Sustainability of the River Environment Related to Hydro-Chemical Stresses of Sewage Treatment Plants in Chienti and Potenza Rivers (Central Italy)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
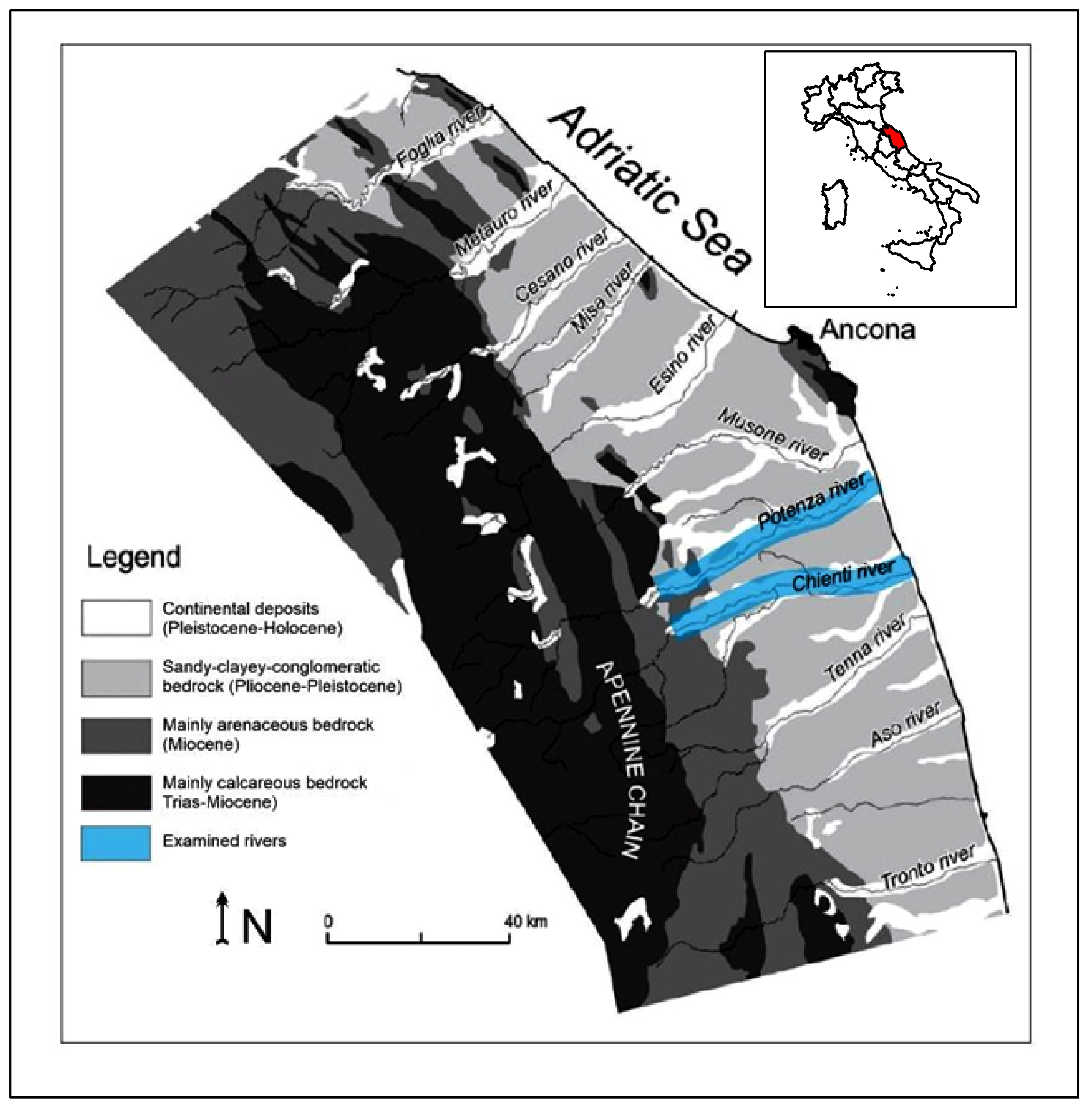
2.1. Study Area
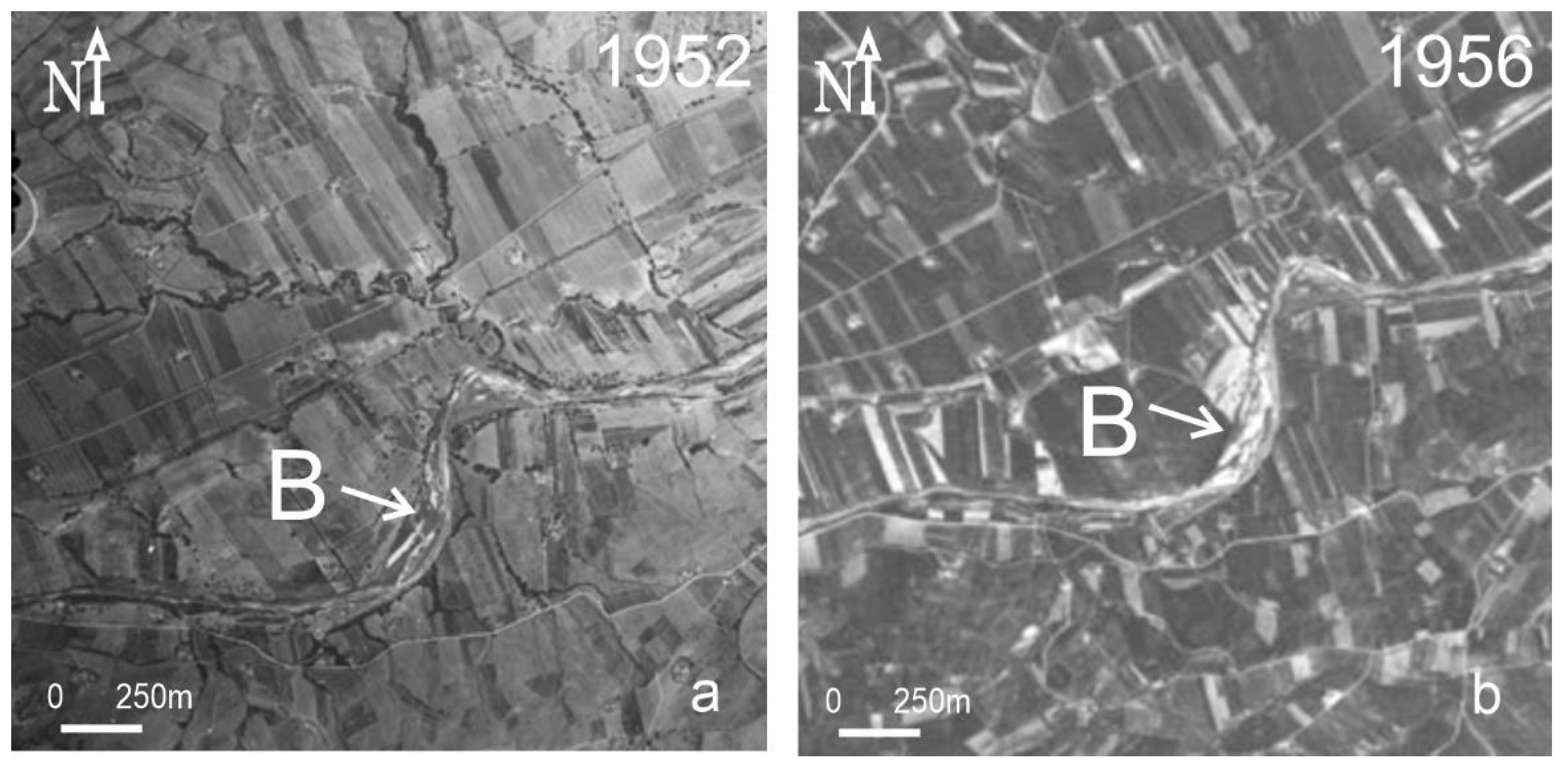
2.2. Erosion and Sedimentation Processes in the 20th Century
2.3. Workflow
3. Results
3.1. Identification of Study Cases
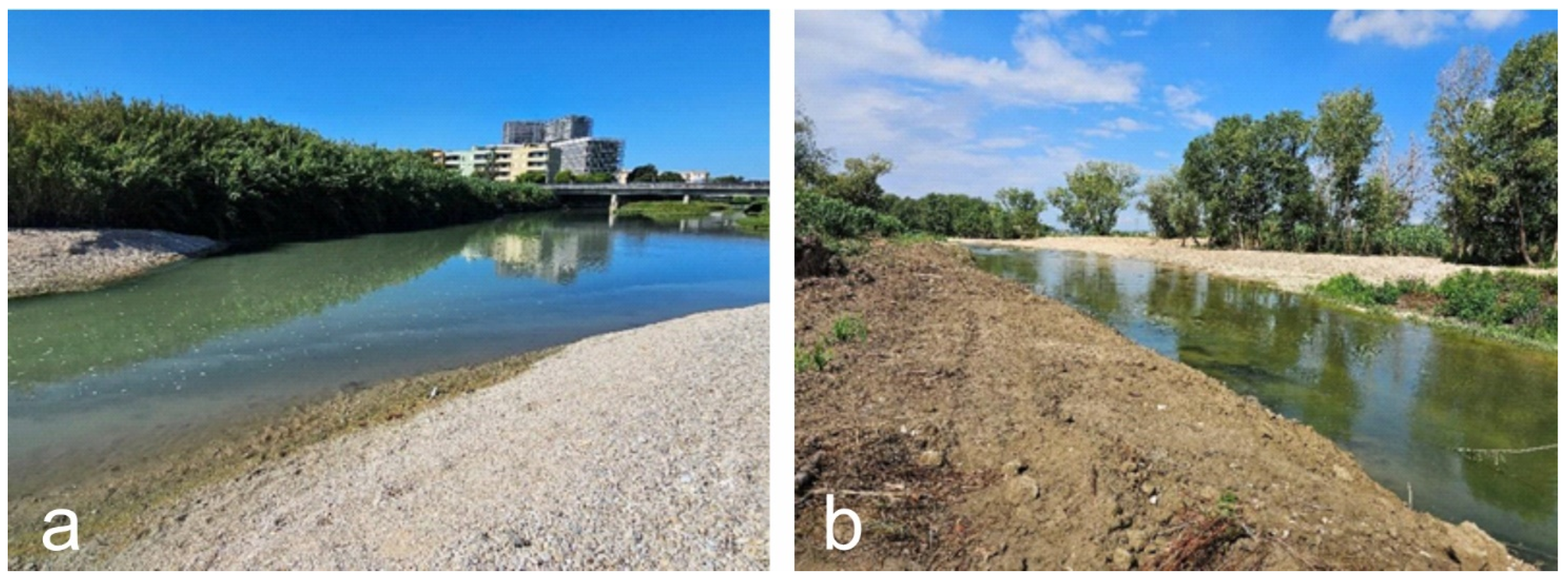
3.1.1. Scenarios of the Lower Part of the Basins
3.1.2. Scenarios of the Middle Part of the Basins
3.1.3. Scenarios of the Higher Part of the Basins
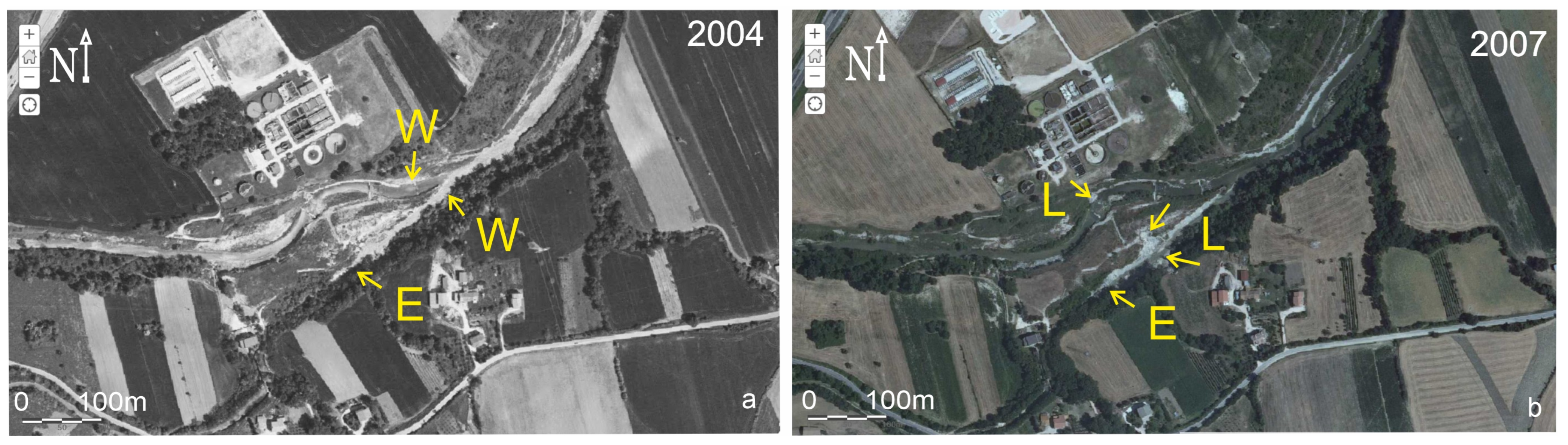
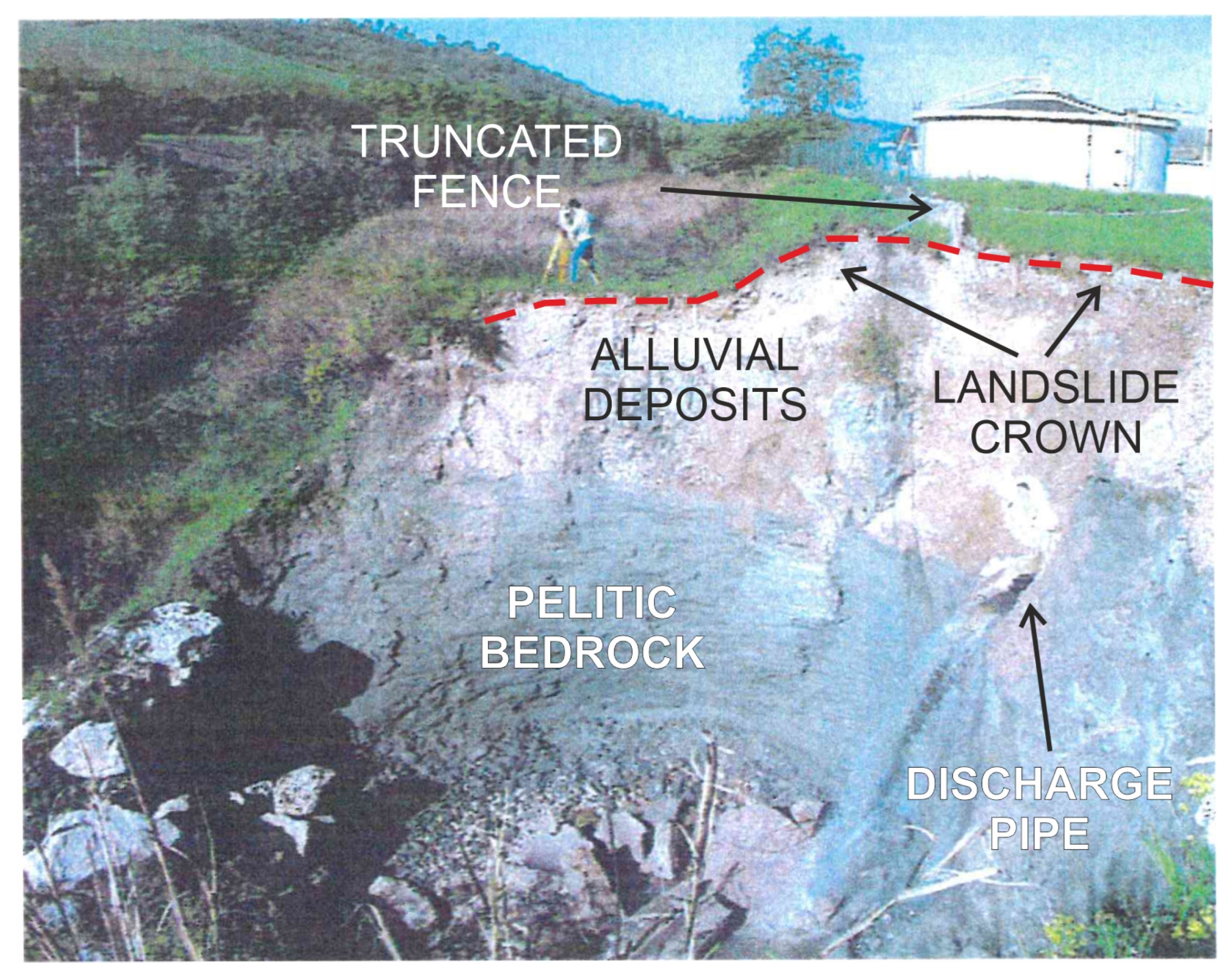
3.2. The Study Case of Tolentino
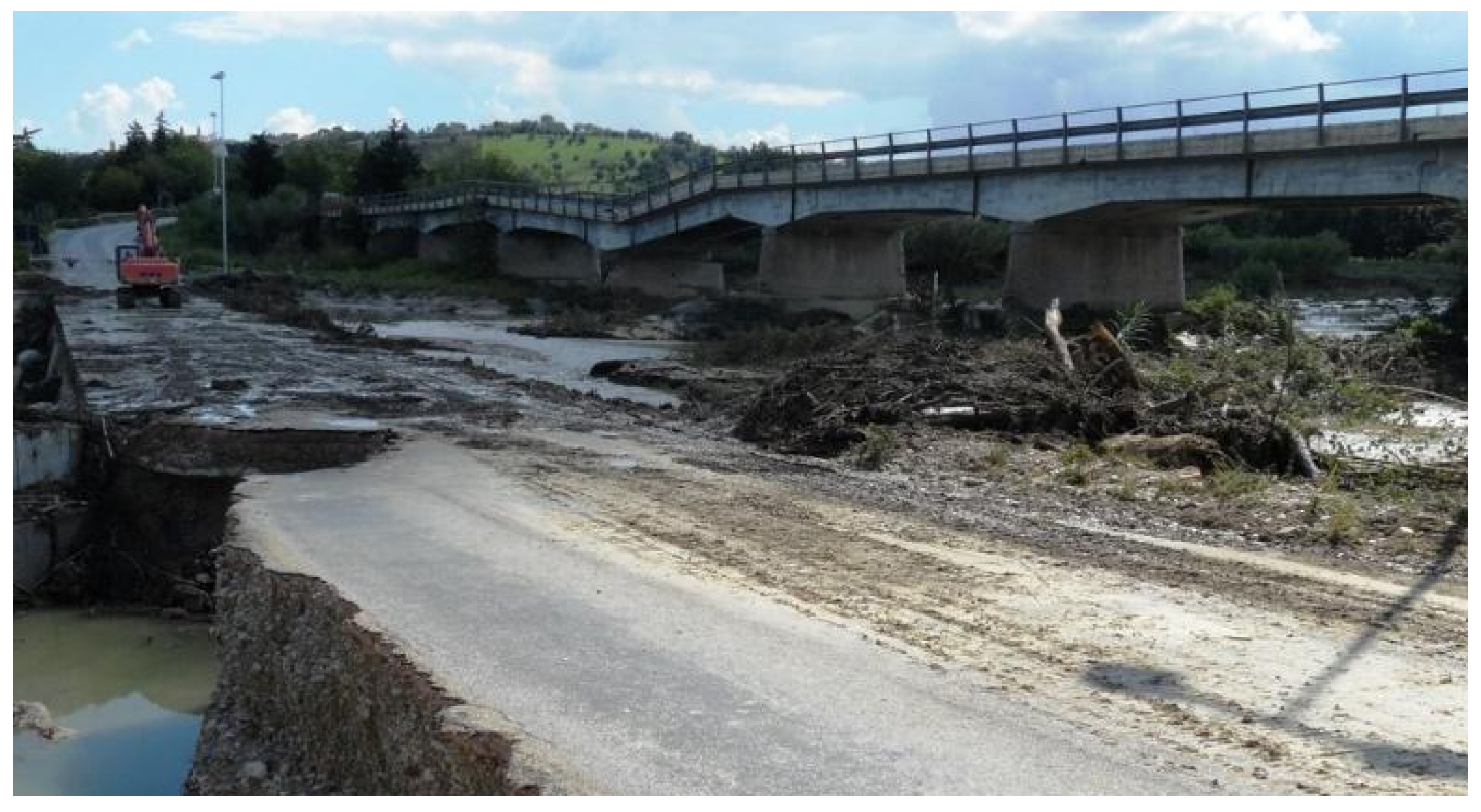
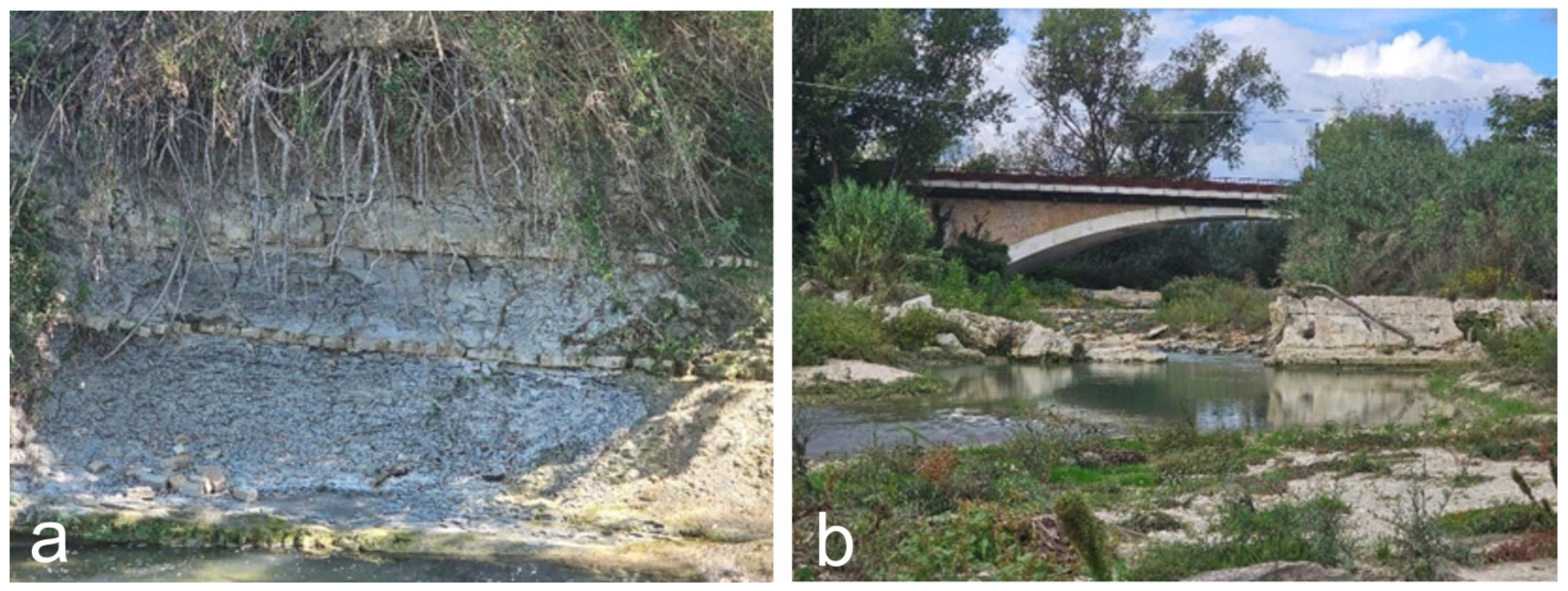
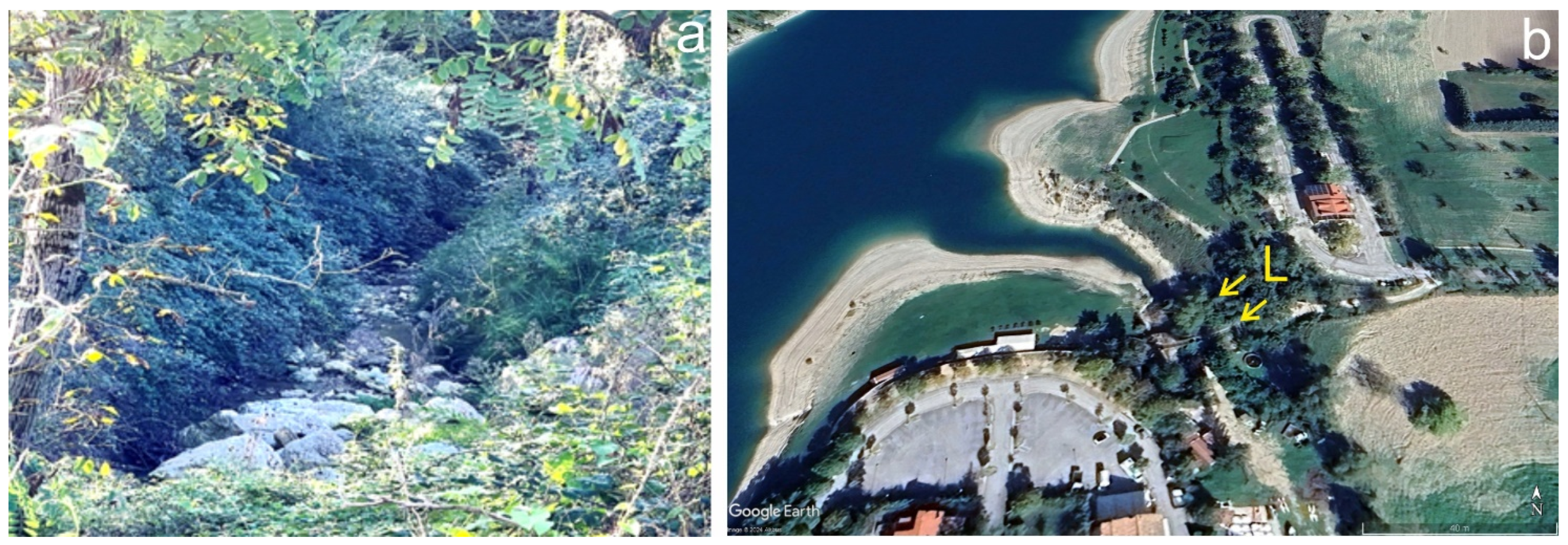
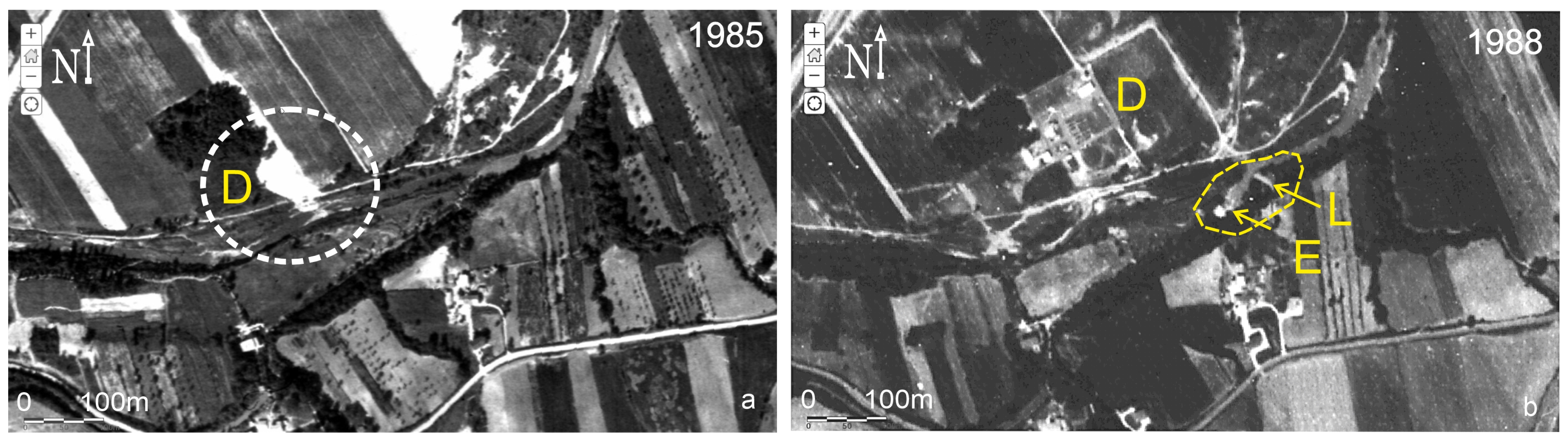
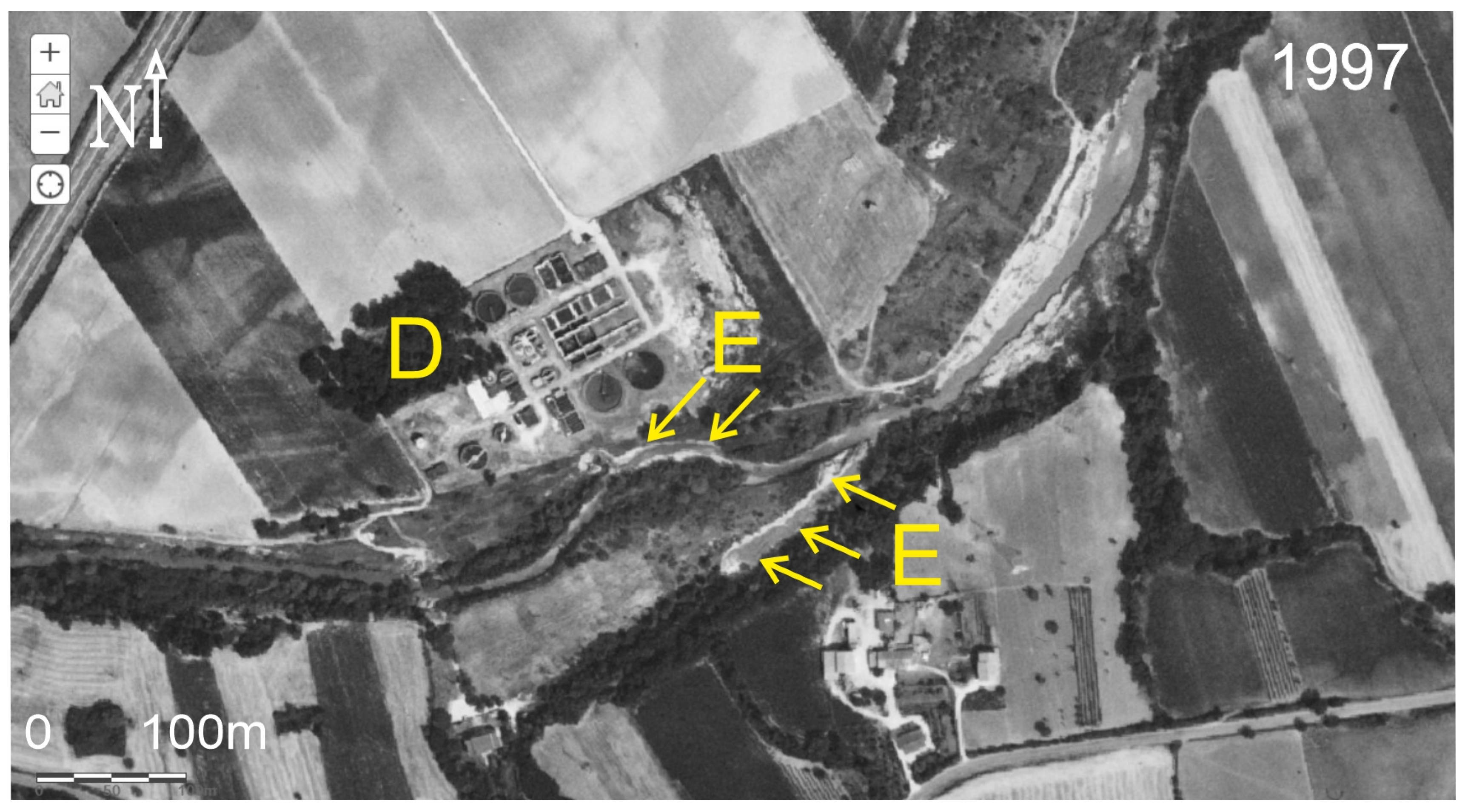
3.2.1. Results of Field Surveys and Analysis on Aerial Photos
3.2.2. Results of Chemical, Geotechnical and XRD Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- -
- Erosion of rivers due to man-made works is a problem that has become increasingly important over the last thirty years.
- -
- Erosion has had increases attributed to physical reasons (change in river flow) and chemical reasons (change in water chemistry).
- -
- Water purification plants can play a role in the degradation of substrates, but also mechanical erosion of channels used to return water after it has fed hydroelectric plants.
- -
- In the Chienti and Potenza Rivers, we verified these processes assessing the changes in the dynamics of the rivers and quantifying the generated erosion.
- -
- Regressive erosion was observed at these plants by means of geomorphological surveys, analyses from aerial photographs, and historical maps.
- -
- By conducting chemical analyses on water samples and mineralogical/geotechnical analyses on clay bedrock, an attempt was made to understand how erosion is influenced by surfactants in wastewater.
- -
- The surveys made it possible to assess the deepening of the riverbed, estimating the erosion rate over time quite accurately, which was found to be as follows.
- ○
- In the 30-year period 1960–1990, there was an average of about 166 mm/year (with peaks of 400 mm/year), a high rate due overall to the numerous excavations in the riverbed that triggered strong erosional phenomena in addition to the natural river dynamics.
- ○
- In the 1990–2020 period, there is a slightly lower but still significant rate of 150 mm/year, no longer due to (disused) quarries, but probably due to inputs from sewage treatment plants that have greatly altered the river dynamics as shown. The effect of decreasing rainfall in recent decades is also considered.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Preece, R.C.; Bridgland, D.R. Holywell Coombe, Folkestone: A 13,000 year history of an English Chalkland Valley. Quat. Sci. Rev. 1999, 18, 1075–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brocard, G.Y.; van der Beek, P.A.; Bourlès, D.L.; Siame, L.L.; Mugnier, J.L. Long-term fluvial incision rates and postglacial river relaxation time in the French Western Alps from 10Be dating of alluvial terraces with assessment of inheritance, soil development and wind ablation effects. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2003, 209, 197–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumm, S.A. River response to baselevel change: Implications for sequence stratigraphy. J. Geol. 1993, 101, 279–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holbrook, J.; Scott, R.W.; Oboh-Ikuenobe, F.E. Base-level buffers and buttresses: A model for upstream versus downstream control on fluvial geometry and architecture within sequences. J. Sediment. Res. 2006, 76, 162–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pszonka, J.; Wendorff, M.; Godlewski, P. Sensitivity of marginal basins in recording global icehouse and regional tectonic controls on sedimentation. Example of the Cergowa Basin, (Oligocene) Outer Carpathians. Sediment. Geol. 2023, 444, 106326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumm, S.A.; Dumont, J.F.; Holbrook, J.M. Active Tectonics and Alluvial Rivers; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2000; p. 276. [Google Scholar]
- Dufaure, J.; Bossuyt, D.; Rasse, M. Déformations quaternaires et morphogénèse de l’Apennin Central Adriatique. Physio-Géo. 1988, 18, 9–46. [Google Scholar]
- Dramis, F. Il ruolo dei sollevamenti tettonici a largo raggio nella genesi del rilievo appenninico. Stud. Geol. Camerti 1992, 1, 9–15. [Google Scholar]
- Ciccacci, S.; D’Alessandro, L.; Dramis, F.; Fredi, P.; Pambianchi, G. Geomorphological and neotectonic evolution of the Umbria-Marche ridge, northern sector. Stud. Geol. Camerti 1985, 10, 7–15. [Google Scholar]
- Surian, N.; Rinaldi, M. Morphological response to river engineering and management in alluvial channels in Italy. Geomorphology 2003, 50, 307–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandarino, A.; Faccini, F.; Terrone, M.; Paliaga, G. Anthropogenic landforms and geo-hydrological hazards of the Bisagno Stream catchment (Liguria, Italy). J. Maps 2021, 17, 122–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baessler, C.; Klotz, S. Effects of changes in agricultural land-use on landscape structure and arable weed vegetation over the last 50 years. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2006, 115, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aringoli, D.; Buccolini, M.; Coco, L.; Dramis, F.; Farabollini, P.; Gentili, B.; Giacopetti, M.; Materazzi, M.; Pambianchi, G. The effects of in-stream gravel mining on river incision: An example from Central Adriatic Italy. Z. Geomorphol. 2015, 59, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collier, M.; Webb, R.H.; Schmidt, J.C. Dams and Rivers: A Primer on the Downstream Effects of Dams; US Department of the Interior: Washington, DC, USA, 1996.
- Petit, F.; Poinsart, D.; Bravard, J.P. Channel incision, gravel mining and bedload transport in the Rhône river upstream of Lyon France (“canal de Miribel”). Catena 1996, 26, 209–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondolf, G.M. Hungry water: Effects of dams and gravel mining on river channels. Environ. Manag. 1997, 21, 533–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Ruiz, J.M.; Valero-Garcés, B.L. Historical Geomorphic Processes and Human Activities in the Central Spanish Pyrenees. Mt. Res. Dev. 1998, 18, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, P.F.; Kesel, R.H. Channel migration and meander-bend curvature in the lower Mississippi River prior to major human modification. Geology 2000, 28, 531–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, P.F.; Middelkoop, H.; Stouthamer, E. Flood management along the Lower Mississippi and Rhine Rivers (The Nethelands) and the continuum of geomorphic adjustment. Geomorphology 2008, 101, 209–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leopold, L.B. River Channel Change with Time: An Example: Address as Retiring President of The Geological Society of America, Minneapolis, Minnesota, November 1972. GSA Bull. 1973, 84, 1845–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, K.J.; Park, C. Adjustment of river channel capacity downstream from a reservoir. Water Resour. Res. 1974, 10, 870–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farabollini, P.; Aringoli, D.; Gentili, B.; Materazzi, M.; Pambianchi, G. Processi di approfondimento dell’erosione in alveo ed effetti dell’inquinamento nei fiumi delle Marche centro-meridionali (Italia centrale). Alp. Mediterr. Quat. 2008, 21, 317–330. [Google Scholar]
- Borelli, P.; Hoelzmann, P.R.; Knitter, D.; Schutt, B. Late Quaternary soil erosion and landscape development in the Apennine region (central Italy). In Proceedings of the LAC 2012: 2nd International Landscape and Archaeology Conference, Berlin, Germany, 6–9 June 2012; Volume 312, pp. 96–108. [Google Scholar]
- Rinaldi, M.; Surian, N.; Comiti, F.; Bussettini, M. A method for the assessment and analysis of the hydromorphological condition of Italian streams: The morphological quality index (MQI). Geomorphology 2013, 180–181, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravard, J.P.; Amoros, C.; Pautou, G.; Bornette, G.; Bournaud, M.; Creuze Des Chatelliers, M.; Gibert, J.; Peiry, G.L.; Perrin, O.; Tachet, H. River incision in south-east France morphological phenomena and ecological effects. Regul. Rivers Res. Manag. 1997, 13, 75–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.V.; Lyttle, M.M.; Brown, K.B. Impacts of Gravel Mining on Gravel Bed Streams. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 1998, 127, 979–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchetti, M. Environmental changes in the central Po Plain (northern Italy) due to fluvial modifications and anthropogenic activities. Geomorphology 2002, 44, 361–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, A.; Rinaldi, M. Disturbance, stream incision, and channel evolution: The roles of excess transport capacity and boundary materials in controlling channel response. Geomorphology 2006, 79, 361–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mossa, J.; Marks, S.R. Pit Avulsions and Planform Change on a Mined River Floodplain: Tangipahoa River, Louisiana. Phys. Geogr. 2011, 32, 512–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alighalehbabakhani, F.; Miller, C.J.; Selegean, J.P.; Barkach, J.; Sadatiyan Abkenar, S.M.; Dahl, T.; Baskaran, M. Estimates of sediment trapping rates for two reservoirs in the Lake Erie watershed: Past and present scenarios. J. Hydrol. 2017, 544, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekonnen, M.; Keesstra, S.D.; Baartman, J.E.; Ritsema, C.J.; Melesse, A.M. Evaluating sediment storage dams: Structural off-site sediment trapping measures in northwest ethiopia. Cuad. Investig. Geográfica 2015, 41, 7–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issa, I.E.; Al-ansari, N.; Knutsson, S.; Sherwany, G. Monitoring and Evaluating the Sedimentation Process in Mosul Dam Reservoir Using Trap Efficiency Approaches. Engineering 2015, 7, 190–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kummu, M.; Lu, X.X.; Wang, J.J.; Varis, O. Geomorphology Basin-wide sediment trapping efficiency of emerging reservoirs along the Mekong. Geomorphology 2010, 119, 181–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulu, A.; Dwarakish, G.S. Different Approach for Using Trap Efficiency for Estimation of Reservoir Sedimentation. An Overview. Aquat. Procedia 2015, 4, 847–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Lu, X.X. Geomorphology Estimate of cumulative sediment trapping by multiple reservoirs in large river basins: An example of the Yangtze River basin. Geomorphology 2014, 227, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conoscenti, C.; Martinello, C.; Alfonso-Torreño, A.; Gómez-Gutiérrez, Á. Predicting sediment deposition rate in check-dams using machine learning techniques and high-resolution DEMs. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arulanandan, K.; Sargunam, A.; Loganathan, P.; Krone, R. Application of Chemical and Electrical parameters to prediction of erodibility. In Soil Erosion: Causes and Mechanisms; Prevention and Control, Special Rep. 135; Highway Research Board: Washington, DC, USA, 1973; pp. 42–51. [Google Scholar]
- Osman, A.M.; Thorne, C.R. Riverbank Stability Analysis. I: Theory. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1988, 114, 134–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, L.; Diogene, G. Effetti dell’inquinamento sul comportamento meccanico dei terreni. Quad. dtai Geol. Appl. 2002, 9, 9–20. [Google Scholar]
- Lavé, J.; Avouac, J.P. Fluvial incision and tectonic uplift across the Himalayas of central Nepal. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2001, 106, 26561–26591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bufalini, M.; Aringoli, D.; Bendia, F.; Farabollini, P.; Gentilucci, M.; Lampa, F.; Martinello, C.; Materazzi, M.; Pambianchi, G. The Role of Wastewater in Controlling Fluvial Erosion Processes on Clayey Bedrock. Land 2023, 12, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dramis, F.; Gentili, B. La frequenza areale di drenaggio ed il suo impiego nella valutazione quantitativa dell’erosione lineare di superfici con caratteristiche omogenee. Mem. Soc. Geol. It. 1975, 14, 337–349. [Google Scholar]
- Nesci, O.; Savelli, D.; Troiani, F. Types and development of stream terraces in the Marche Apennines (central Italy): A review and remarks on recent appraisals. Géomorphologie 2012, 18, 215–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentilucci, M.; Rossi, A.; Pelagagge, N.; Aringoli, D.; Barbieri, M.; Pambianchi, G. GEV Analysis of Extreme Rainfall: Comparing Different Time Intervals to Analyse Model Response in Terms of Return Levels in the Study Area of Central Italy. Sustainability 2023, 15, 11656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentilucci, M.; Domenicucci, S.; Barbieri, M.; Hamed, Y.; Hadji, R.; Missaoui, R.; Pambianchi, G. Spatial Effects of NAO on Temperature and Precipitation Anomalies in Italy. Water 2023, 15, 3727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentilucci, M.; Catorci, A.; Panichella, T.; Moscatelli, S.; Hamed, Y.; Missaoui, R.; Pambianchi, G. Analysis of snow cover in the Sibillini Mountains in Central Italy. Climate 2023, 11, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, W.; Zhang, B. Variations of temperature and precipitation of snowmelt period and its effect on runoff in the mountainous areas of Northwest China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2013, 23, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, D.M.; Huang, D.; Yang, W.D.; Zhu, J.L.; Fu, G.Y. Understanding the triggering mechanism and possible kinematic evolution of a reactivated landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir. Landslides 2017, 14, 2073–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aringoli, D.; Farabollini, P.; Pambianchi, G.; Materazzi, M.; Bufalini, M.; Fuffa, E.; Gentilucci, M.; Scalella, G. Geomorphological hazard in active tectonics area: Study cases from Sibillini mountains thrust system (Central Apennines). Land 2021, 10, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aringoli, D. Hydrogeological and climatic risks: The emblematic case of an exceptional debris flow in central Apennines (Italy). In Advances in Science, Technology & Innovation; Chenchouni, H., Zhang, Z., Bisht, D.S., Gentilucci, M., Chen, M., Chaminé, H.I., Barbieri, M., Jat, M.K., Rodrigo-Comino, J., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 283–290. [Google Scholar]
- Mangifesta, M.; Aringoli, D.; Pambianchi, G.; Giannini, L.M.; Scalella, G.; Sciarra, N. A Methodologic Approach to Study Large and Complex Landslides: An Application in Central Apennines. Geosciences 2024, 14, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Pasquale, G.; Buonincontri, M.P.; Allevato, E.; Saracino, A. Human-derived landscape changes on the northern Etruria coast (western Italy) between Roman times and the late Middle Ages. Holocene 2014, 24, 1491–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sereni, E. Storia del Paesaggio Agrario Italiano; Laterza: Bari, Italy, 1979; 484p. [Google Scholar]
- Conosci L’Italia. Vol. 7 Il Paesaggio Ed. 1963 Touring Club Italiano A11—1 gennaio 1963. Available online: https://www.amazon.it/Conosci-LItalia-Paesaggio-Touring-Italiano/dp/B00W19L3WM (accessed on 10 October 2024).
- Albani, D. Indagine Preventiva Sulle Recenti Variazioni Della Linea di Spiaggia Delle Coste Italiane; Comit. Naz. Geogr. CNR: Roma, Italy, 1933; 93p. [Google Scholar]
- Conti, A.; Di Eusebio, F.; Dramis, F.; Gentili, B. Evoluzione geomorfologica recente e processi in atto nell’alveo del Tenna (Marche meridionali). Atti XXIII Congr. Geogr. It. Catania 1983, 2, 53–56. [Google Scholar]
- Coltorti, M.; Gentili, B.; Pambianchi, G. Evoluzione geomorfologica ed impatto antropico nei sistemi idrografici delle Marche: Riflessi sull’ambiente fisico. Mem. Della Soc. Geogr. Ital. 1995, 53, 271–292. [Google Scholar]
- Coltorti, M. Modificazioni morfologiche oloceniche nelle piane alluvionali marchigiane: Alcuni esempi nei fiumi Misa, Cesano e Musone. Geogr. Fis. Dinam. Quat. 1991, 14, 73–86. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.; Liu, S.C.; Cicerone, R.J.; Shiu, C.J.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y. Trends of extreme precipitation in eastern China and their possible causes. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2015, 32, 1027–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belletti, B.; Nardi, L.; Rinaldi, M. Diagnosing problems induced by past gravel mining and other disturbances in Southern European rivers: The Magra River, Italy. Aquat. Sci. 2016, 78, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anfuso, G.; Pranzini, E.; Vitale, G. An integrated approach to coastal erosion problems in northern Tuscany (Italy): Littoral morphological evolution and cell distribution. Geomorphology 2011, 129, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazzoffi, P. Soil erosion tolerance and water runoff control: Minimum environmental standards. Reg. Environ. Change 2009, 9, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, D.B.; Henshaw, P.C. Rates of channel erosion in small urban streams. In Land Use and Watersheds: Human Influence on Hydrology and Geomorphology in Urban and Forest Areas; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2001; Volume 2, pp. 17–38. [Google Scholar]
- Seidl, M.A.; Dietrich, W.E.; Schmidt, K.H.; De Ploey, J. The problem of channel erosion into bedrock. Funct. Geomorphol. 1992, 23, 101–124. [Google Scholar]
- Herz-Thyhsen, R.J.; Kaszuba, J.P.; Dewey, J.C. Mineral dissolution and precipitation induced by hydraulic fracturing of a mudstone and a tight sandstone in the Powder River Basin, Wyoming, USA. Appl. Geochem. 2020, 119, 104636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuriqi, A.; Pinheiro, A.N.; Sordo-Ward, A.; Bejarano, M.D.; Garrote, L. Ecological impacts of run-of-river hydropower plants—Current status and future prospects on the brink of energy transition. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 142, 110833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darries, G.; Ayeleso, A.; Raji, A. Exploring hydropower options at A wastewater treatment plant-A case study. In Proceedings of the 2022 30th Southern African Universities Power Engineering Conference (SAUPEC), Durban, South Africa, 25–27 January 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]















Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aringoli, D.; Pambianchi, G.; Bendia, F.; Bufalini, M.; Farabollini, P.; Lampa, F.; Materazzi, M.; Gentilucci, M. Sustainability of the River Environment Related to Hydro-Chemical Stresses of Sewage Treatment Plants in Chienti and Potenza Rivers (Central Italy). Sustainability 2025, 17, 2711. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17062711
Aringoli D, Pambianchi G, Bendia F, Bufalini M, Farabollini P, Lampa F, Materazzi M, Gentilucci M. Sustainability of the River Environment Related to Hydro-Chemical Stresses of Sewage Treatment Plants in Chienti and Potenza Rivers (Central Italy). Sustainability. 2025; 17(6):2711. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17062711
Chicago/Turabian StyleAringoli, Domenico, Gilberto Pambianchi, Fabrizio Bendia, Margherita Bufalini, Piero Farabollini, Francesco Lampa, Marco Materazzi, and Matteo Gentilucci. 2025. "Sustainability of the River Environment Related to Hydro-Chemical Stresses of Sewage Treatment Plants in Chienti and Potenza Rivers (Central Italy)" Sustainability 17, no. 6: 2711. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17062711
APA StyleAringoli, D., Pambianchi, G., Bendia, F., Bufalini, M., Farabollini, P., Lampa, F., Materazzi, M., & Gentilucci, M. (2025). Sustainability of the River Environment Related to Hydro-Chemical Stresses of Sewage Treatment Plants in Chienti and Potenza Rivers (Central Italy). Sustainability, 17(6), 2711. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17062711








