Characteristics of Soil and Plant Ecological Stoichiometry of Carbon, Nitrogen, and Phosphorus in Different Wetland Types of the Yellow River
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods and Materials
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling Methods
2.3. Sample Measurement
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Soil Physicochemical Properties in Diverse Wetlands of the Yellow River
3.2. Soil and Plant C, N, and P Concentrations in Different Wetlands of the Yellow River
3.3. Soil and Plant Stoichiometry of C, N, and P in Different Wetlands of the Yellow River
3.4. Relationships Among Soil Physicochemical Properties and Ecological Stoichiometry of Soil and Plants
4. Discussion
4.1. Soil and Plant C, N, and P Stoichiometric Characteristics in the Yellow River Wetland
4.2. Effects of Wetland Type on Soil and Plant Ecological Stoichiometry of C, N, and P
4.3. The Inconsistent Effects of Soil Factors on Soil and Plant Ecological Stoichiometry
4.4. The Negative Coupling Effects Between Soil and Plant Ecological Stoichiometry in the Yellow River Wetland
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Julian, P.; Gerber, S.; Bhomia, R.K.; King, J.; Osborne, T.Z.; Wright, A.L.; Powers, M.; Dombrowski, J. Evaluation of nutrient stoichiometric relationships among ecosystem compartments of a subtropical treatment wetland. Do we have “Redfield wetlands”? Ecol. Process. 2019, 8, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardans, J.; Rivas-Ubach, A.; Penuelas, J. The elemental stoichiometry of aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems and its relationships with organismic lifestyle and ecosystem structure and function: A review and perspectives. Biogeochemistry 2012, 111, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.H.; Li, M.X.; Xu, L.; Zhu, J.X.; Dai, G.H.; He, N.P. C:N:P stoichiometry in terrestrial ecosystems in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 795, 148849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Q.W.; Huai, Z.W.; Riaz, L.; Liu, T.S.; Wang, S.S.; Li, Y.C.; Bai, X.X.; Yan, G.X.; Yu, F.; Ma, J.M. Wetland-type conversion drives the C, N and P stoichiometry change of soil in river plain of lower of the Yellow River. Soil Use Manag. 2023, 39, 1335–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.Y.; Chen, B.B.; Xu, W.Z.; Xiang, C.Y.; Kuang, W.N.; Zhao, X.H. Driving factors for soil C:N ratio in woody plant communities across northeastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Catena 2023, 233, 107504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.F.; Ding, C.X.; Bu, H.; Han, L.L.; Ma, P.; Su, D.R. Effects of submergence frequency on soil C:N:P ecological stoichiometry in riparian zones of Hulunbuir steppe. J. Soils Sed. 2020, 20, 1480–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xue, Z.; Lyu, X.; Tong, S.; Jiang, M. Scaling of soil carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus and C:N:P ratio patterns in peatlands of China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2017, 27, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.H.; He, N.P.; Liu, C.C.; Xu, L.; Chen, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, R.M.; Yu, G.R.; Sun, W.; Xiao, C.W.; et al. Variation and evolution of C:N ratio among different organs enable plants to adapt to N-limited environments. Glob. Change Biol. 2020, 26, 2534–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.H.; He, N.P.; Liu, C.C.; Xu, L.; Yu, Q.; Yu, G.R. Allocation strategies for nitrogen and phosphorus in forest plants. Oikos 2018, 127, 1506–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junk, W.J.; An, S.Q.; Finlayson, C.M.; Gopal, B.; Kvet, J.; Mitchell, S.A.; Mitsch, W.J.; Robarts, R.D. Current state of knowledge regarding the world’s wetlands and their future under global climate change: A synthesis. Aquat. Sci. 2013, 75, 151–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hefting, M.M.; Van Den Heuvel, R.N.; Verhoeven, J.T.A. Wetlands in agricultural landscapes for nitrogen attenuation and biodiversity enhancement: Opportunities and limitations. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 56, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, X.Y.; Cui, L.J.; Li, W.; Lei, Y.R.; Dou, Z.G.; Liu, Z.J.; Cai, Y.; Zhai, X.J. Spartina alterniflora leaf and soil eco-stoichiometry in the Yancheng coastal wetland. Plants 2021, 10, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.K.; Liu, X.Y.; He, N.P.; Pan, X.; Long, S.Y.; Li, W.; Zhang, M.Y.; Cui, L.J. Global patterns in leaf stoichiometry across coastal wetlands. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2021, 30, 852–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.Y.; Pu, L.J.; Li, B.W.; Xu, Y.; Kong, F.B. Coupling mechanism of C:N:P stoichiometry between plant and soil after long-term reclamation in the coastal area, eastern China. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2023, 68, 103178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Li, F.; Xie, Y.H.; Deng, Z.M.; Hou, Z.Y.; Li, X. Spatial distribution and stoichiometry of soil carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus along an elevation gradient in a wetland in China. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2019, 70, 1128–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.Q.; Wang, C.; Sardans, J.; Tong, C.; Jia, R.X.; Zeng, C.S.; Penuelas, J. Flood regime affects soil stoichiometry and the distribution of the invasive plants in subtropical estuarine wetlands in China. Catena 2015, 128, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.Q.; Sardans, J.; Wang, C.; Zeng, C.S.; Tong, C.; Bartrons, M.; Asensio, D.; Penuelas, J. Shifts in plant and soil C, N and P accumulation and C:N:P stoichiometry associated with flooding intensity in subtropical estuarine wetlands in China. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2018, 215, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, R.C.; Yang, H.; Rinklebe, J.; Bolan, N.; Hu, Q.W.; Huang, X.Y.; Wen, X.T.; Zheng, B.F.; Shi, L. Seasonal flooding wetland expansion would strongly affect soil and sediment organic carbon storage and carbon-nutrient stoichiometry. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 828, 154427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.J.; Wang, Z.S.; Xia, S.X.; Zhang, G.S.; Li, S.X.; Yu, D.K.; Yu, X.B. Hydrologic-induced concentrated soil nutrients and improved plant growth increased carbon storage in a floodplain wetland over wet-dry alternating zones. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 822, 153512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Arif, M.; Zheng, J.; Li, C.X. Patterns and drivers of plant carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus stoichiometry in a novel riparian ecosystem. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1354222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Jiao, L.; Qin, H.J.; Li, F. Effect of environmental stress on the nutrient stoichiometry of the clonal plant Phragmites australis in inland riparian wetlands of northwest China. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 705319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.X.; Li, Y.N.; Xie, Y.L.; Cui, B.S.; Ning, Z.H.; Zhang, S.Y.; Bi, Z.G.; Fu, S.Q.; Che, C.G. Effects of ecological restoration on soil biogenic elements and their ecological stoichiometry in the Yellow River Delta, China. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 993202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.F.; Tao, Y.X.; Liu, W.Z.; Xing, W.; Liu, G.H.; Wang, L.; Ma, L. C, N, and P stoichiometry and their interaction with different plant communities and soils in subtropical riparian wetlands. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 1024–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.Q.; Cui, M.M.; Yu, H.C.; Fan, X.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Zhang, H.Y.; Dai, Z.C.; Sun, J.F.; Yang, B.; Du, D.L. Global environmental change shifts ecological stoichiometry coupling between plant and soil in early-stage invasions. J. Soil. Sci. Plant Nutr. 2024, 24, 2402–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.W.; Wang, Y.T.; Sun, D.J.; Li, H.K.; Dong, Y.M.; Wang, Z.C.; Wang, S.Z. Soil nutrients and nutrient ratios influence the ratios of soil microbial biomass and metabolic nutrient limitations in mountain peatlands. Catena 2022, 218, 106528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.Y.; Song, Y.Y.; Li, M.T.; Gong, C.; Liu, Z.D.; Yuan, J.B.; Li, X.Y.; Song, C.C. Ammonia nitrogen and dissolved organic carbon regulate soil microbial gene abundances and enzyme activities in wetlands under different vegetation types. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2024, 196, 105310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.; Butler, O.M.; Chen, C.R.; Liu, W.Z.; Du, M.; Zhang, Q.F. Shifts in characteristics of the plant-soil system associated with flooding and revegetation in the riparian zone of Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Geoderma 2020, 361, 114015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.L.; Feng, R.R.; Han, J.N.; Zhang, Z.C.; Zhang, H.J.; Liu, K. Temporal and spatial differentiation characteristics of ecosystem service values based on the ecogeographical division of China: A case study in the Yellow River Basin, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 30, 8317–8337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, G.F.; Ding, S.Y. Impacts of human activity and natural change on the wetland landscape pattern along the Yellow River in Henan Province. J. Geogr. Sci. 2004, 14, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keddy, P.A. Wetland Ecology, Principles, and Conservation, 2nd ed.; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2018; pp. 10–13. [Google Scholar]
- Mitsch, W.J.; Bernal, B.; Nahlik, A.M.; Mander, U.; Zhang, L.; Anderson, C.J.; Jorgensen, S.E.; Brix, H. Wetlands, carbon, and climate change. Landsc. Ecol. 2013, 28, 583–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.L.; Hu, Y.Y.; Yang, C.M.; Chen, Y.Y. Effects of vegetation types on water-extracted soil organic matter (WSOM) from riparian wetland and its impacts on riverine water quality: Implications for riparian wetland management. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 628–629, 1249–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalembasa, S.J.; Jenkinson, D.S. A comparative study of titrimetric and gravimetric methods for the determination of organic carbon in soil. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1973, 24, 1085–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkinson, J.A.; Allen, S.E. A wet oxidation procedure suitable for the determination of nitrogen and mineral nutrients in biological material. Commun. Soil. Sci. Plant Anal. 1975, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, S.R.; Cole, C.V.; Watanabe, F.S.; Dean, S. Estimation of Available Phosphorus in Soils by Extraction with Sodium Bicarbonate; United States Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1954.
- Bui, E.N.; Henderson, B.L. C:N:P stoichiometry in Australian soils with respect to vegetation and environmental factors. Plant Soil 2013, 373, 553–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.H.; Tang, X.Y.; Cui, L.J.; Li, H.Z.; Lei, Y.R.; Zhao, X.S.; Zhai, X.J.; Li, J.; Wang, J.Z.; Wang, R.M.; et al. Analysis of coupled wetland soil–plant ecological stoichiometric characteristics of carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus under different disturbance intensities. Plant Soil 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, E.A. Soil Microbiology and Biochemistry, 3rd ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2006; p. 254. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, F.Z.; Sun, J.; Ren, C.J.; Kang, D.; Deng, J.; Han, X.H.; Yang, G.H.; Feng, Y.Z.; Ren, G.X. Land use change influences soil C, N, and P stoichiometry under “Grain-to-Green Program” in China. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.X.; Yu, D.; Wang, Z.; Xie, D. Stoichiometry patterns of leaf carbon, nitrogen and phosphorous in aquatic macrophytes in eastern China. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 70, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dibar, D.T.; Zhang, K.; Yuan, S.Q.; Zhang, J.Y.; Zhou, Z.Z.; Ye, X.X. Ecological stoichiometric characteristics of Carbon (C), Nitrogen (N) and Phosphorus (P) in leaf, root, stem, and soil in four wetland plants communities in Shengjin Lake, China. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0230089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Q.; Liu, B.; Chang, F.; Ma, Z.J.; Fan, J.H.; He, X.J.; You, S.X.; Aerziguli, A.; Yang, Y.K.; Shen, X.Y. Plant functional traits and ecological stoichiometric characteristics under water-salt gradient in the lakeshore zone of Bosten Lake. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2022, 46, 961–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.Y.; Xu, W.T.; Zhou, G.Y.; Bai, Y.F.; Li, J.X.; Tang, X.L.; Chen, D.M.; Liu, Q.; Ma, W.H.; Xiong, G.M.; et al. Patterns of plant carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus concentration in relation to productivity in China’s terrestrial ecosystems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 4033–4038. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.; Jiang, Y.F. Spatial characteristics of ecological stoichiometry and their driving factors in farmland soils in Poyang Lake Plain, Southeast China. J. Soils Sed. 2019, 19, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peñuelas, J.; Sardans, J.; Rivas-Ubach, A.; Janssens, I.A. The human-induced imbalance between C, N and P in Earth’s life system. Glob. Change Biol. 2012, 18, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.F.; Zhang, W.L.; Zhang, L.H.; Chen, X.Y.; Lin, W.; Zeng, C.S.; Tong, C. Stoichiometric characteristics of nitrogen and phosphorus in major wetland vegetation of China. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2014, 38, 1041–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koerselman, W.; Meuleman, A.F.M. The vegetation N:P ratio: A new tool to detect the nature of nutrient limitation. J. Appl. Ecol. 1996, 33, 1441–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.H.; Ye, X.F.; Jia, J.; Zhang, G.L.; Zhao, Q.Q.; Cui, B.S.; Liu, X.H. Phosphorus sorption-desorption and effects of temperature, pH and salinity on phosphorus sorption in marsh soils from coastal wetlands with different flooding conditions. Chemosphere 2017, 188, 677–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, K. Nitrogen and phosphorus nutrition under salinity stress. In Ecophysiology and Responses of Plants Under Salt Stress; Ahmad, P., Azooz, M.M., Prasad, M.N.V., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 425–441. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Z.Q.; Fang, H.J.; Bai, J.H.; Jia, J.; Lu, Q.Q.; Wang, J.J.; Chen, B. Spatial and seasonal distributions of soil phosphorus in a short-term flooding wetland of the Yellow River Estuary, China. Ecol. Inform. 2016, 31, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, Y.Q.; Wang, L.L.; Duan, Y.L.; Cao, W.J.; Wang, X.Y.; Li, Y.L. Heterogeneity of leaf stoichiometry of different life forms along environmental transects in typical ecologically fragile areas of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 910, 168495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Liu, Z.C.; Yuan, Z.Y.; Shi, X.R.; Lock, T.R.; Kallenbach, R.L. Aridity modifies the responses of plant stoichiometry to global warming and nitrogen deposition in semi-arid steppes. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 831, 154807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.Y.; Li, L.H.; Han, X.G.; Chen, S.P.; Wang, Z.W.; Chen, Q.S.; Bai, W.M. Nitrogen response efficiency increased monotonically with decreasing soil resource availability: A case study from a semiarid grassland in northern China. Oecologia 2006, 148, 564–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.Z.; Meng, H.Z.; Teng, K.; Fan, X.F.; Zhang, H.; Teng, W.J.; Yue, Y.S.; Wu, J.Y. Effects of nitrogen forms on the growth and nitrogen accumulation in Buchloe dactyloides seedlings. Plants 2022, 11, 2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochoa-Hueso, R.; Pérez-Corona, M.E.; Manrique, E. Impacts of simulated N deposition on plants and mycorrhizae from Spanish semiarid Mediterranean shrublands. Ecosystems 2013, 16, 838–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridgeway, J.R.; Morrissey, E.M.; Brzostek, E.R. Plant litter traits control microbial decomposition and drive soil carbon stabilization. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2022, 175, 108857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.J.; Zhang, H.; Cheng, X.L.; Liu, G.H. Nitrogen addition stimulates litter decomposition rate: From the perspective of the combined effect of soil environment and litter quality. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2023, 179, 108992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusewell, S. N: P ratios in terrestrial plants: Variation and functional significance. New Phytol. 2004, 164, 243–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, D.J.; Duston, S.; Barney, J.N.; Strahm, B.D.; Agarwal, P.; Mangru, A.; Badgley, B.D. Dissolved organic carbon characteristics are associated with changes in soil microbiome under different plant species. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2024, 196, 105313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.T.; Xu, X.F.; Qi, T.C.; Luo, J.H.; Lee, X.H.; Duan, H.T. Lakes shifted from a carbon dioxide source to a sink over past two decades in China. Sci. Bull. 2024, 69, 1857–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
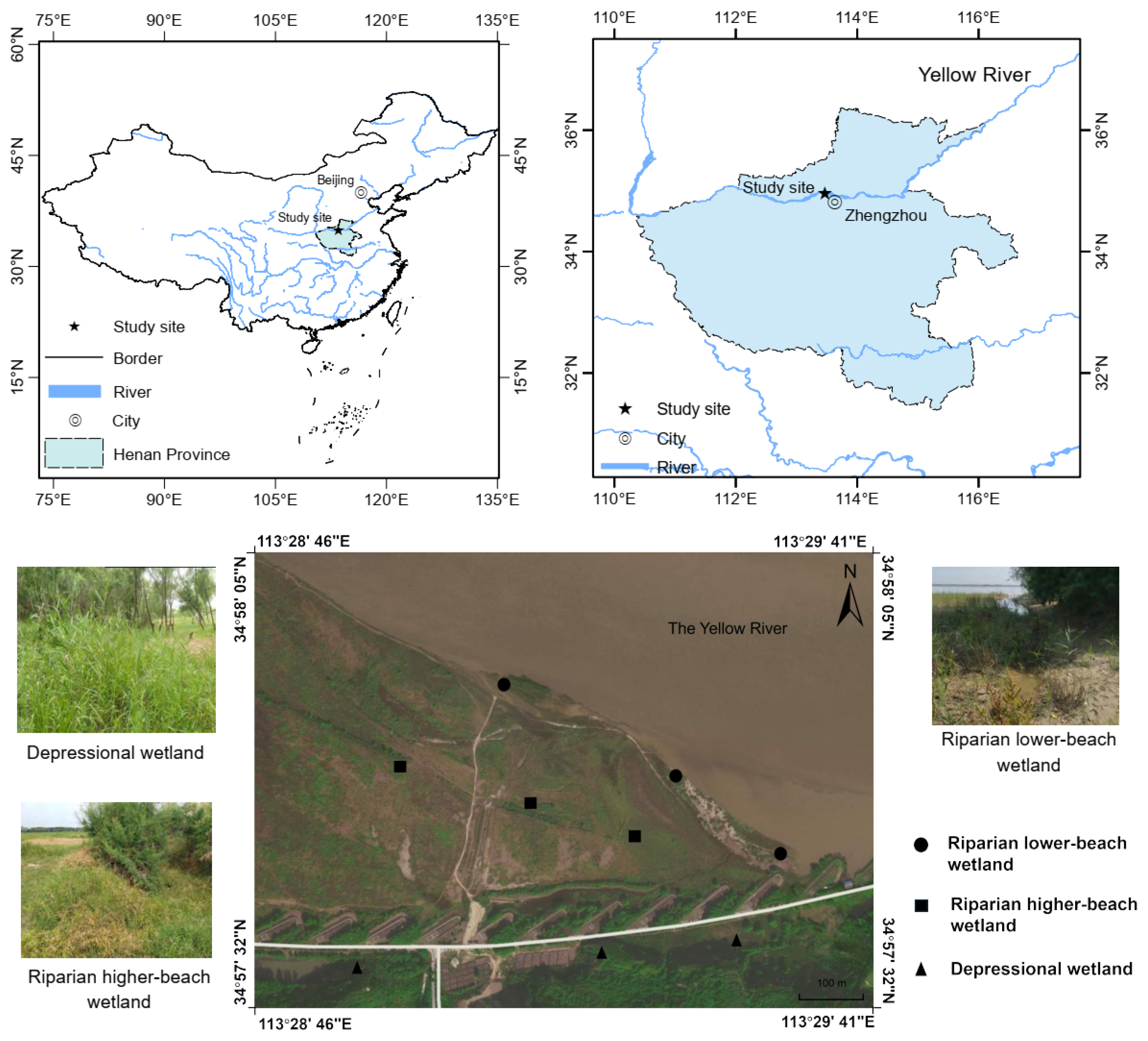
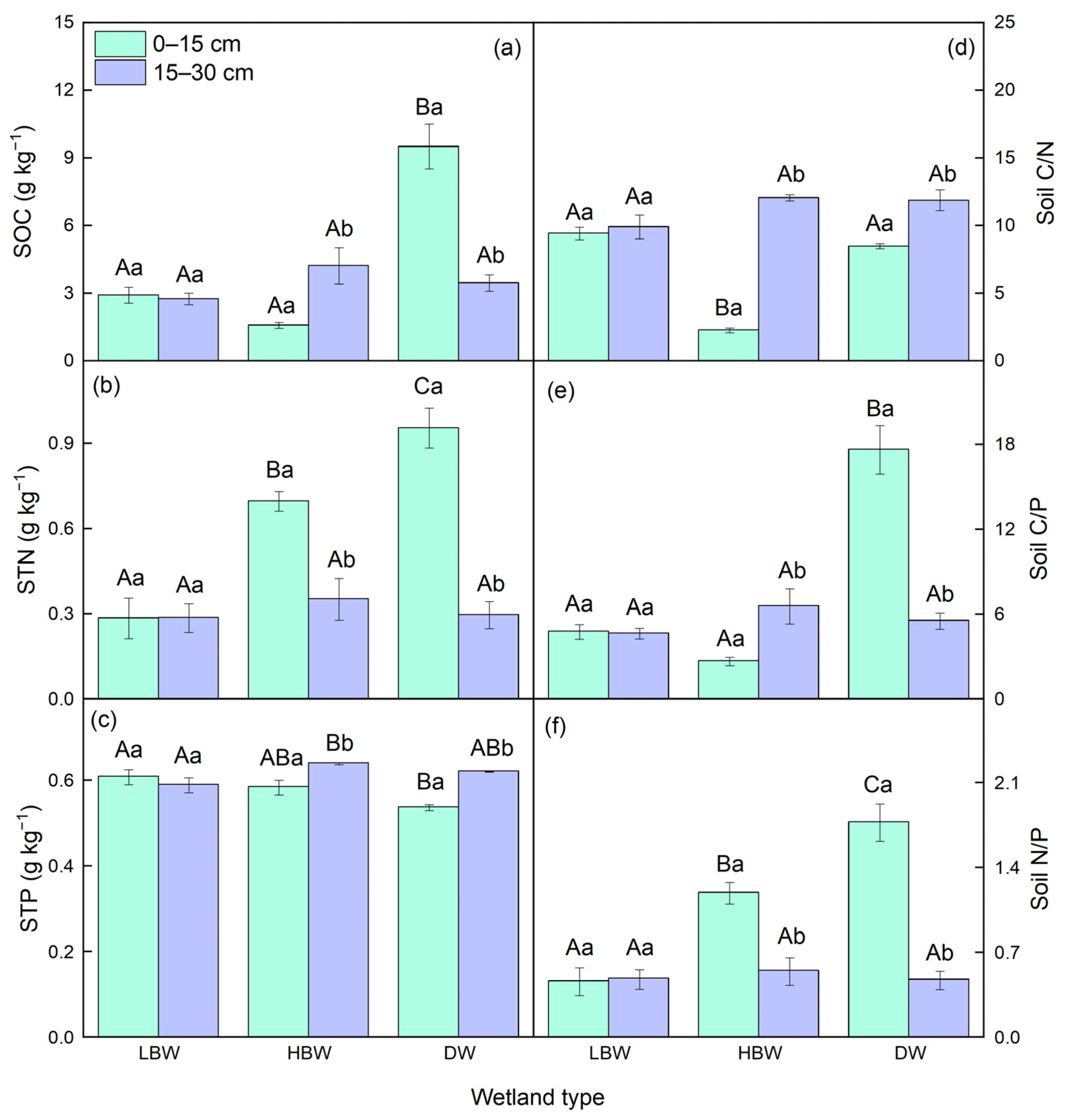
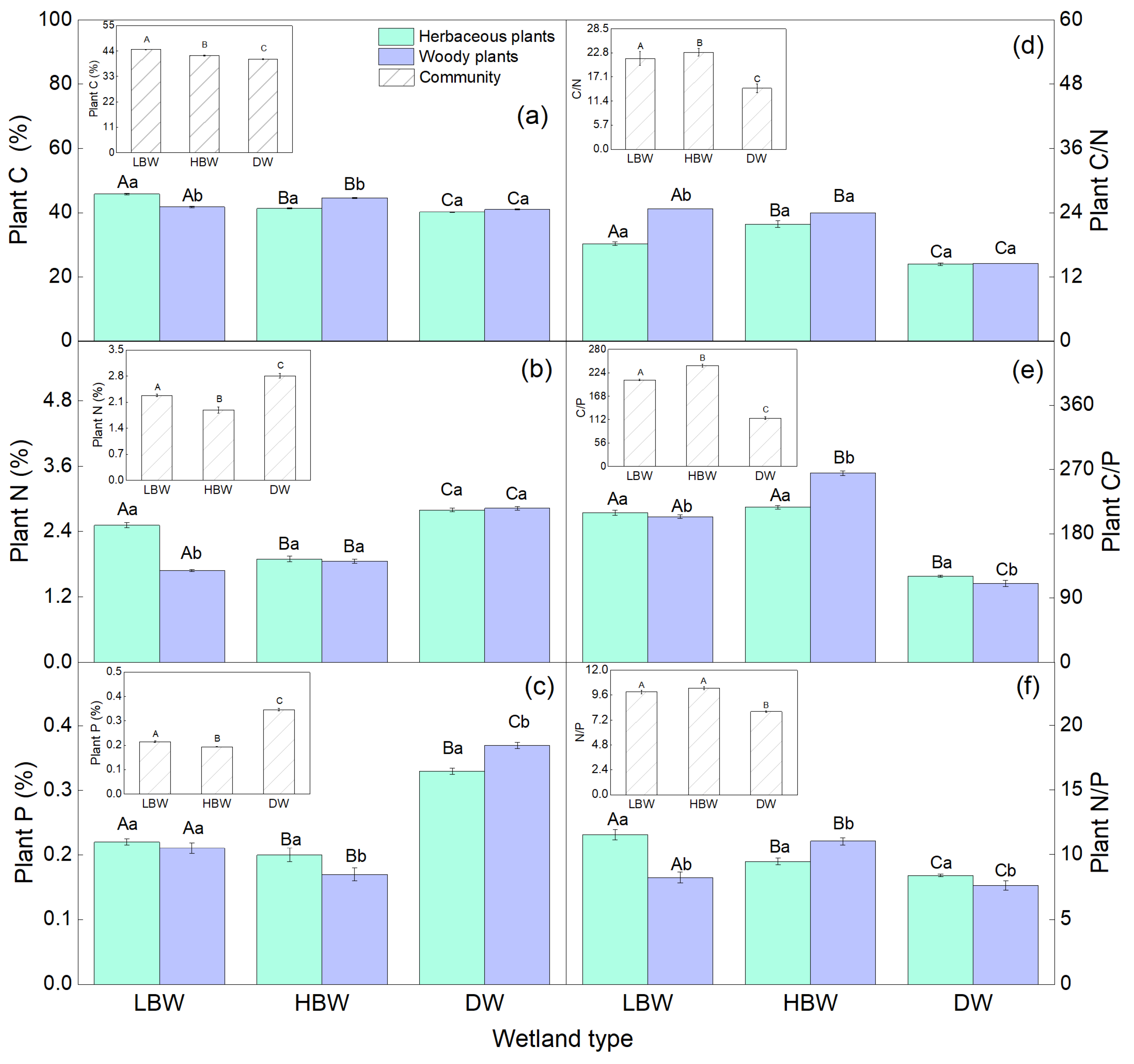


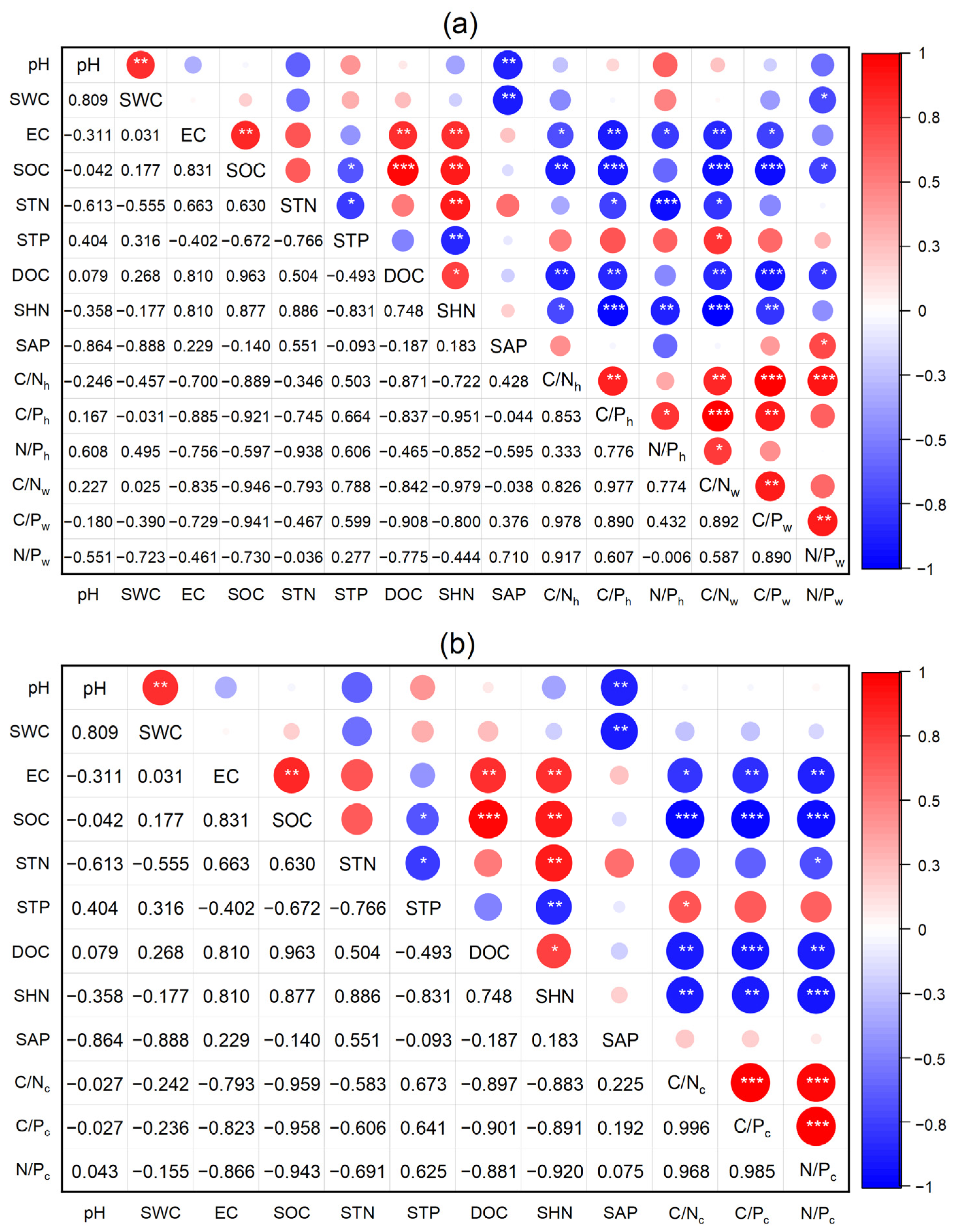

| Wetland Type | Plant Species | Life Form | Growth Cycle | Family |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LBW | Tamarix chinensis | Woody | Perennial | Tamaricaceae |
| Periploca sepium | Woody | Perennial | Apocynaceae | |
| Salix matsudana | Woody | Perennial | Salicaceae | |
| Phragmites australis | Herbaceous | Perennial | Gramineae | |
| Eleusine indica | Herbaceous | Annual | Gramineae | |
| Rumex acetosa | Herbaceous | Perennial | Polygonaceae | |
| Persicaria lapathifolia | Herbaceous | Annual | Polygonaceae | |
| Typha orientalis | Herbaceous | Perennial | Typhaceae | |
| HBW | Tamarix chinensis | Woody | Perennial | Tamaricaceae |
| Phragmites australis | Herbaceous | Perennial | Gramineae | |
| Persicaria lapathifolia | Herbaceous | Annual | Polygonaceae | |
| Typha orientalis | Herbaceous | Perennial | Typhaceae | |
| Polygonum aviculare | Herbaceous | Annual | Polygonaceae | |
| DW | Tamarix chinensis | Woody | Perennial | Tamaricaceae |
| Salix matsudana | Woody | Perennial | Salicaceae | |
| Phragmites australis | Herbaceous | Perennial | Gramineae | |
| Chenopodium album | Herbaceous | Annual | Amaranthaceae | |
| Cynodon dactylon | Herbaceous | Perennial | Gramineae | |
| Klasea centauroides | Herbaceous | Perennial | Asteraceae |
| Index | Variables | pH | EC | SWC | SOC | STN | STP | C/NS | C/PS | N/PS | DOC | SHN | SAP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | W | 21.86 | 1.25 | 55.73 | 26.67 | 17.04 | 3.50 | 11.96 | 27.96 | 62.87 | 18.74 | 206.40 | 10.62 |
| S | 22.43 | 12.45 | 0.61 | 6.51 | 46.78 | 15.38 | 0.46 | 4.76 | 106.51 | 1.77 | 254.50 | 19.98 | |
| W × S | 10.93 | 11.92 | 0.72 | 30.18 | 15.24 | 8.96 | 3.77 | 21.90 | 49.79 | 1.92 | 137.70 | 5.52 | |
| p value | W | <0.001 | 0.320 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.064 | 0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.002 |
| S | <0.001 | 0.004 | 0.450 | 0.025 | <0.001 | 0.002 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.208 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| W × S | 0.002 | 0.001 | 0.507 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.004 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.189 | <0.001 | 0.020 |
| Parameters | LBW | HBW | DW | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–15 cm | 15–30 cm | 0–15 cm | 15–30 cm | 0–15 cm | 15–30 cm | |
| pH | 7.42 ± 0.01 Aa | 7.61 ± 0.00 Ab | 7.12 ± 0.08 Ba | 7.53 ± 0.08 Ab | 7.22 ± 0.00 ABa | 7.18 ± 0.01 Bb |
| EC (µS cm−1) | 226.99 ± 34.26 Aa | 214.93 ± 36.15 ABa | 245.30 ± 38.51 Aa | 253.50 ± 2.31 Aa | 379.50 ± 17.61 Ba | 147.30 ± 14.02 Bb |
| SWC (%) | 25.33 ± 1.91 Aa | 30.24 ± 2.29 Aa | 9.40 ± 0.19 Ba | 5.86 ± 0.58 Ba | 20.95 ± 0.92 Aa | 18.54 ± 1.37 Ca |
| DOC (mg kg−1) | 328.89 ± 34.91 Aa | 716.21 ± 42.51 Ab | 253.86 ± 5.02 Aa | 191.90 ± 10.53 Bb | 484.70 ± 40.09 Ba | 606.98 ± 10.59 Cb |
| SHN (mg kg−1) | 22.17 ± 0.36 Aa | 15.78 ± 1.07 Ab | 52.22 ± 0.43 Ba | 33.40 ± 1.92 Bb | 148.76 ± 8.27 Ca | 33.04 ± 2.12 Bb |
| SAP (mg kg−1) | 3.86 ± 0.97 Aa | 3.87 ± 0.86 Aa | 9.43 ± 0.85 Ba | 4.79 ± 0.83 Ab | 6.54 ± 0.04 ABa | 3.30 ± 0.10 Ab |
| Index | Variables | CP | NP | PP | C/NP | C/PP | N/PP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | W | 41.94 | 56.81 | 65.00 | 24.83 | 14.81 | 16.72 |
| G | 1.36 | 13.86 | 0.41 | 90.56 | 45.99 | 17.33 | |
| W × G | 52.42 | 13.63 | 26.04 | 60.47 | 63.27 | 16.34 | |
| p value | W | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| G | 0.330 | <0.001 | 0.535 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| W × G | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, C.; Li, Y.; Gao, J.; Wang, X. Characteristics of Soil and Plant Ecological Stoichiometry of Carbon, Nitrogen, and Phosphorus in Different Wetland Types of the Yellow River. Sustainability 2025, 17, 3276. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17073276
Yan C, Li Y, Gao J, Wang X. Characteristics of Soil and Plant Ecological Stoichiometry of Carbon, Nitrogen, and Phosphorus in Different Wetland Types of the Yellow River. Sustainability. 2025; 17(7):3276. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17073276
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Chuang, Yuanyuan Li, Jinjuan Gao, and Xiaoyan Wang. 2025. "Characteristics of Soil and Plant Ecological Stoichiometry of Carbon, Nitrogen, and Phosphorus in Different Wetland Types of the Yellow River" Sustainability 17, no. 7: 3276. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17073276
APA StyleYan, C., Li, Y., Gao, J., & Wang, X. (2025). Characteristics of Soil and Plant Ecological Stoichiometry of Carbon, Nitrogen, and Phosphorus in Different Wetland Types of the Yellow River. Sustainability, 17(7), 3276. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17073276






