Combining Novel Membrane Technologies for Sustainable Nutrient Recovery from Digestate: Effect of Solid Content
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Origin of the Raw Digestate and the Liquid Fraction
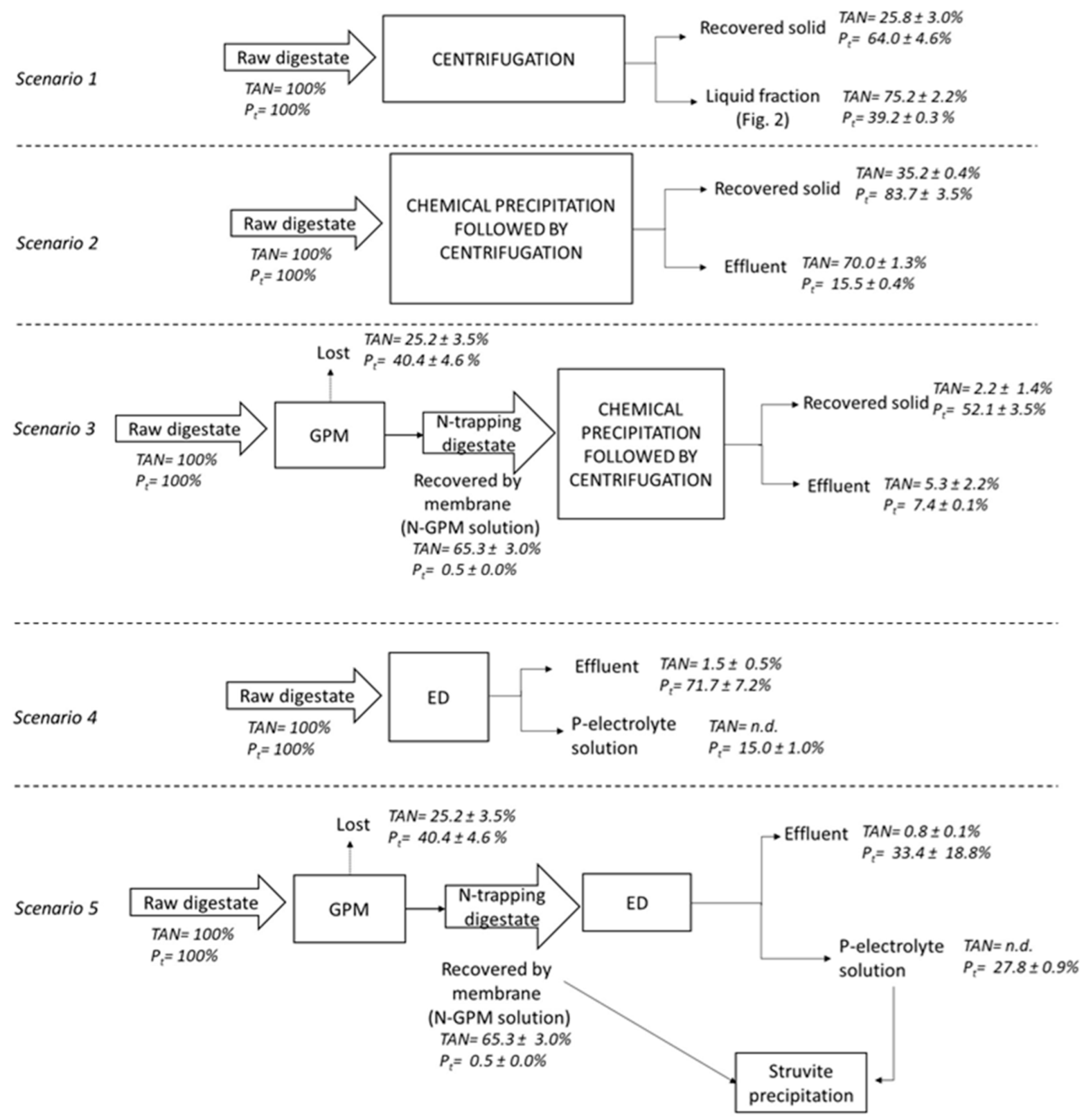
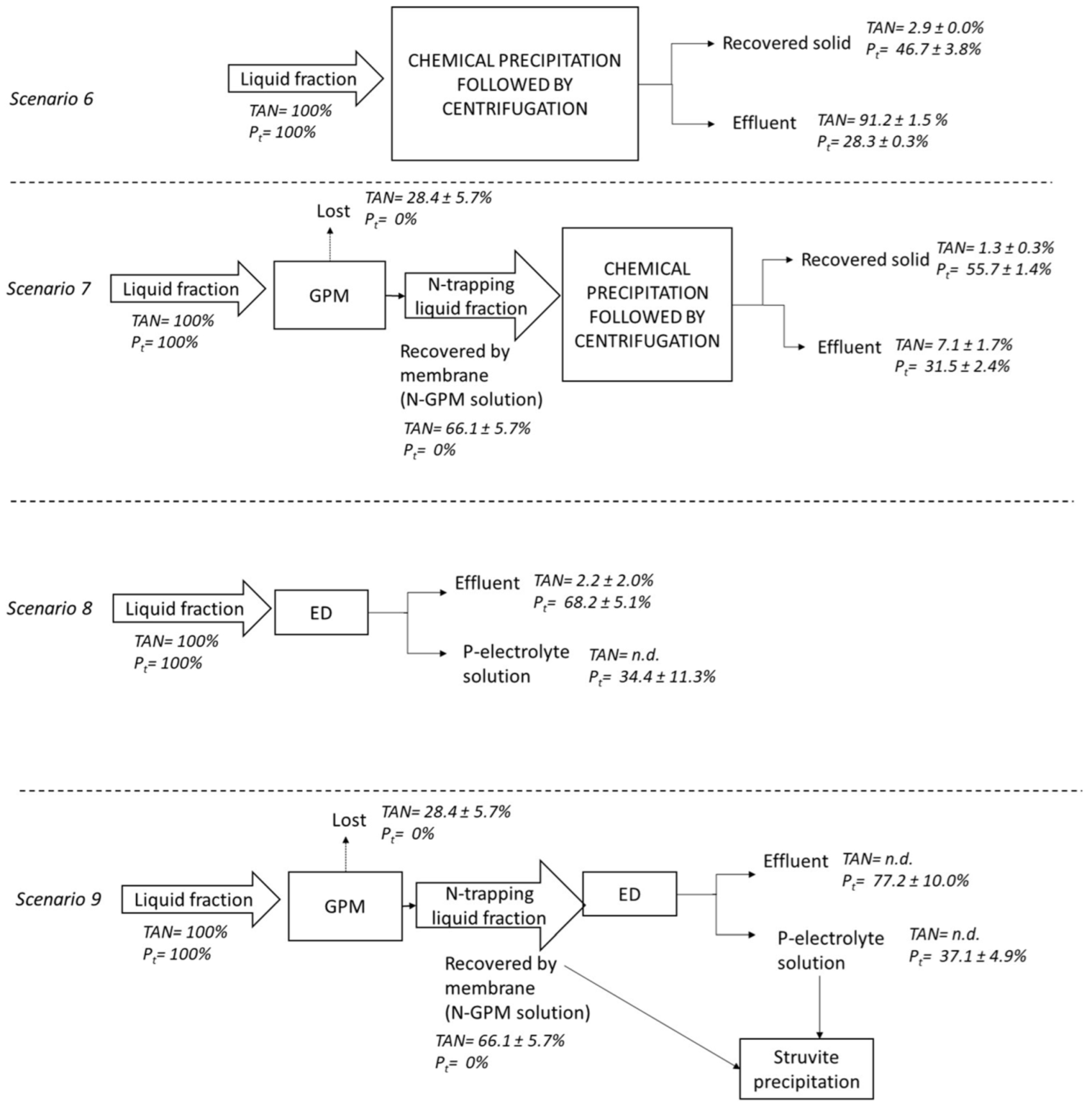
2.2. Nutrient Recovery Scenarios
2.3. N and P Recovery by Chemical Precipitation
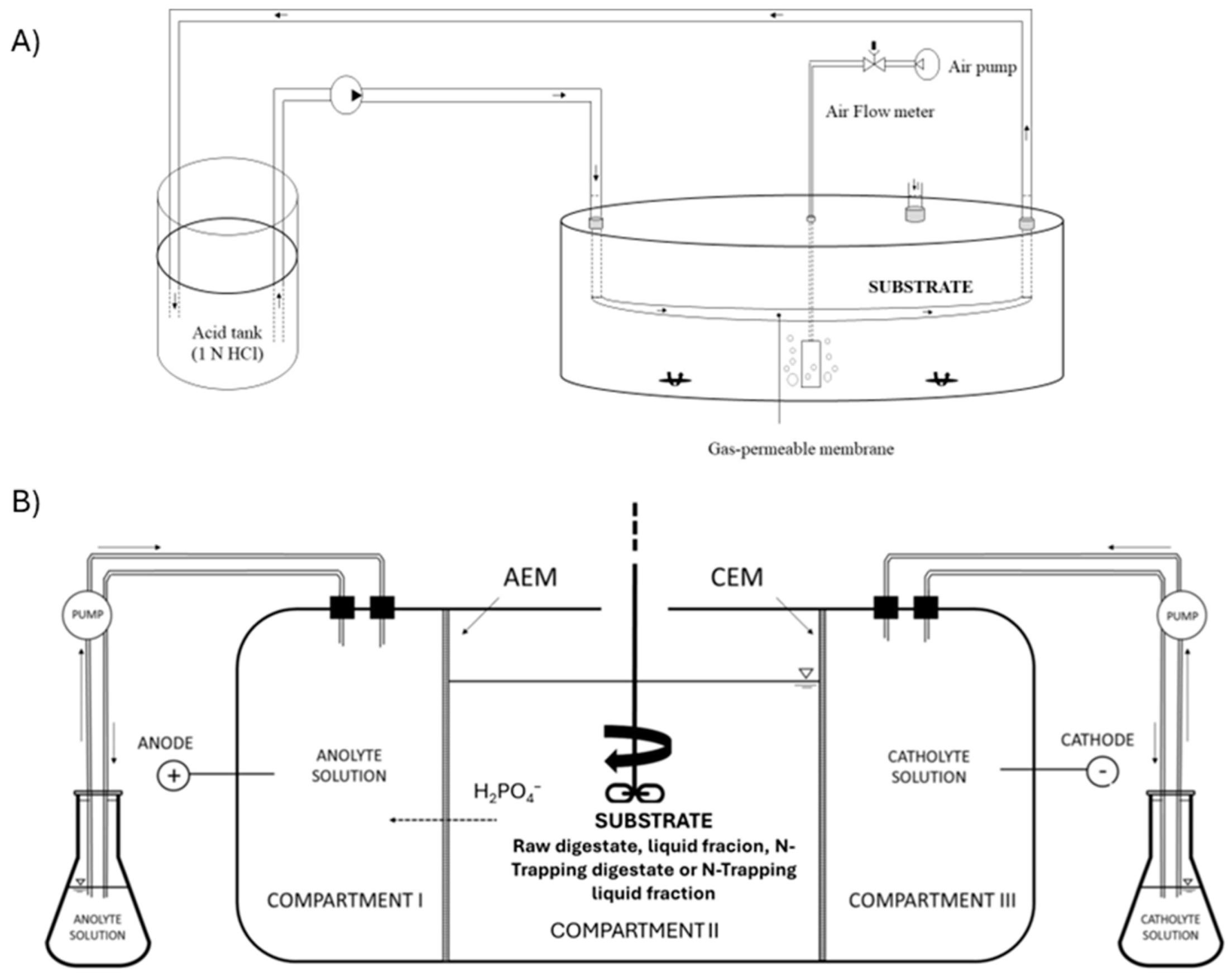
2.4. N Recovery Experiments Using Gas-Permeable Membrane (GPM)
2.5. Phosphorous Recovery by the ED Process
2.6. Analytical Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of the Raw Digestate
3.2. Nutrient Separation Efficiency of the Centrifugation (Scenario 1)
3.3. Effect of the Solid–Liquid Separation on Nutrient Recovery by Chemical Precipitation (Scenarios 2 and 6)
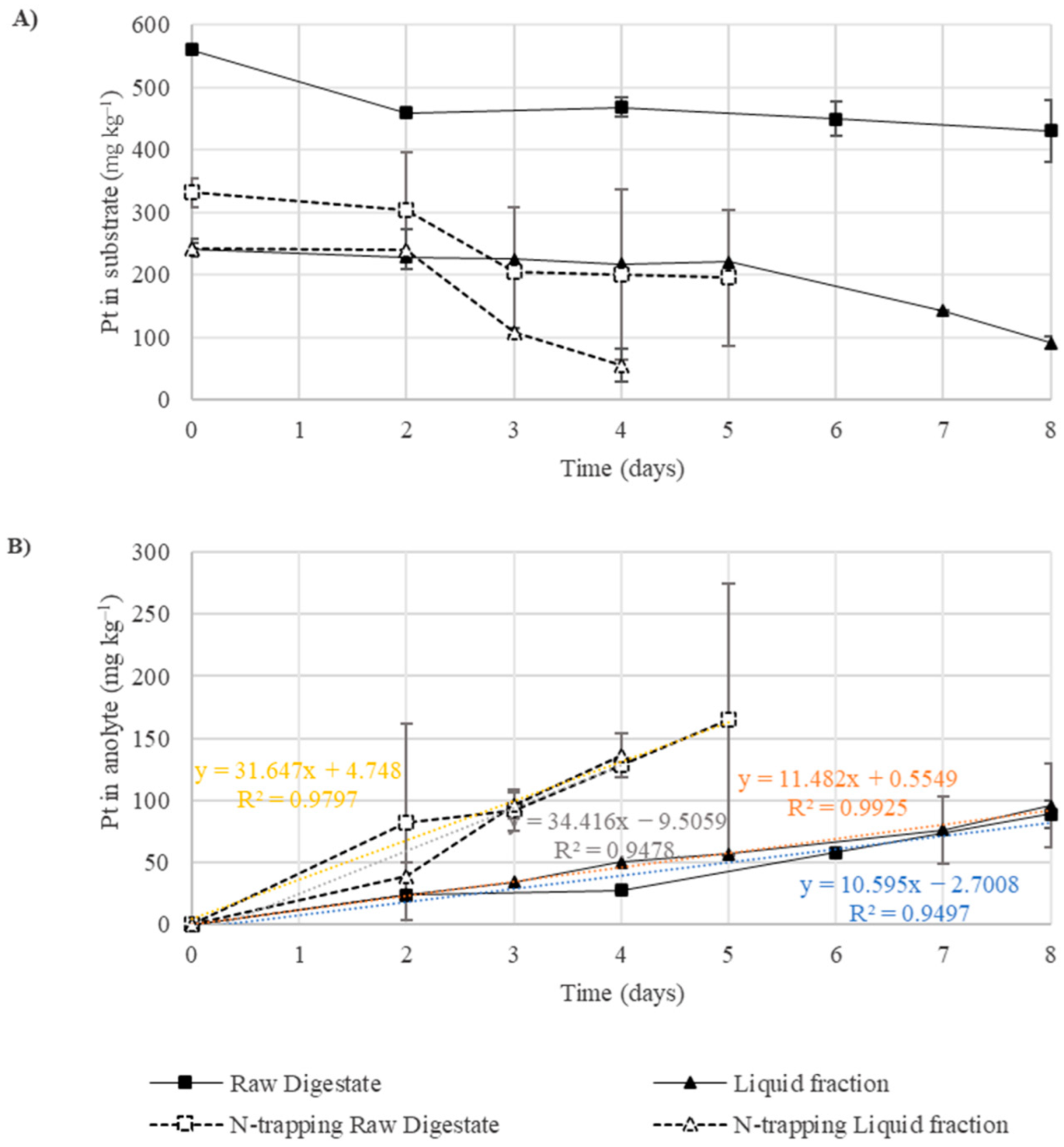
3.4. Performance of GPM Technology for Nutrient Recovery from Raw Digestate and the Liquid Fraction (Scenarios 3 and 7)
3.5. Nutrient Recovery by ED Technology from Raw Digestate and Liquid Fraction (Scenarios 4 and 8)
3.6. Effect of Prior GPM on Nutrient Recovery by ED (Scenarios 5 and 9)
3.7. Overall Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ren, Y.; Yu, M.; Wu, C.; Wang, Q.; Gao, M.; Huang, Q.; Liu, Y. A comprehensive review on food waste anaerobic digestion: Research updates and tendencies. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 247, 1069–1076. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Amini, A.; Aponte-Morales, V.; Wang, M.; Dilbeck, M.; Lahav, O.; Zhang, Q.; Cunningham, J.A.; Ergas, S.J. Cost-effective treatment of swine wastes through recovery of energy and nutrients. Waste Manag. 2017, 69, 508–517. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Guo, Y.; Qin, Y.; Li, Y.Y. Nutrient recovery technologies integrated with energy recovery by waste biomass anaerobic digestion. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 269, 520–531. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, W.; Lü, F.; Hae, L.; Zhang, H.; Shao, L.; He, P. Digestate management for high-solid anaerobic digestion of organic wastes: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 297, 122485. [Google Scholar]
- Campos, J.L.; Crutchik, D.; Franchi, O.; Pavissich, J.P.; Belmonte, M.; Pedrouso, A.; Mosquera-Corral, A.; Val del Río, A. Nitrogen and phosphorus recovery from anaerobically pretreated agro-food wastes: A review. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2019, 2, 91. [Google Scholar]
- Al Seadi, T.; Drosg, B.; Fuchs, W.; Rutz, D.; Janssen, R. Biogas digestate quality and utilization. In The Biogas Handbook; Wellinger, A., Murphy, J., Baxter, D., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing Limited: Sawston, UK, 2013; pp. 267–301. [Google Scholar]
- Delzeit, R.; Kellner, U. The impact of plant size and location on profitability of biogas plants in Germany under consideration of processing digestates. Biomass Bioenerg. 2013, 52, 43–53. [Google Scholar]
- Drosg, B.; Fuchs, W.; Al Seadi, T.; Madsen, M.; Linke, B. Nutrient Recovery by Biogas Digestate Processing; Daxter, IEA Bioenergy: Paris, France, 2015; pp. 7–11. [Google Scholar]
- Otieno, B.; Funani, C.K.; Khune, S.M.; Kabuba, J.; Osifo, P. Struvite recovery from anaerobically digested waste-activated sludge: A short review. J. Mater. Res. 2023, 38, 3815–3826. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Fu, R.; Lv, H.; Zhu, G.; Lu, B.; Zhou, Z.; Wu, X.; Chen, H. Phosphate Recovery from Swine Wastewater by a Struvite Precipitation Electrolyzer. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, V.; Dias-Ferreira, C.; González-García, I.; Labrincha, J.; Horta, C.; García-González, M.C. A novel approach for nutrients recovery from municipal waste as biofertilizers by combining electrodialytic and gas permeable membrane technologies. Waste Manag. 2021, 15, 293–302. [Google Scholar]
- Romero-Güiza, M.S.; Astals, S.; Mata-Álvarez, J.; Chimenos, J.M. Feasibility of coupling anaerobic digestion and struvite precipitation in the same reactor: Evaluation of different magnesium sources. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 270, 542–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, W.; Fattah, K.P.; Huchzermeier, M.P. Struvite recovery from anaerobically digested dairy manure: A review of application potential and hindrances. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 169, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, A.F.; Mendes, L.S.; Alvarenga, P.; Gando-Ferreira, L.M.; Quina, M.J. Nutrient Recovery via Struvite Precipitation from Wastewater Treatment Plants: Influence of Operating Parameters, Coexisting Ions, and Seeding. Water 2024, 16, 1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottosen, L.M.; Jensen, P.E.; Kirkelund, G.M. Electrodialytic separation of phosphorous and heavy metals from two types of sewage sludge ash. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2014, 49, 1910–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedes, P.; Couto, N.; Mateus, E.P.; Ribeiro, A.B. Phosphorus recovery in sewage sludge by Electrokinetic based technologies: A multivariate and circular economy view. Waste Biomass Valoriz. 2017, 8, 1587–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fillingham, M.; Vanderzaag, A.C.; Singh, J.; Burtt, S.; Crolla, A.; Kindsley, C.; McDonald, J.D. Characterizing the performance of gas-permeable membranes as an ammonia recovery strategy from anaerobically digested dairy manure. Membranes 2017, 7, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-García, I.; Oliveira, V.; Molinuevo-Salces, B.; García-González, M.C.; Dias-Ferreira, C.; Riaño, B. Two-phase nutrient recovery from livestock wastewaters combining novel membrane technologies. Biomass Conv. Bioref. 2022, 12, 4563–4574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-García, I.; Riaño, B.; Molinuevo-Salces, B.; García-González, M.C. Effect of alkali and membrane area on the simultaneous recovery of nitrogen and phosphorous from digestate by membrane technology and chemical precipitation. Sustainability 2023, 15, 3909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebbers, B.; Ottosen, L.M.; Jensen, P.E. Comparison of two different electrodialytic cells for separation of phosphorus and heavy metals from sewage sludge ash. Chemosphere 2014, 125, 122–129. [Google Scholar]
- American Public Health Association. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water, Waste Water APHA, 21st ed.; American Water Works Association and Water Environment Federation: Denver, CO, USA; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- USEPA. SW-846 Test Method 6010D: Inductively Coupled Plasma-Optical Emission Spectrometry (ICP-AES); Test Method 6010D; USEPA-Federal Register: Washington, DC, USA, 2014.
- Akhiar, A. Characterization of Liquid Fraction of Digestates After Solid-Liquid Separation From Anaerobic Co-Digestion Plants; English. ffNNT: 2017MONTS004ff. fftel-01684830f; Chemical and Process Engineering, Université Montpellier: Montpellier, France, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Palatsi, J.; Viñas, M.; Guivernau, M.; Fernandez, B.; Flotats, X. Anaerobic digestion of slaughterhouse waste: Main process limitations and microbial community interactions. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 2219–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antezana, W.; De Blas, C.; García-Rebollar, P.; Rodríguez, C.; Beccaccia, A.; Ferrer, P.; Cerisuelo, A.; Moset, V.; Estellés, F.; Cambra-López, M.; et al. Composition, potential emissions and agriculture value of pig slurry from Spanish commercial farms. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2016, 104, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popovic, O.; Gioelli, F.; Dinuccio, E.; Rolle, L. Centrifugation of digestate: The effect of chitosan on separation efficiency. Sustainability 2017, 9, 2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enyemadze, I.; Momade, F.W.Y.; Oduro-Kwarteng, S.; Essandoh, H. Phosphorous recovery by struvite precipitation: A review of the impact of calcium on struvite quality. J. Water Sanit. Hyg. Dev. 2021, 11, 706–718. [Google Scholar]
- Kabdasli, I.; Atalay, Z.; Tünay, O. Effect of solution composition on struvite crystallization. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2017, 92, 2921–2928. [Google Scholar]
- González-Morales, C.; Fernández, B.; Molina, F.J.; Naranjo-Fernández, D.; Matamoros-Veloza, A.; Camargo-Valero, M.A. Influence of pH and Temperature on Struvite Purity and Recovery from Anaerobic Digestate. Sustainability 2021, 13, 10730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzini, S.; Borgonovo, G.; Scaglioni, L.; Bedussi, F.; D’Imporzano, G.; Tambone, F.; Adani, F. Phosphorous speciation during anaerobic digestion and subsequent solid/liquid separation. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 734, 139284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corona, F.; Hidalgo, D.; Martín-Marroquín, J.M.; Meers, E. Study of pig manure digestate pre-treatment for subsequent valorisation of struvite. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 24731–24743. [Google Scholar]
- Moerman, W.; Carballa, M.; Vanderkerckhove, A.; Derycke, D.; Verstraete, W. Phosphate removal in agro-industry: Pilot and full-scale operational considerations of struvite crystallization. Water Res. 2009, 43, 1887–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Xiaomei, L. Nutrient removal from anaerobically digested cattle manure by struvite precipitation. J. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2006, 5, 285–294. [Google Scholar]
- Darestani, M.; Haigh, V.; Couperthwaite, S.J.; Millar, G.J.; Nghiem, L.D. Hollow fibre membrane contactors for ammonia recovery: Current status and future development. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 1349–1359. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-González, M.; Vanotti, M. Recovery of ammonia from swine manure using gas-permeable membranes: Effect of waste strength and pH. Waste Manag. 2015, 38, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanotti, M.B.; Dube, P.J.; Szogi, A.A.; García-González, M.C. Recovery of ammonia and phosphate minerals from swine wastewater using gas-permeable membranes. Water Res. 2017, 112, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ebbers, B.; Ottosen, L.M.; Jensen, P.E. Electrodialytic treatment of municipal wastewater and sludge for the removal of heavy metals and recovery of phosphorus. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 181, 90–99. [Google Scholar]
- Guedes, P.; Couto, N.; Ottosen, L.M.; Ribeiro, A.B. Phosphorus recovery from sewage sludge ash through an electrodialytic process. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 886–892. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ottosen, L.M.; Jensen, P.E.; Kirkelund, G.M. Phosphorous recovery from sewage sludge ash suspended in water in a two-compartment electrodialytic cell. Waste Manag. 2016, 51, 142–148. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, M.M.; Salleh, M.A.M.; Rashid, U.; Ahsan, A.; Hossain, M.M.; Ra, C.S. Production of slow release crystal fertilizer from wastewaters through struvite crystallization—A review. Arab. J. Chem. 2014, 7, 139–155. [Google Scholar]
- Riaño, B.; Molinuevo-Salces, B.; Vanotti, M.B.; García-González, M.C. Application of gas-permeable membranes for semi-continuous ammonia recovery from swine manure. Environments 2019, 6, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Shi, X.; Wang, S.; Hu, Z.; Koseouglu-Imer, D.Y.; Lens, P.N.L.; Zhang, X. Application of electrodialysis technology in nutrient recovery from wastewater: A review. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 65, 105855. [Google Scholar]
- Krishnamoorthy, N.; Baishali, D.; Unpaprom, Y.; Ramaraj, R.; Maniam, G.P.; Govindan, N.; Jayaraman, S.; Arunachalam, T.; Paramasivan, B. Engineering principles and process designs for phosphorus recovery as struvite: A comprehensive review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105579. [Google Scholar]
 ) and from the liquid fraction (
) and from the liquid fraction ( ): (A) evolution of the TAN concentration in the raw digestate and in the liquid fraction; (B) TAN concentration in the acidic solution during the GPM treatment of raw digestate and the liquid fraction; and (C) mass of TAN recovered through GPM treatment in the raw digestate and the liquid fraction. Error bars represent the standard deviation.
): (A) evolution of the TAN concentration in the raw digestate and in the liquid fraction; (B) TAN concentration in the acidic solution during the GPM treatment of raw digestate and the liquid fraction; and (C) mass of TAN recovered through GPM treatment in the raw digestate and the liquid fraction. Error bars represent the standard deviation.
 ) and from the liquid fraction (
) and from the liquid fraction ( ): (A) evolution of the TAN concentration in the raw digestate and in the liquid fraction; (B) TAN concentration in the acidic solution during the GPM treatment of raw digestate and the liquid fraction; and (C) mass of TAN recovered through GPM treatment in the raw digestate and the liquid fraction. Error bars represent the standard deviation.
): (A) evolution of the TAN concentration in the raw digestate and in the liquid fraction; (B) TAN concentration in the acidic solution during the GPM treatment of raw digestate and the liquid fraction; and (C) mass of TAN recovered through GPM treatment in the raw digestate and the liquid fraction. Error bars represent the standard deviation.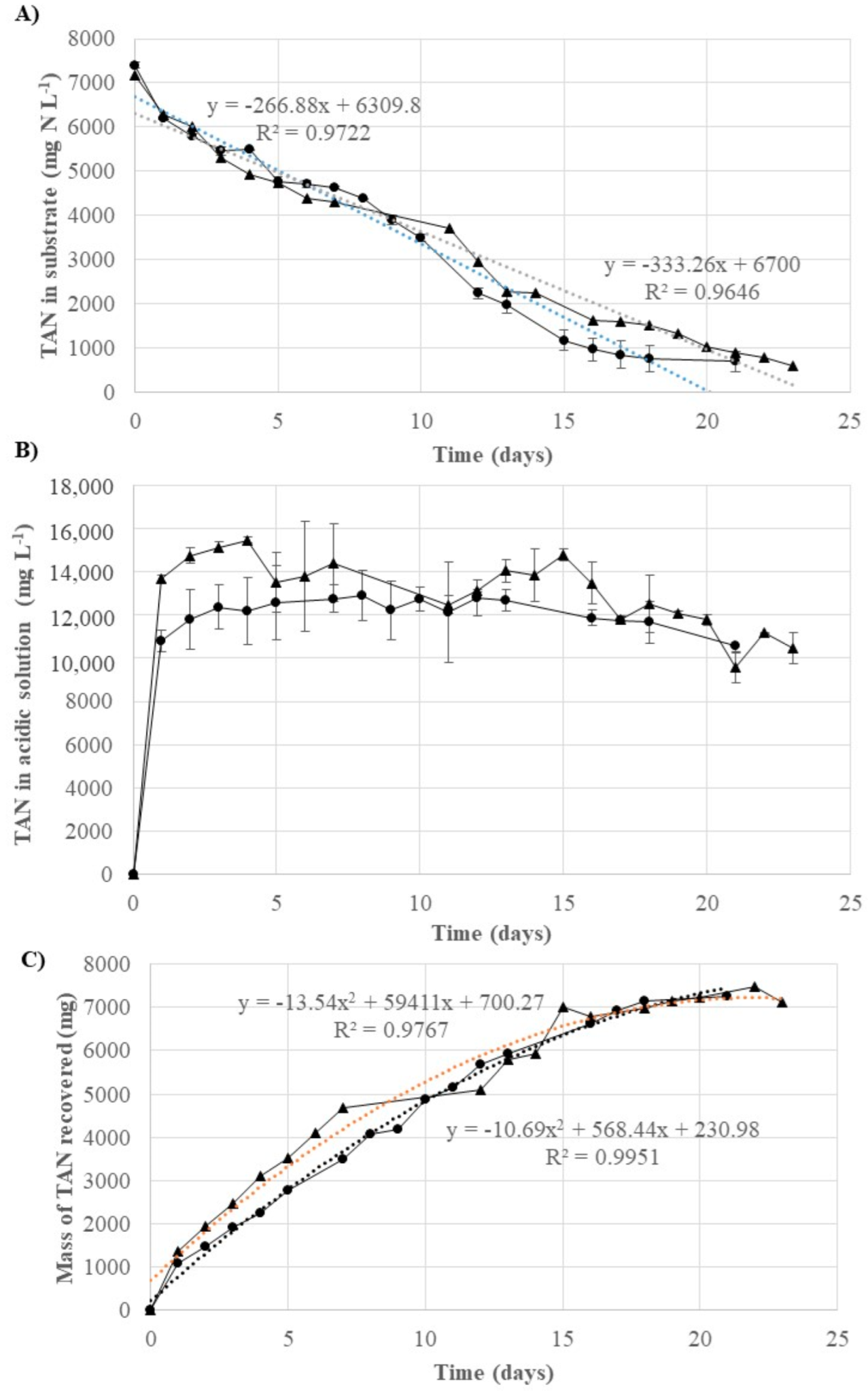

| Raw Digestate | Liquid Fraction | N-Trapping Digestate | N-Trapping Liquid Fraction | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 9.47 ± 0.02 | 9.32 ± 0.03 | 8.00 ± 0.00 | 7.85 ± 0.18 |
| Alkalinity (mg CaCO3 L−1) | 28,283 ± 156 | 26,946 ± 170 | 5343 ± 823 | 5090 ± 155 |
| TS (g kg−1) | 41.50 ± 0.04 | 27.97 ± 0.02 | 40.90 ± 4.91 | 27.67 ± 0.05 |
| VS (g kg−1) | 27.60 ± 0.18 | 16.57 ± 0.00 | 25.44 ± 2.74 | 14.96 ± 0.91 |
| TKN (mg kg−1) | 8520 ± 11 | 8173 ± 106 | 2016 ± 539 | 1998 ± 272 |
| TAN (mg kg−1) | 7402 ± 66 | 7179 ± 86 | 697 ± 232 | 595 ± 3 |
| Pt (mg kg−1) | 561 ± 1 | 242 ± 10 | 334 ± 26 | 236 ± 5 |
| Na (mg kg−1) | 1848 ± 50 | 1758 ± 23 | 1741 ± 82 | 1677 ± 23 |
| Ca (mg kg−1) | 270.48 ± 8.99 | 90.50 ± 3.84 | 308.31 ± 13.99 | 117.03 ± 41.22 |
| Mg (mg kg−1) | 41.24 ± 2.60 | 4.08 ± 0.18 | 53.90 ± 1.39 | 4.33 ± 0.23 |
| K (mg kg−1) | 369.00 ± 9.13 | 370.95 ± 15.99 | 354.88 ± 3.87 | 355.97 ± 19.40 |
| Cu (mg kg−1) | 1.0 ± 0.0 | 0.2 ± 0.0 | 1.2 ± 0.1 | 0.2 ± 0.0 |
| Zn (mg kg−1) | 4.0 ± 0.1 | 1.6 ± 0.1 | 5.0 ± 0.4 | 2.0 ± 0.1 |
| Cd (µg kg−1) | 13.2 ± 1.1 | 3.7 ± 0.4 | 17.8 ± 1.1 | 3.7 ± 0.1 |
| Ni (µg kg−1) | 104.0 ± 3.3 | 121.3 ± 5.7 | 159.5 ± 66.8 | 69.5 ± 3.5 |
| Cr (mg kg−1) | 147.7 ± 6.4 | 90.2 ± 2.3 | 154.6 ± 8.5 | 47.4 ± 4.6 |
| Mn (mg kg−1) | 1.65 ± 0.07 | 0.60 ± 0.00 | 1.95 ± 0.07 | 0.55 ± 0.07 |
| Molar ratio TAN:Pt | 1:0.03 | 1:0.02 | 1:0.22 | 1:0.05 |
| Molar ratio Mg:P | 1:10.68 | 1:46.61 | 1:4.86 | 1:42.77 |
| Scenario | Weight (%) | TAN (mg kg−1) | TAN (mmol N kg−1) | Pt (mg kg−1) | Pt (mmol kg−1) | Estimated Struvite (mmol kg−1) a | Estimated Struvite (g kg−1) b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 22.5 | 8519 | 608 | 1595 | 52 | 52 | 12.7 |
| 2 | 20.8 | 12,500 | 893 | 2252 | 73 | 73 | 17.8 |
| 3 | 12.0 | 1323 | 95 | 2436 | 79 | 79 | 19.8 |
| 6 | 2.9 | 7282 | 520 | 3945 | 127 | 127 | 31.2 |
| 7 | 5.5 | 3433 | 245 | 2436 | 79 | 79 | 19.3 |
| Scena-rio | TAN Balance | P Balance | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N-Trapping (mg N) | Effluent After Centrifugation (mg N) | Solid Fraction After Centrifugation (mg N) | Recovery in Solid Fraction (%) | N-Trapping (mg) | Effluent After Centrifugation (mg) | Solid Fraction After Centrifugation (mg) | Recovery in Solid Fraction (%) | |
| 3 | 697 | 338 | 159 | 23.0 | 334 | 37 | 292 | 88.0 |
| 7 | 595 | 514 | 95 | 16.0 | 233 | 76 | 135 | 57.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Riaño, B.; Oliveira, V.; Dias-Ferreira, C.; Molinuevo-Salces, B.; García-González, M.C. Combining Novel Membrane Technologies for Sustainable Nutrient Recovery from Digestate: Effect of Solid Content. Sustainability 2025, 17, 2917. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17072917
Riaño B, Oliveira V, Dias-Ferreira C, Molinuevo-Salces B, García-González MC. Combining Novel Membrane Technologies for Sustainable Nutrient Recovery from Digestate: Effect of Solid Content. Sustainability. 2025; 17(7):2917. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17072917
Chicago/Turabian StyleRiaño, Berta, Verónica Oliveira, Celia Dias-Ferreira, Beatriz Molinuevo-Salces, and Maria Cruz García-González. 2025. "Combining Novel Membrane Technologies for Sustainable Nutrient Recovery from Digestate: Effect of Solid Content" Sustainability 17, no. 7: 2917. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17072917
APA StyleRiaño, B., Oliveira, V., Dias-Ferreira, C., Molinuevo-Salces, B., & García-González, M. C. (2025). Combining Novel Membrane Technologies for Sustainable Nutrient Recovery from Digestate: Effect of Solid Content. Sustainability, 17(7), 2917. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17072917








