Abstract
The increasingly severe issue of pesticide packaging waste (PPW) pollution poses a significant threat to human health and sustainable agricultural development. Encouraging farmers to recycle PPW is critical to addressing the “tragedy of the commons” problem in rural areas. Using data from the 2020 China Rural Revitalization Survey (CRRS), this paper examines the impact of digital literacy on farmers’ PPW recycling behavior. The results indicate that (1) a one-unit increase in digital literacy raises the likelihood of farmers recycling PPW by 20.1%. (2) Mechanism analysis shows that subjective cognition, information transmission, and social network are the key channels through which digital literacy affects farmers’ PPW recycling behavior. (3) After conducting multiple robustness tests—including Propensity Score Matching (PSM), instrumental variable methods, alternative weighting approaches for digital literacy, and different model specifications and samples—the findings remain robust. Based on these results, we propose the following policy recommendations: improve digital infrastructure in rural areas; enhance farmers’ digital literacy; establish incentive mechanisms; encourage village self-governance; and reinforce social oversight.
1. Introduction
The use of pesticides is vital for enhancing global agricultural productivity and ensuring food security [1]. According to the latest data released by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), global pesticide usage reached 3.70 million tons in 2022, doubling the total amount used in 1990 and maintaining a steady upward trend. However, alongside the extensive use of pesticides, pollution caused by pesticide packaging waste (PPW) has emerged as a significant threat to sustainable agricultural development. On the one hand, PPW is primarily composed of non-degradable materials. The arbitrary disposal of it can inhibit crop growth and contribute to severe agricultural non-point source pollution [2]. On the other hand, PPW often contains 2–5% residual pesticides. These residues may leach into the soil or water sources, posing a threat to ecosystems and human health [3].
PPW recycling management has garnered considerable attention globally. Since 1993, Brazil has implemented an effective PPW recycling model. This model integrates legislation, industry association advocacy, government-supported nonprofit organizations, and active farmer participation, setting a benchmark for developing countries [4]. As a major agricultural nation among developing countries, China generated approximately 126,500 tons of PPW in 2022. However, issues such as direct disposal remain prevalent, highlighting the urgent need to strengthen PPW recycling management. In 2020, China’s Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs and Ministry of Ecology and Environment issued the “Management Measures for the Recycling and Disposal of Pesticide Packaging Waste”, mandating that governments, pesticide producers, operators, and users fulfill their responsibilities in recycling PPW.
Due to the dispersed and widespread nature of PPW, relying solely on government intervention is both costly and inefficient. PPW recycling management faces a “tragedy of the commons” problem. Although recycling PPW offers significant social and ecological benefits, the private gains for farmers are limited, resulting in low voluntary participation. Thus, motivating farmers to actively recycle PPW is a major challenge for the government in establishing an effective recycling management system.
Farmers often lack sufficient knowledge and information about the benefits of recycling PPW, leading to low participation levels. The digital era has greatly expanded the channels and capacity for farmers to access information and engage in environmental governance. With the gradual improvement of rural digital infrastructure, there is increasing attention on farmers’ digital literacy—the ability to acquire digital information, develop digital awareness, and creatively utilize digital resources. In 2024, the Central Cyberspace Administration of China, along with three other departments, issued the “2024 Key Work Points for Enhancing Digital Literacy and Skills of the Whole Population”, emphasizing the need to bridge the digital divide and improve digital literacy, particularly among farmers. Previous research has demonstrated that enhanced digital literacy promotes farmers’ participation in rural development [5], green production [6], and entrepreneurial activities [7]. Therefore, the question in this study arises: does the improvement of farmers’ digital literacy encourage them to recycle PPW? Answering this question is critical to addressing the “tragedy of the commons” problem in PPW recycling management and achieving sustainable agricultural development.
Existing research on the factors influencing farmers’ PPW recycling behavior primarily focuses on individual and social dimensions. At the individual level, factors such as age [8], education level [9], agricultural training [10], economic expectations [11], subjective attitudes [12], ecological literacy [13], and perceived value significantly influence farmers’ PPW recycling behaviors [14]. Household-level factors such as the number of laborers, household income [15], and cultivated land area also play significant roles [10]. At the societal level, social norms [16], economic incentives [17], neighborhood effects, policy interventions [18], and proximity to villages or pesticide service centers have been shown to significantly impact farmers’ PPW recycling behaviors [10]. In addition, some scholars have also studied the effectiveness of biotechnology such as Black Soldier Fly Larvae (BSFL) for the efficient treatment and management of solid waste [19,20]. However, most existing studies have concentrated on micro-level socio-economic characteristics and macro-level economic policies, with limited exploration of how digital literacy influences farmers’ PPW recycling behavior.
To address these gaps in the literature, this study utilizes nationally representative data from the China Rural Revitalization Survey (CRRS) to empirically examine the impact of farmers’ digital literacy on PPW recycling behavior. Additionally, it analyzes the roles of subjective cognition, information dissemination, and social network as mechanisms. These analyses provide valuable insights into promoting farmers’ PPW recycling behavior and comprehensively enhancing sustainable agricultural development.
The primary contributions of this study are as follows: First, it deepens the understanding of the factors influencing farmers’ PPW recycling behavior by establishing a causal linkage between farmers’ digital literacy and PPW recycling behavior. It also enriches the analysis of mechanisms through which digital literacy influences farmers’ PPW recycling behavior via subjective cognition, information dissemination, and social network, providing new perspectives for sustainable agricultural development. Second, it provides insights into enhancing the effectiveness of environmental governance in the digital age. PPW recycling management is constrained by a “tragedy of the commons” problem, and insufficient farmer participation is a key limiting factor. Our study finds that enhanced digital literacy promotes farmers’ PPW recycling behavior. This finding provides novel approaches to utilizing digital tools for establishing comprehensive rural environmental governance systems and addressing the “tragedy of the commons” in PPW recycling management. Third, this study utilizes nationally representative data spanning multiple provinces in China. This provides broader representativeness compared to prior studies, which predominantly depended on single-province datasets. The findings of this study also offer valuable insights into green production and sustainable agricultural development in other developing countries.
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows: Section 2 proposes the research hypotheses and establishes the empirical model. Section 3 describes the data sources, variables, and sample characteristics. Section 4 presents the baseline regression results, examines the underlying mechanisms, conducts robustness tests using various methods, and completes the heterogeneity analysis. Section 5 concludes this paper and provides policy recommendations.
2. Research Hypothesis and Model Specification
2.1. Research Hypothesis
The digital era has witnessed the emergence of a wide array of digital tools, yet the effectiveness of these tools ultimately hinges on individuals’ digital literacy. Digital literacy extends beyond technical skills, encompassing cognitive, social, and moral literacies [21]. Gilster (1997) first defined digital literacy as a composite ability to read, integrate, and evaluate digital information [22]. Martin et al. (2006) described digital literacy as an evolving skill set that includes using digital tools, accessing resources, constructing knowledge, and engaging in communication [23]. Similarly, the European Commission identified five dimensions of digital literacy: information retrieval, communication, digital creation, digital safety, and problem-solving. The Cyberspace Administration of China, in its “Action Plan for Enhancing National Digital Literacy and Skills”, highlighted that digital literacy embodies the ability to acquire, create, utilize, evaluate, interact with, share, innovate, safeguard, and uphold ethical practices in digital spaces. It also emphasized that digital literacy should align with the production and daily lives of the populace while aiming to fulfill their aspirations for a better quality of life.
In the context of digital rural development, digital technologies and platforms have increasingly integrated into diverse areas of rural governance, including environmental management. With the improvement of rural digital infrastructure, the enhancement of farmers’ digital literacy directly affects their willingness and initiative to participate in rural governance. Su and Peng (2022) discovered that farmers with higher digital literacy levels are more likely to participate in rural governance and public affairs such as village management and democratic supervision through channels like WeChat groups and government service apps [5].
Building on existing research and the conceptual framework of digital literacy, we constructed a theoretical analytical model (see Figure 1).
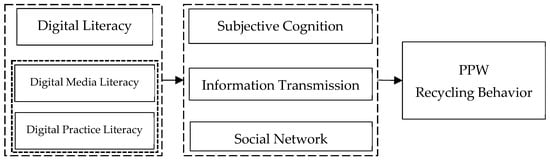
Figure 1.
Theoretical analytical model.
In the digital era, farmers with higher digital literacy are more likely to benefit from the digital economy through changes in subjective cognition, information transmission, and social network, leading to increased PPW recycling behavior. Therefore, the following basic research hypothesis (H1) is proposed:
H1:
Enhanced digital literacy promotes farmers’ PPW recycling behavior.
Subjective cognition refers to farmers’ awareness and satisfaction concerning environmental issues. Higher digital literacy enhances farmers’ attention to PPW by fostering greater environmental concern and satisfaction from ecological improvements. This is achieved through the efficient use of digital tools, enabling farmers to receive environmental information and heighten their awareness of the risks posed by improper PPW disposal. They would recognize the potential threats of rural environmental degradation to their health [24]. Recycling PPW also contributes to the long-term protection of farmers’ health, ensuring their continued ability to earn income. Enhanced digital literacy increases farmers’ likelihood of accessing online information and revising their perceptions. This shift encourages them to expect long-term benefits from recycling PPW. Thus, the following sub-hypothesis is proposed:
H1A:
Digital literacy promotes farmers’ PPW recycling behavior through subjective cognition mechanisms.
Information transmission reduces costs, enhances information sharing, and lowers supervision expenses, thereby promoting farmers’ PPW recycling behavior. Enhanced digital literacy enables farmers to utilize devices such as smartphones and computers to access the internet more frequently and conveniently, significantly lowering information transmission costs. Farmers can easily learn about PPW recycling policies, procedures, and potential benefits through online platforms, effectively lowering the barriers to participation and reshaping internal psychological norms [25]. Moreover, digital literacy equips farmers to actively participate in digital governance by engaging in discussions within transparent rural public spaces, such as WeChat groups. This enables them to stay updated on relevant PPW recycling policies and lowers the costs of environmental monitoring and governance [5]. Accordingly, we propose the following sub-hypothesis:
H1B:
Digital literacy promotes farmers’ PPW recycling behavior through information transmission mechanisms.
Digital literacy provides farmers with opportunities to expand social connections through platforms such as WeChat, TikTok, and Taobao, breaking through geographical and social barriers at minimal cost. This expansion of social network increases the channels for disseminating PPW information and fosters mutual support among network members. On the one hand, enhanced social interaction strengthens farmers’ tendency to follow others, thereby increasing their sense of social recognition and group belonging through recycling PPW [18]. On the other hand, social network foster transparency and social supervision. Under implicit social pressure, farmers’ harmful environmental behaviors are constrained and adjusted, increasing their likelihood of recycling PPW [13]. Therefore, the following sub-hypothesis is proposed:
H1C:
Digital literacy promotes farmers’ PPW recycling behavior through social network mechanisms.
2.2. Model Specification
2.2.1. Baseline Regression Model
The dependent variable in this study was whether farmers recycle PPW, represented as a binary variable (0 or 1). Therefore, we used the Probit model to analyze the impact of digital literacy on farmers’ PPW recycling behavior. The model is specified as follows:
where represents the binary variable indicating whether farmer j recycles PPW or not. indicates the farmer’s level of digital literacy. represents control variables including individual, household, and village characteristics. and denote province fixed effects and random error terms, respectively. represents parameters of control variables. The key parameter of interest, , measures the impact of digital literacy on farmers’ PPW recycling behavior after controlling for control variables and province-fixed effects.
2.2.2. Mechanism Analysis Model
As proposed in the research hypotheses section, digital literacy can promote farmers’ PPW recycling behavior through subjective cognition (SC), information transmission (IT), and social network (SN) mechanisms. Drawing upon previous research [19,26], we constructed linear regression models to evaluate the relationships between digital literacy and these intermediary variables, where coefficients , represent constants and coefficients , , estimate the impacts of digital literacy on SC, IT, and SN, respectively. , , and denote control variables, province fixed effects, and random error terms, respectively. The models are expressed as follows:
3. Data Sources and Variable Definition
3.1. Data Sources
This study utilized data from CRRS, a nationally representative survey administered by the Rural Development Institute (RDI) of the Chinese Academy of Social Sciences (CASS). Conducted through coordinated efforts of over 1000 trained enumerators, this comprehensive survey provided objective insights into rural development status. The first wave of CRRS was conducted between August and September 2020, encompassing 10 provinces (as shown in Figure 2)—Zhejiang, Shandong, Guangdong, Anhui, Henan, Guizhou, Sichuan, Shaanxi, Heilongjiang, and Ningxia—which collectively represent 50 counties and 156 villages. CRRS provided a robust national dataset on key aspects of rural development, including rural population and labor, rural industrial structure, farmers’ income and social welfare, rural consumption, rural governance, and comprehensive rural reform.
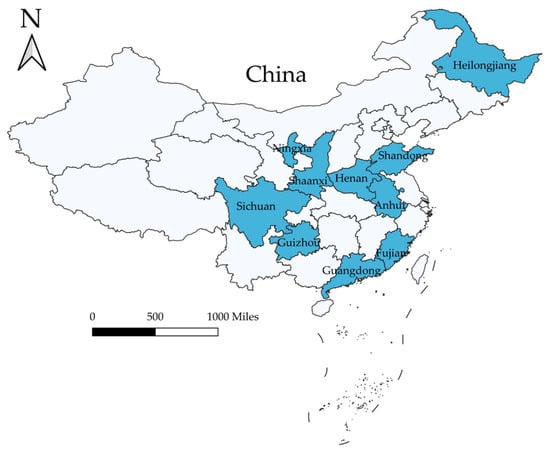
Figure 2.
Map of ten provinces selected in CRRS. The map data in Figure 2 are from DataV.GeoAtlas. https://datav.aliyun.com/portal/school/atlas/area_selector (accessed on 25 February 2025).
The multistage sampling procedure adopted a stratified random approach with four distinct phases. First, provincial stratification was implemented through stratified random sampling based on economic development levels, geographical location, and agricultural conditions across four macro-regions: Eastern, Central, Western, and Northeastern China. Subsequently, county-level sampling employed systematic random selection using county-level GDP per capita rankings, ensuring spatial distribution representativeness within each province. At the village level, analogous systematic random sampling was conducted using local economic development indices. Finally, household samples were randomly drawn from official village registries maintained by village committees.
The sample selection conditions for this study were as follows: first, the sample age was limited to between 16 and 80 years old; second, samples with missing values were excluded. The final sample consists of 8264 farmers.
3.2. Variable Selection
Dependent variable: The dependent variable in this study was the farmers’ PPW recycling behavior. Specifically, the question “How do you dispose of pesticide packaging?” was selected from the questionnaire. To measure farmers’ PPW recycling behavior, the value of the answer “recycling to fixed points, recycling to farmers’ markets, other” was assigned to 1, and the value of the answer “local burial, centralized landfill, incineration, discarded anywhere” was assigned to 0.
Core Explanatory Variables: We referred to the previous literature and constructed indicators to measure farmers’ digital literacy from two dimensions: digital media literacy and digital practice literacy [18,27]. Among them, digital media literacy was defined by whether farmers’ households have smartphones, computers with Internet access, and good network conditions, reflecting farmers’ exposure to the technological possibilities of digital life. Digital practice literacy was measured by whether farmers are proficient in using 4G cell phones, whether they search for information through the Internet, and whether they trade things through the Internet, reflecting the ability of rural residents to use digital technology to solve practical problems.
The digital literacy indicator was constructed by aggregating the sub-indicators of digital media literacy and digital practical literacy. The widely used assignment methods mainly include the equal-weighted method, the principal component analysis method, the factor analysis method, the entropy value method, etc. Different assignment methods have their own advantages and disadvantages. We employed the entropy value method for assignment in the baseline regression and conducted robustness tests using the equal-weighted and factor analysis methods. Detailed digital literacy indicators and assignment weights are provided in Table 1.

Table 1.
Digital literacy measurement dimensions, indicators, and weights.
Control variables: To mitigate potential biases caused by confounding factors, control variables were included, encompassing individual, household, and village characteristics [28]. Among them, individual characteristics include (1) gender, with males coded as 1 and females as 0; (2) age and the squared term of age; (3) marital status, with married individuals coded as 1 and others as 0; (4) ethnicity, with Han ethnicity coded as 1 and ethnic minorities as 0; (5) education level, categorized as no formal education, elementary school, junior high school, high school, secondary school, vocational high school or technical school, university college, university bachelor’s degree and above, are assigned values of 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, and 8, respectively; (6) health status, with individual self-assessed health status assigned values of 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 for very good, good, fair, poor, and very poor health, respectively. Household characteristics include (1) household size, reflecting the demographic structure of the household, and (2) household income, reflecting the level of household wealth. Village characteristics include (1) village per capita income, i.e., per capita disposable income in 2019 as reported by the village council, and (2) urban suburb location, which is assigned a value of 1 if the village is located in an urban suburb, and a value of 0 otherwise.
3.3. Descriptive Statistics
The overall proportion of sampled farmers recycling PPW is 58.0%, and the descriptive statistics of other control variables are presented in Table 2.

Table 2.
Variable definitions and descriptive statistics.
4. Estimation Results and Analysis
4.1. The Baseline Estimation Results
Since the Probit model is nonlinear and its regression coefficients lack direct economic interpretation, we reported the marginal effects, which provide a more intuitive understanding of the results.
The baseline regression results indicate that digital literacy significantly increases the likelihood of farmers’ PPW recycling behavior (see Columns (1) to (3) in Table 3). Column (3) in Table 3 indicates that after controlling individual, household, village characteristics, and provincial fixed effects, a one-unit increase (from 0 to 1) in digital literacy raises the likelihood of farmers’ PPW recycling behavior by 20.1%. Therefore, digital literacy significantly contributes to farmers’ PPW recycling behavior, and the basic hypothesis of this study is verified.

Table 3.
Results of the baseline estimation.
4.2. Mechanism Analysis
Based on the theoretical framework outlined in the previous section, digital literacy may influence farmers’ PPW recycling behavior through mechanisms such as subjective cognition, information transmission, and social network. To verify the indirect mechanisms through which digital literacy affects farmers’ PPW recycling behavior, we employed models (2), (3), and (4) as proposed in the previous chapter.
For the subjective cognition mechanism, we selected from the questionnaire “How satisfied are you with your home living environment?” as a proxy variable for farmers’ subjective perception, and the observations answering “very satisfied, quite satisfied, average, not too satisfied, very dissatisfied” were assigned values of 5, 4, 3, 2, and 1, respectively. Regression analysis was conducted using model (2). Column (1) in Table 4 shows that improved digital literacy significantly enhances farmers’ satisfaction with their living environment. This increased satisfaction likely leads to a greater sense of fulfillment from environmental improvements, which in turn motivates their PPW recycling behavior.

Table 4.
Results of mechanism analysis.
For the information transmission mechanism, we selected “Have you ever communicated with the village on important public affairs through WeChat groups” as a proxy variable question. Responses were coded as 0 for “never” and 1 for “frequently”, “occasionally”, or “rarely”. Model (3) was used for regression analysis. Column (2) in Table 4 reveals that enhanced digital literacy significantly increases the likelihood of farmers using WeChat groups to engage in public affairs. This increased participation provides farmers with better access to environmental governance information, thereby promoting their PPW recycling behavior.
For the social network mechanism, we used the question “How many relatives or friends do you have who could lend you more than 5000 yuan (regardless of interest charges)?” as a proxy variable. Prior studies suggested that financial lending behaviors within farmers’ immediate social circles (relatives, neighbors, and friends) serve as a robust proxy for evaluating the depth of relational intimacy and mutual trust [29]. The number of these relatives and friends quantitatively represents the scale of farmers’ social networks. Regression analysis was conducted using model (4). Column (3) in Table 4 indicates that improved digital literacy significantly expands farmers’ social networks. These broader social networks, influenced by social pressure and social recognition, encourage farmers to recycle PPW.
4.3. Robustness Check
4.3.1. Propensity Score Matching (PSM) Method
The distribution of farmers’ digital literacy levels is not random, as it is influenced by various aspects such as individual education level, household income level, and Internet infrastructure at the village level, etc., which may result in selection bias problem. To address this issue, we employed the Propensity Score Matching (PSM) method for verification.
First, we divided the sample into a treatment group (those with above-average digital literacy) and a control group (those with below-average digital literacy). Second, we estimated the propensity of farmers’ digital literacy levels using the Probit model, with the same control variables as in the baseline regression. Then, we matched the samples using the commonly used 1:4 nearest-neighbor matching method. The balance test results in Figure 3 clearly show that after performing 1:4 nearest-neighbor matching, the standardized biases of the control variables between the treatment group and control group have significantly decreased, and nearly all control variables no longer exhibit statistically significant differences. This suggests that the PSM method successfully achieves a better balance between the samples.
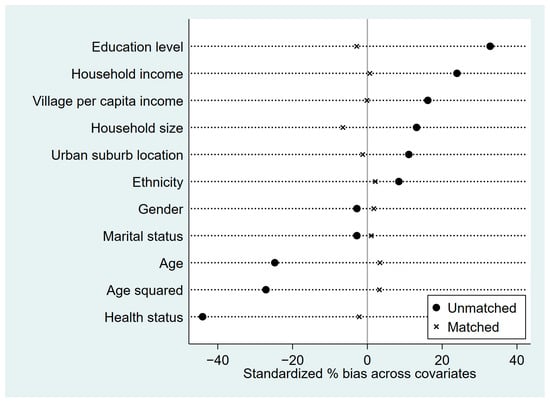
Figure 3.
Balance of matching results test.
The results of the average treatment effect (ATT) after PSM are shown in Column (1) of Table 5, where the probability of farmers’ PPW recycling behavior is significantly higher in the treatment group than in the control group. Subsequently, we conducted a regression analysis using the PSM-matched samples, and the results show (Column (2) in Table 5) that farmers’ digital literacy level significantly increases their probability of recycling PPW, which is consistent with the baseline regression results. The conclusions of this study are further supported by the fact that the PSM approach mitigates the problem of selection bias to some extent.

Table 5.
PSM results.
4.3.2. Instrumental Variables Approach
In addition to the control variables used in the baseline model, unobservable factors such as farmers’ subjective attitudes, learning abilities, and personality traits may also influence their PPW recycling behavior. To address potential omitted variable bias, this study employed the instrumental variable (IV) method. Following prior studies [18,30,31], we selected “the average digital literacy of other farmers in the same village, excluding the respondent” as the instrumental variable for the respondent’s digital literacy level. Since the digital environments within the same village are similar, a respondent’s digital literacy will be influenced by the average digital literacy of others in the same village, which meets the correlation requirement of the instrumental variable; in addition, the respondent’s PPW recycling behavior is unlikely to be directly affected by the digital literacy level of others in the village, thus satisfying the exogeneity condition of the instrumental variable.
First, we used two-stage least squares (2SLS) to conduct the test; second, considering that the dependent variable is binary (taking values of 0 or 1), we also employed the IV-Probit model to address the potential limitations of 2SLS. The results are shown in Table 6, where the first-stage F-statistics of the instrumental variables are significantly greater than 10, indicating that the instrumental variables are strongly correlated with the endogenous explanatory variables. The Wald test of the IV-Probit model rejects the exogeneity hypothesis of digital literacy at the 1% significance level, demonstrating the explanatory power of the instrumental variable. The regression results in Table 6 confirm that, even after accounting for omitted variable bias and applying the instrumental variable approach, the impact of digital literacy on farmers’ PPW recycling behavior remains statistically significant at the 1% level.

Table 6.
Instrumental variable estimation results.
4.3.3. Alternative Measures of Digital Literacy
In the baseline estimation section, we used the entropy value method to measure farmers’ digital literacy levels. In this section, we employed three alternative methods: the equal-weighted average method, factor analysis method, and direct summation method to address the potential measurement errors. Specifically, the equal-weighted average method assigns equal weights to all digital literacy indicators, with a range from 0 to 1. The factor analysis method retains factors with eigenvalues greater than 1. The KMO value of the sample adequacy test is 0.661, indicating a good correlation between the indicators. The chi-square value of Bartlett’s spherical test is significant at the 1% level, confirming the validity of the factor analysis results. The final digital literacy scores are derived from the contribution rate of the factors, with a range from 0 to 1. The direct summation method sums the six corresponding indicators of digital media literacy and digital practice literacy from Table 1, resulting in a digital literacy score with a range from 0 to 6.
Columns (1) to (3) in Table 7 present the results of estimating digital literacy levels obtained by the equal-weighted average method, the factor analysis method, and the direct summation method. All methods confirm that digital literacy significantly promotes farmers’ PPW recycling behavior, further substantiating the robustness of the conclusions.

Table 7.
Results of the robustness test.
4.3.4. Replacement of the Estimation Model
To ensure the reliability of the results, we replaced the Probit model estimation used in the baseline regression with the OLS model and Logit model for re-estimation. Columns (4) and (5) in Table 7 demonstrate that the results are generally consistent with the baseline findings, further validating the robustness of the conclusions.
4.3.5. Replacement of the Estimation Sample
We further adjusted the sample selection criteria, and the core conclusions remain unchanged. First, we excluded the mobile population whose household registration location is not in the village to avoid potential interference, and we obtained 8031 observations after excluding the mobile population; second, we removed the age restriction and included all eligible samples, resulting in 10,259 observations. Columns (6) and (7) in Table 7 report the results. These results show that farmers’ digital literacy significantly promotes their PPW recycling behavior.
4.4. Heterogeneity Analysis
We analyzed the sample for heterogeneity based on farmers’ gender, age, education level, and household economic status. First, farmers were categorized into male and female groups based on gender. Second, we divided the farmers into two groups according to their education level: those with at least 9 years of education (junior high school or above) were categorized as the high education group, while those with less than 9 years of education were classified as the low education group. Third, farmers were grouped by age: those under 45 were categorized as the young group, and those 45 and older were categorized as the elderly group. Finally, households were classified as economically better-off or worse-off based on whether their total income was above or below the median income for the sample.
The results, as presented in Columns (1) to (8) in Table 8, indicate that the effect of digital literacy on farmers’ PPW recycling behavior is significant across all subgroups, regardless of gender, age, education level, or household economic status. This demonstrates that the positive effect of digital literacy on farmers’ PPW recycling behavior is universal and does not exhibit significant differences across these demographic and socio-economic dimensions.

Table 8.
Results of heterogeneity analysis.
5. Main Conclusions and Policy Implication
5.1. Main Conclusions
PPW pollution poses a serious threat to human health and sustainable agricultural development. The “tragedy of the commons” issue in PPW recycling management underscores the indispensable role of farmers’ active participation in its effective operation. Advanced digital tools have significantly reduced the costs associated with information dissemination, mutual supervision, and participation in public affairs. However, the effective utilization of these tools ultimately depends on the enhancement of farmers’ digital literacy. This raises an important question in establishing a PPW recycling management system: Can digital literacy play a role in promoting farmers’ PPW recycling behavior?
Drawing on data from the 2020 CRRS, this paper constructs an analytical framework to examine the impact of digital literacy on farmers’ PPW recycling behaviors and explores the mechanism behind this influence. This study finds that, first, digital literacy significantly and positively influences farmers’ PPW recycling behavior, with results remaining robust even after addressing potential endogeneity issues. Second, the heterogeneity analysis indicates that the effect of digital literacy improvement does not significantly differ across groups with varying genders, ages, educational levels, or household economic statuses. Third, the mechanism analysis suggests that digital literacy may influence farmers’ PPW recycling behavior through mechanisms including subjective cognition, information transmission, and social network.
5.2. Policy Implication
Based on the above findings, this study proposes the following policy insights:
First, the government should continue to improve digital infrastructure in rural areas. In particular, it should vigorously promote the construction of 5G base stations and expand fixed broadband access for rural residents. These measures will facilitate the smooth upgrade of both mobile and fixed networks. Enhanced digital infrastructure will help farmers improve their digital literacy, thereby increasing their PPW recycling behavior and supporting rural ecological conservation.
Second, the government should adopt multiple approaches to enhance farmers’ digital literacy. For example, village committees could serve as training centers to offer regular introductory courses in digital literacy for farmers. Training should integrate agricultural production contexts and highlight the importance of recycling PPW.
Third, the government may establish incentive mechanisms to encourage participation in digital literacy training and recycling PPW. A village-based point system could be introduced to reward farmers who cooperate with government initiatives. Points could be exchanged for fertilizer, seed discount vouchers, or other essential goods.
Fourth, village self-governance should be encouraged and social oversight reinforced. Through village assemblies, a system of rewards and penalties could be established to harness the power of social network, and farmers who actively recycle PPW could be conferred with special honorary titles and awards.
5.3. Limitations and Future Research Directions
However, this study has certain limitations that require further investigation. First, the CRRS database used in this study only provides data from the first wave of the 2020 survey. As a result, we could not perform panel data analysis. Future research may utilize more comprehensive databases with longitudinal data to validate our findings and offer more robust evidence on the impact of digital literacy on farmers’ PPW recycling behavior.
Second, in our mechanism analysis, we used the question “How many relatives or friends do you have who could lend you more than 5000 yuan (regardless of interest charges)?” as a proxy variable for the social network mechanism. Due to data limitations, we were unable to employ alternative measures of social network such as gift money income and expenditure, communication costs, or social interactions. Future studies can leverage more complete datasets to provide additional evidence on how digital literacy influences PPW recycling behavior through various social network channels.
Author Contributions
H.T.: Data curation, statistical analysis, writing of the original draft. L.F.: Conceptualization, critically edited and reviewed the original draft. J.L.: Data curation, editing. X.S.: Participated in writing, critically edited and reviewed the original draft. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Humanities and Social Sciences Foundation of the Ministry of Education of China (20YJA840004), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities in UIBE (20QN01), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities in UIBE (22PY050-72103040).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical review and approval were waived for this study as it primarily involved the analysis of publicly accessible data and did not include direct interactions with human or animal subjects. Additionally, the database used has anonymized personal information; therefore, this study was exempted from ethical review and approval. In accordance with the ethical principles outlined in the Declaration of Helsinki, all participants provided informed consent before participation, and their involvement was completely voluntary.
Informed Consent Statement
Written informed consent was obtained from all participants.
Data Availability Statement
The data used in this study were provided by the Rural Development Institute, Chinese Academy of Social Sciences. The data are third-party data, and the authors did not produce any of the original data.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Rural Development Institute, and the Chinese Academy of Social Sciences for providing the data and all persons who provided guidance for this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
References
- Delcour, I.; Spanoghe, P.; Uyttendaele, M. Literature Review: Impact of Climate Change on Pesticide Use. Food Res. Int. 2015, 68, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Bluemling, B.; Mol, A.P. Mitigating Land Pollution through Pesticide Packages–The Case of a Collection Scheme in Rural China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 622, 502–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Elahi, E. Farmers’ Preferences for Recycling Pesticide Packaging Waste: An Implication of a Discrete Choice Experiment Method. Sustainability 2022, 14, 14245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsola, K.B.; de Oliveira, A.L.R.; Neto, B. Life Cycle Assessment of Reverse Logistics of Empty Pesticide Containers in Brazil: Assessment of Current and Previous Management Practices. Production 2022, 32, e20210105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Peng, Y.L. Farmers’ Digital Literacy, Elite Identity and Participation in Rural Digital Governance. J. Agrotech. Econ. 2022, 1, 34–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Sun, Z.; Huang, M. The Impact of Digital Literacy on Farmers’ pro-Environmental Behavior: An Analysis with the Theory of Planned Behavior. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2024, 8, 1432184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.; Zhuang, J. The Impact Path of Digital Literacy on Farmers’ Entrepreneurial Performance: Based on Survey Data in Jiangsu Province. Sustainability 2023, 15, 11159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Huo, X. Estimating the Effects of Joining Cooperatives on Farmers’ Recycling Behaviors of Pesticide Packaging Waste: Insights from Apple Farmers of China. Ciênc. Rural 2022, 53, e20220229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadlinger, N.; Mmochi, A.J.; Dobo, S.; Gyllbäck, E.; Kumblad, L. Pesticide Use among Smallholder Rice Farmers in Tanzania. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2011, 13, 641–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondori, A.; Bagheri, A.; Allahyari, M.S.; Damalas, C.A. Pesticide Waste Disposal among Farmers of Moghan Region of Iran: Current Trends and Determinants of Behavior. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trujillo-Barrera, A.; Pennings, J.M.; Hofenk, D. Understanding Producers’ Motives for Adopting Sustainable Practices: The Role of Expected Rewards, Risk Perception and Risk Tolerance. Eur. Rev. Agric. Econ. 2016, 43, 359–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, D.; Deng, J.; Zhang, Y. Associated Factors of Pesticide Packaging Waste Recycling Behavior Based on the Theory of Planned Behavior in Chinese Fruit Farmers. Sustainability 2022, 14, 10937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Cui, H.; Zong, Y.; Yin, S. Effect of Ecoliteracy on Farmers’ Participation in Pesticide Packaging Waste Governance Behavior in Rural North China. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 23103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wang, J.; Chen, K.; Wu, L. Willingness and Behaviors of Farmers’ Green Disposal of Pesticide Packaging Waste in Henan, China: A Perceived Value Formation Mechanism Perspective. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Yin, S. Incentive Mechanism for the Development of Rural New Energy Industry: New Energy Enterprise–Village Collective Linkages Considering the Quantum Entanglement and Benefit Relationship. Int. J. Energy Res. 2023, 2023, 1675858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Weng, Z.; Gao, X.; Liao, W. The Influence of Social Norms and Environmental Regulations on Rural Households’ Pesticide Packaging Waste Disposal Behavior. Sustainability 2023, 15, 15938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, N.; Zhang, Q.; Li, C.; Sun, H. Policy Intervention Effect Research on Pesticide Packaging Waste Recycling: Evidence from Jiangsu, China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 922711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xing, L.; Li, B.; Zhang, Y. Substitution or Complementary Effects: The Impact of Neighborhood Effects and Policy Interventions on Farmers’ Pesticide Packaging Waste Recycling Behavior. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 482, 144198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salam, M.; Alam, F.; Dezhi, S.; Nabi, G.; Shahzadi, A.; Hassan, S.U.; Ali, M.; Saeed, M.A.; Hassan, J.; Ali, N.; et al. Exploring the Role of Black Soldier Fly Larva Technology for Sustainable Management of Municipal Solid Waste in Developing Countries. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 24, 101934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salam, M.; Shahzadi, A.; Zheng, H.; Alam, F.; Nabi, G.; Dezhi, S.; Ullah, W.; Ammara, S.; Ali, N.; Bilal, M. Effect of Different Environmental Conditions on the Growth and Development of Black Soldier Fly Larvae and Its Utilization in Solid Waste Management and Pollution Mitigation. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2022, 28, 102649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, P.; Sharma, B.; Chaudhary, K. Digital Literacy: A Review of Literature. Int. J. Technoethics (IJT) 2020, 11, 65–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilster, P. Digital Literacy; Heanaem: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, A.; Grudziecki, J. DigEuLit: Concepts and Tools for Digital Literacy Development. Innov. Teach. Learn. Inf. Comput. Sci. 2006, 5, 249–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Xu, T.; Qiao, D.; Liu, Z. Exploring the Impact of Digital Literacy and Policy Cognition on Rural Residents’ Eco-Friendly Behaviors. Environ. Manag. 2024, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrum, K. “Hey Friend, Buy Green”: Social Media Use to Influence Eco-Purchasing Involvement. Environ. Commun. 2019, 13, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T. Mediating Effects and Moderating Effects in Causal Inference. China Ind. Econ. 2022, 5, 100–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, S.; Sun, Z.; Wang, B.; Yu, Z. Could Digital Literacy Contribute to the Improvement of Green Production Efficiency in Agriculture? Sage Open 2024, 14, 21582440241232789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, T. A Study on Farmers’ Participation in Environmental Protection in the Context of Rural Revitalization: The Moderating Role of Policy Environment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Guo, Y. The Effect of Environmental Regulation and Social Capital on Farmers’ Adoption Behavior of Low-Carbon Agricultural Technology. J. Nat. Resour. 2023, 38, 2872–2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, Z.; Han, X. The Impact of Digital Literacy on Farmers’ Green Production Behavior: Mediating Effects Based on Ecological Cognition. Sustainability 2024, 16, 7507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Dong, J.; Pan, W.; Yu, Y. Associations between Digital Literacy, Health Literacy, and Digital Health Behaviors among Rural Residents: Evidence from Zhejiang, China. Int. J. Equity Health 2024, 23, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).