1. Introduction
The digital economy has fundamentally reshaped industries worldwide, unimaginably driving innovation, efficiency, and sustainability [
1]. Recently, the digital economy has been driving global economic growth, with businesses leveraging digital tools to enhance productivity, reach new markets, and create value in once-unimaginable ways. As digital technologies evolve, they reshape industries and challenge traditional economic structures, making the digital economy a central element in shaping the future of global business and sustainability [
2]. It transformed traditional business models by enabling more excellent connectivity, efficiency, and scalability. Among the various forces in digital transformation, green innovation, and technology adoption have emerged as pivotal factors in advancing sustainability [
3]. As the global awareness of environmental issues intensifies, businesses are increasingly called upon to integrate environmentally friendly practices into their operations. Adopting green innovations and technologies contributes to ecological sustainability and aligns with the growing demand from consumers, governments, and stakeholders for businesses to embrace more responsible and sustainable practices [
4]. In the context of the digital economy, these green practices are often fueled by advancements in digital technologies, making it critical to understand how they interact and impact overall business success [
5].
A prime example of this transformation can be seen in BYD (Build Your Dreams), one of the world’s largest electric vehicle (EV) manufacturers [
6]. BYD has successfully integrated green innovation and technology adoption into its business strategy. The company’s adoption of cutting-edge battery technology and energy-efficient manufacturing processes has significantly reduced carbon emissions while enhancing operational efficiency. By leveraging digital economy integration (DEI), BYD has optimized its supply chain and improved production forecasting through AI-driven analytics. These green innovations have strengthened the company’s financial performance and positioned it as a leader in sustainable mobility, enhancing its corporate reputation and competitive advantage [
7]. This case exemplifies how green innovation and technology can drive environmental and financial success within the digital economy.
China is the largest manufacturer in the world and a global leader in technological innovation because of its potential to influence sustainable practices on a massive scale. The country is increasingly adopting digital solutions, such as artificial intelligence, big data, and cloud computing, to optimize manufacturing processes and reduce environmental impact [
8]. At the same time, China’s commitment to green development and environmental sustainability has led to policies encouraging the adoption of green technologies, particularly in the energy, transportation, and industrial sectors [
9]. The convergence of these digital and green initiatives presents a powerful opportunity for businesses to integrate sustainability into their operations while navigating the pressures of a competitive global market. This dynamic environment makes China ideal for studying how traditional industries can innovate and implement green technologies within the evolving digital economy. The automotive industry in China is undergoing a significant transformation driven by rapid digitalization, sustainability, and innovation advancements [
10]. With the government’s strong push towards reducing carbon emissions, promoting energy efficiency, and accelerating the adoption of electric mobility, Chinese automakers are increasingly investing in green technologies and digital solutions [
11].
For instance, state-owned and private automotive firms in China operate under different regulatory frameworks, ownership structures, and financial incentives, which shape their ability to invest in and implement green technologies. State-owned enterprises (SOEs) often benefit from government subsidies and policy support, enabling large-scale EV production and infrastructure development [
12]. In contrast, private firms may face higher financial constraints and competitive pressures, influencing their investment strategies and risk appetite in adopting green innovations. Additionally, the transition to electric vehicles (EVs) is heavily shaped by national policies, such as subsidies, carbon credit trading, and infrastructure investments, which mediate the speed and scope of green technology adoption across the sector. By contextualizing these industry-specific factors that mediate GIA/GTA, we can better understand how state ownership, market orientation, and regulatory environments interact with corporate entrepreneurship and financial capabilities to influence digital and green transformation.
The relationship between green innovation and technology adoption is complex and multifaceted. While GIA typically introduces novel ideas and practices that reduce environmental impact, GTA focuses on implementing and using technological solutions to minimize adverse environmental effects. Together, they form the foundation for companies aiming to operate sustainably within the digital economy. A creative enterprise characterized by a company’s capacity for innovative thinking and entrepreneurial spirit is crucial in transforming abstract green innovations into practical, marketable technologies [
13]. Moreover, the financial resources available to an organization significantly affect its ability to adopt and scale green technologies, as these technologies often require substantial investment in research, infrastructure, and implementation. However, the successful adoption of green innovations and technologies does not occur in isolation [
14]. Factors such as creative enterprise and financial capability influence how these innovations and technologies are embraced and integrated into business practices.
The automotive industry in Guangdong, China, is a compelling case study for this research due to its significance in manufacturing and technological advancement. Known for its robust industrial base and leadership in technological development, Guangdong provides a unique context to examine how companies within traditional industries, such as automotive manufacturing, can leverage digital and green technologies to address pressing environmental challenges [
15]. While several studies have explored the relationship between green innovation adoption (GIA) and green technology adoption (GTA) within industries such as textiles and fashion or have examined the construction industry to explore innovative design and digital transformation, there is a notable gap in research focusing on GTA and GIA within the automotive sector, particularly in Guangdong’s rapidly evolving digital economy. This gap presents an opportunity to extend the existing literature by exploring how creative enterprise (CE) and financial capability (FC) mediate and moderate the relationship between GIA and GTA in the context of the digital economy. While there has been substantial research on creative enterprises, many studies overlook their role as a mediator in the relationship between green innovation and technology adoption. Moreover, several studies have considered financial capability primarily as a dependent variable, particularly with Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR), without exploring its moderating role in adopting sustainable practices and technologies. This leaves a significant gap in understanding the combined impact of environmental sustainability, innovation adoption, and technology integration within the digital economy. This study addresses these gaps by examining the role of green innovation and technology adoption within the digital economy. It focuses on how creative enterprise mediates and how financial capability moderates its effects. The conceptual framework of
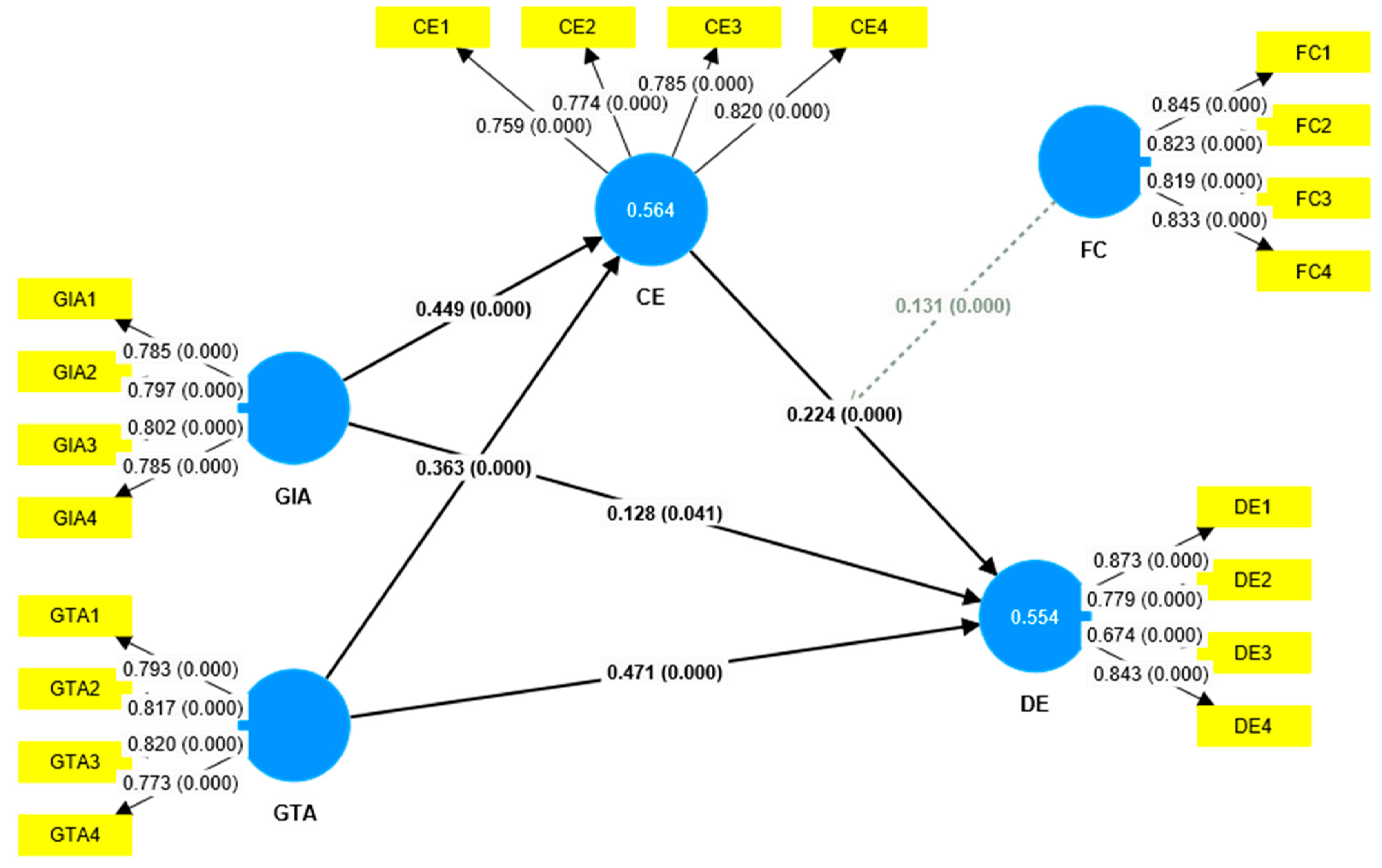
Figure 1 illustrates the dynamic interplay between GIA, GTA, creative enterprise, and financial capability within the context of the DE. The research will provide novel insights into how these factors influence adopting sustainable practices and technologies in the automotive industry, specifically in Guangdong, China. By doing so, this study will contribute to both theoretical understanding and practical applications for companies aiming to navigate sustainability challenges in a rapidly digitalizing world. In light of the above discussion, this study seeks to address the following research questions:
How do green innovation adoption (GIA) and green technology adoption (GTA) influence the digital economy in the automotive industry?
In what ways does creative enterprise (CE) mediate the relationship between GIA, GTA, and the digital economy?
How does financial capability (FC) moderate the relationship between creative enterprise and the digital economy?
This study contributes significantly to three key areas: First, this study addresses the gaps in understanding green innovation adoption (GIA) and green technology adoption (GTA) within the digital economy, particularly in the automotive industry. By integrating environmental sustainability, innovation adoption, and digital transformation, the research offers a holistic perspective on how traditional industries can leverage green and digital technologies to achieve sustainability goals. This aligns with existing literature on sustainable innovation but expands the discussion by contextualizing it within the automotive sector’s transition toward a greener future. Second, this research investigates the mediating role of creative enterprise and the moderating effect of financial capability in this relationship. While previous studies have explored innovation adoption and financial capability separately, this study uniquely positions creative enterprise as a mediator and financial capability as a moderator. The findings provide fresh insights into their impact on adopting sustainable practices and technologies, highlighting the synergistic link between these elements. By integrating these perspectives, this study builds on prior research while offering novel insights into how these factors collectively influence the digital economy. Third, grounded in the Dynamic Capability Theory (DCT), our findings emphasize the need for a holistic approach to the digital economy. By integrating GIA and GTA, this study provides a robust framework to understand how firms respond to the dual imperatives of sustainability and digital transformation. This theoretical perspective enhances previous discussions on dynamic capabilities by demonstrating how firms develop resilience through green innovation. Moreover, by offering region-specific insights, this study contributes to both theoretical advancements and practical strategies for fostering sustainable development in the rapidly evolving digital economy.
The structure of this paper is as follows: The next section provides a comprehensive review of the relevant literature, laying the foundation for the study. The third section introduces the proposed mechanism and hypotheses. The fourth section presents the development of the research model and the selection of key variables. The fifth section examines the variations in the progress of the digital economy across different regions. The sixth section details the empirical research, including the methodology, findings, and interpretations of the data analysis. Finally, the last section summarizes the key research findings and offers practical recommendations and insights.
Conceptual Model Legends
Table 1 provides an overview of the key constructs and their definitions.
3. Discussion
This study explores the dynamic role of green innovation adoption (GIA) and green technology adoption (GTA) within the digital economy (DE), focusing on how creative enterprise and financial capability mediate and moderate the implementation of environmentally friendly innovation and technology. Grounded in Dynamic Capability Theory (DCT), which emphasizes a firm’s ability to sense opportunities, seize them, and reconfigure resources to adapt to environmental and technological changes, the research investigates how businesses can strategically address sustainability challenges in the evolving digital landscape. By examining the interconnectedness of green practices, creativity, and financial resources, this study aims to provide insights into how firms can leverage their dynamic capabilities to drive environmental sustainability and economic growth. The hypotheses proposed were empirically validated, with significant results showing how these capabilities enhance businesses’ ability to innovate, adapt, and thrive in the digital era.
The findings of this study indicate that green innovation adoption (GIA) has a positive and significant impact on the digital economy (DE). This aligns with the work of [
80], which emphasizes the importance of integrating environmentally sustainable technology to drive economic progress within the digital environment. Similarly, Hashem and Aboelmaged (2023) [
81] organizations adopting environmentally responsible technologies showed superior performance in DE, further reinforcing that sustainability practices play a crucial role in the modern, technology-driven landscape. The increasing importance of sustainable practices in the digital age underscores their contribution to innovation and economic growth. These results deepen our understanding of the complex relationship between the adoption of green innovation and the successful transformation of businesses within the DE, highlighting how sustainability drives both competitive advantage and long-term performance.
The results also reveal that green technology adoption (GTA) significantly impacts the digital economy (DE). These findings align with previous research, such as the work by [
82], highlighting eco-friendly technologies’ transformative potential across various sectors. Similarly, the research conducted by [
83] emphasized the role of sustainable practices in driving digital advancements, establishing a favorable correlation between adopting environmentally friendly technology and economic development. Furthermore, Sahoo and Kumar (2023) [
84] underscored the importance of integrating green technology for achieving long-term economic and environmental sustainability, advocating for governments and businesses to prioritize such technologies. Building on these prior studies, our research reinforces the argument for incorporating environmentally responsible technologies into the digital realm, thereby contributing to both the academic literature and the practical understanding of sustainable digital innovation.
The findings of this study demonstrate that green innovation adoption (GIA) has a positive and significant impact on creative enterprises. This result is consistent with existing literature, which emphasizes the catalytic role of environmental innovation in fostering creativity and promoting sustainable business practices, as evidenced by the work of [
85]. Additionally, it aligns with empirical studies, such as those by [
86], which shows the positive impact of green innovation on organizational performance, particularly in enhancing environmental sustainability and internal innovative practices. The results highlight how green innovation stimulates creative thinking within organizations, driving the development of new ideas and solutions that contribute to environmental goals and improve long-term sustainability and operational efficiency. This underscores the potential of GIA to serve as a key driver of innovation and sustainability in modern business environments.
Based on the available evidence, green technology adoption (GTA) positively and significantly impacts creative enterprises. The results of [
87] highlight the significant role of incorporating environmentally sustainable technology in fostering innovation and creativity within organizations. These findings are consistent with the present study, demonstrating the beneficial effects of green technology adoption on organizational creativity. Moreover, the favorable correlation between green technology adoption and creativity, as highlighted by [
88], aligns with the broader body of research on this topic. The results indicate that using green technology leads to positive environmental outcomes and acts as a catalyst for driving innovative initiatives within organizations. This underscores the dynamic relationship between sustainability, innovation, and organizational creativity, positioning GTA as a key driver in the evolving landscape of sustainable business practices and innovation.
The findings reveal that creative enterprises significantly and positively influence the digital economy (DE). This is consistent with earlier studies, such as those by [
89], which highlight the crucial role of creative activities in promoting digital economic growth. Similarly, Zhou et al. (2022) [
90] emphasizes the strong connection between creative entrepreneurship and digital economic success, suggesting that creative efforts play a key role in fostering economic development in the digital era. To provide a more comprehensive understanding, this study acknowledges that CE is not a unidimensional construct but rather consists of multiple interrelated aspects, including entrepreneurial creativity, technological adaptability, and innovation capacity. These dimensions enable organizations to navigate digital transformation, implement green innovations, and enhance market responsiveness. While our study measured CE through four key items, we recognize the need for more refined, multi-dimensional scales that capture its dynamic and evolving nature. The positive impact observed in this study underscores the importance of encouraging creativity within organizations as a strategic method for adapting to and thriving in the ever-evolving DE. This highlights the value of creative enterprises in establishing a competitive edge, helping organizations navigate the complexities of the digital world, and driving sustained economic growth.
The findings of this study show that creative enterprise has a positive and significant impact on the digital economy (DE). Previous research, such as the study by [
91], has demonstrated that creativity plays a crucial role in developing novel digital technologies and driving economic growth. This aligns with earlier studies by [
92], highlighting the positive relationship between creative entrepreneurship and DE. The confirmed positive impact further strengthens the argument that creative pursuits are integral to economic expansion in the digital era. It underscores the importance of nurturing creative processes within organizations as a key strategy for achieving success and maintaining competitiveness in the rapidly evolving digital landscape.
The results indicate that creative enterprise mediates the relationship between green innovation adoption (GIA) and the digital economy (DE). This aligns with previous research, such as the study by [
93], which emphasizes the significant role of creative processes in converting sustainable practices into economic advantages. Additionally, it supports the existing body of work on innovation and sustainability, as demonstrated by [
94], highlighting innovative enterprises’ crucial role in linking green innovation to positive economic outcomes. These findings strengthen the argument that creative enterprises serve as intermediaries, facilitating the positive impacts of green innovation on digital economic outcomes. The mediating role of creative business practices has been empirically validated, offering a deeper understanding of the complex dynamics between green innovation adoption and DE. This underscores the essential function of creativity in bridging the gap between sustainability and economic prosperity in the digital era.
The study’s findings indicate that creative enterprise positively mediates the relationship between green technology adoption (GTA) and the digital economy (DE). This aligns with existing scholarly research, such as the investigation by [
23], which emphasizes the intermediary function of creative processes in driving the positive outcomes of incorporating green technology to advance the DE. Similarly, the results align with the [
95] study, which underscores the positive correlation between creative entrepreneurship and DE. The confirmed significance of creative entrepreneurship as an intermediary between the adoption of green technology and the DE adds a layer of complexity to this relationship, highlighting the influential role of creativity in linking sustainable practices with economic prosperity. These findings reinforce the idea that creative enterprises are essential for fostering the transition to a more sustainable and economically robust digital economy.
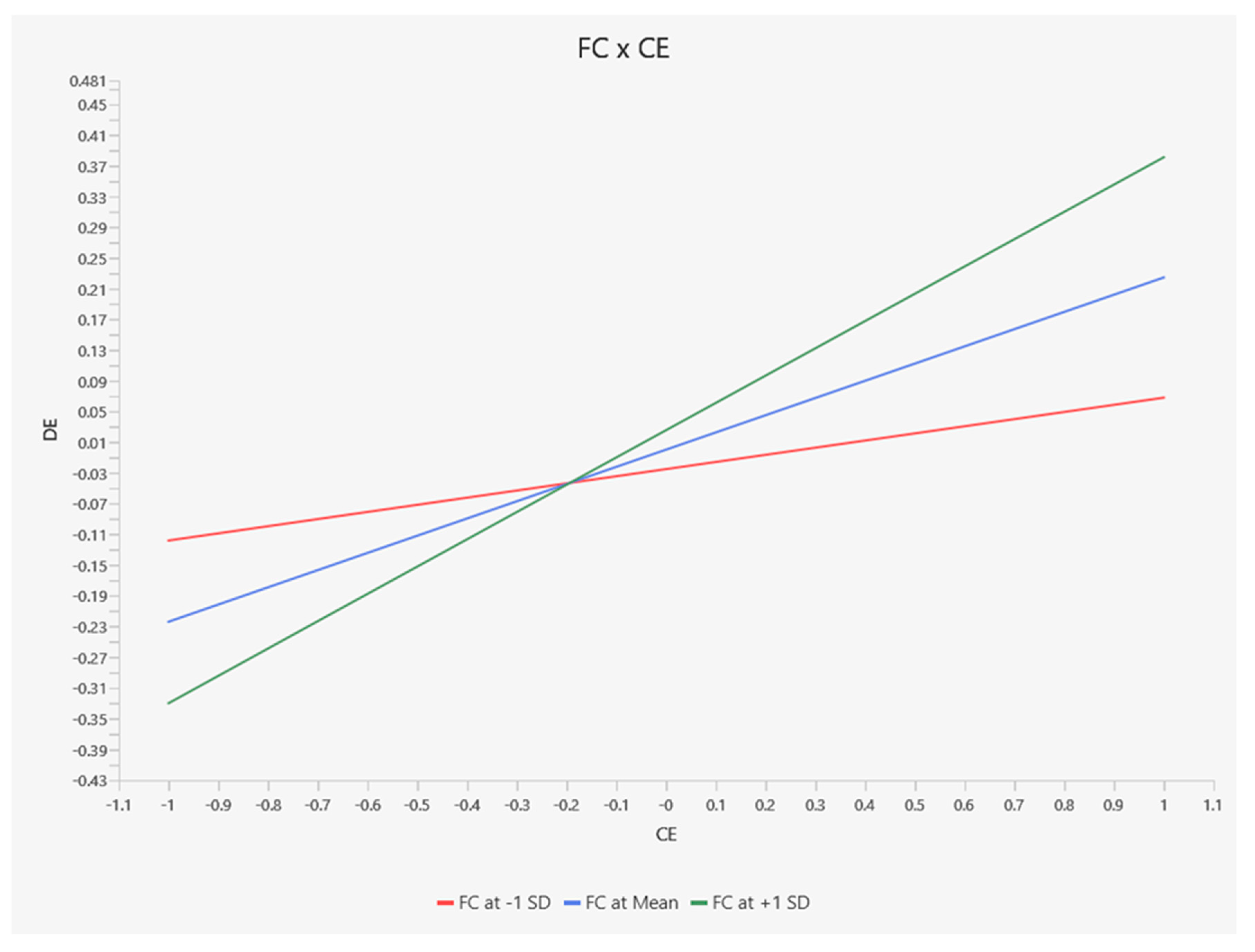
The findings indicate that financing capability significantly moderates the relationship between creative enterprises and the digital economy (DE). This conclusion aligns with previous research by [
96], highlighting the importance of financial capabilities in determining the impact of creative endeavors on digital economic outcomes. Additionally, this aligns with the study by [
21], which emphasized financial capabilities’ influential role in shaping corporate strategies and broader economic dynamics. The moderating influence of financing capabilities further enriches our understanding of how financial resources can impact the performance of creative enterprises within the DE. These findings underscore the crucial role that financial support plays in fostering the success of creative activities, ultimately driving economic growth and innovation in the digital era.
4. Theoretical and Practical Implications of the Study
4.1. Theoretical Implications
This study enriches the existing body of knowledge by illustrating the synergies between sustainable practices, innovation adoption, and economic growth in the DE. The findings underscore the pivotal role of green innovation in promoting economic prosperity through environmentally sustainable practices. Similarly, the transformative potential of adopting sustainable technologies to foster creativity within organizations aligns with this study’s findings on green technology’s positive impact on enterprise creativity.
As revealed in this study, the mediating role of creative enterprises contributes to a more nuanced understanding of how green innovation drives economic outcomes ascertaining that innovation serves as a bridge between sustainability and economic growth. Furthermore, the moderating role of Financial Capability introduces new dimensions to theoretical frameworks, emphasizing its significance in amplifying the impact of creative endeavors on economic outcomes.
This study contributes to multiple theoretical domains, including environmental sustainability, innovation adoption, and the DE. It underscores the necessity of incorporating creative enterprises into theoretical models that explore the green-digital nexus, particularly given the role of financial capacity in enhancing this relationship. Integrating these perspectives deepens our understanding of how businesses can navigate the complexities of sustainability and digital transformation.
4.2. Practical Implications
From a practical standpoint, the findings offer actionable insights for organizations striving to balance sustainability with economic growth in the digital era. The demonstrated positive impact of GIA and GTA on the DE highlights the importance of prioritizing environmentally sustainable practices and technological advancements. This entails integrating green innovation as a core strategy to enhance creativity and organizational performance for businesses.
The mediating role of creative enterprises suggests that fostering innovation within organizations can amplify the benefits of green practices, enabling businesses to achieve greater economic and environmental outcomes. Furthermore, the moderating role of financial capability underscores the necessity of robust financial strategies to support creative processes. Organizations are encouraged to allocate financial resources effectively to strengthen the link between creativity and digital economic success.
These insights are particularly valuable for enterprises operating in digital commerce, where sustainability challenges and opportunities coexist. Businesses can optimize their operations by leveraging green innovation, creative thinking, and financial resources while contributing to broader environmental and economic objectives.
5. Conclusions
This study sheds light on the dynamic roles of green innovation adoption (GIA) and green technology adoption (GTA) in the digital economy (DE), emphasizing the mediating influence of creative enterprises and the moderating role of financial capability. The findings highlight GIA’s positive and significant effects on both the DE and creative enterprises, reinforcing the value of integrating sustainable practices within the digital business landscape. Prior studies, such as [
97], underscore the catalytic role of creativity in transforming sustainable practices into measurable economic benefits, a notion further supported by this research. Creative enterprises act as intermediaries, enhancing the impact of GIA on the DE, as proposed by [
98]. This underscores the importance of fostering innovation within organizations to maximize the benefits of environmentally friendly initiatives on economic outcomes. While GIA demonstrated significant effects, the results suggest that GTA has an insignificant direct impact on the DE, as evidenced by the lack of statistical significance. This finding calls for a deeper and more nuanced exploration of the mechanisms by which the adoption of environmentally sustainable technology influences the DE. Future research should aim to unravel these complex relationships, furthering our understanding of how green technologies can contribute to digital economic growth.
The study also highlights the critical role of financial capability in moderating the relationship between creative enterprises and the DE. Organizations operating in the DE must strategically allocate financial resources to amplify the impact of creative initiatives on long-term economic development. By addressing this interplay between financial capability, creativity, and sustainability, businesses can navigate the challenges of the digital era while maintaining their commitment to environmental stewardship.
In conclusion, this study significantly contributes to understanding how creative and environmentally sustainable business practices can drive success in the digital age. Organizations can achieve economic growth by integrating innovation, sustainability, and strategic resource management while addressing global environmental challenges. Future research should explore additional dimensions of this interplay to provide a more comprehensive understanding of sustainable business practices in the DE.
6. Limitations and Future Study
This study acknowledges several limitations that warrant careful consideration when interpreting its findings. Firstly, the research relies on a cross-sectional questionnaire survey to test and confirm the hypotheses. While this approach provides valuable insights, it limits the ability to infer causation among the variables. The evolving dynamics of Green Innovation Adoption (GIA) and Green Technology Adoption (GTA), particularly across different stages of growth in the creative industry in China, are not fully captured. To address this limitation, future research should adopt a longitudinal approach to examine these relationships over time, offering a more comprehensive understanding of how these factors interact and evolve. Additionally, external factors, like government policies and market competition, could influence the relationship between green innovation adoption (GIA) and the digital economy (DE), yet they were not considered in the model. Future studies could employ instrumental variable techniques or control variables to account for unobserved factors like government regulations, industry dynamics, and market competition. Secondly, this study’s sample is confined to automotive industries in China. This focus, while insightful, limits the generalizability of the findings to other industries and geographical contexts. Organizations seeking to apply these results should be mindful of potential variations in factors affecting outcomes and performance in different sectors. Technology maturity levels, decision-making processes, and adoption strategies are likely to vary across nations and industries. Future studies should expand the research model to include a broader spectrum of businesses and regions to overcome this limitation. Conducting similar research in diverse national and industrial contexts will facilitate comparative analyses and provide richer insights. By exploring these dynamics across a broader range of organizations, researchers can uncover industry-specific and region-specific factors that influence the impact of GIA and GTA on creative enterprises and the digital economy. Finally, replicating this study in different countries and industries would enhance its applicability and provide a more robust understanding of the interplay between environmental sustainability, innovation, and economic growth. Such efforts would contribute to developing universally applicable frameworks and strategies for fostering green practices and innovation in the global digital economy.