Comprehensive Risk Assessment of Smart Energy Information Security: An Enhanced MCDM-Based Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Information Security Risks in Smart Energy Systems
2.2. Application of MCDM Methods in Smart Energy Information Security Risk Assessment
3. Methodology
4. Case Study
4.1. Implementation of the Methodology
| Objective | Secondary Indicator | Tertiary Indicator | Indicator Quantification | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Smart Energy Information Security Risk | Environmental Risk | Climate Change Risk | Severe, Moderate, Mild | [37] |
| Resource Supply Stability | Strong, Moderate, Weak | [38] | ||
| Environmental Pollution Pressure | Severe, Moderate, Mild | [39] | ||
| Policy and Regulatory Intensity | Severe, Moderate, Mild | [40] | ||
| Legal Protection for Information Security | Severe, Moderate, Mild | [41] | ||
| Information Security Management System | Severe, Moderate, Mild | [42] | ||
| Information Security Standards | Available, In Progress, None | [43] | ||
| Technical Risk | Infrastructure Completeness | (Normal Operating Time/Total Operating Time) × 100% | [44] | |
| Critical Facility Redundancy | (Backup Equipment/Total Critical Equipment) × 100% | [45] | ||
| Energy Information Transmission Stability | (Lost Data Packets/Total Sent Data Packets) × 100% | [46] | ||
| Fault Response Capability | Average Fault Recovery Time (MTTR): The average time from fault occurrence to recovery | [47] | ||
| Data Encryption Strength | (Encrypted Data/Total Data) × 100% | [48] | ||
| Unauthorized Access Detection Rate | (Successfully Detected Unauthorized Access/Actual Unauthorized Access) × 100% | [49] | ||
| System Vulnerability Management | (Fixed Vulnerabilities/Total Found Vulnerabilities) × 100% | [50] | ||
| Network Attack Defense Capability | (Successfully Blocked Attacks/Total Attacks) × 100% | [51] | ||
| Economic Risk | Initial Investment Deviation | [(Actual Initial Investment−Budgeted Initial Investment)/Budgeted Initial Investment] × 100% | [52] | |
| Operational Cost Growth Rate | [(Current Operational Cost−Previous Operational Cost)/Previous Operational Cost] × 100% | [53] | ||
| Technology Update Cost Share | (Technology Update Cost/Total Cost) × 100% | [54] | ||
| Unit Energy Production Cost | Total Production Cost/Total Energy Output | [55] | ||
| Energy Price Volatility | [(Current Energy Price−Previous Energy Price)/Previous Energy Price] × 100% | [56] | ||
| Market Demand Growth Rate | [(Current Market Demand−Previous Market Demand)/Previous Market Demand] × 100% | [53] | ||
| Investment Return Period | Total Investment/Average Annual Net Profit | [57] | ||
| Revenue Volatility | [(Current Revenue−Previous Revenue)/Previous Revenue] × 100% | [58] | ||
| Management Risk | Information Security Responsibility Implementation | Strong, Moderate, Weak | [59] | |
| Security Training Coverage Rate | (Actual Participants/Required Participants) × 100% | [60] | ||
| Emergency Plan Drill Frequency | Annual Drills/Planned Drills | [61] | ||
| Timeliness of Security Incident Response | (Incidents Responded to within the Specified Time/Total Incidents) × 100% | [62] | ||
| Operations and Maintenance Compliance Rate | (Compliant Operations/Total Operations) × 100% | [63] | ||
| Outsourced Security Management Capability | Strong, Moderate, Weak | [64] |
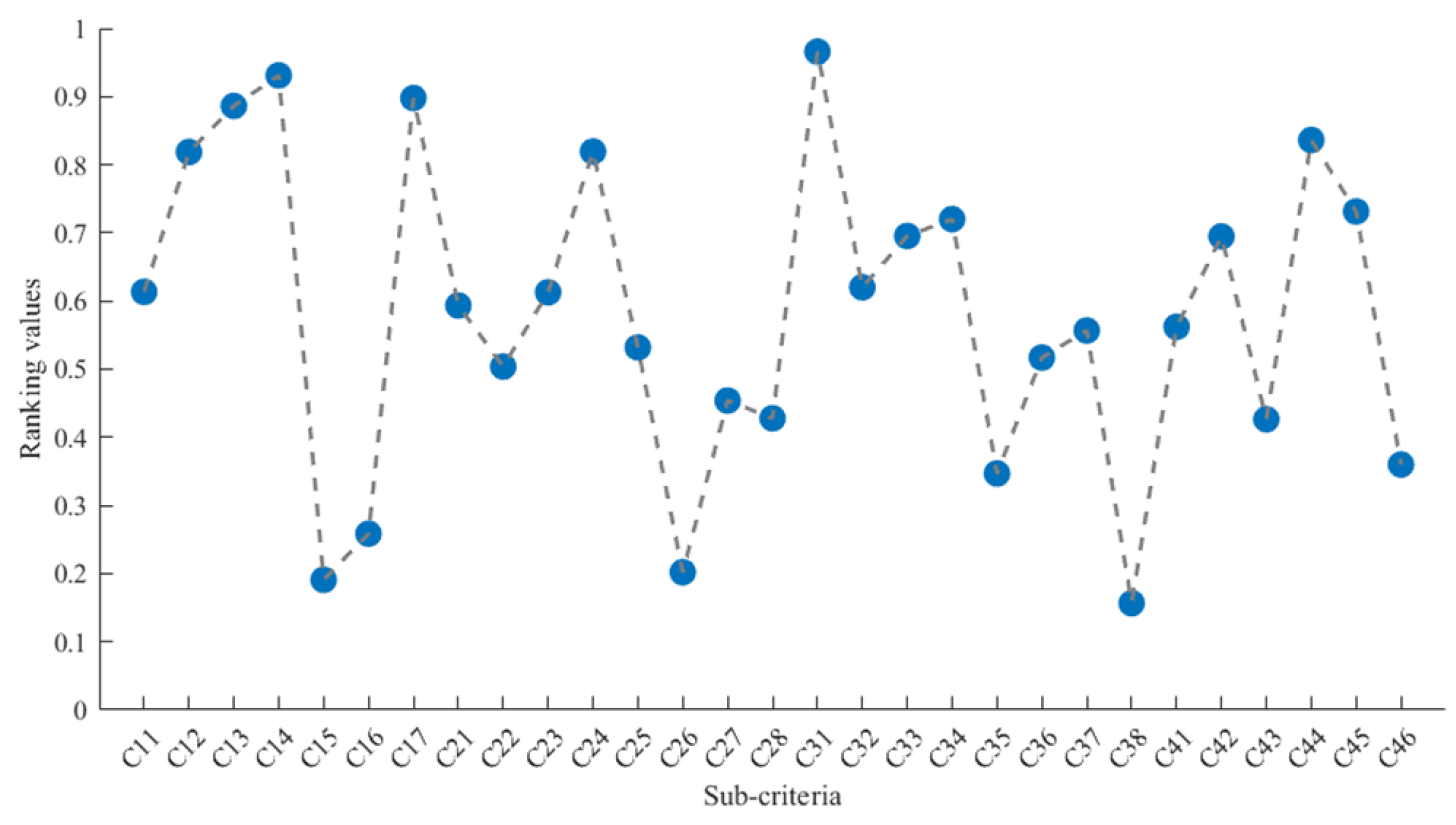
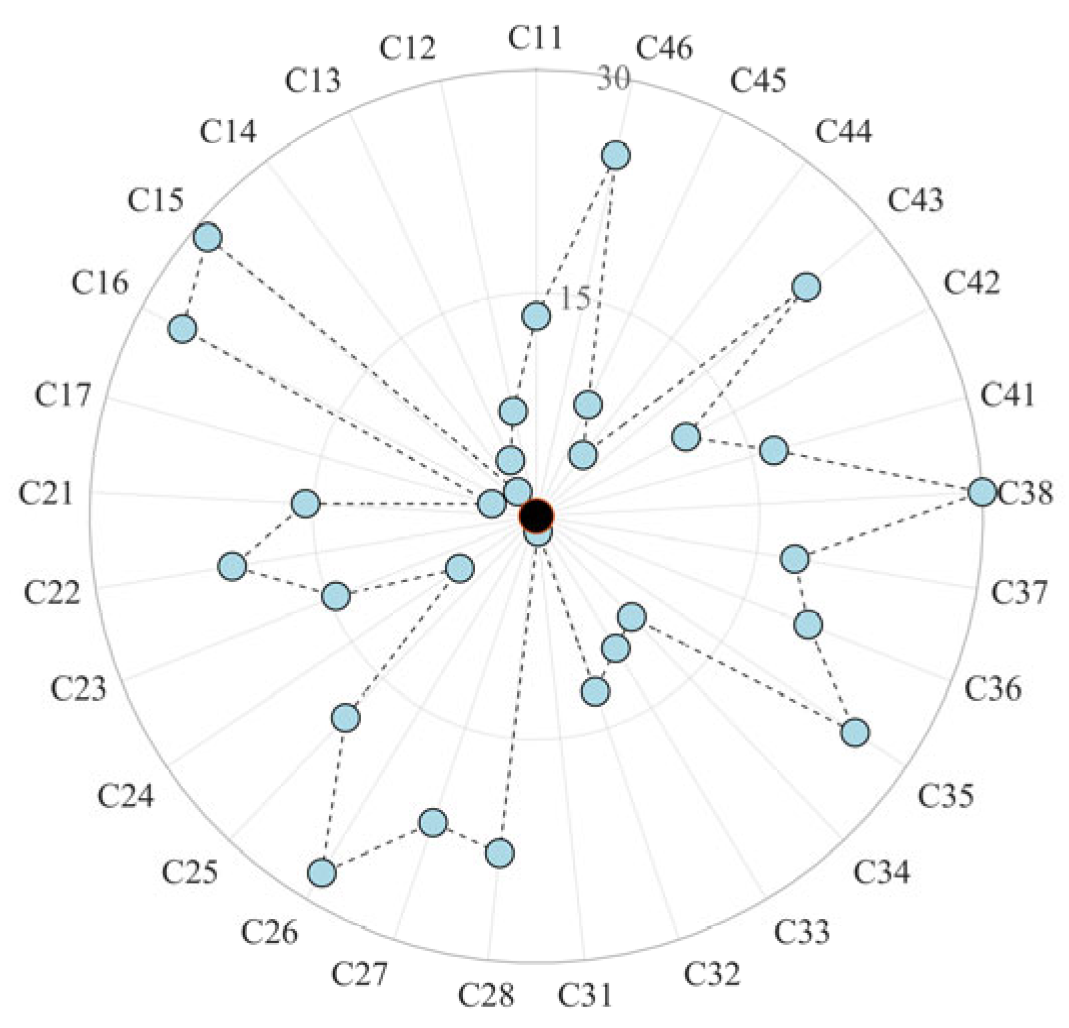
4.2. Evaluation Results
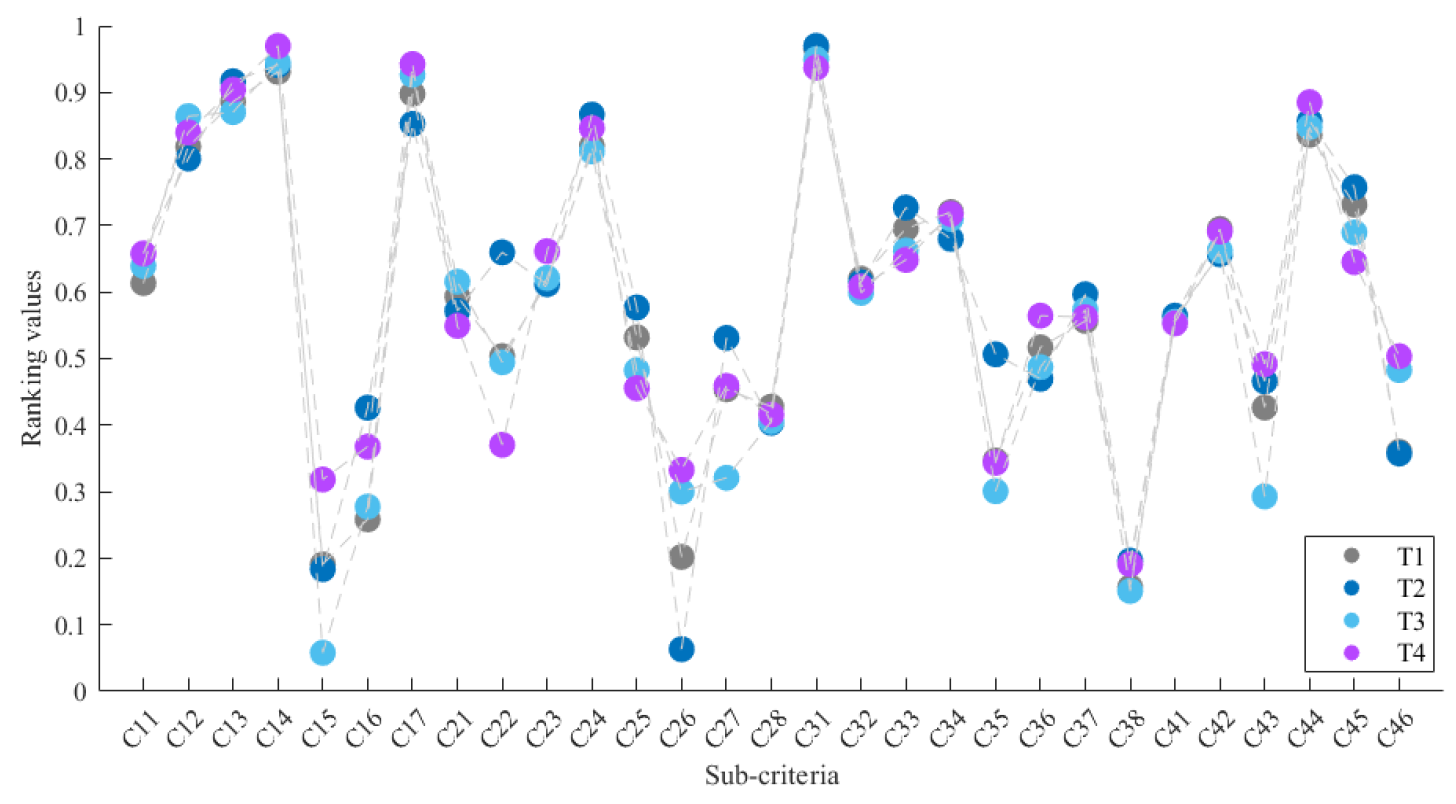
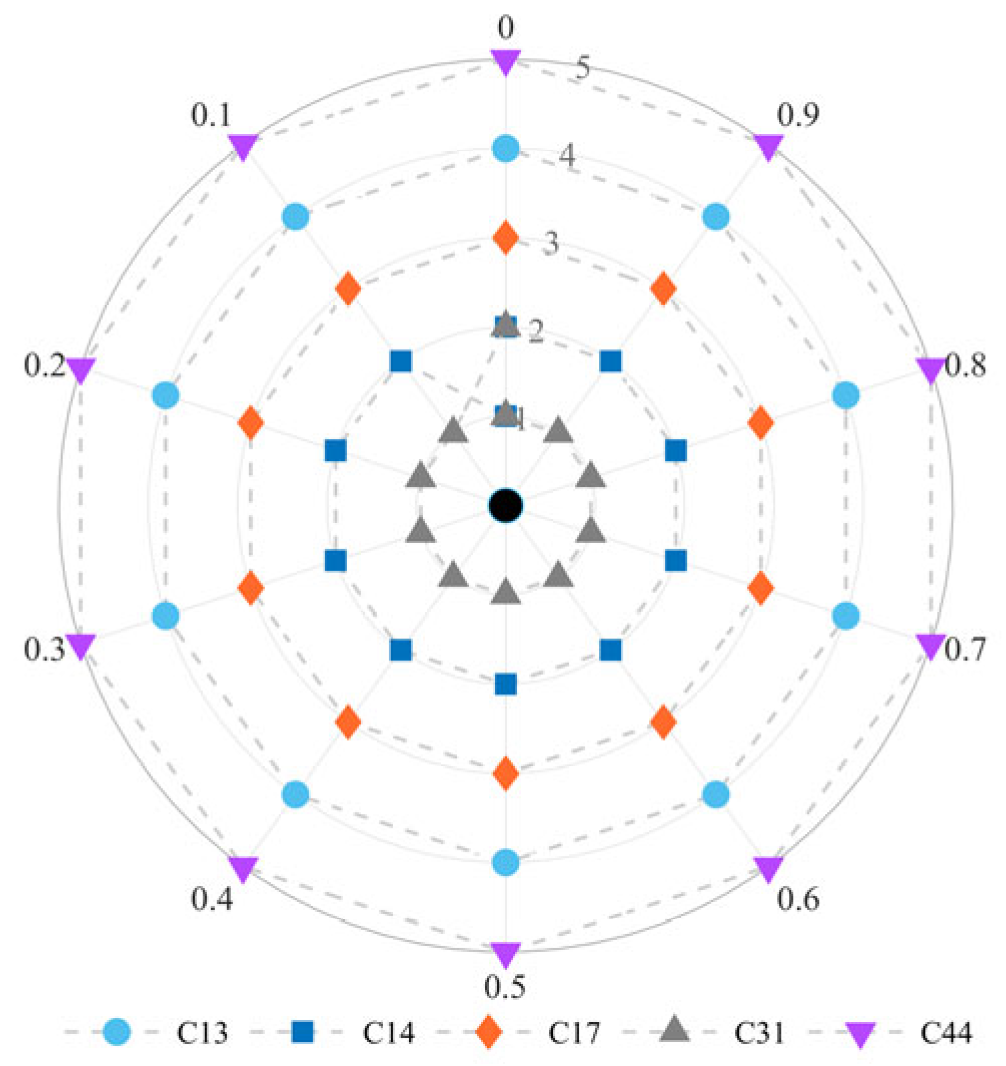
4.3. Sensitivity Analysis
5. Discussion and Conclusions
5.1. Discussion
5.2. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix A.1
Appendix A.2
References
- APERC, A. Quest for Energy Security in the 21st Century: Resources and Constraints; Asia Pacific Energy Research Centre: Tokyo, Japan, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Usman, A.; Naqvi, S.M.M.A.; Ozturk, I.; Hassan, A.; Arif, A. ICT-driven urbanization and energy security risk: Empirical evidence from Group 7 and Emerging 7 economies. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2025, 112, 107809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.J.; Zhang, N.; Mao, Y.H.; Chen, J.Y.; Tian, X.T.; Zhong, W. A review of the transformation from urban centralized heating system to integrated energy system in smart city. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2024, 240, 122272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Yang, W.; Liu, Z.; Kang, J.; Niyato, D.; Lam, K.-Y.; Du, H. Understanding Security in Smart City Domains from the ANT-Centric Perspective. IEEE Internet Things J. 2023, 10, 11199–11223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodell, J.W.; Corbet, S. Commodity market exposure to energy-firm distress: Evidence from the Colonial Pipeline ransomware attack. Financ. Res. Lett. 2023, 51, 103329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volue. Volue Releases Postmortem Report on Cyberattack. Available online: https://www.volue.com/news/volue-releases-postmortem-report-cyberattack (accessed on 23 June 2021).
- Gordon, A. What to Know About the Hacker Group That Shut Down 70% of Iran’s Gas Stations. TIME 2023. Available online: https://time.com/6548680/iran-hacker-gas-station-cyberattack-israel/ (accessed on 18 December 2023).
- Janta, P.; Leeraphun, N.; Thapmanee, K.; Niyomna, P.; Sintuya, H.; Setthapun, W.; Maneechot, P.; Sriprapakhan, P.; Chollacoop, N.; Silva, K. Energy resilience assessment: Incorporating consideration of recoverability and adaptability in risk assessment of energy infrastructure. Energy Sustain. Dev. 2024, 81, 101506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Xue, X.; Xi, S.; Xin, W. Balancing Possibilist-probabilistic risk assessment for smart energy hubs: Enabling secure peer-to-peer energy sharing with CCUS technology and cyber-security. Energy 2024, 304, 132102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvaneh, F.; Hammad, A. Application of Multi-Criteria Decision-Making (MCDM) to Select the Most Sustainable Power-Generating Technology. Sustainability 2024, 16, 3287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanif, M.Z.; Yaqoob, N. Prioritized Decision Support System for Cybersecurity Selection Based on Extended Symmetrical Linear Diophantine Fuzzy Hamacher Aggregation Operators. Symmetry 2025, 17, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, N.N.; Thokchom, S.; Srivastava, G.; Jhaveri, R.H.; Roy, D.S. Demcrp-et: Decentralized multi-criteria ranked prosumers energy trading using distributed ledger technology. Peer-to-Peer Netw. Appl. 2024, 17, 549–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, G.; Deng, J.; Ren, S.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, J.; Duan, X.; Zhang, L. Effect of oxygen deficient conditions on oxidative spontaneous combustion characteristics of raw coal and water-immersed air-dried bituminous coal. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2025, 196, 106859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.-S.; Zheng, X.-J. Enhancing smart city assessment: An advanced MCDM approach for urban performance evaluation. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2025, 118, 105930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraj, R.; Kuthadi, V.M.; Baskar, S. Smart building energy management and monitoring system based on artificial intelligence in smart city. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2023, 56, 103090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, S.; Rahman, M.A. A Comprehensive Survey on Enabling Techniques in Secure and Resilient Smart Grids. Electronics 2024, 13, 2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsecularatne, B.; Rodrigo, N.; Chang, R. Digital Twins for Reducing Energy Consumption in Buildings: A Review. Sustainability 2024, 16, 9275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awan, K.A.; Din, I.U.; Almogren, A.; Rodrigues, J.J.P.C. Quantum-Assisted Intelligent Decision Support Systems for Trustworthy Renewable Energy Management in Consumer Devices. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2024, 70, 4665–4672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatziamanetoglou, D.; Rantos, K. Blockchain-Based Security Configuration Management for ICT Systems. Electronics 2023, 12, 1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.-L.; Chen, Y.-C.; Yang, Y.-P. The Development and Issues of Energy-ICT: A Review of Literature with Economic and Managerial Viewpoints. Energies 2022, 15, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaqat, M.; Adnan, M.; Ahmad, M.; Iqbal, M.S.; Ahmad, F.; Din, S.U. Hybrid Multi-Criteria Decision Framework for Prosumers Energy Storage Systems in Smart Grids. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 188046–188071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhakami, W. Computational Study of Security Risk Evaluation in Energy Management and Control Systems Based on a Fuzzy MCDM Method. Processes 2023, 11, 1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, F.; Ma, Y.; You, I.; Zhang, H. Smart Collaborative Evolvement for Virtual Group Creation in Customized Industrial IoT. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2023, 10, 2514–2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Wang, D.; Xu, B.; Zhang, F.; Ling, X. An improved Interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy MCGDM for the evaluation of agricultural products live-streaming e-commerce platform. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2023, 45, 9591–9604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.H.; Li, X.Y.; Su, C.; Wang, X.P.; Yuan, X.F. Analysis of dynamic strategies for decision-making on retrofitting carbon capture, utilization, and storage technology in coal-fired power plants. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2025, 264, 125371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foggo, B.; Yamashita, K.; Yu, N. pmuBAGE: The Benchmarking Assortment of Generated PMU Data for Power System Events. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2024, 39, 3485–3496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.; Deng, J.; Li, X.Y.; Cheng, F.M.; Huang, W.H.; Wang, C.P.; He, W.B.; Wang, X.P. Research on the Game Strategy of Mutual Safety Risk Prevention and Control of Industrial Park Enterprises under Blockchain Technology. Systems 2024, 12, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Dai, X.; Zhou, L.; Yang, W. Multi-criteria constrained interval type-2 fuzzy decision-making: A space analysis perspective. Inf. Sci. 2024, 669, 120581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilic, B.; Gulgen, F.; Celen, M. Comparative Evaluation of Multi-Criteria Decision Making Methods for River Hydromorphology Assessment: Case Study of the Saz-Çayırova Basin, Türkiye. In River Research and Applications; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Orazbayev, B.; Ospanov, Y.; Makhatova, V.; Salybek, L.; Abdugulova, Z.; Kulmagambetova, Z.; Suleimenova, S.; Orazbayeva, K. Methods of Fuzzy Multi-Criteria Decision Making for Controlling the Operating Modes of the Stabilization Column of the Primary Oil-Refining Unit. Mathematics 2023, 11, 2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yacheur, B.Y.; Ahmed, T.; Mosbah, M. Efficient DRL-Based Selection Strategy in Hybrid Vehicular Networks. IEEE Trans. Netw. Serv. Manag. 2023, 20, 2400–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Liu, H. Application of focus theory of choice in large scale multi-criteria group decision making. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2024, 46, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Niu, L.-l.; Chen, Q.; Li, M. Optimization models of consensus measurement and improvement processes with hesitant fuzzy linguistic evaluation information. Appl. Intell. 2023, 53, 29414–29432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Mao, J.; Xu, W. A Personalized Individual Semantic Extraction Model Based on Criterion for Adaptive Consensus Reaching Process Under Improved Basic Uncertain Linguistic Environment. Int. J. Inf. Technol. Decis. Mak. 2023, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahim, M.; Eldin, E.M.T.; Khan, S.; Ghamry, N.A.; Alanzi, A.M.; Khalifa, H.A.E.-W. Multi-criteria group decision-making based on dombi aggregation operators under p, q-quasirung orthopair fuzzy sets. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2024, 46, 53–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gölcük, I.; Durmaz, E.D.; Şahin, R. Interval type-2 fuzzy development of FUCOM and activity relationship charts along with MARCOS for facilities layout evaluation. Appl. Soft Comput. 2022, 128, 109414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulpiani, G.; Vetters, N. On the risks associated with transitioning to climate neutrality in Europe: A city perspective. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2023, 183, 113448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musleh, A.S.; Ahmed, J.; Ahmed, N.; Xu, H.; Chen, G.; Kerr, S.; Jha, S. Experimental Cybersecurity Evaluation of Distributed Solar Inverters: Vulnerabilities and Impacts on the Australian Grid. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2024, 15, 5139–5150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minea, M.; Dumitrescu, C.M. Urban Traffic Noise Analysis Using UAV-Based Array of Microphones. Sensors 2023, 23, 1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun, J.S.; Park, C.J.; Park, G.-L.; Lee, J. Correlation Analysis between the Renewable Energy Source Generation and the Utilization for Smart Grid in Korea. Trans. Korean Inst. Electr. Eng. 2017, 66, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Dong, Y.; Sun, X. Can environmental regulations facilitate total-factor efficiencies in OECD countries? Energy-saving target VS emission-reduction target. Int. J. Green. Energy 2023, 20, 1488–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirmer, P.A.; Mporas, I. On the non-intrusive extraction of residents’ privacy- and security-sensitive information from energy smart meters. Neural Comput. Appl. 2023, 35, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rekeraho, A.; Cotfas, D.T.; Cotfas, P.A.; Tuyishime, E.; Balan, T.C.; Acheampong, R. Enhancing Security for IoT-Based Smart Renewable Energy Remote Monitoring Systems. Electronics 2024, 13, 756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caiping, W.; Xiadan, D.; Jun, D.; Zujin, B.; Weile, C.; Yin, D.; Gaoyang, Q. Characteristics of antioxidant temperature-sensitive hydrogel inhibiting coal spontaneous combustion. Fuel 2025, 394, 135089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, A.; Qiao, Z.; Li, X.; Lyu, J.; Li, X. A review on methods and applications of artificial intelligence on Fault Detection and Diagnosis in nuclear power plants. Prog. Nucl. Energy 2024, 177, 105474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamble, T.; Ghuge, M.; Jain, R.; Bodade, V.S. Secure data transmission in cloud computing using a cyber-security trust model with multi-risk protection scheme in smart IOT application. Clust. Comput. J. Netw. Softw. Tools Appl. 2025, 28, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Chen, S.; Liang, X.; Jin, X.; Du, Z. Next-generation generalist energy artificial intelligence for navigating smart energy. Cell Rep. Phys. Sci. 2024, 5, 102192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Shen, L.; Liu, Y.; Fang, X. Enhancing IoT security in smart grids with quantum-resistant hybrid encryption. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, W.; Din, I.U.; Almogren, A.; Khan, M.Y.; Altameem, A. PowerTrust: AI-Based Trustworthiness Assessment in the Internet of Grid Things. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 161884–161896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Xie, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, B. Resilient energy management strategy in smart residential buildings considering price attack: An aggregative game perspective. Energy Build. 2024, 320, 114593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Q.; Sun, W.; Li, X.; Jiang, S.; Tian, J. A new ensemble classification approach based on Rotation Forest and LightGBM. Neural Comput. Appl. 2023, 35, 11287–11308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.G.; Park, K.; Kim, H.J.; Cho, S.-H. Creating portfolios of firm-specific energy R&D investment under market uncertainty. Energy Environ. 2023, 34, 1548–1563. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, T.; Liu, J.; Feng, W.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Lou, S. A Three-Layer Scheduling Framework with Dynamic Peer-to-Peer Energy Trading for Multi-Regional Power Balance. Energies 2024, 17, 6239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alavi, S.A.; Javadipour, M.; Rahimian, A.; Mehran, K. A novel distributed privacy-preserving control and data collection method for IoT-centric microgrids. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2023, 17, 2249–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, B.S.; Qamar, A.; Wadood, A.; Almuhanna, K.; Al-Shamma, A.A. Integrating economic load dispatch information into the blockchain smart contracts based on the fractional-order swarming optimizer. Front. Energy Res. 2024, 12, 1350076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Ge, Y.; Jia, L. Double Robust Federated Digital Twin Modeling in Smart Grid. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 11, 39913–39931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, R.R.; Depra, M.C.; Severo, I.A.; Zepka, L.Q.; Jacob-Lopes, E. Smart override of the energy matrix in commercial microalgae facilities: A transition path to a low-carbon bioeconomy. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2022, 52, 102073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Ju, C.; Yang, G.; Chu, J. Multi-agent modeling for energy storage charging station scheduling strategies in the electricity market: A cooperative learning approach. J. Energy Storage 2025, 106, 114226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, A.M.; Gia, T.N.; Negash, B.; Anzanpour, A.; Azimi, I.; Jiang, M.; Liljeberg, P. Exploiting smart e-Health gateways at the edge of healthcare Internet-of-Things:A fog computing approach. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. Int. J. Escience 2018, 78, 641–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unnisa, N.; Tatineni, M.; Fatima, K.; Pasha, M.M. Intelligent deep learning-aided future beam and proactive handoff prediction model in Unmanned Aerial Vehicle-assisted anti-jamming Terahertz communication system. Int. J. Commun. Syst. 2023, 36, e5504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grudz, V.; Grudz, Y.; Pavlenko, I.; Liaposhchenko, O.; Ochowiak, M.; Pidluskiy, V.; Portechyn, O.; Iakymiv, M.; Wlodarczak, S.; Krupinska, A.; et al. Ensuring the Reliability of Gas Supply Systems by Optimizing the Overhaul Planning. Energies 2023, 16, 986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, H.; Qiu, J.; Fang, B.; Tian, Z. ThreatInsight: Innovating Early Threat Detection Through Threat-Intelligence-Driven Analysis and Attribution. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2024, 36, 9388–9402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.-K.; Shih, S.-G.; Perng, Y.-H. Competitive Advantage Evaluation Model of Sustainable Housing Design. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarma, R.; Moulik, S. e-SAFE: A secure and efficient access control scheme with attribute convergence and user revocation in fog enhanced IoT for E-Health. J. Inf. Secur. Appl. 2024, 85, 103859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindan, K.; Dua, R.; Mehbub Anwar, A.H.M.; Bansal, P. Enabling net-zero shipping: An expert review-based agenda for emerging techno-economic and policy research. Transp. Res. Part. E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2024, 192, 103753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulme, P.E.; Beggs, J.R.; Binny, R.N.; Bray, J.P.; Cogger, N.; Dhami, M.K.; Finlay-Smits, S.C.; French, N.P.; Grant, A.; Hewitt, C.L.; et al. Emerging advances in biosecurity to underpin human, animal, plant, and ecosystem health. iScience 2023, 26, 107462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litvinenko, V. Advances in Raw Material Industries for Sustainable Development Goals. In Proceedings of the XII Russian-German Raw Materials Conference, Saint-Petersburg, Russia, 27–29 November 2019; Taylor & Francis: Oxfordshire, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]




| Parameter | Value/Description |
|---|---|
| Expert Weight Calculation Parameter () | (weight coefficient balancing expert experience and domain influence in Equation (1)) |
| Parameters of IT2TrFN Membership Functions | Linguistic terms mapped to interval type-2 trapezoidal fuzzy numbers (IT2TrFN) with bounds calibrated via expert consensus |
| Consistency Threshold () | (re-calibration required if exceeded). |
| Sensitivity Analysis Range () | (step size 0.1) to test weight coefficient variations. |
| IT2FWA and IT2FGA Operators | IT2FWA: Weighted aggregated operator (Equation (8)); IT2FGA: Weighted geometric operator (Equation (16)) |
| Risk Level Thresholds | High (), Medium (), Low () |
| Linguistic Term | |
|---|---|
| Extremely High(EH) | |
| Very High(VH) | |
| High(H) | |
| Medium(M) | |
| Low(L) | |
| Very low(VL) | |
| Extremely low(EL) |
| Scenario | Description |
|---|---|
| Scenario 1 () | Different expert weights () |
| Scenario 2 () | Equal expert weights () |
| Scenario 3 () | Different expert weights () |
| Scenario 4 () | Equal expert weights () |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Du, P.; Li, T. Comprehensive Risk Assessment of Smart Energy Information Security: An Enhanced MCDM-Based Approach. Sustainability 2025, 17, 3417. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17083417
Li Z, Du P, Li T. Comprehensive Risk Assessment of Smart Energy Information Security: An Enhanced MCDM-Based Approach. Sustainability. 2025; 17(8):3417. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17083417
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Zhenyu, Pan Du, and Tiezhi Li. 2025. "Comprehensive Risk Assessment of Smart Energy Information Security: An Enhanced MCDM-Based Approach" Sustainability 17, no. 8: 3417. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17083417
APA StyleLi, Z., Du, P., & Li, T. (2025). Comprehensive Risk Assessment of Smart Energy Information Security: An Enhanced MCDM-Based Approach. Sustainability, 17(8), 3417. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17083417






