Abstract
This conceptual paper aims to discuss the crucial transformation of the impacts of big data analytics capability (BDAC) elements on business performance using the framework of sustainability reporting. The authors applied a literature review, content analysis, and bibliometric analysis as the core methodology for this study to define the key success factors for BDAC development in the organisation. The results are based on the theoretical framework of resource-based theory and knowledge-based theory and illustrate the link between BDAC elements and the financial and sustainability conceptualisation of business performance presented in the novel conceptual model. This study contributes to the literature by presenting a sustainability reporting diamond that defines BDAC elements’ key success factors necessary to integrate sustainability reporting in the organisational processes.
1. Introduction
Though the fifth industrial revolution is focusing the minds of scholars worldwide, its practical mechanisms and consequences remain vague and unexplored. Industry 5.0 embraces synergy between humans and Industry 4.0 technologies [1,2]. Until now, the concept of Industry 5.0 has been surfing the free waves of the economy, and the most advanced market participants have driven modern technology readiness. This will change with novel sustainability reporting regulatory requirements globally, led by the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) [3] reporting framework of the EU. The new CSRD legislative reporting framework requires large EU organisations to include sustainability reports in their audited annual management reports. Thus, it puts sustainability reports on the same level of importance for users as financial reports. In parallel with CSRD, global International Sustainability Standards Board [4] reporting standards are being adopted in Brazil, Costa Rica, Sri Lanka, Nigeria, and Turkey, and consultation processes are taking place in Australia, Malaysia, Canada, Japan, and Singapore [5]. These regulative frameworks demand new rational, systematic approaches to implementing sustainability reporting in the organisational processes.
Sustainability reporting as a concept is not new, but it is attracting increased attention from researchers [6,7,8,9]. In line with [10], the authors argue that sustainability reporting remains understudied, specifically from the perspective of inner-organisational process change. This is a major research gap that this study aims to fill. Thus, the authors claim that the impact of BDAC elements on business performance provides the necessary theoretical framework for successfully integrating sustainability reporting. This framework expands conventional financial understanding of business performance to include the broader perspective of sustainability.
Thus, considering the novelty and dynamism of BDAC, this study provides scientific discussion around the up-to-date definitions of its key success elements. Further, the study presents a new conceptual model that fills the research gap by framing the relationship between BDAC elements and the dual financial and sustainability conceptualisation of business performance. According to the European Commission [11], Industry 5.0 supplements Industry 4.0 by particularly focusing research and innovation on transitioning to a sustainable, human-centric, and resilient EU economy. It creates another paradigm of the higher-level system that integrates human-centric elements and sustainability aspects with machines. Big data drove the historical rise of Industry 4.0 [12], considering that big data provides decent food for its exploitation progress and expands opportunities for new advanced technologies to arise.
Big data specifies massive, multifaceted data sets whose size and disunity become a challenge for users [13]. The authors introduce the BDAC concept by considering the recent regulatory sustainability reporting context that challenges the organisation’s readiness for granular reporting to feed external advanced big data analytics (BDA) systems. BDAC is perceived as necessary for sustainability reporting, which defines an organisation’s ability to provide resilient and reliable data for reporting. Thus, it is crucial to identify the key success factors for BDAC in an organisation to increase their influence on sustainability reporting.
The substantial literature establishes that the effective integration of BDA with an organisation’s high-level strategy could serve as a foundation for ensuring stable future business performance [14,15,16,17]. BDAC is considered a driver of the management revolution [18] aimed at effectively navigating organisational changes. Thus, the authors seek to examine the key conceptual elements of business performance that determine BDAC’s impact. In the context of this research, the focus is placed on BDAC to unveil the necessary conditional factors for turning BDAC-delivered insights into proper decision-making to achieve superior business performance in the environment of regulatory sustainability reporting.
As the global trend of sustainability disclosure gains momentum, investors and other stakeholders will demand more qualitative and comparable information. The flow of information and data is essential to transition to a sustainable economy [19]. Trustworthy information about sustainability-related business performance is key to meeting the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development [7]. Therefore, sustainability should be integrated into an organisation’s processes as a quality aspect to ensure traceable data sets and real-time digital reporting [20]. According to Minbaeva (2018) [16], this is required for corporate modelling purposes and analytics-based decision-making to avoid bias and effectively manage the transition through organisational change. Thus, the practical introduction of regulatory sustainability reporting calls for executive management to effectively and efficiently reinvent existing business reporting practises.
This study aims to show the impacts of BDAC elements on business performance in the new sustainability reporting framework. It provides a pathway for the management to controlled changes for integrating standardised sustainability reporting. To understand the key challenges and tendencies behind the required shift in organisational information systems, processes, and required capabilities, the authors pose the following research questions (RQs):
- RQ1. What are the key success factors for BDAC development in an organisation?
- RQ2. How do BDAC elements relate to the dual financial and sustainability conceptualisation of business performance?
The study is structured as follows: First, we perform a literature review and the elements of bibliometric analysis on BDAC and its operationalisation elements. Further, we define the key success development factors of BDAC for enhanced sustainability reporting and draw them into the sustainability reporting diamond. Then, we show the results of the literature review and ground business performance construct based on the financial and sustainability aspects of business performance and present a conceptual model for BDAC elements. Finally, in the Discussion section, we highlight theoretical, practical, and policy implications, as well as provide conclusions of the study.
2. Literature Review
To build a theoretical background that presents the essence and development trends of BDAC and its crucial elements, as well as identify the gaps in ongoing research in relation to business performance, the authors conducted the academic literature review, bibliometric analysis, and content analyses.
2.1. Literature Review Related to BDAC
Interest in big data rapidly expanded [21] following its extensive cross-border application within many scientific fields, such as healthcare, manufacturing, finance, marketing, and others [22]. Studies argue that an increasing number of organisations use big data to retain their competitive advantage and even change their business models based on the insights they have gained [12,23]. These companies introduce new technologies, such as machine learning and cloud computing, using them as digital techniques to turn big data into information.
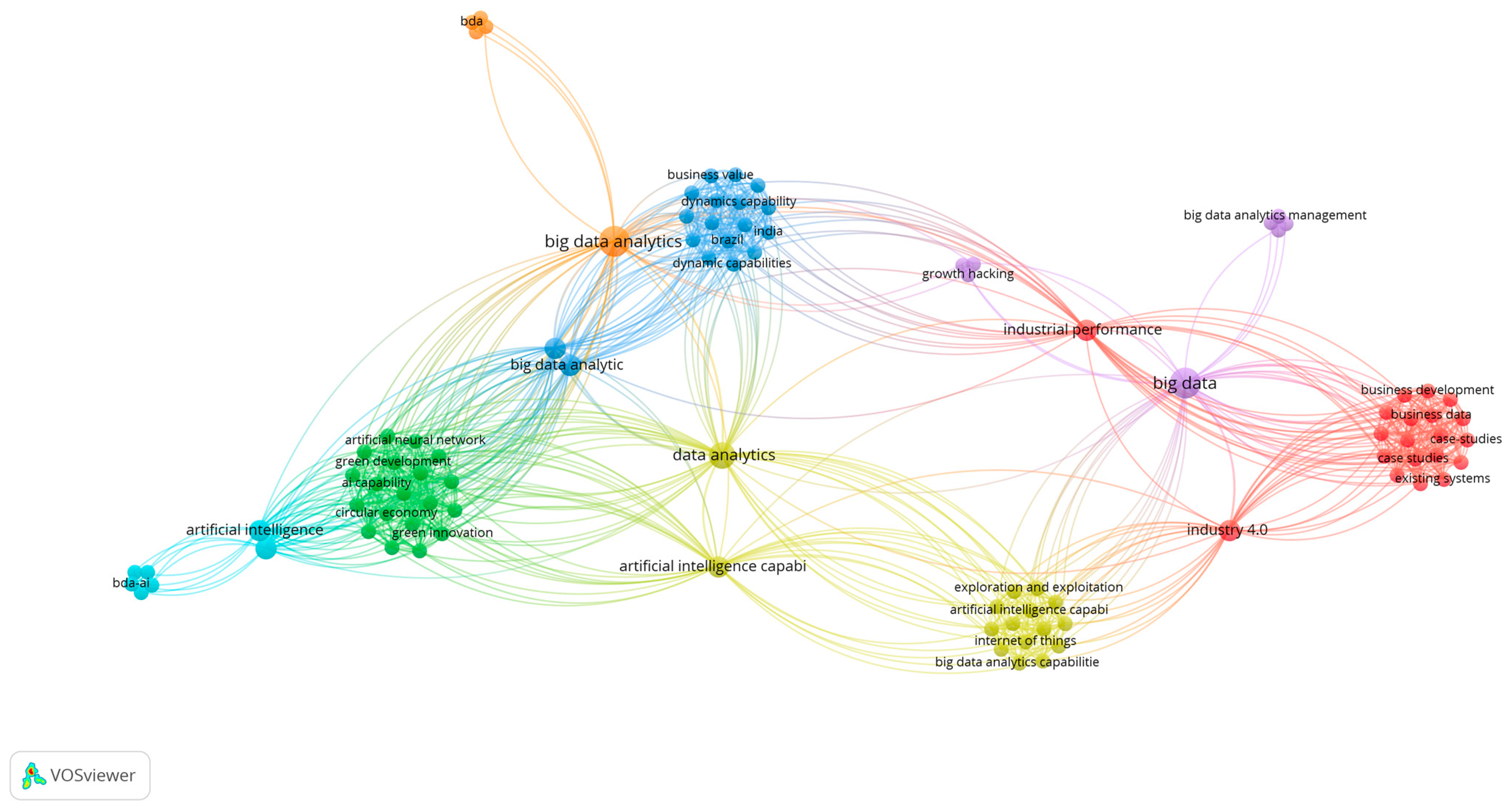
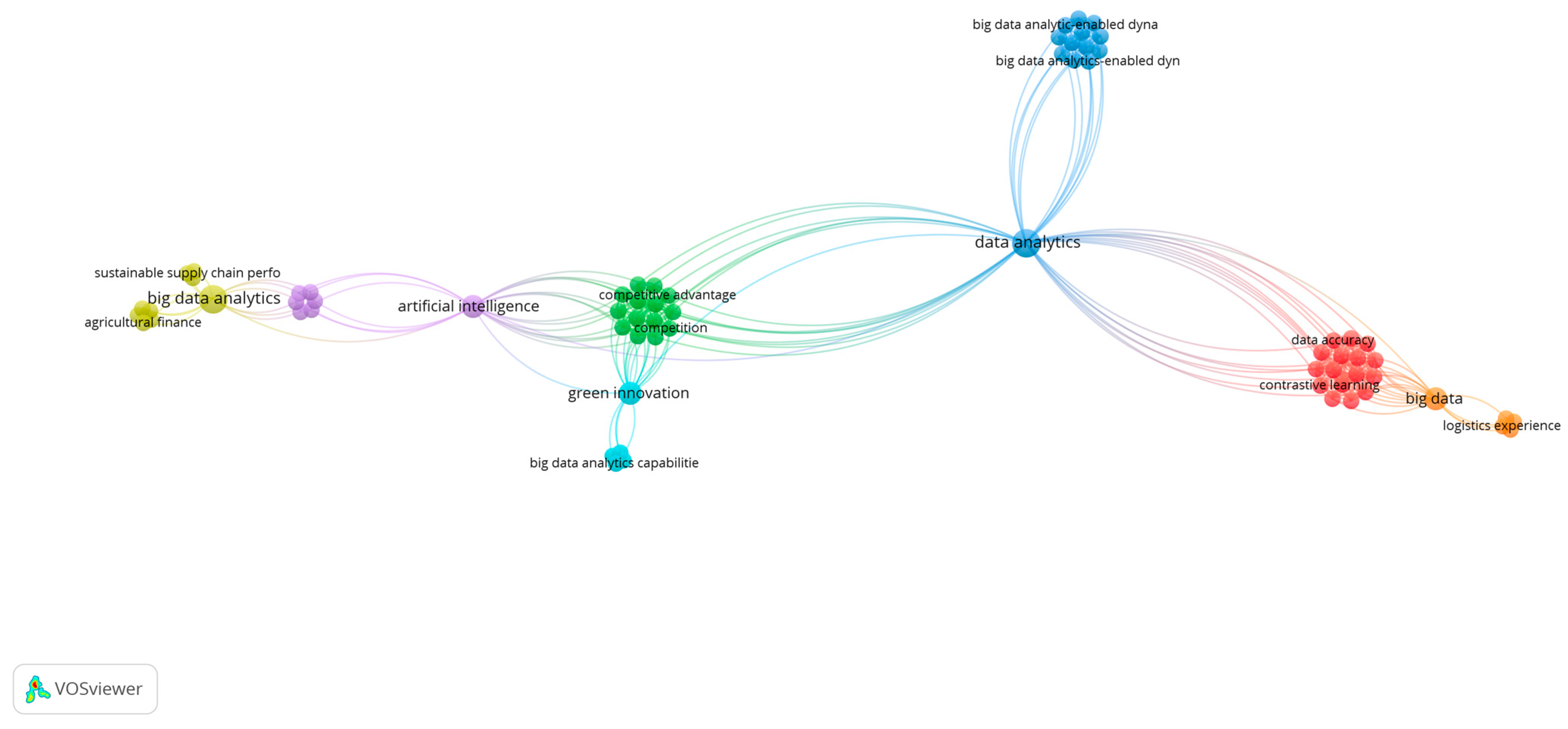
To understand the current state of the BDAC literature, the authors conducted longitudinal bibliometric analyses within the two timeframes in the leading Scopus database, which showed 1094 publications in English as of 16 January 2025. The publications were filtered based on the subject areas of “business management and accounting”, “decision science”, and “economics, econometrics, and finance”. The Web of Science database had fewer, with 898 publications identified with the same search criteria. First, we looked for the research papers published with the keyword “Big data analytics capability” from 2014 to 2024, as visualised in Figure 1. The earlier period was irrelevant as the big data research stream evolved only early in the 2000s, and searches for BDAC before 2014 brought insignificant results. A search with the same criteria was performed from 2020 to 2024, when the most significant increase in article quantity was observed. The results were visualised using VOSviewer (version 1.6.20), as shown in Figure 2. The longitudinal bibliometric analyses compared the evolution of BDAC-related keyword clusters and identified related research trends.
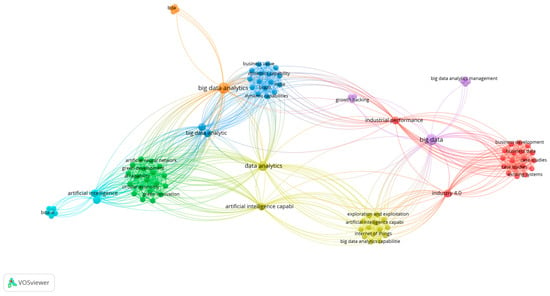
Figure 1.
Bibliometric analysis of BDAC: 2014–2024 timeframe perspective. Source(s): figure created by the authors using VOSviewer.
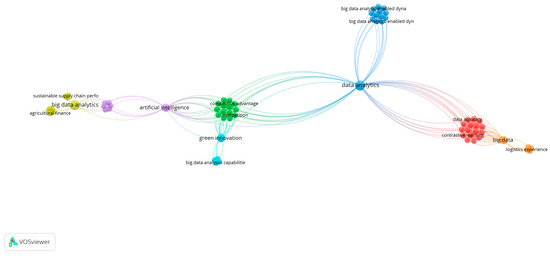
Figure 2.
Bibliometric analysis of BDAC: 2020–2024 timeframe perspectives. Source(s): figure created by the authors using VOSviewer.
As shown in Figure 1, the overall results of the ten-year analysis period showed 98 related keywords, with the most frequent BDAC-related keywords—big data and big data analytics. The stream of research related to BDAC studies is visualised in the yellow cluster. It directly belongs to the technological framework that is expressed in proximity to the artificial intelligence (AI) and Industry 4.0 keywords. In the academic literature, researchers emphasise the impact of BDAC on business performance [24,25]. Figure 1 also demonstrates that in the historical context, BDAC has an indirect relationship to business development (red cluster), business value (blue cluster), and green development (green cluster), guided by the technology perspective. That positions BDAC conceptual studies in a complementary role in relation to the well-established Industry 4.0 research stream.
The overall results shown in Figure 2 within the recent timeframe indicated 69 BDAC-related keywords, with the most frequent keywords including data analytics, big data, green innovation, and artificial intelligence. The recent analysed period visualised in Figure 2 shows that BDAC (light blue cluster) emerged as a separate nascent research cluster, studied separately from the technological framework where it belonged to in the longer historical frame (Figure 1). Outside of the direct relation to the technology studies, it became primarily related to the organisational competitive advantage (green cluster) driven by green innovation studies (light blue cluster). The difference in the research frameworks between Figure 1 and Figure 2 demonstrates the emerging nature of BDAC literature in relation to business performance and the rising power of green innovation. Altogether, this indicates the positive tendency of the BDAC-focused studies and suggests the growing topicality and the maturity of phenomena compared to the longer observed period.
Nonetheless, BDAC and its formation of key success elements require drawing a clear theoretical framework. Thus, to contribute to the BDAC literature, we summarise the definitions of BDAC provided by the scholars over time in Table 1.

Table 1.
The development of the definition of BDAC over time, 2007–2024.
Based on the literature review conducted by the authors, two research clusters influence the definition of big data in academia. The first closely defines it based on hard or soft mechanisms, such as distinct up-to-date gathering, validating, storage, processing, analyses, and distribution systems and techniques [36,37], applied to perform actions related to big data to achieve the desired informative results. This research stream agrees that big data differs from traditional data due to its powerful potential for deriving advanced business knowledge gains [38]. Past studies agree that no “silver pill” is available in the market that would quickly transform scattered corporate big data into valuable information ready for knowledge absorption. Thus, this cluster supports the findings of [39] and considers the research gap regarding the need for a unified decision-centric BDAC framework to ease and foster big data transformation into valuable insights for business performance measurement.
The second research cluster focuses on qualitative characteristics as the cornerstone of big data. According to [12,36,40], three fundamental dimensional attributes of big data differ from smaller data sets. Those are as follows: (I) volume—larger data sets; (II) velocity—the speed of the new data generation and analysis is significantly higher, often in real time; (III) variety—the heterogeneity of the structured and unstructured widespread data. Explicitly, such big data are called “3V”. However, some sources indicate “5Vs” when providing big data characteristics, adding (IV) veracity—the truthfulness and quality of data—and (V) value—the ultimate prerequisite of big data analytics to bring tangible or intangible benefits for its users [41,42,43].
Analysing the recent tendencies of “5Vs” in big data, an area of particular interest is the construct of value. It links big data itself to the value created by it through different modern systems and techniques. The identified relationship brings forth the concept of the fifth industrial revolution, which combines Industry 4.0 technologies and people [1]. Industry 5.0 is founded on three main components: human orientation, sustainability, and resilience [2]. It is a new stage of industrialisation in which humans collaborate with advanced technologies and AI-driven robots to improve corporate processes and safeguard the triple bottom line. Industry 5.0 does not substitute Industry 4.0 itself, which is still far from maturity as its technologies evolve rapidly. As mentioned in the introductory part of this research, big data could be treated as a basis for Industry 4.0 technologies. Nonetheless, it includes value elements close to Industry 5.0. Thus, big data will be primarily observed in this study from the Industry 5.0 perspective.
Therefore, it is necessary to develop BDAC to bridge the potential insights brought by big data and informed strategic decisions [42]. According to Minbaeva (2018) [16], BDAC fills the organisational gap between intention to succeed and desired business performance outcomes. From the perspective of this research, BDA, first explicitly explained by [26], is treated as an organisational resource. Verhoef et al. (2021) [44] specifically depicted BDAC as one of an organisation’s key digital resources. The authors argue that digitalisation is related to BDAC; however, it does not define it.
Consequently, when adapting BDAC definitions from the literature, big data analytics capability is defined as thethe organisational ability to leverage big data insights for more sound, effective, and efficient strategic decisions facilitated by information governance tools, techniques, and processes. Organisational application examples of BDAC include setting an optimal price to achieve desired market share, detecting and solving quality problems, deciding on the lowest possible inventory level to ensure efficient turnover of financial resources, and identifying loyal and profitable customers for defining sales strategy.
2.2. Literature Review Related to Key Elements of BDAC
The authors shape the theoretical framework and operationalise BDAC, defining its manifestation forms. The systematic literature review conducted by [28] states that the current state of the art in the literature lists the following four generic BDAC typologies as core elements:
- Big data analytics technology capability (BDA technology capability);
- Big data analytics management (or organisational) capability (BDA management capability);
- Big data analytics infrastructure capability (BDA infrastructure capability);
- Big data analytics human capability (BDA human capability).
The most extensive part of the literature treats information technology (IT) capability as the backbone of the BDAC conceptualisation logic [14,28,29]. IT capability is a well-established part of information systems studies, underlining the role of technology in strengthening business performance [14,45,46]. Mikalef et al. (2020) [47] qualify the difference between BDAC and IT capabilities by emphasising that the value brought by BDAC lies in the broader scope of organisational proficiency that relies on big data utilisation through information systems (IS) but is not limited to it. Notably, the performance of BDAC is vital for an organisation’s ability to transform and adapt based on generated data-driven insights and strategic management decisions.
2.2.1. BDA Technology Capability
Consequently, many studies outline BDA technology capability as the main component of BDAC, claiming that a strong BDAC fulfils an organisation’s digital transformation, which would be impossible without a strong technological background [14,47,48]. BDA technology capability uncovers big data’s potential as an informative resource hindered by the legacy of existing technological solutions embedded in organisations [17]. Historically, technological solutions were often built to deliver data in strict, unflexible, silo-based batches [49]. The potential unification and integration of unstructured fragmented data in real time using a novel technological information system brings valuable insights previously unobtainable by an organisation’s management [25]. IBM experts define unstructured data as data whose pre-defined data model is unavailable, leading to more complicated data collection, processing, and analysis [50]. According to them, unstructured data comprise most of the data generated today. Therefore, the BDAC elements aim to find mechanisms that leverage the smart use of this pool of structured and unstructured data to create useful knowledge based on the unity of IT systems.
Many authors agree that data-driven firms have a competitive advantage, as they can access and beneficially exploit structured and unstructured data through modern technologies [12,18,51]. Technology is the necessary platform for data-driven information, building BDAC’s foundation. Although BDA technology capability is not the only element defining the BDAC, big data could not be operationalised without it.
Based on Verhoef et al. (2021) [44], who stated that the functionality of digital technologies relies on big data, BDA technology capability is ultimately important for the implementation of digitalisation and sustainability. Thus, similar to [14,47,48], the authors argue that BDA technology capability is a crucial BDAC measurement element. Here, BDA technology capability is defined as the organisational ability to deploy the technological universalism of analytics systems that process network-structured and unstructured big data across different organisational functions to enhance evidence-based decision making.
2.2.2. BDA Management Capability
Another BDAC typology that is gaining momentum and requires a clear theoretical framework is BDA management capability [28]. According to Davenport et al. (2012) [52], management capability in relation to big data operationalisation is core in determining BDAC’s positive influence on business performance. This view is supported by [15,49], who specify that BDA management capability is essential to streamline organisational decision models. Some scholars explicitly define BDA management capability as the dynamic capability of an organisation that reflects its ability to successfully respond to rapidly changing environments by creating value from big data [53,54,55].
Dynamic capability is the organisational ability to reactively address and adapt to altering environments by integrating, building, and reconfiguring internal and external competencies [56]. The dynamic capability theory explains how organisations can continuously redesign their resources to ensure a competitive advantage in a changing environment [57]. It provides a sound foundation for enhanced competitive advantage in an uncertain environment resulting from smart BDA-driven management decisions [12,14,15]. Dynamic capability ensures incoming big data is transformed from information systems into knowledge to improve business performance. Thus, it contributes to knowledge management within an organisation. Knowledge management is an organisation’s ability to utilise existing processes and practises to learn, create, gain, organise, store, and share knowledge to attain superior business performance [58,59]. The authors of this research enhance the construct’s theoretical framework by arguing that BDA management capability has characteristics of BDA-driven dynamic capability that embrace its knowledge management capacity.
As per [18,60], organisations do not gain a competitive advantage due to access to more or higher-quality big data; rather, they succeed as their management has enough knowledge to use this resource. Therefore, the authors claim that management capability is targeted at the personal knowledge, skills, and abilities necessary for the beneficial application of BDA in a certain moment of time. Ransbotham et al. (2015) [61] conducted a survey of 2719 managers from around the world and identified that the main barrier to delivering business value from analytics is not data management or complex modelling skills but the ability to translate analytics into business actions. From the authors’ point of view, the most decisive positive influence of BDA management capability on business performance concerns those organisations whose management can efficiently adapt to the changing environment and correctly interpret BDA results for making profitable steering decisions.
To summarise, BDA management capability reveals that BDAC demands Industry 5.0-driven human knowledge-related elements to fully reach its potential for ensuring resilient and sustainable business results. Accordingly, here, BDA management capability is the synchronic and timely ability of the organisation’s BDA unit’s management and executive management to implement Industry 5.0 systems and leverage their presented insights for more effective and efficient evidence-driven strategic decision-making, ensuring a structured approach to addressing a rapidly changing environment while aligning with business needs and priorities.
2.2.3. BDA Human Capability
Using AI in the symbiosis of big data provides machines with extra functions that partly overlap with people’s abilities to reason, analyse, and make decisions, making some human professional skills redundant [62]. Although AI does not signify the end of human capability power in an organisation, it represents a drastic change in how human power is executed for organisational needs in the context of Industry 5.0. Therefore, scholars agree that BDA human capability is another crucial element of BDAC [14,16,26,63]. As Popovič et al. (2018) [25] stated, it is not about the purely technological conditions to influence business performance but the organisational human capability to utilise BDA.
Leading scholars define BDA human capability as “the BDA staff’s professional ability (e.g., skills or knowledge) to undertake assigned tasks” (adapted from [64] by [15], p. 358). First, from the authors’ point of view, this definition limits BDA’s human capability to the BDA unit. It argues that the BDA unit’s functions are the core of the organisational big data environment. However, they do not provide a holistic picture of BDA human capability. Comprehensively addressing BDAC is possible only when including the staff’s analytical capability at different organisational levels to leverage necessary business analytical competencies [36].
Similarly, Cascio and Bourdeau (2011) [65] and Minbaeva (2018) [16] argue that BDA human capability is considered a building block of analytical competence throughout an organisation, balancing statistical accuracy and practical relevance. Related human competencies within different levels of organisations are vital to ensure an ability to “change the performance of existing routines or create new ones” Leonardi (2011) [66], as adapted by Troshani and Rowbottom (2024, p. 6) [10]. In the fast-changing market and regulatory environment where organisations exist, the ability of staff to “go beyond Excel” [16] and readiness to “connect the dots” among departments may become a gold mine for the BDA unit and executive management, allowing them to capture real-time changes and act accordingly to achieve competitive advantage.
Scholars state that investment in human capability analytics across an organisation is necessary for data-driven decision-making and to, consequently, ensure its competitive advantage [16,26,67,68,69]. Thus, Minbaeva (2018) [16] propose three explicit pillars constituting human capital analytics: data quality, analytical competencies, and strategic acting ability. In the context of BDA human capability, the authors adapt these pillars for conceptualisation purposes, emphasising human analytical competencies.
The challenge of BDA human capability lies in the novel human competencies to interpret data and convert acquired insights to ensure increased knowledge management [13,59,70]. Therefore, in this study, human analytical competencies are defined as staff’s ability to measure and interpret the available data, link them with the business context on a relevant operational unit level, and learn from this process to ensure necessary knowledge management skills. Based on the nascent literature available, the authors create the following definition for BDA human capability: the organisational capacity to effectively apply the professional abilities of BDA and other staff in executing analytical competencies and leveraging derived insights to enhance internal knowledge management.
2.2.4. BDA Infrastructure Capability
Most BDAC authors agree that BDA infrastructure capability is necessary to operationalise the organisational capacity for handling big data [15,71,72]. As per Lnenicak and Komarova (2019) [73], the significance of big data infrastructure is underrated, leading to a lack of the necessary platforms, tools, and techniques for using available data. With this in mind, scholars must be more specific about providing a theoretical framework for the BDA infrastructure capability.
Several scholars have merged BDA technology capability and BDA infrastructure capability. They defined infrastructure ontology purely from a technical perspective [74], identifying technological infrastructure as a crucial element of BDAC [48,73,75]. This research stream is rooted in the historical advancement of BDAC. It was derived from the IT capability literature stream, of which the IT infrastructure component is among its three main functional elements, involving a shared information delivery base [48]. Today, as the BDAC literature evolves, the system’s universalism and reach have been differentiated in compliance with the BDA technology capability definition, excluding BDA infrastructure capability. As demonstrated in the systematic literature review by Huynh et al. (2023) [28], even though BDA technology and infrastructure capabilities are interlinked and can influence each other’s outcomes, they should not be merged. Ref. [76] describes technologies as a facilitating factor of infrastructure.
Expanding on this point, other prominent BDAC researchers argue that BDA technology capability and BDA human capability are perceived as antecedents of BDA infrastructure capability, serving as its foundation, although not in its entirety [28]. Thus, BDA infrastructure capability is on the edge of the emerging Industry 5.0, where value is provided by the synergy of up-to-date digital components and human knowledge. Scholars define BDA infrastructure capability as “the ability of the BDA infrastructure (e.g., applications, hardware, data, and networks) to enable the BDA staff to quickly develop, deploy, and support necessary system components for a firm” (adapted from Kim et al. (2012) [64] by Wamba et al. (2017, p. 358) [15]). This definition reveals the flexibility crucial for BDA infrastructure capability to react in a fast-changing environment.
According to [77], flexibility is the degree to which an organisation possesses control over diverse existing and potential artefacts and routines and the speed at which it can implement these artefacts and routines to enhance management control capability and improve organisational controllability in a changing environment. Thus, flexibility directly relates to promoting management’s control capacity in the changing organisation’s environment.
Bruno et al. (2023) [78] state that infrastructure is a crucial determinant of productivity-related changes. Thus, for the successful execution of changes, it is important to determine the synchronic impact of BDA infrastructure capability at an organisational level, including but not limited to the targeted BDA unit.
According to [10], there are theoretical grounds for a socio-technical perspective on infrastructure. Therefore, infrastructure lies at the intersection of humans and technology. It is the cumulative result of the actions performed by both sides, which BDA technology capability and BDA human capability influence at a semiotic level. Troshani and Rowbottom (2024, p. 4) [10] base their definition of information infrastructure on [79], considering it “as an emergent socio-technical assemblage, a product of the interplay between the human and technical agencies of heterogeneous actors such as people, information systems, software, and processes”. This approach is also supported by the relational sociomaterialism concept brought in by Orlikowski (2007) [80] and adapted by Akter et al. (2016) [14], which presents the balanced symbiosis of technology, management, and human elements, as social and material dimensions are inseparable. The socio-technical and sociomaterialist perspectives serve as the basis for the conceptualisation of BDA infrastructure capability in this research.
The logic developed by [66,81] and adapted by Troshani and Rowbottom (2024) [10] states that infrastructure is formed by artefacts and routines per human and technical relations. An artefact is a stable, structured combination of components, physical and non-physical, such as IT systems and policies, created by people to achieve their aims [82]. Routines define the “repetitive, recognisable patterns of interdependent actions, carried out by multiple actors” (Feldman and Pentland (2003, p. 96)) [83] that support the use of artefacts across an organisation [10]. Thus, big data analytics infrastructure capability is defined as the organisational ability to utilise big data artefacts through analytical routines that integrate human and technological interaction, enabling flexible adaptation to a dynamic environment and generating valuable insights to enhance business performance.
3. The Results
The latest literature reveals that the mechanisms of BDAC relations’ successful application to business performance remain vague and underexplored. Some studies argue that organisations that invest in big data utilisation still struggle with achieving good business performance [84], and the antecedents of success and failure remain unexplored.
Therefore, to complement the literature on the key success factors of the BDAC elements, as demonstrated in Table 2, the authors defined formative BDAC elements as big data analytics technology capability, big data analytics management capability, big data analytics human capability, and big data analytics infrastructure capability.

Table 2.
The key factors of the BDAC elements.
The authors contribute to the literature by summarising the key factors of BDAC elements, as listed in Table 2, that drive BDAC’s successful application for enhancing business performance through delivering evidence-based insights.
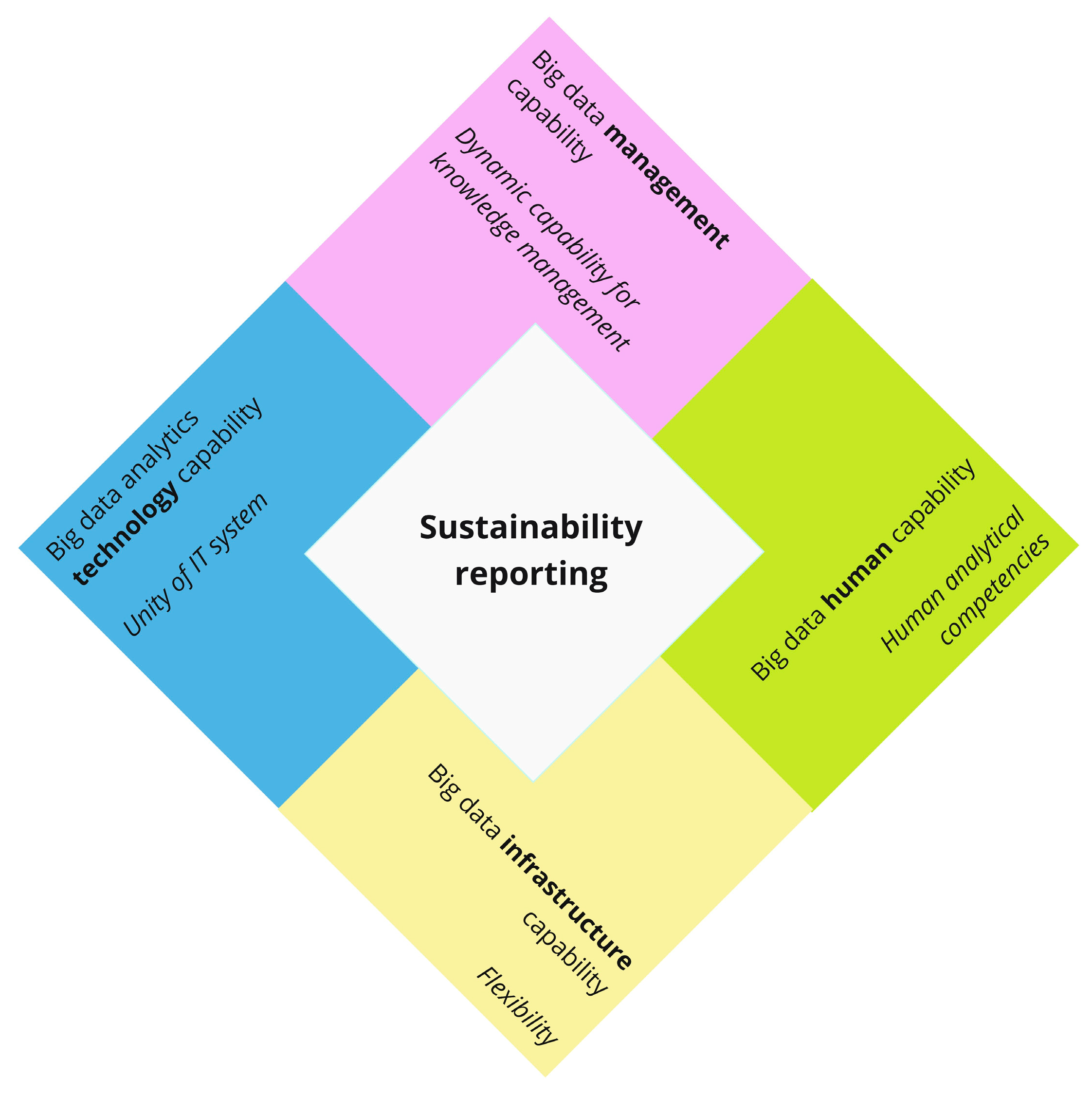
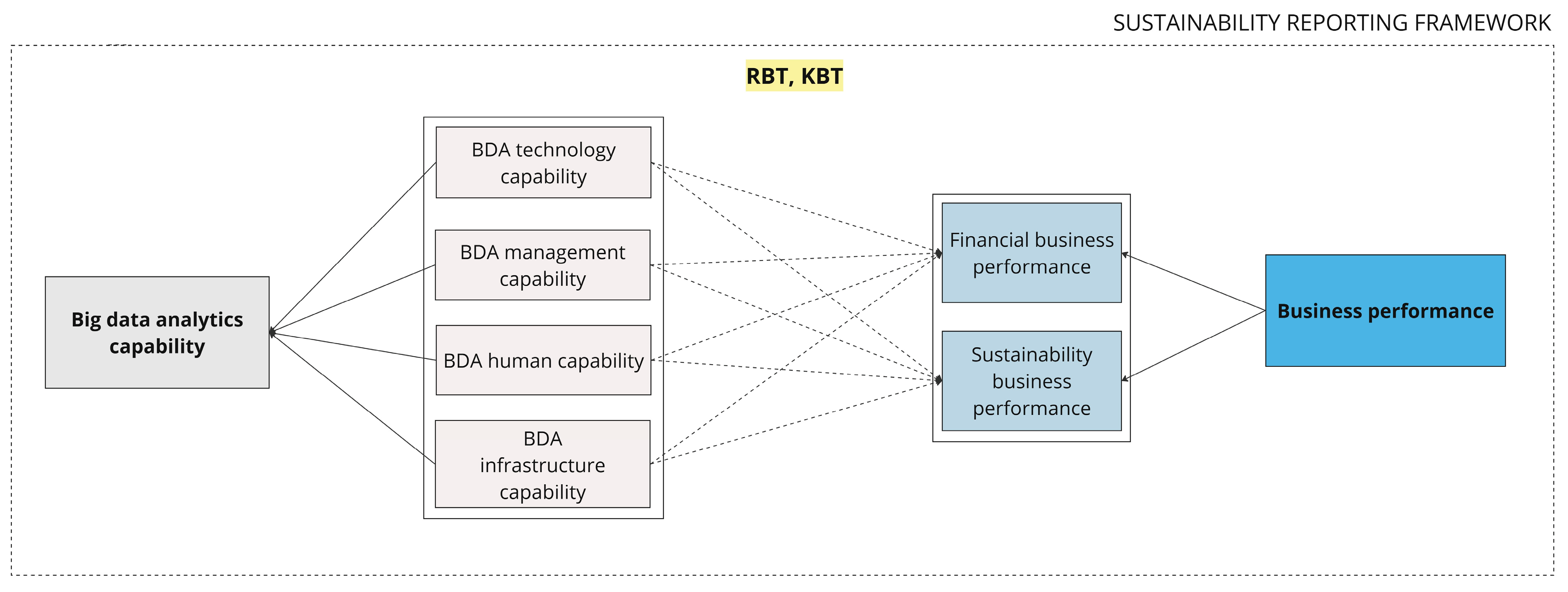
The novel regulated sustainability reporting framework calls for new organisational approaches to deliver precise and reliable information to users. Further, to fill the research gap stated earlier, we apply the results from Table 2 and model them in relation to sustainability reporting, thus presenting the sustainability reporting diamond shown in Figure 3.
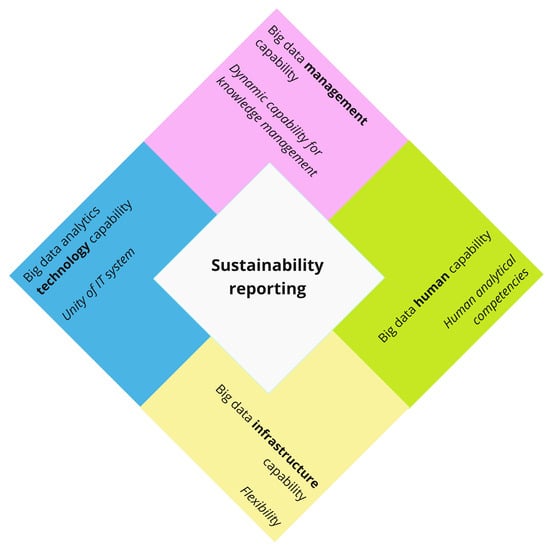
Figure 3.
Sustainability reporting diamond. Source(s): created by the authors.
As shown in Figure 3, to successfully establish robust sustainability reporting, organisations based on the defined key success factors shall develop all four elements of BDAC. The sustainability reporting diamond provides much-needed guidance for top management to structurally approach the integration of sustainability reporting into organisational processes.
Our results provide a further discussion path of BDAC’s relation to business performance. Janssen et al. (2017) [68] argue that decision-making quality depends on how much organisations have developed their BDACs. Mikalef et al. (2020) [47] surveyed the sample of the 202 largest organisations in Norway, one of the most competitive countries globally; empirical findings showed that more mature BDAC positively affects the dynamic capabilities of the organisation, expanding the management responsiveness to big data-generated insights that ensure informed actions and reconfigurations, leading to the augmentation of the competitive performance. Smart processing of structured and unstructured big data and the ability to derive valuable economically worthy insights for decision-making within the organisation lead to increasing the efficiency of the processes, optimising services, and enhancing business practises [84].
Kim et al. (2012) [64] and Akter et al. (2016) [14] consider the role of the organisational capability in compliance with the operational and market changes by utilising BDAC in cost reduction and business learning to enhance business performance. This is confirmed by Minbaeva (2018) [16], who finds that failing to record operational business changes in digitised traceable data and validate them in real time leads to an organisation’s failure to document and follow the changes. The organisation then lacks the information to make precise projections on changing events, which leads to the setting of biassed objectives and uninformed decision-making based on false monitoring results.
Thus, scholars agree that strong BDAC could lead to enhanced business performance [14,15,16,17].
3.1. The Impact of BDAC on Financial Business Performance
According to Huynh et al. (2023) [28], the most often applied theory among BDAC scholars is the resource-based theory (RBT). The literature often uses RBT to explain the company’s enhanced business performance compared to that of its competitors based on its owned and controlled resources [34,36,85,86,87]. From an organisation’s perspective, big data are a core intangible resource. However, could it be treated as a source of competitive advantage for an organisation? One study states that “The theory argues that firms gain a competitive advantage by acquiring tangible and intangible organisational resources that are valuable, rare, inimitable, and non-substitutable (VRIN)” (adapted from Barney (1991) [85] by Kristoffersen et al. (2021), p. 2) [36]). Hence, according to RBT, raw big data does not possess VRIN characteristics and cannot be qualified as a driver of enhanced business performance [36,88]. Further, past scholars have split resources into two elements: resource-picking and capability-building resources [89]. In the present study, we consider BDAC, driven by its four main capabilities’ elements, which possess VRIN attributes, a resource that provides a competitive advantage. Thus, in the RBT framework, we identify BDAC as a necessary precondition resource for generating management knowledge for informed business decisions, as it is an antecedent of superior business performance [90].
As VRIN characteristics of BDAC are directly linked to knowledge generation within the company, the recent theoretical completion of RBT is added here in the form of a knowledge-based theory (KBT), as introduced by [91]. KBT adds a crucial dimension of knowledge as a necessary element for the beneficial utilisation of organisational VRIN resources. KBT argues that there is no delivered value for an organisation without extending resources to a knowledge area of how to use them beneficially and to generate income [70]. Thus, the theoretical and practical underpinning of the four formative BDAC elements that create mechanisms for idiosyncratic development through existing environmental dependencies and causal ambiguity is crucial for enhanced business performance in the KBT of an organisation [92]. The nature of BDAC as a knowledge-based resource is mostly intangible and is relevant to learning and building the business intelligence required to execute relevant capabilities [35,90,91,93].
To gain knowledge about the enterprise success achieved by an organisation compared to its market competitors, it is important to define business performance. Investors use business performance to correctly direct capital flows to the market. Shareholders and executive management at an organisation require regular updates on business performance to make informed decisions and, thus, ensure long-term success. Scholars are unified in their approach of focusing on measuring main outcome-related financial ratios under the umbrella of profitability and revenue growth when identifying key metrics related to business performance [44]. According to Teece (2010) [94], business performance is considered in the value delivered to clients, which is converted into income and profit through the effective and efficient utilisation of the organisational resources. Thus, scholars agree that business performance is measured by organisational profitability and market growth in comparison to those of competitors [84,95,96,97].
3.2. The Impact of BDAC on Sustainability Business Performance
A separate research stream expands the business performance theoretical framework to the triple-bottom-line dimensions [36,98,99]. Notably, only measured sustainability can be managed. Accordingly, big data are required to operationalise related sustainability processes and traceable goals within an organisation [100] to gain insights for sustainability business performance enhancement. In line with [101], we ground sustainability business performance in the economic, environmental, and social (profit, planet, and people) factors of the triple bottom line introduced by [102]. While organisations are well positioned to measure the economic aspect, measuring environmental and social impacts is challenging [103]. Accordingly, integrating BDAC for producing trustful sustainability metrics is crucial for sustainability business performance measurement practises that shall be established based on the new regulated sustainability reporting frameworks. This perspective of our research extends the substantial literature stream exploring BDAC’s impact on business performance from the conventional financial perspective to the sustainability business performance.
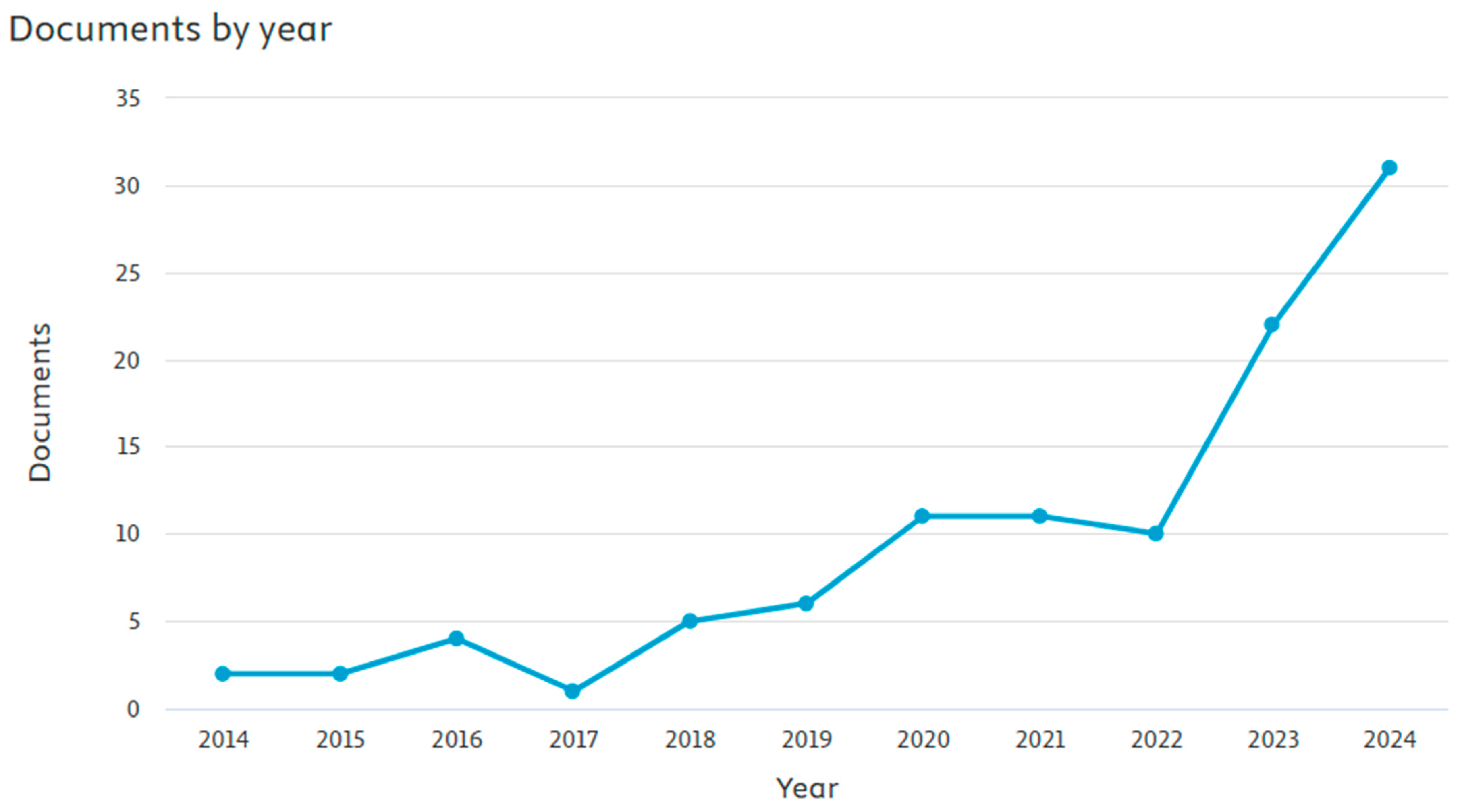
Bibliometric analyses in the Scopus database were performed to explore the current literature state contributing to cross-border research between BDAC and sustainability business performance. This search was performed based on the keywords “sustainability business performance” and “big data analytics capability” or “big data”, and it was limited to the subject areas of “Business, Management and Accounting”, “Decision Sciences”, and “Economics, Econometrics and Finance”. Conducted on 16 January 2025. As the phenomenon is new, no timeframe limitation was applied. For the analyses, only articles in English were filtered. This approach resulted in 105 articles starting from 2014, as reflected in Figure 4. The topicality was proved by the increasing number of publications issued within the last three years, growing from ten articles in 2022 to thirty-one articles in 2024, showing the rapidly growing scholarly research interest in the relationship between BDAC and sustainability business performance.
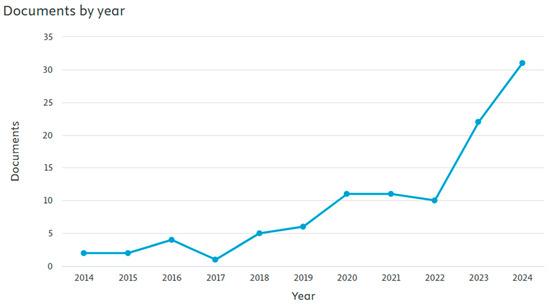
Figure 4.
Published articles containing the keywords “sustainability business performance” and “big data analytics capability” or “big data” by year, 2014–2024. Source(s): created by the authors using the Scopus database.
A significant number of scholars argue that when effectively integrating digital tools into processes to increase efficiency [104], organisations also contribute to environmental, social, and economic targets, leading to sustained competitive advantage [39,87,105,106]. Other researchers outline that BDAC enhances sustainability in an organisation [42,107,108,109]. However, Halbusi et al. (2024) [110] state that in today’s fast-changing market, digitalisation is not enough to achieve enhanced sustainability business performance. Based on the RBT, they find that BDA significantly impacts sustainability business performance. Empirical findings by [111] suggest that BDA has an indirect positive effect on business sustainability performance through enhanced financial accounting practises. The results of the quantitative cross-industry study conducted among IT professionals and managers by [112] confirm that BDAC significantly positively impacts data-driven competitive sustainability and corporate sustainable performance. Additionally, they find that the relationship between BDA and corporate sustainable performance is mediated by data-driven competitive sustainability. Up to now, only a few prior studies, as identified by Huynh et al. (2023) [28], have researched sustainability- or digitalisation-related BDAC constructs.
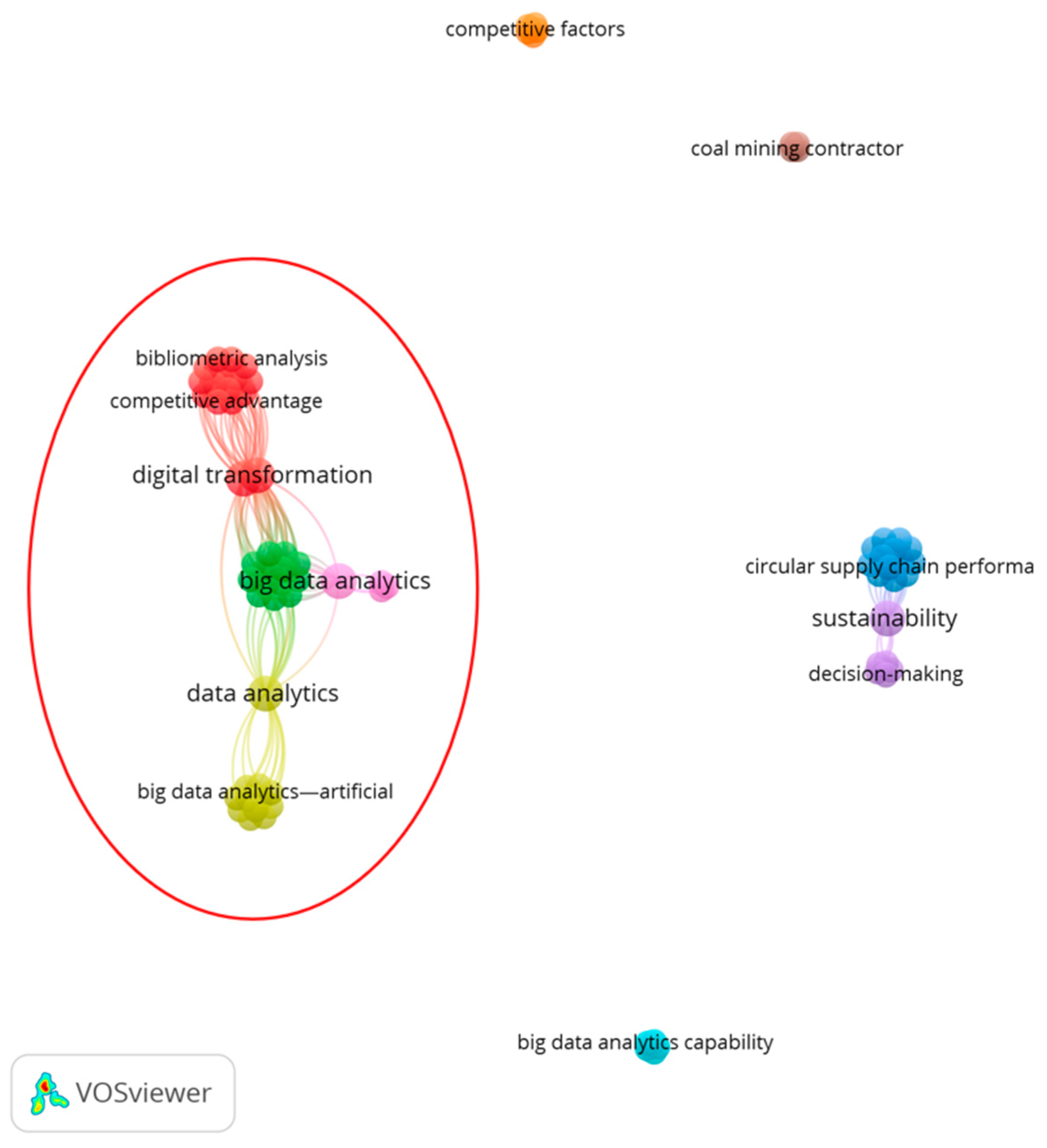
Thus, to contribute to the theoretical framework of related research stream trends that connect BDAC and sustainability business performance, VOSviewer (version 1.6.20) was used to visualise bibliometric analysis results from Scopus using the criteria described above. Bibliometric analysis data were used as an input file for VOSviewer, representing the visual output of the related networks of keywords in different colours, as shown in Figure 5. This led to nine different clusters of networks and 78 related keywords.
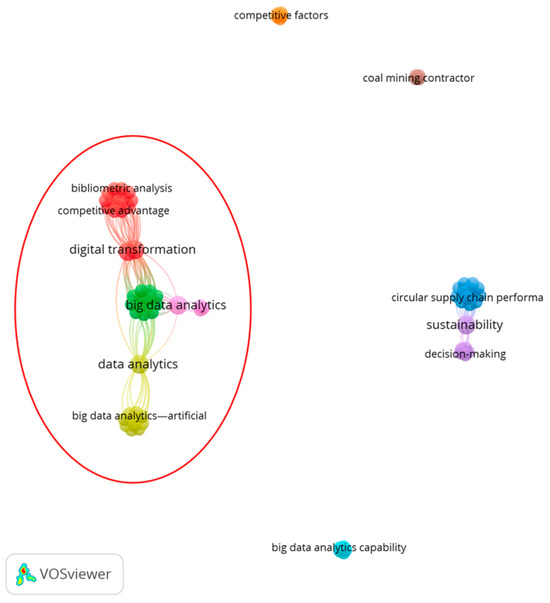
Figure 5.
The visualisation of the keyword clusters related to “sustainability business performance” and “big data analytics capability” or “big data”. Source: created by the authors using VOSviewer.
As demonstrated in Figure 5, there is one large, well-established set of connected clusters, formed by 45 related keywords (highlighted in the red circle) and 4 emerging small networks unrelated to the largest one and each other. The scattered networks demonstrate the emerging nature of the research stream, which calls for the future formalisation of the theoretical framework. More detailed analyses of the largest network reveal the following four research clusters:
- Digital transformation and sustainable development (red cluster);
- Big data analytics and sustainability performance (green cluster);
- Big data analytics—artificial intelligence and decision-making (yellow cluster);
- Sustainable supply chain performance and entrepreneurial orientation (pink cluster).
The leading network to which most historical studies belong demonstrates the relationship between digital transformation, BDA, and sustainability performance. A more in-depth analysis of the keyword data in line with the results of the systematic literature review by [28] finds that the majority of studies in the main network were conducted within the manufacturing sectors of developing countries, with a particular focus on studies on sustainable supply chain management. According to the results of the bibliometric analysis, there are no current studies on BDAC and sustainability business performance in the context of sustainability reporting.
The visualisation of the bibliometric analysis in Figure 4 shows four new research streams that appear as independent networks. These demonstrate different ways of raising scholarly interest in the topic of BDAC and sustainability business performance relationships. These studies have the following foci:
- (1)
- Circular supply chain performance and the environmental or green economy (dark blue cluster), as well as sustainability and decision-making (purple cluster);
- (2)
- Big data analytics capability, financial performance, and technology management (light blue cluster);
- (3)
- Competitive factors and sustainable entrepreneurship (orange cluster);
- (4)
- Coal mining contractor and sustainability practises (brown cluster).
The analysis of the emerging networks in Figure 5 demonstrates that in the framework of BDAC, researchers are leaning towards linking sustainability business performance with financial business performance [101,111,113]. Converging with previous studies that demonstrated BDAC’s positive impact on financial business performance, the results suggest that BDAC’ has a similar effect on sustainability business performance. Studies presenting the theoretical framework of BDAC’s impact on sustainability business performance are scarce, and none describe the relationships of BDAC elements with business performance through the intersectional lens of financial and sustainability business performance.
Based on the theoretical underpinnings [101], we rationalise sustainability business performance in the triple-bottom-line principle, which includes economic (profit) performance as one of the key factors that is conventionally reflected in the financial report of the organisation. Thus, the authors argue that the business performance construct is conceptually based on the corresponding and complementary meaning of financial and sustainability business performances. Thus, the authors define business performance as the result of the organisational capability to effectively structure, bundle, and leverage existing and new resources to improve sales and profitability while safeguarding the boundaries of environmental systems and social responsibility.
After analysing the qualitative content, we contribute to the literature by presenting a conceptual model, shown in Figure 6, that presents BDAC within the environment of raising regulatory sustainability reporting power that aims to standardise the measurement of sustainability business performance in line with financial business performance.
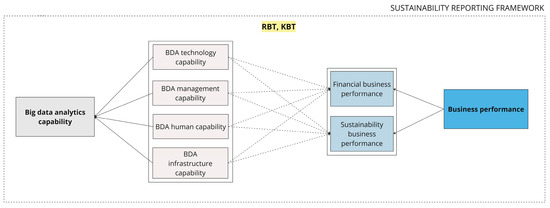
Figure 6.
Conceptual model. Source: created by the authors.
Our study demonstrates its utility in framing the entanglement of BDAC key elements in relation to the dually presented concept of the business performance construct in the framework of RBT and KBT.
4. Discussions
Our study provides essential theoretical discussion paths. To address the first RQ (what are the key success factors for BDAC development in the organisation?) we conduct a literature review to provide an up-to-date BDAC definition and, grounding our study in it, derive BDAC operationalisation. Based on the scientific discussion, in line with [28], we list and provide the up-to-date definitions of four core BDAC elements: BDA technology capability, BDA management capability, BDA human capability, and BDA infrastructure capability. Further, we extend the literature by identifying key factors for each BDAC element that drive the favourable development of BDAC, that is, the unity of the IT system in the case of BDA technology capability, dynamic capability for knowledge management in the case of BDA management capability, human analytical competencies for BDA human capability, and the flexibility aspect of BDA infrastructure capability.
In addressing the second RQ (how do BDAC elements relate to the dual financial and sustainability conceptualisation of business performance?) we first perform a literature review with the elements of the bibliometric analysis to provide the theoretical framework of the BDAC in relation to conventional financial business performance and sustainability business performance. We introduce a novel, vivid umbrella definition of business performance that was extended to cover triple-bottom-line aspects. We contribute to overcoming identified gap by creating a conceptual model that, in the framework of sustainability reporting, links BDAC elements and the financial and sustainability perspectives of business performance in the theoretical framework of RBT and KBT.
Our theoretical implications contribute to the conceptual study of the field of BDAC’s impact on business performance by adding a sustainability reporting framework. Our study uncovers the essential roles of BDAC elements in providing trustful metrics for knowledge creation in relation to sustainability business performance [101,111,113] as one of the two reflective sub-constructs for business performance. Based on that logic, we present the sustainability reporting diamond (Figure 3) as a crucial theoretical implication for the sustainability reporting literature stream development. Our main theoretical implication is the presented conceptual model (Figure 6) that demonstrates the relationship of BDAC elements with business performance that transcends the conventional financial perspective and adds the construct of sustainability business performance.
Our results also have practical implications. In the sustainability reporting diamond (Figure 3), we highlight the importance of considering four BDAC elements: BDA technology capability, BDA management capability, BDA infrastructure capability, and BDA human capability, and their key success factors for reporting on sustainability matters within the annual report to ensure objective business performance measurement. As well as, when performing a cost–benefit analysis for the integration of BDAC elements from the sustainability reporting diamond (Figure 3) into a reporting process, it may be essential for management to consider each relationship as reflected in the presented conceptual model (Figure 6). Additionally, understanding the impact of BDAC elements through the lens of VRIN characteristics on business performance measurement blocks provides managers with practical instruments to control changes and diminish the influence of uncertainty.
There are also some policy implications that are useful for governmental bodies. The new sustainability reporting regulative frameworks introduced in the EU and globally have an evolving nature, going through the first probation by the market. Thus, the presented conceptual model that reflects the up-to-date link between the BDAC and business performance in the new sustainability reporting environment provides policymakers with essential support in rationalising analyses of the market feedback and articulating debates about the level of complexity regarding sustainability report implementation for the organisations.
5. Conclusions
In this conceptual paper, a theoretical framework is drawn based on BDAC, sustainability, and business performance. To this end, we conduct scientific discussions to derive core BDAC elements. We extend the existing literature knowledge state by providing a list of the key success factors for BDAC elements and modelling them in relation to sustainability reporting in the developed sustainability reporting diamond. Based on the implication of the sustainability reporting framework for the business performance construct measurement, we make a theoretical contribution to a novel business performance definition that includes elements of the triple bottom line. Finally, the study proposes a new conceptual model for assessing the BDAC impact on business performance as a reflectively measured construct by financial and sustainability business performance sub-constructs in the new sustainability reporting framework.
6. Limitations and Future Research
The authors acknowledge the limitations of the research. First, the BDAC literature in the context of sustainability reporting is nascent. Secondly, academic research on BDAC’s impact on sustainability business performance is scarce and requires further exploration. Future research could empirically test and validate the proposed conceptual model. Future tests could be conducted at the cross-industry level to ensure the generalisation of the framework and shed more light on the BDAC elements’ impacts on the dual concept of business performance.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.N. and T.V.; methodology, J.N.; software, J.N.; validation, T.V.; formal analysis, J.N.; investigation, J.N. and T.V.; resources, J.N.; data curation, J.N.; writing—original draft preparation, J.N.; writing—review and editing, J.N. and T.V.; visualization, J.N.; supervision, T.V.; project administration, J.N.; funding acquisition, J.N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data can be requested via correspondence contacts.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Bajic, B.; Suzic, N.; Moraca, S.; Stefanović, M.; Jovicic, M.; Rikalovic, A. Edge Computing Data Optimization for Smart Quality Management: Industry 5.0 Perspective. Sustainability 2023, 15, 6032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carayannis, E.G.; Morawska-Jancelewicz, J. The Futures of Europe: Society 5.0 and Industry 5.0 as Driving Forces of Future Universities. J. Knowl. Econ. 2022, 13, 3445–3471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Directive (EU) 2022/2464 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 14 December 2022 Amending Regulation (EU) No 537/2014, Directive 2004/109/EC, Directive 2006/43/EC and Directive 2013/34/EU, as Regards Corporate Sustainability Reporting, Official Journal of European Union. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32022L2464 (accessed on 19 July 2024).
- International Sustainability Standards Board. IFRS S1: General Requirements for Disclosure of Sustainability-Related Financial Information. 2023. Available online: https://www.ifrs.org/content/dam/ifrs/publications/pdf-standards-issb/english/2023/issued/part-a/issb-2023-a-ifrs-s1-general-requirements-for-disclosure-of-sustainability-related-financial-information.pdf?bypass=on (accessed on 10 July 2024).
- IFRS Foundation. Progress Towards Adoption of ISSB Standards as Jurisdictions Consult. Available online: https://www.ifrs.org/news-and-events/news/2024/04/progress-towards-adoption-of-issb-standards-as-jurisdictions-consult/ (accessed on 22 August 2024).
- García-Sánchez, I.; Hussain, N.; Khan, S.A.; Martínez-Ferrero, J. Managerial entrenchment, corporate social responsibility, and earnings management. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2020, 27, 1818–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paridhi; Ritika. Sustainability reporting for boosting national commitment and overcoming challenges: A hierarchical model. Bus. Strategy Dev. 2024, 7, e334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, A.K.; Dutzi, A. What Earnings Management Has to Do with Corporate Social Responsibility. Sustainability 2024, 16, 2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastrandrea, R.; Ter Burg, R.; Shan, Y.; Hubacek, K.; Ruzzenenti, F. Assessments of the environmental performance of global companies need to account for company size. Commun. Earth Environ. 2024, 5, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troshani, I.; Rowbottom, N. Corporate sustainability reporting and information infrastructure. Account. Audit. Account. J. 2024, 37, 1209–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission Research and Innovation. Industry 5.0. 2024. Available online: https://research-and-innovation.ec.europa.eu/research-area/industrial-research-and-innovation/industry-50_en (accessed on 27 June 2024).
- Knudsen, E.S.; Lien, L.B.; Timmermans, B.; Belik, I.; Pandey, S. Stability in turbulent times? The effect of digitalization on the sustainability of competitive advantage. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 128, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muraro, V.; Salles-Filho, S. Big data, machine learning and uncertainty in foresight studies. Foresight 2024, 26, 436–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akter, S.; Wamba, S.F.; Gunasekaran, A.; Dubey, R.; Childe, S.J. How to improve firm performance using big data analytics capability and business strategy alignment? Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2016, 182, 113–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wamba, S.F.; Gunasekaran, A.; Akter, S.; Ren, S.J.; Dubey, R.; Childe, S.J. Big data analytics and firm performance: Effects of dynamic capabilities. J. Bus. Res. 2017, 70, 356–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minbaeva, D.B. Building credible human capital analytics for organizational competitive advantage. Hum. Resour. Manag. 2018, 57, 701–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, R.; Gunasekaran, A.; Childe, S.J.; Papadopoulos, T.; Luo, Z.; Wamba, S.F.; Roubaud, D. Can big data and predictive analytics improve social and environmental sustainability? Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2019, 144, 534–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAfee, A.; Brynjolfsson, E. Big Data: The management revolution. Harv. Bus. Rev. 2012, 90, 60–66. [Google Scholar]
- Jabbour, C.J.C.; Jabbour, A.B.L.D.S.; Sarkis, J.; Filho, M.G. Unlocking the circular economy through new business models based on large-scale data: An integrative framework and research agenda. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2019, 144, 546–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanathan, S.; Isaksson, R. Sustainability reporting as a 21st century problem statement: Using a quality lens to understand and analyse the challenges. TQM J. 2023, 35, 1310–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seddon, J.J.J.M.; Currie, W.L. A model for unpacking big data analytics in high-frequency trading. J. Bus. Res. 2017, 70, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosi, D.; Kokaj, R.; Roccetti, M. 15 years of Big Data: A systematic literature review. J. Big Data 2024, 11, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikalef, P.; Boura, M.; Lekakos, G.; Krogstie, J. Big data analytics and firm performance: Findings from a mixed-method approach. J. Bus. Res. 2019, 98, 261–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delen, D.; Demirkan, H. Data, information and analytics as services. Decis. Support Syst. 2013, 55, 359–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popovič, A.; Hackney, R.; Tassabehji, R.; Castelli, M. The impact of big data analytics on firms’ high value business performance. Inform. Syst. Front. 2018, 20, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.; George, J.F. Toward the development of a big data analytics capability. Inf. Manag. 2016, 53, 1049–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikalef, P.; Pappas, I.O.; Krogstie, J.; Giannakos, M. Big data analytics capabilities: A systematic literature review and research agenda. Inf. Syst. E-Bus. Manag. 2018, 16, 547–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, M.-T.; Nippa, M.; Aichner, T. Big data analytics capabilities: Patchwork or progress? A systematic review of the status quo and implications for future research. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2023, 197, 122884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davenport, T.H. Competing on Analytics. Harv. Bus. Rev. 2007, 84, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasan, R.; Swink, M. An Investigation of Visibility and Flexibility as Complements to Supply Chain Analytics: An Organizational Information Processing Theory Perspective. Prod. Oper. Manag. 2018, 27, 1849–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Xie, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, S.; Jones, P.; Lopez, C. Barrier analysis to improve big data analytics capability of the maritime industry: A mixed-method approach. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2024, 203, 123345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Hajli, N. Exploring the path to big data analytics success in healthcare. J. Bus. Res. 2017, 70, 287–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Kung, L.; Byrd, T.A. Big data analytics: Understanding its capabilities and potential benefits for healthcare organizations. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2018, 126, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.-Y.; Park, J. Do data-driven CSR initiatives improve CSR performance? The importance of big data analytics capability. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2022, 182, 121802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikalef, P.; Boura, M.; Lekakos, G.; Krogstie, J. The role of information governance in big data analytics driven innovation. Inf. Manag. 2020, 57, 103361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristoffersen, E.; Mikalef, P.; Blomsma, F.; Li, J. The effects of business analytics capability on circular economy implementation, resource orchestration capability, and firm performance. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2021, 239, 108205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gartner. Big Data—Information Technology Glossary. Garter Glossary. 2023. Available online: https://www.gartner.com/en/information-technology/glossary/big-data (accessed on 5 July 2024).
- Duan, W.; Khurshid, A.; Khan, K.; Calin, A.C. Transforming industry: Investigating 4.0 technologies for sustainable product evolution in china through a novel fuzzy three-way decision-making process. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2024, 200, 123125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denicolai, S.; Zucchella, A.; Magnani, G. Internationalization, digitalization, and sustainability: Are SMEs ready? A survey on synergies and substituting effects among growth paths. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2021, 166, 120650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calic, G.; Ghasemaghaei, M. Big data for social benefits: Innovation as a mediator of the relationship between big data and corporate social performance. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 131, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, R.; Gunasekaran, A.; Childe, S.J.; Fosso Wamba, S.; Roubaud, D.; Foropon, C. Empirical investigation of data analytics capability and organizational flexibility as complements to supply chain resilience. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2021, 59, 110–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Wong, C.Y.; Chavez, R.; Jacobs, M.A. Integrating big data analytics into supply chain finance: The roles of information processing and data-driven culture. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2021, 236, 108135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ACCA. Big Data 1: What Is Big Data? 2024. Available online: https://www.accaglobal.com/ubcs/en/student/exam-support-resources/fundamentals-exams-study-resources/f5/technical-articles/what-is-big-data.html (accessed on 26 June 2024).
- Verhoef, P.C.; Broekhuizen, T.; Bart, Y.; Bhattacharya, A.; Qi Dong, J.; Fabian, N.; Haenlein, M. Digital transformation: A multidisciplinary reflection and research agenda. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 122, 889–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhanam, R.; Hartono, E. Hartono Issues in Linking Information Technology Capability to Firm Performance. MIS Q. 2003, 27, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Ramamurthy, K. Understanding the Link Between Information Technology Capability and Organizational Agility: An Empirical Examination. MIS Q. 2011, 35, 931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikalef, P.; Krogstie, J.; Pappas, I.O.; Pavlou, P. Exploring the relationship between big data analytics capability and competitive performance: The mediating roles of dynamic and operational capabilities. Inf. Manag. 2020, 57, 103169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharadwaj, A.S. A Resource-Based Perspective on Information Technology Capability and Firm Performance: An Empirical Investigation. MIS Q. 2000, 24, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, D.; Court, D. Making Advanced Analytics Work for You. Harv. Bus. Rev. 2012, 90, 78–83. [Google Scholar]
- Mucci, T.; Stryker, C. What Is Big Data Analytics? IBM—Big Data Analytics. 2024. Available online: https://www.ibm.com/topics/big-data-analytics (accessed on 1 July 2024).
- Taddy, M. The Technological Elements of Artificial Intelligence; National Bureau of Economic Research: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; p. w24301. [Google Scholar]
- Davenport, H.T.; Barth, P.; Bean, R. How ‘Big Data’ Is Different. MIT Sloan Manag. Rev. 2012, 54, 43–46. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.L.; Ahmed, P.K. Dynamic capabilities: A review and research agenda. Int. J. Manag. Rev. 2007, 9, 31–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamim, S.; Zeng, J.; Shafi Choksy, U.; Shariq, S.M. Connecting big data management capabilities with employee ambidexterity in Chinese multinational enterprises through the mediation of big data value creation at the employee level. Int. Bus. Rev. 2020, 29, 101604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamim, S.; Yang, Y.; Zia, N.U.; Shah, M.H. Big data management capabilities in the hospitality sector: Service innovation and customer generated online quality ratings. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2021, 121, 106777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teece, D.J.; Pisano, G.; Shuen, A. Dynamic capabilities and strategic management. Strat. Mgmt. J. 1997, 18, 509–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Wan, J.; Ma, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, J. How digital platform capabilities improve sustainable innovation performance of firms: The mediating role of open innovation. J. Bus. Res. 2023, 167, 114080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron Cockrell, R.; Stone, D.N. Industry culture influences pseudo-knowledge sharing: A multiple mediation analysis. J. Knowl. Manag. 2010, 14, 841–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.; Vorley, T. Big data text analytics: An enabler of knowledge management. J. Knowl. Manag. 2017, 21, 18–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korherr, P.; Kanbach, D. Human-related capabilities in big data analytics: A taxonomy of human factors with impact on firm performance. Rev. Manag. Sci. 2023, 17, 1943–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ransbotham, S.; Kiron, D.; Kirk Prentice, P. Minding the Analytics Gap. MIT Sloan Manag. Rev. 2015, 56, 63. [Google Scholar]
- Rotman, D. How Technology Is Destroying Jobs. MIT Technol. Rev. 2013, 16, 28–35. [Google Scholar]
- Munir, S.; Abdul Rasid, S.Z.; Aamir, M.; Jamil, F.; Ahmed, I. Big data analytics capabilities and innovation effect of dynamic capabilities, organizational culture and role of management accountants. Foresight 2023, 25, 41–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.; Shin, B.; Kwon, O. Investigating the Value of Sociomaterialism in Conceptualizing IT Capability of a Firm. J. Manag. Inf. Syst. 2012, 29, 327–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascio, W.F.; Boudreau, J.W. Investing in People: Financial Impact of Human Resource Initiatives, 2nd ed.; FT Press: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2011; ISBN 978-0-13-707092-3. [Google Scholar]
- Leonardi, P.M. When Flexible Routines Meet Flexible Technologies: Affordance, Constraint, and the Imbrication of Human and Material Agencies. MIS Q. 2011, 35, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waller, M.A.; Fawcett, S.E. Data Science, Predictive Analytics, and Big Data: A Revolution That Will Transform Supply Chain Design and Management. J. Bus. Logist. 2013, 34, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, M.; Van Der Voort, H.; Wahyudi, A. Factors influencing big data decision-making quality. J. Bus. Res. 2017, 70, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Sanders, K.; Marler, J.H.; Zou, Y. Determinants of effective HR analytics Implementation: An In-Depth review and a dynamic framework for future research. J. Bus. Res. 2024, 170, 114312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Den Berg, H.A. Three shapes of organisational knowledge. J. Knowl. Manag. 2013, 17, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, A.K.; Agi, M.A.N.; Ngai, E.W.T. A note on big data analytics capability development in supply chain. Decis. Support Syst. 2020, 138, 113382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Chaudhuri, R.; Gupta, S.; Sivarajah, U.; Bag, S. Assessing the impact of big data analytics on decision-making processes, forecasting, and performance of a firm. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2023, 196, 122824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lnenicka, M.; Komarkova, J. Big and open linked data analytics ecosystem: Theoretical background and essential elements. Gov. Inf. Q. 2019, 36, 129–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydiner, A.S.; Tatoglu, E.; Bayraktar, E.; Zaim, S. Information system capabilities and firm performance: Opening the black box through decision-making performance and business-process performance. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2019, 47, 168–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlNuaimi, B.K.; Khan, M.; Ajmal, M.M. The role of big data analytics capabilities in greening e-procurement: A higher order PLS-SEM analysis. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2021, 169, 120808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghobakhloo, M.; Iranmanesh, M.; Grybauskas, A.; Vilkas, M.; Petraitė, M. Industry 4.0, innovation, and sustainable development: A systematic review and a roadmap to sustainable innovation. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2021, 30, 4237–4257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Leeuw, A.C.J.; Volberda, H.W. On the concept of flexibility: A dual control perspective. Omega 1996, 24, 121–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, R.; Matusiak, M.; Osaulenko, K.; Radosevic, S. “Digitalisation” and “Greening” as Components of Technology Upgrading and Sustainable Economic Performance. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickering, A. The Mangle of Practice: Agency and Emergence in the Sociology of Science. Am. J. Sociol. 1993, 99, 559–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlikowski, W.J. Sociomaterial Practices: Exploring Technology at Work. Organ. Stud. 2007, 28, 1435–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latour, B. Reassembling the Social: An Introduction to Actor-Network-Theory; Clarendon Lectures in Management Studies; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2007; ISBN 978-0-19-925605-1. [Google Scholar]
- Faulkner, P.; Runde, J. Theorizing the digital object. MIS Q. 2019, 43, 1279–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldman, M.S.; Pentland, B.T. Reconceptualizing Organizational Routines as a Source of Flexibility and Change. Adm. Sci. Q. 2003, 48, 94–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemaghaei, M. Understanding the impact of big data on firm performance: The necessity of conceptually differentiating among big data characteristics. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2021, 57, 102055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barney, J. Firm Resources and Sustained Competitive Advantage. J. Manag. 1991, 17, 99–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, R.; Oberländer, A.M.; Faisst, U.; Röglinger, M. Disentangling Capabilities for Industry 4.0—An Information Systems Capability Perspective. Inform. Syst. Front. 2022, 26, 1667–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, J.J.; Lopes, J.M.; Gomes, S.; Rammal, H.G. Industry 4.0 implementation: Environmental and social sustainability in manufacturing multinational enterprises. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 404, 136841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braganza, A.; Brooks, L.; Nepelski, D.; Ali, M.; Moro, R. Resource management in big data initiatives: Processes and dynamic capabilities. J. Bus. Res. 2017, 70, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikalef, P.; Framnes, V.A.; Danielsen, F.; Krogstie, J.; Olsen, G.H. Big Data Analytics Capability: Antecedents and Business Value. In Proceedings of the PACIS 2017, Langkawi, Malaysia, 16–20 July 2017; Volume 136, pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Kale, P.; Dyer, J.H.; Singh, H. Alliance capability, stock market response, and long-term alliance success: The role of the alliance function. Strateg. Manag. J. 2002, 23, 747–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, R.M. Toward a knowledge-based theory of the firm. Strateg. Manag. J. 1996, 17, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curado, C.; Bontis, N. The knowledge-based view of the firm and its theoretical precursor. Int. J. Learn. Intellect. Cap. 2006, 3, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kale, P.; Singh, H. Building firm capabilities through learning: The role of the alliance learning process in alliance capability and firm-level alliance success. Strateg. Manag. J. 2007, 28, 981–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teece, D.J. Business Models, Business Strategy and Innovation. Long Range Plan. 2010, 43, 172–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, T.C. Total quality management as competitive advantage: A review and empirical study. Strateg. Manag. J. 1995, 16, 15–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, T.C.; Dent-Micallef, A. Information technology as competitive advantage: The role of human, business, and technology resources. Strateg. Manag. J. 1997, 18, 375–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunday, G.; Ulusoy, G.; Kilic, K.; Alpkan, L. Effects of innovation types on firm performance. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2011, 133, 662–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, A.; Patnayakuni, R.; Seth, N. Seth Firm Performance Impacts of Digitally Enabled Supply Chain Integration Capabilities. MIS Q. 2006, 30, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, O.; Daddi, T.; Iraldo, F. The role of dynamic capabilities in circular economy implementation and performance of companies. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2020, 27, 3018–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, J.; Overby, S. Digital Transformation: A Force Multiplier for Sustainability. SAP Insights. 2024. Available online: https://www.sap.com/poland/insights/viewpoints/digital-transformations-force-multiplier-sustainability.html (accessed on 27 June 2024).
- Ertz, M.; Latrous, I.; Dakhlaoui, A.; Sun, S. The impact of Big Data Analytics on firm sustainable performance. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2025, 32, 1261–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkington, J. The Triple Bottom Line, 1st ed.; Routledge: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Székely, F.; Knirsch, M. Responsible Leadership and Corporate Social Responsibility: Metrics for Sustainable Performance. Eur. Manag. J. 2005, 23, 628–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrbsky, S.V.; Galloway, M.; Carr, R.; Nori, R.; Grubic, D. Decreasing power consumption with energy efficient data aware strategies. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2013, 29, 1152–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtenthaler, U. Digitainability: The Combined Effects of the Megatrends Digitalization and Sustainability. J. Innov. Manag. 2021, 9, 64–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranta, V.; Aarikka-Stenroos, L.; Väisänen, J.-M. Digital technologies catalyzing business model innovation for circular economy—Multiple case study. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 164, 105155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashaari, M.A.; Singh, K.S.D.; Abbasi, G.A.; Amran, A.; Liebana-Cabanillas, F.J. Big data analytics capability for improved performance of higher education institutions in the Era of IR 4.0: A multi-analytical SEM & ANN perspective. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2021, 173, 121119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behl, A.; Gaur, J.; Pereira, V.; Yadav, R.; Laker, B. Role of big data analytics capabilities to improve sustainable competitive advantage of MSME service firms during COVID-19—A multi-theoretical approach. J. Bus. Res. 2022, 148, 378–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.T.; Li, X.; Yuen, K.F. Digital transformation as an enabler of sustainability innovation and performance—Information processing and innovation ambidexterity perspectives. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2023, 196, 122860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halbusi, H.A.; Soto-Acosta, P.; Popa, S.; Hassani, A. The Role of Green Digital Learning Orientation and Big Data Analytics in the Green Innovation–Sustainable Performance Relationship. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2024, 71, 12886–12896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzam, M.E.A.Y.; Alsayed, M.S.H.; Alsultan, A.; Hassanein, A. How big data features drive financial accounting and firm sustainability in the energy industry. J. Financ. Report. Account. 2024, 22, 29–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Sarfraz, M.; Sun, J.; Ivascu, L.; Ozturk, I. Advancing corporate sustainability via big data analytics, blockchain innovation, and organizational dynamics—A cross-validated predictive approach. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2025, 34, 1399–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Chaudhuri, R.; Vrontis, D.; Thrassou, A. Impacts of big data analytics adoption on firm sustainability performance. Qual. Res. Financ. Mark. 2023, 15, 589–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).