Sediment Chemistry and Ecological Risk Assessment in Andean Lakes of Central Ecuador: Influence of Trophic Status on Accumulation Patterns
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Location and Characteristics of the Study Area
2.2. Sampling
2.3. Samples Analysis
2.4. Data Analysis
2.4.1. Identification of Sources of Sedimentary Organic Matter
2.4.2. Ecological Risk Assessment Methodology
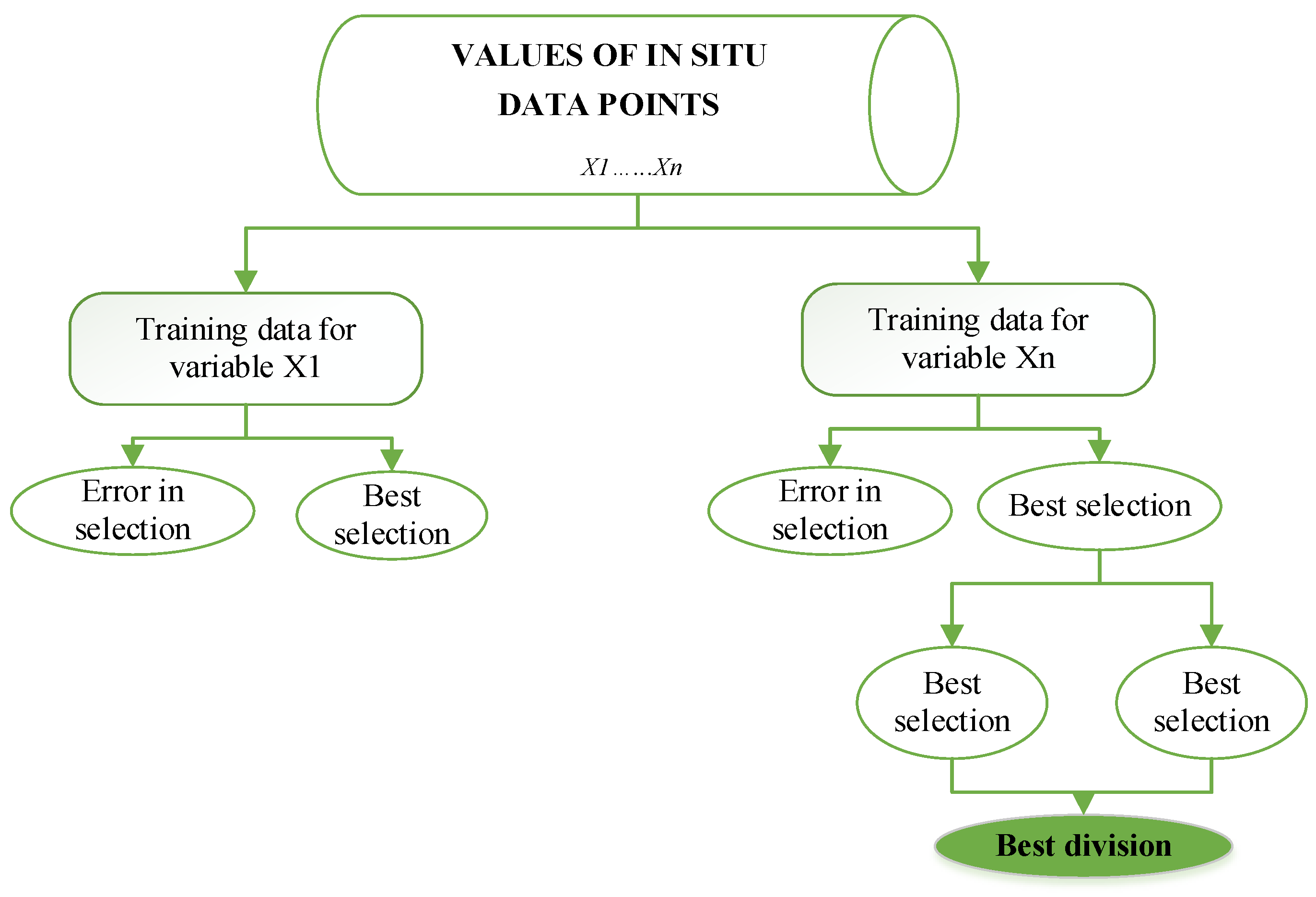
2.4.3. Classification and Regression Tree (CART) Algorithm
2.4.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Physicochemical Characteristics of Sediments
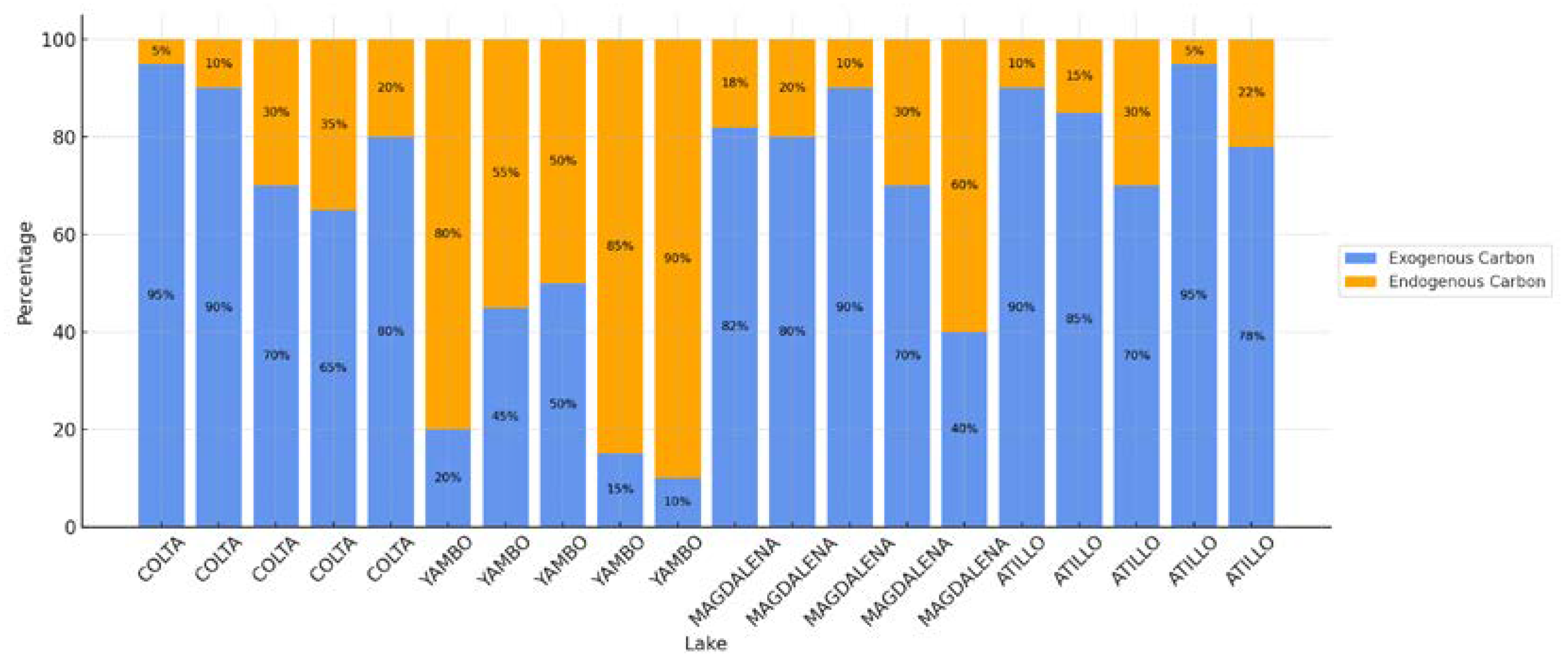
3.2. Identification of Sedimentary Organic Carbon Content and Its Sources
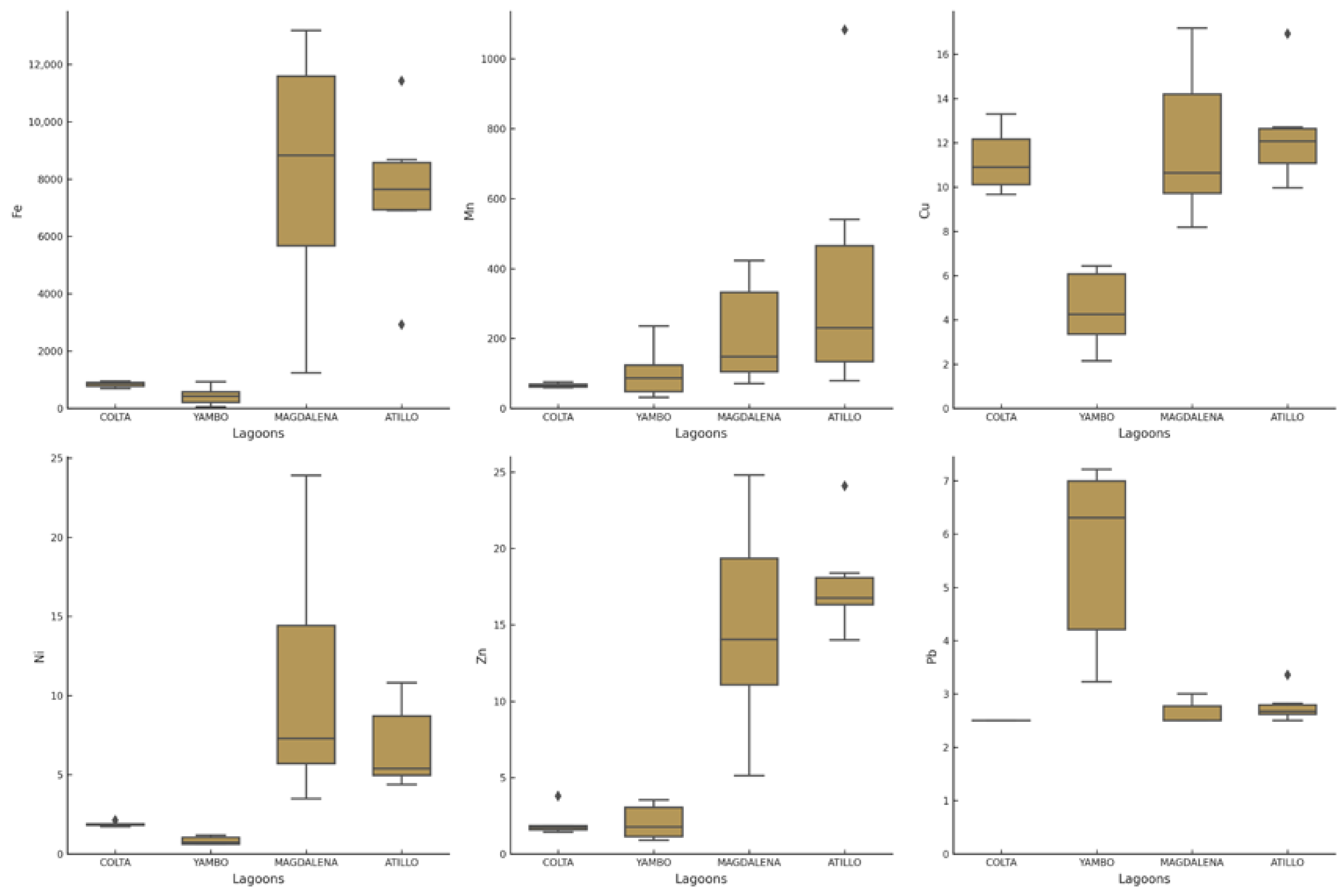
3.3. Sediments Heavy Metals
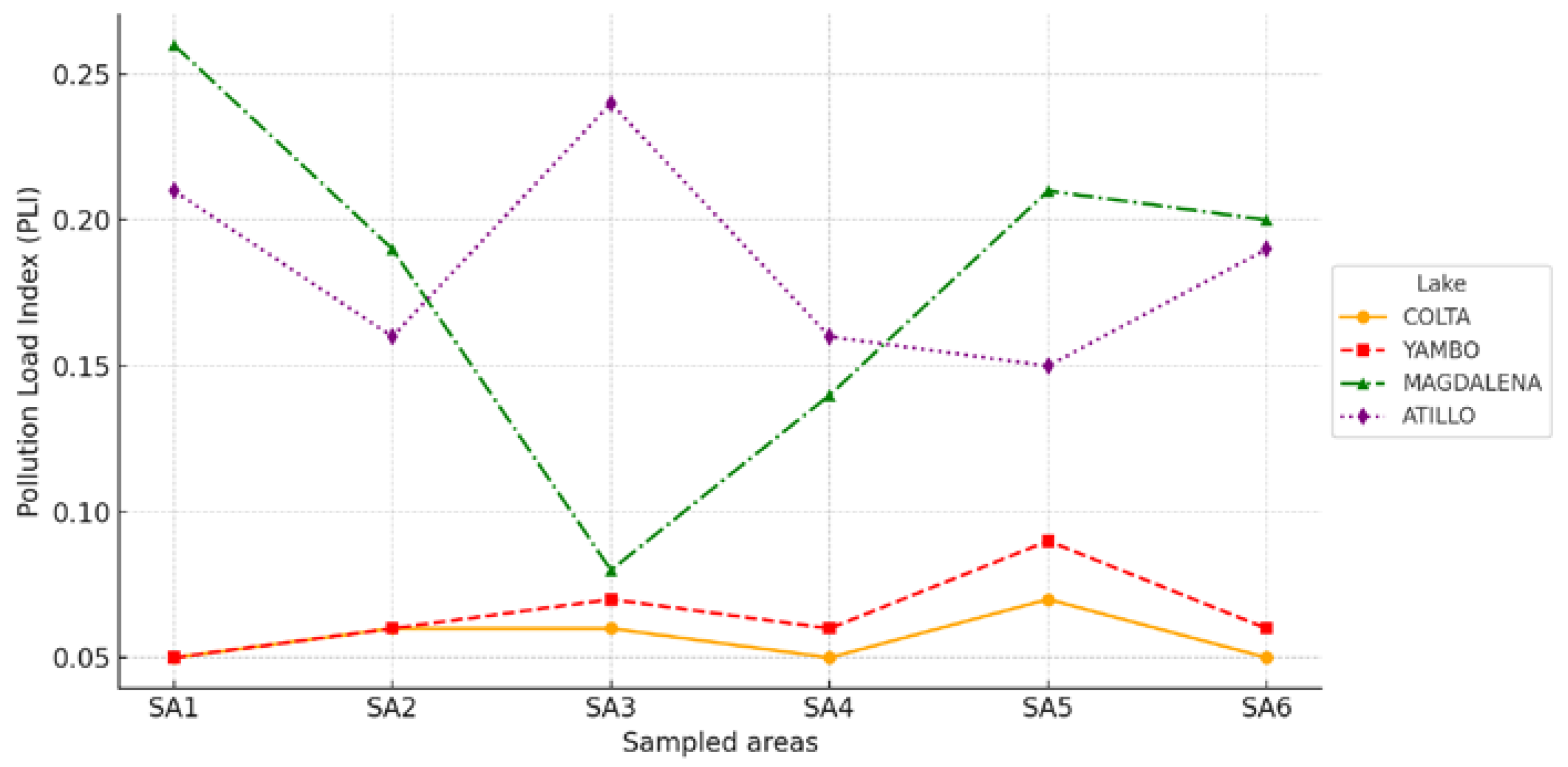
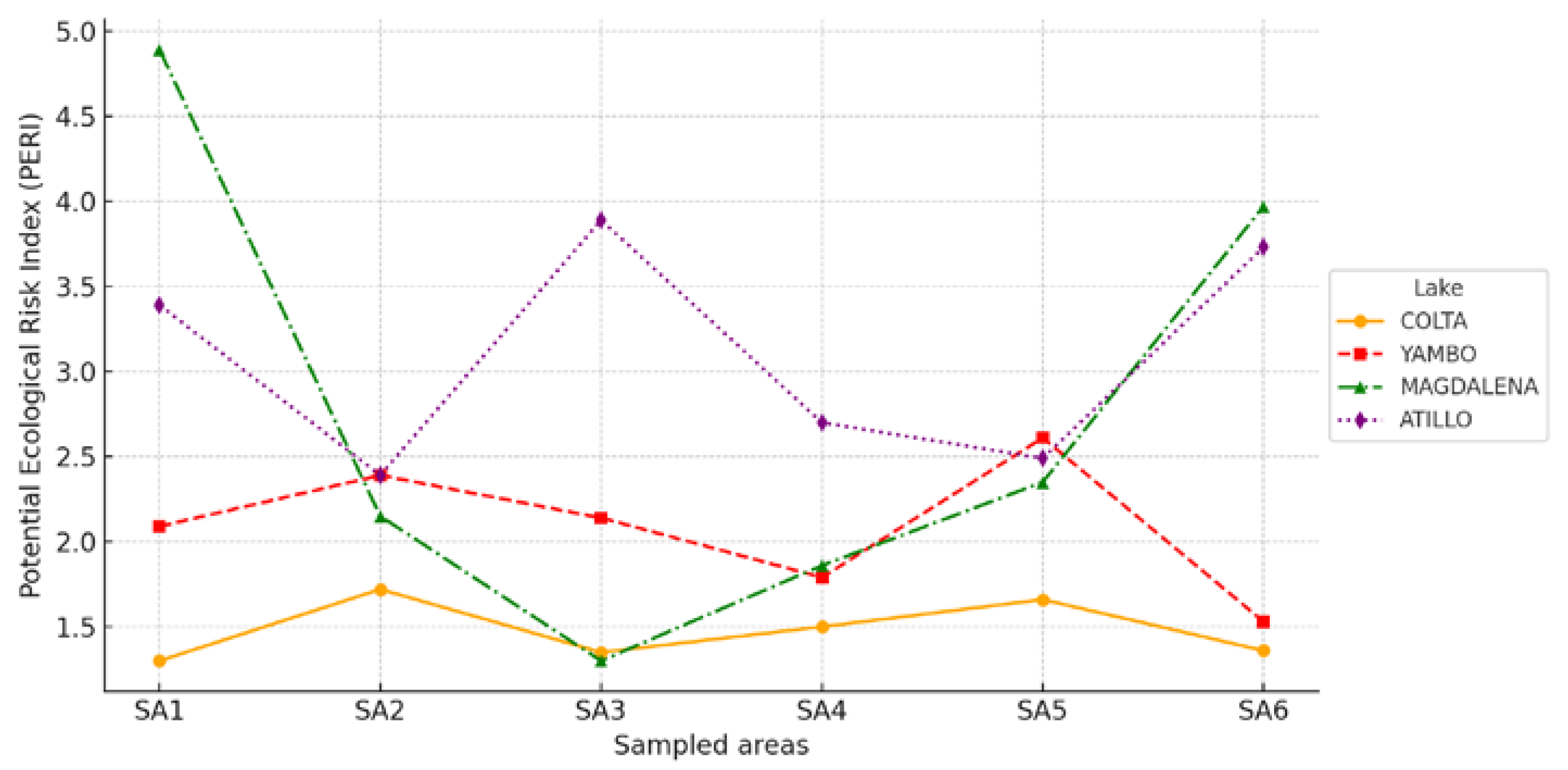
3.4. Ecological Risk Assessment Findings
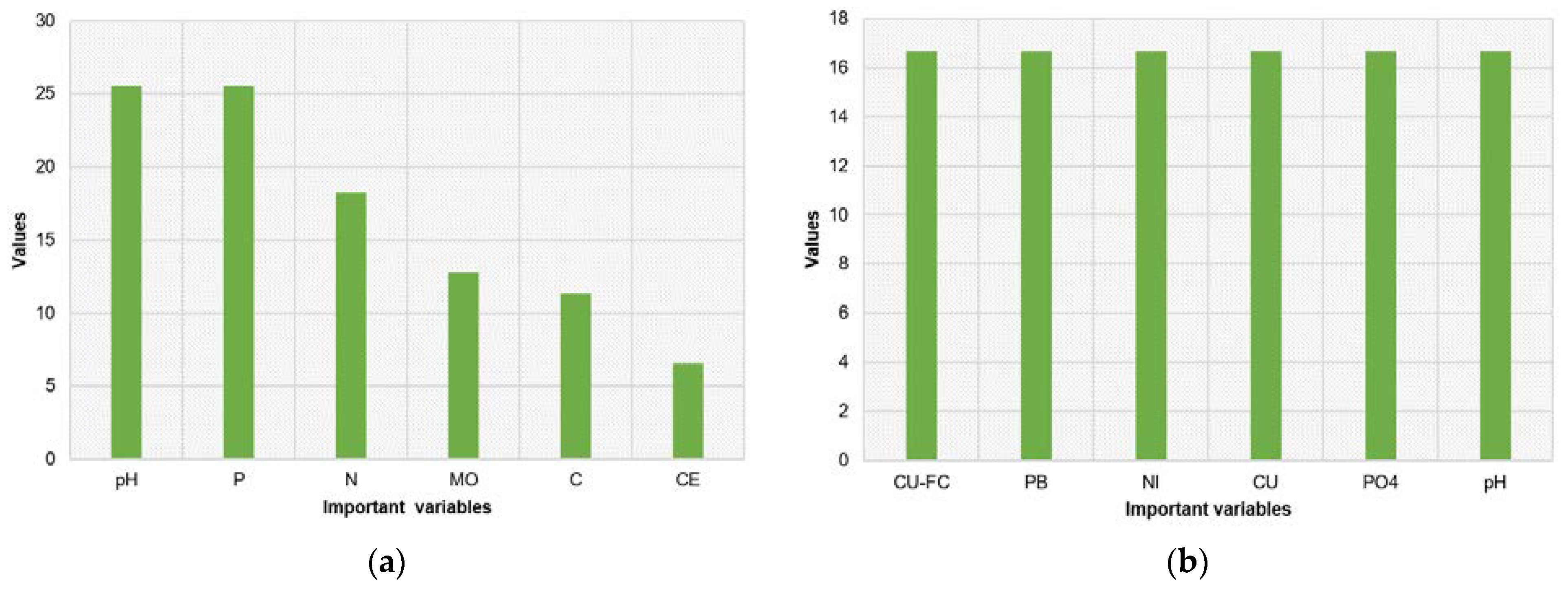
3.5. CART Predictor Model Findings
4. Discussion
4.1. Physicochemical Properties of Lake Sediments
4.2. Organic Carbon Content and Trophic Levels
4.3. Nitrogen and Phosphorus Dynamics
4.4. Sedimentary Organic Matter Sources
4.5. Heavy Metal Concentrations in Lake Sediments
4.6. Ecological Risk Assessment
4.7. CART Predictor Model
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, M.; Wang, R.; Sun, W.; Wang, D.; Wu, X. Source Identification and Ecological Risk of Potentially Harmful Trace Elements in Lacustrine Sediments from the Middle and Lower Reaches of Huaihe River. Water 2023, 15, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatri, N.; Tyagi, S. Influences of Natural and Anthropogenic Factors on Surface and Groundwater Quality in Rural and Urban Areas. Front. Life Sci. 2015, 8, 23–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopittke, P.M.; Menzies, N.W.; Wang, P.; McKenna, B.A.; Lombi, E. Soil and the Intensification of Agriculture for Global Food Security. Environ. Int. 2019, 132, 105078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjumea Hoyos, C.A.; Suárez-Segura, M.A.; Villabona-González, S.L. Variación Espacial y Temporal de Nutrientes y Total de Sólidos en Suspensión en la Cuenca de un Río de Alta Montaña Tropical. Rev. Acad. Colomb. Cienc. Exactas Fís. Nat. 2018, 42, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, J.A.; Alonso, A. Contaminación por Nitrógeno Inorgánico en los Ecosistemas Acuáticos: Problemas Medioambientales, Criterios de Calidad del Agua e Implicaciones del Cambio Climático. Rev. Ecosist. 2007, 16, 98–110. [Google Scholar]
- Campero, M.; Balseiro, E.; Fernández, C.E.; Modenutti, B.; Prado, P.E.; Rivera-Rondon, C.A.; Steinitz-Kannan, M. Andean Lakes: Endangered by Natural and Anthropogenic Threats. Inland Waters 2025, 1, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizarro, S.; Custodio, M.; Solórzano-Acosta, R.; Contreras, D.; Verástegui-Martínez, P. Water Storage–Discharge Relationship with Water Quality Parameters of Carhuacocha and Vichecocha Lagoons in the Peruvian Puna Highlands. Water 2024, 16, 2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilera, X.; Lazzaro, X.; Coronel, J.S. Tropical High-Altitude Andean Lakes Located Above the Tree Line Attenuate UV-A Radiation More Strongly than Typical Temperate Alpine Lakes. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2013, 12, 1649–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizarro, J.; Vergara, P.M.; Cerda, S.; Briones, D. Cooling and Eutrophication of Southern Chilean Lakes. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 541, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanamé-Zapata, F.; Custodio, M.; Poma-Chávez, C.; Cruz, A.H.-D. Nutrient Concentrations and Trophic State of Three Andean Lakes from Junín, Perú. Ambiente Agua Interdiscip. Rev. Ambient. Água 2020, 15, e2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala, R.; Acosta, F.; Mooij, W.M.; Rejas, D.; Van Damme, P. A Management of Laguna Alalay: A Case Study of Lake Restoration in Andean Valleys in Bolivia. Aquat. Ecol. 2007, 41, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glibert, P.M.; Hinkle, D.C.; Sturgis, B.; Jesien, R.V. Eutrophication of a Maryland/Virginia Coastal Lagoon: A Tipping Point, Ecosystem Changes, and Potential Causes. Estuaries Coasts 2014, 37, 128–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahecha-Pulido, J.D.; Trujillo-González, J.M.; Torres-Mora, M.A. Análisis de Estudios en Metales Pesados en Zonas Agrícolas de Colombia. Orinoquia 2017, 21, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafra-Mejía, C.; Rondón-Quintana, H.; Gutiérrez-Malaxechebarria, Á. Heavy Metal Contribution by Runoff in a High-Altitude Megacity: A Method Based on the Road-Deposited Sediment Characterization. Dyna 2018, 85, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala Izurieta, J.E.; Beltrán Dávalos, A.A.; Jara Santillán, C.A.; Godoy Ponce, S.C.; Van Wittenberghe, S.; Verrelst, J.; Delegido, J. Spatial and Temporal Analysis of Water Quality in High Andean Lakes with Sentinel-2 Satellite Automatic Water Products. Sensors 2023, 23, 8774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soria, D.; Soria, A. Evaluación de la Eutrofización y Variabilidad Vertical de las Concentraciones de Nutrientes en la Laguna de Colta. Bachelor’s Thesis, Escuela Superior Politécnica de Chimborazo, Riobamba, Ecuador, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Rivera, B.; Patarón, N. Influencia de la Estructura Térmica en los Parámetros Fisicoquímicos y Químicos de la Laguna Magdalena-Atillo del Parque Nacional Sangay. Bachelor’s Thesis, Escuela Superior Politécnica de Chimborazo, Riobamba, Ecuador, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Orquera, E.; Cabrera, M. Caracterización del Estado Trófico de la Laguna de Yambo Mediante Análisis de Fósforo. Infoanalítica 2020, 8, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltrán-Dávalos, A.A.; Ayala Izurieta, J.E.; Echeverria Guadalupe, M.M.; Van Wittenberghe, S.; Delegido, J.; Otero Pérez, X.L.; Merino, A. Evaluation of Soil Organic Carbon Storage of Atillo in the Ecuadorian Andean Wetlands. Soil Syst. 2022, 6, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erazo Fierro, G.A.; Aldás Núñez, R.J. Cordillera Real: Variación de Metamorfismo en el Trayecto Atillo-Normandía. FIGEMPA Investig. Desarro. 2020, 9, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zehetner, F.; Miller, W.P.; West, L.T. Pedogenesis of Volcanic Ash Soils in Andean Ecuador. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2003, 67, 1797–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aalto, J.; Niittynen, P.; Riihimäki, H.; Luoto, M. Cryogenic Land Surface Processes Shape Vegetation Biomass Patterns in Northern European Tundra. Commun. Earth Environ. 2021, 2, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buytaert, W.; Célleri, R.; De Biévre, B.; Cisneros, F. Hidrología del Páramo Andino: Propiedades, Importancia y Vulnerabilidad. Soil Water 2003, 1–26. Available online: https://paramo.cc.ic.ac.uk/pubs/ES/Hidroparamo2.pdf (accessed on 7 March 2025).
- Gobierno Autónomo Descentralizado Parroquial Rural Panzaleo. Plan de Desarrollo y Ordenamiento Territorial PDyOT. 2020. Available online: https://www.gadpanzaleo.gob.ec/wp-content/uploads/2020/10/PDOT-PANZALEO-ACTUALIZACION-2019_2023.pdf (accessed on 10 January 2025).
- Winckell, A.; Marocco, R.; Winter, T.; Huttel, C.; Pourrut, P.; Zebrowski, C.; Sourdat, M. Los Paisajes Naturales del Ecuador: Las Condiciones Generales del Medio Natural; Centro Ecu: Quito, Ecuador, 1997; Volume 1, Available online: https://horizon.documentation.ird.fr/exl-doc/pleins_textes/doc34-07/010022380.pdf (accessed on 30 January 2025).
- Escobar-Arrieta, S.; Albuja, A.; Andueza-Leal, F.D. Calidad Fisicoquímica del Agua de la Laguna Colta, Chimborazo, Ecuador. FIGEMPA Investig. Desarro. 2021, 11, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudroch, A.; MacKnight, S.D. Handbook of Techniques for Aquatic Sediments Sampling, 2nd ed.; Lewis Publisher: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1994; Available online: https://books.google.com.ec/books?id=b8opvqirlg8C&printsec=copyright&hl=es#v=onepage&q&f=false (accessed on 30 January 2025).
- Kurek, M.R.; Harir, M.; Shukle, J.T.; Schroth, A.W.; Schmitt-Kopplin, P.; Druschel, G.K. Chemical Fractionation of Organic Matter and Organic Phosphorus Extractions from Freshwater Lake Sediment. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1130, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NTE INEN-ISO 10381-1; Soil Quality—Sampling—Part 1: Guidance on the Design of Sampling Programmes. Instituto Ecuatoriano de Normalización: Quito, Ecuador, 2014.
- Rubio, R.; Ure, A.M. Approaches to Sampling and Sample Pretreatments for Metal Speciation in Soils and Sediments. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 1993, 51, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano-Zarto, H.; Garay-Tinoco, J.; Ramírez, G.; Betancourt, J.; Marín, B.; Cadavid, B.; Franco-Herrera, A. Manual de Técnicas Analíticas para la Determinación de Parámetros Fisicoquímicos y Contaminantes Marinos: Aguas, Sedimentos y Organismos; Instituto de Investigaciones Marinas y Costeras (INVEMAR): Santa Marta, Colombia, 2003; Available online: https://www.invemar.org.co/redcostera1/invemar/docs/7010manualTecnicasanaliticas.pdf (accessed on 8 March 2025).
- Gonzalez, M.; Souza, G.; Oliveira, R.; Forato, L.; Nóbrega, J.; Nogueira, A.R. Microwave-Assisted Digestion Procedures for Biological Samples with Diluted Nitric Acid: Identification of Reaction Products. Talanta 2009, 79, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matusiewicz, H. Sample Preparation for Inorganic Trace Element Analysis. Phys. Sci. Rev. 2017, 2, 20178001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakutinskiene, I.; Kiuberis, J.; Bezdicka, P.; Senvaitiene, J.; Kareiva, A. Analytical Characterization of Baltic Amber by FTIR, XRD, and SEM. Can. J. Anal. Sci. Spectrosc. 2007, 52, 287–293. [Google Scholar]
- Heiri, O.; Lotter, A.F.; Lemcke, G. Loss on Ignition as a Method for Estimating Organic and Carbonate Content in Sediments: Reproducibility and Comparability of Results. J. Paleolimnol. 2001, 25, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cargua Catagña, F.E.; Rodríguez Llerena, M.V.; Damián Carrión, D.A.; Recalde Moreno, C.G.; Santillán Lima, G.P. Analytical Methods Comparison for Soil Organic Carbon Determination in Andean Forest of Sangay National Park-Ecuador. Acta Agron. 2017, 66, 408–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yujra Ticona, E.; Miranda Casas, R. Evaluation of the Bray-Kurtz and Olsen Methodology for the Determination of Available Phosphorus in Soils. Apthapi 2019, 5, 1407–1414. [Google Scholar]
- García Flores, M.E.; Zanor, G.A. Evaluación de la Contaminación por Elementos Traza en Sedimentos de la Presa La Purísima (Guanajuato). Jóvenes Cienc. 2017, 2, 475–479. [Google Scholar]
- Azcarate, M.P.; Baglioni, M.; Brambilla, C.; Brambilla, E.; Fernandez, R.; Kloster, N.S.; Savio, M. Métodos de Análisis e Implementación de Calidad en el Laboratorio de Suelos; Ediciones INTA: Anguil, Argentina, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Tian, J.; Li, C.; Yu, K.; Zhang, M.; Sun, T. A Sediment Record of Terrestrial Organic Matter Inputs to Dongting Lake and Its Environmental Significance from 1855 to 2019. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 108, 108090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyers, P.A. Organic Geochemical Proxies of Paleoceanographic, Paleolimnologic, and Paleoclimatic Processes. Org. Geochem. 1997, 27, 213–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.L.; Yang, C.; He, W.; He, Q.S.; Li, Y.L.; Kang, L.; Xing, B. Bias and Association of Sediment Organic Matter Source Apportionment Indicators: A Case Study in a Eutrophic Lake Chaohu, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 581–582, 874–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Lu, S.; Wang, D.; Xu, M.; Gan, S.; Jin, X. Nitrogen, Phosphorous and Organic Matter Spatial Distribution Characteristics and Their Pollution Status Evaluation of Sediments Nutrients in Lakeside Zones of Taihu Lake. China Environ. Sci. 2012, 32, 703–709. [Google Scholar]
- Hakanson, L. An Ecological Risk Index for Aquatic Pollution Control: A Sedimentological Approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, P.; Krishnakumar, S.; Pradhap, D.; Silva, J.D.; Arumugam, K.; Magesh, N.S.; Srinivasalu, S. Elemental Concentration-Based Potential Ecological Risk (PER) Status of the Surface Sediments, Pulicat Lagoon, Southeast Coast of India. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 133, 854–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Custodio, M.; Fow, A.; Peñaloza, R.; Chanamé, F.; Cano, D. Evaluation of Surface Sediment Quality in Rivers with Fish Farming Potential (Peru) Using Indicators of Contamination, Accumulation and Ecological Risk of Heavy Metals and Arsenic. J. Ecol. Eng. 2021, 22, 32–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Custodio, M.; Fow, A.; Chanamé, F.; Orellana-Mendoza, E.; Peñaloza, R.; Alvarado, J.C.; Cano, D.; Pizarro, S. Ecological Risk Due to Heavy Metal Contamination in Sediment and Water of Natural Wetlands with Tourist Influence in the Central Region of Peru. Water 2021, 13, 2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafarabadi, A.R.; Riyahi Bakhtiyari, A.; Toosi, A.S.; Jadot, C. Spatial Distribution, Ecological and Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Marine Surface Sediments and Coastal Seawaters of Fringing Coral Reefs of the Persian Gulf, Iran. Chemosphere 2017, 185, 1090–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidoruk, M. Pollution and Potential Ecological Risk Evaluation of Heavy Metals in the Bottom Sediments: A Case Study of Eutrophic Bukwałd Lake Located in an Agricultural Catchment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomlinson, D.L.; Wilson, J.G.; Harris, C.R.; Jeffrey, D.W. Problems in the Assessment of Heavy-Metal Levels in Estuaries and the Formation of a Pollution Index. Helgoländer Meeresunters. 1980, 33, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedinia, A.; Seydi, V. Building Semi-Supervised Decision Trees with Semi-CART Algorithm. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Cybern. 2024, 15, 4493–4510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, N.J.; Bennion, H.; Lotter, A.F. Lake Eutrophication and Its Implications for Organic Carbon Sequestration in Europe. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2014, 20, 2741–2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaia, E.; Ribeiro-Guevara, S.; Rizzo, A.; Arribére, M. Occurrence of Discaria trinervis Nodulating Frankia in Dated Sediments of Glacial Andean Lakes. Symbiosis 2005, 39, 65–75. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, A.; McGlue, M.M.; Ellis, G.S.; Zani, H.; Swarzenski, P.W.; Assine, M.L.; Silva, A. Lake Formation, Characteristics, and Evolution in Retroarc Deposystems: A Synthesis of the Modern Andean Orogen and Its Associated Basins. In Geodynamics of a Cordilleran Orogenic System: The Central Andes of Argentina and Northern Chile; DeCelles, P.G., Ducea, M.N., Carrapa, B., Kapp, P.A., Eds.; Geological Society of America: Boulder, CO, USA, 2015; pp. 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhihao, W.; Xia, J.; Shuhang, W.; Li, Z.; Lixin, J.; Junyi, C.; Cheng, Y. Mobilization and Geochemistry of Nutrients in Sediment Evaluated by Diffusive Gradients in Thin Films: Significance for Lake Management. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 292, 112770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, O.E.; Lawson, E.O. Physico-Chemical Parameters and Heavy Metal Contents of Water from the Mangrove Swamps of Lagos Lagoon, Lagos, Nigeria. Adv. Biol. Res. 2011, 5, 8–21. [Google Scholar]
- Junakova, N.; Junak, J.; Balintova, M. The Effect of Physicochemical Properties of Bottom Sediments on Nitrogen and Phosphorus Sorption. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2022, 1252, 012059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.M.; Li, R.H.; Zhang, G.L.; Wang, D.R.; Du, J.Z.; Herbeck, L.S.; Ren, J.L. The Impact of Anthropogenic Activities on Nutrient Dynamics in the Tropical Wenchanghe and Wenjiaohe Estuary and Lagoon System in East Hainan, China. Mar. Chem. 2011, 125, 49–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chislock, M.F.; Doster, E.; Zitomer, R.A.; Wilson, A.E. Eutrophication: Causes, Consequences, and Controls in Aquatic Ecosystems. Nat. Educ. Knowl. 2013, 4, 10. Available online: https://www.nature.com/scitable/knowledge/library/eutrophication-causes-consequences-and-controls-in-aquatic-102364466/ (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- Yu, K.; Zhang, Y.; He, X.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, M.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y. Characteristics and Environmental Significance of Organic Carbon in Sediments from Taihu Lake, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 138, 108796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Chen, F.; Xiao, K.; Song, C.; He, H.; Zhang, Q.; Lu, Y. Water Residence Time and Temperature Drive the Dynamics of Dissolved Organic Matter in Alpine Lakes in the Tibetan Plateau. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2021, 35, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariñelarena, A.; Gómez, S. Eutrofización en las Lagunas Pampeanas. Biol. Acuát. 2008, 24, 43–48. [Google Scholar]
- Estrada-Herrera, I.R.; Hidalgo-Moreno, C.; Guzmán-Plazola, R.; Almaraz Suárez, J.J.; Navarro-Garza, H.; Etchevers-Barra, J.D. Soil Quality Indicators to Evaluate Soil Fertility. Agrociencia 2017, 51, 813–831. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, H.; Tai, Z.; Li, Q.; Zhang, F. Characterization and Source Identification of Organic Phosphorus in Sediments of a Hypereutrophic Lake. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 257, 113500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baigún, C.; Mugni, H.; Bonetto, C. Nutrient Concentrations and Trophic State of Small Patagonian Andean Lakes. J. Freshw. Ecol. 2006, 21, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorador, C.; Pardo, R.; Vila, I. Variaciones Temporales de Parámetros Físicos, Químicos y Biológicos de un Lago de Altura: El Caso del Lago Chungará. Rev. Chil. Hist. Nat. 2003, 76, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Sierra, Y.V.; Pedroza-Ramos, A.X.; Aranguren-Riaño, N.J. Estructura del Fitoplancton Según la Condición Metabólica de Lagos Andinos Ubicados en Diferente Rango Altitudinal. Intropica 2021, 16, 153–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stets, E.G.; Striegl, R.G.; Aiken, G.R.; Rosenberry, D.O.; Winter, T.C. Hydrologic Support of Carbon Dioxide Flux Revealed by Whole-Lake Carbon Budgets. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114, G01008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DelSontro, T.; Beaulieu, J.J.; Downing, J.A. Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Lakes and Impoundments: Upscaling in the Face of Global Change. Limnol. Oceanogr. Lett. 2018, 3, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Li, M.; Yang, Y.; Yu, H.; Xiao, F.; Mao, C.; Yan, Q. Nitrite and Nitrate Reduction Drive Sediment Microbial Nitrogen Cycling in a Eutrophic Lake. Water Res. 2022, 220, 118637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urrutia, R.; Yevenes, M.; Barra, R. Determinación de los Niveles Basales de Metales Traza en Sedimentos de Tres Lagos Andinos de Chile: Lagos Chungará, Laja y Castor. Bol. Soc. Chil. Quím. 2002, 47, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno Terrazas, E.; Argota Pérez, G.; Alfaro Tapia, R.; Aparicio Saavedra, M.; Atencio Limachi, S.; Goyzueta Camacho, G. Cuantificación de Metales en Sedimentos Superficiales de la Bahía Interior, Lago Titicaca-Perú. Rev. Investig. Altoandinas 2018, 20, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, A.; Daga, R.; Arcagni, M.; Pérez Catán, S.; Bubach, D.; Sánchez, R.; Ribeiro Guevara, S.; Arribére, M.A. Heavy Metal Concentrations in Different Compartments of Andean Lakes of Northern Patagonia. Ecol. Austral 2010, 20, 155–167. [Google Scholar]
- Arias, H.R.; Leyva, P.F.M.; Palacios, L.C.; Rivero, J.M.O.; De la Mora Orozco, C. Metales Pesados en Sedimentos de la Laguna de Bustillos, Chihuahua, México y Comparación de Agua Regia y Peróxido de Hidrógeno como Métodos de Digestión. Investig. Cienc. 2018, 74, 39–47. [Google Scholar]
- Márquez, A.; Senior, W.; Fermín, I.; Martínez, G.; Castañeda, J.; González, Á. Cuantificación de las Concentraciones de Metales Pesados en Tejidos de Peces y Crustáceos de la Laguna de Unare, Venezuela. Rev. Cienc. 2008, 18, 73–86. [Google Scholar]
- Gierlowski-Kordesch, E. Paleolimnology: The History and Evolution of Lake Systems. PALAIOS 2004, 19, 184–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Zeng, L.; Che, F.; Yang, F.; Wang, D.; Luo, Z.; Wang, X. High-Resolution Characterization of Arsenic Mobility and Its Correlation to Labile Iron and Manganese in Sediments of a Shallow Eutrophic Lake in China. J. Soils Sediments 2018, 18, 1929–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avramidis, P.; Barouchas, P.; Dünwald, T.; Unkel, I.; Panagiotaras, D. The Influence of Olive Orchards Copper-Based Fungicide Use in Soils and Sediments—The Case of Aetoliko Lagoon, Western Greece. Geosciences 2019, 9, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nys, C.; Janssen, C.R.; Van Sprang, P.; De Schamphelaere, K.A.C. The Effect of pH on Chronic Aquatic Nickel Toxicity Is Dependent on the pH Itself: Extending the Chronic Nickel Bioavailability Models. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2015, 35, 1097–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostka, A.; Leśniak, A. Spatial and Geochemical Aspects of Heavy Metal Distribution in Lacustrine Sediments, Using the Example of Lake Wigry (Poland). Chemosphere 2020, 240, 124879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ndimele, P.O.; Jenyo-Oni, A.; Jibuike, C.O. The Levels of Lead (Pb) in Water, Sediment and a Commercially Important Fish Species (Chrysichthys nigrodigitatus) from Ologe Lagoon, Lagos, Nigeria. J. Environ. Ext. 2010, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Rose, N.L.; Battarbee, R.W. Distribution of Some Trace Metals in Lochnagar, a Scottish Mountain Lake Ecosystem and Its Catchment. Sci. Total Environ. 2002, 285, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.X.; Li, X.D.; Shen, Z.G.; Wang, D.C.; Wai, O.W.H.; Li, Y.S. Multivariate Statistical Study of Heavy Metal Enrichment in Sediments of the Pearl River Estuary. Environ. Pollut. 2003, 121, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, P.O.; Rashid, A.; Nkinahamira, F.; Wang, H.; Sun, Q.; Gad, M.; Hu, A. Integrated Assessment of Major and Trace Elements in Surface and Core Sediments from an Urban Lagoon, China: Potential Ecological Risks and Influencing Factors. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 170, 112651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nõges, T. Relationships Between Morphometry, Geographic Location and Water Quality Parameters of European Lakes. Hydrobiologia 2009, 633, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, T.; Tang, Y.; Li, Y.J.; Liu, Y.; Hu, H. An Experimental Study About the Effects of Phosphorus Loading in River Sediment on the Transport of Lead and Cadmium at the Sediment-Water Interface. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 720, 137535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wu, F.; He, Z.; Giesy, J.P.; Feng, W.; Mu, Y.; Tang, Z. Influence of Natural Organic Matter on the Bioavailability and Preservation of Organic Phosphorus in Lake Sediments. Chem. Geol. 2015, 397, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, T.A.; Amirbahman, A.; Norton, S.A.; Voytek, M.A. A Record of Phosphorus Dynamics in Oligotrophic Lake Sediment. J. Paleolimnol. 2010, 44, 279–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiani, M.; Tammeorg, P.; Niemistö, J.; Simojoki, A.; Tammeorg, O. Internal Phosphorus Loading in a Small Shallow Lake: Response After Sediment Removal. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 725, 138279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Lake | Altitude (m a.s.l.) | Area (ha) | Depth (m) | Avg. Temperature (°C) | Annual Precipitation (mm) | Trophic State | Protection Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atillo | 3485 | 257.2 | 20–25 | 5–6 | ~1000 | Oligotrophic | Protected (SNAP *) |
| Magdalena | 3485 | ~10 | ~5 | 5–6 | ~1000 | Oligotrophic | Protected (SNAP *) |
| Colta | 3312 | 280 | 3.5–8 | 12–15 | ~717 | Mesotrophic | Unprotected |
| Yambo | 2600 | 32 | ~17.1 | ~13 | ~500 | Hypertrophic | Unprotected |
| Parameter | Colta (n = 26) | Yambo (n = 25) | Magdalena (n = 24) | Atillo (n = 21) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SOC (mg/kg) | 1.9 ± 0.1 b | 4.0 ± 0.3 a | 3.7 ± 0.5 a | 3.8 ± 0.6 a | 0.000 |
| % OC | 2.1 ± 0.1 a,c | 1.8 ± 0.2 a | 2.8 ± 0.3 a,c | 3.2 ± 0.5 c | 0.009 |
| % N | 0.3 ± 0.03 a | 0.5 ± 0.05 b | 0.3 ± 0.04 a | 0.5 ± 0.1 b | 0.005 |
| PO43⁻ (mg/kg) | 94.9 ± 2.1 a | 678.5 ± 162.7 b | 126.5 ± 11.6 a | 122.2 ± 9.5 a | 0.000 |
| % OM | 3.3 ± 0.2 a | 6.9 ± 0.6 b | 6.4 ± 0.8 b | 6.5 ± 0.9 b | 0.000 |
| CEC (Cmol/kg) | 18.9 ± 0.6 b | 26.7 ± 3.6 c | 1.2 ± 0.03 a | 1.4 ± 0.06 a | 0.000 |
| Lagoons/Altitude | Location | Chromium (µg/g) | Cadmium (µg/g) | Iron (µg/g) | Manganese (µg/g) | Nickel (µg/g) | Zinc (µg/g) | Copper (µg/g) | Lead (µ/g) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chungará—4520 m a.s.l. | Chile | 44.19 ± 4.57 | 0.13 ± 2.09 | NA | NA | NA | 40.61 ± 2.39 | 21.51 ± 2.19 | 4.10 ± 0.53 | [72] |
| Laja—2362 m a.s.l. | Chile | 43.0 ± 3.64 | 0.12 ± 7.36 | NA | NA | NA | 36.3 ± 1.06 | 46.0 ± 3.19 | 11.1 ± 0.83 | [72] |
| Titicaca—3812 m a.s.l. | Perú | NA | 0.04215 | NA | NA | NA | 8.20 ± NA | 6.95 ± NA | 0.04 ± NA | [73] |
| Traful Lake—975 m a.s.l. | Argentina | 19.5 ± NA | NA | 46.7 ± NA | 918 | 33.6 | 101.6 ± NA | NA | NA | [74] |
| Bahía López Lagoon—2075 m a.s.l. | Argentina | 57.1 ± NA | NA | 45.2 ± NA | 931 ± NA | 40.2 ± NA | 90.7 ± NA | NA | NA | [74] |
| Bariloche Lagoon—764 m a.s.l. | Argentina | 53.83 ± NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | [74] |
| Bahía Llao-Llao Lagoon—1050 m a.s.l. | Argentina | NA | NA | 45.2 | 931 ± NA | 42.4 ± NA | 155.8 ± NA | NA | NA | [74] |
| Punto Panorámico Lagoon—945 m a.s.l. | Argentina | 51.6 ± NA | NA | NA | 2760 ± NA | 27.9 ± NA | 172.5 ± NA | NA | NA | [74] |
| Escondido Lagoon—770 m a.s.l. | Argentina | 37.4 | NA | NA | 1992 ± NA | 42.6 ± NA | 91.3 ± NA | NA | NA | [74] |
| Morenito Lagoon—780 m a.s.l. | Argentina | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 567 ± NA | NA | NA | [74] |
| Bustillos Lagoon—2000 m a.s.l. | Mexico | 25 ± NA | 1.51 ± NA | NA | 300 ± NA | 20 ± NA | 90 ± NA | 25 ± NA | 90 ± NA | [75] |
| Unare Lagoon—600 m a.s.l. | Venezuela | 51.69 ± NA | NA | NA | 516.37 ± NA | 52.41 ± NA | 127.49 ± NA | 41.13 ± NA | 29 ± NA | [76] |
| Presa la Purisma—1902 m a.s.l. | Mexico | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 67.6 ± NA | 30.76 ± NA | 22.76 ± NA | [38] |
| Colta Lake—3312 m a.s.l. | Ecuador | <2.5 | <1.25 | 843 ± 40 | 66 ± 2 | 1.9 ± 0.1 | 2.0 ± 0.4 | 11.2 ± 0.6 | <2.5 | Actual study |
| Yambo Lake—2600 m a.s.l. | Ecuador | <2.5 | <1.25 | 433 ± 131 | 102 ± 31 | 0.84 ± 0.1 | 2.1 ± 0.5 | 4.5 ± 0.7 | 5.6 ± 0.7 | Actual study |
| Atillo Lake—3485 m a.s.l. | Ecuador | <2.5 | <1.25 | 7532 ± 1138 | 378 ± 156 | 6.8 ± 1.1 | 15 ± 3 | 12.4 ± 0.9 | 2.8 ± 0.1 | Actual study |
| Magdalena Lake—3485 m a.s.l. | Ecuador | <2.5 | <1.25 | 8197 ± 1848 | 212 ± 62 | 10.7 ± 3.2 | 18 ± 1.4 | 11.9 ± 1.4 | 2.6 ± 0.1 | Actual study |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Beltrán-Dávalos, A.A.; Salazar, C.; Kurbatova, A.I.; Echeverría, M.; Merino, A.; Otero, X.L. Sediment Chemistry and Ecological Risk Assessment in Andean Lakes of Central Ecuador: Influence of Trophic Status on Accumulation Patterns. Sustainability 2025, 17, 3397. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17083397
Beltrán-Dávalos AA, Salazar C, Kurbatova AI, Echeverría M, Merino A, Otero XL. Sediment Chemistry and Ecological Risk Assessment in Andean Lakes of Central Ecuador: Influence of Trophic Status on Accumulation Patterns. Sustainability. 2025; 17(8):3397. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17083397
Chicago/Turabian StyleBeltrán-Dávalos, Andrés A., Cristian Salazar, Anna I. Kurbatova, Magdy Echeverría, Agustín Merino, and Xose Luis Otero. 2025. "Sediment Chemistry and Ecological Risk Assessment in Andean Lakes of Central Ecuador: Influence of Trophic Status on Accumulation Patterns" Sustainability 17, no. 8: 3397. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17083397
APA StyleBeltrán-Dávalos, A. A., Salazar, C., Kurbatova, A. I., Echeverría, M., Merino, A., & Otero, X. L. (2025). Sediment Chemistry and Ecological Risk Assessment in Andean Lakes of Central Ecuador: Influence of Trophic Status on Accumulation Patterns. Sustainability, 17(8), 3397. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17083397








