of antimicrobial residues in COFs.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Target Analytes
A total of fifty-seven veterinary antimicrobials, covering five classes (twenty-three sulfonamides, nineteen quinolones, seven macrolides, six tetracyclines, and two lincosamides), were selected as the target analytes due to their widely veterinary use and high detection frequencies and contents in livestock manure worldwide. Mixed standards of the target analytes were purchased from Alta Scientific (Tianjin, China). Further details on these target analytes are shown in Table A1.
2.2. Sample Collection and Pretreatment
A total of 93 COFs were collected from twelve cities in Hebei Province, Shandong Province, Hubei Province, Jiangsu Province, and the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region. While 47 out of 93 COFs were primarily made from poultry manure, pig manure, cattle manure, or sheep manure, the other samples contained mixed feedstocks and bio-organic ingredients, with detailed information on the raw materials unknown (Table A2).
Pretreatment and extraction of the target antimicrobials were conducted following the procedures developed in our previous work [9]. Briefly, 0.5 g of freeze-dried and sieved COF samples were spiked with the surrogates then added with 30 mL of EDTA–McIlvaine buffer/acetonitrile/methanol/acetone (5:2:2:1 by vol.), vortexed for 30 s, and then ultrasonicated for 10 min. After centrifugation, the supernatants were diluted to 250 mL with ultrapure water. The solid phase extraction process involved the sequential use of a strong anion exchange cartridge (SAX, 500 mg, 6 mL) and a hydrophile–lipophile balance cartridge (HLB, 500 mg, 6 mL; CNW, Anpel Laboratory Technologies, Shanghai, China). The final reconstitution solutions were filtered with 0.22 μm polytetrafluorethylene (PTFE) syringe filters and then transferred into sample vials. Twenty nanograms of enrofloxacin-d5 was added into each sample as an internal standard. All samples were stored at −20 °C until analysis, typically within a week.
2.3. Instrumental Analysis and Quality Assurance and Quality Control (QA/QC)
The target antimicrobials were analyzed on a Qsight LX50 ultra-high pressure liquid chromatograph coupled with a QSight 210 triple quadrupole mass spectrometer (UPLC-MS/MS, PerkinElmer, Waltham, MA, USA) using the analytical method developed in our previous work [9]. Compound separation was performed on an XBridge BEH C18 column (2.1 × 150 mm; 2.7 μm) at 40 °C. The analytes were separated by gradient elution using ultrapure water with 0.1% formic acid (mobile phase A) and LC-MS grade acetonitrile (mobile phase B). The flow rate was 0.35 mL/min, and the sample injection volume was 5 μL. The electrospray ionization (ESI) source was operated under positive mode, and the source temperature was set at 300 °C. The temperature of the desolvation gas was set at 250 °C. The capillary voltage was at 5500 V. The limits of detection (LODs) for individual antimicrobials ranged from 1 to 75 ng/L during the instrumental analysis, while their method detection limits (MDLs) in the COF samples ranged from 0.002 to 0.206 ng/g, which is sufficient for quantitative analysis. Further details on compound-specific operating parameters and instrumental detection limits are also shown in Table A1.
Laboratory blanks were routinely analyzed, and no antimicrobial was detected. The recoveries were evaluated by adding 50 μL of 1 mg/L mixture of deuterated chemicals (i.e., ciprofloxacin-d8, erythromycin-d3, sulfadiazine-d4, sulfamethoxazole-d4, and tetracycline-d6), and the matrix effect was quantified by spiking 20 μL of 1 mg/L enrofloxacin-d5 as an internal standard into each sample prior to instrumental analysis. The recoveries were generally >70%, whereas the matrix factors (i.e., the ratios of the analyte peaks in the presence and absence of matrix component) were between 1.05 and 1.09. The effectiveness of pretreatment procedures and the accuracy and robustness of the instrumental analysis method have been comprehensively validated in our previous work [9]. Figure 1 shows selected ion monitoring chromatograms of ofloxacin and sulfamethoxazole in a mixed standard (20 µg/L) and the extract of a representative COF sample. The excellent consistency in peak shape and retention time, as well as the low noises, demonstrate the effectiveness of sample pretreatment and the sensitivity of instrumental detection.
Figure 1.
Selected ion monitoring chromatograms of two antimicrobials in the 20 µg/L standard and the extract of a representative COF sample: (a) ofloxacin in the 20 µg/L standard, (b) sulfamethoxazole in the 20 µg/L standard, (c) ofloxacin in the extract of a representative COF sample, and (d) sulfamethoxazole in the extract of a representative COF sample.
2.4. Risk Assessment
For risk assessment of these antimicrobials in the COFs on agricultural soils, the contents of antimicrobials transferred from COF to soil were estimated as follows:
where Csoil is the estimated content of individual antimicrobials transferred from COF to soil, CCOF is the measured content of individual antimicrobials in the COF sample, M is the annual applied amount of COFs (6000 kg), As is the field area where manure was applied (0.067 ha), Hs is the depth of the ploughed soil layer (20 cm), and ρs is the soil density (1500 kg/m3) [10]. It is worth mentioning that the annual applied amount of COFs was estimated based on the inquiry from the local farmers, which is also at a comparable level with that reported in the literature [10]. Other processes that may occur during the migration of antimicrobials from COF to soil, such as runoff, plant uptake, and degradation, were not considered for a conservative assessment. The potential ecological risk of the individual antimicrobial on soil was evaluated by calculating the risk quotient (RQ):
where PNECsoil is the predicted no-effect concentration of individual antimicrobial to the sensitive species (ng/g). The PNECsoil values of the target antimicrobials were calculated as follows:
where TOX is the toxicity data collected from the ECOTOX database, including median lethal concentration (LC50), median effect concentration (EC50), lowest observed effect concentration/lowest observed effect level (LOEC/LOEL), and no observed effect concentration/no observed effect level (NOEC/NOEL) for soil organisms. The assessment factor (AF) for LC50, EC50, LOEC/LOEL, and NOEC/NOEL were 1000, 1000, 10, and 10, respectively. The lowest value was adopted for a conservative assessment when multiple toxicity data were available for the same species. The lowest toxicity data within the same class were used when the toxicity data for a given analyte was not available.
Mixture toxicity models, such as concentration addition (CA) and independent action (IA), have been used to predict the toxicity of chemical mixtures. The CA model is commonly applied to chemicals that share the same mode of action, while the IA model is suitable for chemicals with different modes of action. For this study, the co-occurrence of different antimicrobials often exhibits synergistic or additive effects. We chose to evaluate the ecological risk on an individual basis to avoid bias and obtain a robust assessment. The ecological risk of individual antimicrobials was evaluated based on the commonly used ranking criteria: RQ ≥ 1, high risk; 0.1 ≤ RQ < 1, medium risk; 0.01 ≤ RQ < 0.1, low risk; RQ < 0.01, no risk.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Levels of Antimicrobials in the COFs
Among the ninety-three COF samples analyzed, a total of twenty-two veterinary antimicrobials were detected, including eleven quinolones, six sulfonamides, four macrolides, and one lincosamide (Figure 2 and Table A3). The total contents of antimicrobials ranged between 0.95 and 3870 ng/g, with a median content of 53.8 ng/g and a detection frequency of 86% (Figure 2 and Table A3). No tetracyclines were detected in the COFs. Previous studies have also reported the absence of tetracyclines in livestock manure, likely due to their relatively fast degradation in the processing of livestock manure [6,11,12]. It was reported that chlortetracycline in cattle manure was transformed into several degradation products, including iso-chlortetracycline, 4-epi-chlortetracycline, and anhydro-chlortetracycline, during composting [11]. In addition, no antimicrobials were detected in thirteen COFs, which were mostly made from bio-organic materials, such as mushroom residues and Chinese herbal residues.
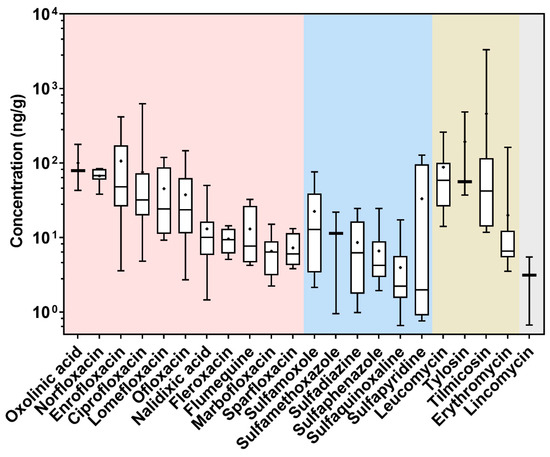
Figure 2.
Box and whisker plot for the levels of veterinary antimicrobials in the COF samples (n = 93). The box and whiskers represent the median, interquartile range, and maximum/minimum values, and the black cross represents the mean value. The pink, blue, yellow, and grey shades indicate quinolones, sulfonamides, macrolides, and lincosamides, respectively.
The contents of individual antimicrobials in the COF samples ranged from 0.66 to 3310 ng/g (Figure 2 and Table A3). Ofloxacin was the most abundant quinolone, with a detection frequency of 49% and a median content of 23.6 ng/g, while ciprofloxacin was detected at content up to 621 ng/g. Ciprofloxacin is both a commonly used antimicrobial and a main metabolite from enrofloxacin, which is one of the most widely consumed veterinary antimicrobials in China [1]. The overall detection frequencies of sulfonamides, macrolides, and lincosamides were generally low (i.e., ≤20%). Sulfaquinoxaline was the most frequently detected sulfonamide, with a detection frequency of 17% and a median content of 2.23 ng/g. Sulfaquinoxaline is a veterinary antimicrobial that is widely administered on cattle and sheep to treat coccidiosis, and it has been detected in livestock manure at levels up to 6100 ng/g [13]. Among the macrolides, leucomycin was the most abundant compound (detection frequency: 20%), whereas tilmicosin had the highest maximum content (3310 ng/g). Lincomycin was the only lincosamide detected at a rather low detection frequency (3%) and low contents (median: 3.12 ng/g).
Veterinary antimicrobials, such as ciprofloxacin, fleroxacin, sulfamethoxazole, and tylosin, were among the most commonly monitored antimicrobials in livestock manure and organic fertilizers (Table 1). The levels of ciprofloxacin, enrofloxacin, fleroxacin, norfloxacin, sulfadiazine, and sulfamethoxazole quantified in this study were generally 1–2 orders of magnitude lower compared to those measured in the livestock manure (Table 1) [4,14,15,16,17]. However, compared to more recent studies [13,18,19,20,21,22], the levels of antimicrobials in this study were comparable or higher than those reported in the literature (Table 1). For example, ciprofloxacin and enrofloxacin at levels up to 70.4 and 65.1 ng/g were reported in cattle manure [20], whereas their mean contents in the COF samples of this study were 75.7 and 106 ng/g, respectively. Qian and co-workers reported high levels of sulfamethoxazole (mean: 608 ng/g) in the organic fertilizers [23], but generally low levels of sulfonamides were often reported in pig manure, cow manure, and duck manure (Table 1) [13,22,24]. Although several studies have investigated the occurrence of a few common antimicrobials in livestock manure and organic fertilizers, other antimicrobials have yet to receive adequate attention.

Table 1.
Comparison of levels of antimicrobial residues in the COF samples of this study with those reported for animal manure and COF in the literature (unit: ng/g).
3.2. Antimicrobial Residues in COFs Made from Different Raw Materials
The antimicrobials in COFs originate from the various types of raw materials used, such as cattle manure, sheep manure, poultry manure, pig manure, and other bio-organic materials. Overall, the COFs made from bio-organic materials, such as mushroom residues and bean dregs, exhibited the lowest levels of antimicrobial residues, whereas the antimicrobial contents in the COFs made from livestock manure generally decreased in the order of cattle manure > sheep manure > poultry manure > pig manure (Figure 3a). Quinolones were the dominant class of antimicrobials in the COFs made from sheep manure, poultry manure, cattle manure, and other bio-organic materials, whereas only macrolides were detected in the COFs processed from pig manure (Figure 3b).
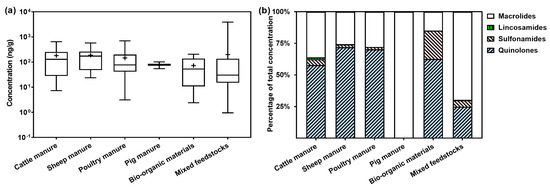
Figure 3.
Levels (a) and composition (b) of veterinary antimicrobials in COFs made from different raw materials. The box and whiskers in (a) represent the median, interquartile range, and maximum/minimum values, and the black cross represents the mean value.
Besides animal manure, a range of organic wastes, such as mushroom residues, furfural residues, and Chinese herbal residues, are also utilized to produce COFs. These materials often contain low levels of antimicrobial residues (or no antimicrobial residues) compared to livestock manure. No antimicrobials were detected in the COF samples made from mushroom residues, furfural residues, and Chinese herbal residues in this study. Therefore, the choice of raw materials for COFs significantly impacts the composition and contents of antimicrobial residues. Using alternative organic materials, such as agricultural waste or biogas residues, can reduce the levels of antimicrobial residues in the COFs and the associated ecological risk.
3.3. Antimicrobial Residues in COFs Made by Different Processes
Minerals (e.g., lime and clay) and salts (e.g., ferrous sulfate and calcium/magnesium superphosphate) are often added in the composting of manure or in the granulation of COFs. As a result, the contents in COFs in different shapes, which are made by different processes, could vary significantly. The total contents of antimicrobials in the powdered COFs (mean: 114 ng/g) were higher than those in the granular COFs (mean: 51.4 ng/g; Figure 4a). The composition also varied between the powdered and granular COFs. Macrolides dominated in powdered COFs, whereas quinolones were the dominant class in granular COFs (Figure 4b). Powdered COFs, mainly derived from livestock manure or other bio-organic materials, generally contained higher levels of antimicrobials compared to granular COFs. This is likely due to the fact that powdered COFs are less processed and retain higher levels of antimicrobials from the raw materials, whereas granular COFs often undergo more controlled production processes and contain additives, such as clay and turfy soil, which dilute the levels of antimicrobials in the final product. Composting, a commonly used method for producing granular COFs, can reduce the residues of antimicrobials, such as tetracyclines and sulfonamides, by over 60% during the process [25]. Nevertheless, the effectiveness of composting depends on many factors, such as temperature, duration, and microbial activity. Interestingly, the pellet COFs exhibited even higher levels of antimicrobials compared to the powdered and granular COFs. This is attributed to the fact that their main raw materials were livestock manure (e.g., sheep manure), which often contains high levels of antimicrobial residues.
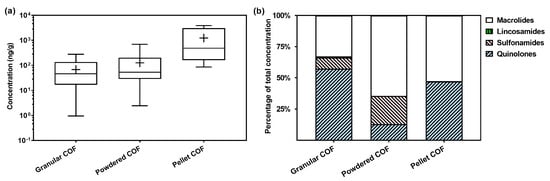
Figure 4.
Levels (a) and composition (b) of veterinary antimicrobials in COF samples of different shapes (i.e., made by different processes). The box and whiskers in (a) represent the median, interquartile range, and maximum/minimum values, and the black cross represents the mean value.
The shape of COFs may impact the release rates and transfer of antimicrobials in agricultural soils. It is expected that antimicrobials and nutrients would be released from the granular COFs more slowly compared to the powdered COFs, which is beneficial for long-term soil conditioning and sustained plant growth. While the production processes may result in COF products with different levels of antimicrobial residues, it is important to reduce and even eliminate their contents in the raw materials used in COF production.
3.4. Antimicrobial Residues in COFs Produced from Different Regions
Antimicrobial residues in COFs vary widely across source regions, with hotspots in the areas characterized by intensive agricultural activities and high livestock density. A comprehensive study analyzed the antimicrobial resistance genes (ARGs) in agricultural soils from seventeen countries and reported that Central North America, Eastern Europe, Western Asia, and Northeast China were the hotspots for antimicrobial resistance burden because of dense population and intensive agricultural activities, such as crop farming, livestock husbandry, and manure application [26]. Regions with intensive livestock farming and frequent use of antimicrobials in livestock husbandry tend to have higher levels of antimicrobial residues in COFs. Seventeen antimicrobials were detected in the manure-based COFs collected in East China, with total contents exceeding 15 mg/kg, which highlights the substantial enrichment of antimicrobial residues in the COFs produced in this region [27].
The COF samples in this study were collected from twelve cities in Hebei Province, Shandong Province, Jiangsu Province, Hubei Province, and the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, which are among the major agricultural provinces in China. For example, Shandong Province has a total agricultural output, including crop farming, animal husbandry, fishery, and forestry, of CNY 1.28 trillion in 2024, ranking first in the country [28]. COFs from Nantong, Jiangsu Province, exhibited the highest levels of antimicrobial residues (mean: 451 ng/g), followed by those from Tianjin (mean: 302 ng/g), Cangzhou (mean: 174 ng/g), Ji’ning (mean: 163 ng/g), and Shijiazhuang (mean: 159 ng/g; Figure 5a). Nantong is a major livestock and poultry breeding region and ranks fourth in the total number of livestock and poultry farmed in Jiangsu Province. The contents of antimicrobial residues in the COFs collected from Ji’ning and Ji’nan, Shandong Province, were relatively high, which is also consistent with the fact that they are both important livestock and poultry breeding bases in Shandong Province. On the contrary, the levels of antimicrobial residues in the COFs collected from Bayannur, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, were much lower compared to the others. Bayannur is renowned for the production of sheep and cows by free-range farming, which uses much less antimicrobials compared to the factory farming of pigs and poultry. The is also a significant difference in the composition of antimicrobials in the COF samples produced from different regions (Figure 5b). For example, macrolides were the dominant class of antimicrobials in the COFs from Shijiazhuang, Handan, and Ji’ning, whereas quinolones were the most abundant antimicrobial class in those from Huanggang and Nantong. These results are consistent with the findings of a previous study, which reports that fluoroquinolones were used more heavily in animal farming in Southeast China compared to North China [17].
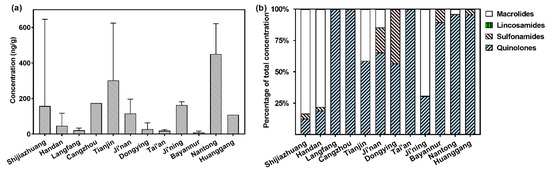
Figure 5.
Levels (a) and composition (b) of veterinary antimicrobials in the COFs produced from different regions in China. The column and error bars in (a) represent mean values with standard deviation.
3.5. Ecological Risk of Antimicrobials in COFs on Agricultural Soils
The antimicrobial residues in COFs would be transferred into agricultural soils with their amendment and subsequently pose a potential ecological risk to soil organisms. Based on the estimated RQ values, only tilmicosin could pose low to medium ecological risk, while six antimicrobials, including ciprofloxacin, enrofloxacin, oxolinic acid, erythromycin, leucomycin, and tylosin, would pose low ecological risk (Figure 6). Among these seven antimicrobials, the potential ecological risk posed by individual compounds decreases in the order of tilmicosin > tylosin > ciprofloxacin > enrofloxacin > leucomycin > erythromycin > oxolinic acid. The other antimicrobials in the COF samples would pose no ecological risk to soil organisms. It is worth noting that only the risk from individual compounds is assessed here, while the co-occurrence of multiple antimicrobials could result in additive, synergistic, or antagonistic effects and, thus, have a much more complex toxic effect on soil organisms. For instance, ciprofloxacin and norfloxacin can exhibit strong synergistic effects, whereas erythromycin and tetracycline are known to present antagonistic effects on aquatic organisms [29,30]. Detailed knowledge of the mode of action of these antimicrobials is needed for more accurate prediction of their potential ecological risk.
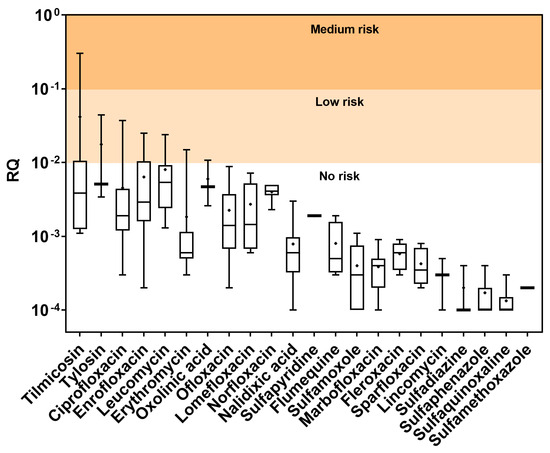
Figure 6.
Risk quotient (RQ) values of the antimicrobials in the COF samples of this study. Results are sorted by decreasing maximum RQ from left to right. Compounds with RQ < 10−4 are not shown.
The application of COFs is a major source of antimicrobials in agricultural soils [31]. The above results demonstrate that the continuous application of COFs could result in the accumulation of antimicrobials and pose a potential ecological risk to soil organisms. In addition, COFs could function as crucial reservoirs of ARGs and pathogens, along with a wide range of contaminants [32]. The antimicrobials inputted by long-term amendment of COFs could significantly reduce the bacterial diversity in agricultural soils and change the dominant bacterial species in the microbial community [33]. Moreover, the long-term application of COFs could greatly increase the abundance and diversity of ARGs in agricultural soils and accelerate the spread of ARGs from soil to plants, eventually threatening human health [25,34]. Therefore, it is critical to lower the residues of antimicrobials in COFs to control and prevent antimicrobial pollution in soil from the source. There is an urgent need to establish regulatory standards for the levels of antimicrobial residues in COFs, as no such regulations exist at the moment [35]. The composting and other production processes of COFs should be optimized to enhance the removal efficiency of antimicrobials in animal manure. The removal of antimicrobials during common aerobic composting and anaerobic digestion varies largely. Several sulfonamides, such as sulfadiazine, sulfadimethoxine, and sulfamethoxazole, could be almost completely removed during anaerobic digestion, whereas other sulfonamides, including sulfamethoxypyridazine, sulfamethazine, and sulfathiazole, are quite recalcitrant [36]. It was reported that aerobic composting could effectively remove tetracyclines, quinolones, and sulfonamides [37,38]. However, the degradation efficiency of antimicrobials could be significantly affected by their initial levels. For example, the degradation of ciprofloxacin in swine manure during composting was inhibited when its initial content exceeded 10 mg/kg [39]. To reduce the level of antimicrobial residues in animal manure, it is necessary to curb the prevalent overuse and misuse of antimicrobials in animal husbandry in China [40,41,42].
4. Conclusions
The occurrence of twenty-two veterinary antimicrobials, including eleven quinolones, six sulfonamides, four macrolides, and one lincosamide, were quantified in ninety-three COF samples collected from five provinces in China. While the total contents of antimicrobials in these COF samples ranged between 0.95 and 3870 ng/g, the levels of individual antimicrobials were up to 3310 ng/g. The composition and contents of antimicrobials in the COFs varied largely with different raw materials, production processes, and source regions. Seven antimicrobials could pose low to medium ecological risk to soil organisms, and their risk decreased in the order of tilmicosin > tylosin > ciprofloxacin > enrofloxacin > leucomycin > erythromycin > oxolinic acid. Although the majority of antimicrobials could pose only very low or no ecological risk, the actual risk to soil organisms in the amended soils from exposure to multiple antimicrobials introduced by COFs is difficult to predict. While COF application has been widely promoted as an alternative to chemical fertilization to improve soil fertility and develop green agriculture, the negative impact associated with the antimicrobial residues deserves significant attention. The wide occurrence of antimicrobials in COFs and their potential ecological risk indicate the urgent need to lower the antimicrobial residues in COFs to control and prevent antimicrobial pollution in agricultural soils.
Author Contributions
H.Z.: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Visualization, Writing—original draft, Writing—review and editing. H.F.: Data curation, Methodology, Writing—original draft. H.C.: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Writing—original draft, Writing—review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded in part by the Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 42307313, U23A2005, and U2006212).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available on request.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Xinpeng Yue and Xi Wang for their help in sample pretreatment.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no financial/commercial conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| COFs | Commercial organic fertilizers |
| ARGs | Antimicrobial resistance genes |
Appendix A

Table A1.
Instrumental details for the analysis of the target antimicrobials in this study.
Table A1.
Instrumental details for the analysis of the target antimicrobials in this study.
| Analyte | Precursor Ion (m/z) | Quantitative Ion (m/z) | Qualitive Ion (m/z) | Retention Time (min) | Collision Energy (V) | Entrance Voltage (V) | Lens Voltage (V) | MDL (ng/L) | MQL (ng/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chlortetracycline | 479 | 444 | 462 | 9.18 | −28/−20 | 30/30 | −122/−92 | 24 | 80 |
| Cinoxacin | 263 | 217 | 245 | 9.11 | −29/−21 | 16/19 | −52/−48 | 13 | 43 |
| Ciprofloxacin | 332 | 314 | 288 | 8.45 | −31/−24 | 1/0 | −68/−56 | 14 | 47 |
| Clindamycin | 425 | 126.3 | 377 | 9.54 | −40/−25 | 25/36 | −76/−84 | 13 | 45 |
| Danofloxacin | 358 | 340 | 82 | 8.55 | −33/−58 | 0/4 | −76/−80 | 8 | 26 |
| Demeclocycline | 465 | 448 | 430 | 8.88 | −23/−27 | 18/22 | −100/−116 | 75 | 249 |
| Difluoxacin | 400 | 382 | 356 | 8.71 | −32/−27 | 17/33 | −76/−68 | 11 | 36 |
| Doxycycline | 445 | 428 | 154 | 9.47 | −24/−40 | 30/30 | −80/−82 | 34 | 112 |
| Enoxacin | 321 | 303 | 234 | 8.12 | −27/−29 | 22/0 | −60/−64 | 8 | 28 |
| Enrofloxacin | 360 | 316 | 342 | 8.52 | −27/−31 | 22/35 | −60/−64 | 9 | 31 |
| Erythromycin | 734 | 158 | 576 | 9.8 | −38/−24 | 29/30 | −128/−168 | 58 | 193 |
| Fleroxacin | 370 | 326 | 269 | 7.81 | −25/−36 | 28/13 | −72/−92 | 21 | 71 |
| Flumequine | 262 | 244 | 202 | 9.71 | −26/−44 | 10/6 | −44/−72 | 3 | 10 |
| Isochlortetracycline | 479 | 461.9 | 444 | 8.71 | −27/−29 | 16/6 | −92/−124 | 40 | 134 |
| Josamycin | 828 | 174.2 | 109.4 | 9.92 | −45/−58 | 36/47 | −144/−124 | 22 | 73 |
| Leucomycin | 702 | 174.2 | 558.2 | 9.14 | −40/−32 | 40/36 | −112/−128 | 55 | 184 |
| Lincomycin | 407 | 126 | 359 | 7.81 | −38/−24 | 25/30 | −80/−84 | 1 | 3 |
| Lomefloxacin | 352 | 265 | 308 | 8.64 | −32/−23 | 28/18 | −60/−56 | 17 | 55 |
| Marbofloxacin | 363 | 72 | 319 | 7.67 | −31/−24 | 31/24 | −64/−76 | 15 | 50 |
| Nalidixic acid | 233 | 215 | 187 | 9.63 | −19/−34 | 6/6 | −48/−68 | 6 | 20 |
| Norfloxacin | 320 | 302 | 276 | 8.26 | −31/−24 | 2/2 | −60/−52 | 14 | 46 |
| Ofloxacin | 362 | 318 | 261 | 8.1 | −27/−37 | 28/35 | −68/−72 | 13 | 43 |
| Oleandomycin | 688 | 158.3 | 544.4 | 9.59 | −38/−23 | 16/16 | −116/−96 | 28 | 94 |
| Orbifloxacin | 396 | 352 | 295 | 8.69 | −23/−30 | 0/16 | −76/−96 | 6 | 22 |
| Oxolinic acid | 461 | 426 | 443 | 8.52 | −24/−17 | 20/20 | −76/−72 | 4 | 15 |
| Oxytetracycline | 262 | 244 | 202 | 9.26 | −24/−42 | 13/7 | −64/−108 | 23 | 76 |
| Pefloxacin | 334 | 316 | 290 | 8.12 | −29/−24 | 0/0 | −64/−56 | 9 | 31 |
| Pipemidic acid | 304 | 217 | 189 | 7.39 | −30/−44 | 4/21 | −72/−68 | 19 | 64 |
| Sarafloxacin | 386 | 299 | 368 | 8.81 | −39/−33 | 16/19 | −88/−72 | 15 | 51 |
| Sparfloxacin | 393 | 292 | 349 | 8.97 | −30/−27 | 8/15 | −88/−80 | 18 | 59 |
| Spiramycin | 844 | 174 | 109 | 9.82 | −45/−56 | 42/52 | −168/−144 | 32 | 107 |
| Sulfabenzamide | 277 | 156 | 92 | 8.9 | −16/−47 | 14/6 | −40/−52 | 4 | 12 |
| Sulfacetamide | 215 | 156.1 | 108 | 1.63 | −15/−30 | 9/7 | −36/−44 | 8 | 26 |
| Sulfachlorpyridazine | 284.9 | 156 | 108.1 | 8.29 | −20/−37 | 18/15 | −56/−56 | 11 | 36 |
| Sulfadiazine | 250.9 | 156.1 | 108.2 | 4.76 | −21/−36 | 15/16 | −52/−56 | 15 | 50 |
| Sulfadimethoxine | 311 | 156 | 108.1 | 8.71 | −26/−38 | 14/19 | −60/−68 | 7 | 23 |
| Sulfadoxine | 311 | 156 | 108.1 | 9.16 | −27/−38 | 14/15 | −60/−64 | 12 | 40 |
| Sulfaguanidine | 215 | 156 | 92.1 | 3.5 | −18/−34 | 13/10 | −36–32 | 17 | 56 |
| Sulfisomidine | 279 | 124 | 185.9 | 7.79 | −26/−22 | 12/15 | −48/−56 | 6 | 18 |
| Sulfamerazine | 264.9 | 155.9 | 172.2 | 6.6 | −23/−22 | 14/24 | −52/−52 | 6 | 19 |
| Sulfameter | 280.9 | 156 | 108 | 8.55 | −23/−38 | 20/19 | −64/−64 | 23 | 76 |
| Sulfamethazine | 279 | 186 | 156 | 5.23 | −24/−25 | 24/22 | −52/−60 | 8 | 26 |
| Sulfamethiazole | 271 | 156.1 | 108.2 | 7.62 | −19/−34 | 19/19 | −52/−56 | 21 | 71 |
| Sulfamethoxazole | 254 | 155.9 | 108.1 | 8.47 | −21/−35 | 18/20 | −48/−48 | 26 | 87 |
| Sulfamethoxypyridazine | 281 | 155.9 | 92 | 7.43 | −22/−42 | 18/17 | −56/−52 | 15 | 50 |
| Sulfamonomethoxine | 280.9 | 156 | 108 | 8 | −23/−38 | 24/24 | −56/−64 | 14 | 48 |
| Sulfamoxole | 268 | 92 | 155.9 | 8.73 | −46/−20 | 25/14 | −56/−44 | 7 | 22 |
| Sulfanitran | 336 | 134.2 | 197.8 | 9.54 | −38/−29 | 22/26 | −80/−48 | 7 | 25 |
| Sulfaphenazole | 315 | 156 | 222 | 9.02 | −28/−26 | 29/31 | −72/−68 | 6 | 21 |
| Sulfapyridine | 249.9 | 156 | 184.1 | 6.13 | −23/−23 | 23/26 | −52/−48 | 10 | 34 |
| Sulfaquinoxaline | 301 | 156 | 92 | 9.26 | −25/−56 | 28/28 | −48/−68 | 6 | 22 |
| Sulfathiazole | 255.9 | 156.1 | 108 | 5.63 | −20/−34 | 22/24 | −52/−48 | 20 | 67 |
| Sulfisoxazole | 268 | 156.1 | 107.9 | 7.6 | −19/−35 | 17/21 | −48/−56 | 7 | 23 |
| Tetracycline | 445 | 410 | 427 | 8.38 | −25/−17 | 20/27 | −88/−66 | 21 | 71 |
| Tilmicosin | 869 | 174 | 132 | 9.35 | −60/−67 | 30/51 | −280/−196 | 3 | 11 |
| Trimethoprim | 291 | 230 | 261 | 7.84 | −31/−33 | 34/33 | −52/−56 | 13 | 42 |
| Tylosin | 917 | 773.2 | 174.2 | 9.68 | −40/−51 | 44/39 | −164/−172 | 11 | 35 |

Table A2.
Description of the 93 COF samples collected in this study.
Table A2.
Description of the 93 COF samples collected in this study.
| Raw Material | Sample Number | Main Treatment and Processes |
|---|---|---|
| Poultry manure | 20 | Mix, ferment, crush |
| Sheep manure | 17 | Mix, ferment, crush |
| Cattle manure | 8 | Mix, ferment, crush |
| Pig manure | 2 | Mix, ferment, crush |
| Bio-organic materials (mushroom residues, bean dreg, Chinese herb residues, etc.) | 14 | Ferment, mix, crush, pellet |
| Mixed feedstocks | 32 | Ferment, mix, crush, pellet |
| Total | 93 | Mix, ferment, crush, pellet |

Table A3.
Summary of the contents of antimicrobial residues in the 93 COF samples.
Table A3.
Summary of the contents of antimicrobial residues in the 93 COF samples.
| Antimicrobial | Maximum (ng/g) | Median (ng/g) | Minimum (ng/g) | Mean (ng/g) | Standard Deviation (ng/g) | Detection Frequency (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quinolones | ||||||
| Ciprofloxacin | 621 | 32.0 | 4.84 | 75.7 | 144 | 17 |
| Enrofloxacin | 417 | 47.9 | 3.60 | 106 | 119 | 20 |
| Fleroxacin | 14.4 | 9.32 | 5.07 | 9.58 | 3.32 | 5 |
| Flumequine | 32.5 | 7.65 | 4.25 | 13.0 | 11.4 | 4 |
| Lomefloxacin | 119 | 24.1 | 9.18 | 45.2 | 39.4 | 11 |
| Marbofloxacin | 15.1 | 6.37 | 2.24 | 6.55 | 4.13 | 8 |
| Nalidixic acid | 50.0 | 10.1 | 1.45 | 13.1 | 10.3 | 30 |
| Norfloxacin | 83.9 | 68.0 | 38.1 | 66.9 | 14.4 | 8 |
| Ofloxacin | 146 | 23.6 | 2.71 | 37.4 | 36.2 | 49 |
| Oxolinic acid | 178 | 79.0 | 43.1 | 100 | 57.2 | 3 |
| Sparfloxacin | 13.2 | 6.04 | 3.81 | 7.27 | 3.54 | 4 |
| Sulfonamides | ||||||
| Sulfadiazine | 24.5 | 6.27 | 0.99 | 8.58 | 8.39 | 5 |
| Sulfamethoxazole | 21.8 | 11.4 | 0.95 | 11.4 | 10.4 | 2 |
| Sulfaphenazole | 24.5 | 4.23 | 1.94 | 6.61 | 6.06 | 14 |
| Sulfapyridine | 128 | 1.98 | 0.76 | 33.1 | 54.6 | 4 |
| Sulfaquinoxaline | 17.3 | 2.23 | 0.66 | 3.95 | 4.04 | 17 |
| Sulfamoxole | 76.2 | 12.8 | 2.14 | 22.4 | 25.9 | 6 |
| Macrolides | ||||||
| Erythromycin | 163 | 6.59 | 3.54 | 19.9 | 41.5 | 14 |
| Leucomycin | 260 | 58.7 | 14.1 | 87.9 | 79.7 | 20 |
| Tilmicosin | 3310 | 42.2 | 11.8 | 458 | 1080 | 9 |
| Tylosin | 485 | 55.9 | 37.3 | 193 | 207 | 3 |
| Lincosamides | ||||||
| Lincomycin | 5.47 | 3.12 | 0.67 | 3.09 | 1.96 | 3 |
References
- Zhang, Q.Q.; Ying, G.G.; Pan, C.G.; Liu, Y.S.; Zhao, J.L. Comprehensive Evaluation of Antibiotics Emission and Fate in the River Basins of China: Source Analysis, Multimedia Modeling, and Linkage to Bacterial Resistance. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 6772–6782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, R.; Li, C.; Xie, S.; You, F.; Cao, Z.; Xu, Z.; Yu, G.; Wang, Y. Preparation of Biochar via Pyrolysis at Laboratory and Pilot Scales to Remove Antibiotics and Immobilize Heavy Metals in Livestock Feces. J. Soils Sediments 2019, 19, 2891–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezzariai, A.; Hafidi, M.; Khadra, A.; Aemig, Q.; El Fels, L.; Barret, M.; Merlina, G.; Patureau, D.; Pinelli, E. Human and Veterinary Antibiotics during Composting of Sludge or Manure: Global Perspectives on Persistence, Degradation, and Resistance Genes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 359, 465–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Dong, Y.H.; Wang, H. Residues of Veterinary Antibiotics in Manures from Feedlot Livestock in Eight Provinces of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 1069–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, Y.B.; Zakaria, M.P.; Latif, P.A.; Saari, N. Occurrence of Veterinary Antibiotics and Progesterone in Broiler Manure and Agricultural Soil in Malaysia. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 488–489, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Carballo, E.; González-Barreiro, C.; Scharf, S.; Gans, O. Environmental Monitoring Study of Selected Veterinary Antibiotics in Animal Manure and Soils in Austria. Environ. Pollut. 2007, 148, 570–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Union. Regulation (EU) No. 37/2010 of 22 December 2009 on Pharmacologically Active Substances and Their Classification Regarding Maximum Residue Limits in Foodstuffs of Animal Origin. Off. J. Eur. Commun. 2010, L15, 1–72. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Xue, W.; Miao, W.; Sun, H.; Wu, R.; Du, Y.; Tan, Y.; Li, Y. Characteristics and Development Trend of Organic Fertilizer Industry. Vegetables 2018, 12, 26–29. [Google Scholar]
- Zhi, H.; Cheng, H. Development and Validation of a Solid Phase Extraction-UPLC-MS/MS Method for the Determination of Fifty-Nine Antimicrobials in Commercial Organic Fertilizers and Amended Soils. Microchem. J. 2022, 183, 108007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Zhou, Q.; Luo, Y. Occurrence and Source Analysis of Typical Veterinary Antibiotics in Manure, Soil, Vegetables and Groundwater from Organic Vegetable Bases, Northern China. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 2992–2998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Jeong, S.; Ju, M.; Kim, J.Y. Fate of Chlortetracycline Antibiotics During Anaerobic Degradation of Cattle Manure. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 386, 121894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spielmeyer, A.; Stahl, F.; Petri, M.S.; Zerr, W.; Brunn, H.; Hamscher, G. Transformation of Sulfonamides and Tetracyclines during Anaerobic Fermentation of Liquid Manure. J. Environ. Qual. 2017, 46, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Fan, L.; Dong, Y.; Li, D.; Zhao, L.; Yuan, X.; Wang, L.; Zhao, S. Determination of Sulfonamide Residues in Livestock and Poultry Manure Using Carbon Nanotube Extraction Combined with UPLC-MS/MS. Food Anal. Methods 2021, 14, 641–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.G.; Luo, Y.; Zhou, Q.X.; Xu, L. Determination of Thirteen Antibiotics Residues in Manure by Solid Phase Extraction and High Performance Liquid Chromatography. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2008, 36, 1162–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.; Zakaria, M.P.; Latif, P.A.; Saari, N. Simultaneous Determination of Veterinary Antibiotics and Hormone in Broiler Manure, Soil and Manure Compost by Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1262, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Chen, J.; Wang, J.; Ma, Z.; Han, P.; Luan, Y.; Lu, A. Occurrence of Antibiotics in Soils and Manures from Greenhouse Vegetable Production Bases of Beijing, China and an Associated Risk Assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 521–522, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Wan, W.; Mao, D.; Wang, C.; Mu, Q.; Qin, S.; Luo, Y. Occurrence and Distribution of Sulfonamides, Tetracyclines, Quinolones, Macrolides, and Nitrofurans in Livestock Manure and Amended Soils of Northern China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 4545–4554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Wei, C.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z.; Hu, H.; Xue, J.; Davis, M. A Simple and Economic Method for Simultaneous Determination of 11 Antibiotics in Manure by Solid-Phase Extraction and High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. J. Soils Sediments 2016, 16, 2242–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, N.; Sun, P.; Sun, Q.; Li, X.; Yang, X.; Ji, X.; Zou, H.; Ottoson, J.; Nilsson, L.E.; Berglund, B.; et al. Presence of Antibiotic Residues in Various Environmental Compartments of Shandong Province in Eastern China: Its Potential for Resistance Development and Ecological and Human Risk. Environ. Int. 2018, 114, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.-F.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, J.; Ren, Y.-P. Determination of Fluoroquinolones in Cattle Manure-Based Biogas Residue by Ultrasonic-Enhanced Microwave-Assisted Extraction Followed by Online Solid Phase Extraction-Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2018, 1086, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xuan, Y.; Song, W.; Si, W.; Zhao, Z.; Rao, Q. Ion-Exchange Solid-Phase Extraction Combined with Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry for the Determination of Veterinary Drugs in Organic Fertilizers. J. Chromatogr. B 2016, 1022, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhi, S.; Zhou, J.; Liu, H.; Wu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, K. Simultaneous Extraction and Determination of 45 Veterinary Antibiotics in Swine Manure by Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2020, 1154, 122286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, S.; Lan, Y.; Liu, Q.; Si, W.; Sun, M.; Wang, L.; Shen, G. Response Surface Optimization of Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry Method for Simultaneous Determination of 14 Kinds of Sulfonamide Antibiotics in Organic Fertilizers. Huadong Ligong Daxue Xuebao/J. East China Univ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 47, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Ma, X.; Ru, S.; Qiu, T.; Lu, A. Veterinary Antibiotics and Estrogen Hormones in Manures from Concentrated Animal Feedlots and Their Potential Ecological Risks. Environ. Res. 2021, 198, 110463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Yao, H. Effects of Composting Different Types of Organic Fertilizer on the Microbial Community Structure and Antibiotic Resistance Genes. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.T.; Ma, R.A.; Zhu, D.; Konstantinidis, K.T.; Zhu, Y.G.; Zhang, S.Y. Organic Fertilization Co-Selects Genetically Linked Antibiotic and Metal(Loid) Resistance Genes in Global Soil Microbiome. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 5168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.; Li, W.; Xu, W. Effects of Partial Organic Substitution for Chemical Fertilizer on Antibiotic Residues in Peri-Urban Agricultural Soil in China. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shandong Provincial Bureau of Statistics Shandong Statistical Yearbook in 2024. Available online: http://tjj.shandong.gov.cn/tjnj/nj2024/zk/indexch.htm (accessed on 12 March 2025).
- Yang, L.H.; Ying, G.G.; Su, H.C.; Stauber, J.L.; Adams, M.S.; Binet, M.T. Growth-Inhibiting Effects of 12 Antibacterial Agents and Their Mixtures on the Freshwater Microalga Pseudokirchneriella Subcapitata. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2008, 27, 1201–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Pleiter, M.; Gonzalo, S.; Rodea-Palomares, I.; Leganés, F.; Rosal, R.; Boltes, K.; Marco, E.; Fernández-Piñas, F. Toxicity of Five Antibiotics and Their Mixtures towards Photosynthetic Aquatic Organisms: Implications for Environmental Risk Assessment. Water Res. 2013, 47, 2050–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odinga, E.S.; Chen, X.; Mbao, E.O.; Waigi, M.G.; Gudda, F.O.; Zhou, X.; Ling, W.; Czech, B.; Oleszczuk, P.; Abdalmegeed, D.; et al. Estrogens and Xenoestrogen Residues in Manure-Based Fertilizers and Their Potential Ecological Risks. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 344, 118609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brar, B.S.; Singh, J.; Singh, G.; Kaur, G. Effects of Long Term Application of Inorganic and Organic Fertilizers on Soil Organic Carbon and Physical Properties in Maize-Wheat Rotation. Agronomy 2015, 5, 220–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Yang, L.; Chen, L.; Xiang, Q.; Li, S.; Sun, L.; Yu, X.; Fang, L. Soil Contamination with Antibiotics in a Typical Peri-Urban Area in Eastern China: Seasonal Variation, Risk Assessment, and Microbial Responses. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 79, 200–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.Q.; Yuan, L.; Li, Z.H.; Zhang, H.C.; Sheng, G.P. Tetracycline Exposure Shifted Microbial Communities and Enriched Antibiotic Resistance Genes in the Aerobic Granular Sludge. Environ. Int. 2019, 130, 104902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.M.; Cheng, H. Overcoming China’s Animal Waste Disposal Challenge Brought by Elevated Levels of Veterinary Antimicrobial Residues and Antimicrobial Resistance. Environ. Int. 2024, 191, 109009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohring, S.A.I.; Strzysch, I.; Fernandes, M.R.; Kiffmeyer, T.K.; Tuerk, J.; Hamscher, G. Degradation and Elimination of Various Sulfonamides during Anaerobic Fermentation: A Promising Step on the Way to Sustainable Pharmacy? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 2569–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.B.; Zakaria, M.P.; Latif, P.A.; Saari, N. Degradation of Veterinary Antibiotics and Hormone during Broiler Manure Composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 131, 476–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arikan, O.A.; Sikora, L.J.; Mulbry, W.; Khan, S.U.; Foster, G.D. Composting Rapidly Reduces Levels of Extractable Oxytetracycline in Manure from Therapeutically Treated Beef Calves. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvam, A.; Zhao, Z.; Wong, J.W.C. Composting of Swine Manure Spiked with Sulfadiazine, Chlortetracycline and Ciprofloxacin. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 126, 412–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Cheng, H. Use of Veterinary Antimicrobials in China and Efforts on Improving Their Rational Use. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2015, 3, 144–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Cheng, H. Health Risk from Veterinary Antimicrobial Use in China’s Food Animal Production and Its Reduction. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 219, 993–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Cheng, H.; Tao, S. Environmental and Human Health Challenges of Industrial Livestock and Poultry Farming in China and Their Mitigation. Environ. Int. 2017, 107, 111–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).