A New Endogenous Direction Selection Mechanism for the Direction Distance Function Method Applied to Different Economic–Environmental Development Modes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Preliminaries
2.1. Weak Disposability
2.2. Exogenous DDF
2.3. Endogenous DDF
3. Methodology
3.1. Economic Concern Model (ECM1)
3.2. Environmental Concern Model (ECM2)
3.3. Coordinated Development Model (CDM)
3.4. Priority Development Model (PDM)
3.4.1. Optimal Efficiency Priority Development Model (OPDM)
3.4.2. Non-Optimal Efficiency Priority Development Model (NPDM)
3.4.3. Non-Optimal Environmental Efficiency Priority Development Model (NEPDM)
4. Illustrative Examples
4.1. Variable Selection and Data Sources
4.2. Comparison of Emission Reduction Potential Under Extended DDF Models
4.3. Comparison of Economic Growth Potential Under Extended DDF Models
4.4. Comparison of Improved Path Under Extended DDF Models
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Daniel, A.; Du, J.G.; Stephen Ntiri, A.; Agnes, A. Energy generation and carbon dioxide emission-The role of renewable energy for green development. Energy Rep. 2024, 12, 1420–1430. [Google Scholar]
- Pittman, R.W. Multilateral productivity comparisons with undesirable outputs. Econ. J. 1983, 93, 883–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stergiou, E. The effect of heterogeneity on environmental efficiency: Evidence from European industries across sectors. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 441, 141036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano, S.; Gutiérrez, E.; Aguilera, E. Environmental efficiency of rainfed and irrigated wheat crops in Spain. A stochastic DEA metafrontier approach. OR Spectr. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, Y.H.; Färe, R.; Grosskopf, S. Productivity and undesirable outputs: A directional distance function approach. J. Environ. Manag. 1997, 51, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, R.; Chung, Y.H.; Färe, R. Profit, Directional distance functions, and Nerlovian efficiency. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 1998, 98, 351–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Bi, X.; Li, C.H.; Xu, X.H.; Jing, L.; Chen, J.L. A united framework modeling of spatial-temporal characteristics for county-level agricultural carbon emission with an application to Hunan in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 364, 121321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, X.Y. Carbon emission efficiency measurement and influencing factor analysis of nine provinces in the Yellow River basin: Based on SBM-DDF model and Tobit-CCD model. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 33263–33280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.W.; Zhang, C.J.; Zhou, Y. Spatio-temporal evolution characteristics and influencing factors of carbon emission reduction potential in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 59925–59944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Pan, Y.B.; Ding, T.; Wu, H.Q.; Deng, G.W. A three-level meta-frontier directional distance function approach for carbon emission efficiency analysis in China: Convexity versus non-convexity. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2024, 62, 6493–6517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, M.M.; Ji, D.D.; Han, C.F.; Liu, P.H. Optimizing the Allocation of CO2 Emission Rights in the Yangtze River Delta City Agglomeration Region of China Based on Equity, Efficiency and Sustainability. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2025, 19, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.B.; Hailu, A.; You, C.Y. A critical review of distance function based economic research on China’s marginal abatement cost of carbon dioxide emissions. Energy Econ. 2019, 84, 104533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wang, Y.M. Game directional distance function in meta-frontier data envelopment analysis. Omega 2023, 121, 102935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulati, R. Global and local banking crises and risk-adjusted efficiency of Indian banks: Are the impacts really perspective-dependent? Q. Rev. Econ. Financ. 2022, 84, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbero, J.; Zofío, J.L. The measurement of profit, profitability, cost and revenue efficiency through data envelopment analysis: A comparison of models using BenchmarkingEconomicEfficiency.jl. Socio-Econ. Plan. Sci. 2023, 89, 101656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nepomuceno, T.C.C.; Agasisti, T.; Bertoletti, A.; Daraio, C. Multicriteria panel-data directional distances and the efficiency measurement of multidimensional higher education systems. Omega 2024, 125, 103044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Ji, D.J.; Zha, D.L.; Zhou, D.Q.; Zhou, P. A nonparametric distance function approach with endogenous direction for estimating marginal abatement costs of CO2 emissions. J. Manag. Sci. Eng. 2022, 7, 330–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.L.; Hu, S.; Li, J.L. Using machine learning to model technological heterogeneity in carbon emission efficiency evaluation: The case of China’s cities. Energy Econ. 2022, 114, 106238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Färe, R.; Grosskopf, S.; Lovell, C.; Pasurka, C. Multilateral Productivity Comparisons When Some Outputs are Undesirable: A nonparametric Approach. Rev. Econ. Stat. 1989, 71, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, S.; Fujii, H.; Sawazy, N.; Fjikura, R. Financial allocation strategy for the regional pollution abatement cost of reducing sulfur dioxide emissions in the thermal power sector in China. Energ. Policy 2010, 38, 2131–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Färe, R.; Grosskopf, S.; Whittaker, G. Directional output distance functions: Endogenous directions based on exogenous normalization constraints. J. Prod. Anal. 2013, 40, 267–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampf, B.; Krüger, J.J. Optimal directions for directional distance functions: An exploration of potential reductions of greenhouse gases. Am. J. Agric. Econ. 2015, 97, 920–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, F.S.; Anwar, A.; Hsu, C.C.; Sharif, A.; Razzaq, A.; Sinha, A. The role of information and communication technology in encountering environmental degradation: Proposing an SDG framework for the BRICS countries. Technol. Soc. 2021, 65, 101587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Wu, J.; Cook, W.D.; Zhu, J. Alternative secondary goals in DEA cross-efficiency evaluation. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2008, 113, 1025–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troutt, M.D. Derivation of the maximin efficiency ratio model from the maximum decisional efficiency principle. Ann. Oper. Res. 1997, 73, 323–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.C.; Wu, J.; Zhu, Q.Y.; Pan, Y.H. Fixed cost allocation based on data envelopment analysis from inequality aversion perspectives. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2024, 313, 281–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Zhao, T.; Xia, H.M.; Cui, X.Y.; Li, Z.Y. Allocation of carbon emission quotas in Chinese provinces based on Super-SBM model and ZSG-DEA model. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2021, 23, 2285–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.X.; Jin, W.X.; Yang, G.L.; Li, H.; Ke, Y.J.; Philbin, S.P. Optimizing regional allocation of CO2 emissions considering output under overall efficiency. Socio-Econ. Plan. Sci. 2021, 77, 101012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.Z.; Hao, J.X.; Wang, C.A.; Tang, X.; Yuan, X.Z. Embodied CO2 emissions and efficiency of the service sector: Evidence from China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 247, 119116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikheeva, N. Qualitative Aspect of the Regional Growth in Russia: Inclusive Development Index. Reg. Sci. Policy Pract. 2020, 12, 611–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreica, R.; Jaradat, M. Analysis of economic development and sustainable development of Romania. Metal. Int. 2011, 16, 9–12. [Google Scholar]






| Authors | Year | Input | Output |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chen et al. [27] | 2021 | (1) Labor, (2) Asset, (3) Energy | (1) GDP, (2) CO2 emission |
| Li et al. [9] | 2021 | (1) Labor, (2) Capital, (3) Energy consumption | (1) GDP, (2) CO2 emission |
| Zhang et al. [28] | 2021 | (1) Labor, (2) Energy consumption | (1) GDP, (2) CO2 emission |
| Wang et al. [29] | 2020 | (1) Labor, (2) Capital stock, (3) Energy consumption | (1) Value-added, (2) CO2 emission |
| City | DDF | ECM1 | ECM2 | CDM | OPDM | NPDM | NEPDM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Tianjin | 0.50 | 0.03 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.41 | 0.50 | 0.54 |
| Hebei | 0.67 | 0.17 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.68 | 0.66 | 0.78 |
| Shanxi | 0.83 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.86 | 0.83 | 0.90 |
| Inner Mongolia | 0.80 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.81 | 0.80 | 0.86 |
| Liaoning | 0.69 | 0.32 | 0.11 | 0.11 | 0.69 | 0.69 | 0.78 |
| Jilin | 0.46 | 0.14 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.54 | 0.46 | 0.68 |
| Heilongjiang | 0.63 | 0.30 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.62 | 0.63 | 0.73 |
| Shanghai | 0.14 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.13 | 0.14 | 0.14 |
| Jiangsu | 0.35 | 0.10 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.29 | 0.35 | 0.37 |
| Zhejiang | 0.38 | 0.10 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.25 | 0.38 | 0.42 |
| Anhui | 0.58 | 0.41 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.47 | 0.58 | 0.64 |
| Fujian | 0.30 | 0.10 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.18 | 0.30 | 0.41 |
| Jiangxi | 0.47 | 0.15 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.31 | 0.47 | 0.52 |
| Shandong | 0.61 | 0.39 | 0.14 | 0.14 | 0.57 | 0.61 | 0.70 |
| Henan | 0.45 | 0.25 | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.46 | 0.45 | 0.63 |
| Hubei | 0.46 | 0.18 | 0.11 | 0.10 | 0.33 | 0.46 | 0.56 |
| Hunan | 0.41 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.24 | 0.41 | 0.46 |
| Guangdong | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.04 |
| Guangxi | 0.35 | 0.18 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.32 | 0.35 | 0.54 |
| Hainan | 0.59 | 0.49 | 0.26 | 0.26 | 0.53 | 0.59 | 0.68 |
| Chongqing | 0.34 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.22 | 0.34 | 0.49 |
| Sichuan | 0.42 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.25 | 0.42 | 0.49 |
| Guizhou | 0.70 | 0.07 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.80 |
| Yunnan | 0.49 | 0.17 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.51 | 0.49 | 0.67 |
| Shaanxi | 0.65 | 0.48 | 0.36 | 0.36 | 0.64 | 0.65 | 0.76 |
| Gansu | 0.69 | 0.04 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.70 | 0.69 | 0.80 |
| Qinghai | 0.47 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.64 | 0.47 | 0.76 |
| Ningxia | 0.81 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.87 | 0.81 | 0.91 |
| Xinjiang | 0.76 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.80 | 0.76 | 0.87 |
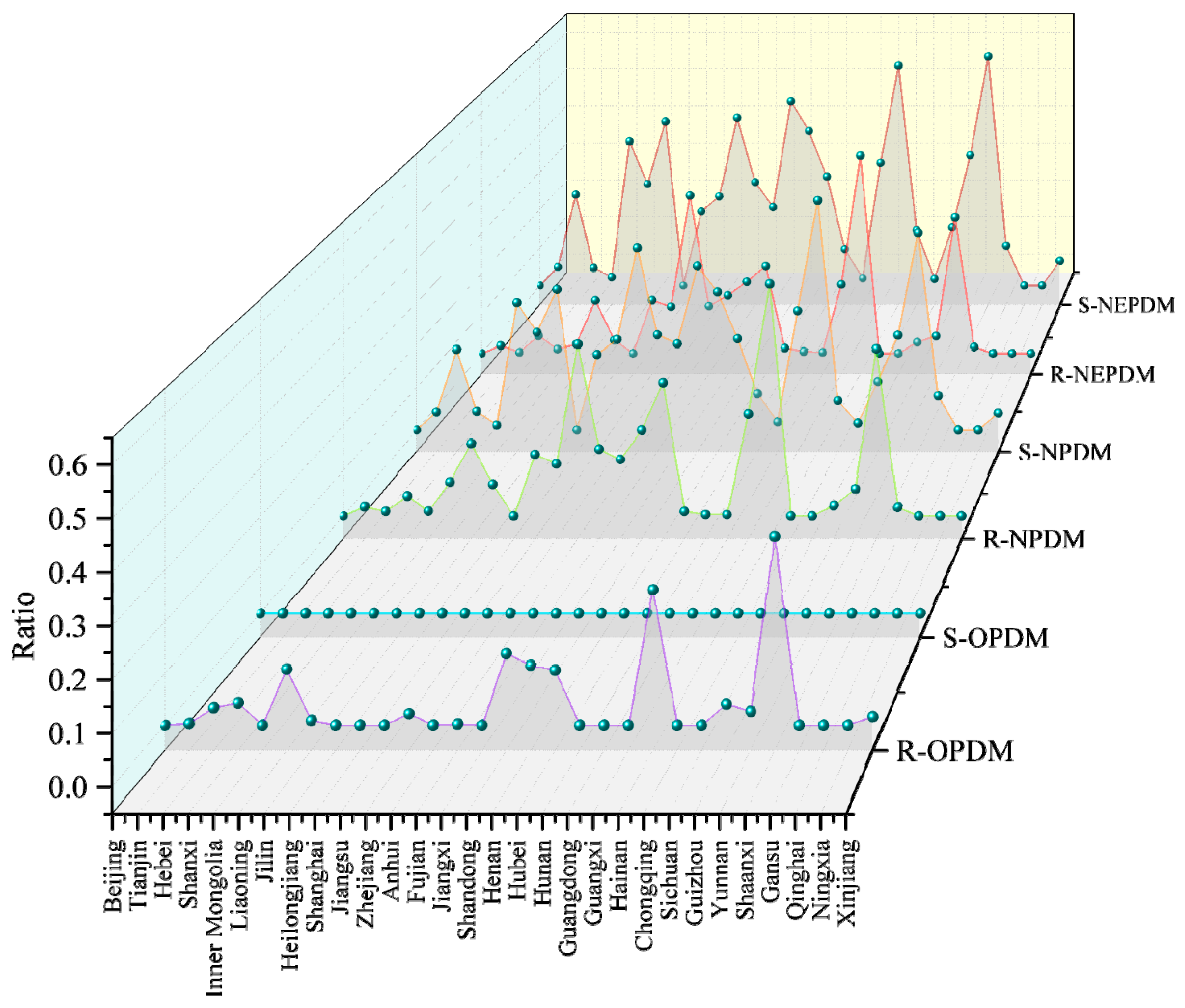
| City | R-OPDM | S-OPDM | R-NPDM | S-NPDM | R-NEPDM | S-NEPDM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Tianjin | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.05 |
| Hebei | 0.03 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.19 | 0.00 | 0.24 |
| Shanxi | 0.04 | 0.00 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.05 |
| Inner Mongolia | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 |
| Liaoning | 0.11 | 0.00 | 0.07 | 0.30 | 0.02 | 0.38 |
| Jilin | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.16 | 0.23 | 0.13 | 0.27 |
| Heilongjiang | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.07 | 0.33 | 0.03 | 0.43 |
| Shanghai | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Jiangsu | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.14 | 0.18 | 0.13 | 0.19 |
| Zhejiang | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.11 | 0.21 | 0.12 | 0.23 |
| Anhui | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.38 | 0.43 | 0.39 | 0.44 |
| Fujian | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.15 | 0.22 | 0.12 | 0.27 |
| Jiangxi | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.12 | 0.20 | 0.14 | 0.21 |
| Shandong | 0.14 | 0.00 | 0.19 | 0.38 | 0.18 | 0.48 |
| Henan | 0.12 | 0.00 | 0.29 | 0.32 | 0.22 | 0.41 |
| Hubei | 0.11 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.21 | 0.01 | 0.29 |
| Hunan | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.09 | 0.00 | 0.09 |
| Guangdong | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.02 |
| Guangxi | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.23 | 0.28 | 0.17 | 0.32 |
| Hainan | 0.26 | 0.00 | 0.51 | 0.54 | 0.49 | 0.58 |
| Chongqing | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.07 | 0.00 | 0.14 |
| Sichuan | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.02 |
| Guizhou | 0.04 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.11 | 0.03 | 0.15 |
| Yunnan | 0.03 | 0.00 | 0.06 | 0.22 | 0.04 | 0.34 |
| Shaanxi | 0.36 | 0.00 | 0.37 | 0.46 | 0.34 | 0.60 |
| Gansu | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.08 | 0.02 | 0.10 |
| Qinghai | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Ningxia | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Xinjiang | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.04 | 0.00 | 0.06 |
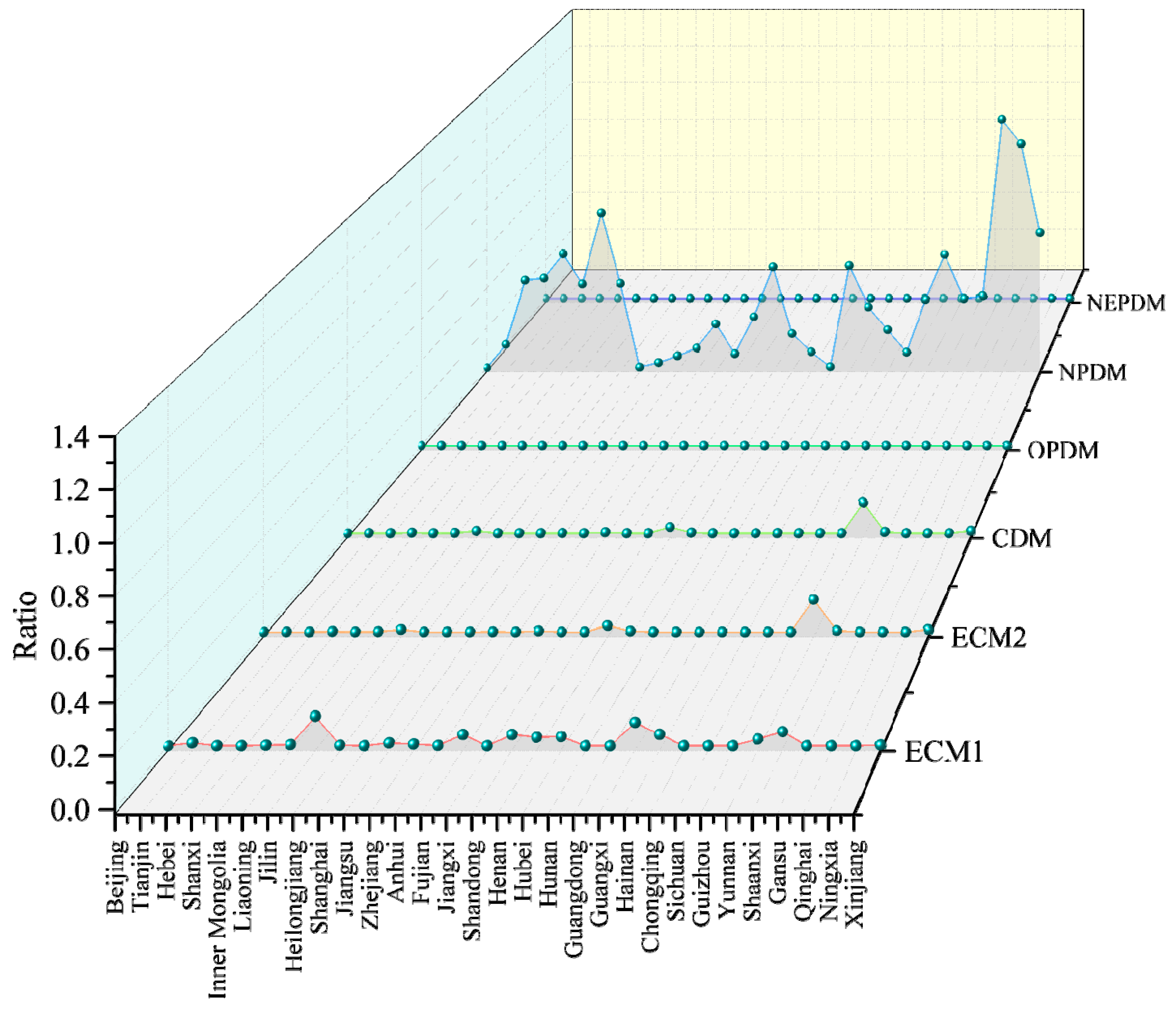
| City | DDF | ECM1 | ECM2 | CDM | OPDM | NPDM | NEPDM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Tianjin | 0.12 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.12 | 0.00 |
| Hebei | 0.43 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.44 | 0.00 |
| Shanxi | 0.45 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.45 | 0.00 |
| Inner Mongolia | 0.57 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.57 | 0.00 |
| Liaoning | 0.42 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.42 | 0.00 |
| Jilin | 0.77 | 0.12 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.77 | 0.00 |
| Heilongjiang | 0.42 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.42 | 0.00 |
| Shanghai | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Jiangsu | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.03 | 0.00 |
| Zhejiang | 0.06 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.06 | 0.00 |
| Anhui | 0.10 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.10 | 0.00 |
| Fujian | 0.22 | 0.04 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.22 | 0.00 |
| Jiangxi | 0.07 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.07 | 0.00 |
| Shandong | 0.26 | 0.04 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.26 | 0.00 |
| Henan | 0.51 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.00 | 0.51 | 0.00 |
| Hubei | 0.17 | 0.04 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.17 | 0.00 |
| Hunan | 0.08 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.08 | 0.00 |
| Guangdong | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Guangxi | 0.51 | 0.09 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.51 | 0.00 |
| Hainan | 0.31 | 0.05 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.31 | 0.00 |
| Chongqing | 0.19 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.19 | 0.00 |
| Sichuan | 0.08 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.08 | 0.00 |
| Guizhou | 0.34 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.34 | 0.00 |
| Yunnan | 0.57 | 0.03 | 0.14 | 0.14 | 0.00 | 0.57 | 0.00 |
| Shaanxi | 0.35 | 0.06 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.35 | 0.00 |
| Gansu | 0.36 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.36 | 0.00 |
| Qinghai | 1.25 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.25 | 0.00 |
| Ningxia | 1.13 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.13 | 0.00 |
| Xinjiang | 0.67 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.68 | 0.00 |
| City | R-OPDM | S-OPDM | R-NPDM | S-NPDM | R-NEPDM | S-NEPDM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Tianjin | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| Hebei | 0.00 | 0.05 | 0.17 | 0.10 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Shanxi | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Inner Mongolia | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.00 |
| Liaoning | 0.00 | 0.03 | 0.27 | 0.15 | 0.00 | 0.01 |
| Jilin | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.33 | 0.30 | 0.11 | 0.23 |
| Heilongjiang | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.38 | 0.31 | 0.00 | 0.05 |
| Shanghai | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Jiangsu | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Zhejiang | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.09 | 0.03 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Anhui | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Fujian | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.24 | 0.20 | 0.00 | 0.12 |
| Jiangxi | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Shandong | 0.00 | 0.03 | 0.25 | 0.19 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Henan | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.48 | 0.48 | 0.00 | 0.35 |
| Hubei | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.17 | 0.11 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Hunan | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Guangdong | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Guangxi | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.46 | 0.44 | 0.08 | 0.34 |
| Hainan | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.26 | 0.25 | 0.00 | 0.16 |
| Chongqing | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.16 | 0.11 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Sichuan | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Guizhou | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.10 | 0.09 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Yunnan | 0.14 | 0.02 | 0.50 | 0.49 | 0.00 | 0.24 |
| Shaanxi | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.34 | 0.32 | 0.00 | 0.01 |
| Gansu | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Qinghai | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Ningxia | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Xinjiang | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Ye, J.-H.; Chen, L. A New Endogenous Direction Selection Mechanism for the Direction Distance Function Method Applied to Different Economic–Environmental Development Modes. Sustainability 2025, 17, 3151. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17073151
Wang J, Ye J-H, Chen L. A New Endogenous Direction Selection Mechanism for the Direction Distance Function Method Applied to Different Economic–Environmental Development Modes. Sustainability. 2025; 17(7):3151. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17073151
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Junchao, Jun-Hong Ye, and Lei Chen. 2025. "A New Endogenous Direction Selection Mechanism for the Direction Distance Function Method Applied to Different Economic–Environmental Development Modes" Sustainability 17, no. 7: 3151. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17073151
APA StyleWang, J., Ye, J.-H., & Chen, L. (2025). A New Endogenous Direction Selection Mechanism for the Direction Distance Function Method Applied to Different Economic–Environmental Development Modes. Sustainability, 17(7), 3151. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17073151





