Artificial Intelligence and Enterprise Green Innovation: Evidence from a Quasi-Natural Experiment in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review and Theoretical Analysis
2.1. Literature Review
2.2. Theoretical Analysis
2.2.1. Direct Impact of AI on GI in Enterprises
2.2.2. Indirect Impact of AI on GI in Enterprises
- (1)
- Optimization of internal governance
- (2)
- Upgrading human capital
2.2.3. Regulatory Effect of Industry Competition
3. Research Design
3.1. Model Settings
3.2. Data Source and Variable Description
3.2.1. Data Sources
3.2.2. Variable Description
4. Results Analysis
4.1. Benchmark Regression
4.2. Robustness Tests
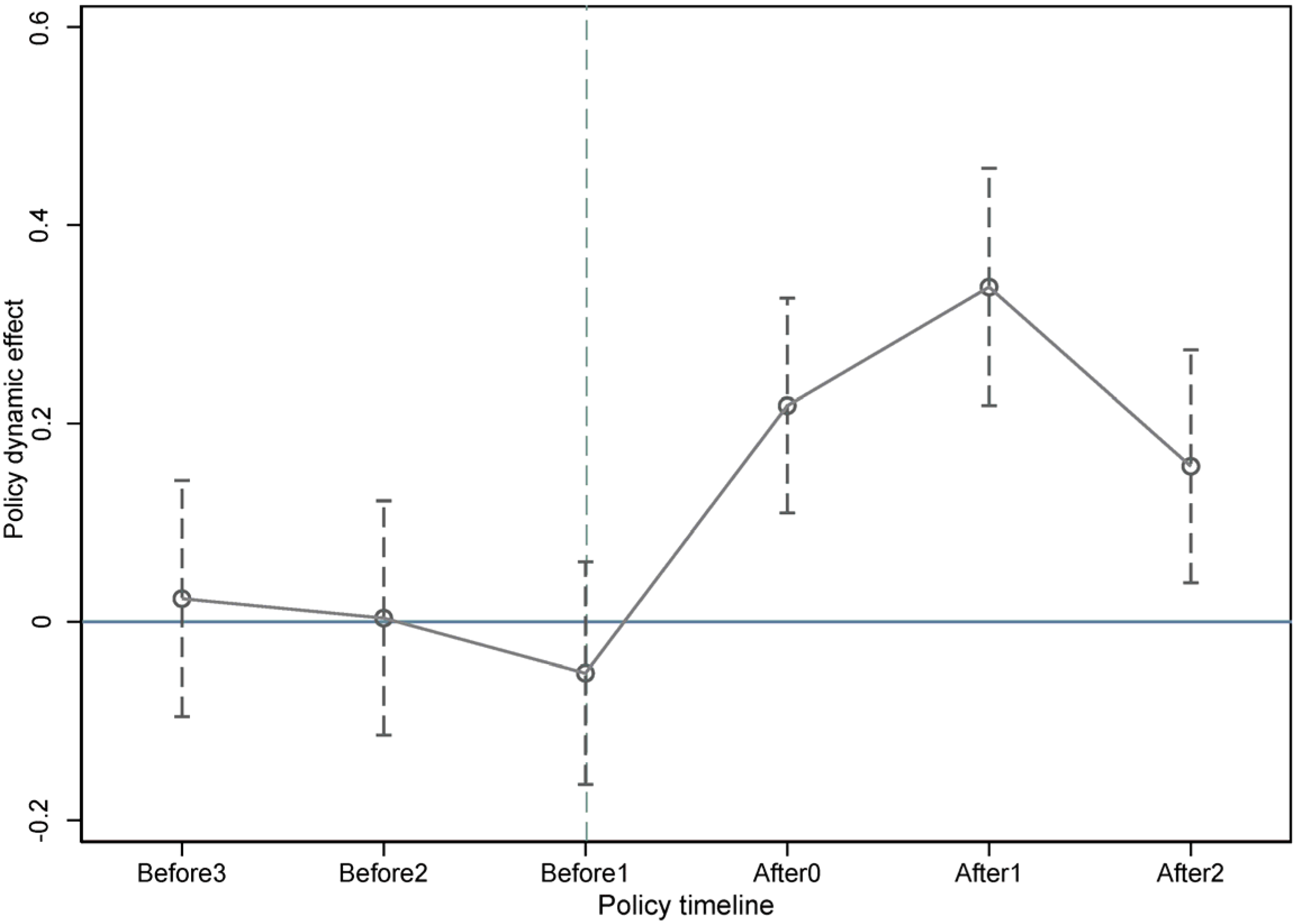
4.2.1. Parallel Trend
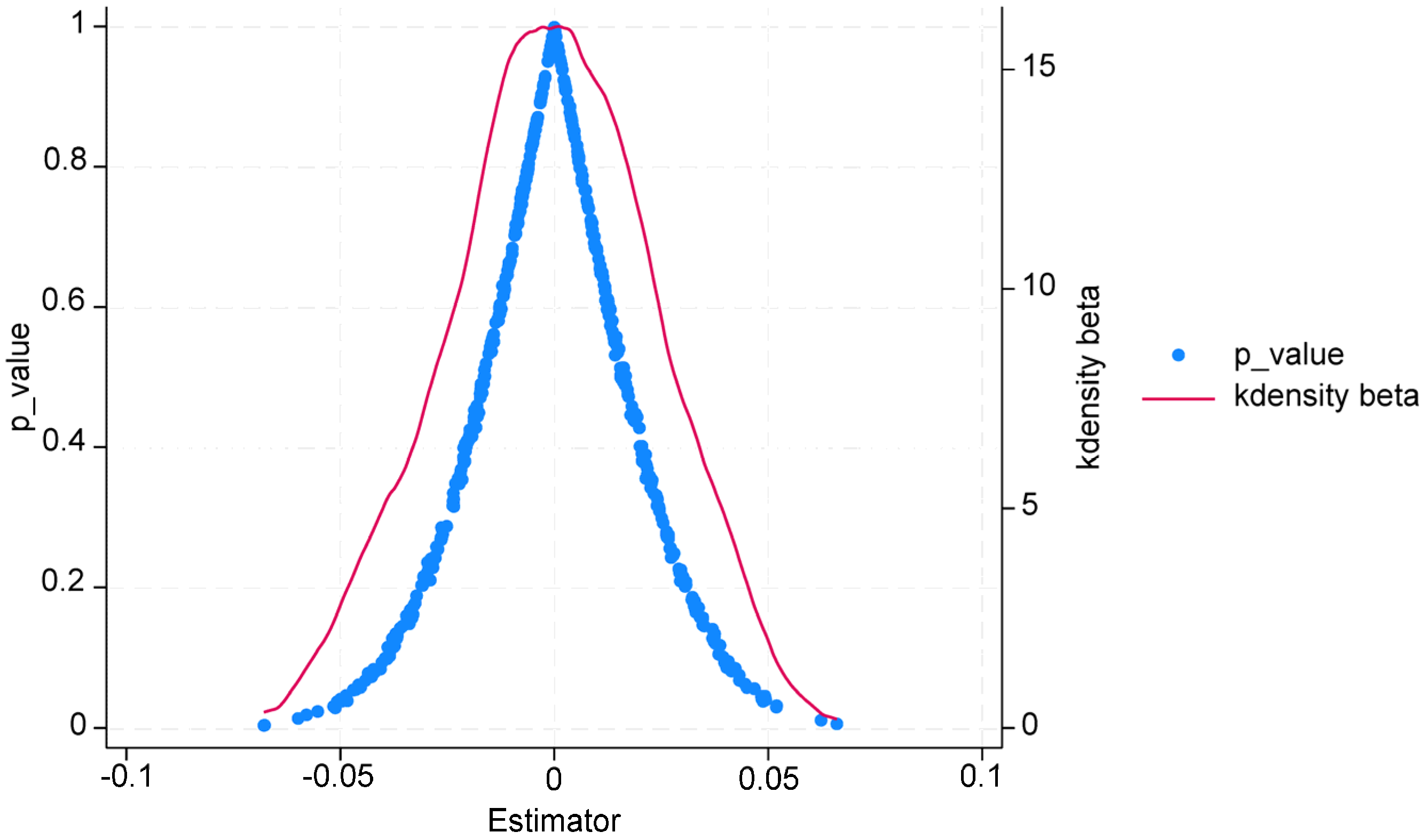
4.2.2. Placebo Test
4.2.3. Replace Core Variable
4.2.4. Exclusion of the Effects of Environmental Policies
4.2.5. Propensity Score Matching (PSM)-DID
4.2.6. Other Robustness Tests
4.3. Mechanism Verification
4.3.1. Analysis of Intermediary Effect
4.3.2. The Regulatory Effect of Industry Competition
4.4. Heterogeneity Analysis
4.4.1. Geographical Position
4.4.2. Industry Heterogeneity
4.4.3. Property Rights Nature
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chang, L.; Taghizadeh-Hesary, F.; Mohsin, M. Role of artificial intelligence on green economic development: Joint determinates of natural resources and green total factor productivity. Resour. Policy 2023, 82, 103508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Gao, Y.; Sun, X. How does artificial intelligence affect green economic growth?—Evidence from China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 834, 155306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, K.; Cai, F.; Huang, C. How does artificial intelligence development affect green technology innovation in China? Evidence from dynamic panel data analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 28066–28090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolón-Canedo, V.; Morán-Fernández, L.; Cancela, B.; Alonso-Betanzos, A. A review of green artificial intelligence: Towards a more sustainable future. Neurocomputing 2024, 599, 128096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzoubi, Y.I.; Mishra, A. Green artificial intelligence initiatives: Potentials and challenges. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 468, 143090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nylén, D.; Holmström, J. Digital innovation strategy: A framework for diagnosing and improving digital product and service innovation. Bus. Horiz. 2015, 58, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Gao, D.; Song, D.; Li, Y. Environmental regulation, pollution reduction and green innovation: The case of the Chinese Water Ecological Civilization City Pilot policy. Econ. Syst. 2021, 45, 100911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Woodward, R.T.; Liu, J.Y. The impact of exogenous pollution on green innovation. Environ. Resour. Econ. 2022, 81, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Sun, T.; Li, R. Does artificial intelligence promote green innovation? An assessment based on direct, indirect, spillover, and heterogeneity effects. Energy Environ. 2023, 0958305X231220520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, P.; Sun, X.; Qi, L. Does artificial intelligence technology enhance green transformation of enterprises: Based on green innovation perspective. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2024, 26, 21651–21687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graetz, G.; Michaels, G. Robots at work. Rev. Econ. Stat. 2018, 100, 753–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cockburn, I.M.; Henderson, R.; Stern, S. The impact of artificial intelligence on innovation: An exploratory analysis. In The Economics of Artificial Intelligence: An Agenda; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 2018; pp. 115–146. [Google Scholar]
- Frey, C.B.; Osborne, M.A. The future of employment: How susceptible are jobs to computerisation? Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2017, 114, 254–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghion, P.; Bergeaud, A.; Lequien, M.; Melitz, M. The heterogeneous impact of market size on innovation: Evidence from French firm-level exports. Rev. Econ. Stat. 2022, 106, 608–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J. Impacts of high-speed rail on urban smog pollution in China: A spatial difference-in-difference approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 777, 146153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.B.; Li, M.Y. The Environmental Power of Automation: The Emission Reduction Effect of Industrial Robot Applications. J. Shanghai Univ. Financ. Econ. 2023, 25, 88–103. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, F.; Hu, H.L.; Li, L. How can industrial robots promote green production? Evidence from Chinese micro-firms. Ind. Econ. Res. 2022, 4, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, H.; Shen, N.; Ying, H.; Wang, Q. Can environmental regulation directly promote green innovation behavior? Based on situation of industrial agglomeration. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 314, 128044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, S.Z.; Zhou, C.B.; Li, K. Influence of a pilot carbon trading policy on enterprises’ low-carbon innovation in China. Clim. Policy 2021, 3, 318–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.B. Green innovation: A key strategy for enterprises and countries to gain a competitive edge in the global market. Technol. Anal. Strateg. Manag. 2024, 5, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunnermeier, S.B.; Cohen, M.A. Determinants of environmental innovation in US manufacturing industries. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2003, 45, 278–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leeuwen, G.; Mohnen, P. Revisiting the Porter hypothesis: An empirical analysis of green innovation for the Netherlands. Econ. Innov. New Technol. 2017, 26, 63–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, D.S.; Wang, Y.; Tang, Q.Q. Has Digital Economy Realized the “Increase of Quantity and Improvement of Quality” of Green Innovation. From the Perspective of Heterogeneous Environmental Concern. J. Shanxi Univ. Financ. Econ. 2023, 45, 55–68. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.; Sun, G.; Kong, T. The impact of digital transformation on enterprise green innovation. Int. Rev. Econ. Financ. 2024, 90, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Liu, S.; Gan, J.; Liu, B.; Wu, Y. How does the construction of new generation of national AI innovative development pilot zones drive enterprise ESG development? Empirical evidence from China. Energy Econ. 2024, 140, 108011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Qi, J.; Zheng, Y. How can AI reduce carbon emissions? Insights from a quasi-natural experiment using generalized random forest. Energy Econ. 2025, 141, 108040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zdravković, M.; Panetto, H. Artificial intelligence-enabled enterprise information systems. Enterp. Inf. Syst. 2022, 16, 1973570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolton, C.; Machová, V.; Kovacova, M.; Valaskova, K. The power of human–machine collaboration: Artificial intelligence, business automation, and the smart economy. Econ. Manag. Financ. Mark. 2018, 13, 51–56. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Pongtornkulpanich, A. The Impact of Enterprise Artificial Intelligence Capability on R&D Leaps. Pak. J. Life Soc. Sci. 2024, 22, 3687–3713. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, X.; Xu, B.; Razzaq, A. Can application of artificial intelligence in enterprises promote the corporate governance? Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 944467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornelli, F.; Kominek, Z.; Ljungqvist, A. Monitoring managers: Does it matter? J. Financ. 2013, 68, 431–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafarre, A.; Van der Elst, C. Blockchain Technology for Corporate Governance and Shareholder Activism; Law Working Paper; European Corporate Governance Institute (ECGI): Brussels, Belgium, 2018; Volume 390. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Bu, H.; Liu, F. Internal control and enterprise green innovation. Energies 2022, 15, 2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Shen, W. Can corporate digitalization promote green innovation? The moderating roles of internal control and institutional ownership. Sustainability 2021, 13, 13983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, C.; Shi, D.; Wang, B. The impact of green human capital of entrepreneur on enterprise green innovation: A study based on the theory of pro-environmental behavior. Financ. Res. Lett. 2023, 58, 104453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobaih AE, E.; Hasanein, A.; Elshaer, I. Influences of green human resources management on environmental performance in small lodging enterprises: The role of green innovation. Sustainability 2020, 12, 10371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.H.; Choi, C.H. How does Digitalization Affect Trade in Goods and Services? Evidence from G20 Countries. J. Knowl. Econ. 2024, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Fan, L.; Yuan, X. Market competition, financialization, and green innovation: Evidence from China’s manufacturing industries. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 836019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Wang, S. Market competition, green technology progress and comparative advantages in China. Manag. Decis. 2018, 56, 188–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, N.R.; Yun, H.S.; Choi, C.H. Green Trade and Cultural Innovation: Examining the Impact on GTFP and Greenhouse Gas Emissions in OECD Countries. Sustainability 2024, 16, 8339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, X.; Liu, C.; Yang, M. Who is financing corporate green innovation? Int. Rev. Econ. Financ. 2022, 78, 321–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, A.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, W. Micro green technology innovation effects of green finance pilot policy—From the perspectives of action points and green value. J. Bus. Res. 2023, 159, 113724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.B.; Qi, S.Z.; Li, Y.K. Environmental policy uncertainty and green transformation dilemma of Chinese enterprises. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 370, 122891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.C.; Qin, S.; Li, Y. Does industrial robot application promote green technology innovation in the manufacturing industry? Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2022, 183, 121893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.C.; Zou, J.; Chen, P.F. The impact of artificial intelligence on the energy consumption of corporations: The role of human capital. Energy Econ. 2025, 143, 108231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.C.; Yan, J. Will artificial intelligence make energy cleaner? Evidence of nonlinearity. Appl. Energy 2024, 363, 123081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Ferrara, E.; Duryea, S.; Chong, A.E. Soap Operas and Fertility: Evidence from Brazil. Am. Econ. J. Appl. Econ. 2012, 4, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.X.; Lin, Z.Y.; Wang, X.B. Industrial Robot Application and Global Value Chain Reconstruction: Based on the Perspective of Bargaining Power of Export Products. China Ind. Econ. 2023, 3, 74–92. [Google Scholar]
| Variable | Symbol | Definition | Mean | SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Green innovation | GI | The logarithm of the number of green patents authorized | 1.004 | 1.291 |
| Enterprise size | Size | Ln (enterprise total assets) | 22.19 | 1.193 |
| Asset liability ratio | Lev | Ratio of total liabilities to total assets | 0.392 | 0.181 |
| Return on assets | Roa | Ratio of net profit to total assets | 0.048 | 0.063 |
| Board size | Board | Ln (the number of board members) | 2.112 | 0.19 |
| Ownership concentration | Top | Proportion of shares held by the largest shareholder | 0.332 | 0.138 |
| Tobin’s Q value | TobinQ | Ratio of market value to asset replacement value | 2.176 | 1.34 |
| Enterprise age | Age | Ln (enterprise age + 1) | 2.91 | 0.296 |
| Fixed asset ratio | Fixed | Ratio of net fixed assets to total assets | 0.222 | 0.127 |
| Enterprise R&D investment | Rd | Ratio of R&D investment to operating revenue | 0.052 | 0.045 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| GI | GI | GI | |
| AI | 0.207 *** | 0.384 *** | 0.197 *** |
| (0.0350) | (0.0387) | (0.0351) | |
| Size | 0.388 *** | 0.129 *** | |
| (0.0165) | (0.0359) | ||
| Lev | 1.036 *** | −0.0830 | |
| (0.0880) | (0.122) | ||
| Roa | 0.785 *** | 0.261 | |
| (0.212) | (0.200) | ||
| Board | −0.0230 | −0.0331 | |
| (0.0705) | (0.0972) | ||
| Top | −0.251 *** | 0.0831 | |
| (0.0936) | (0.207) | ||
| TobinQ | −0.0145 | 0.00506 | |
| (0.00959) | (0.00951) | ||
| Age | −0.140 *** | 0.122 | |
| (0.0478) | (0.234) | ||
| Fixed | −0.993 *** | −0.103 | |
| (0.107) | (0.160) | ||
| Rd | 0.405 *** | 0.0996 ** | |
| (0.0419) | (0.0436) | ||
| Firm FE | YES | NO | YES |
| Year FE | YES | YES | YES |
| Observations | 9055 | 9055 | 9055 |
| R-squared | 0.731 | 0.212 | 0.732 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| GI | GI | GI | |
| AI | 0.166 *** | 0.162 *** | 0.102 *** |
| (0.0437) | (0.0388) | (0.0335) | |
| CV | NO | YES | YES |
| Firm FE | YES | NO | YES |
| Year FE | YES | YES | YES |
| Observations | 9055 | 9055 | 9055 |
| R-squared | 0.73 | 0.206 | 0.731 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| GI | GI | GI | |
| AI | 0.267 *** | 0.102 * | 0.212 *** |
| (0.0519) | (0.057) | (0.0370) | |
| CV | YES | YES | YES |
| Firm FE | YES | YES | YES |
| Year FE | YES | YES | YES |
| Observations | 9040 | 8505 | 9016 |
| R-squared | 0.742 | 0.769 | 0.743 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| GI | GI | GI | |
| AI | 0.159 * | 0.199 *** | 0.197 *** |
| (0.08) | (0.0352) | (0.0351) | |
| CV | YES | YES | YES |
| Firm FE | YES | YES | YES |
| Year FE | YES | YES | YES |
| Observations | 2305 | 9010 | 9002 |
| R-squared | 0.808 | 0.733 | 0.732 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GI | GI | GI | GI | |
| AI | 0.197 *** | 0.197 *** | 0.204 *** | 0.216 *** |
| (0.0424) | (0.0504) | (0.043) | (0.062) | |
| CV | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Firm FE | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Year FE | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Observations | 9055 | 9055 | 6353 | 9055 |
| R-squared | 0.732 | 0.732 | 0.762 | 0.743 |
| (1) | (2) | |
|---|---|---|
| IC | HC | |
| AI | 0.0323 * | 0.125 * |
| (0.0179) | (0.0672) | |
| CV | YES | YES |
| Firm FE | YES | YES |
| Year FE | YES | YES |
| Observations | 9055 | 9055 |
| R-squared | 0.449 | 0.81 |
| (1) | (2) | |
|---|---|---|
| GI | GI | |
| AI*HHI | −0.104 * | −0.075 * |
| (0.057) | (0.04) | |
| AI | 0.225 *** | 0.212 *** |
| (0.0545) | (0.055) | |
| HHI | −0.176 * | −0.233 * |
| (0.095) | (0.122) | |
| CV | NO | YES |
| Firm FE | YES | YES |
| Year FE | YES | YES |
| Observations | 9055 | 9055 |
| R-squared | 0.731 | 0.733 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eastern | Mid-West | Labor -Intensive | Capital -Intensive | Technology -Intensive | SOEs | Non-SOEs | |
| GI | GI | GI | GI | GI | GI | GI | |
| AI | 0.234 *** | 0.181 * | 0.217 *** | 0.0249 | 0.266 ** | 0.2 *** | 0.229 *** |
| (0.066) | (0.095) | (0.0442) | (0.0708) | (0.110) | (0.042) | (0.071) | |
| CV | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Firm FE | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Year FE | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Observations | 6790 | 2265 | 761 | 2556 | 5738 | 2432 | 6623 |
| R-squared | 0.711 | 0.673 | 0.564 | 0.666 | 0.753 | 0.775 | 0.703 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, C.; Wang, L. Artificial Intelligence and Enterprise Green Innovation: Evidence from a Quasi-Natural Experiment in China. Sustainability 2025, 17, 2455. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17062455
Zhao C, Wang L. Artificial Intelligence and Enterprise Green Innovation: Evidence from a Quasi-Natural Experiment in China. Sustainability. 2025; 17(6):2455. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17062455
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Chunyan, and Linjing Wang. 2025. "Artificial Intelligence and Enterprise Green Innovation: Evidence from a Quasi-Natural Experiment in China" Sustainability 17, no. 6: 2455. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17062455
APA StyleZhao, C., & Wang, L. (2025). Artificial Intelligence and Enterprise Green Innovation: Evidence from a Quasi-Natural Experiment in China. Sustainability, 17(6), 2455. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17062455




