Improving Wheat Yield, Fertilizer Use Efficiency, and Economic Benefits Through Farmer-Participation Nutrient Management
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
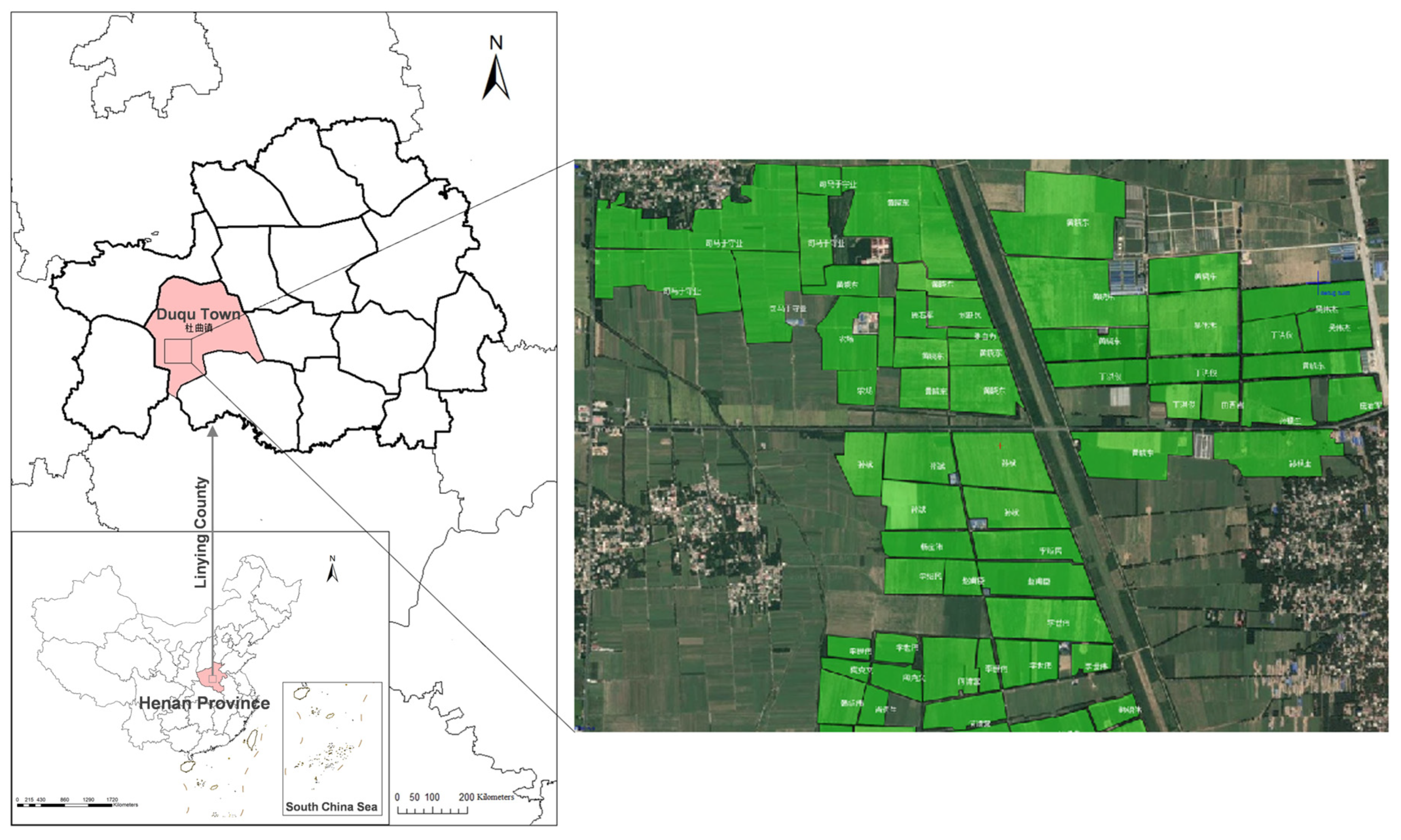
2.1. Experimental Site and Design
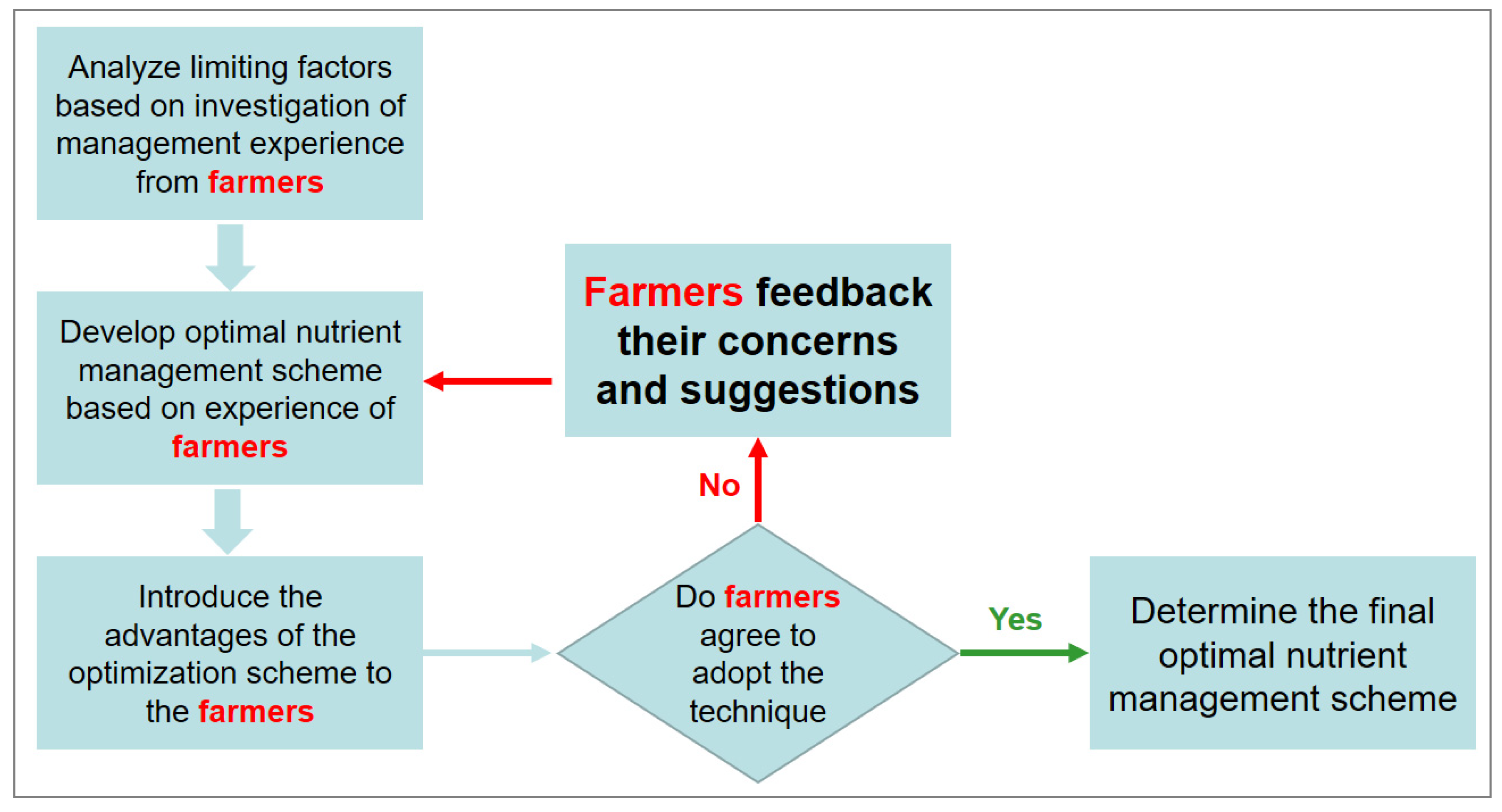
2.2. Data Collection and Measurement
2.3. Data Processing
3. Results
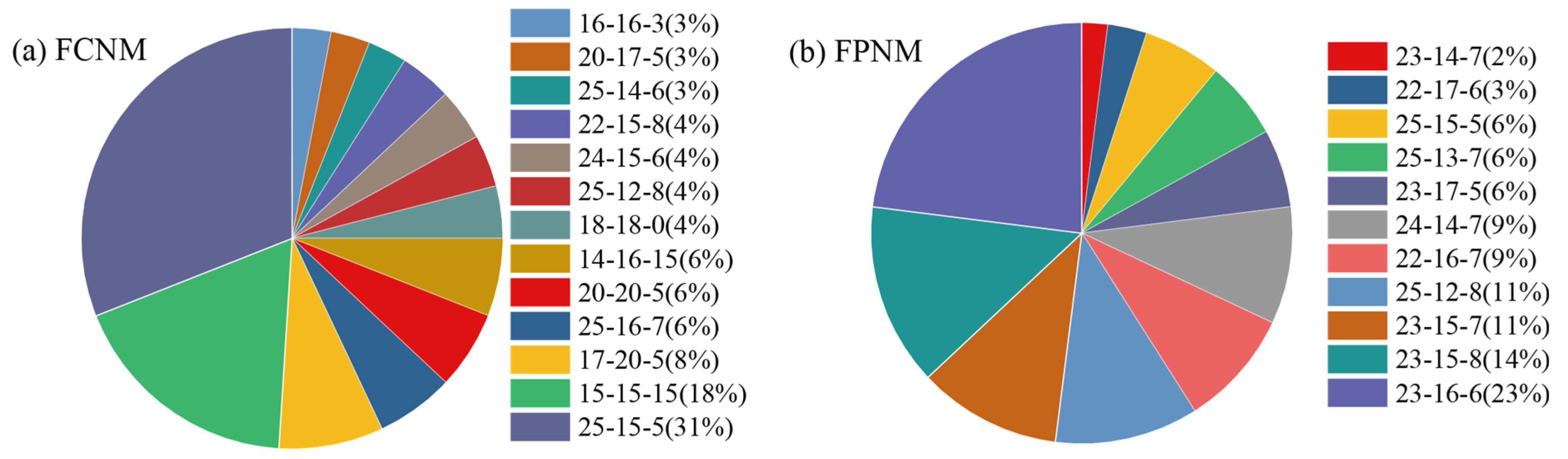
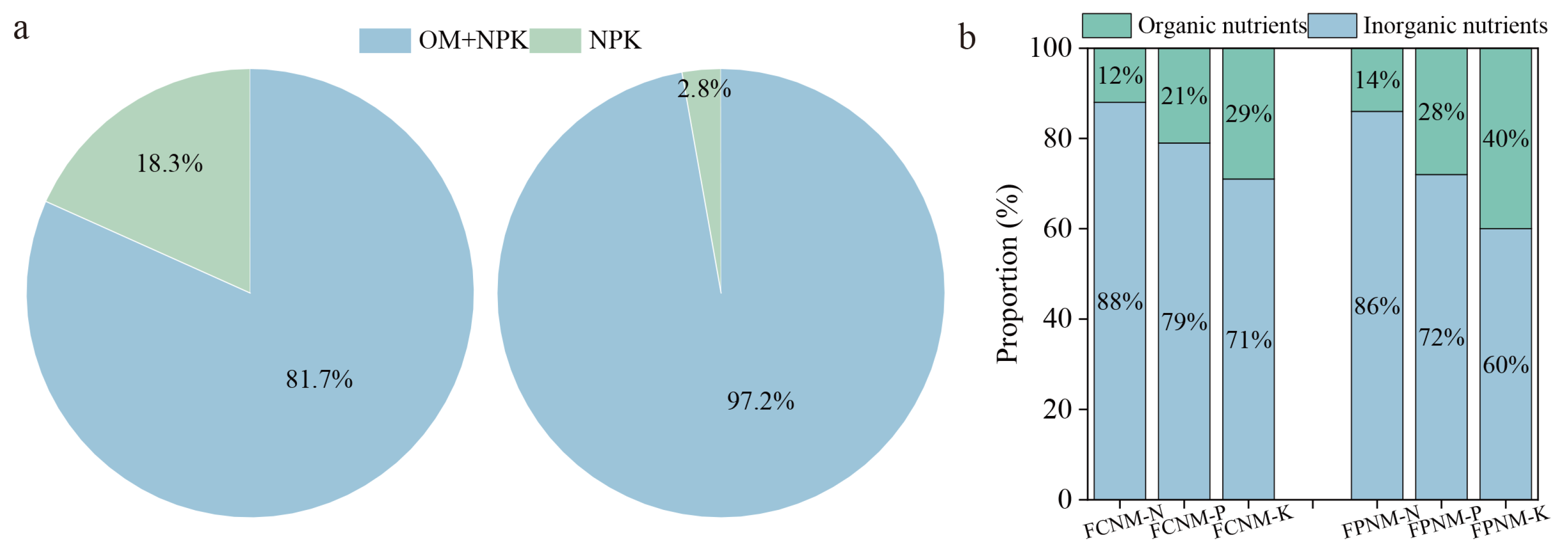
3.1. Fertilizer Formulations
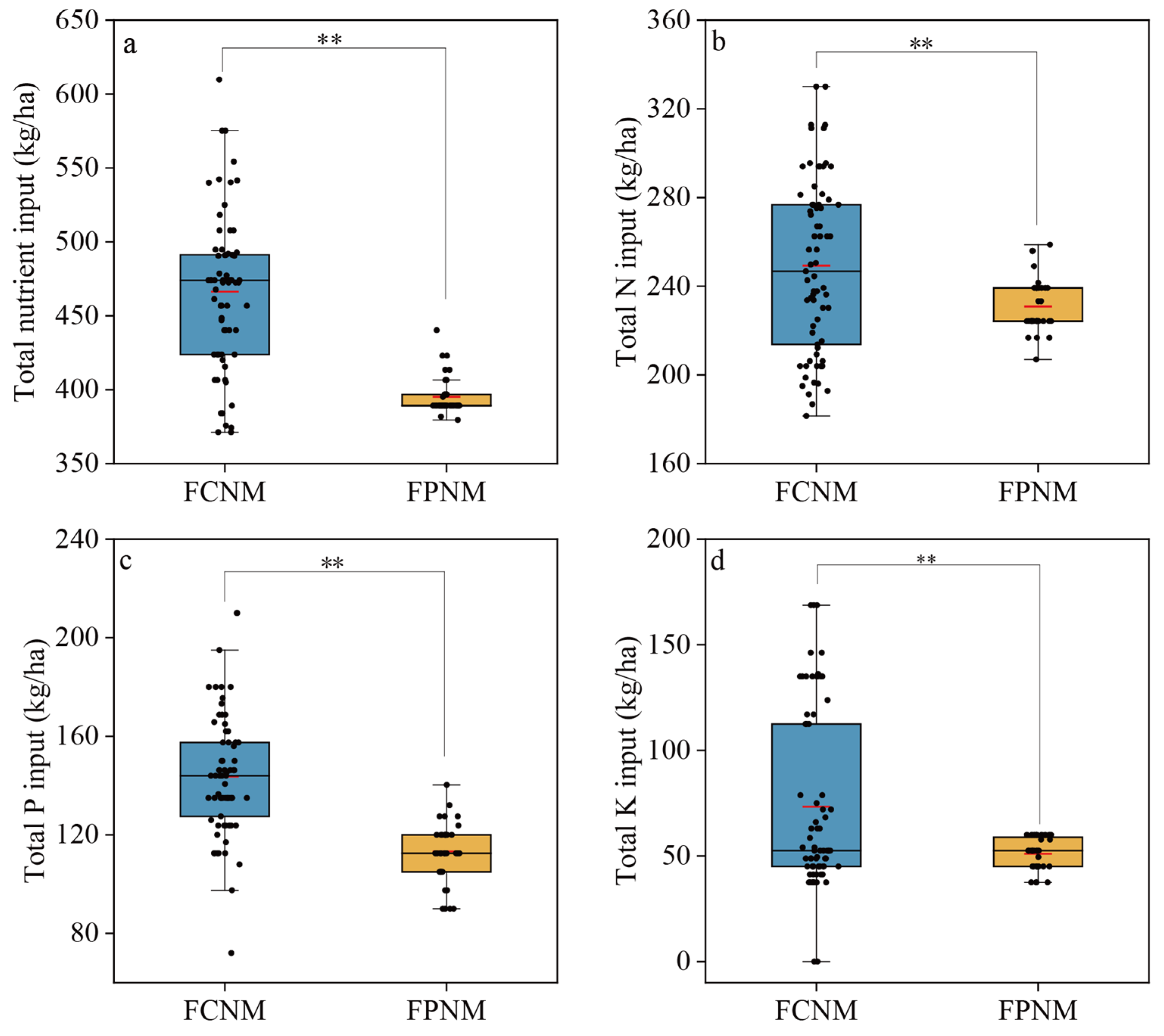
3.2. Nutrient Inputs from Chemical Fertilizer
3.3. Organic Fertilizer Application
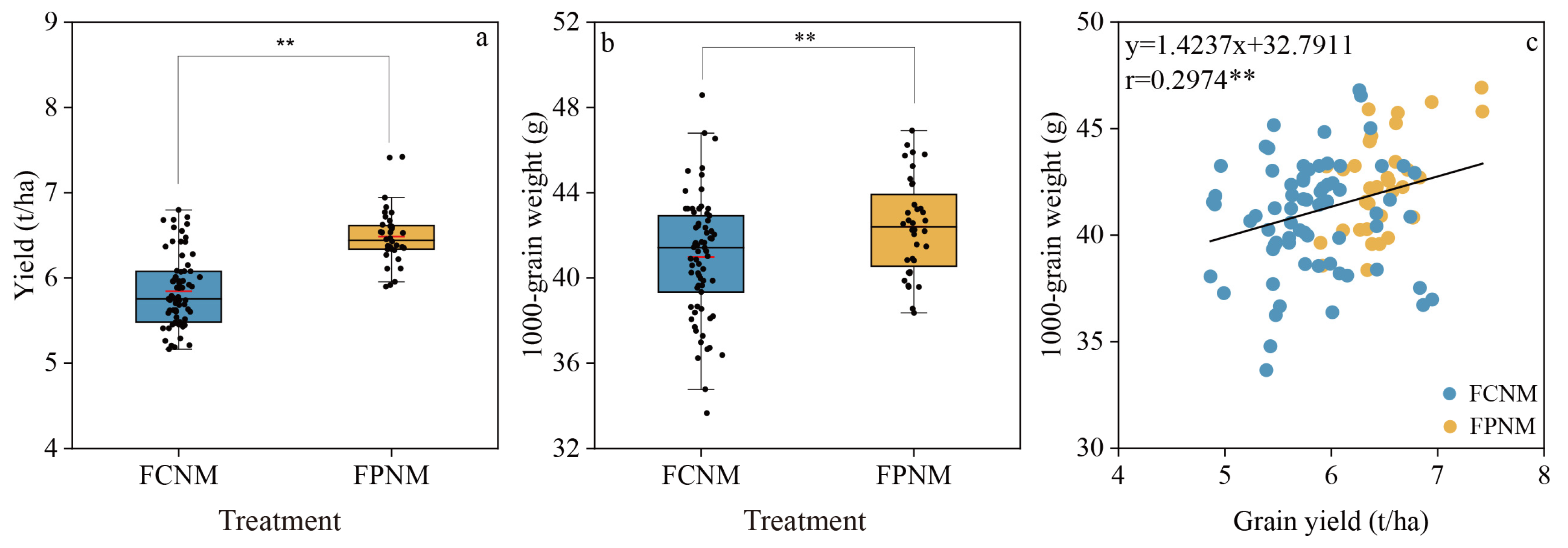
3.4. Wheat Grain Yield
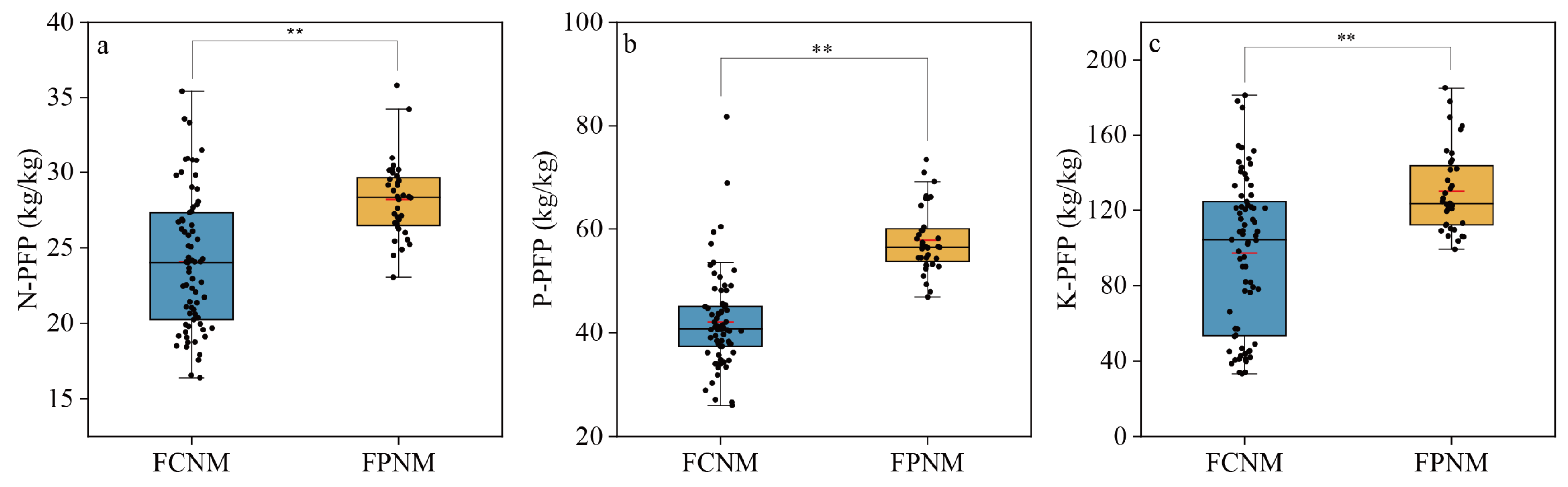
3.5. PFPN, PFPP, and PFPK
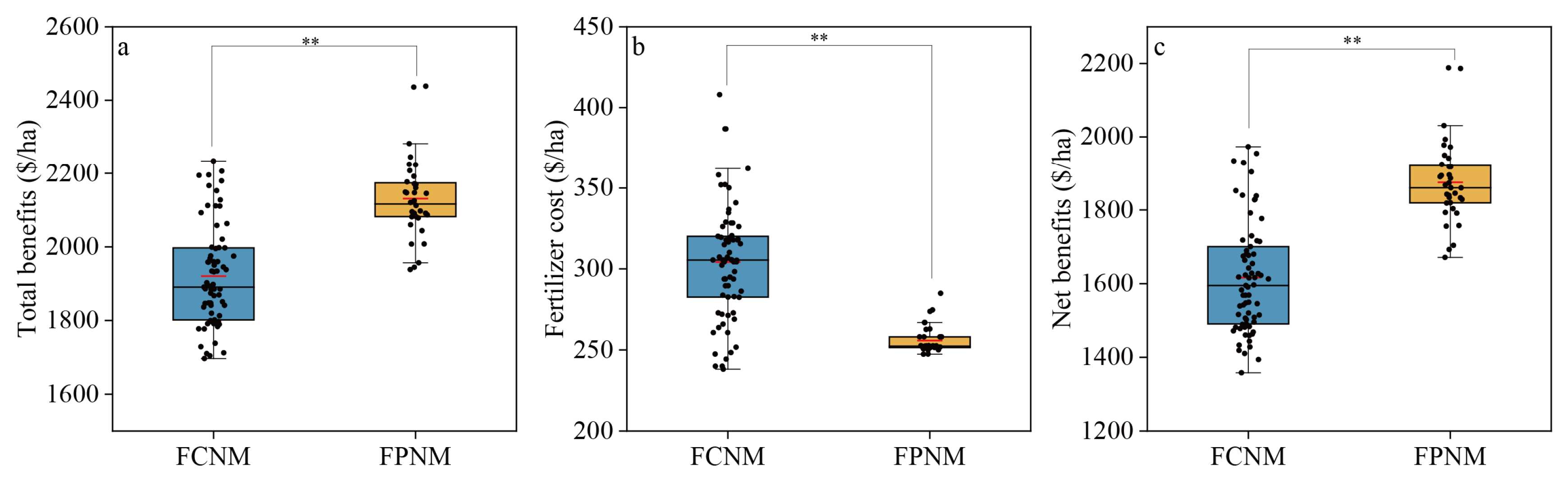
3.6. Economic Benefits
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tilman, D.; Balzer, C.; Hill, J.; Befort, B.L. Global food demand and the sustainable intensification of agriculture. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 50, 20260–20264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, N.D.; Gerber, J.S.; Johnston, M.; Ray, D.K.; Ramankutty, N.; Foley, J.A. Closing yield gaps through nutrient and water management. Nature 2012, 7419, 254–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Cui, Z.; Fan, M.; Vitousek, P.; Zhao, M.; Ma, W.; Wang, Z.L.; Zhang, W.J.; Yan, X.Y.; Yang, J.C.; et al. Producing more grain with lower environmental costs. Nature 2014, 7523, 486–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Hou, P.; Gao, Q.; Tan, Q.; Jiang, D.; Dai, T.; Tian, Z. Optimizing nitrogen fertilizer and straw management promote root extension and nitrogen uptake to improve grain yield and nitrogen use efficiency of winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2024, 70, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Bureau of Statistics of the People’s Republic of China. China Statistical Yearbook; Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2021.
- Yan, L.; Wang, Y.Y.; Tumbalam, P.; Zhang, T.L.; Gao, Q.; Zhang, W.J.; Wei, D.M.; Yaa, O.K. Spatiotemporal distribution of chemical fertilizer application and manure application potential in China. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2019, 10, 1337–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhu, T.; Xin, L. Effectiveness of agricultural technology services on fertilizer reduction in wheat production in China. Sustainability 2025, 17, 2840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejigu, D.; Pushpalatha, R.; Jayaprakash, S.K.; Gangadharan, B.; Himanshu, S.K.; Gopakumar, S. Integrated fertilizers for sustainable wheat production to improve food security—A comprehensive review. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2025, 188, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanyaolu, M.; Sadowski, A. The role of precision agriculture technologies in enhancing sustainable agriculture. Sustainability 2024, 16, 6668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheoran, S.; Prakash, D.; Yadav, P.K.; Siddiqui, M.H.; Alamri, S.; Gupta, R.K. Grain quality, wheat productivity and microbial properties in sandy loam soil under pearl millet-wheat sequence: Long-term effects of organic manure and fertilizer N application. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2025, 71, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Ortega, J.; Álvaro-Fuentes, J.; Cantero-Martínez, C. The use of double-cropping in combination with no-tillage and optimized nitrogen fertilization reduces soil N2O emissions under irrigation. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 857, 159458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamopoulos, T.; Restuccia, D. The size distribution of farms and international productivity differences. Am. Econ. Rev. 2014, 6, 1667–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, X.T.; Gu, B.J.; Wu, Y.Y.; Galloway, J.N. Reducing China’s fertilizer use by increasing farm size. Glob. Environ. Change 2016, 41, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.L.; Zhang, H.Y.; Chen, X.P.; Zhang, C.C.; Ma, W.Q.; Huang, C.D.; Zhang, W.F.; Mi, G.H.; Miao, Y.X.; Li, X.L.; et al. Pursuing sustainable productivity with millions of smallholder farmers. Nature 2018, 7696, 363–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.J. Current situations and prospects of smart agriculture. J. South China Agric. Univ. 2021, 6, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Lei, Y.D.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Liu, J.G.; Shi, X.Y.; Jia, H.; Wang, C.; Chen, F.; Chu, Q.Q. Rational trade-offs between yield increase and fertilizer inputs are essential for sustainable intensification: A case study in wheat-maize cropping systems in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 679, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.F.; Cao, G.X.; Li, X.L.; Zhang, H.Y.; Wang, C.; Liu, Q.Q.; Chen, X.P.; Cui, Z.L.; Shen, J.B.; Jiang, R.F.; et al. Closing yield gaps in China by empowering smallholder farmers. Nature 2016, 7622, 671–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.J.; Wu, Q.H.; Zhao, Y.N.; Ye, Y.L.; Huang, Y.F. Effects of different formula fertilizers on population dynamics, stress resistance and grain yield of winter wheat. Soil Fertil. Sci. China 2021, 3, 300–307. [Google Scholar]
- An, Z.; Yang, Y.; Yang, X.; Ma, W.; Li, Y.; Chen, G.; Zhang, W.; Zhuang, M.; Wang, C.; Zhang, F. Promoting sustainable smallholder farming via multistakeholder collaboration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2319519121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.Q.; He, H.X.; Wang, J.; Li, M.; Guan, Q.C.; Hao, J.M. A study on the arable land demand for food security in China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, X.Q.; He, G.; Cui, Z.L.; Shen, J.B.; Zhang, F.S. Agri-environment policy for grain production in China: Toward sustainable intensification. China Agric. Econ. Rev. 2018, 1, 78–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, G.X. Study on the Restricting Factors and Countermeasures for Sustainable Intensified Grain Production Technology Application in Smallholder Farming System. Ph.D. Dissertation, China Agricultural University, Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Mirosavljević, M.; Mikić, S.; Špika, A.K.; Župunski, V.; Zhou, R.; Abdelhakim, L.; Ottosen, C.O. The effect of heat stress on some main spike traits in 12 wheat cultivars at anthesis and mid-grain filling stage. Plant Soil Environ. 2021, 2, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Hu, Y.; Liang, B.; Chen, G.; Feng, L.; Pu, T.; Sun, X.; Yong, T.; Liu, W.; Liu, J.; et al. Coordination of density and nitrogen fertilization improves stalk lodging resistance of strip-intercropped maize with soybeans by affecting stalk quality traits. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, G.; Wang, Z. Organic fertilizer application in wheat production of China: History, bottleneck, and strategy. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2025, 1, 12–31. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, H. Research on the Impact of Land Fragmentation, off Farm Labor Supply on Land Transfer. Ph.D. Dissertation, Nanjing Agricultural University, Nanjing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Faruque, A.S.; Huang, Z.H.; Karimanzira, T.T.P. Investigating key factors influencing farming decisions based on soil testing and fertilizer recommendation facilities (STFRF)—A case study on rural Bangladesh. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.Z.; Luo, X.F. Farming experience and farmers’ adoption of low-carbon management practices: The case of soil testing and fertilizer recommendations in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 5, 6755–6765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, S.; He, X.; Huang, Y.; Ye, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Yan, J. Reduction in nitrogen rate and improvement of nitrogen use efficiency without loss of peanut yield by regional mean optimal rate of chemical fertilizer based on a multi-site field experiment in the North China Plain. Plants 2023, 12, 1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerf, M.; Jeuffroy, M.H.; Prost, L.; Meynard, J.M. Participatory design of agricultural decision support tools: Taking account of the use situations. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2012, 4, 899–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ren, Z.; Zhang, H.; Li, H.; Wu, Q.; Huang, Y.; Ye, Y.; Zhao, Y. Improving Wheat Yield, Fertilizer Use Efficiency, and Economic Benefits Through Farmer-Participation Nutrient Management. Sustainability 2025, 17, 3481. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17083481
Ren Z, Zhang H, Li H, Wu Q, Huang Y, Ye Y, Zhao Y. Improving Wheat Yield, Fertilizer Use Efficiency, and Economic Benefits Through Farmer-Participation Nutrient Management. Sustainability. 2025; 17(8):3481. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17083481
Chicago/Turabian StyleRen, Zhijie, Hui Zhang, Hongjie Li, Qinghui Wu, Yufang Huang, Youliang Ye, and Yanan Zhao. 2025. "Improving Wheat Yield, Fertilizer Use Efficiency, and Economic Benefits Through Farmer-Participation Nutrient Management" Sustainability 17, no. 8: 3481. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17083481
APA StyleRen, Z., Zhang, H., Li, H., Wu, Q., Huang, Y., Ye, Y., & Zhao, Y. (2025). Improving Wheat Yield, Fertilizer Use Efficiency, and Economic Benefits Through Farmer-Participation Nutrient Management. Sustainability, 17(8), 3481. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17083481






