Abstract
The accurate identification of combustion status can effectively improve the efficiency of municipal solid waste incineration and reduce the risk of secondary pollution, which plays a key role in promoting the sustainable development of the waste treatment industry. Due to the low accuracy of the incinerator flame combustion state recognition in the current municipal solid waste incineration process, this paper proposes a Res-Transformer flame combustion state recognition model based on three feature enhancement strategies. In this paper, Res-Transformer is used as the backbone network of the model to effectively integrate local flame combustion features and global features. Firstly, an efficient multi-scale attention module is introduced into Resnet, which uses a multi-scale parallel sub-network to establish long and short dependencies. Then, a deformable multi-head attention module is designed in the Transformer layer, and the deformable self-attention is used to extract long-term feature dependencies. Finally, we design a context feature fusion module to efficiently aggregate the spatial information of the shallow network and the channel information of the deep network, and enhance the cross-layer features extracted by the network. In order to verify the effectiveness of the model proposed in this paper, comparative experiments and ablation experiments were conducted on the municipal solid waste incineration image dataset. The results showed that the Acc, Pre, Rec and F1 score indices of the model proposed in this paper were 96.16%, 96.15%, 96.07% and 96.11%, respectively. Experiments demonstrate the effectiveness and robustness of this method.
1. Introduction
With the global industrialization process and social and economic development, the amount of municipal solid waste (MSW) is increasing significantly [1,2]. This rapid growth has brought serious challenges to municipal solid waste treatment [3]. In this context, municipal solid waste incineration (MSWI) technology stands out as a widely adopted treatment method [4]. MSWI is an efficient waste treatment method. The core of the technology is to convert municipal solid waste into ash, flue gas and recoverable heat energy through a high-temperature combustion process [5]. This technology can not only greatly reduce the volume of waste, but also effectively control the generation of secondary pollution, and can also realize the reuse of resources [6]. The technological advantages of municipal solid waste incineration are reshaping the solid waste treatment industry: reduction has reduced the original mountain of garbage to less than one-tenth, significantly easing the garbage siege dilemma. Pollution control is like installing an “air purifier” in an incinerator, which reduces the generation of pollutants through intelligent adjustment of combustion status and effectively prevents dioxins from polluting soil and water [7]. Recycling is turning waste into treasure, converting heat generated by combustion into electric energy and processing waste residue into various building materials [8]. This virtuous cycle not only reduces the land pressure on landfill sites, but also transforms waste treatment plants into urban energy stations, and promotes the transformation and upgrading of solid waste treatment industry to a green and low-carbon direction, and promote its sustainable development [9]. In the process flow of MSWI, there are six stages, which are as follows: solid waste fermentation, solid waste incineration, waste heat exchange, steam generation, flue gas purification, and flue gas emission [10]. In the second stage, the solid waste incineration stage occupies a core position in the MSWI process, which is not only an effective way to reduce and recycle waste, but also its technical control directly affects the flue gas purification and emission quality [11]. Reasonable regulation of the incineration process can reduce the generation of harmful substances, ensure that environmental standards are met, and protect the environment and public health [12]. The essence of solid waste combustion is a thermochemical treatment process; its core lies in the oxidation reaction under high-temperature conditions, the combustible substances in solid waste into gaseous products (such as carbon dioxide, water vapor, nitrogen, etc.) and a small amount of solid residues (such as ash). This process not only realizes the volume reduction and harmless treatment of waste, but is also accompanied by the release and conversion of energy, which provides the basis for subsequent energy recovery and utilization [13].
Therefore, the reasonable regulation of the solid waste incineration process is particularly important. However, this process still faces multiple challenges. Among them, the instability of the combustion state is a particularly intractable problem, which directly leads to the difficulty of pollutant discharge meeting the established standards [14]. At the same time, the instability of the combustion process will also aggravate the accumulation of slag and ash in the furnace, and accelerate the high temperature corrosion of the metal heating surface. If the thermal imbalance is not alleviated by combustion regulation in time, it may further induce local detonation or thermal imbalance accidents. In view of this, it is particularly important to maintain the combustion stability during the incineration process [15], which is directly related to the efficiency and environmental effectiveness of the entire treatment process. However, the operation of many current MSWI facilities still relies on manual intuitive judgment of the flame burning state during solid waste incineration to adjust the control strategy. Although this method is practical to some extent, it is easily limited by personal experience, subjective judgment and insufficient intelligence level. As a result, the existing regulation mode cannot meet the efficiency threshold requirements of the optimal operation of the MSWI process. Therefore, exploring and constructing a combustion state recognition model that can not only adapt to the complex and variable environment of MSWI, but also have a high degree of robustness has become an important direction of current research. The construction of the model needs to meet two key requirements: one is to accurately identify the combustion state, and the other is to effectively guide the control strategy adjustment. These two aspects jointly ensure the efficient and stable operation of the municipal solid waste treatment process and the compliance of strict environmental emission standards.
The recognition of MSWI combustion states has seen increasingly widespread application of artificial intelligence technology in recent years. For instance, Duan et al. [16] innovatively combined the multi-scale analysis framework with machine learning to construct the MSWI combustion condition identification model. The technical implementation of the model includes a preprocessing module based on image restoration technology, a multi-resolution color moment feature extraction module and a random forest classification module integrated with a feature selection mechanism. The final system uses classification accuracy as the core evaluation index. However, the development of such models is constrained by the rarity of abnormal burning state samples and the costly labeling process; the acquisition of adequate abnormal burning state imagery presents significant difficulties. Therefore, Guo et al. [17] proposed a deep convolutional generation-based burning state adversarial Network (DCGAN) for abnormal image generation. Moreover, Ding et al. [18] firstly systematically expounds the typical MSWI process and summarizes the key control elements. Then, the technical characteristics and application progress of related control methods are summarized. Finally, the technical bottlenecks to be solved in the field of incineration process control are pointed out. Moreover, Pan et al. [19] combined the experience of industry experts and the research results in related fields to study the construction of the classification standard and benchmark database of the flame combustion state of waste disposal. The combustion classification criteria based on normal burning, partial burning, channeling burning and smoldering are expounded, and the flame combustion state image database for machine learning is constructed. Finally, based on various classical algorithms in the field of machine vision, the flame combustion image database is modeled and tested.
In addition, in other related fields, Guo et al. [20] proposed a method for recognizing the burning state of a waste incinerator based on image recognition technology, which realized the rapid judgment of the burning state in the furnace and connected the judgment results to the automatic control system, so as to improve the intelligent control level of the incinerator. In order to accurately identify the burning state of a rotary kiln, Wang et al. [21] proposed a recognition model based on lightweight network and knowledge distillation. On the basis of accurately identifying the burning state, the problem of large-scale network and large computing resources of the model was solved, so as to meet the requirements of real-time and low cost in actual production. In the field of working condition recognition methods of an electric fused magnesium furnace, Li et al. [22] proposed a working condition recognition method based on multi-modal information, which combined multi-modal information, Transformer and reinforcement learning, and introduced reinforcement learning into the working condition recognition of an electric fused magnesium furnace for the first time. At the same time, Li et al. [23] also proposed a working condition recognition method based on a deep convolutional random configuration network, which uses feature map visualization technology to adaptively adjust the number of convolution layers, thereby improving the recognition accuracy and interpretability of the model.
The above studies show that artificial intelligence techniques, especially deep learning-based methods, are able to show good performance in the existing MSWI burning state recognition due to their strong feature learning and expression capabilities. However, there are still some problems in the existing recognition methods. For example, the burning flames of MSWI images are diverse, the shapes are complex, the sizes are also very different, and the boundary with the background image is fuzzy, which leads to the model not being able to fully extract effective features for recognition. To address these challenges, this study proposes M3RTNet model, and uses three different feature enhancement strategies to improve the discriminative representation ability of the model for flame combustion characteristics, to better extract flame burning features. The main contributions are as follows: (1) This study uses the Res-Transformer structure as the backbone network, because the Resnet has strong local feature extraction ability, and the Transformer has great advantages in global feature extraction; through their combination, the local burning information and global information of the flame can be effectively extracted. (2) An efficient multi-scale attention module is introduced into the Resnet network, and a multi-scale parallel sub-network is used to establish the long and short dependence relationship to strengthen the recognition ability of the flame burning area, so as to improve the classification performance of the residual neural network. (3) A deformable multi-head attention module (DMAM) is designed in the Transformer layer, which uses deformable self-attention to extract long-term feature dependencies and enhance its global feature extraction ability. (4) A context feature fusion module (CFFM) is designed to efficiently aggregate the spatial information of the shallow network and the channel information of the deep network, and enhance the cross-layer features extracted by the network.
2. Materials and Methods
In order to systematically deconstruct the realization path of the flame state recognition algorithm for municipal solid waste incineration, this section systematically elaborates from two dimensions of experimental materials and methods: First, an analysis benchmark is established based on the data features of the flame combustion image, and then an innovative method system is proposed to integrate three feature enhancement strategies, including local semantic modeling based on a multi-scale attention residual network, global timing correlation based on a deformable multi-head attention Transformer and multi-modal interaction optimization based on a context feature fusion module. Finally, the end-to-end recognition of the combustion state is realized by a classifier.
2.1. Introduction of Flame Combustion Image
In the solid waste combustion stage, the combustion process can be subdivided into three stages, namely, drying, burning and embers. After solid waste enters the incinerator from the feed port, it first enters the drying stage. At this stage, the water in the waste is rapidly evaporated by the action of the high temperature furnace gas. With the removal of moisture, the waste gradually enters the combustion phase. At this stage, the combustible components in the waste react violently with the oxygen in the furnace, releasing a large amount of heat energy and generating flue gas and ash. This process is the key link of energy conversion in solid waste incineration, and it is also the stage with the highest temperature and the most intense reaction. Subsequently, the gas produced by combustion and some incompletely burned solid particles enter the embers stage. At this stage, the remaining combustible material continues to react with oxygen until it is completely burned out, forming the final flue gas. At the same time, ash and slag accumulate at the bottom of the furnace and are eventually discharged out of the furnace through the slag discharge system. In this study, combined with Pan et al.’s work in Ref. [19], the MSWI flame burning states are divided into four states: normal burning, partial burning, channeling burning and smoldering.
Figure 1 shows four typical flame burning states. Figure 1a shows normal burning. It can be seen that the burning line shows obvious linear geometric characteristics, and its high-brightness pixels form a continuous ribbon distribution in the combustion section area, showing remarkable smooth continuity and uniform radiation characteristics. Figure 1b shows partial burning. It can be seen that the burning line is curvilinear and runs through the burning area. The flame heights are scattered, bright but scattered. Figure 1c shows the channeling combustion, the combustion line is scattered distribution, and the flame is locally channeling. Figure 1d shows the braising. It can be seen that there is a large area of black block area caused by lack of fire inside the furnace.

Figure 1.
Typical flame burning states: (a) normal burning, (b) partial burning, (c) channeling burning, (d) smoldering.
2.2. Methods
In order to effectively use the global and local features in MSWI flame burning images and improve the model’s ability to characterize complex combustion conditions, so that it can accurately identify four different combustion states, an MSWI flame burning state recognition model is proposed based on three feature enhancement strategies, named M3RTNet. Figure 2 shows the overall structure of the model.
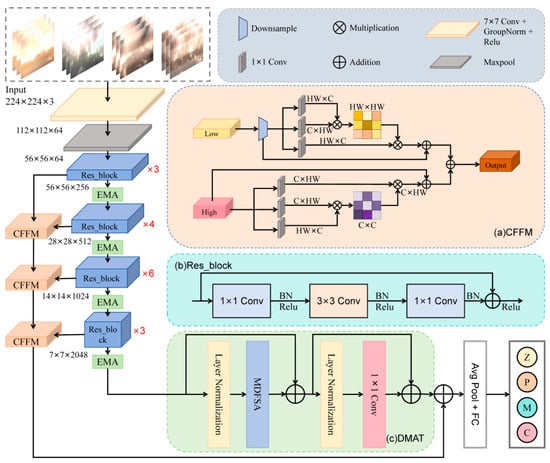
Figure 2.
The overall structure of the M3RTNet model.
M3RTNet is a model of an end-to-end architecture. It mainly contains four key components: a multi-scale attention residual network, a deformable multi-head attention Transformer (DMAT), three context feature fusion modules (CFFM) and a classifier.
Firstly, the flame burning image is input into the multi-scale attention residual network to initially extract the flame features. Subsequently, the feature map after extracting features from the first component is fed into the proposed DMAT module to establish a wide range of feature dependencies. Thus, the multi-head attention feature map is obtained. At the same time, features from each Resnet layer are extracted for context information fusion, to improve the classification performance of the model. Finally, the features obtained by the deformable multi-head attention Transformer and the context feature fusion modules are fused, and then input into the classification layer to realize the recognition of MSWI images. Each submodule of M3RTNet will be discussed in detail in the following subsections.
2.2.1. The Multi-Scale Attention Residual Network
The multi-scale attention residual feature extraction network is improved on the basis of Resnet50 [24], which is mainly composed of a Stem module, residual block (Res_block) and Efficient Multi-scale Attention (EMA) module. Firstly, the flame burning image is input into the Stem module, which adopts a cascade structure. Firstly, feature extraction is performed by 7 × 7 large kernel convolution, followed by group standardization processing, and then by Relu nonlinear activation and finally feature dimension reduction is achieved by the Max pooling operation. Then, three residual blocks are stacked repeatedly in Stage 1, four residual blocks in Stage 2, nine residual blocks in Stage 3 and six residual blocks in Stage 4. All residual blocks adopt the basic bottleneck residual block, as shown in Figure 2b. The residual block consists of 1 × 1 convolution, 3 × 3 convolution, batch normalization and Relu activation function, and the residual connection is used to effectively alleviate the gradient disappearance problem. On this basis, an efficient multi-scale attention module [25] is introduced after each stage, which makes the model focus on the burning area to extract more useful features in the flame burning image.
The architecture of the EMA module is illustrated in Figure 3. It uses the feature grouping strategy to process the input feature data in parallel, so as to accelerate the model training. At the same time, it integrates multi-scale parallel processing architecture and a cross-space interaction mechanism, which can simultaneously model local detail features and global temporal correlation.
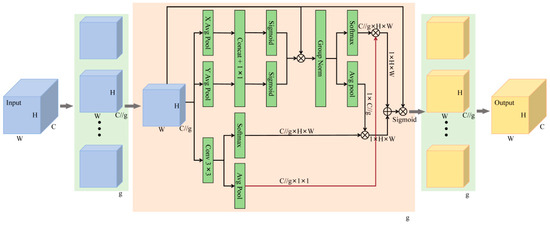
Figure 3.
The overall architecture of the EMA module.
As shown in Figure 3, this module uses a grouping processing strategy to decompose the input feature map into g parallel processing channels, and each channel performs feature transformation independently, thus letting each sub-feature group learn different semantics. The feature grouping method enables the model to allocate and process the model on more GPU resources. This grouping method not only strengthens the feature learning of semantic regions, but also compresses the noise. Then, the EMA module extracts feature attention weights through a three-way parallel architecture: it contains two 1 × 1 convolution branches for local feature encoding, and a 3 × 3 convolution branch responsible for capturing broader context information. The module adopts 1 × 1 convolution with bidirectional one-dimensional global pooling strategy, and realized the spatial dimension coding of channel information by performing feature compression along the height and width dimensions, respectively. The 3 × 3 branch captures the multi-scale feature representation. In this way, the EMA module achieves a dual optimization: on the one hand, the cross-channel correlation is modeled to dynamically calibrate the feature channel weights, and on the other hand, the fine-grained spatial structural features are encoded into the channel dimension through the spatial-channel interaction mechanism. In the specific implementation, the 1 × 1 convolution branch uses two-dimensional global feature compression to extract the spatial statistical features of the whole image, while the 3 × 3 convolution branch realizes dimensional alignment by the feature remodeling operation. Then, the matrix dot product is used to fuse the features of the two branches to generate the primary spatial attention feature map. Finally, through the Sigmoid gated fusion mechanism of dual-channel spatial attention weights, the pixel-level correlation modeling within the feature map group is realized, which effectively enhances the global context representation ability [26].
In summary, the EMA module is a parallel attention mechanism that is mainly used in computer vision tasks. Its main goal is to help the model capture the interaction between features at different scales and thus improve the performance of the model.
2.2.2. The Deformable Multi-Head Attention Transformer
The feature map extracted by the multi-scale attention residual network learns the local context details from the input image, but it does not contain the global context information. Therefore, a deformable multi-head attention Transformer [27] is introduced to capture local and global feature relationships within feature maps, establishing a unified representation of spatial-contextual dependencies. This ultimately helps the model to learn salient patterns from burning regions. The framework of this module is shown in Figure 2c, which consists of several main components, namely, layer normalization, deformable multi-head attention module, 1 × 1 convolution and residual connection. The purpose of introducing the deformable multi-head attention module is to use the self-attention of deformable convolutions to extract long-term feature dependencies, so as to obtain a refined feature map.
The deformable multi-head attention Transformer takes as input the feature maps generated in the backbone network and then uses the Layer Normalization mechanism to standardize the activation values of each channel, which effectively improves the stability of model training and accelerates the convergence process. Then, the normalized feature map is input into the deformable multi-head attention module to obtain the attention feature map. Moreover, the Residual Connection mechanism is introduced to significantly improve the gradient flow and information transfer efficiency of deep features between modules through the construction of cross-layer feature fusion paths. The residual connection is first utilized to integrate the input with the output. Subsequently, layer normalization and a 1 × 1 convolution are applied to refine the feature representation. Finally, the enhanced features are propagated through the residual pathway, generating the optimized final feature map.
Figure 4 illustrates the structure of the deformable multi-head attention module used in this study. In the solid waste incineration flame image, the burning area has a unique pattern of random spatial distribution. Therefore, extracting these features from different burning regions is extremely important for better recognition. Self-attention is a core component of the Version Transformer, which establishes a global feature correlation modeling framework, which can effectively capture long-range dependencies across regions, and realizes dynamic focus optimization of key regions through adaptive attention weight allocation. However, the traditional self-attention mechanism usually uses a fixed 1 × 1 convolution kernel for feature extraction, and this single-scale receptive field design limits the adaptability of the model to features at different spatial scales. Especially when dealing with multi-scale objects, the lack of ability to dynamically adjust the receptive field becomes the performance bottleneck. Therefore, a dynamic filtering method termed deformable convolution [28] is applied to the spatial dimension of SA, generating adaptive feature tensors through spatially-variant kernel transformations. The deformable convolution is able to intelligently adjust the sensing range according to the complexity of the input features that varies according to the scale of the burning region, and thus has the ability to adapt to geometric changes in the burning region. The deformable convolution gives the convolution window I = {(−1, −1), (−1, 0), …, (1, 1)} on the feature map adds an offset {Δdn|n = 1, …, D}, where D = |I|. Therefore, for each position d0 in the output feature map, DFConv is calculated as follows:
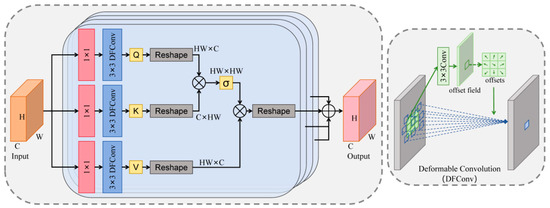
Figure 4.
The overall structure of the deformable multi-head attention module.
For the input feature map Fn in Figure 4, we first apply a convolution operation to it with a kernel size of 1 × 1, and then calculate its query, key and value by deformable convolution as follows:
Spatial reshaping is first performed, followed by the computation of feature vector similarity through matrix multiplication. Finally, the spatial attention feature map is synthesized by applying the activation function:
Furthermore, the spatial attention feature map is multiplied with V(Fn), and then the reshaping operation is performed again to obtain the attention feature map based on deformable convolution. To comprehensively explore spatial contextual information from the input feature maps, four empirically configured attention heads are employed. In the feature fusion stage, the system adopts the multi-branch feature aggregation strategy to perform element-by-element weighted fusion of the four feature maps processed by the deformable attention mechanism, and finally generates an enhanced attention feature map with multi-scale context information.
2.2.3. The Context Feature Fusion Module
The convolution operation in the residual network loses the underlying texture details while extracting features, so that the deep-layer features and shallow-layer features are distributed at both ends of the network. High-level features have stronger semantic information, but their resolution is low and their perception of details is poor. Shallow features have high resolution and contain more information such as location details, edges and textures, but they are low semantic and noisy due to inadequate feature extraction. In addition, the information concerned by different layers in the feature extraction network is also different, and using the features of different layers to fuse context information can improve the classification performance of the network. However, simple addition easily causes information redundancy and cannot make full use of the advantages of both. Therefore, this paper designs a context information fusion module to make up for the lack of deep semantic information with shallow semantic information, as shown in Figure 1a. The low-semantic information such as texture and shape of the shallow network is enhanced by spatial attention, and the high-semantic information of the deep network is enhanced by channel. The filtered channel and spatial information were added to efficiently fuse the context information of the shallow and deep layers of the image, so as to retain more useful information and improve the classification performance of the model.
For the low-level feature map of the original input, it is first downsampled to adjust its shape to be consistent with the high-level feature map. Then, it goes through three identical 1 × 1 convolution branches for feature mapping, whose original size is C × H × W, and then transposes them to map the 3D features into 2D features, and the shapes become HW × C, C × HW and HW × C, respectively. The first two branches are multiplied to obtain the spatial attention value, and then the third branch is multiplied to obtain the feature map filtered in the spatial dimension. Finally, the shape of the feature map is transposed to C × H × W.
For the high semantic feature map E, the same three 1 × 1 convolution branches were used for feature mapping, and then the transpose operation was performed to make their shapes into C × HW, C × HW and HW × C. The feature maps of the last two branches were multiplied to obtain the channel attention value, and then the filtered feature map in the channel dimension was obtained by multiplying it with the first branch. Finally, the feature map shape is transposed to C × H × W.
Finally, the feature maps filtered by high and low layers were added to obtain the feature result map.
2.2.4. The Classifier
In the classification layer, the feature maps derived from the deformable multi-head attention layer and the context feature fusion attention layer are additively fused, subsequently processed through the global average pooling layer, and ultimately fed into a two-node fully connected layer for burning state classification of the MSWI image.
3. Experiments and Results
In this chapter, a series of experiments are carried out to test the effectiveness of the algorithm. Firstly, based on the requirements of actual combustion identification, experimental equipment and schemes are prepared, evaluation criteria are formulated and flame image data used in this research are described in detail. Then, the verification was carried out in three steps: first, the overall performance of the algorithm was tested, and then the comparison experiment and the ablation experiment were carried out, respectively. Finally, the advantages of the proposed method in accuracy and practical application are proved.
3.1. Experimental Environment and Design
The experiments in this study used an Intel (R) Core (TM) i5-13400F processor 4.60 GHz CPU, Windows 11 (64-bit) operating system, pytorch2.1.0 framework and NVIDIA CUDA interface model for acceleration.
The network input image size is 224 × 224 × 3 pixels, and the selected optimization strategy is the Adam algorithm. The model was trained for 100 epochs using a batch size of 16, empirically configured to optimize memory utilization while maintaining gradient stability during backpropagation. No pre-trained models were used in any of the experiments, and each model was trained starting from an initial state.
3.2. Evaluation Metrics
Through the quantitative comparison of the experimental results of the classification model, the advantages and disadvantages of the classification model can be judged. The recognition efficacy of the proposed network model for MSWI burning state monitoring is quantitatively evaluated using accuracy (Acc), precision (Pre), recall (Rec) and F1 score as primary metrics, specifically selected for their complementary sensitivity to both false-positive and false-negative combustion patterns. The mathematical expression of the evaluation index is as follows:
In the equation, TP is the number of model predictions correctly labeled as positive, FP is the number of model predictions incorrectly labeled as positive, TN is the number of model predictions correctly labeled as negative and FN is the number of model predictions incorrectly labeled as negative.
3.3. Flame Burning Images Dataset
The dataset used in this experiment is the flame burning image dataset created by Pan et al. in Ref. [19], which is from an MSWI factory in Beijing. The dataset mainly divides the flame combustion state into four categories, namely, normal burning, partial burning, channeling burning and smoldering. The typical combustion images are shown in Figure 1. Inside the incinerator, the left and right sides are equipped with high-temperature-resistant cameras for capturing flame video. After collecting the flame video from the left and right cameras in the field, the first step was to remove the segments that did not describe the burning state clearly. Next, according to the burning state classification standard shown in Figure 1, the field operation experts of the municipal solid waste treatment plant screened the stable burning frames under typical working conditions, and marked the burning state of the remaining video clips. Then, the timing sampling algorithm developed based on the MATLAB 7.0 platform is used to complete the standardized processing process of the classified burning video data by setting a fixed time interval (1 frame/min) video key frame extraction mechanism. Through quantitative statistics, 3289 and 2685 effective image samples were obtained, respectively, under typical combustion conditions of the left and right grate, successfully covering the multi-dimensional flame characteristics of different combustion states. Due to the symmetrical distribution of the left and right grate images, in order to improve the generalization ability of the model in this paper, the left and right grate images are merged into a dataset for experiments, and the ratio of training set, validation set and test set is 0.7:0.15:0.15. The amount of data corresponding to each typical burning state is shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
The distribution of the flame burning image dataset.
3.4. Model Experimental Results
Figure 5 represents the loss and accuracy during model training. The left figure shows the loss plotted against epochs for the training and validation sets. It can be observed that both the training loss and the validation loss gradually decrease with the increase of epochs, which indicates that the performance of the model on both the training and validation sets is constantly improving. In particular, the loss decreases relatively fast in the first 20 epochs, after which the loss gradually levels off and the validation loss fluctuates up and down around the training loss.
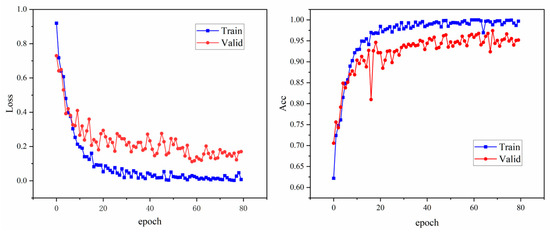
Figure 5.
The training process of M3RTNet.
The right figure shows the training and validation set accuracy plotted against epochs. It can be seen from the figure that both the training accuracy and the validation accuracy gradually increase with the increase of epochs and become stable after about 20 epochs. The training accuracy is always higher than the validation accuracy, which reflects that the model performs better on the training set than on the validation set, but the gap between the two is not large, indicating that the model does not significantly overfit.
The two figures reveal a significant optimization trend in model performance: loss function values show a continuous decline, while classification accuracy steadily improves, and it tends to be stable after a certain number of epochs, which achieves a good training effect, indicating that the model has effectively learned the features of the flame burning image.
3.5. Results of Ablation Experiments
In order to evaluate the effectiveness of the modules, each module is tested through different network models, as shown in Table 2, and eight experiments are conducted in turn based on the residual network in this experiment.

Table 2.
The results of ablation experiments.
Figure 6 shows the ablation experimental results of different network configurations in the flame burning state recognition task of the MSWI process, and the effectiveness of the proposed method is verified by comparing the training and validation accuracy. As can be seen from the left figure, the proposed method shows the characteristics of rapid convergence at the early stage of training, and the training accuracy is significantly higher than other configurations. It is also seen from the right figure that the proposed model architecture keeps the optimal performance on the validation set, and its classification accuracy is greatly improved compared with the benchmark model, which proves the key role of the three feature enhancement strategies proposed in this paper.
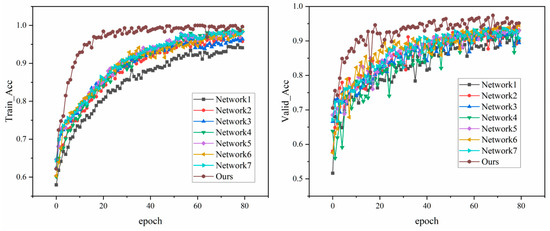
Figure 6.
Training and validation accuracy during ablation experiments.
Table 2 provides detailed experimental results for each model. Compared with Network1, the performance parameters of Network2 are improved after adding the EMA module, and the accuracy, precision, recall and F1 score of Network2 are increased by 0.93%, 1.2%, 0.55% and 0.88%, respectively, which proves the effectiveness of the EMA module. After adding the DMAT module, the accuracy, precision, recall and F1 score of Network3 are increased by 0.4%, 1.14%, 0.2% and 0.67%, respectively, which proves that the DMAT module can make the network have better extracted features. After adding the CFFM module to Network4, the accuracy rate is increased by 0.27%, the precision rate is increased by 0.57%, the recall rate is increased by 0.05% and the F1 score is increased by 0.31%. It is verified that the CFFM module can enhance the feature fusion of different stages and enhance the feature extraction ability of the model.
The evaluation indices of Network5, 6 and 7 with two modules are higher than those of Network2, 3 and 4 with only one module. The model with three modules has the best performance, and compared with the initial Network1 model, the accuracy of combustion state recognition in MSWI process is increased from 91.92% to 96.16%, the precision is increased from 91.45% to 96.15%, the recall is increased from 92.5% to 96.07% and the F1 score is increased from 91.97% to 96.11%. It can be concluded that the proposed model has the best performance and the best performance in MSWI combustion state recognition.
In addition, in order to investigate the difference between the labels predicted by different models for the classification of four types of samples and the real situation, this paper uses a confusion matrix to visualize the test results of ablation experiments, as shown in Figure 7. Through the comparison of the confusion matrix, it can be seen that the proposed model has a better classification effect and can realize the accurate identification of the MSWI burning state.
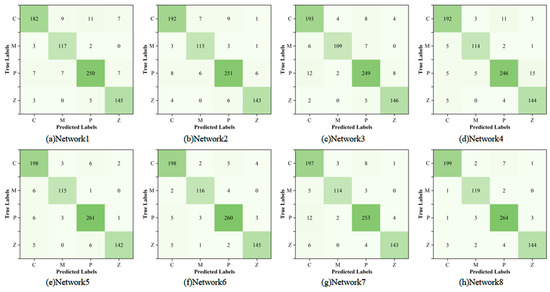
Figure 7.
The confusion matrix for ablation experiments.
3.6. Results of Comparative Experiment
In order to verify the recognition ability of the proposed model for an MSWI burning state, it is compared with the classical deep learning method in Table 3 on the same dataset. The comparison model selected in the experiment systematically covered the evolution path of the mainstream architecture: the classic convolutional network VGGNet strengthened the spatial feature extraction ability with the deep architecture of stacked 3 × 3 convolutions. MobileNet realized lightweight design through deep separable convolutions, and DenseNet innovatively used dense cross-layer connections to promote feature reuse. EfficientNet uses a composite scaling strategy to coordinate network depth, width and resolution optimization, RegNet deduces a hierarchical structure for hardware adaptation based on regular design and Vision Transformer is a breakthrough application of Transformer in the vision field. It relies on a global self-attention mechanism to model long-range dependencies. The experimental results are as follows:

Table 3.
The results of comparative experiments.
Figure 8 shows the performance of different models in the training process; the left figure shows the accuracy of each model on the training set, and the right figure shows the accuracy on the validation set. In conclusion, the proposed model not only performs well on the training set, but also has a strong generalization ability on the validation set. The specific experimental results are shown in Table 3.
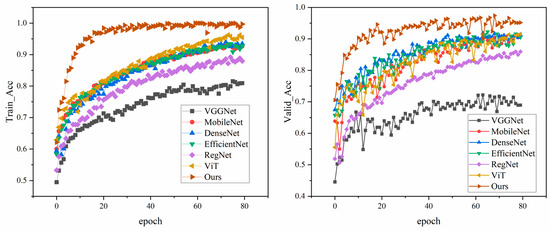
Figure 8.
Training and validation accuracy during comparative experiments.
The experimental results show that the accuracy rate, precision rate, recall rate and F1 score of the proposed model are 96.16%, 96.15%, 96.07% and 96.11%, respectively, which are better than other networks and have better classification performance. In this study, the confusion matrix is used to visualize the results of the test set of each model, and the results are shown in Figure 9. From the comparison of the confusion matrix, it can be seen that the recognition ability of the model proposed in this paper for MSWI states is more balanced and more effective than other classification networks.
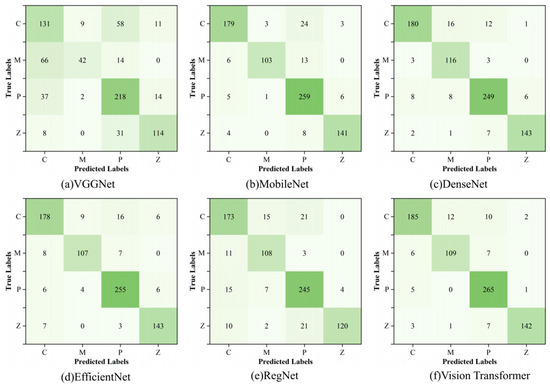
Figure 9.
The confusion matrix for comparative experiments.
4. Conclusions
In this study, an MSWI flame burning state recognition model is developed through three synergistic feature enhancement strategies, which integrate the EMA module, greatly enhance the model’s ability in multi-scale feature extraction and efficient attention allocation and effectively alleviate the limitations of traditional attention mechanisms in computational complexity and feature fusion. The DMAT module is used at the end of the network. The advantages of CNN and Transformer were combined to make the network fully extract the global features and local features of MSWI images, and the high-level semantic information was globally modeled to obtain the global features of high-level semantic information. The CFFM module is designed to fuse the spatial information such as texture and edge of the shallow network and the channel information of the deep network to further enhance the feature extraction ability of the network. The experimental results on the MSWI dataset show that the accuracy, precision, recall and F1 score of the proposed model are 96.16%, 96.15%, 96.07% and 96.11%, respectively, which proves that the model proposed in this study can accurately identify the flame burning state in the MSWI process. The model proposed in this study not only provides a high-precision solution for the intelligent identification of MSWI combustion states, but also provides key technical support for the sustainable development of industrial combustion processes by its multi-scale feature fusion idea. Through the collaborative mechanism of dynamic optimization of combustion efficiency and precise control of carbon emissions, the high-energy-consuming industries can realize the transformation of green production.
Author Contributions
Methodology, J.Z. and R.S.; Software, J.Z.; Validation, R.S.; Investigation, J.T.; Resources, J.Z. and J.T.; Data curation, J.T. and H.P.; Writing—original draft, J.Z. and R.S.; Writing—review & editing, J.Z. and J.T.; Visualization, H.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Due to project restrictions, data will not be provided to the public.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Li, M.; Li, S.; Chen, S.; Meng, Q.; Wang, Y.; Yang, W.; Shi, L.; Ding, F.; Zhu, J.; Ma, R.; et al. Measures for Controlling Gaseous Emissions During Composting: A Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 3587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.M.C.; Bodirsky, B.L.; Krueger, T.; Mishra, A.; Popp, A. The world’s growing municipal solid waste: Trends and impacts. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funari, V.; Dalconi, M.C.; Farnaud, S.; Nawab, J.; Gupta, N.; Yadav, K.K.; Kremser, K.; Toller, S. Modern management options for solid waste and by-products: Sustainable treatment and environmental benefits. Front. Environ. Sci. 2024, 12, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.S.; Mubeen, I.; Yu, C.M.; Zhu, G.J.; Khalid, A.; Yan, M. Waste to energy incineration technology: Recent development under climate change scenarios. Waste Manag. Res. 2022, 40, 1708–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasinski, S.; Debowski, M. Municipal Solid Waste as a Renewable Energy Source: Advances in Thermochemical Conversion Technologies and Environmental Impacts. Energies 2024, 17, 4704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Deng, J.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, W.Y.; Zhang, T.; Tian, C.; Ma, J.W.; Shao, Y.Y.; Yang, Y.F.; Shao, Y.Q. Utilization of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash with different pretreatments with gold tailings and coal fly ash for environmentally friendly geopolymers. Waste Manag. 2025, 194, 342–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, J.; Xie, B.; Wu, H.; Wu, S.; Fang, H. Boiler Flame Combustion State Identification Based on Multi-feature Fusion and WOA-SVM. China Spec. Equip. Saf. 2024, 40, 13–18+54. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Tang, D.; Zhang, S.; Wang, T. Overview of Combustion Status Monitoring Technology for Power Plant Boilers. China Spec. Equip. Saf. 2024, 40, 28–33. [Google Scholar]
- Borisova, M.A.; Ryshikova, M.V.; Gomazova, A.A. Municipal Solid Waste Management in China. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference “Management of Municipal Waste as an Important Factor of Sustainable Urban Development” (WASTE), Saint Petersburg, Russia, 4–6 October 2018; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 10–13. [Google Scholar]
- Gabbar, H.A.; Herra, E.V.; Galvan-Perez, D.; Cruz, J.E.E.; Aldeeb, M.A. Semiautomated Control System of Microwave Plasma Torch for Waste-to-Energy Treatment. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2024, 52, 5573–5580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Song, G.W.; Liu, J.Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, H.L.; Hao, Z.P. A comprehensive emission inventory of air pollutants from municipal solid waste incineration in China’s megacity, Beijing based on the field measurements. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 948, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, M.T.; Li, B.; Naqvi, M. Revolutionizing municipal solid waste management (MSWM) with machine learning as a clean resource: Opportunities, challenges and solutions. Fuel 2023, 348, 128548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.Q.; Bian, R.X.; Li, P.; Yin, C.Y.; Teng, X.; Zhang, J.R.; Gao, S.D.; Niu, Y.T.; Sun, Y.J.; Wang, Y.A.; et al. Analysis of carbon reduction potential from typical municipal solid waste incineration plants under MSW classification. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 373, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Lu, Y.; Wei, Q.; Xu, H. Research on Dynamic Modeling Method of Waste Incinerator Combustion Process. Proc. CSEE 2024, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Cao, Y.; Yang, S. Video Based Combustion State Identification for Municipal Solid Waste Incineration. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2020, 53, 13448–13453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Tang, J.; Qiao, J. Recognition of Combustion Condition in MSWI Process Based on Multi-Scale Color Moment Features and Random Forest. In Proceedings of the Chinese Automation Congress (CAC), Hangzhou, China, 22–24 November 2019; pp. 2542–2547. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.; Tang, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, D. A method for generating images of abnormal combustion state in MSWI process based on DCGAN. In Proceedings of the 2021 3rd International Conference on Industrial Artificial Intelligence (IAI), Shenyang, China, 8–11 November 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, H.; Tang, J.; Qiao, J. Control Methods of Municipal Solid Wastes Incineration Process: A Survey. In Proceedings of the 2021 40th Chinese Control Conference (CCC), Shanghai, China, 26–28 July 2021; pp. 662–667. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, X.; Tang, J.; Xia, H.; Tian, H.; Wang, T.; Xu, W. Construction of flame image classification criteria and reference database for municipal solid waste incineration process. In Proceedings of the 2023 35th Chinese Control and Decision Conference (CCDC), Yichang, China, 20–22 May 2023; pp. 343–348. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, T.; Yao, X.; He, D.; Liu, B. Diagnosis Method of Combustion State in Waste Incinerator Based on Image Recognition. Nonferrous Metall. Equip. 2022, 36, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Deng, Z.; Qin, B. Working condition recognition based on lightweight network and knowledge distillation for rotary kilns. J. Electron. Meas. Instrum. 2023, 37, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.T.; Gu, J.; Wang, D.; Wu, G.C. Research on intelligent recognition method of multi-modal information working condition in electric magnesium melting furnace. Control Theory Appl. 2024, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.T.; Tong, Q.Q.; Wang, D.; Wu, G.C. Research on Fused Magnesium Furnace Working Condition Recognition Method Based on Deep Convolutional Stochastic Configuration Networks. Acta Autom. Sin. 2024, 50, 527–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, D.; He, S.; Zhang, G.; Luo, M.; Guo, H.; Zhan, J.; Huang, Z. Efficient Multi-Scale Attention Module with Cross-Spatial Learning. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2023—2023 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Rhodes Island, Greece, 4–10 June 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Liew, J.H.; Zou, Y.; Zhou, D.; Feng, J. PANet: Few-Shot Image Semantic Segmentation with Prototype Alignment. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 9196–9205. [Google Scholar]
- Nayak, D.R. RDTNet: A residual deformable attention based transformer network for breast cancer classification. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 249, 123569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Qi, H.; Xiong, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, G.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y. Deformable Convolutional Networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 764–773. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, A.G.; Zhu, M.; Chen, B.; Kalenichenko, D.; Wang, W.; Weyand, T.; Andreetto, M.; Adam, H. MobileNets: Efficient Convolutional Neural Networks for Mobile Vision Applications. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.04861. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; Weinberger, K.Q. Densely Connected Convolutional Networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2261–2269. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, M.; Le, Q. Efficientnet: Rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Long Beach, CA, USA, 10–15 June 2019; pp. 6105–6114. [Google Scholar]
- Radosavovic, I.; Kosaraju, R.P.; Girshick, R.B.; He, K.; Dollár, P. Designing Network Design Spaces. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 10425–10433. [Google Scholar]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An Image is Worth 16x16 Words: Transformers for Image Recognition at Scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).