Sustainable Chromium Remediation: Sorption of Chromium from Leaching Solutions of Refined
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Part
Materials and Methods
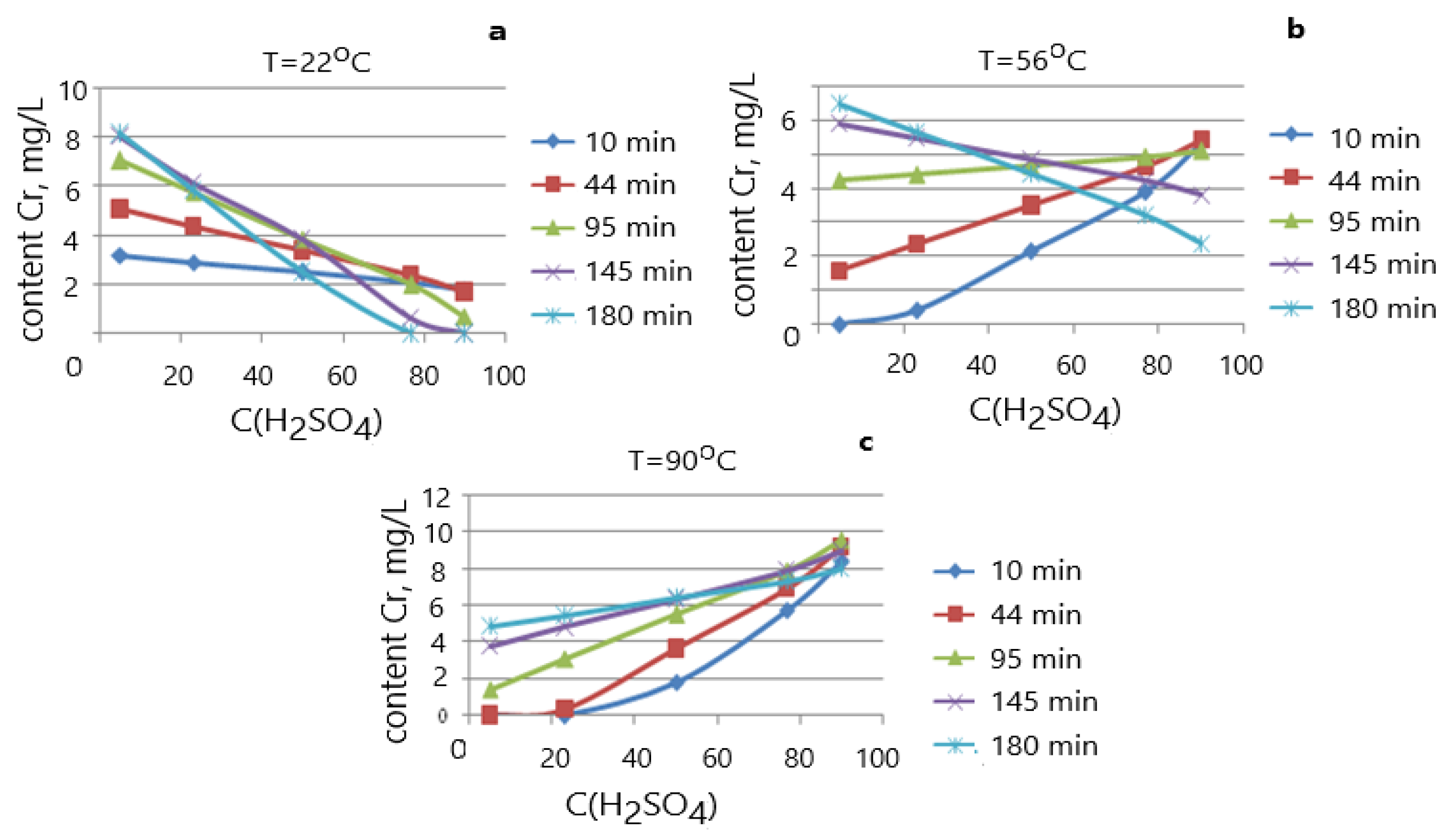
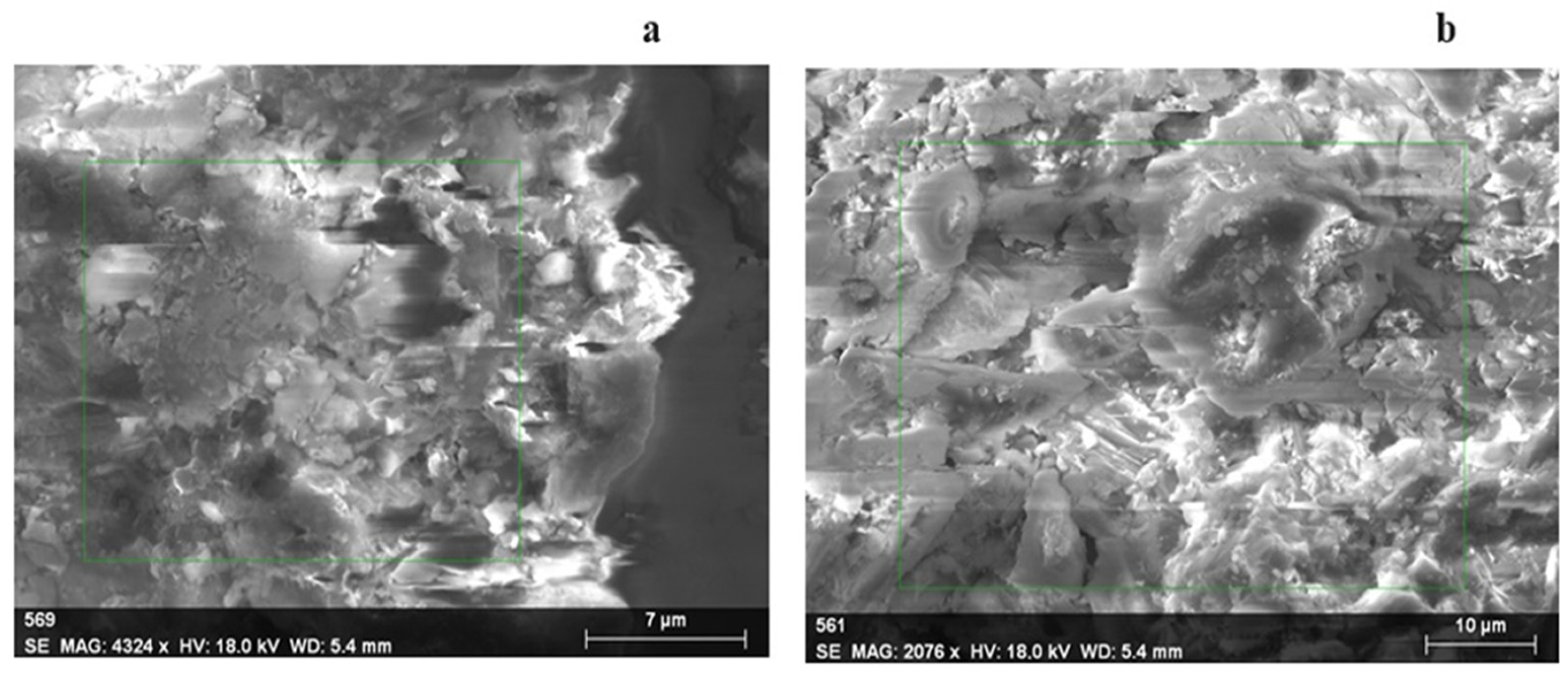
3. Results and Discussion
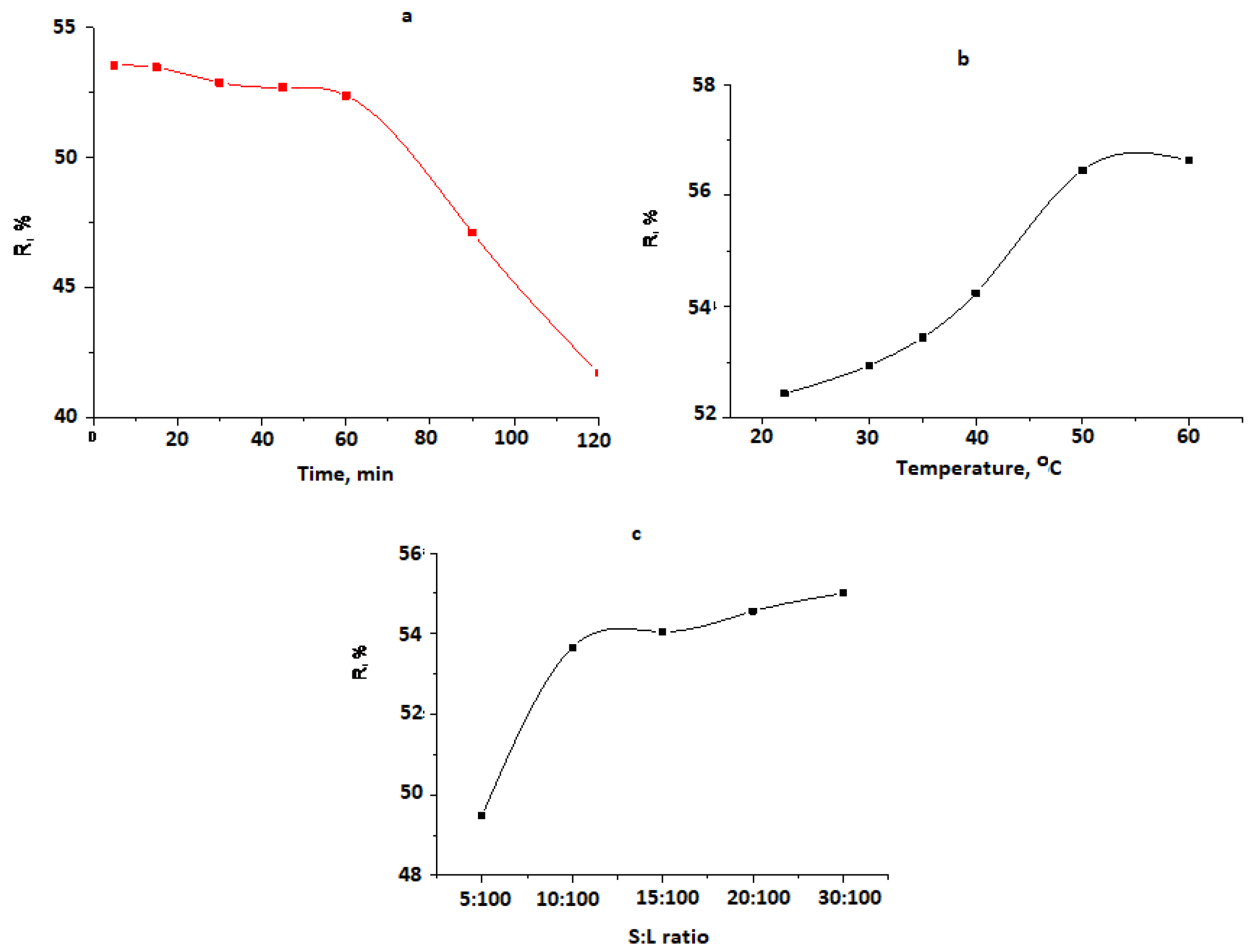
Study of Chromium Cation Sorption by Natural Zeolite
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tumolo, M.; Ancona, V.; De Paola, D.; Losacco, D.; Campanale, C.; Massarelli, C.; Uricchio, V.F. Chromium Pollution in European Water, Sources, Health Risk, and Remediation Strategies: An Overview. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohanty, S.; Benya, A.; Hota, S.; Kumar, M.S.; Singh, S. Eco-Toxicity of Hexavalent Chromium and Its Adverse Impact on Environment and Human Health in Sukinda Valley of India: A Review on Pollution and Prevention Strategies. Environ. Chem. Ecotoxicol. 2023, 5, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Gao, J.; Zhao, S.; Lei, Y.; Yuan, Y.; He, C.; Gao, C.; Deng, L. Hexavalent Chromium Removal from Aqueous Solution by Adsorption on Modified Zeolites Coated with Mg-Layered Double Hydroxides. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 32928–32941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hama Aziz, K.H.; Mustafa, F.S.; Omer, K.M.; Hama, S.; Hamarawf, R.F.; Rahman, K.O. Heavy Metal Pollution in the Aquatic Environment: Efficient and Low-Cost Removal Approaches to Eliminate Their Toxicity: A Review. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 17595–17610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coetzee, J.J.; Bansal, N.; Chirwa, E.M.N. Chromium in Environment, Its Toxic Effect from Chromite-Mining and Ferrochrome Industries, and Its Possible Bioremediation. Expo. Health 2020, 12, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Su, Z.; Tu, Y.; Liu, S.; Jiang, T. Recovery of Chromium from Chromium-Bearing Slags Produced in the Stainless-Steel Smelting: A Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 296, 126467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pikna, L.; Hezelova, M.; Morillon, A.; Algermissen, D.; Milkovic, O.; Findorak, R.; Cesnek, M.; Briancin, J. Recovery of Chromium from Slags Leachates by Electrocoagulation and Solid Product Characterization. Metals 2020, 10, 1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John Clark Stouter, R.T.-S.Y. Method for Extracting Chromium from Chromite. Patent No. CN201510157785.8A, 3 May 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Q.; Liu, C.; Shi, P.; Sun, L.; Jiang, M.; Saxen, H.; Zevenhoven, R. Cleaner Production of Chromium Oxide from Low Fe(II)-Chromite. Minerals 2020, 10, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, C.; Shi, P.; Zhang, B.; Yang, D.; Saxén, H.; Zevenhoven, R. Sulfuric Acid Leaching of South African Chromite. Part 2: Optimization of Leaching Conditions. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2014, 130, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Li, J.; Wang, Z.; Zeng, Y.; Ren, Q. Long-term leaching characterization and geochemical modeling of chromium released from AOD slag. J. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 921–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ustaoğlu, E. Optimization of Conditions in Sulfuric Acid Leaching of Turkish Chromite Concentrates; Middle East Technical University: Ankara, Türkiye, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Barbooti, M.M.; Ageena, A.N.; Tooma, A.M. Removal Of Chromium From Electroplating Wastewater By Simple Chemical Treatment And Ion Exchange. Eng. Technol. J. 2008, 26, 1396–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbooti, M.M.; Mumtaz, A.; Zablouk, U.A.A. Recovery of Chromium from Waste Taning Liquors by Magnesium Oxide. Int. J. Ind. Chem. 2010, 1, 29–38. [Google Scholar]
- RU 96111304A Method for Neutralizing Chromate Production Sludge. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/RU96111304A/ru (accessed on 10 March 2025).
- RU 2281249C1 Method for Processing Chromate Production Sludge. 2006. Available online: https://patenton.ru/patent/RU2281249C1 (accessed on 10 March 2025).
- RU 2312912C2 Method for Obtaining Chromite Concentrat. 2007. Available online: https://patenton.ru/patent/RU2312912C2 (accessed on 10 March 2025).
- Oreshkina, Y.L.; Perederin, Y.V.; Usoltseva, I.O. Extraction of Magnesium Oxide from Chromium-Containing Raw Materials; Tomsk, I.A., Aleshkovsky, A.V., Andriyanov, E.A.A., Eds.; MAKS Press: Tomsk, Russia, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Kadirbekov, K.A.; Chernyakova, R.M.; Kaiynbayeva, R.A.; Sultanbayeva, G.S.; Jussipbekov, U.Z.; Kozhabekova, N.N. Prospects For The Extractıon Of Chromıum From Slag Ferrochrome Productıon By Acıd Method. Chem. J. Kazakhstan 2023, 3, 37–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassovsky, A.G. Natural Zeolites; Kassovsky, A.G., Ed.; Nauka: Moscova, Russia, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Sandimirova, E.I.; Rychagov, S.N.; Sergeeva, A.V.; Chubarov, V.M. Zeolite Mineralization in Mudstones of the East Pauzhetka Thermal Field As an Indicator of the Discharge of Alkaline Fluids in a Present-Day Hydrothermal System, Southern Kamchatka. J. Volcanol. Seismol. 2022, 16, 432–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhailovna, C.R.; Shamilyevna, S.G.; Alibekovna, K.R.; Zhumasilovich, J.U.; Abdualiyevna, A.A.; Şahin, S.; Temel, H. Sorption of Indium(III) and Gallium(III) by Iron(II) Hexacyanoferrate. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2024, 59, 929–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, P.; Fan, M.; Yang, D.; He, H.; Liu, D.; Yuan, A.; Zhu, J.; Chen, T. Montmorillonite-Supported Magnetite Nanoparticles for the Removal of Hexavalent Chromium [Cr(VI)] from Aqueous Solutions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 166, 821–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, D.L.; Oliveira, H.C.P.; da Costa, P.C.C.; Viana, R.R.; Airoldi, C. Adsorption of Chromium(VI) Ions on Brazilian Smectite: Effect of Contact Time, PH, Concentration, and Calorimetric Investigation. CATENA 2010, 82, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanees, S.A.M.; Ahmed, A.M.; Adam, M.S.; Mohamed, M.A. Adsorption Studies on the Removal of Hexavalent Chromium-Contaminated Wastewater Using Activated Carbon and Bentonite. Asian J. Chem. 2013, 25, 8245–8252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarasevich, Y.I. Application of Natural Adsorbents and Adsorption-Active Materials Based Thereon in the Processes of Water Purification; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1999; pp. 659–722. [Google Scholar]
- Inglezakis, V.J.; Loizidou, M.D.; Grigoropoulou, H.P. Ion Exchange of Pb2+, Cu2+, Fe3+, and Cr3+ on Natural Clinoptilolite: Selectivity Determination and Influence of Acidity on Metal Uptake. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2003, 261, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultanbayeva, G.; Agatayeva, A.; Kaiynbayeva, R.; Kozhabekova, N.; Chernyakova, R.; Jussipbekov, U. Study of the Sorption Properties of Natural Zeolite in Relation to Indium(III) and Gallium(III) Cations on the Model Systems. Crystals 2022, 12, 1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idrisheva, Z.K.; Daumova, G.K.; Zhamanbayeva, M.K. Sorption of Chromium Ions from Wastewater Using Mechanically Activated Zeolites Bull. of the East Kazakhstan; Idrisheva, Z.K., Daumova, G.K., Zhamanbayeva, M.K., Eds.; Bull. of the East Kazakhstan; State Technical University: Rostov-on-Don, Russia, 2019; Available online: https://elibrary.ru/item.asp?id=44527810 (accessed on 10 March 2025).
- Adryshev, A.K.; Strunnikova, N.A.; Karibayeva, M.K. Extraction of Metal Ions from Contaminated Groundwater with Zeolites. Bull. EKSTU Ecol. 2008, 2, 102–108. Available online: https://www.ektu.kz/files/vestnik/ecol02_2008.pdf (accessed on 10 March 2025).
- Adryshev, A.K.; Strunnikova, N.A.; Khairulina, A.A.; Karibaeva, M.K. On the Possibility of Using Spent Zeolites as Building Materials: Electronic Resource. Available online: https://www.rusnauka.com/3_SND_2010/Ecologia/58201.doc.htm (accessed on 1 March 2019).
- Vasil’yanova, L.S.; Lazareva, E.A. Zeolites in Ecology. Science News of Kazakhstan. 2016. No. 1 (127). pp. 61–85. Available online: https://vestnik.nauka.kz/articles/323 (accessed on 14 August 2018).
- Bondarenko, I.V.; Tastanov, Y.A.; Sadykov, N.M.; Ismagulova, M.S. Processing of Mineral Part of Refined Ferrochrome Slags to Obtain Pelleted Porous Heat Insulator. Kompleks. IspolʹZovanie Miner. Syrʹâ/Complex Use Miner. Resour. Shikisattardy Keshendi Paid. 2018, 307, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhnazarova, S.L.; Kafarov, V.V. Optimization of the Experiment in Chemistry and Chemical Technology—M., Higher School. 1985. Available online: https://studizba.com/show/218440-1-sl-ahnazarova-vv-kafarov-metody.html (accessed on 12 June 2017).
- Su, Y.; Luo, B.; Luo, Z.; Xu, F.; Huang, H.; Long, Z.; Shen, C. Mechanical characteristics and solidification mechanism of slag/fly ash-based geopolymer and cement solidified organic clay: A comparative study. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 71, 106459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurgali, N.Z.; Almagambetov, M.S.; Baysanov, A.S.; Zhumagaliev, E.U.; Kelamanov, B.S. Technological Assessment of the Processing of Titanium and Chromite Raw Materials from the Perspective of Thermodynamic Diagram Analysis of Systems Based on Titanium and Chromium Oxides; Nurgali, N.Z., Almagambetov, M.S., Baysanov, A.S., Zhumagaliev, E.U., Kelamanov, B.S., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Chemistry Handbook 21. Available online: https://chem21.info/page/202049158153055235059255009019228197041121145204/ (accessed on 10 March 2025).

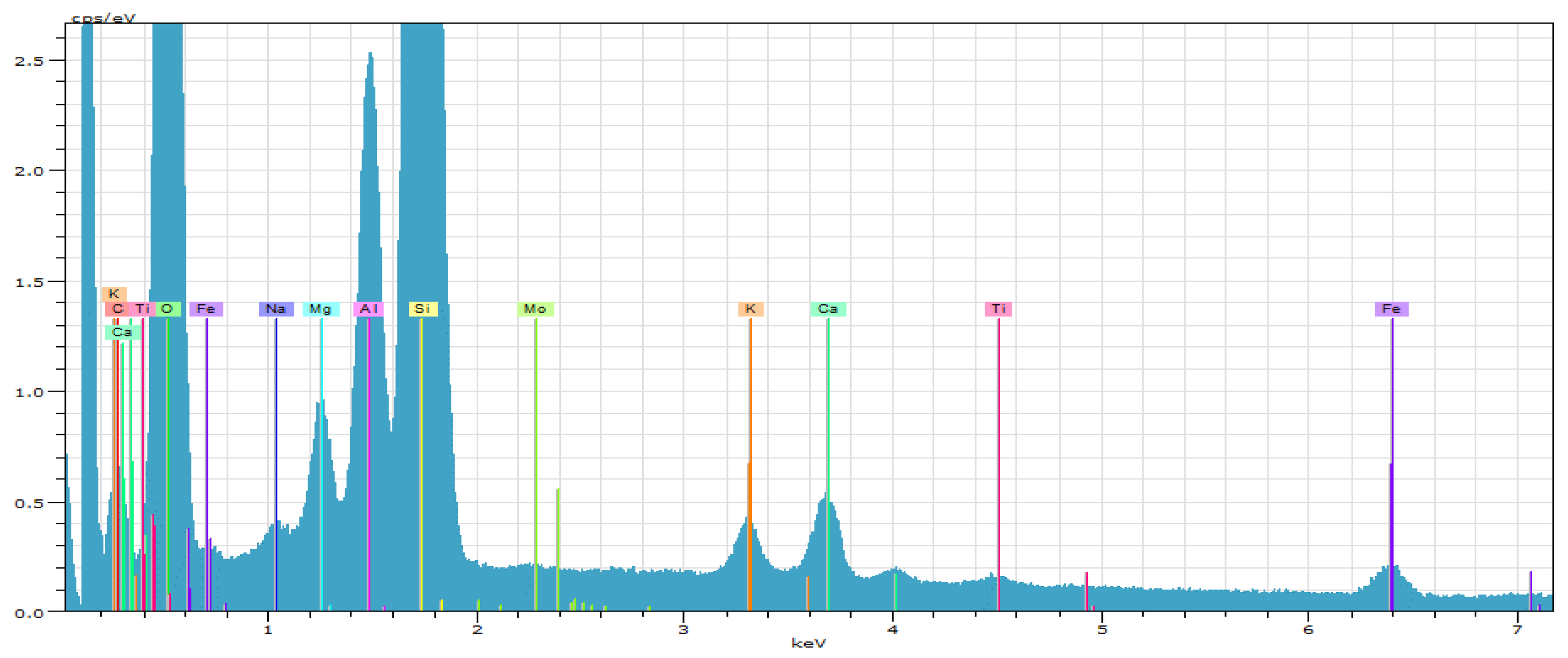
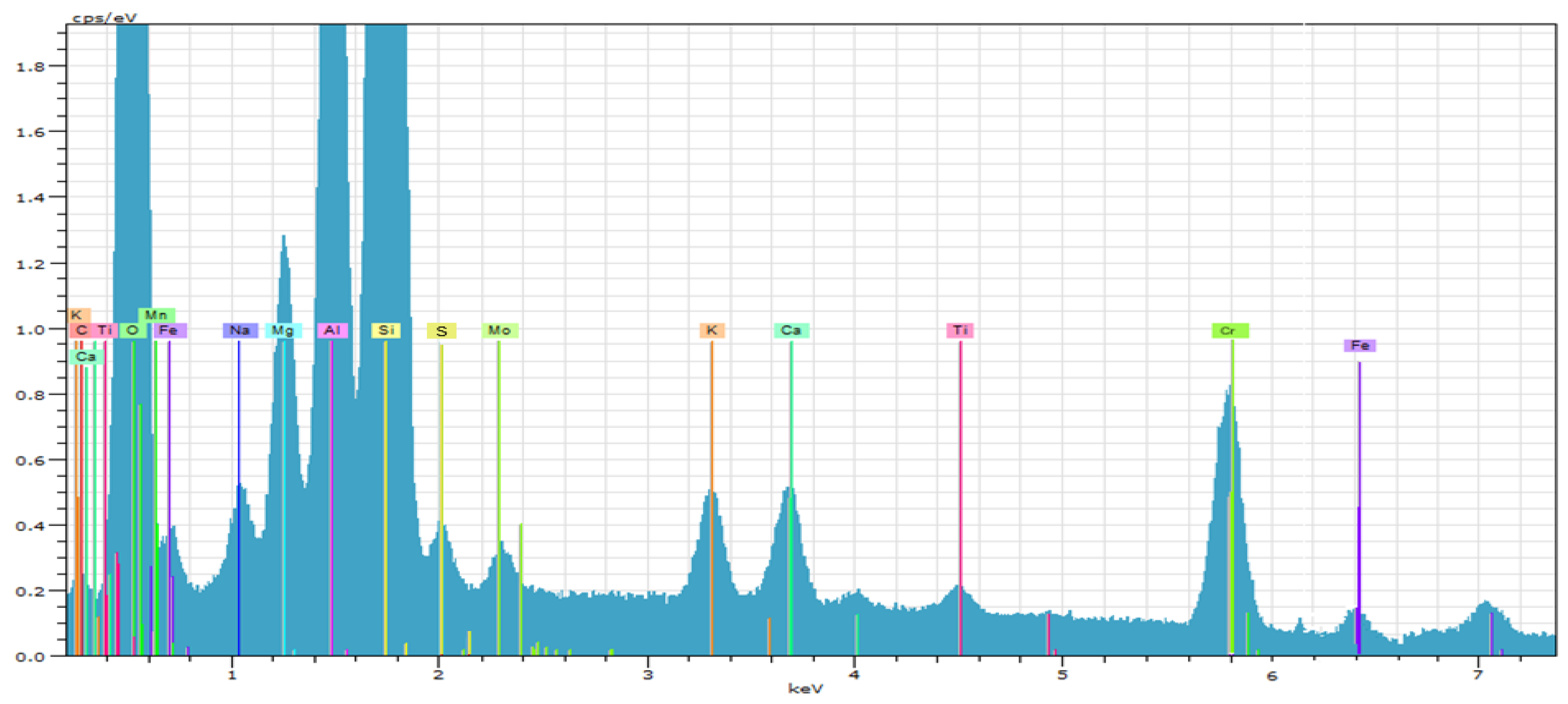
| Spectrum | Oxides Content, % | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cr2O3 | CaO | MgO | Al2O3 | SiO2 | FeO | Total | |
| Spectrum 1 | 7.04 | 49.48 | 12.29 | 4.14 | 25.96 | 1.09 | 100 |
| Spectrum 2 | 6.50 | 51.65 | 9.38 | 4.39 | 27.05 | 1.05 | 100 |
| Spectrum 3 | 6.58 | 52.50 | 8.12 | 4.42 | 27.11 | 1.27 | 100 |
| Average | 6.71 | 51.21 | 9.93 | 4.32 | 26.71 | 1.13 | 100 |
| Standard Deviation | 0.30 | 1.56 | 2.14 | 0.15 | 0.65 | 0.12 | |
| Max. | 7.04 | 52.50 | 12.29 | 4.42 | 27.11 | 1.27 | |
| Min. | 6.50 | 49.48 | 8.12 | 4.14 | 25.96 | 1.05 | |
| Mineral (Phase) | Formula | C, % |
|---|---|---|
| Olivine-(Ca) | Ca2SiO4 | 50.7 |
| Magnesium Oxide | MgO | 20.3 |
| Quarts | SiO2 | 6.3 |
| Mg-Cr-Oxide | (Mg7.92Cr1.08)Cr16O32 | 6.3 |
| Ca-Cr-Oxide | CaCr2O4 | 4.6 |
| Ca-Mg-Fe Silicate | Ca2Fe1.2Mg0.4Si0.4O5 | 11.8 |
| Oxides Content, % | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cr2O3total | CaO | MgO | Al2O3 | SiO2 | FeO | SO3 |
| RFC slag | ||||||
| 6.93 | 44.57 | 12.12 | 5.11 | 24.63 | 1.56 | - |
| Cake from RFC slag | ||||||
| 3.61 | 27.75 | 2.07 | 2.40 | 17.37 | 0.23 | 46.57 |
| № | X1 T °C | X2 t, Min | X3 CH2SO4, % | Y1, Residual Content Cr (mg/L) | Degree of Cr Leaching, Rel., % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 35.8 | 44.4 | 23.2 | 4.15 | 11.53 |
| 2 | 76.2 | 44.4 | 23.2 | 7.26 | 20.17 |
| 3 | 35.8 | 145.6 | 23.2 | 4.96 | 13.78 |
| 4 | 76.2 | 145.6 | 23.2 | 4.56 | 12.67 |
| 5 | 35.8 | 44.4 | 76.8 | 3.15 | 8.75 |
| 6 | 76.2 | 44.4 | 76.8 | 3.85 | 10.69 |
| 7 | 35.8 | 145.6 | 76.8 | 3.15 | 8.75 |
| 8 | 76.2 | 145.6 | 76.8 | 3.78 | 10.5 |
| 9 | 22 | 95 | 50 | 3.74 | 10.5 |
| 10 | 90 | 95 | 50 | 6.67 | 18.53 |
| 11 | 56 | 10 | 50 | 3.20 | 8.88 |
| 12 | 56 | 180 | 50 | 6.04 | 16.78 |
| 13 | 56 | 95 | 5 | 6.96 | 19.33 |
| 14 | 56 | 95 | 95 | 3.06 | 8.5 |
| 15 | 56 | 95 | 50 | 5.72 | 15.89 |
| 16 | 56 | 95 | 50 | 3.96 | 11.0 |
| 17 | 56 | 95 | 50 | 6.13 | 17.03 |
| 18 | 56 | 95 | 50 | 4.80 | 13.33 |
| 19 | 56 | 95 | 50 | 3.80 | 10.55 |
| 20 | 56 | 95 | 50 | 3.81 | 10.58 |
| CCr, mg/L | Cr Content After Sorption, mg/L | Extracted Cr Content, mg/L | R, % |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20 | 12.0 | 8.0 | 40.0 |
| 30 | 10.0 | 19.1 | 63.6 |
| 50 | 15.5 | 34.5 | 69.0 |
| 70 | 32.0 | 38.0 | 54.3 |
| 98 | 44.4 | 53.6 | 54.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sultanbayeva, G.; Kaiynbayeva, R.; Chernyakova, R.; Temel, H.; Jussipbekov, U.; Tassibekov, K. Sustainable Chromium Remediation: Sorption of Chromium from Leaching Solutions of Refined. Sustainability 2025, 17, 2726. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17062726
Sultanbayeva G, Kaiynbayeva R, Chernyakova R, Temel H, Jussipbekov U, Tassibekov K. Sustainable Chromium Remediation: Sorption of Chromium from Leaching Solutions of Refined. Sustainability. 2025; 17(6):2726. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17062726
Chicago/Turabian StyleSultanbayeva, Gita, Raushan Kaiynbayeva, Raissa Chernyakova, Hamdi Temel, Umirzak Jussipbekov, and Khaidar Tassibekov. 2025. "Sustainable Chromium Remediation: Sorption of Chromium from Leaching Solutions of Refined" Sustainability 17, no. 6: 2726. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17062726
APA StyleSultanbayeva, G., Kaiynbayeva, R., Chernyakova, R., Temel, H., Jussipbekov, U., & Tassibekov, K. (2025). Sustainable Chromium Remediation: Sorption of Chromium from Leaching Solutions of Refined. Sustainability, 17(6), 2726. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17062726







